Conceptualization and numerical simulation of a karst subterranean river and its outlets using MODFLOW
-
摘要:
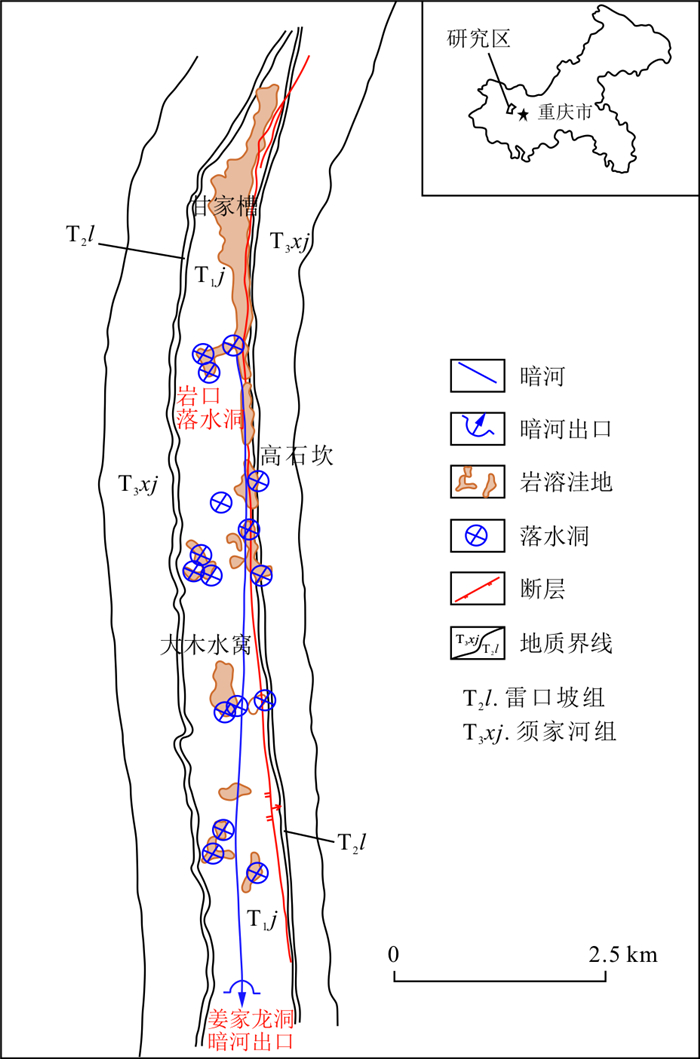
在MODFLOW的三维渗流模拟程序集中, Conduit Flow Process(CFP)模块已被广泛用于模拟岩溶含水层中的管道流, 是岩溶地下水流模拟的重要工具。使用CFP模块概化暗河管道时, 暗河出口的概化有2种方案: 将暗河出口设置在管道模型中(FH方案)或等效多孔介质中(Dr方案), 其模拟效果有待评价。以重庆缙云山姜家龙洞暗河为例, 建立了考虑管道流的地下水流数值模型, 分别使用2种方案概化了暗河出口, 对比分析了稳定流和非稳定流的模拟结果。结果表明: 以排水沟(Drain)模块概化暗河出口的Dr方案, 暗河管道的上游段排泄地下水, 下游段反而补给含水层, 最终在排水沟单元排泄, 而定水头(Fix Head)概化的FH方案则准确模拟了暗河全段汇集地下水并在出口排泄出含水层的实际情况。进一步的水均衡分析揭示了模拟差异产生的原理。在模拟岩溶区地下水向暗河管道汇集的水文过程时, 如果使用CFP概化管道, 则宜配合使用CFP中的定水头边界概化暗河出口。
-
关键词:
- 岩溶管道 /
- 管道-等效多孔介质耦合模型 /
- MODFLOW-CFP /
- 暗河
Abstract:Objective In the set of 3D seepage simulation programs of MODFLOW, the Conduit Flow Process (CFP) module has been widely used to represent karst conduits and karst aquifers and provides an important tool for groundwater simulation in karst areas.
Methods When using CFP module to conceptualize the subterranean river conduits and their outlets, there are two schemes for the conceptualization of the outlets: setting the subterranean river outlet in the conduit model (FH scheme) or in the equivalent porous medium (Dr scheme), whose simulation effects are to be evaluated. In this paper, a groundwater numerical model with conduit flow was constructed, taking the Jiangjia Subterranean River in Jinyun Mountain, Chongqing as an example. The outlets of the subterranean river were conceptualized by the aforementioned two schemes, and then the differences between the subsequent two simulations were analyzed and compared.
Results The results show that the FH scheme is better than the Dr scheme. The fixed head setting in the FH scheme can achieve the effect of groundwater discharge in all segments of the subterranean river, while the drain setting in the Dr scheme only discharges groundwater in the upstream of the subterranean river conduit, then recharges the aquifer in the downstream, and finally, the groundwater is discharged in the drain unit.
Conclusion The water balance analysis also demonstrates the advantage of the FH scheme in terms of the capacity of groundwater discharge and the function of aquifer storage.
-
表 1 模型主要参数取值[32]
Table 1. Values of main parameter for the model
CFP
管道参数直径/m 2.57 管道壁平均起伏高度/m 1.00 实际长度/km 11.16 管道壁平均起伏高度/m 1.00 下临界雷诺数 2 000.00 上临界雷诺数 40 000.00 管道内水流雷诺数 127 980.00 模型参数 渗透系数/(m·d-1) 0.25 给水度 0.40 表 2 非稳定流模拟降雨量[35]
Table 2. Rainfall used in non-steady flow
时段 历时 总降雨量/mm 识别期 2007/09/16 19:48-09/17 07:33 12 h 31.0 2007/10/10 08:03-10/15 08:05 5 d 59.4 验证期 2008/08/14 18:02-08/16 08:07 1 d14 h10 min 11.2 2008/08/25 01:42-08/25 20:12 18 h30 min 48.2 2008/08/26 06:27-08/30 09:42 4 d3 h20 min 41.2 -
[1] Xu Z Y, Hu B X, Xu Z X, et al. Simulating seawater intrusion in a complex coastal karst aquifer using an improved variable-density flow and solute transport-conduit flow process model[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2019, 27(4): 1277-1289. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1903-2 [2] 陈喜, 刘传杰, 胡忠明, 等. 泉域地下水数值模拟及泉流量动态变化预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006, 43(2): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200602009.htmChen X, Liu C J, Hu Z M, et al. Numerical modeling of groundwater in a spring catchment and prediction of variations in the spring discharge[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2006, 43(2): 36-40(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200602009.htm [3] 束龙仓, 许杨, 吴佩鹏. 基于MODFLOW参数不确定性的地下水水流数值模拟方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2017, 47(6): 1803-1809. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201706017.htmShu L C, Xu Y, Wu P P. Groundwater flow numeric simulation method based on uncertainties of MODFLOW parameters[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2017, 47(6): 1803-1809(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201706017.htm [4] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 等. 基于MODFLOW的岩溶管道水流模拟方法探讨与应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3): 346-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201703008.htmZhao L J, Xia R Y, Yang Y, et al. Discussion and application of simulation methods for karst conduit flow based on MODFLOW[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3): 346-351(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201703008.htm [5] 秦品瑞. 济南岩溶水系统数值模拟与保泉供水开采方案[J]. 水资源保护, 2018, 34(3): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB201803005.htmQin P R. Numerical simulation of Jinan karst water system and groundwater exploitation scheme of keeping spring spurting and water supply[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2018, 34(3): 30-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB201803005.htm [6] 任增平, 迟宝明, 余国光, 等. 数值模拟方法在岩溶大泉泉口集中供水评价中的应用研究[J]. 长春科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 1998, 94(4): 58-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ804.009.htmRen Z P, Chi B M, Yu G G, et al. Application of numerical simulation method in evaluation of centralized water supply at the mouth of karst spring[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 1998, 94(4): 58-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ804.009.htm [7] 卢文喜. 泉流行为的数值模拟[J]. 中国岩溶, 1992, 11(2): 47-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199202005.htmLu W X. Numerical simulation of spring flow behavior[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1992, 11(2): 47-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199202005.htm [8] 周焱钰, 陈喜, 张志才. 西南喀斯特小流域地下水数值模拟[J]. 工程勘察, 2011, 39(4): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201104011.htmZhou Y Y, Chen X, Zhang Z C. Numerical groundwater modeling in a small karst watershed of the Southwest China[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2011, 39(4): 43-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201104011.htm [9] 成建梅, 罗一鸣. 岩溶多重介质地下水模拟技术及应用进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 220-229. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0220Cheng J M, Luo Y M. Overview of groundwater modeling technology and its application in karst areas with multiple-void media[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 220-229(in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0220 [10] 陈崇希. 岩溶管道-裂隙-孔隙三重空隙介质地下水流模型及模拟方法研究[J]. 地球科学, 1995, 23(4): 361-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199504000.htmChen C X. Groundwater flow model and simulation method in triple media of karstic tube-fissure-pore[J]. Earth Science, 1995, 23(4): 361-366(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199504000.htm [11] Shoemaker W B, Kuniansky E L, Birk S, et al. Documentation of a conduit flow process(CFP) for MODFLOW-2005[M]. USGS: Techniques and Methods, 2007. [12] Dal Soglio L, Danquigny C, Mazzilli N, et al. Modeling the matrix-conduit exchanges in both the epikarst and the transmission zone of karst systems[J]. Water, 2020, 12(11): 3219. doi: 10.3390/w12113219 [13] Chang Y, Wu J C, Jiang G H, et al. Modelling spring discharge and solute transport in conduits by coupling CFPv2 to an epikarst reservoir for a karst aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 569(14): 587-599. [14] 刘丽红, 吴潇潇, 颜冰. 岩块尺度达西流非达西流流态转化研究[J]. 科技通报, 2017, 33(1): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201701007.htmLiu L H, Wu X X, Yan B. Research of transition between the Darcian and non-Darcian flow of rock block scale[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2017, 33(1): 32-38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201701007.htm [15] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 苏春田, 等. 基于CFP的岩溶管道流溶质运移数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(4): 51-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904008.htmYang Y, Zhao L J, Su C T, et al. A study of the solute transport model for karst conduits based on CFP[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 51-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904008.htm [16] 陈崇希, 胡立堂. 渗流-管流耦合模型及其应用综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2008, 221(3): 70-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200803016.htmChen C X, Hu L T. A review of the seepage-pipe coupling model and its application[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2008, 221(3): 70-75(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200803016.htm [17] 陈崇希, 万军伟, 詹红兵, 等. "渗流-管流耦合模型"的物理模拟及其数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2004, 31(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200401000.htmChen C X, Wan W J, Zhan H B, et al. Physical and numerical simulation of seepage-pipe coupling model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology. 2004, 31(1): 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200401000.htm [18] Michael J R. Influence of conduit network geometry on solute transport in karst aquifers with a permeable matrix[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2013, 56(6): 27-34. [19] 赵良杰. 岩溶裂隙-管道双重含水介质水流交换机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.Zhao L J. Study of water exchange mechanism of karst matrix and conduit medium[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 等. 基于CFP的岩溶管道流数值模拟研究: 以桂林寨底地下河子系统为例[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(2): 225-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201802010.htmZhao L J, Xia R Y, Yang Y, et al. Research onnumerical simulation of karst conduit media based on CFP: A case study of Zhaidi karst underground river subsystem of Guilin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(2): 225-232(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201802010.htm [21] Saller S P, Ronayne M J, Long A J. Comparison of a karst groundwater model with and without discrete conduit flow[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2013, 21(7): 1555-1566. [22] 刘丽红, 束龙仓, 鲁程鹏. 基于管道流模型的岩溶含水系统降雨泉流量响应规律: 以贵州后寨典型小流域为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2010, 40(5): 1083-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005017.htmLiu L H, Shu L C, Lu C P. Precipitation and discharge response mechanism based on conduit flow model in karstic water system: Application the Houzhai karstic water system of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2010, 40(5): 1083-1089(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005017.htm [23] 覃夏南, 姜光辉, 夏源. 考虑非饱和带作用及管道流的岩溶泉流量模拟[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(3): 622-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201903011.htmQin X N, Jiang G H, Xia Y. Karst spring flow simulation considering the effects of unsaturated zone and pipe flow[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(3): 622-627(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201903011.htm [24] Quinn J J Q A, Tomasko D, Kuiper J A. Modeling complex flow in a karst aquifer[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 184(3/4): 343-351. [25] 夏强. 地下水不确定性问题的多模型分析方法及应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.Xia Q. Methods and applications of multiple model analysis on groundwater uncertainties[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2011(in Chinese with English abstract). [26] Gallegos J J, Hu B X, Davis H. Simulating flow in karst aquifers at laboratory and sub-regional scales using MODFLOW-CFP[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2013, 21(8): 1749-1760. [27] 常勇. 裂隙—管道二元结构的岩溶泉水文过程分析与模拟[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015.Chang Y. Analysis and simulation of the hydrological process of the karst aquifer with fracture-conduit dual structure[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 水文地质七二级联队. 观音峡、温塘峡两背斜青木关地区的暗河水及其开发[J]. 成都地质学院学报, 1975, 6(C1): 68-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG1975Z1007.htmHydrogeology Regimentof Grade 72. Subterranean river water and its exploitation in Qingmuguan area of Guanyin Gorge and Wentang Gorge anticline[J]. Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 1975, 6(C1): 68-78(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG1975Z1007.htm [29] 杨平恒, 罗鉴银, 彭稳, 等. 在线技术在岩溶地下水示踪试验中的应用: 以青木关地下河系统岩口落水洞至姜家泉段为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2008, 27(3): 215-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200803006.htmYang P H, Luo J Y, Peng W, et al. Application of online technique in tracer test: A case in Qingmuguan subterranean river system, Chongqing, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(3): 215-220(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200803006.htm [30] Winston R B. ModelMuse: A graphical user interface for MODFLOW-2005 and PHAST[M]. USGS: Techniques and Methods, 2009. [31] 李雅依, 夏强, 许模, 等. 隔档式构造区岩溶地下水流系统多级次嵌套结构的水化学识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 405-413. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0162Li Y Y, Xia Q, Xu M, et al. Hydrogeochemical indicators of hierarchically nested structure of karst groundwater flow systems in the ejective folds area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 405-413(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0162 [32] 陈雪彬. 重庆青木关岩溶地下河水文过程模拟[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014.Chen X B. The Simulation of hydrological process in Qingmuguan karst underground river, Chongqing, China[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] 杨平恒, 张宇, 田萍, 等. 川东平行岭谷典型岩溶含水介质特征的识别方法探讨: 以重庆青木关地下水系统为例[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 38(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNND201602015.htmYang P H, Zhang Y, Tian P, et al. Discussion on the identification method of typical karst water-bearing media in the parallel ridge valley of eastern Sichuan: A case study of Qingmuguan groundwater system in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 38(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNND201602015.htm [34] 杨平恒, 罗鉴银, 袁道先, 等. 降雨条件下岩溶槽谷泉水的水文地球化学特征[J]. 水利学报, 2009, 40(1): 67-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB200901011.htmYang P H, Luo J Y, Yuan D X, et al. Response of spring water hydrochemical behaviors to rainfall in karst subterranean river system[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2009, 40(1): 67-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB200901011.htm [35] 扈志勇. 不同降雨过程下岩溶水文系统信息的响应研究: 以重庆青木关岩溶槽谷为例[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2010.Hu Z Y. Response of karst hydrology system under different rainfall: A case study in Qingmuguan karst valley, Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2010(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: