Numerical simulation studies on monitored natural attenuation of phenol in aquifers considering the biodegradation effect
-
摘要:
监测自然衰减(MNA)是一种应用较广的经济有效的土壤和地下水污染修复技术, 而非水相液体(NAPL)在非均质地层中的运移过程是自然衰减效果评估的重要内容。为了准确刻画多相流体在土壤及地下水中的生物降解过程, 以我国北方某典型苯酚污染场地为例, 基于连续三年的地下水质动态监测数据, 利用多相流数值模拟软件TOUGH3/TMVOCBio构建了考虑Monod生物降解过程的苯酚运移的多相流数值模型。模型再现了现状条件下多相态苯酚的空间分布和时间变化过程, 分析了吸附和Monod生物降解参数的敏感性。最后, 讨论了吸附和微生物降解参数不确定条件下, 溶解、挥发、吸附和生物降解作用去除苯酚贡献率, 对污染源处置的2种情景进行了模拟预测。研究发现, 苯酚呈现间歇性泄漏, 在地下介质中以吸附相为主, 其次为液相和气相, 最少为自由相。在参数不确定性影响下, 生物降解作用为17.91%~58.02%, 并且降水条件会影响苯酚浓度的季节性变化。在未来20年内, 在苯酚污染源完全去除和保持现状泄漏条件时, 第20年末苯酚总质量去除率分别达到98%和80%以上。识别了多相流模型中敏感性较高的生物降解参数, 为石化场地有机物生物降解过程数值模拟提供参考, 同时可为我国MNA技术的应用提供理论依据。
Abstract:Objective Monitoring natural attenuation (MNA) is a widely used, economical and effective remediation technique for soil and groundwater contamination. The migration of nonaqueous phase liquid (NAPL) in heterogeneous strata is an important element in the assessment for the efficiency of MNA.
Methods Based on three consecutive years of dynamic groundwater quality monitoring data, the purpose of this study is to accurately characterize the biodegradation processes of multiphase fluids at a typical phenol contaminated site in northern China. A multiphase flow numerical model of phenol transport considering Monod biodegradation processes based on TOUGH3/TMVOCBio software was developed and applied. The model depicted the spatial distribution and temporal variation of phenol under the current conditions well and analysed the sensitivities of the adsorption and biodegradation parameters. The paper also discussed the removal contributions of dissolution, volatilization, adsorption and biodegradation effects under uncertainty of adsorption and microbial degradation parameters and predicted two different natural attenuation scenarios for source disposal.
Results The contribution of phenol removal varies over a range under the influence of parameter uncertainty, with 17.91% to 58.02% for biodegradation, and precipitation conditions affect the seasonal variation in phenol concentrations. In the future 20 years, under the conditions with complete removal of the phenol source and the present leakage model, the total mass removal rate of phenol will arrive at 98% and 80% at the end of the 20th year, respectively.
Conclusion This paper identifies the biodegradation parameters with high sensitivity in the multiphase flow model, which provides a reference for the numerical simulation of the organic matter biodegradation process at petrochemical sites and can also provide a theoretical basis for the application of MNA technology in China.
-
非水相液体(non-aqueous phase liquid, 简称NAPL)是地下水中最常见的污染组分之一,主要来源于石油化工企业的泄漏。该类污染物水相溶解度小、泄漏过程隐蔽,且大多数组分具有“三致”作用,严重危害生态环境及人类健康。随着环境问题的加剧和政府环境治理力度的加强,NAPL污染及修复已成为当前备受公众和社会关注的环境问题。NAPL在地下水中的迁移机制复杂,以吸附态、自由态、溶解态、挥发态等形态存在于土壤地下水系统中,随着地下水位的变动对地下水造成长期的污染。对于NAPL污染迁移规律的研究,最早集中在油品泄漏后在地下水中的迁移趋势及其物理机制的相关实验研究[1]。自Dam[2]将NAPL在地下水的运动作为两相流问题研究以来,关于NAPL在地下介质中的运动一般以多相流的角度进行研究[3]。直到20世纪70年代随着大型计算机的发展,数值模拟在实践领域中被大量应用[4-6],这为求解多相流体迁移转化模型开拓了新的空间。NAPL污染物在土壤和地下水中的迁移和转化涉及多相流、多组分运移,往往难以实现对这些复杂过程的实际探测[7],因此目前广泛采用数学和计算机模型来模拟NAPL污染物的迁移和归趋[8]。将多相流动简化为溶质的单相流动,则可以利用溶质运移模拟软件模拟溶质的迁移转化过程,主要考虑溶质的吸附解吸、反应和生物降解过程,代表性的软件如RT3D[9-10]。部分学者[11-13]根据多组分多相流运移的控制方程和附加方程自主开发了模拟软件,主要用于描述考虑溶解和吸附过程的石油污染物运移,但软件推广和普及率低。UTChem和TMVOC软件是国内外广泛应用的多相流数值模拟器,UTChem的优势在于描述地下水污染修复过程[14-15],而TMVOC能有效模拟区域尺度多组分多相流的运移过程[16]。在增加了生物降解模块后,TMVOC包括了NAPL的溶解、吸附、挥发和生物降解等过程的描述。
监测自然衰减技术(monitored natural attenuation,简称MNA)是石化污染场地中较为常用的地下水原位修复技术,由于具有成本低、环境影响小和绿色可持续等技术优势,受到广泛关注[17-19]。最初,美国空军环境中心将自然衰减定义为由吸附、弥散、稀释、挥发和生物降解等衰减机制的集合[20]。美国地质调查局[21]对某垃圾填埋场污染羽进行了长达12年的监测,发现随着场地电子受体含量降低,污染羽有机物浓度逐渐下降。卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院等[22]监测了德国某焦油污染场地地下水中复合有机污染物的自然衰减作用。挥发性酚是石化场地污染的主要来源之一,在检测中通常以苯酚对其进行计量。苯酚泄漏后一般会在土壤环境中富集,由于地下水动力条件等原因造成地下水污染。由于生物毒性大,苯酚在地下水污染研究中非常重要,但据国内外已有文献的检索,难以找到地下水系统中监测自然衰减技术应用于苯酚的案例。实验表明[23],石化污染场地中的土著微生物菌群在苯酚生物降解中发挥着重要作用,苯酚的好氧降解以氧气为电子受体,将苯酚最终降解为H2O和CO2等无害产物,生物降解对石化污染土壤和地下水的修复起着重要的作用。石化场地中苯酚的泄漏可能是历史原因或事故引起,但随着企业管理水平的不断提高,事故情景下的泄漏一般难以发生,即使发生,因为一般具有应急管理预案,污染也具有一定的可控性。地下水污染溯源的难点在于历史泄漏条件的查明,而现状监测到的地下水苯酚浓度可间接反映地下水动力影响下的泄漏条件。TMVOCBio作为模拟NAPL在土壤和地下水中运移的有效工具,不仅包括了从非饱和土壤泄漏到饱和地下水的挥发、吸附过程的描述,同时加入Monod方程描述受微生物、氧气影响下的有机物生物降解过程。MacQuarrie等[24]采用双重Monod方程与对流-弥散模型计算了有机物在电子受体(溶解氧)和细菌群影响下的衰减作用。Jean等[25]对比了基于Monod方程和一级动力学反应的苯-甲苯-二甲苯(BTX)多组分有机物自然衰减模型,发现Monod方程的模型比一级动力学反应模型更接近实验结果。赵梦等[26]将Monod方程嵌入到RT3D模块中,构建了承压含水层中DNAPL自然衰减模型。目前,对于生物降解过程的应用案例较少[27],而多相流数值模拟计算耗时长,特别是缺乏对吸附和生物降解等反应参数不确定性的研究,监测自然衰减效果的案例稀少。
笔者拟以中国北方某石油化工固废垃圾处置场的风化花岗岩含水层为例,结合近3年场地地下水位和水质监测数据,选择苯酚为代表性污染物,利用多相流数值模拟技术对苯酚自然衰减效果进行评价和分析,探讨反应参数不确定性对自然衰减效果的影响,为研究区内地下水中MNA技术的应用评价提供理论依据。
1. 研究方法
1.1 多相流数值模型
本研究采用TOUGH3/TMVOCBio模块进行模拟。TMVOCBio模块是由美国劳伦斯伯克利国家实验室开发的水、气体和挥发性有机物(volatile organic chemicals, 简称VOCs)在多维非均质多孔介质中三相非等温流动的数值模拟软件[28],专为解决碳氢燃料或有机溶剂在饱和区和不饱和区泄漏造成的污染问题而设计,涉及到对流、扩散、吸附、生物降解等过程,可以分析气相-液相-NAPL相三相系统间的相互转化[29]。针对多相流控制方程具有强非线性的特点,TOUGH3/TMVOCBio采用Newton-Raphson迭代法、并行迭代解法器库AZTEC或PETSc库进行非线性方程组求解,并行计算显著提高了软件的应用效率[30]。在TMVOCBio中,对于任一体积为Vm,表面积为Гm的渗流区,组分i(i=w(水),a(空气),n(NAPL))的质量守恒方程为:
ddt∫VmMidVm=∫ΓmFimdΓm+∫VmqidVm (1) 式中:Vm为流动单元体的体积;Γm为表面积;Mi为组分i在单位土壤介质中质量;Fi为进入到流体单元体的组分i的总通量;qk为组分i在单元体的源汇相;m为流动区单元体表面的外法向单位矢量。
Mi包含了气相、液相和NAPL相的总和。单位体积内水相、气相和NAPL相的总质量表示为:
{M^i} = \mathit{\Phi} \sum\nolimits_{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }} {{S_{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }}}{\rho _{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }}}X_{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }}^i + M_{{\rm{ads}}}^i} (2) 式中:Φ为多孔介质的孔隙度;Sβ为β相的饱和度(β=w, a, NAPL,即为水、气和NAPL相);ρβ为β相的密度;Xβi为组分i在β相中的质量分数;Madsi为组分被土壤介质瞬时解吸的吸附量,对于水相和气相为0,NAPL相可表示为:
M_{{\text{ads}}}^{\text{i}} = (1 - \mathit{\Phi }){\rho _{\text{R}}}{\rho _{\text{w}}}X_{\text{w}}^i{K_\varepsilon }{f_\varepsilon } (3) 式中:Xwi为组分i在水相中的摩尔分数;ρR为多孔介质颗粒密度;Kε为有机碳分配系数;fε为土壤中有机碳质量分数。
各组分流量通量包含各相态的总和,而且不同相态在重力与毛细压力的共同作用下遵循达西定律:
{F^{\rm{i}}} = \sum\nolimits_\beta {F_\beta ^i} = \sum\nolimits_\beta { - k\frac{{{k_{{\rm{r \mathit{ β} }}}}{\rho _{\rm{w}}}}}{{{u_\beta }}}\left( {\nabla {P_{\rm{ \mathit{ β} }}} - {P_{\rm{ \mathit{ β} }}}g} \right)} (4) 式中:k为岩石的固有渗透率;krβ是β相的相对渗透率;uβ为β相的动力黏度;Pβ为β相的压力;g是重力加速度。
1.2 自然衰减过程模块的算法
VOCs的自然衰减涉及挥发、吸附和生物降解等过程。本文模拟的VOCs污染物为苯酚。苯酚的挥发和溶解过程采用亨利定律表征,具体可参考文献[28]和[30]。在固体颗粒表面的吸附用可逆的线性平衡吸附模型刻画,见式(3)。生物降解速率由修正后的Monod动力学方程计算[31],该方程可以解释各种限制因素对微生物降解速率的影响。本研究采用乘法Monod模型,即假设所有限制因素同时影响底物吸收速率[32-33],不考虑毒性抑制和微生物竞争带来的抑制效应。含水层中微生物对主要基质的降解过程表示为:
\frac{\mathrm{d} C_{\text {bio }}}{\mathrm{d} t}=-\mu_{0, \mathrm{~B}} B (5) 式中:Cbio为作为基质的碳氢化合物浓度,即单位质量水体中化合物的质量;B为微生物浓度,即单位质量水体中的微生物质量;μ0, B为单位质量微生物对特定基质的利用速率,可由式(6)确定:
\mu_{0, \mathrm{~B}}=\mu_{\max , \mathrm{B}} \frac{C_{\text {bio }}}{K_{\mathrm{C}}+C_{\text {bio }}} \frac{E}{K_{\mathrm{E}}+E} (6) 式中:μmax, B为单位质量微生物对特定基质的最大利用速率;E为电子受体浓度;KC为基质半饱和常数;KE为电子受体半饱和常数。
地下水中微生物浓度增长率与基质吸收带来的浓度增加和自然死亡带来的浓度减少两方面相关。微生物浓度变化速率用一阶衰变过程表示为:
\frac{\mathrm{d} B}{\mathrm{~d} t}=Y \mu_{0, \mathrm{~B}} B-\delta B (7) 式中:Y为微生物产生系数,即单位质量有机物产生的生物质;δ为微生物一阶死亡速率常数。
1.3 参数敏感性分析方法
苯酚在地下介质中的吸附以及生物降解参数具有不确定性,因此以观测井中苯酚在液相中的质量分数为输出变量,分析不同参数取值对质量分数的敏感性。本研究设置不同参数取值,分别进行模拟计算,再采用手动计算敏感度。灵敏度分析利用结果对参数求偏导数,反映参数变化对结果的影响程度,即:
S_i=\partial y / \partial \alpha_j (8) 式中:Sj为当αj参数变化时对输出结果y的影响程度,也就是灵敏度系数。由于不同参数单位不同,将式(8)标准化后得到灵敏度系数的计算公式为:
\begin{aligned} S_j & =(\partial y / y) /\left(\partial \alpha_j / \alpha_j\right) \\ & \approx \frac{\left(y_{\left(\alpha_j+\Delta \alpha_j\right)}-y_{\left(\alpha_j\right)}\right) / y_{\left(\alpha_j\right)}}{\left(\Delta \alpha_j / \alpha_j\right)} \end{aligned} (9) 2. 场地特征和模型设计
2.1 污染场地概况
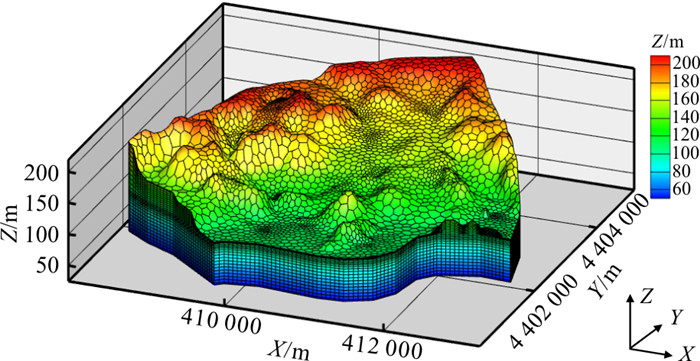
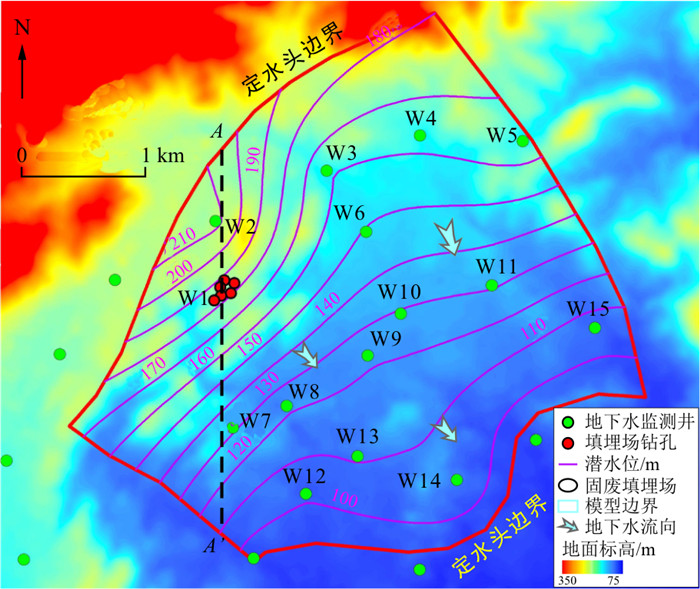
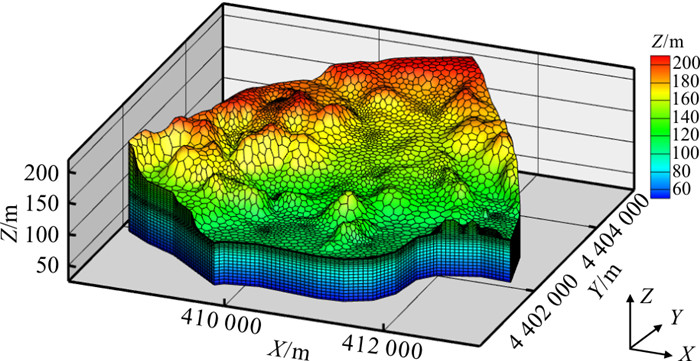
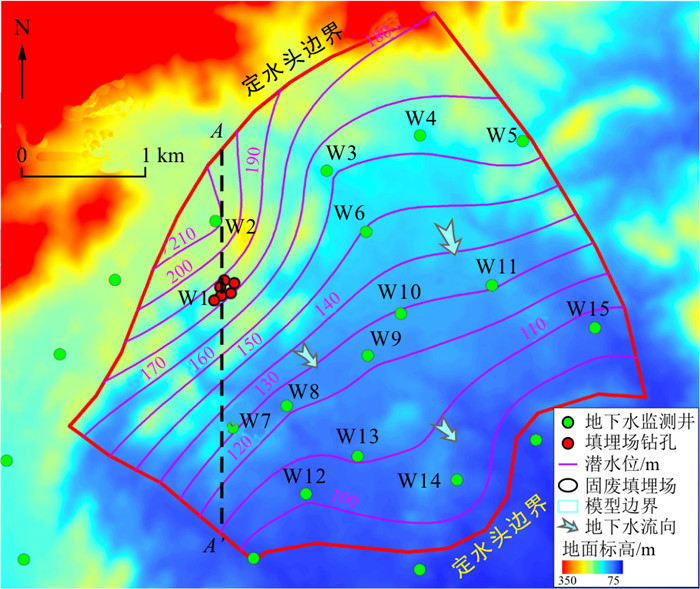
研究区为中国北方风化花岗岩风化裂隙含水层,海拔在75~350 m之间,其坡降平均为2‰~4‰(图 1)。研究区属暖温带半湿润季风性大陆性气候区,2000-2020年平均年降水量约为530 mm,降水量集中在汛期,6~9月降水量约占年降水量的75%。研究区没有常年性的河流。已有钻孔揭露地下35~40 m深度从上至下依次为回填土、全风化和强风化花岗岩、中等风化花岗岩、弱风化和无风化花岗岩。全风化和强风化花岗岩深度一般为5~15 m,构成了区域主要含水层。研究区内地下水位埋深1~11 m,季节波动性不大。地下水由西北向东南流动。固废填埋场在近几年按正规填埋场要求进行改建,但由于存在历史遗留的潜在污染源,2018-2020年监测到填埋场附近以苯酚等为主的挥发性有机物在地下水中的浓度为0.003~0.032 mg/L,间歇性地超过了地下水Ⅴ类标准(0.01 mg/L),而在离填埋场1 km的下游观测井尚未发现苯酚超标。本研究主要考虑由固废垃圾填埋场污染源泄漏产生的苯酚污染运移和自然衰减过程。
2.2 模型设计
根据含水层分布及地下水流动特征,以可能的污染源泄漏范围为重点研究区,从而确定了多相流模型范围,模拟区面积约12.8 km2。模型西北侧和东南边界为已知压力边界,其他边界为零通量边界。假定模型在入渗补给条件下形成静态的压力平衡条件,进而研究NAPL在土壤及地下水系统中的运移过程。垂向上划分为4层,自上而下的4层岩性及厚度分别为:回填土(2~27 m);强风化花岗岩(10 m);中风化花岗岩(7 m);弱风化花岗岩(50 m),每个概化层再细分为5个模拟层。中风化和弱风化的花岗岩可能存在裂隙引起的不连续流体运移,但考虑到污染物和地下水主要在全风化土层和强风化带运移,本研究忽略不连续裂隙水流作用,按照等效多孔介质进行模拟。
利用IGMESH[34]软件进行网格剖分,水平方向剖分为非规则网格,在泄漏点附近进行加密。平面上,研究区划分为2 884个网格单元;垂向上划分为29个非等间距网格,在潜水面附近等关键位置进行网格加密,共剖分为2 884×29=83 636个网格(图 2)。模型顶部为大气压力边界,其边界层厚度设置为0.1 m;模型底部为隔水的定压边界,其厚度划为0.1 m;其他层从上至下分别细分为10层,5层,2层和10层,分层情况如表 1。现状条件下,场区浅层地下水无人工开采,主要接受降水入渗补给,通过侧向流出进行排泄。取入渗系数为0.05,大气降水在地面的入渗补给强度为0.004 8~0.185 5 mm/d。模拟时段为1 080 d(2018-2020年),模型的时间步长根据源汇项、输出时间断面和收敛情况进行自动调整。
表 1 模型分层和孔隙度与渗透率参数列表Table 1. List of model layers, porosity and permeability分层岩性 分层号 厚度/m 垂向饱和渗透率/m2 孔隙度/% 人工回填土 2~11 2~27 5×10-12 15 全-强风化层 12~16 10 3×10-12 12 中风化层 17~18 7 1×10-12 11 弱-微风化层 19~28 50 1×10-13 10 模型中地下水初始压力分布和苯酚初始浓度分布的确定是个难点。研究区西北侧及东南侧均为已知压力边界,根据西北和东南侧的压力根据2018-2020年的地下水位埋深来设定,取多年平均的月降水量以及到地面的降水入渗补给系数进行长时间的动态模拟,从而获得多相流数值模型的初始压力条件。由于含水层厚度不大,研究中采用等温模型计算,假定环境温度恒定为20℃。根据2018-2020年地下水中苯酚浓度的监测数据分析,苯酚泄漏点在填埋场附近,呈现间歇式超出五类地下水质特征。填埋场存在近40 a,企业高速发展的历史可能有数十年,苯酚的历史泄漏无法判断。假定苯酚持续泄漏3 a,之后间歇泄漏6 a,根据模型计算而获得苯酚的初始空间分布。2018-2020年的苯酚源强根据监测的苯酚浓度来间接确定,推测分别发生在450~460, 990~1 000 d,泄漏速率分别为8.1, 4.05 kg/d。余诗航等[35]曾于2020年11月对填埋场取50 cm深度取土样和水样测定污染组分,土壤含水率范围在6.27%~9.54%,土壤总有机碳为0.27%~1.77%,而在地下水中未检测到苯酚,因此说明苯酚可能主要在非饱和土层泄漏。
2.3 模型参数设置
根据已有钻孔的抽水试验结果,中等和全风化层的渗透系数为0.8~2.5 m/d,因此垂向的渗透率参数如表 1所示,假定水平向饱和渗透率为垂向渗透率的2倍。在常温常压条件下,苯酚的摩尔质量是94.111 g/mol,密度为1017 kg/m3,沸点为455.2 K,亨利定律常数为0.22,在水体中的溶解度为517 mg/L。由于不同介质的苯酚吸附分配参数未知,参照TMVOCBio的VOCs参数库以及中国土壤有机质数据集,不同介质中苯酚的固-液分配系数为0.146 m3/kg,介质中ρ(TOC)为0.05%。修正的Stone三相渗透率计算公式,水、NAPL和气的残余饱和度分别取为0.20,0.05,0.01,孔径指数取为3.0;毛细压力采用Parker等的三相毛细压力计算公式,水的残余饱和度为0.0,指数取为1.84,NAPL与气和水与NAPL的经验系数分别取为10和11。
与生物降解有关的过程涉及多个反应参数,由于缺乏针对性的试验,参考TMVOCBio手册[36]和Battistelli等人的研究结果[31]选取生物降解反应参数,见表 2,取基准取值的0.1~10倍范围作为参数敏感性范围。苯酚或者被生物降解被去除,或者由于物理化学作用,在介质中呈现气相、水溶液相、吸附相、NAPL相并在不同相态之间转化。
Table 2. Major parameters related to phenol adsorption and biodegradation参数 基准取值 敏感性范围 固-液分配系数/(m3·kg-1) 0.146 0.0146~1.460 介质有机碳质量浓度/% 0.05 0.01~0.2 微生物最大利用速率/10-7s-1 1.27 0.25~6.35 基质半饱和常数/10-6(kg·kg-1) 2 1~4 微生物产出系数/(kg·kg-1) 0.5 0.1~2.5 氧气利用率/(mol·mol-1) 7.5 3.75~15.0 氧气半饱和常数/10-7(kg·kg-1) 10 2.0~50 微生物死亡速率/10-9s-1 23.1 4.10~102 3. 模拟结果分析
3.1 压力和苯酚浓度的模拟结果
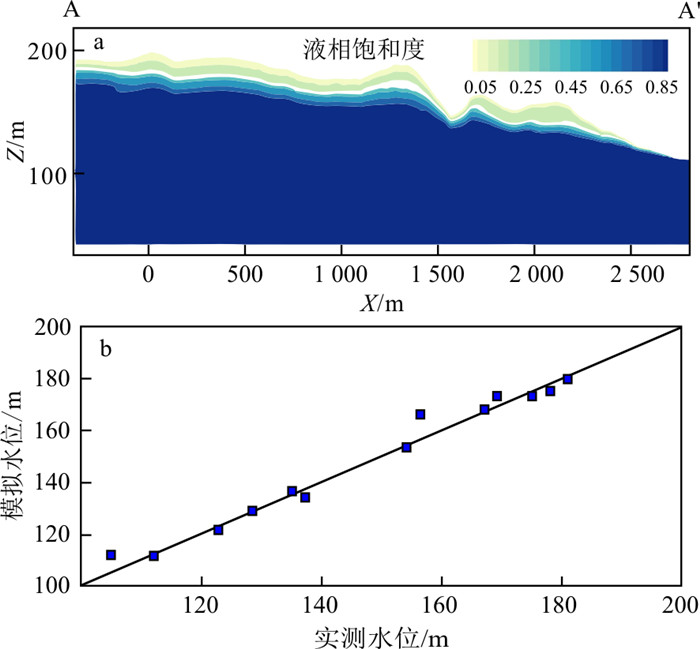
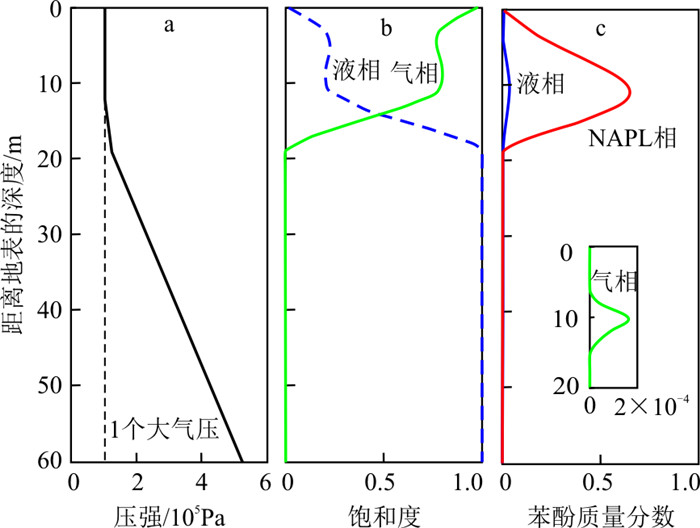
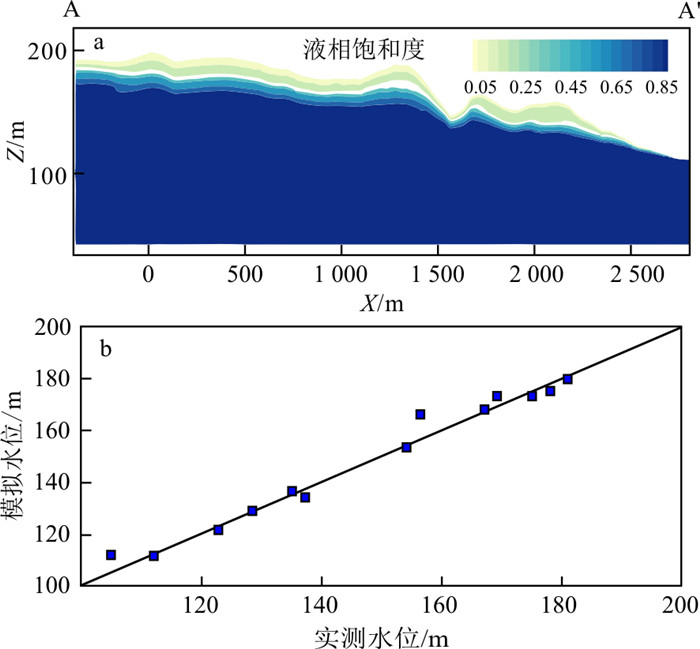
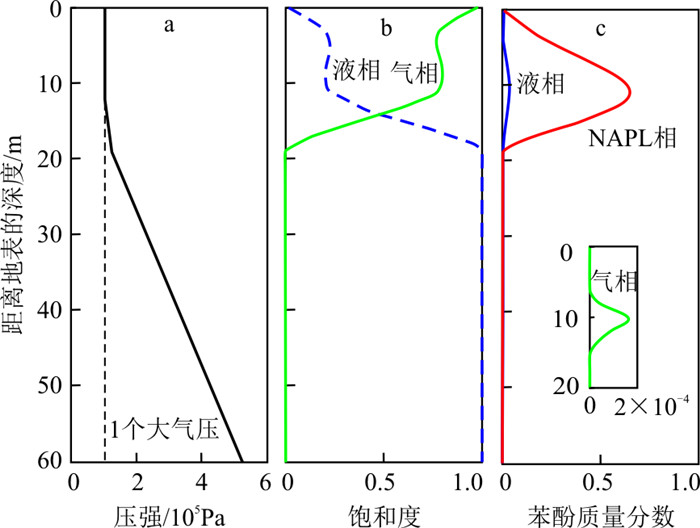
典型观测井位于垃圾填埋场内,测定的是潜水中地下水位和苯酚浓度。沿典型剖面A—A′的初始液相饱和度分布如图 3-a示,在地表以下2~30 m内液相饱和度由0.05增加到1.00,即由非饱和变为饱和状态。将压力转化为地下水位,获得监测点的模拟与实测水位的关系如图 3-b示,相对误差范围为0.18%~6.54%,整体拟合效果较好。研究区西北地区地下水位高,东南地区地下水位低,地下水流由西北流向东南。
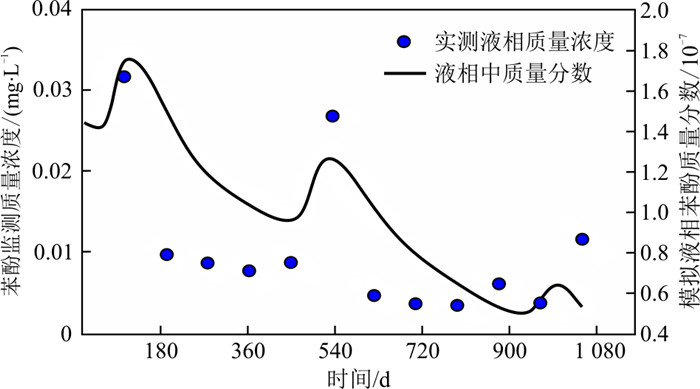
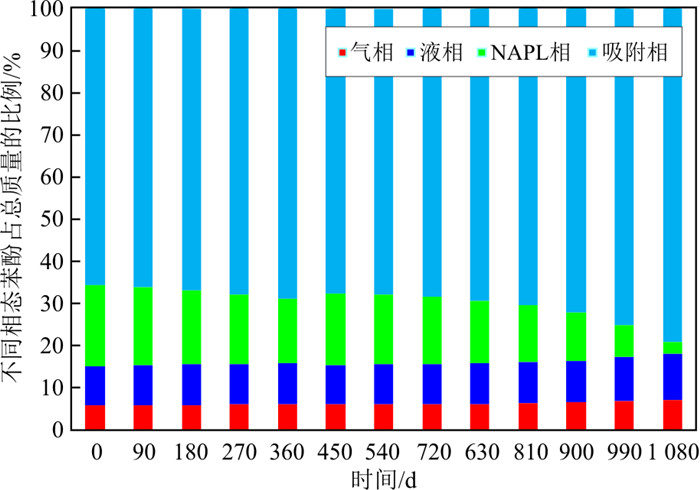
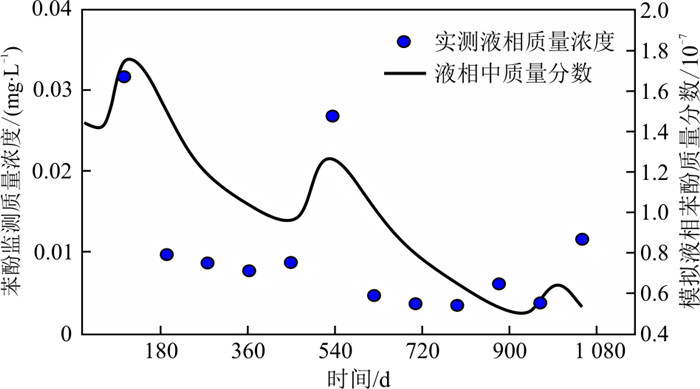
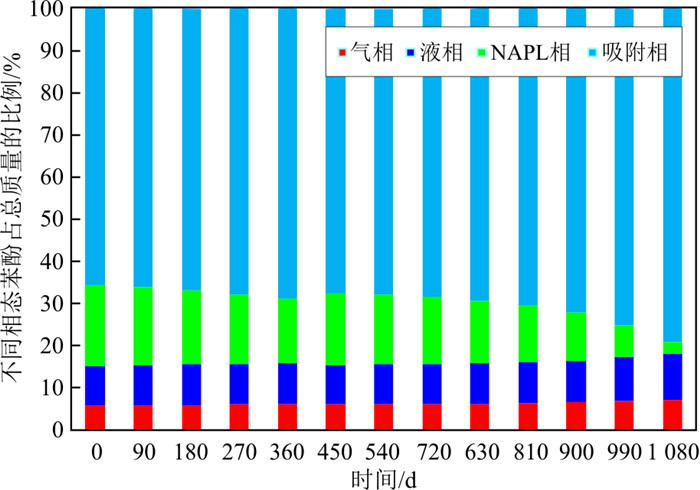
图 4为1 080 d内模拟的固废填埋场W1井液相苯酚质量分数与实测液相浓度变化的对比曲线,两者变化趋势基本一致。当苯酚发生泄漏时,苯酚质量分数升高并到达峰值,之后由于吸附、生物降解等自然衰减作用,苯酚质量分数降低。在此期间,苯酚的间歇性泄漏(第450~460, 990~1 000 d)使介质中苯酚含量再次增加,1080 d内共泄漏121.5 kg。模型可计算出介质中苯酚的气相、液相、吸附相、自由相和总质量的变化,计算出每个时间断面的不同相态质量占总质量的比例(图 5)。由图可见,介质中苯酚主要以吸附相存在(占比65.00%以上),其次为液相苯酚(占比约9.72%)、气相苯酚(占比约6.44%),最少的为NAPL相苯酚(占比为2.47%~19.20%)。自由相NAPL比例呈现逐渐减少的趋势,也可发现吸附相NAPL比例有增大的趋势,因为苯酚总质量总体呈现减少趋势(图 4)。
3.2 微生物变化
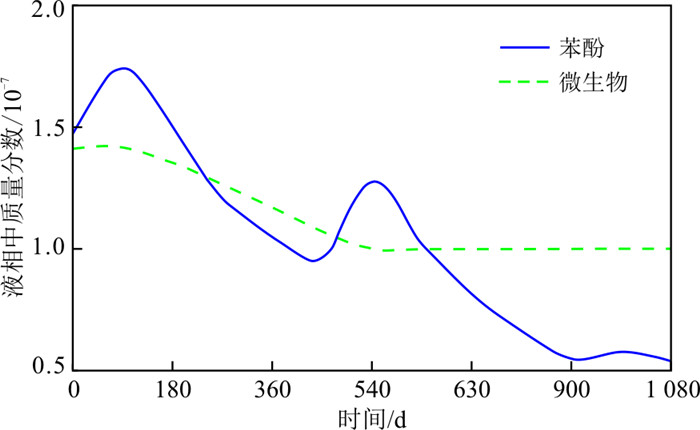
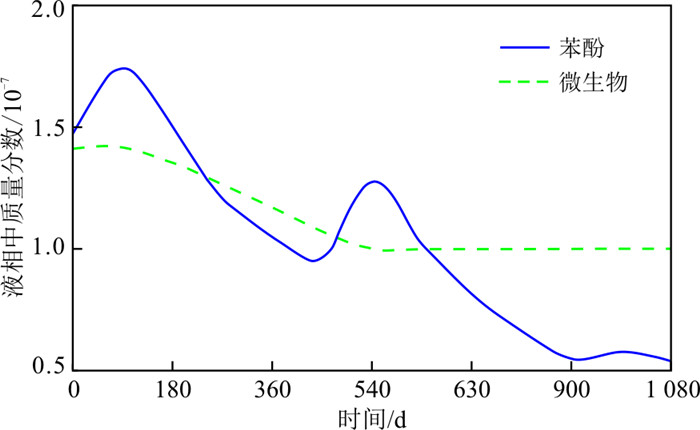
为了解生物降解作用的强度及变化规律,做出填埋场典型观测井微生物质量分数与苯酚液相质量分数之间的关系(图 6),微生物在液相中的质量分数变化范围为1.0×10-7~1.4×10-7,泄漏时苯酚液相质量分数快速增加,随后由于生物降解作用及其他物理化学反应,苯酚液相质量分数逐渐下降。介质中由于苯酚降解过程中微生物逐渐消耗,微生物生长速率小于死亡速率,微生物质量分数先呈现下降趋势,之后达到稳定,说明其生长和死亡速率达到平衡。
3.3 不同相态苯酚的垂向分布
以典型泄漏点为例,绘制1 080 d的气相压力、饱和度和苯酚质量分数变化如图 7示。气压由地表向下逐渐增大,在约11.5 m处达到1个大气压,在60 m达到5.6个大气压,压力分布如图 7-a所示。自地面向下的气相饱和度由地面的0.99先变化到0.78,再降到0,而液相饱和度由地面的0.01增加到0.21,然后在地面深度19.0 m处变为1.00(图 7-b)。在地面深度3.0~19.0 m范围内苯酚的液相质量分数、气相质量分数和NAPL相质量分数变化明显,最大峰值位于泄漏点,而且NAPL相质量分数大于液相和气相质量分数(图 7-c)。
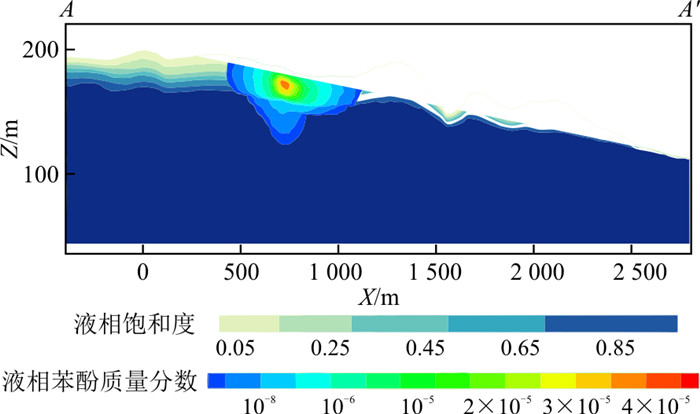
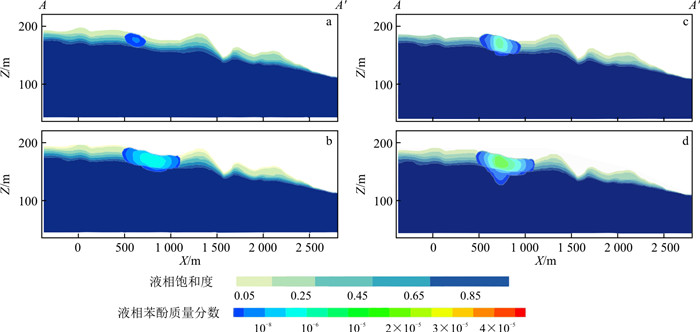
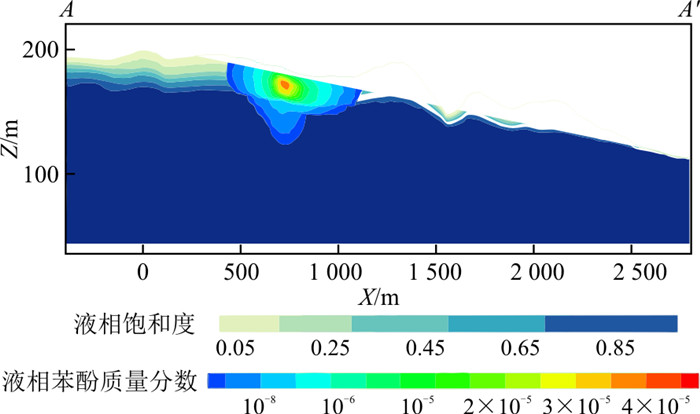
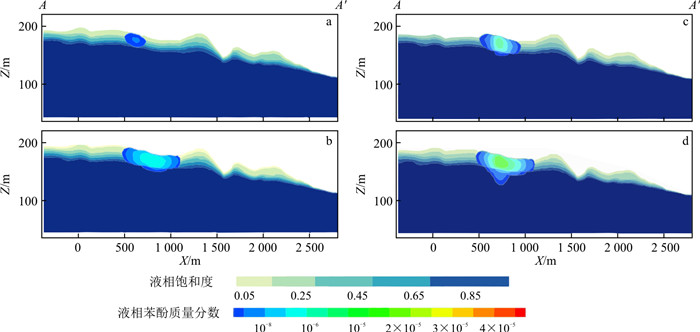
为了解泄漏点附近苯酚的空间分布,绘制了沿典型剖面A-A′(图 1)的液相苯酚质量分数变化图(图 8)。液相苯酚质量分数最大值位于泄漏点下方包气带,向四周的质量分数逐渐减少,在泄漏点下苯酚到达潜水面以下的含水层。到1 080 d,泄漏点处苯酚横向迁移距离为500 m,垂向迁移距离约为80 m。
3.4 参数敏感性分析
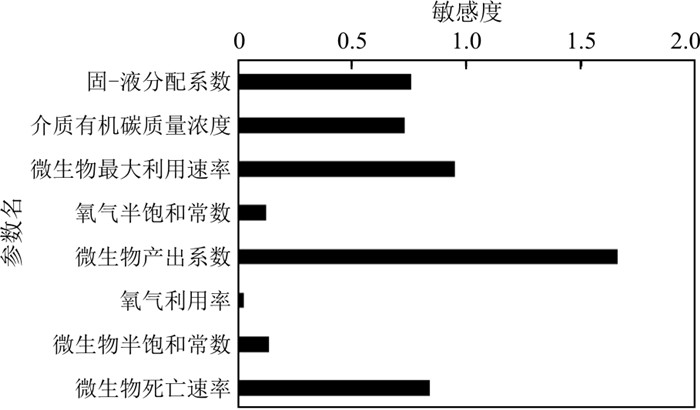
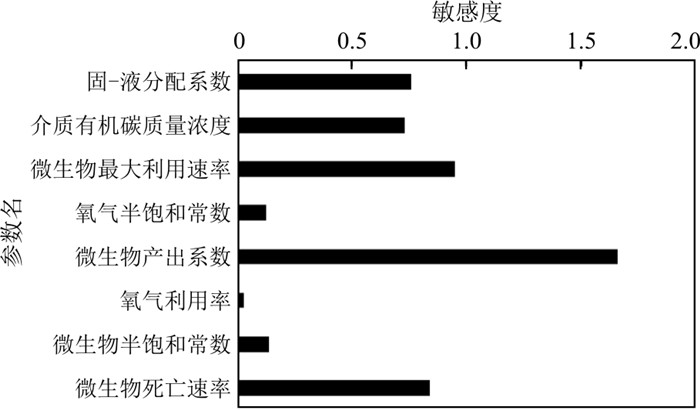
根据表 2确定的参数变化范围,采用敏感度计算方法,以液相苯酚质量分数为目标可获得主要参数的敏感性(图 9)。通过多情景模拟和分析发现微生物产出系数的敏感度最高,达到1.66;微生物最大利用速率、微生物死亡速率、固-液分配系数、介质有机碳含量的敏感度其次,为0.73~0.95;微生物半饱和常数、氧气利用率、氧气半饱和常数敏感度低。在2018-2020年的模拟期可获得1 080 d末溶解、挥发、吸附以及生物降解去除的苯酚质量,考虑到主要参数的不确定性,计算得到溶解、挥发、吸附和生物降解作用去除苯酚的贡献率分别为1.11%~9.14%,0.77%~6.03%,33.91%~83.01%,17.91%~58.02%。
3.5 降水条件对模型影响分析
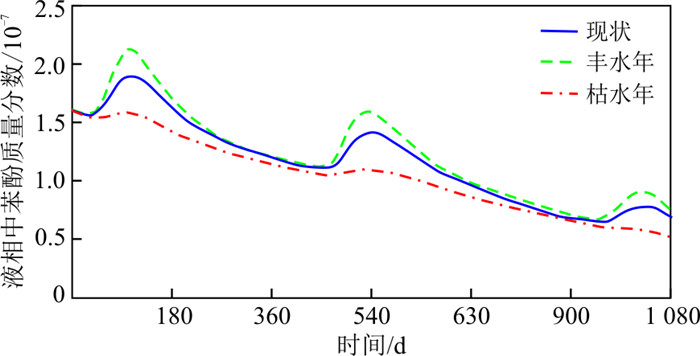
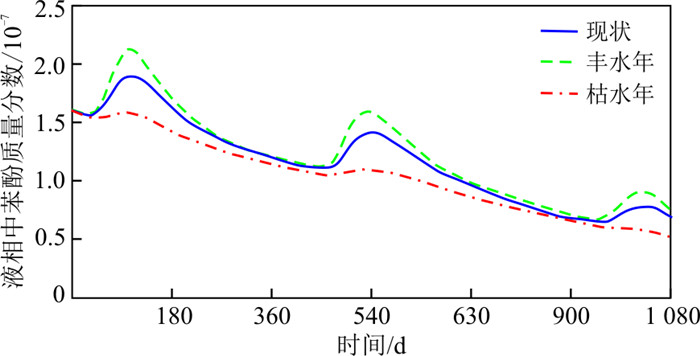
降水入渗补给将会改变介质中压力场分布,从而影响苯酚的迁移。为评价降水条件对模型的影响,根据现状的降水条件(平均年降水量546 mm),设置丰水年(平均年降水量655 mm)和枯水年(平均年降水量273 mm)的降水情景,苯酚泄漏情景与现状条件保持相同。模拟的3种降水条件下典型观测井地下水中液相苯酚随时间变化如图 10所示,可以发现,苯酚变化的趋势基本相同,但在峰值上存在显著差异。降水量越大,液相苯酚的质量分数越大。在1 080 d末的现状年、丰和枯水年的液相苯酚沿剖面A-A′的空间分布范围没有明显变化。
4. 自然衰减效果预测与讨论
4.1 污染源完全去除情景的自然衰减效果预测
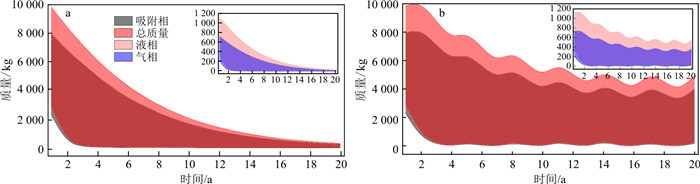
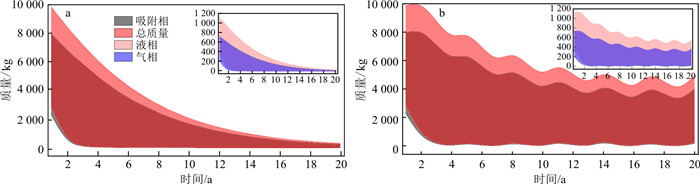
自然衰减情景一中,以1 080 d末介质中苯酚分布为初始条件,假定间歇性的污染源被完全去除,模拟未来20 a自然衰减作用下场地苯酚含量变化。微生物产出系数为0.10,2.50时,自然衰减20 a后介质中液相苯酚质量分数见图 11-a, b,微生物产出系数为0.10时,微生物生物降解作用减弱,液相苯酚晕范围明显大于产出系数为0.25时的晕范围。考虑介质参数的不确定性,介质中不同相态苯酚质量随时间的变化见图 12-a。在未来20 a,气相、液相、吸附相苯酚和总质量均呈现减小趋势,而且不同相态苯酚质量随时间变化的规律基本一致。在前10 a苯酚质量下降较快,不同相态苯酚最大和最小质量的差也迅速减少,总质量去除率达到了65.00%以上,最大去除率可达到99.71%;在后10 a,苯酚质量降低速率减慢,进入较长时间的拖尾期,到第20年末,介质中仍存在不同相态的苯酚,但残留的苯酚质量最大值仅占总质量的2.00%,总质量去除率大于98.00%,说明经过20 a的自然衰减作用能够有效去除介质中泄漏的苯酚。
4.2 污染源间歇泄漏情景的自然衰减效果预测
自然衰减情景二中,以1 080 d末介质中苯酚分布为初始条件,假定污染源仍按2020年现状的间歇性泄漏,模拟未来20 a自然衰减作用下场地苯酚浓度变化。微生物产出系数为0.10,2.50时,自然衰减20 a后介质中苯酚液相质量分数见图 11-c,d,介质中仍存在一定体积的污染晕。考虑介质参数的不确定性,介质中各相态苯酚质量随时间变化见图 12-b,苯酚总质量不断波动,在前10 a总体呈快速下降趋势,总质量去除率在51.90%~99.30%;到后10 a,苯酚质量在一定范围内上下波动,整体呈缓慢下降趋势,由于间歇有苯酚泄露,场地降解苯酚速率较慢,到20 a末,介质中仍残留一定量苯酚,残余苯酚的最大质量可达4 950.4 kg,总质量去除率大于80.00%。在污染源继续泄漏情况下,介质中苯酚质量在一定范围内上下波动,应密切监控场地中苯酚含量变化。
5. 结论
(1) TOUGH3/TMVOCBio模块可模拟监测衰减作用的挥发、溶解、吸附和生物降解作用,本研究构建了区域非饱和-饱和含水层的多相流数值模型,模拟的压力变化与实际地下水流条件吻合较好,模拟的不同相态苯酚变化趋势与实际观测的变化规律一致。
(2) 吸附和生物降解作用是场地自然衰减的主要作用,但其效果受到参数的不确定性影响,在涉及的主要参数中,微生物产出系数敏感度最高,微生物半饱和常数、氧气利用率、氧气半饱和常数敏感度低;不同降水条件主要影响季节性苯酚峰值的高低,在3 a的模拟期内对不同苯酚空间分布影响不显著。
(3) 现状条件苯酚主要以吸附相存在(占比65.00%以上),考虑反应参数不确定的影响,溶解、挥发、吸附和生物降解作用去除苯酚的贡献率在一定范围内变化,分别为1.11%~9.14%, 0.77%~6.03%, 33.91%~83.01%, 17.91%~58.02%,总体以生物降解和吸附作用为主要降解途径。考虑污染源完全去除和不存在间歇性的苯酚泄漏的两种情况,经过20 a自然衰减,在参数不确定性影响下,第一种情景20 a后苯酚去除率大于80.00%,第二种情景苯酚总质量去除率大于98.00%。由于参数不确定性的影响,挥发、吸附、生物降解等作用去除苯酚的贡献率不是一个定值,同样地,自然衰减作用对苯酚总去除率也不是一个定值,考虑反应参数不确定性的自然衰减效果预测评价更加科学。
(4) 污染源的泄漏历史和强度是土壤和地下水污染数值模拟中的难点问题,本研究基于企业历史和现状监测,估算了初始苯酚的初始条件和泄漏条件,而且不同介质吸附和微生物降解相关的参数对自然降解效率影响大,需要进一步结合场地条件识别参数范围从而减少不确定范围。
(所有作者声明不存在利益冲突) -
表 1 模型分层和孔隙度与渗透率参数列表
Table 1. List of model layers, porosity and permeability
分层岩性 分层号 厚度/m 垂向饱和渗透率/m2 孔隙度/% 人工回填土 2~11 2~27 5×10-12 15 全-强风化层 12~16 10 3×10-12 12 中风化层 17~18 7 1×10-12 11 弱-微风化层 19~28 50 1×10-13 10 Table 2. Major parameters related to phenol adsorption and biodegradation
参数 基准取值 敏感性范围 固-液分配系数/(m3·kg-1) 0.146 0.0146~1.460 介质有机碳质量浓度/% 0.05 0.01~0.2 微生物最大利用速率/10-7s-1 1.27 0.25~6.35 基质半饱和常数/10-6(kg·kg-1) 2 1~4 微生物产出系数/(kg·kg-1) 0.5 0.1~2.5 氧气利用率/(mol·mol-1) 7.5 3.75~15.0 氧气半饱和常数/10-7(kg·kg-1) 10 2.0~50 微生物死亡速率/10-9s-1 23.1 4.10~102 -
[1] Bear J. Dynamics of fluids in porous media[M]. New York: Elsevier, 1972. [2] Dam J van. The migration of hydrocarbons in a water bearing stratum [M]. London: Inst. Petrol., 1967. [3] 薛卉, 舒彪, 陈科平, 等. CO2基增强型地热系统中流体-花岗岩相互作用研究进展及展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 45-53. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0021Xue H, Shu B, Chen K P, et al. Research progress of fluid-granite interaction in CO2 based enhanced geothermal system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 45-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0021 [4] Huyakorn P S, Panday S, Wu Y S. A three-dimensional multiphase flow model for assessing NAPL contamination in porous and fractured media. 1. Formulation [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 1994, 16(2): 109-130. doi: 10.1016/0169-7722(94)90048-5 [5] Lari K S, Davis G B, Rayner J L, et al. Natural source zone depletion of LNAPL: A critical review supporting modelling approaches [J]. Water Research, 2019, 157: 630-646. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.001 [6] 马欣程, 徐红霞, 孙媛媛, 等. 氯代烃污染场地生物自然衰减修复研究进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(11): 5285-5298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.11.035Ma X C, Xu H X, Sun Y Y, et al. Research progress on biotic natural attenuation for the remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbon-contaminated sites[J]. China Environmental Sciences, 2022, 42(11): 5285-5298(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.11.035 [7] 周媛, 杨盼瑞, 郭会荣, 等. 注入丁醇调节重非水液相密度的微空隙试验模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 223-230. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0016Zhou Y, Yang P R, Guo H R, et al. Injecting n-BuOH to achieve density conversion of dense non-aqueous phase liquid: Pore-scale experimental simulation [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 223-230(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0016 [8] 宋美钰, 施小清, 康学远, 等. DNAPL场地污染通量升尺度预测的敏感性分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 327-335. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220262Song M Y, Shi X Q, Kang X Y, et al. Sensitivity analysis of upscaling prediction of the mass flux at DNAPL contaminated sites[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 327-335(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220262 [9] 曹红, 高宗军, 蔡五田, 等. 典型污染场地含水层天然净化能力溶质模拟[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2014, 12(3): 65-68, 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201403014.htmCao H, Gao Z J, Cai W T, et al. Solute transport simulation of natural purification ability in an aquifer at a typical contaminated site[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2014, 12(3): 65-68, 103(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201403014.htm [10] 程亚平, 陈余道, 夏源, 等. 地下水位波动对燃油泄漏源区BTEX溶解影响的数值模拟[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(1): 161-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201901020.htmCheng Y P, Chen Y D, Xia Y, et al. Numerical simulation influence of groundwater level fluctuation on BTEX dissolution in fuel oil leakage source area [J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(1): 161-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201901020.htm [11] 薛强. 石油污染物在地下环境系统中运移的多相流模型研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2003.Xue Q. Research on multiphase flow model of petroleum pollutant transport in subsurface system[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning Technical University, 2003(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 胡黎明, 邢巍巍, 吴照群. 多孔介质中非水相流体运移的数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(5): 951-955. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.05.018Hu L M, Xing W W, Wu Z Q. Numerical simulation of non-aqueous phase liquids migration in porous media[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(5): 951-955(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.05.018 [13] 贾智淳. 全隐式化学驱油藏数值模拟研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016.Jia Z C. Fully implicit reservoir simulation for chemical flooding[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 陈梦佳, 吴剑锋, 孙晓敏, 等. 地下水典型非水相液体污染运移模拟的尺度提升研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(1): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202001002.htmChen M J, Wu J F, Sun X M, et al. Upscaling of PCE transport modeling based on UTCHEM in heterogeneous porous media[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(1): 11-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202001002.htm [15] 谢文逸, 姜登登, 李旭伟, 等. 污染地块巨厚含水层典型DNAPLs运移模拟及安全利用深度评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(7): 2287-2295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202207016.htmXie W Y, Jiang D D, Li X W, et al. Transport simulation of typical DNAPLs in deep aquifer and safe utilization depth evaluation of polluted plot[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(7): 2287-2295(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202207016.htm [16] 田蕾, 胡立堂, 张梦琳. 低渗透石化污染场地多相抽提修复效率的数值模拟[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 925-935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ202202047.htmTian L, Hu L T, Zhang M L. A numeriacla simulation study on remediation efficiency of multi-phase extraction (MPE) in petrochemical contaminated sites of low permeability[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 925-935(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ202202047.htm [17] Pope D F, Jones J. Monitored natural attenuation of petroleum hydrocarbons(EPA/600/F-98/021) [M]. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1999. [18] 陈然然, 祝欣, 林玉锁, 等. 氯代有机物污染场地的监控自然衰减修复初探[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2361-2369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201507001.htmChen R R, Zhu X, Lin Y S, et al. Preliminary inquiry of monitored natural attenuation remediation of chlorinated organic compounds contaminated sites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(7): 2361-2369(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSZ201507001.htm [19] Surampalli R Y, Ong S K, Seagren E, et al. Natural attenuation of hazardous wastes[M]. Reston, Va: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2004. [20] U.S. Army. Remediation of contaminated army sites: Utility of natural attenuation (Report) [R]. [S. l. ]: U.S. Army Science Advisory Board, Infrastructure and Environmental Group, Department of Army, 1995. [21] Cozzarelli I M, Böhlke J K, Masoner J, et al. Biogeochemical evolution of a landfill leachate plume, norman, oklahoma[J]. Groundwater, 2011, 49(5): 663-687. [22] Blum P, Sagner A, Tiehm A, et al. Importance of heterocylic aromatic compounds in monitored natural attenuation for coal tar contaminated aquifers: A review[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2011, 126(3/4): 181-194. [23] 王孝维, 韩钰洁, 岳秀萍. 苯酚反硝化降解特征分析[J]. 中北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 37(6): 620-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBGG201606013.htmWang X W, Han Y J, Yue X P. Degradation characteristics analysis of phenol during denitrification [J]. Journal of North University of China: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 37(6): 620-625(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBGG201606013.htm [24] MacQuarrie K T B, Sudicky E A, Frind E O. Simulation of biodegradable organic contaminants in groundwater: 1. Numerical formulation in principal directions[J]. Water Resources Research, 1990, 26(2): 207-222. [25] Jean J, Tsai C, Ju S, et al. Biodegradation and transport of benzene, toluene, and xylenes in a simulated aquifer: Comparison of modelled and experimental results[J]. Hydrol Proc, 2002, 16(6): 3151-3168. [26] 赵梦, 骆乾坤, 刘蒙, 等. 地下水中氯代烃污染原位生物修复精细模拟研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(6): 178-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202206018.htmZhao M, Luo Q K, Liu M, et al. Simulation of in-situ bioremediation of chlorinated hydrocarbon contamination in groundwater[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantia, 2022, 42(6): 178-187(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202206018.htm [27] Justin W, Veronica K, William B, et al. Bacterial community dynamics in Dichloromethane-contaminated groundwater undergoing natural attenuation[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2300. [28] Pruess K. TOUGH2 user's guide, version 2.0[R]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 1999. [29] 沈晓芳, 万玉玉, 王利刚, 等. 基于多相流数值模拟的某石油污染场地地下水中VOCs自然衰减过程识别及能力评估[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(5): 90-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202105013.htmShen X F, Wan Y Y, Wang L G, et al. Multiphase flow modeling of natural attenuation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in a petroleum contaminated site[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(5): 90-103(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202105013.htm [30] Jung Y, Pau G S H, Finsterle S, et al. TOUGH3 User's guide version 1.0, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Report LBL-2001093[R]. Berkeley, CA: Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, 2018. [31] Battistelli A. Modeling biodegradation of organic contaminants under multiphase conditions with TMVOCBio[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2004, 3(3): 875-883. [32] Borden R C, Bedient P B. Transport of dissolved hydrocarbons influenced by oxygen-limited biodegradation. 1. Theoretical development[J]. Water Resource Research, 1986, 22(13): 1973-1982. [33] Waddill D W, Widdowson M A. SEAM3D: A numerical model for three dimensional solute transport and sequential electron acceptor-based bioremediation in groundwater[R]. Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic Institute, 1998. [34] Hu L T, Zhang K, Cao X Y, et al. IGMESH: A convenient irregular-grid-based pre- and post- processing tool for TOUGH2 simulator [J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2016, 95: 11-17. [35] 余诗航, 刘珈佑, 李占杰, 等. 高通量测序揭示某石化固废填埋场污染对土壤微生物群落结构和功能的影响[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 58(2): 277-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ202202013.htmYu S H, Liu J Y, Li Z J, et al. Influence of pollutants on soil microbial community structure and function at a petrochemical landfill site: A high-throughput sequencing study[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University: Natural Science, 2022, 58(2): 277-285(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ202202013.htm [36] Jung Y, Battistelli A. User's guide for biodegradation reactions in TMVOCBio[R]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2016. -






 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载: