Role of the large-scale strike-slip transform zone in controlling the differential hydrocarbon distribution: A case of the Côte d'Ivoire Basin in West Africa
-
摘要:
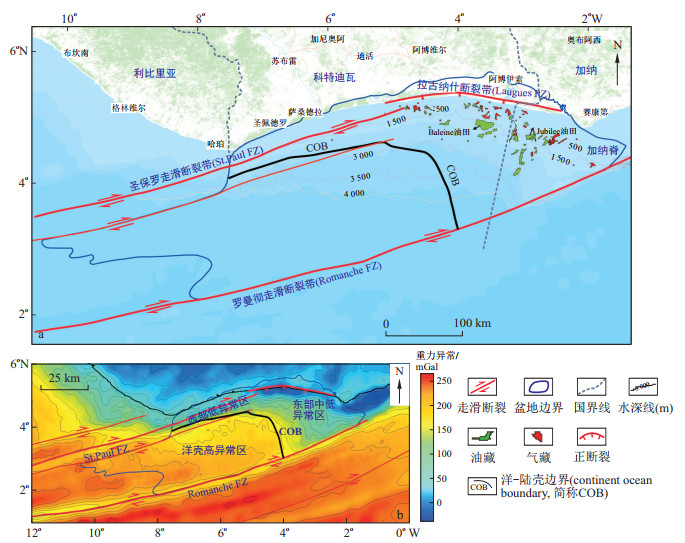
科特迪瓦盆地位于西非赤道段, 发育大型走滑转换带, 为典型的转换型被动陆缘盆地, 是当前油气勘探热点区域, 勘探潜力巨大, 但油气平面分布、纵向富集均存在较大的差异性。基于前人研究, 利用井、震资料并结合近年来新发现油气藏数据, 重点从构造和沉积2个方面阐述了走滑转换带对油气分布差异性的控制作用。研究表明, 盆地经历了陆内裂谷、洋陆转换和被动陆缘3个主要的构造-沉积演化阶段, 形成了总体上"西窄东宽"的斧型构造格局特征, 西部为陡窄转换边缘, 东部为宽缓离散边缘, 中部为过渡边缘, 宏观上控制了油气"西少东多"的分布规律。走滑转换作用应力主要响应区为中部过渡边缘, 中部隆起马尾带发育大量的构造圈闭, 具有南北双向供烃特征, 控制了北部凸起阿尔比构造油气藏的形成与分布。走滑转换作用形成的古地貌对转换早期上阿尔比-森诺曼和转换晚期土伦阶储层的空间展布特征均有重要的控制作用, 内斜坡洼陷(盆地)往往是最为有利的富砂处, 同时也是最有利的地层-岩性圈闭发育区, 油气分布与沉积体系展布具有较好的一致性, 即转换控储, 分布控藏。
Abstract:Objective The Côte d'Ivoire Basin, which is located in the equatorial section of West Africa and features large-scale strike-slip transform zones, is a typical transformed passive continental margin basin. This area is currently a hot spot for oil and gas exploration and has great exploration potential but has an uneven distribution of hydrocarbons both horizontally and vertically.
Methods Based on previous results, well data, seismic data and new discoveries, this paper focuses on the differential controls of hydrocarbon distribution from two perspectives: structure and sedimentation.
Results The results show that the basin has experienced three main tectonic-sedimentary evolution stages, namely, intracontinental rift, ocean-continent transition, and passive margin, forming the "narrow west-wide east" axe structure. The basin has a narrow and steep transform margin in the west, a wide and gentle divergent margin in the east, and a transitional margin in the central region, which controls the overall oil and gas distribution of "less in the west and more in the east" in macro-scale. The main response area of the strike-slip transformation stress in the central transitional margin and the central uplift developed many structural traps, which were sourced from both the northern and southern depression and ultimately controlled the distribution of the Albian oil and gas reservoirs.
Conclusion The palaeomorphology formed by the strike-slip transform zone plays an important role in controlling the spatial distribution of both the Upper Albian-Cenomanian reservoirs in the early stage and the Turonian reservoirs in the late stage. The stepped or intra-slope ponds on slopes formed by strike-slip transform zone are often the most favourable sand-rich places and benefit stratigraphic-lithologic traps. Additionally, the distribution of oil and gas reservoirs has good consistency with the distribution of sedimentary systems; that is, the transformation controls the reservoirs, and the distribution controls the oil and gas reservoirs.
-
图 4 科特迪瓦盆地边缘演化地质剖面示意图(左.转换边缘; 右.离散边缘,据文献[25]修改)
Figure 4. Evolution profile at margin of the Côte d′ Ivoire Basin
-
[1] DAHLSTROM C D A. Balanced cross sections[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1969, 6(4): 743-757. doi: 10.1139/e69-069 [2] DAHLSTROM C D A. Structural geology in the eastern margin of the Canadian Rocky Mountains[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1970, 18(3): 332-406. [3] MORLEY C K, NELSON R A, PATTON T L, et al. Transfer zones in the East African Rift System and their relevance to hydrocarbon exploration in rifts (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(8): 1234-1253. [4] GAWTHORPE R L, HURST J M. Transfer zones in extensional basins: Their structural style and influence on drainage development and stratigraphy[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1993, 150(6): 1137-1152. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.150.6.1137 [5] PEACOCK D C P, SANDERSON D J. Geometry and development of relay ramps in normal fault systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(2): 147-165. [6] 叶洪. 断块构造理论在研究"走滑转换构造"中的应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 1988.YE H. Application of fault block tectonic theory to the study of "strike-slip transform structures"[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1988. (in Chinese) [7] 宋鸿林. 斜向滑动与走滑转换构造[J]. 地质科技情报, 1996, 15(4): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ604.007.htmSONG H L. Oblique slip and strike-slip transform structures[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1996, 15(4): 33-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ604.007.htm [8] 朱秀香, 吕修祥, 王德英, 等. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷走滑转换带对油气聚集的控制[J]. 石油天然气与地质, 2009, 30(4): 476-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200904018.htmZHU X X, LÜ X X, WANG D Y, et al. Controlling effect of a strike-slip transform belt on hydrocarbon accumulations in the Huanghekou Sag, the Bohai Sea waters[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(4): 476-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200904018.htm [9] 徐长贵. 渤海走滑转换带及其对大中型油气田形成的控制作用[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(9): 1548-1560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201609010.htmXU C G. Strike-slip transfer zone and its control on formation of medium and large-sized oilfields in Bohai Sea area[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(9): 1548-1560. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201609010.htm [10] 柳屿博, 黄晓波, 徐长贵, 等. 渤海海域辽西构造带S型走滑转换带特征及控藏作用定量表征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(1): 20-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801004.htmLIU Y B, HUANG X B, XU C G, et al. Characteristics of S-shaped strike-slip transfer zones and quantitative analysis of their influence on hydrocarbon accumulation in Liaoxi structural belt, Bohai Sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(1): 20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801004.htm [11] 柳永军, 徐长贵, 朱文森, 等. 辽东湾坳陷挤压型和拉张型走滑转换带特征及其控藏作用[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2018, 37(1): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201801003.htmLIU Y J, XU C G, ZHU W S, et al. Characteristics of the compressional and extensional strike-slip transform belts and their controlling actions on the hydrocarbon accumulation for Liaodong Bay Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2018, 37(1): 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201801003.htm [12] 徐长贵. 渤海海域大型伸展-走滑复合断裂特征与控藏作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(6): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202206001.htmXU C G. Characteristics and reservoir controlling of large-scale extension-strike slip composite faults in Bohai Sea area[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(6): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202206001.htm [13] 吴智平, 张勐, 张晓庆, 等. 渤海湾盆地"埕北-垦东"构造转换带形成演化及成藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1321-1333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206004.htmWU Z P, ZHANG M, ZHANG X Q, et al. Evolution and reservoir characteristics of the "Chengbei-Kendong" structural transfer zone in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1321-1333. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206004.htm [14] 王冰洁, 王德英, 王鑫, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽中凹陷南洼走滑转换带特征及其对大、中型油田的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1347-1358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206006.htmWANG B J, WANG D Y, WANG X, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip transition zone in southern Liaozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin and its control on large-, medium-sized oilfields[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1347-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206006.htm [15] MERCIER DE LÉPINAY M, LONCKE L, BASILE C, et al. Transform continental margins: Part 2. A worldwide review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 693: 96-115. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.05.038 [16] MASCLE J, BLAREZ E. Evidence for transform margin evolution from the Ivory Coast-Ghana continental margin[J]. Nature, 1987, 326: 378-381. doi: 10.1038/326378a0 [17] BLAREZ E, MASCLE J. Shallow structures and evolution of the Ivory Coast and Ghana transform margin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1988, 5(1): 54-64. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(88)90039-6 [18] BASILE C, BRUN J P, MASCLE J. The Ivory Coast-Ghana transform margin, structure and formation: Seismic reflection data versus experimental modelization[J]. Bulletin De La Societe Geologique De France, 1992, 163(3): 207-216. [19] BASILE C, MASCLE J, POPOFF M, et al. The Ivory Coast-Ghana transform margin: A marginal ridge structure deduced from seismic data[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993, 222(1): 1-19. [20] LAMARCHE G, BASILE C, MASCLE J, et al. The Côte d'Ivoire-Ghana transform margin: Sedimentary and tectonic structure from multichannel seismic data[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1997, 17(1): 62-69. [21] ANTOBREH A A, FALEIDE J I, TSIKALAS F, et al. Rift-shear architecture and tectonic development of the Ghana margin deduced from multichannel seismic reflection and potential field data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(3): 345-368. [22] BASILE C. Transform continental margins: Part 1. Concepts and models[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 661: 1-10. [23] DAVISON I, FAULL T, GREENHALGH J, et al. Transpressional structures and hydrocarbon potential along the Romanche Fracture Zone: A review[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 2016, 431(1): 235-248. [24] NEMCOK M, RYBÁR S, SINHA S T, et al. Transform margins: Development, controls and petroleum systems: An introduction[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 2016, 431(1): 1-38. [25] YE J, ROUBY D, CHARDON D, et al. Post-rift stratigraphic architectures along the African margin of the Equatorial Atlantic: Part Ⅰ. The influence of extension obliquity[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019, 753: 49-62. [26] LONCKE L, ROEST W R, KLINGELHOEFER F, et al. Transform marginal plateaus[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 102940. [27] TAVARES A C, DE CASTRO D L, CLAUSEN O R, et al. Continental-scale structural heritage from rift extension to postrift inversion: Implications for the central Brazilian equatorial margin evolution[J]. Tectonophysics, 2022, 837: 229446. [28] 刘剑平, 潘校华, 马君, 等. 赤道西非科特迪瓦-加纳转换边缘油气勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(1): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001007.htmLIU J P, PAN X H, MA J, et al. Exploration targets in Côte d'Ivoire -Ghana transform margin in equatorial West Africa[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(1): 43-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001007.htm [29] 程建, 段铁军, 倪春华, 等. 西非科特迪瓦盆地石油地质特征及成藏规律研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(3): 291-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201303013.htmCHENG J, DUAN T J, NI C H, et al. Petroleum geologic features and accumulation rules of Côte d'Ivoire Basin, West Africa[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(3): 291-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201303013.htm [30] 秦雁群, 张光亚, 巴丹, 等. 转换型被动陆缘盆地地质特征与深水油气聚集规律: 以赤道大西洋西非边缘盆地群为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 229-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601024.htmQIN Y Q, ZHANG G Y, BA D, et al. Geological characteristics and deep water hydrocarbon accumulation patterns of transformed passive continental marginal basins: A case history from basins of West Africa margin in Equatorial Atlantic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 229-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601024.htm [31] 张凤廉, 屈红军, 张功成, 等. 西非科特迪瓦盆地深水区油气地质特征及成藏主控因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5): 112-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705015.htmZHANG F L, QU H J, ZHANG G C, et al. Petroleum geological features and main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in deepwater areas of Côte d'Ivoire Basin, West Africa[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5): 112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705015.htm [32] 盖海洋, 姜烨, 张科, 等. 转换型边缘盆地转换边缘类型识别与特征分析: 以非洲科特迪瓦盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 83-90. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0033GAI H Y, JIANG Y, ZHANG K, et al. Recognition and characteristic analysis of the transition boundary for transform marginal basin: A case of Côte d'Ivoire Basin, Africa[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0033 [33] 孔令武, 赵红岩, 梁建设, 等. 转换大陆边缘盆地深水浊积砂岩油气成藏差异性研究: 以西非北段科特迪瓦盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(1): 244-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202201018.htmKONG L W, ZHAO H Y, LIANG J S, et al. Differences in hydrocarbon accumulation of deep-water turbidite sandstone in a transform continental margin basin: A case study of Côte d'Ivoire Basin, West Africa[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(1): 244-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202201018.htm [34] IHS Markit. IHS Basin Monitor: Cote d'Ivoire, Liberia, Ghana[R]. [S. l.]: IHS Markit, 2021. [35] 张科, 张义娜, 李全, 等. 西非科特迪瓦盆地重力场特征与构造区划[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 1025-1031. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB202106021.htmZHANG K, ZHANG Y N, LI Q, et al. Gravity field characteristics and structural division of the Cote d'Ivoire Basin in West Africa[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41(6): 1025-1031. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB202106021.htm [36] 李梁, 孙庭斌, 陈迎楠, 等. 塔里木盆地肖塘南地区走滑断裂特征与断溶体勘探研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 239-245. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0148LI L, SUN T B, CHEN Y N, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip faults and exploration of fault-dissolution body in Xiaotangnan area of Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 239-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0148 [37] 李峻颉, 侯国伟, 秦兰芝, 等. 构造转换带制约下的砂体富集效应: 以平湖斜坡孔雀亭区平湖组为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(4): 459-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202104008.htmLI J J, HOU G W, QIN L Z, et al. Sand enrichment constrained by structural conversion zone: The Pinghu Formation in the Kongqueting area of the Pinghu slope[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(4): 459-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202104008.htm [38] 田立新. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷转换体控沉-控储特性及其油气地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(11): 4043-4056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202111018.htmTIAN L X. Sedimentary-reservoir characteristics under control of transfer model and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(11): 4043-4056. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202111018.htm [39] 陶文芳, 葛家旺, 雷永昌, 等. 转换斜坡型辫状河三角洲沉积特征: 以珠江口盆地惠州凹陷始新统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 103-114. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220202TAO W F, GE J W, LEI Y C, et al. Depositional characteristics of a relay ramp controlled braided deltaic system: A case study in the Eocene Huizhou Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 103-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220202 [40] BROOKS H L, HODGSON D M, BRUNT R L, et al. Disconnected submarine lobes as a record of stepped slope evolution over multiple sea-level cycles[J]. Geosphere, 2018, 14(4): 1753-1779. [41] AMY L A. A review of producing fields inferred to have upslope stratigraphically trapped turbidite reservoirs: Trapping styles (pure and combined), pinch-out formation, and depositional setting[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(12): 2861-2889. [42] BARTON M D. Evolution of intra-slope apron, offshore Niger delta slope: Impact of step geometry on apron architecture[C]//Anon. Application of principles of seismic geomorphology to continental-slope and base-of-slope systems: Case studies from seafloor and near-seafloor analogues. Tulsa Oklahoma: SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology), 2012: 181-197. [43] 秦雁群, 梁英波, 张光亚, 等. 巴西东部海域深水盐上碎屑岩油气成藏条件与勘探方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(5): 63-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201505007.htmQIN Y Q, LIANG Y B, ZHANG G Y, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and further exploration of post-salt clastic rock in Brazil's eastern deepwater area[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(5): 63-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201505007.htm -





 下载:
下载: