Formation time and fluid source of calcite veins and geological significance: An example from the Triassic Qinglong Formation carbonate reservoirs in the Huangqiao area, Subei Basin
-
摘要:
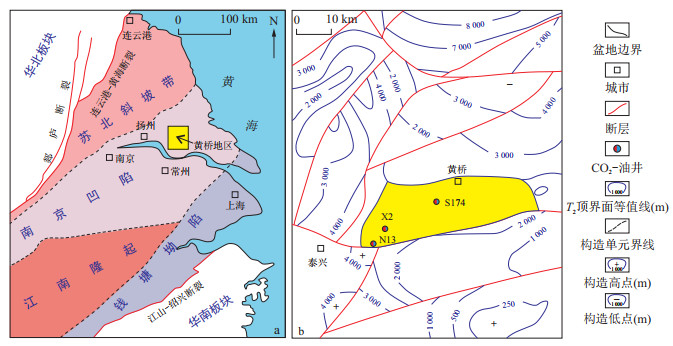
裂缝方解石脉是构造成岩作用的产物, 记录了裂缝开启和流体活动的信息。基于岩石薄片观察、阴极发光和U-Pb同位素定年在厘清苏北盆地黄桥地区三叠系青龙组碳酸盐岩中方解石脉发育期次和形成时间, 通过稀土元素特征, C、O、Sr同位素特征综合分析了方解石脉体成脉流体来源。结果表明: 黄桥地区青龙组发育4期方解石脉体, 4期方解石脉体形成时间分别为(115.30±0.42), (97.03±0.43), (85.29±0.25), (45.5±19.0) Ma。第1和第2期方解石成脉流体分别来源于深部热液流体和大气淡水以及海水的混合流体。第3期方解石成脉流体来源于同层地层水和深部壳源热液流体的混合流体。第4期成脉流体来源于同层地层水和深部幔源热液流体的混合流体。苏北盆地黄桥地区三叠系青龙组碳酸盐岩储层中4期脉体的形成时间与不同期次构造活动具有对应关系, 表明构造活动对流体活动的控制作用。储层中3期深部热液流体的注入是因为构造活动导致深大断裂沟通深部流体而注入到储层中的结果, 多期的深部热液流体活动可能指示了黄桥地区三叠系青龙组储层具有多期油气成藏的特征。
Abstract:Objective Calcite veins are the products of tectonic diagenesis. Information about fracture opening and fluid activity was recorded by calcite veins.
Methods Multiple approaches, consisting of thin section observation, cathodoluminescence, U-Pb isotope dating, and REE, C, O and Sr isotope analyses of calcite veins from the Triassic Qinglong carbonate reservoirs in the Huangqiao area, Subei Basin, are used to analyse the origin of vein-forming fluid.
Results Four stages of calcite veins were identified in the Qinglong Formation and successively formed at (115.30±0.42), (97.03±0.43), (85.29±0.25), (45.5±19.0) Ma. In the first stage, the calcite veins were derived from deep hydrothermal fluids.And in the second stage, the calcite veins were derived from mixed fluids of atmospheric fresh water and seawater. Formation water and deep shell-source hydrothermal fluid mixed in the vein-forming fluid of the third-stage calcite veins. In the fourth stage of calcite veins formation, deep mantle-source hydrothermal fluid mixed with the formation water, resulting in the precipitation of calcite veins. The formation timing of the four stages of calcite veins corresponds to multistage tectonic movements during different periods, indicating that fluid evolution in the Triassic Qinglong carbonate reservoirs was controlled by multiple stages of tectonic movements.
Conclusion Importantly, three stages of deep hydrothermal fluid injectionin the reservoir were the result of deep fault opening caused by tectonic movements, which possibly indicate multistage hydrocarbon accumulation in the Triassic Qinglong Formation in the Huangqiao area.
-
Key words:
- calcite vein /
- carbonate reservoir /
- U-Pb isotope age /
- fluid source /
- fluid activity /
- Huangqiao gas field /
- Subei Basin
-
图 3 苏北盆地黄桥地区三叠系青龙组方解石脉体岩相学和阴极发光特征
a~c.S174井,1 610.5 m,青龙组,裂缝充填C1方解石,C1方解石阴极发光呈亮红色;d~f.X2井1 738.36 m,青龙组,缝洞充填C2和裂缝充填C3方解石,C2方解石阴极发光呈暗红色,C3方解石阴极发光呈橘黄色;g, h.N13井1 438.56 m,青龙组,孔洞中充填C4方解石,阴极发光呈暗红色
Figure 3. Petrography and cathodeluminescence characteristics of calcite veins from the Triassic Qinglong Formation in the Huangqiao area, Subei Basin
图 8 苏北盆地黄桥地区埋藏史(改自文献[51])
Figure 8. Burial history of the Huangqiao area, Subei Basin
表 1 苏北盆地黄桥地区三叠系青龙组方解石脉体与围岩特征元素参数
Table 1. Characteristic elemental parameters of calcite veins and surrounding rocks from the Triassic Qinglong Formation in the Huangqiao area, Subei Basin
样品 w(Fe)/10-6 w(Mn)/10-6 w(Sr)/10-6 Fe/Mn Mn/Sr Y/Ho La/Ho C1方解石脉体 5 468.55 2 211.82 2 485.52 2.47 0.89 30.27 6.45 C1方解石脉体 5 664.54 2 159.44 2 665.74 2.62 0.81 32.90 6.96 C1方解石脉体 6 112.30 2 198.66 3 097.30 2.78 0.71 35.37 9.34 C1方解石脉体 6 078.90 2 185.26 3 189.04 2.78 0.69 33.75 9.11 C1方解石脉体 3 792.93 1 652.97 8 14.50 2.29 2.03 32.23 3.84 C1方解石脉体 5 509.96 2 076.61 2 546.05 2.65 0.82 38.33 11.35 C2方解石脉体 134.08 219.18 1 852.69 0.61 0.12 59.82 1.08 C2方解石脉体 127.66 219.35 1 426.23 0.58 0.15 47.44 0.41 C2方解石脉体 115.36 211.10 1 797.10 0.55 0.12 48.00 0.35 C3方解石脉体 171.00 998.41 452.22 0.17 2.21 34.82 0.04 C3方解石脉体 165.88 1 268.72 506.04 0.13 2.51 35.77 0.05 C3方解石脉体 181.73 1 512.56 23 254.05 0.12 0.07 41.56 0.12 C4方解石脉体 4 829.25 247.76 661.94 19.49 0.37 30.53 6.95 C4方解石脉体 4 702.50 250.32 340.08 18.79 0.74 29.07 6.66 C4方解石脉体 4 476.20 253.72 476.45 17.64 0.53 30.15 6.88 围岩 589.09 57.21 637.30 10.30 0.09 34.72 4.81 围岩 1 062.09 42.90 551.68 24.76 0.08 30.41 13.94 围岩 2 883.60 132.09 897.39 21.83 0.15 32.26 33.20 围岩 2 173.29 103.35 923.87 21.03 0.11 26.74 23.98 -
[1] DAVIES G R, SMITHJR L B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1641-1690. doi: 10.1306/05220605164 [2] 金之钧, 张刘平, 杨雷, 等. 沉积盆地深部流体的地球化学特征及油气成藏效应[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2002, 27(6): 659-665. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGSY200309001024.htmJIN Z J, ZHANG L P, YANG L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of deep fluids and hydrocarbon accumulation effects in sedimentary basins[J]. Earth Sciences (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2002, 27(6): 659-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGSY200309001024.htm [3] 解习农, 成建梅, 孟元林. 沉积盆地流体活动及其成岩响应[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 863-871. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200905011.htmXIE X N, CHENG J M, MENG Y L. Basin fluid flow and associated diagenetic processes[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 863-871. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200905011.htm [4] 刘恩涛, ZHAO J X, 潘松圻, 等. 盆地流体年代学研究新技术: 方解石激光原位U-Pb定年法[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 698-712. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903002.htmLIU E T, ZHAO J X, PAN S Q, et al. A new technology of basin fluid geochronology: In-situ U-Pb dating of calcite[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 698-712. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903002.htm [5] OLIVER J. Fluids expelled tectonically from orogenic belts: Their role in hydrocarbon migration and other geologic phenomena[J]. Geology, 1986, 14(2): 99-102. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<99:FETFOB>2.0.CO;2 [6] 姜磊, 邓宾, 刘树根, 等. 焦石坝-武隆构造带古流体活动差异及对页岩气保存条件的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2): 524-538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902015.htmJIANG L, DENG B, LIU S G, et al. Paleo-fluid migration and conservation conditions of shale gas in Jiaoshiba-Wulong area[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2): 524-538. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902015.htm [7] MARFIL R, CAJA M A, TSIGE M, et al. Carbonate-cemented stylolites and fractures in the Upper Jurassic limestones of the eastern Iberian Range, Spain: A record of palaeofluids composition and thermal history[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 178(3/4): 237-257. [8] KATZ D A, EBERLI G P, SWART P K, et al. Tectonic-hydrothermal brecciation associated with calcite precipitation and permeability destruction in Mississippian carbonate reservoirs, Montana and Wyoming[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1803-1841. doi: 10.1306/03200605072 [9] LIU Q Y, ZHU D Y, JIN Z J, et al. Effects of deep CO2 on petroleum and thermal alteration: The case of the Huangqiao oil and gas field[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 469: 214-229. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.06.031 [10] 李海庆. 江苏黄桥CO2气田成藏条件研究及意义[J]. 能源技术与管理, 2012, 37(1): 128-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSMT201201052.htmLI H Q. Study on reservoir-forming conditions of CO2 gas field in Huangqiao, Jiangsu and its significance[J]. Energy Technology and Management, 2012, 37(1): 128-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSMT201201052.htm [11] 刘志华. 下扬子黄桥地区构造样式分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(4): 502-507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201804007.htmLIU Z H. Structural styles of Huangqiao area, Lower Yangtze region[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(4): 502-507. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201804007.htm [12] 张淮, 郭念发. 苏北盆地黄桥CO2气田储集层裂隙特征[J]. 江苏地质, 2004, 28(4): 201-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200404002.htmZHANG H, GUO N F. Fracture features of Huangqiao CO2 gas field in North Jiangsu Basin[J]. Geology of Jiangsu Province, 2004, 28(4): 201-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200404002.htm [13] CHEN J X, GUO X W, TAO Z, et al. U-Pb dating of oil charge in superimposed basins: A case study from the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2022, 134(11/12): 3176-3188. [14] 罗涛, 何治亮, 郭小文, 等. 川东南丁山地区石牛栏组成脉流体来源与油气成藏[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 231-241. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0024LUO T, HE Z L, GUO X W, et al. Origins of vein-forming fluid and hydrocarbon accumulation in Shiniulan Formation in Dingshan, Southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 231-241. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0024 [15] 罗涛, 郭小文, 舒志国, 等. 四川盆地焦石坝南部地区五峰组-龙马溪组裂缝脉体流体来源及形成时间[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(5): 611-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202105005.htmLUO T, GUO X W, SHU Z G, et al., Fluid source and formation time of fracture veins of Wufeng Formation and Longmaxi Formation in the south of Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 611-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202105005.htm [16] 徐豪, 郭小文, 曹自成, 等. 运用方解石中流体包裹体最小均一温度确定塔河油田奥陶系油气成藏时间: 来自激光原位方解石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(10): 3535-3548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202110009.htmXU H, GUO X W, CAO Z C, et al. Application of minimum homogenization temperatures of aqueous inclusions in calcite veins to determine time of hydrocarbon accumulation in Ordovician of Tahe oilfield: Evidence from in-situ calcite U-Pb dating by laser ablation[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(10): 3535-3548. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202110009.htm [17] 杨毅, 王斌, 曹自成, 等. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒低隆起北部中下奥陶统储层方解石脉成因及形成时间[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6): 2246-2257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106021.htmYANG Y, WANG B, CAO Z C, et al. Genesis and formation time of calcite veins of Middle-Lower Ordovician reservoirs in northern Shuntuoguole low-uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(6): 2246-2257. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106021.htm [18] 郭小文, 陈家旭, 袁圣强, 等. 含油气盆地激光原位方解石U-Pb年龄对油气成藏年代的约束: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(3): 284-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htmGUO X W, CHEN J X, YUAN S Q, et al. Constraint of in situ calcite U-Pb dating by laser ablation on geochronology of hydrocarbon accumulation in petroliferous basins: A case study of Dongying Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 284-291. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htm [19] 谢文雅, 牛漫兰, 曹洋. 郯庐断裂带早白垩世岩浆活动与断裂带的活动关系[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 32(3): 293-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE200903003.htmXIE W Y, NIU M L, CAO Y. Research on Early Cretaceous magmatic activity in the middle-southern segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone and its evolution[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2009, 32(3): 293-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE200903003.htm [20] 徐佑德. 郯庐断裂带构造演化特征及其与相邻盆地的关系[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2009.XU Y D. Structural evolution characteristics of Tan-Lu fault zone and its relationship with adjacent basins[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] ZHU D Y, MENG Q Q, LIU Q Y, et al. Natural enhancement and mobility of oil reservoirs by supercritical CO2 and implication for vertical multi-trap CO2 geological storage[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 161: 77-95. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.026 [22] 柴铭. 苏北盆地走滑构造特征与油气分布规律[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.CHAI M. Characteristics of strike-slip structure and it's relationship to hydrocarbon distribution in the Subei Basin[D]. Qingdao Shandong: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 刘国勇, 金之钧, 张刘平. 深源CO2对沉积盆地油气成藏的影响[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(11): 31-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200611010.htmLIU G Y, JIN Z J, ZHANG L P. Influences of anatectic CO2 on hydrocarbon reservoiring in sedimentary basins[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(11): 31-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200611010.htm [24] 李伶俐. 下扬子黄桥地区上古生界碳酸盐岩储层裂缝特征研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2013, 33(14): 124-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201314111.htmLI L L. Study on fracture characteristics of Upper Paleozoic carbonate reservoir in Huangqiao area of Lower Yangtze River, Lower Yangzi[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2013, 33(14): 124-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201314111.htm [25] 李海庆. 江苏黄桥CO2气田成藏的特殊地质条件[J]. 中国高新技术企业, 2011(6): 81-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGX201106037.htmLI H Q. Special geological conditions of reservoir formation in Huangqiao CO2 gas field, Jiangsu Province[J]. China High-Tech Enterprises, 2011(6): 81-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGX201106037.htm [26] 任以发. 黄桥二氧化碳气田成藏特征与进一步勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(5): 632-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200505017.htmREN Y F. The becoming store character and explorating object about carbon dioxide gas field in Huangqiao[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(5): 632-636. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200505017.htm [27] 龚与觐, 曾维雄. 苏北黄桥二氧化碳气田: 一种特殊的成藏类型[J]. 石油实验地质, 1998, 20(4): 374-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD804.009.htmGONG Y J, ZENG W X. A carbon dioxide gas field in Huangqiao, North Jiangsu Province: A special pool forming type[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1998, 20(4): 374-378. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD804.009.htm [28] 马立桥, 陈汉林, 董庸. 等. 苏北-南黄海南部叠合盆地构造演化与海相油气勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(1): 35-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200701004.htmMA L Q, CHEN H L, DONG Y, et al. Tectonic evolution of Subei-South Nanhuanghai superimposed basin from the Late Mesozoic to the Cenozoic and marine petroleumpotential[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(1): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200701004.htm [29] 许红, 焦里力, 蔡乾忠, 等. 苏北盆地中古生代油气勘探发现与生储盖组合特征及现实意义[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2007, 23(9): 24-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200709006.htmXU H, JIAO L L, CAI Q Z, et al. Middle Paleozoic oil and gas exploration and characteristics of sourced-reservoir-cap assemblages and their practical significance in Subei Basin[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2007, 23(9): 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200709006.htm [30] 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等. 郯庐断裂带的演化及其对西太平洋板块运动的响应[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(1): 36-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200401005.htmZHU G, WANG D X, LIU G S, et al. Evolution of the Tan-Lu fault zone and its responses to plate movements in West Pacific Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2004, 39(1): 36-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200401005.htm [31] 张永鸿. 下扬子区构造演化中的黄桥转换事件与中、古生界油气勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1991, 12(4): 439-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199104009.htmZHANG Y H. Huangqiao transform event in tectonic evolution of Lower Yangtze region and the meso-Paleozoic hydrocarbon exploration target[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1991, 12(4): 439-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199104009.htm [32] 王坤, 李伟, 陆进, 等. 川东地区石炭系碳酸盐岩碳、氧、锶同位素特征及其成因分析[J]. 地球化学, 2011, 40(4): 351-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201104005.htmWANG K, LI W, LU J, et al. Carbon, oxygen, strontium isotope characteristics and cause analysis of Carboniferous carbonate rocks in the eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2011, 40(4): 351-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201104005.htm [33] KAUFMAN A J, KNOLL A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isotopic composition of seawater: Stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73: 27-49. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(94)00070-8 [34] KEITH M L, ANDERSON G M, EICHLER R. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of mollusk shells from marine and fresh-water environments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964, 28(10/11): 1757-1786. [35] PAYNE J L, LEHRMANN D J, WEI J Y, et al. Large perturbations of the carbon cycle during recovery from the end-permian extinction[J]. Science, 2004, 305: 506-509. doi: 10.1126/science.1097023 [36] 黄可可, 黄思静, 兰叶芳, 等. 早三叠世海相碳酸盐碳同位素研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(3): 357-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201303009.htmHUANG K K, HUANG S J, LAN Y F, et al. Review of the carbon isotope of Early Triassic carbonates[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(3): 357-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201303009.htm [37] VEIZER J. 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic oceans[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1998, 62(3): 1586. [38] BROOM-FENDLEY S, WALL F, SPIRO B, et al. Deducing the source and composition of rare earth mineralising fluids in carbonatites: Insights from isotopic (C, O, 87Sr/86Sr) data from Kangankunde, Malawi[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology Beitrage Zur Mineralogie und Petrologie, 2017, 172(11): 96. [39] 陈少伟, 刘建章. 含油气盆地微观裂缝脉体期次、成因与流体演化研究进展及展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 81-92. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0426CHEN S W, LIU J Z. Research progress and prospects of the stages, genesis and fluid evolution of micro-fracture veins in petroliferous basins[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 81-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0426 [40] 赵彦彦, 李三忠, 李达, 等. 碳酸盐(岩)的稀土元素特征及其古环境指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(1): 141-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htmZHAO Y Y, LI S Z, LI D, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of carbonate and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2019, 43(1): 141-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htm [41] ZHAO Y Y, WEI W, SANTOSH M, et al. A review of retrieving pristine rare earth element signatures from carbonates[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 586: 110765. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110765 [42] 高键. 渝东地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩裂缝脉体古温压及古流体成因[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.GAO J. Paleotemperature pressure and paleofluid genesis of shale fracture veins in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, eastern Chongqing area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [43] 刘存革, 李国蓉, 朱传玲, 等. 塔河油田中下奥陶统岩溶缝洞方解石碳、氧、锶同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2008, 33(3): 377-386. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200803013.htmLIU C G, LI G R, ZHU C L, et al. Geochemistry characteristics of carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopes of calcites filled in karstic fissure-cave in Lower-Middle Ordovician of Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2008, 33(3): 377-386. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200803013.htm [44] 陈丽清, 吴娟, 何一凡, 等. 四川盆地绵阳-长宁拉张槽中段下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩裂缝脉体特征及古流体活动过程[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 142-152. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220584CHEN L Q, WU J, HE Y F, et al. Fracture vein characteristics and paleofluid activities in the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi shale in the central portion of the Mianyang-Changning intracratonic sag, Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 142-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220584 [45] BANNER J L. Radiogenic isotopes: Systematics and applications to earth surface processes and chemical stratigraphy[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 65(3/4): 141-194. [46] 黄思静, 卿海若, 胡作维, 等. 川东三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩的阴极发光特征与成岩作用[J]. 地球科学, 2008, 33(1): 26-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200801007.htmHUANG S J, QING H R, HU Z W, et al. Cathodoluminescence and diagenesis of the carbonate rocks in Feixianguan Formation of Triassic, eastern Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Earth Science, 2008, 33(1): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200801007.htm [47] BAU M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1996, 123(3): 323-333. doi: 10.1007/s004100050159 [48] NOZAKI Y, ZHANG J, AMAKAWA H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1/2): 329-340. [49] NOZAKI Y, LERCHE D, ALIBO D S, et al. The estuarine geochemistry of rare earth elements and indium in the Chao Phraya River, Thailand[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(23): 3983-3994. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00473-7 [50] ZHU D Y, LIU Q Y, MENG Q Q, et al. Enhanced effects of large-scale CO2 transportation on oil accumulation in oil-gas-bearing basins: Implications from supercritical CO2 extraction of source rocks and a typical case study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 493-504. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.11.017 [51] 杜婷, 邢凤存, 陆永潮, 等. 下扬子黄桥地区龙潭组致密砂岩胶结物流体特征与演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(3): 292-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201803004.htmDU T, XING F C, LU Y C, et al. Fluid characteristics and evolution of Longtan Formation tight sandstone cements in Huangqiao area, Lower Yangtze, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2018, 45(3): 292-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201803004.htm [52] 杨力. 苏北盆地中新生代构造演化及其与油气的关系[D]. 湖北荆州: 长江大学, 2015.YANG L. Middle Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the North Jiangsu Basin and its relationship with hydrocarbons[D]. Jingzhou Hubei: Yangtze University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [53] 赵斐宇, 姜素华, 李三忠, 等. 中国东部无机CO2气藏与(古)太平洋板块俯冲关联[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 370-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704039.htmZHAO F Y, JIANG S H, LI S Z, et al. Correlation of inorganic CO2 reservoirs in East China to subduction of (Paleo-) Pacific Plate[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 370-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704039.htm [54] 沈淑鑫, 李一泉, 崔键, 等. 下扬子黄桥地区构造特征及其与油气的关系[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(3): 538-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201503017.htmSHEN S X, LI Y Q, CUI J, et al. The structural characteristics in Huangqiao area in the Lower Yangtze region and its relationship to oil and gas accumulation[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2015, 21(3): 538-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201503017.htm [55] GUO X W, LIU K Y, HE S, et al. Petroleum generation and charge history of the northern Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Insight from integrated fluid inclusion analysis and basin modelling[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 32(1): 21-35. -





 下载:
下载: