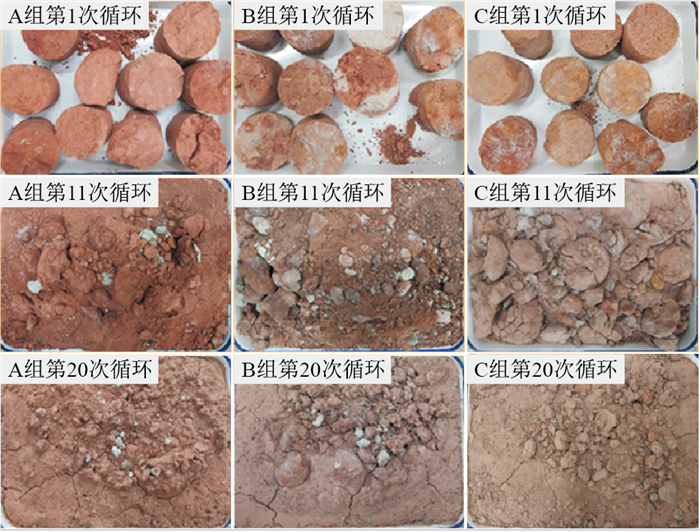
Energy dissipation during disintegration of red-bed soft rock in the Shengzhou-Xinchang area of Zhejiang Province, China
-
摘要:
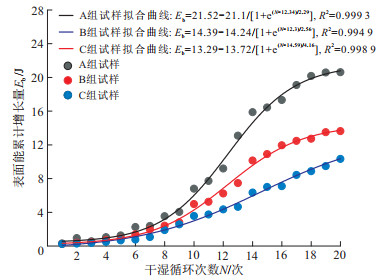
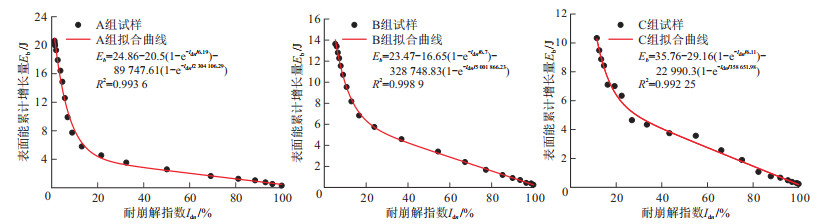
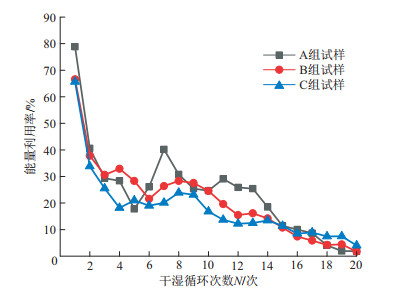
以浙江嵊州-新昌地区红层软岩为研究对象, 探究该地区红层软岩崩解表面能特性。基于能量耗散原理, 通过分析该地区3组不同组成成分的红层软岩在干湿循环作用下崩解过程中能量的转化、传递和耗散, 得出红层软岩崩解过程中吸收的能量向表面能转化的规律。结果表明, 该地区红层软岩随着干湿循环次数的不断增多, 表面能累计增长量有3个变化过程: 初期呈平缓增长; 中期表面能急剧增加, 增长速率越来越快; 崩解后期其表面能累计增长量逐渐保持平稳状态。试验还表明黏土矿物含量越高的红层软岩, 产生的表面能越多, 耐崩解性越差。本研究提出的能量耗散模型, 为治理浙江嵊州-新昌地区各种红层软岩问题提供了参考价值。
Abstract:Objective This study focused on the surface energy characteristics of red-bed soft rocks during disintegration in the Shengzhou-Xinchang area of Zhejiang Province.
Methods Based on the principle of energy dissipation, this study analyzed the conversion, transfer, and dissipation of energy during the process of disintegration under dry-wet cycles for three groups of red-bed soft rocks, considering different compositions in the study area. This study aimed to explore the law of energy absorption and transformation into surface energy during the process of red-bed soft rock disintegration.
Results The results show that the surface energy accumulation of the red-bed soft rock in the study area undergoes three stages with an increasing number of dry-wet cycles: a slow growth stage, a rapid growth stage, and a stable stage. The results also indicate that the higher the content of clay minerals in the red-bed soft rock is, the more surface energy it generates, and the poorer its resistance to disintegration.
Conclusion The energy dissipation model proposed in this study provides a reference for the governance of various failure problems of the red-bed soft rock in the Shengzhou-Xinchang area of Zhejiang Province.
-
Key words:
- red-bed soft rock /
- dry and wet cycle /
- disintegration phenomenon /
- surface energy /
- energy dissipation
-
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
-
表 1 岩样矿物成份
Table 1. Mineral composition of the rock samples
岩样编号 蒙脱石 伊利石 石英 钠长石 方解石 微斜长石 赤铁矿 绿泥石 胶结物 φB/% A组 21.98 22.05 21.73 10.70 14.08 8.50 0.96 — 泥质为主,少量砂质 B组 18.52 15.81 22.32 24.31 8.71 10.33 — — 泥质为主,少量砂质 C组 9.98 14.40 51.28 10.57 11.58 — 2.2 砂质为主,泥质次之 表 2 3组红层软岩不同粒径试样吸水质量
Table 2. Water absorption quality of each particle size of the three groups of red bed soft rocks
粒径/mm 17.3 24.6 30.6 43.8 56.3 72.7 91.6 104.2 112.6 116.2 吸水质量/g A组 2.7 3.4 4.2 6.3 14.7 25.5 40.9 60.7 68.9 79.5 B组 1.6 2.5 3.3 5.3 8.1 18.3 33.1 49.9 58.7 65.5 C组 1.5 2.2 2.7 5.2 7.0 12.8 25.2 30.6 41.1 47.4 -
[1] 彭华, 吴志才. 关于红层特点及分布规律的初步探讨[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 42(5): 109-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ200305029.htmPENG H, WU Z C. A preliminary study on the characteristics and the distribution of red beds[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2003, 42(5): 109-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ200305029.htm [2] 郭永春, 谢强, 文江泉. 我国红层分布特征及主要工程地质问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2007, 34(6): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200706014.htmGUO Y C, XIE Q, WEN J Q. Red beds distribution and engineering geological problem in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2007, 34(6): 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200706014.htm [3] 赵珂, 刘心蕊, 李宸, 等. 江陵凹陷新沟咀组古红层沉积特征及地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806006.htmZHAO K, LIU X R, LI C, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and geological significance of the paleo-red sediment in Xingouzui Formation of Jiangling Depression, Qianjiang Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806006.htm [4] 谢妮, 王丁浩, 吕阳, 等. 酸腐蚀作用下川渝红层砂岩蠕变特性试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 141-149. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0142XIE N, WANG D H, Lü Y, et al. Experimental study on creep behaviors of red sandstone in Sichuan and Chongqing under acid corrosion[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 141-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0142 [5] ZHANG Z T, GAO W H, ZENG C F, et al. Evolution of the disintegration breakage of red-bed soft rock using a logistic regression model[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 24: 100382. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2020.100382 [6] 王晓强, 姚华彦, 代领, 等. 皖南红层软岩崩解特性试验分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(3): 683-691. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202103006.htmWANG X Q, YAO H Y, DAI L, et al. Experimental study on slaking characteristics of red-bed soft rock in southern Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(3): 683-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202103006.htm [7] 吴道祥, 刘宏杰, 王国强. 红层软岩崩解性室内试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(增刊2): 4173-4179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2010S2104.htmWU D X, LIU H J, WANG G Q. Laboratory experimental study of slaking characteristics of red-bed soft rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(S2): 4173-4179. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2010S2104.htm [8] ZHANG M, YIN Y P, HUANG B L. Mechanisms of rainfall-induced landslides in gently inclined red beds in the eastern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Landslides, 2015, 12(5): 973-983. [9] HATAMURA Y, CHIJIIWA K. Analysis of the mechanism of soil cutting (1st report). Cutting patterns of soils[J]. Bulletin of the JSME, 1975, 18(120): 619-626. [10] HATAMURA Y, CHIJIIWA K. Analysis of the mechanism of soil cutting (3rd report). Distribution of stresses on cutting blade and cutting force)[J]. Bulletin of the JSME, 1976, 19(137): 1376-1384. [11] 曾铃, 张华麟, 戚双星, 等. 基于能量耗散原理的炭质泥岩崩解特征试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(11): 4181-4189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202111032.htmZENG L, ZHANG H L, QI S X, et al. Experimental study on disintegration characteristics of carbonaceous mudstone based on energy dissipation principle[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology Edition), 2021, 52(11): 4181-4189. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202111032.htm [12] 谢和平, 彭瑞东, 鞠杨. 岩石变形破坏过程中的能量耗散分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(21): 3565-3570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200421001.htmXIE H P, PENG R D, JU Y. Energy dissipation of rock deformation and fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(21): 3565-3570. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200421001.htm [13] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 工程岩体试验方法标准: GB/T 50266-2013[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2013.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of engineering rock mass: GB/T 50266-2013[S]. Beijing: China Planning Publishing House, 2013. (in Chinese) [14] 胡学涛. 干湿循环作用下红层软岩力学特性的试验与模拟研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2020.HU X T. Experimental and simulation study on the mechanical properties of red bed soft rock under the action of dry-wet cycle[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 中华人民共和国地质矿业行业标准: DZ/T 0276-2015岩石物理力学性质试验规程[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2015.Geological and Mining Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China: DZ/T 0276-2015 Test code for physical and mechanical properties of rocks[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 郑明新, 徐朋威, 杨汶明, 等. 江西白垩系泥质粉砂岩崩解试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(2): 374-381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202102008.htmZHENG M X, XU P W, YANG W M, et al. Experimental study ondisintegration of Cretaceous argillaceous siltstone in Jiangxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(2): 374-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202102008.htm [17] 常树人. 热学[M]. 天津: 南开大学出版社, 2009.CHANG S R. Thermology[M]. Tianjin: Nankai University Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [18] 熊力. 红层软岩崩解机理研究及工程应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2011.XIONG L. Study and application of slaking mechanism of red bed soft rock[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 赵建生. 断裂力学及断裂物理[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2003: 234-236.ZHAO J S. Fracture mechanics and fracture physics[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2003: 234-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] LÖRINCZ J, IMRE E, FITYUS S, et al. The grading entropy-based criteria for structural stability of granular materials and filters[J]. Entropy, 2015, 17(5): 2781-2811. [21] ERGULER Z A, SHAKOOR A. Relative contribution of various climatic processes in disintegration of clay-bearing rocks[J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 108(1/2): 36-42. [22] 刘晓明, 熊力, 刘建华, 等. 基于能量耗散原理的红砂岩崩解机制研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(10): 3143-3149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201110043.htmLIU X M, XIONG L, LIU J H, et al. Slacking mechanism of redsandstone based on energy dissipation principle[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology Edition), 2011, 42(10): 3143-3149. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201110043.htm -






 下载:
下载: