Enrichment conditions and main controlling factors of continental shale gas in the Permian Lower Wuerhe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
为探明准噶尔盆地二叠系下乌尔禾组页岩气富集条件及主控因素, 以东道海子凹陷下乌尔禾组为研究对象, 通过野外地质观察、录井、测井、地震等资料的收集, 结合总有机碳含量测定、X衍射全岩分析、岩心观察、气体吸附(N2、CO2)等手段, 对下乌尔禾组页岩的分布特征、有机质发育特征、储层特征及含气性特征进行了研究。结果表明: (1)下乌尔禾组页岩总有机碳含量(
w (TOC))较高, 平均1.58%;有机质类型以Ⅱ2型和Ⅲ型为主; 镜质体反射率R o平均1.46%, 处于成熟阶段; 烃源岩厚度平均75 m, 烃源岩较好, 生气潜力大。盆地模拟结果表明下乌尔禾组页岩含气量较好, 平均1.89 m3/t。(2)页岩储集层粒内孔和微裂缝较为发育; 气体主要吸附于微孔和介孔; 孔隙度均值6.10%, 渗透率均值为0.27×10-3 μm2, 有利于页岩气的聚集。(3)页岩黏土矿物体积分数较高, 均值29.6%, 能提供较高的比表面积, 增加页岩的气体吸附能力; 脆性矿物体积分数均值50.9%, 压裂改造性良好。(4)页岩储层压力系数较大, 均值为1.58, 具有良好的保存条件。结合区域构造—沉积环境以及地化参数的分析表明, 东道海子凹陷下乌尔禾组页岩气成藏的主控因素包括地化参数和保存条件, 其中有机质热演化成熟度高、页岩厚度大、w (TOC)高、良好的保存条件等是影响页岩气富集的关键因素。基于上述条件, 提出东道海子凹陷页岩气勘探开发有利区位于凹陷的腹部偏东北斜坡地区。该研究成果揭示了东道海子凹陷下乌尔禾组页岩气富集条件及主控因素, 对准噶尔盆地腹部地区深层油气勘探具有借鉴意义。Abstract:Objective To explore the enrichment conditions and main controlling factors of shale gas in the Lower Wuerhe Formation of the Permian System in the Junggar Basin, the Lower Wuerhe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag was selected as the research object.
Methods Based on the data of outcrop, core, well logging, well-calibrated seismic reflections and the technologies of total organic carbon (TOC) content determination, whole-rock X-ray diffraction, gas adsorption (N2, CO2), the distribution characteristics, organic matter development characteristics, reservoir characteristics, and gas bearing characteristics of the Lower Wuerhe Formation shale were studied.
Results The results show that: (1) The organic matter of the Lower Wuerhe Formation shale is dominated by Ⅱ2 and Ⅲ types and shows an average TOC content of 1.58%. The average vitrinite reflectance (
R o) of organic matter is 1.46%, which indicates the mature stage. The average thickness of the source rock is 75 m. Summarily, the source rock is good and has a high gas potential. The basin simulation results show an average shale gas content of 1.89 m3/t in the Lower Wuerhe Formation. (2) The pores and microfractures in shale reservoirs are highly developed, and gas is primarily adsorbed in micropores and mesopores. The average porosity and permeability are 6.10% and 0.27×10-3 μm2 respectively, which are favourable for shale gas accumulation. (3) The shale has a high clay mineral content, with an average of 29.6%, providing a significant specific surface area and enhancing the gas adsorption capacity of the shale. Additionally, the average brittle mineral content is 50.9%, indicating good frackability. (4) Moreover, the shale reservoir exhibits a relatively large pressure coefficient of 1.58, indicating the favourable conservation conditions. The analysis of the regional tectonic-sedimentary environment and geochemical parameters indicates that the main factors controlling shale gas accumulation in the Lower Wuerhe Formation of the Dongdaohaizi Sag are geochemical parameters and preservation conditions. The key factors influencing shale gas accumulation include the high thermal evolution maturity of organic matter, large shale thickness, high TOC content, and good preservation conditions. These conditions suggest that the favourable area for shale gas exploration and development in the Dongdaohaizi Sag is located in the northeastern slope area of the sag's abdomen.Conclusion The results of this research reveal the enrichment conditions and main controlling factors of shale gas in the Lower Wuerhe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag, which has reference value for deep oil and gas exploration in the abdominal area of the Junggar Basin.
-
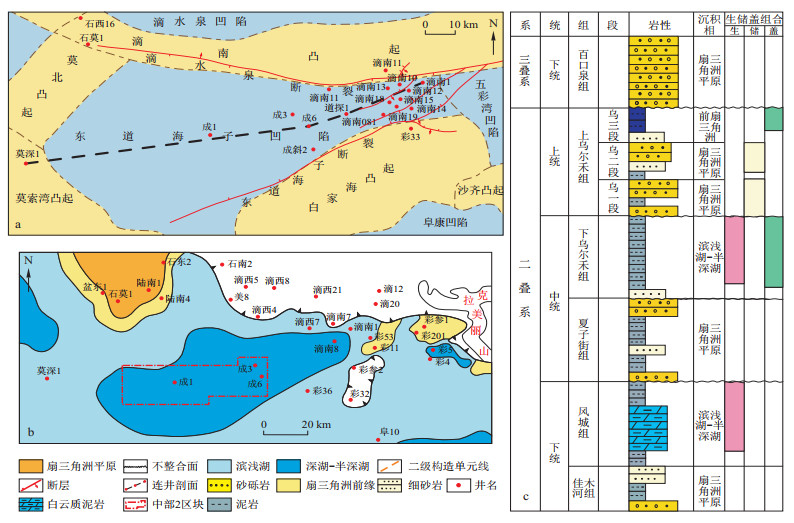
图 2 东道海子凹陷下乌尔禾组连井剖面图(剖面位置见图 1a)
Figure 2. Well cross-section of the Lower Wuerhe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag
图 6 下乌尔禾组陆相页岩与龙马溪组典型海相页岩矿物组成对比图(龙马溪组海相页岩数据来自文献[26])
Figure 6. Comparison of mineral composition between continental shales of the Lower Wuerhe Formation and typical marine shales of Longmaxi Formation
图 11 东道海子凹陷下乌尔禾组页岩孔隙度与石英体积分数以及渗透率与孔隙度的关系图(图b部分数据源于文献[19])
Figure 11. Relationship between porosity and quartz content, permeability and porosity of shale in the Lower Wuerhe Formation in Dongdaohaizi Sag
表 1 准噶尔盆地下乌尔禾组陆相页岩气组分与四川盆地龙马溪组典型海相页岩气组分分析对比
Table 1. Comparison of shale gas components between continental shale of the Lower Wuerhe Formation in Junggar Basin and typical marine shale of the Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin
盆地名称 井号 层位 气体组成/% CH4 C2H6 C3H8 CO2 N2 四川盆地 W201井 龙马溪组 98.54 0.52 0.03 0.30 0.56 W203井 龙马溪组 97.93 0.54 0.04 0.92 0.54 准噶尔盆地 成6井 下乌尔禾组 96.43 0.34 0.02 1.60 1.58 注:四川盆地龙马溪组海相页岩气组分资料来自于参考文献[26] 表 2 东道海子凹陷及邻区勘探井试气成果
Table 2. Gas test results of exploration wells in the Dongdaohaizi Sag and its adjacent areas
地区 井号 层位 井深/m 日产气量/104 m3 东道海子凹陷 成6井 P2w 6 400 3.429 滴南8井 P2p 3 956~3 972 0.261 克拉美丽气田 滴西5井 P2w 3 568~3 590 2.380 滴西17井 P2w 3 519 2.255 -
[1] 邹才能, 赵群, 丛连铸, 等. 中国页岩气开发进展、潜力及前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202101002.htmZOU C N, ZHAO Q, CONG L Z, et al. Development progress, potential and prospect of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202101002.htm [2] 徐红卫, 李贤庆, 周宝刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区陆相页岩气储层特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 45(6): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201706008.htmXU H W, LI X Q, ZHOU B G, et al. Characteristics of terrestrial shale gas reservoir in Yanchang exploration area of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2017, 45(6): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201706008.htm [3] 冯动军. 四川盆地侏罗系大安寨段陆相页岩油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(2): 219-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202202003.htmFENG D J. Geological characteristics and exploration direction of continental shale gas in Jurassic Da'anzhai Member, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(2): 219-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202202003.htm [4] 白静, 徐兴友, 刘卫彬, 等. 松辽盆地下白垩统沙河子组陆相页岩气首获高产突破[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(3): 1121-1123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202203025.htmBAI J, XU X Y, LIU W B, et al. The breakthrough of continental shale gas in Lower Cretaceous Shahezi Formation of Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(3): 1121-1123. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202203025.htm [5] 张仲培, 张宇, 张明利, 等. 准噶尔盆地中部凹陷区二叠系-三叠系油气成藏主控因素与勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 559-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202204001.htmZHANG Z P, ZHANG Y, ZHANG M L, et al. Main controlling factors and exploration direction of Permian to Triassic reservior in the central sag of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(4): 559-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202204001.htm [6] 何海清, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷康探1井重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202102001.htmHE H Q, ZHI D M, TANG Y, et al. A great discovery of Well Kangtan 1 in the Fukang Sag in the Junggar Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202102001.htm [7] 孙靖, 宋永, 王仕莉, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层致密油储层特征及致密化成因: 以莫索湾-莫北地区侏罗系八道湾组为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(1): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201701003.htmSUN J, SONG Y, WANG S L, et al. Deep tight oil reservoir characteristics and densification causes of Junggar Basin: A case from Jurassic Badaowan Formation in Mosuowan-Mobei area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(1): 25-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201701003.htm [8] 何文军, 王绪龙, 邹阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201902008.htmHE W J, WANG X L, ZOU Y, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction of oil in Junggar Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201902008.htm [9] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 邓春萍, 等. 准噶尔盆地烃源岩与原油地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(1): 37-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201601003.htmCHEN J P, WANG X L, DENG C P, et al. Geochemical features of source rocks and crude oil in the Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(1): 37-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201601003.htm [10] 郑孟林, 樊向东, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层地质结构叠加演变与油气赋存[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htmZHENG M L, FAN X D, HE W J, et al. Superposition of deep geological structural evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htm [11] 杜世涛, 田继军, 李沼鹈, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系页岩气储层特征及潜力区优选[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(2): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201802009.htmDU S T, TIAN J J, LI Z T, et al. Permian shale gas reservoir characterization and favorable area identification in Junggar Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(2): 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201802009.htm [12] 袁述武, 邱争科, 张有印, 等. 克拉玛依油田八区下乌尔禾组油藏北部控藏因素探讨[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2014, 10(1): 7-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201401002.htmYUAN S W, QIU Z K, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Probe into Xiawuerhe reservoir controlling factors in No. 8 area of Karamay Oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2014, 10(1): 7-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201401002.htm [13] 李博偲, 李美俊, 唐友军, 等. 烃源岩生物标志化合物分布特征及其地质意义: 以准噶尔盆地腹部地区中二叠统下乌尔禾组为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2022, 46(5): 68-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202205006.htmLI B C, LI M J, TANG Y J, et al. Distribution characteristics and geological significance of biomarkers in source rocks of Lower Wuerhe Formation of Middle Permian in Central Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2022, 46(5): 68-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202205006.htm [14] 唐勇, 王智强, 庞燕青, 等. 准噶尔盆地西部坳陷二叠系下乌尔禾组烃源岩生烃潜力评价[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(4): 16-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202304002.htmTANG Y, WANG Z Q, PANG Y Q, et al. Hydrocarbon-generating potential of source rocks of Permian Lower Urho Formation in Western Depression, Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(4): 16-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202304002.htm [15] 靳军, 罗小平, 廖健德, 等. 准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷平地泉组烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 42(2): 196-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201502007.htmJIN J, LUO X P, LIAO J D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Permian Pingdiquan Formation hydrocarbon source rocks in Dongdaohaizi Sag, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2015, 42(2): 196-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201502007.htm [16] 杨海波, 王屿涛, 郭建辰, 等. 准噶尔盆地天然气地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10): 1518-1530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201810013.htmYANG H B, WANG Y T, GUO J C, et al. Geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction of natural gas in Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(10): 1518-1530. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201810013.htm [17] 冯陶然. 准噶尔盆地二叠系构造-地层层序与盆地演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.FENG T R. Permian tectono-stratigraphic sequence and basin evolution in Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 丁湘华. 准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷油气成因及成藏期次分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(10): 80-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201610015.htmDING X H. Analysis of hydrocarbon genesis and accumulation stage of Dongdaohaizi Sag in Junggar Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(10): 80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201610015.htm [19] 匡立春, 支东明, 王小军, 等. 准噶尔盆地上二叠统上乌尔禾组大面积岩性-地层油气藏形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(3): 325-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202203001.htmKUANG L C, ZHI D M, WANG X J, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration directions of large-scale lithologic-stratigraphic oil and gas reservoirs in Upper Wuerhe Formation of Upper Permian in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(3): 325-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202203001.htm [20] 蒲泊伶, 董大忠, 管全中, 等. 川南地区龙马溪组页岩气富集高产主控因素分析[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(5): 918-928. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT202205016.htmPU B L, DONG D Z, GUAN Q Z, et al. Analysis of main controlling factors for the enrichment and high productivity of the Longmaxi shale gas in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(5): 918-928. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT202205016.htm [21] 蔡宁波, 何磊, 王晓龙, 等. 川西坳陷须三段致密砂岩气藏源储特征及成藏模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 1-14. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0528CAI N B, HE L, WANG X L, et al. Characteristics of reservoir-source rock and hydrocarbon accumulation model of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Third Member of Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0528 [22] 谢通, 潘诗洋, 王亿, 等. 鄂西恩地1井上二叠统大隆组页岩气富集主控因素分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2022, 36(2): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202202003.htmXIE T, PAN S Y, WANG Y, et al. Analysis on main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment in Upper Permian Dalong Formation in Well Endi 1, western Hubei[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(2): 149-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202202003.htm [23] 张焱林, 段轲, 刘早学, 等. 鄂西下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩特征及页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 691-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201905010.htmZHANG Y L, DUAN K, LIU Z X, et al. Characteristics of shale and main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in western Hubei[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 691-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201905010.htm [24] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 甘华军, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段页岩形成环境及页岩油潜力综合评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233ZHOU L H, CHEN C W, GAN H J, et al. Shale formation environment and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233 [25] 张毅, 郑书粲, 高波, 等. 四川广元上寺剖面上二叠统大隆组有机质分布特征与富集因素[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(6): 1008-1025. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201706011.htmZHANG Y, ZHENG S C, GAO B, et al. Distribution characteristics and enrichment factors of organic matter in Upper Permian Dalong Formation of Shangsi Section, Guangyuan, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(6): 1008-1025. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201706011.htm [26] 邹晓艳, 李贤庆, 王元, 等. 川南地区五峰组-龙马溪组深层页岩储层特征和含气性[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(4): 654-665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202204013.htmZOU X Y, LI X Q, WANG Y, et al. Reservoir characteristics and gas content of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations deep shale in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(4): 654-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202204013.htm [27] 胡东风. 四川盆地东南缘向斜构造五峰组-龙马溪组常压页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(5): 605-615. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201905001.htmHU D F. Main controlling factors on normal pressure shale gas enrichments in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in synclines, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(5): 605-615. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201905001.htm [28] 魏力民, 王岩, 张天操, 等. 页岩气富集与高产主控因素: 以川南地区五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(6): 700-704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006006.htmWEI L M, WANG Y, ZHANG TC, et al. Main control factors of enrichment and high-production of shale gas: A case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in southern Sichuan[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(6): 700-704. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006006.htm [29] 郭旭升. 四川盆地涪陵平桥页岩气田五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901001.htmGUO X S. Controlling factors on shale gas accumulations of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Pingqiao shale gas field in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901001.htm [30] 刘雨林. 四川盆地南川区块页岩气富集地质特征及主控因素[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.LIU Y L. Geological characteristics and main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment in Nanchuan Block, Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 方栋梁, 孟志勇. 页岩气富集高产主控因素分析: 以四川盆地涪陵地区五峰组-龙马溪组一段页岩为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 37-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202001007.htmFANG D L, MENG Z Y. Main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment and high yield: A case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202001007.htm [32] 王社教, 杨涛, 张国生, 等. 页岩气主要富集因素与核心区选择及评价[J]. 中国工程科学, 2012, 14(6): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201206012.htmWANG S J, YANG T, ZHANG G S, et al. Shale gas enrichment factors and the selection and evaluation of the core area[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2012, 14(6): 94-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201206012.htm [33] 乔锦琪. 准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷东部二叠系油气成藏条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.QIAO J Q. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of the Permian reserviors in the eastern Dongdaohaizi Sag, Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 何希鹏, 齐艳平, 何贵松, 等. 渝东南构造复杂区常压页岩气富集高产主控因素再认识[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(5): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905004.htmHE X P, QI Y P, HE G S, et al. Further understanding of main controlling factors of normal pressure shale gas enrichment and high yield in the area with complex structure of the southeast area of Chongqing[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(5): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905004.htm [35] 邓模, 翟常博, 杨振恒, 等. 低成熟海相黑色页岩生烃特征的热模拟实验[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(1): 130-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202101018.htmDENG M, ZHAI C B, YANG Z H, et al. Thermal simulation experiment on hydrocarbon generation characteristics of low-mature marine black shale[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 130-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202101018.htm [36] 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(5): 1313-1323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202205011.htmLI E T, MA W Y, LI J, et al. Thermal simulation experiment for hydrocarbon generation: A case study of Jurassic coal from the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(5): 1313-1323. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202205011.htm [37] 陈承声, 史树勇, 王云鹏. 基于PetroMod四川盆地长宁地区五峰-龙马溪组优质页岩段吸附模拟研究[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(6): 602-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201906009.htmCHEN C S, SHI S Y, WANG Y P. Adsorption simulation based on PetroMod of high-quality shale segment of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Changning area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2019, 48(6): 602-612. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201906009.htm [38] 王瑶琳, 徐胜林, 侯明才, 等. 云南保山地区下仁和桥组页岩特征、有机质富集因素及富集模型[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2022, 41(5): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202205005.htmWANG Y L, XU S L, HOU M C, et al. Shale characteristics, organic matter enrichment factors and enrichment model of Xiarenheqiao Formation in Baoshan area in Yunnan[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(5): 37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202205005.htm [39] 吴静. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷北部隆起区油气远源富集与主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 117-124. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0020WU J. Key factors of far-source hydrocarbon enrichment in the northern uplift area of Enping Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0020 [40] ZHANG J F, XU X Y, BAI J, et al. Accumulation and exploration of continental shale gas resources of Cretaceous Shahezi Formation in Lishu fault depression, Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(3): 502-515. [41] HU D F, WEI Z H, LIU R B, et al. Development characteristics and exploration potential of the Lower Carboniferous black shale in the Guizhong Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2019, 6(3): 205-214. [42] HU D F, WEI Z H, LIU R B, et al. Enrichment control factors and exploration potential of lacustrine shale oil and gas: A case study of Jurassic in the Fuling area of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2022, 9(1): 1-8. [43] HU S Y, WANG X J, CAO Z L, et al. Formation conditions and exploration direction of large and medium gas reservoirs in the Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 266-279. [44] WANG K, WANG Y Y, WANG F Q, et al. Formation conditions and the main controlling factors for the enrichment of shale gas of Shanxi Formation in the southeast of Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 8(1): 49-62. [45] FAN C H, LI H, QIN Q R, et al. Geological conditions and exploration potential of shale gas reservoir in Wufeng and Longmaxi Formation of southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 191: 107138. [46] 张洪洁, 王凤琴, 刘航, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部长7段页岩气含气量及影响因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(6): 666-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201906005.htmZHANG H J, WANG F Q, LIU H, et al. Shale gas content and its influencing factors in Chang 7 Member of southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(6): 666-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201906005.htm [47] 秦黎明, 张枝焕, 朱雷, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中二叠统烃源岩封闭体系生烃热模拟实验分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(5): 860-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201105018.htmQIN L M, ZHANG Z H, ZHU L, et al. Productions of closed system experiments for Middle Permian source rock in southern Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(5): 860-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201105018.htm -





 下载:
下载: