Pore characteristics and seepage simulation of sandstone-type uranium ore in the 512 deposit, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
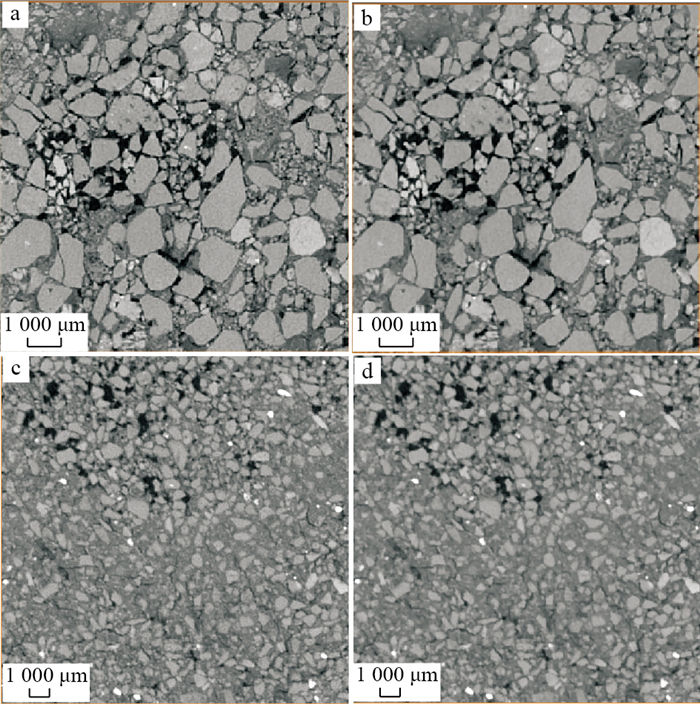
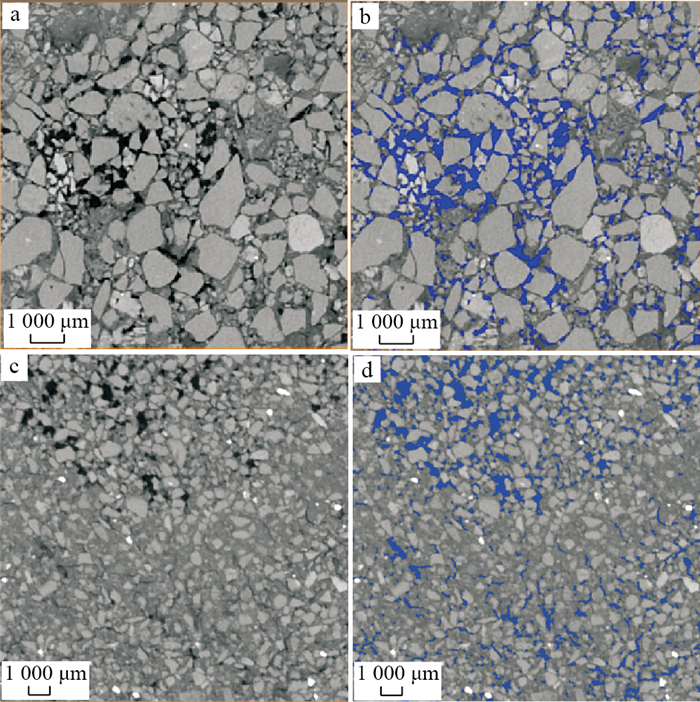
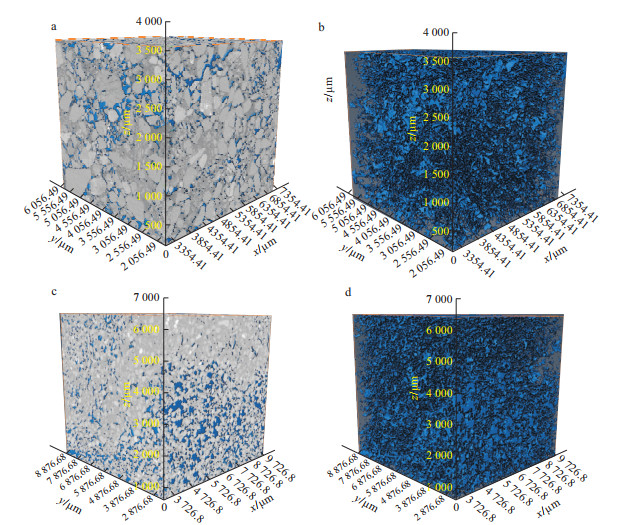
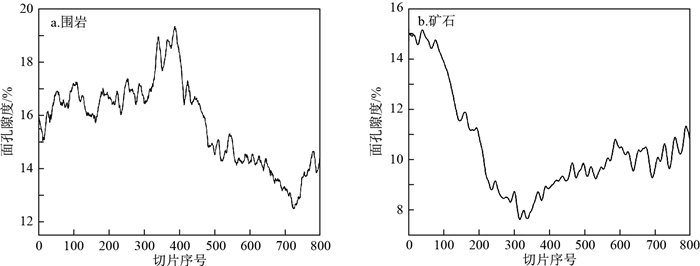
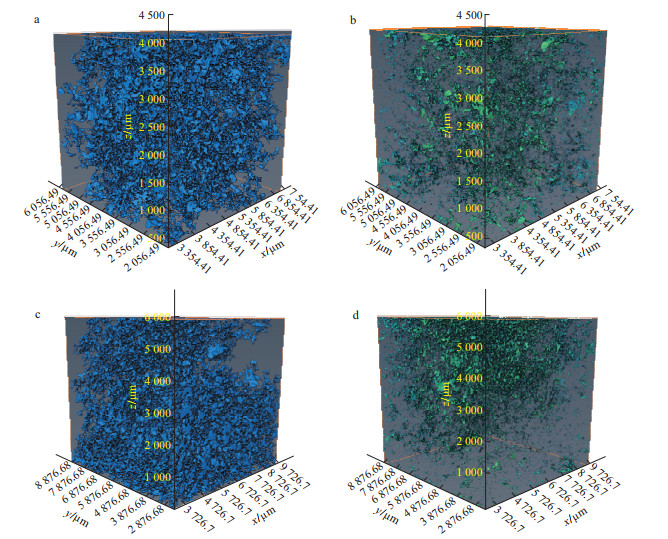
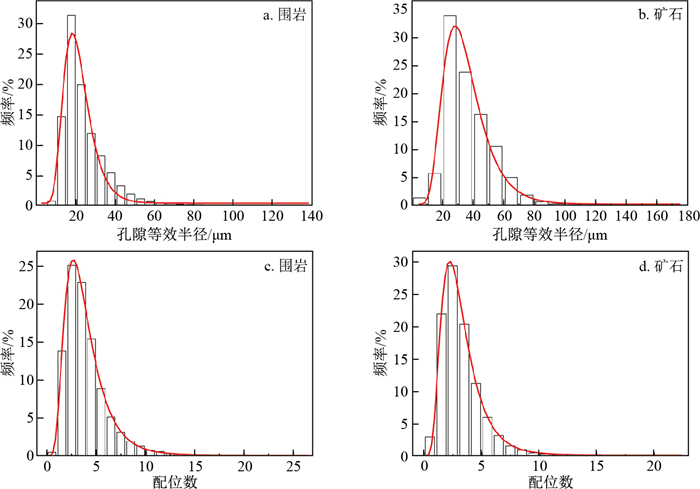
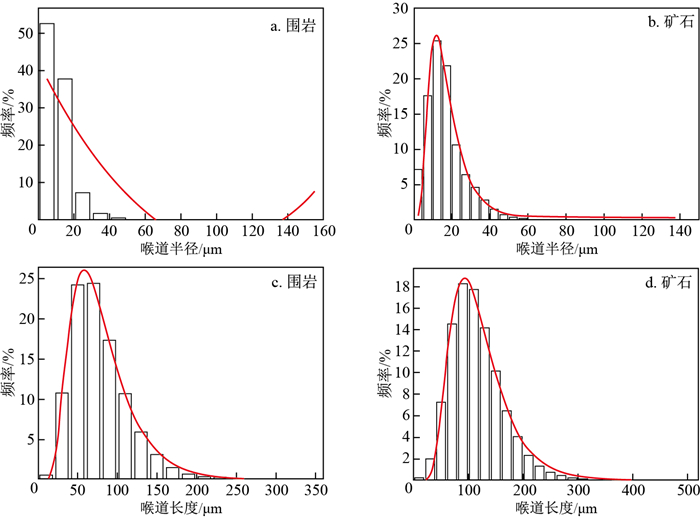
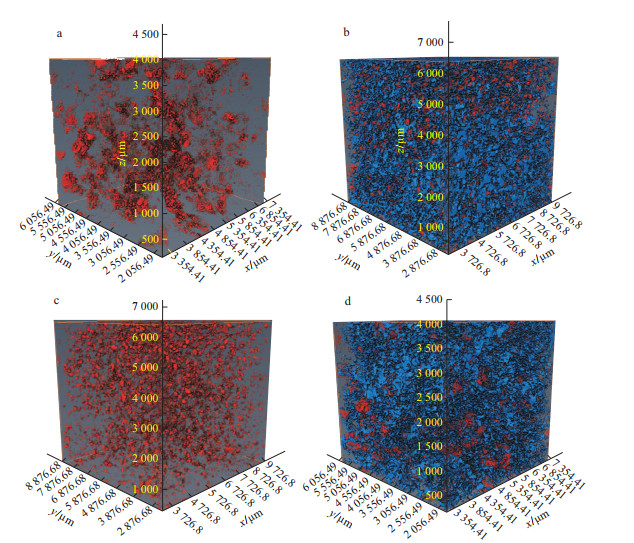
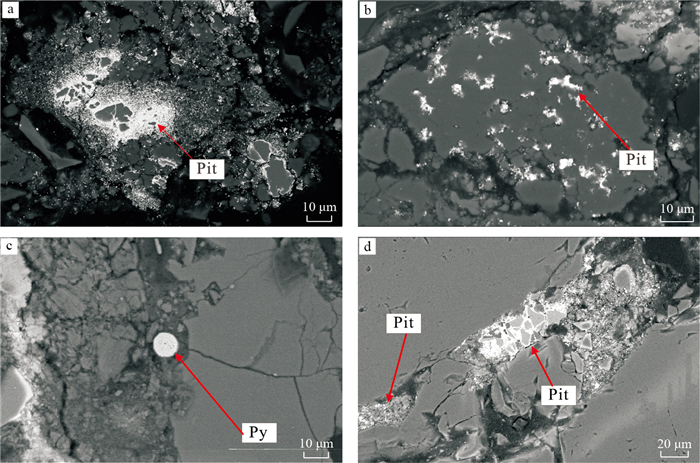
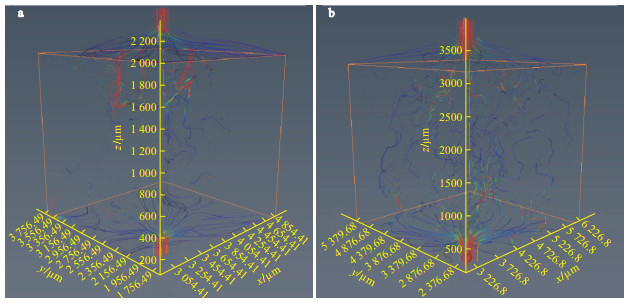
地浸采铀工艺是溶浸液在含矿含水层中与铀矿物发生反应, 铀元素随溶浸液迁移至地表的一种提铀工艺, 精确了解矿区岩石内部结构及金属矿物的分布, 对地浸工艺应用具有重要的指导意义。为了解512矿床岩石内部结构及渗流路径, 选取该矿床代表性围岩和矿石岩心进行CT扫描, 经过图像降噪滤波、图像分割提取孔隙、构建孔隙网络模型等处理与分析, 获得各孔喉参数; 通过Avizo软件模拟得到绝对渗透率、迂曲率和渗流速度变化。结果表明: 围岩和矿石的孔隙度相近, 分别为15.42%, 15.18%;连通孔隙度分别是9.61%, 13.82%。围岩中高密度物质为一些金属矿物, 体积分数约为0.54%, 矿石中高密度矿物多为次生铀矿物, 体积分数为1.06%, 其在浸出过程中可与溶浸液充分接触。孔隙内部具有强烈的非均质性, 导致流速在流动路径中逐渐降低。围岩和矿石连通的大孔数量多于小孔, 指示大孔是决定孔隙发育程度的主要因素。根据速度流线推断围岩和矿石中虽然存在堵塞区, 但流通区域占主导地位。
Abstract:Objective In situ leaching is a uranium extraction process in which a solution reacts with uranium-bearing minerals in a saturated aquifer and then uranium in the flowing solution is extracted through exchange. To understand the internal structure and seepage path of the 512 deposits,
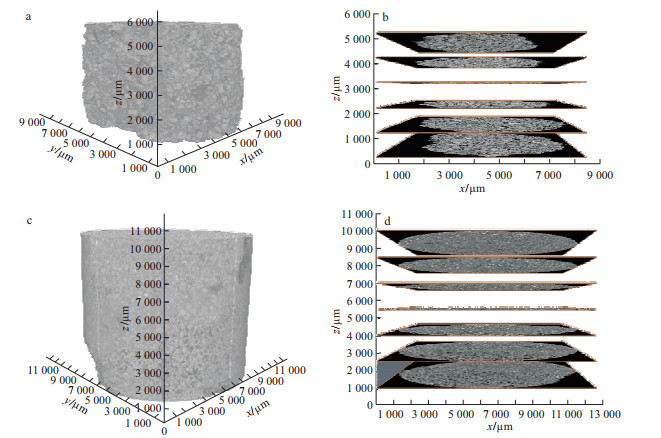
Methods representative wallrock and ore cores of the deposit were selected for CT scanning, and the pore throat parameters were obtained via image noise reduction filtering, image segmentation to extract pores, and the construction of pore network models. The changes in the absolute permeability, tortuosity and seepage velocity are simulated with Avizo software.
Results The results showed that the porosity of the wallrock was 15.42%, the connected porosity was 9.61%, the ore porosity was 15.18%, the connected porosity was 13.82%, and the water permeability was better than that of the wallrock. The high-density materials in the wallrock are metal minerals, accounting for approximately 0.54%, and most of the high-density minerals in the ore are secondary uranium minerals, accounting for 1.06%. It can be fully in contact with the solution during the leaching process.
Conclusion There is strong heterogeneity inside the pores, which causes the flow rate to gradually decrease in the flow path. The number of large pores connecting the wallrock and ore is greater than that of small pores, indicating that large pores are the main factors determining the degree of pore development. According to the velocity streamlines, although there is a blockage area in the wallrock and ore, the circulation area is dominant.
-
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
-
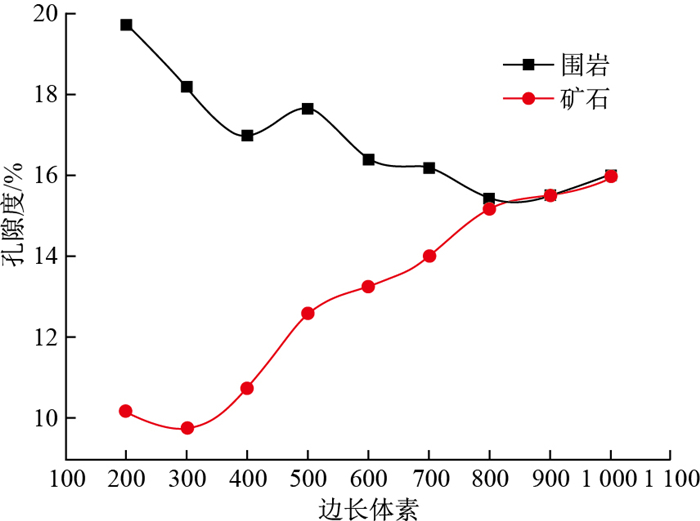
表 1 围岩和矿石不同边长体素正方体孔隙度
Table 1. Porosity of cubes with different side lengths voxels of wallrock and ore
序号 边长体素 围岩孔隙度/% 矿石孔隙度/% 1 200 19.73 10.19 2 300 18.18 9.78 3 400 16.97 10.77 4 500 17.63 12.59 5 600 16.40 13.26 6 700 16.18 14.02 7 800 15.42 15.18 8 900 15.51 15.51 9 1 000 16.00 15.92 表 2 样品渗流模拟结果
Table 2. Seepage simulation results for the wall rock samples
样品 方向 流量/mm3 迂曲率 绝对渗透率/10-3 μm2 矿石 X 8.67 1.98 344.8 Y 6.71 1.87 266.9 Z 5.81 1.71 231.1 围岩 X 0.53 1.89 13.3 Y 0.54 2.02 13.5 Z 0.13 1.83 3.2 -
[1] 阙为民, 王海峰, 田时丰, 等. 我国地浸采铀研究现状与发展[J]. 铀矿冶, 2005, 32(3): 113-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI200503000.htmQUE W M, WANG H F, TIAN S F, et al. Research status and development of in-situ leaching uranium techniques in China[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2005, 32(3): 113-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI200503000.htm [2] 胡鹏华, 李先杰, 陈刚, 等. 中国地浸采铀安全环保现状与展望[J]. 铀矿冶, 2019, 38(1): 70-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI201901014.htmHU P H, LI X J, CHEN G, et al. Present situation and development of ISL radiation protection and regulation in China[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2019, 38(1): 70-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI201901014.htm [3] 黎广荣, 周义朋, 赵凯, 等. 砂岩型铀矿浸出矿物工艺学研究进展[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2021(8): 9-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2021.08.002LI G R, ZHOU Y P, ZHAO K, et al. Research progress on mineral leaching technology of sandstone type uranium deposits[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2021(8): 9-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2021.08.002 [4] 孙占学, FIAZ A, 赵凯, 等. 中国铀矿采冶回顾与展望[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2021(8): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202108002.htmSUN Z X, FIAZ A, ZHAO K, et al. Review and prospect of uranium mining and metallurgy in China[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2021(8): 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202108002.htm [5] 王军, 耿树方. 伊犁盆地库捷尔太铀矿床层间氧化带与铀矿化特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 705-713. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.017WANG J, GENG S F. Characteristics of the interlayer oxidation zone and the Kujieertai uranium deposit in Yili Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(3): 705-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.017 [6] MIN M Z, XU H F, BARTON L L, et al. Biomineralization of uranium: A simulated experiment and its significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(1): 134-138. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2005.tb00874.x [7] 魏观辉. 试论512铀矿床富矿控矿因素、成矿模式及其判别标志[J]. 铀矿地质, 1999, 15(6): 321-328, 337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.1999.06.001WEI G H. Preliminary discussion on ore controlling factors, genetic model and recognition criteria of rich uranium mineralization of uranium deposit No. 512[J]. Uranium Geology, 1999, 15(6): 321-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.1999.06.001 [8] 秦明宽, 王正邦, 赵瑞全. 伊犁盆地512铀矿床黏土矿物特征与铀成矿作用[J]. 地球科学, 1998, 23(5): 74-78.QIN M K, WANG Z B, ZHAO R Q. Characteristics of clay minerals and their relationships with uranium mineralization in uranium deposit No. 512, Yili Basin[J]. Earth Science, 1998, 23(5): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 刘金辉, 孙占学. 伊犁盆地512铀矿床成矿水文地球化学作用研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2003, 18(3): 208-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2003.03.013LIU J H, SUN Z X. The study on ore-forming hydrogeochemistry of 512 uranium deposit, Yili Basin[J]. Journal of Geological Prospecting, 2003, 18(3): 208-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2003.03.013 [10] ZHOU Y, LI G, XU L, et al. Uranium recovery from sandstone-type uranium deposit by acid in-situ leaching: An example from the Kujieertai-Science Direct[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 191: 105209. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105209 [11] 赵凯, 黎广荣, 周义朋, 等. 砂岩型铀矿浸出研究进展[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019(6): 40-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202108003.htmZHAO K, LI G R, ZHOU Y P, et al. Research progress of leaching of sandstone-type uranium ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2019(6): 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202108003.htm [12] 何小同, 陈立, 谢希良, 等. 512矿床化学解堵及酸法地浸堵塞物形成原因分析[C]//佚名. 中国核科学技术进展报告(第六卷). [出版社地不详]: [出版社不详], 2019: 346-352.HE X T, CHEN L, XIE X L, et al. Analysis of blockage formation reason during the acid in-situ leaching and chemical deblocking of 512 deposit[C]//Anon. Progress Report on China Nuclear Science & Technology. [S. l.]: [s. n.], 2019: 346-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 陈鑫睿, 刘金辉, 邢拥国, 等. 内蒙古巴彦乌拉铀矿含矿层堵塞的水文地球化学机理[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2021(10): 58-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202110008.htmCHEN X R, LIU J H, XING Y G, et al. Hydrogeochemical mechanism of ore bearing bed plugging in Bayanwula uraniun deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2021(10): 58-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202110008.htm [14] 刘石玉, 刘金辉, 周义朋, 等. 地浸采铀过程中含矿层堵塞特征研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2022(8): 65-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202208011.htmLIU S Y, LIU J H, ZHOU Y P, et al. Study on characteristics of ore-containing layer blockage during in-situ leaching of uranium mining[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2022(8): 65-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202208011.htm [15] 刘亚洲, 罗跃, 李寻, 等. 巴彦乌拉铀矿床酸法浸铀的水岩反应堵塞机理[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2022, 74(5): 44-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU202205008.htmLIU Y Z, LUO Y, LI X, et al. Water rock reaction plugging mechanism of acid leaching uranium in Bayanwula uranium deposit[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section), 2022, 74(5): 44-51(in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU202205008.htm [16] 刘迎九, 谢水波, 周泉, 等. 某铀矿床酸法地浸现场试验及化学堵塞成因分析[J]. 南华大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 21(1): 10-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGB200701002.htmLIU Y J, XIE S B, ZHOU Q, et al. The field test of acid in-stiu leaching in the uranium deposit and study on the chemical jamming[J]. Journal of University of South China (Science and Technology Edition), 2007, 21(1): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGB200701002.htm [17] 张子涵, 魏文, 张杰, 等. 基于CT扫描红层砂岩孔隙多标度分形维数的确定方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 254-263. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0066ZHANG Z H, WEI W, ZHANG J, et al. Determining method of multiscale fractal dimension of red bed sandstone pores based on CT scanning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 254-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0066 [18] YANG X L. Effect of pore-water pressure on 3D stability of rock slope[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(9): 06017015. [19] SOULAINE C, CREUX P, TCHELEPI H A. Micro-continuum framework for pore-scale multiphase fluid transport in shale formations[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2019, 127(1): 85-112. [20] YAN C Z, ZHENG H. Fdem-flow3D: A 3D hydro-mechanical coupled model considering the pore seepage of rock matrix for simulating three-dimensional hydraulic fracturing[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 81: 212-228. [21] ANDREW M. A quantified study of segmentation techniques on synthetic geological XRM and FIB-SEM images[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2018, 22(6): 1503-1512. [22] TANG C S, ZHU C, LENG T, et al. Three-dimensional characterization of desiccation cracking behavior of compacted clayey soil using X-ray computed tomography[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 255: 1-10. [23] 郑佳, 庄建琦, 孔嘉旭, 等. 基于CT扫描的黄土孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 211-222. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0210ZHENG J, ZHUANG J Q, KONG J X, et al. Study of loess pore structure characteristics based on CT scanning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 211-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0210 [24] ZHAO Y X, SUN Y F, LIU S M, et al. Pore structure characterization of coal by synchrotron radiation nano-CT[J]. Fuel, 2018, 215: 102-110. [25] LI Y R, SHI W H, AYDIN A, et al. Loess genesis and worldwide distribution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 201: 102947. [26] 胡心玲, 雷浩. 基于CT扫描技术的低渗油藏水敏效应后微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 178-185. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0092HU X L, LEI H. Using CT scanning technology to investigate microscopic pore structure characteristics of low-permeability reservoir rocks after water sensitivity experiments[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 178-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0092 [27] TANG Y J, ZHANG J Z, LI M J, et al. Origin of crude oils from the Paleogene Xingouzui Formation in the Jiangling Depression of Jianghan Basin, Central China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107976. [28] LEI H, HE L, LI R S, et al. Effects of boundary layer and stress sensitivity on the performance of low-velocity and one-phase flow in a shale oil reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 180: 186-196. [29] 高建, 吕静. 应用CT成像技术研究岩心孔隙度分布特征[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2009, 18(2): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTLL200902010.htmGAO J, Lü J. Study of porosity distribution features using X-Ray CT[J]. Computerized Tomography Theory and Applications, 2009, 18(2): 50-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTLL200902010.htm [30] 马文国, 刘傲雄. CT扫描技术对岩石孔隙结构的研究[J]. 中外能源, 2011, 16(7): 54-56 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201107008.htmMA W G, LIU A X. The study of the pore structure parameters in rocks by CT scanning technology[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2011, 16(7): 54-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201107008.htm [31] 刘向君, 熊健, 梁利喜, 等. 基于微CT技术的致密砂岩孔隙结构特征及其对流体流动的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(3): 1019-1028. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201703010.htmLIU X J, XIONG J, LIANG L X, et al. Study on the characteristics of pore structure of tight sand based on micro-CT scanning and its influence on fluid flow[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(3): 1019-1028. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201703010.htm [32] TIWARI P, DEO M, LIN C L, et al. Characterization of oil shale pore structure before and after pyrolysis by using X-ray micro CT[J]. Fuel, 2013, 107: 547-554. [33] WANG Y, PU J, WANG L H, et al. Characterization of typical 3D pore networks of Jiulaodong Formation shale using nano-transmission X-ray microscopy[J]. Fuel, 2016, 170: 84-91. [34] 潘汝江, 何翔, 肖维民, 等. CT扫描技术在岩心三维重建中的应用[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2018, 27(3): 349-356 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTLL201803011.htmPAN R J, HE X, XIAO W M, et al. Application of CT scanning technique in core 3D reconstruction[J]. Computerized Tomography Theory and Applications, 2018, 27(3): 349-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTLL201803011.htm [35] 郭源, 欧阳传湘. 基于CT扫描的低渗岩心正反向驱替提升驱油效率分析[J]. 中国科技论文, 2020, 15(4): 476-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKZX202004017.htmGUO Y, OU YANG C X. Experimental study on improving oil displacement efficiency of low-permeability core with CT scan[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2020, 15(4): 476-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKZX202004017.htm [36] 莫邵元, 何顺利, 栾国华, 等. 利用CT技术的超低渗岩心油水驱替特征研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(9): 1671-1815. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201409006.htmMO S Y, HE S L, LUAN G H, et al. Use of CT technology to investigate water flooding in ultra-low permeability sandstone[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(9): 1671-1815. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201409006.htm [37] 施兴华. 煤中微裂隙结构特征及其对煤渗透性的控制机理[D]. 河南焦作: 河南理工大学, 2018.SHI X H. Coal microfracture characteristics and its controlling mechanism on coal permeability[D]. Jiaozhuo Henan: Henan Polytechnic University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] GAMSON P, BEAMISH B, JOHNSON D. Coal microstructure and secondary mineralization: Their effect on methane recovery[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 109(1): 165-179. [39] GAMSON P D, BEAMISH B B, JOHNSON D P. Coal microstructure and micropermeability and their effects on natural gas recovery[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(1): 87-99. [40] HERIAWAN M N, KOIKE K. Coal quality related to microfractures identified by CT image analysis[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 140: 97-110. [41] ZHANG Y H, LEBEDEV M, SARMADIVALEH M, et al. Swelling effect on coal micro structure and associated permeability reduction[J]. Fuel, 2016, 182: 568-576. [42] LI T, WU C F, LIU Q. Characteristics of coal fractures and the influence of coal facies on coalbed methane productivity in the South Yanchuan Block, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 22: 625-632. [43] CHEN Y, TANG D Z, XU H, et al. Pore and fracture characteristics of different rank coals in the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 26: 1264-1277. [44] VANDERSTEEN K, BUSSELEN B, VAN DEN ABEELE K, et al. Quantitative characterization of fracture apertures using microfocus computed tomography[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 215(1): 61-68. [45] LUO X P, ZHANG Y B, ZHOU H P, et al. Pore structure characterization and seepage analysis of ionic rare earth orebodies based on computed tomography images[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2022, 32(2): 411-421. [46] CHEN W X, ZHOU F, WANG H Q, et al. The occurrence states of rare earth elements bearing phosphorite ores and rare earth enrichment through the selective reverse flotation[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(11): 698-707. [47] WANG X B, YAO M T, LI J S, et al. China's rare earths production forecasting and sustainable development policy implications[J]. Sustainability, 2017, 9(6): 1003. [48] FENG J, ZHOU F, CHI R A, et al. Effect of a novel compound on leaching process of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 129: 63-70. [49] ZHOU L B, WANG X J, HUANG C G, et al. Development of pore structure characteristics of a weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore during leaching with different valence cations[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2021, 201: 105579. [50] LIANG Z J, WANG C S, ZHOU Y. Analysis of seepage characteristics of complex pore structure rock by digital core method[J]. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, 2020, 55(6): 756-64. [51] YIN S H, CHEN X, YAN R F, et al. Pore structure characterization of undisturbed weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore based on X-ray micro-CT scanning[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(3): 236. [52] HUANG S X, FENG J, YU J X, et al. Adsorption and desorption performances of ammonium on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 613: 126139. [53] WANG G, QIN X J, HAN D Y, et al. Study on seepage and deformation characteristics of coal microstructure by 3D reconstruction of CT images at high temperatures[J]. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol., 2021, 31(2): 175-185. [54] 廖强. 致密砂岩数字岩心重构及渗流模拟[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.LIAO Q. Digital core reconstruction and seepage simulation of tight sandstone[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [55] 王伟明, 卢双舫, 李杰, 等. 致密砂岩储层微观孔隙特征评价: 以中国吐哈盆地为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(10): 1828-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201610008.htmWANG W M, LU S F, LI J, et al. Analyses of micro-pore structural characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study in Turpan-Hami Basin, northwestern China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(10): 1828-1836. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201610008.htm [56] 沈珊, 卢双舫, 唐明明等. 致密砂岩储层微观孔喉表征及渗流模拟[J]. 河南科学, 2016, 34(10): 1699-1705. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201610020.htmSHEN S, LU S F, TANG M M, et al. Micro scopic pore throat characterization and seepage stimulation of tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Henan Science, 2016, 34(10): 1699-1705. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201610020.htm [57] 殷艳玲, 孙志刚, 王军, 等. 胜利油田致密砂岩油藏微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6): 693-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506011.htmYIN Y L, SUN Z G, WANG J, et al. Micro scopic pore structure characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs in Shengli Oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6): 693-695. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506011.htm [58] 周义朋, 黎广荣, 徐玲玲, 等. 地浸采铀钻孔过滤器对溶液渗流影响的数值模拟[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(4): 301-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201804001.htmZHOU Y P, LI G R, XU L L, et al. Numerical simulation of influence of drilling filter on solution seepage during in-situ leaching of uranium[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 41(4): 301-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201804001.htm [59] ZHOU Y, SHEN Z, SHI W, et al. A method for setting the artificial boundary conditions of groundwater model[J]. Open Journal of Geology, 2013, 3(2): 50-54. [60] WEN H, PAN Z Z, GIAMMAR D E, et al. Enhanced uranium immo bilization by phosphate amendment under variable geochemical and flow conditions: Insights from reactive transport modeling[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(10): 5841-5850. [61] 祝永进, 史维浚, 孙占学, 等. 弱酸-中-弱碱性介质中的水-碳酸钙作用: 砂岩铀矿地浸过程中碳酸钙堵塞机理及其预防[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(4): 369-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201004012.htmZHU Y J, SHI W J, SUN Z X, et al. The water-calcite reaction in weakacid-nutral-weakalkility media: The mechanism of block-up by carbonate in leaching and its protect[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 33(4): 369-373. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201004012.htm -






 下载:
下载: