Geochemical factors affecting oxidation dissolution and permeability enhancement of Yichang gas-producing shale in Hubei Province
-
摘要:
为探究湖北宜昌地区产气页岩氧化溶蚀增渗的地球化学影响因素, 以宜昌地区陡山沱组页岩为研究对象, 选取了H2O2(
w B=15%)和Na2S2O8(c B=0.5 mol/L)2种氧化剂开展了氧化溶蚀实验, 探究了不同pH值、温度、地下水水化学离子浓度对氧化溶蚀效果的影响。研究结果表明, Na2S2O8氧化溶蚀效果优于H2O2, H2O2和Na2S2O8在酸性条件下氧化溶蚀效果均优于碱性条件, 碱性环境不利于2种氧化剂的氧化; 升温会促进Na2S2O8和H2O2的热分解, 分别产生H2SO4和O2, 对页岩的氧化溶蚀有积极影响。外源Na+(氯化物)的添加能促进页岩在Na2S2O8和H2O2氧化过程下Ca2+和Mg2+的释放, 增强氧化溶蚀效果; 而外源Ca2+、SO42-的添加, 容易与碳酸盐酸蚀产生的SO42-、Ca2+形成石膏沉淀, 从而引起页岩孔隙堵塞, 降低页岩渗透性; 同时, 外源Mg2+易在弱碱性环境下生成硅酸镁沉淀, 对页岩的氧化溶蚀产生负面影响。建议今后在页岩气氧化压裂开采过程中, 预先调查开采地层的水化学参数, 根据地层温度、pH值和阴阳离子来选择氧化液和开采方式。Abstract:Objective Chemical oxidation and infiltration technology has become a mature method for shale gas exploitation. This study aims to investigate the influence of geochemical factors on the exploitation process.
Methods In this study, the Doushantuo Formation shale in Yichang, Hubei Province, which exhibits significant potential for shale gas exploitation and contains a high organic matter content along with pyrite, was selected as the research object. Two commonly used oxidants, 15% H2O2 and 0.5 mol/L Na2S2O8, were selected for oxidation corrosion experiments conducted at normal temperature and pressure. Post-reaction measurements included cation concentration, pH, Eh, mass loss and XRD analysis.
Results The results show that Na2S2O8 outperforms H2O2, and the advanced oxidation process driven by pyrite and the erosion effect of carbonate under acid production make the acidic environment more suitable for the dissolution of carbonate-rich shale. An increase in temperature enhances the thermal decomposition of Na2S2O8 and H2O2. The thermal decomposition of H2O2 produces O2, and Na2S2O8 produces H2SO4, O2 and SO4- with strong oxidation. Thus, the temperature's enhancement effect on Na2S2O8 is greater than that on H2O2. Sodium ions (chloride) can promote the release of Ca2+ and Mg2+ during Na2S2O8 and H2O2 oxidation, indicating that a high concentration of NaCl in groundwater plays a positive role in the oxidation and dissolution of shale. Both calcium ions and sulfate ions can cause gypsum precipitation by influencing the interactions between the reactions, thus affecting the oxidative dissolution of shale. Low concentrations of exogenous calcium ions reduce the buffering effect of carbonate and promote its dissolution, while high concentrations of exogenous calcium ions cause secondary mineral precipitation, block shale pores and hinder the oxidation and dissolution of shale. However, the effect of sulfate ions on the oxidative corrosion of shale differs from that of calcium ions. A low concentration of exogenous sulfate ions inhibits the oxidative corrosion of shale by generating secondary ore and impeding the oxidation of pyrite.
Conclusion Therefore, in the future process of shale gas oxidative fracturing for extraction, it is necessary to preassess the water chemical parameters of the exploitation formation in advance and select the oxidation liquid and mining modes based on the temperature, pH and cationions.
-
Key words:
- shale /
- H2O2 /
- Na2S2O8 /
- oxidation dissolution /
- Yichang area, Hubei Province
-
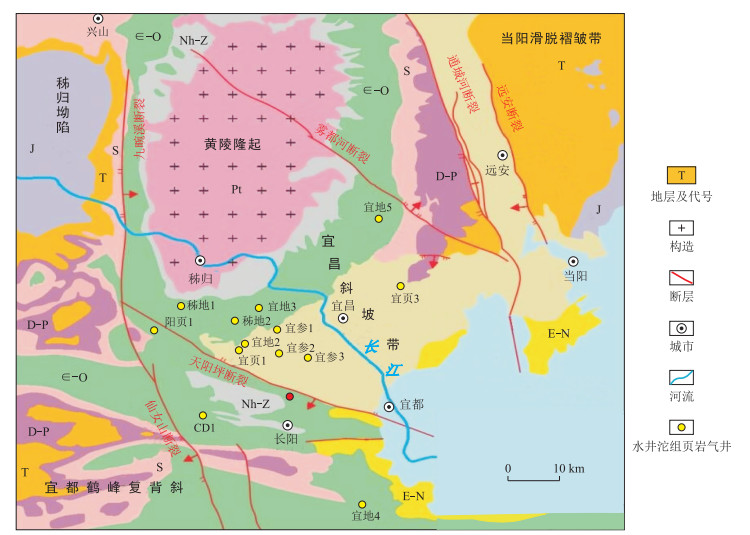
图 1 湖北宜昌地区地质构造简图[31]
Nh.南华系; Z.震旦系; ∈.寒武系; O.奥陶系; S.志留系; D.泥盆系; P.二叠系; T.三叠系; J.侏罗系; K.白垩系; E.古近系
Figure 1. Sketch map of tectonics in the Yichang area, Hubei Province
表 1 湘鄂西区海相地层水化学参数统计
Table 1. Statistical table of chemical parameters in marine formation water in western Hunan and Hubei Provinces ρB/(mg·L-1)
储层 井号 Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- 矿化度 水型 震旦系 宜3 1 597.90 568.45 201.98 1 156.11 3 786.30 166.43 7 460.50 SO4-Na 宜4 1 746.16 534.93 179.88 1 138.98 3 954.10 175.95 7 730.27 SO4-Na 宜7 1 590.27 538.69 194.54 1 083.88 3 783.06 153.77 7 348.37 SO4-Na 宜8 1 675.00 550.00 203.00 1 238.00 3 749.00 245.00 7 660.00 SO4-Na 均值(ρ) 1 652.33 548.02 194.85 1 154.24 3 818.12 185.29 7 549.79 SO4-Na 表 2 实验设计
Table 2. Experimental design
组别 pH值 温度/℃ 阴阳离子 质量浓度ρB A 1,2,3,7,9,11 25 — — B — 25,45,60 — — C — 25 Na+ 0,0.5ρ,ρ,1.5ρ,2ρ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42- -
[1] 邹才能, 杨智, 董大忠, 等. 非常规源岩层系油气形成分布与前景展望[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(5): 1517-1533.ZOU C N, YANG Z, DONG D Z, et al. Formation, distribution and prospect of unconventional hydrocarbons in source rock strata in China[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(5): 1517-1533. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] ADMINISTRATION E I. Technically recoverable shale oil and shale gas resources: An assessment of 137 shale formations in 41 countries outside the United States[J]. US Department of Energy, 2013. [3] 国家能源局. 中国天然气发展报告[R]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2022.National Energy Administration. China natural gas development report[R]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2022. (in Chinese) [4] 王小龙. 扩展有限元法应用于页岩气藏水力压裂数值模拟研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.WANG X L. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing in shale gas reservoirs based on the extended finite element method[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] BAIHLY J, ALTMAN R, MALPANI R, et al. Shale gas production decline trend comparison over time and basins[C]//Anon. All Days. Florence, Italy. SPE, 2010. [6] CIPOLLA C L, LOLON E P, MAYERHOFER M J. Reservoir modeling and production evaluation in shale-gas reservoirs[C]//Anon. IPTC 2009: International petroleum technology conference. Doha, Qatar: European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2009. [7] CURTIS M E, SONDERGELD C H, AMBROSE R J, et al. Microstructural investigation of gas shales in two and three dimensions using nanometer-scale resolution imaging[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(4): 665-677. doi: 10.1306/08151110188 [8] YOU L J, KANG Y L, CHEN Q, et al. Prospect of shale gas recovery enhancement by oxidation-induced rock burst[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2017, 4(6): 449-456. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2017.05.014 [9] 舒志国, 舒逸, 陈绵琨, 等. 陆相页岩岩相非均质性及储层孔隙发育特征: 以四川盆地自流井组东岳庙段页岩为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 1-15. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220446SHU Z G, SHU Y, CHEN M K, et al. Lithofacies heterogeneity and reservoir pore development characteristics of continental shale: A case study of the Dongyuemiao shale of the Ziliujing Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220446 [10] 刘树根, 王世玉, 孙玮, 等. 四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组黑色页岩特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(6): 621-639.LIU S G, WANG S Y, SUN W, et al. Characteristics of black shale in Wufeng Formation and Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its peripheral areas[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(6): 621-639. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] GHANBARI E, DEHGHANPOUR H. Impact of rock fabric on water imbibition and salt diffusion in gas shales[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 138: 55-67. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2014.11.003 [12] MAKHANOV K, DEHGHANPOUR H, KURU E. Measuring liquid uptake of organic shales: A workflow to estimate water loss during shut-in periods[C]//Anon. All days. Calgary, Alberta, Canada: SPE, 2013. [13] TAKAHASHI S, KOVSCEK A R. Spontaneous countercurrent imbibition and forced displacement characteristics of low-permeability, siliceous shale rocks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2010, 71(1/2): 47-55. [14] ENGELDER T, CATHLES L M, BRYNDZIA L T. The fate of residual treatment water in gas shale[J]. Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, 2014, 7: 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.juogr.2014.03.002 [15] SHANLEY K W, CLUFF R M, ROBINSON J W. Factors controlling prolific gas production from low-permeability sandstone reservoirs: Implications for resource assessment, prospect development, and risk analysis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(8): 1083-1121. doi: 10.1306/03250403051 [16] FAN Y, PENG H, CHEN G, et al. Experimental study of the influences of different factors on the acid-rock reaction rate of carbonate rocks[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 63: 107064. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.107064 [17] GUO T K, LI Y C, DING Y, et al. Evaluation of acid fracturing treatments in shale formation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(10): 10479-10489. [18] ZOU Y S, LI S H, MA X F, et al. Effects of CO2-brine-rock interaction on porosity/permeability and mechanical properties during supercritical-CO2 fracturing in shale reservoirs[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 49: 157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.11.004 [19] HAZRA B, VISHAL V, SETHI C, et al. Impact of supercritical CO2 on shale reservoirs and its implication for CO2 sequestration[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(17): 9882-9903. [20] WANG M W, WU W, CHEN S Y, et al. Experimental evaluation of the rheological properties and influencing factors of gel fracturing fluid mixed with CO2 for shale gas reservoir stimulation[J]. Gels, 2022, 8(9): 527. doi: 10.3390/gels8090527 [21] ZHOU Y, YOU L J, KANG Y L, et al. Application prospect of oxidative stimulation of organic-rich shale gas reservoir: A case study of Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(5): 2530-2541. [22] CHENG Q Y, YOU L J, KANG Y L, et al. Oxidative dissolution kinetics of organic-rich shale by hydrogen peroxide(H2O2) and its positive effects on improving fracture conductivity[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 89: 103875. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2021.103875 [23] SHAO J X, KANG Y L, YOU L J, et al. Experimental investigation on inorganic scaling induced by the shale reaction with oxidation solution[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2022, 106: 104717. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2022.104717 [24] JEW A D, DUSTIN M K, HARRISON A L, et al. Impact of organics and carbonates on the oxidation and precipitation of iron during hydraulic fracturing of shale[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(4): 3643-3658. [25] BLAUCH M E, MYERS R R, MOORE T R, et al. Marcellus shale post-frac flowback waters: Where is all the salt coming from and what are the implications?[C]//Anon. All days. Charleston, West Virginia, USA: SPE, 2009. [26] 蔡全升, 刘安, 张保民, 等. 宜昌页岩气揭开神秘面纱[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2018, 34(2): 183-186.CAI Q S, LIU A, ZHANG B M, et al. The mystery of Yichang shale gas[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2018, 34(2): 183-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 陈孝红, 张保民, 张国涛, 等. 湖北宜昌地区奥陶系五峰组-志留系龙马溪组获页岩气高产工业气流[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(1): 199-200.CHEN X H, ZHANG B M, ZHANG G T, et al. High shale gas industry flow obtained from the Ordovician Wufeng Formation and the Silurian Longmaxi Formation of Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(1): 199-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 陈孝红, 王传尚, 刘安, 等. 湖北宜昌地区寒武系水井沱组探获页岩气[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(1): 188-189.CHEN X H, WANG C S, LIU A, et al. The discovery of the shale gas in the Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation of Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(1): 188-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] YANG W, HE S, ZHAI G Y, et al. Pore characteristics of the Lower Sinian Doushantuo shale in the Mid-Yangtze Yichang area of China: Insights into a distinct shale gas reservoir in the Neoproterozoic Formation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 73: 103085. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2019.103085 [30] 刘伟, 段佳文, 赵瑞超, 等. 宜昌长江南岸岩溶地下水中水生动物群落分布特征及其环境响应[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 273-282. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0218LIU W, DUAN J W, ZHAO R C, et al. Distribution of aquatic fauna in karstic groundwater and its environmental response on the south bank of the Yangtze River in Yichang[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 273-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0218 [31] 杨森. 宜昌地区产气页岩氧化溶蚀增渗机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2021.YANG S. Study on the mechanism of oxidative dissolution for permeability enhancement of gas shale in Yichang area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 张君峰, 许浩, 周志, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区页岩气成藏地质特征[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(8): 887-899.ZHANG J F, XU H, ZHOU Z, et al. Geological characteristics of shale gas reservoir in Yichang area, western Hubei[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(8): 887-899. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] ZHAO S, PU W F, VARFOLOMEEV M A, et al. Influence of water on thermo-oxidative behavior and kinetic triplets of shale oil during combustion[J]. Fuel, 2022, 318: 123690. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123690 [34] 李小勇, 叶义成, 聂邦亮, 等. 宜昌市城区一带地下热水资源成因类型及成矿模式浅析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2020, 34(1): 87-91.LI X Y, YE Y C, NIE B L, et al. Genetic types and metallogenic models of geothermal water resources in Yichang City[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2020, 34(1): 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 楼章华, 朱蓉. 中国南方海相地层水文地质地球化学特征与油气保存条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(5): 584-593. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.05.002LOU Z H, ZHU R. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon preservation conditions in marine strata in southern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(5): 584-593. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.05.002 [36] 张婉婷. 鄂西黄陵断穹北部区域岩溶水系统特征及隧道工程适宜性探析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.ZHANG W T. Karst water system analysis and its suitability with the tunnel engineering in the north of Huangling faulted dome[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 王玉芳, 翟刚毅, 胡志方, 等. 湖北宜昌震旦系陡山沱组储层特征及复杂体积压裂效果评价[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(4): 1447-1459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.021WANG Y F, ZHAI G Y, HU Z F, et al. Reservoir characteristics of the Sinian Doushantuo Formation and the effectevaluation of complex fracturing in Yichang, Hubei Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(4): 1447-1459. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.021 [38] 翟刚毅, 包书景, 王玉芳, 等. 古隆起边缘成藏模式与湖北宜昌页岩气重大发现[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4): 441-447.ZHAI G Y, BAO S J, WANG Y F, et al. Reservoir accumulation model at the edge of palaeohigh and significant discovery of shale gas in Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 441-447. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] CHEN Q, KANG Y L, YOU L J, et al. Change in composition and pore structure of Longmaxi black shale during oxidative dissolution[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 172: 95-111. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.01.011 [40] LIU D Q, YI M L, YANG S, et al. Performance and mechanism of the pyrite-kerogen complexes oxidation with H2O2 at low temperature during shale stimulation: An experimental and modeling study[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2022, 143: 105382. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105382 [41] XU P, SHENG M, LIN T Y, et al. Influences of rock microstructure on acid dissolution at a dolomite surface[J]. Geothermics, 2022, 100: 102324. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102324 [42] YANG S, LIU D Q, LI Y L, et al. Experimental study on the oxidative dissolution of carbonate-rich shale and silicate-rich shale with H2O2, Na2S2O8 and NaClO: Implication to the shale gas recovery with oxidation stimulation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 76: 103207. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103207 [43] 赵进英. 零价铁/过硫酸钠体系产生硫酸根自由基氧化降解氯酚的研究[D]. 辽宁大连: 大连理工大学, 2010.ZHAO J Y. Sulfate radical-based oxidation of chlorophenols using zero-valent iron/sodium peroxydisulfate system[D]. Dalian Liaoning: Dalian University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] ROSS G J. Acid dissolution of chlorites: Release of magnesium, iron and aluminum and mode of acid attack[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1969, 17(6): 347-354. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1969.0170604 [45] KHALFAOUI A, KACIM S, HAJJAJI M. Sintering mechanism and ceramic phases of an illitic-chloritic raw clay[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(1/2): 161-167. [46] KNAUSS K G, WOLERY T J. Dependence of albite dissolution kinetics on pH and time at 25 ℃ and 70 ℃[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(11): 2481-2497. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90031-1 [47] 信云霞, 张帆, 贾学五, 等. 过氧化氢催化分解研究进展[J]. 石化技术, 2017, 24(6): 50-51.XIN Y X, ZHANG F, JIA X W, et al. Research progress of catalysts used for hydrogen peroxide decomposition[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2017, 24(6): 50-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) [48] 蒋慧灵, 臧娜, 钱新明, 等. 过硫酸钠和过硫酸钾的热稳定性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2006, 57(12): 2798-2800. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2006.12.002JIANG H L, ZANG N, QIAN X M, et al. Thermal stability of potassium supersulphate and sodium supersulphate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2006, 57(12): 2798-2800. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2006.12.002 [49] 陆绍信, 王廷芬. 不同氧化剂对黄县油页岩氧化的影响[J]. 华东石油学院学报(自然科学版), 1987, 11(1): 78-85.LU S X, WANG T F. Effect of different oxidants on the oxidation of Huangxian oil shale[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(East China)(Edition of Natural Science), 1987, 11(1): 78-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] ILTON E S, EUGSTER H P. Base metal exchange between magnetite and a chloride-rich hydrothermal fluid[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(2): 291-301. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90381-5 [51] LI Y L, YANG S, LIU D Q, et al. Experimental study of shale-fluids interaction during oxidative dissolution with hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite and sodium persulfate[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 113: 104503. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104503 [52] ZHU X X, LI J F, XIE B, et al. Accelerating effects of biochar for pyrite-catalyzed Fenton-like oxidation of herbicide 2, 4-D[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 391: 123605. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123605 [53] WANG C Q, SUN R R, HUANG R, et al. A novel strategy for enhancing heterogeneous Fenton degradation of dye wastewater using natural pyrite: Kinetics and mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 272: 129883. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129883 [54] CHEN S H, XIONG P, ZHAN W, et al. Degradation of ethylthionocarbamate by pyrite-activated persulfate[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 122: 38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.03.022 [55] DU M M, KUANG H N, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Enhancement of ball-milling on pyrite/zero-valent iron for persulfate activation on imidacloprid removal in aqueous solution: A mechanistic study[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(4): 105647. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105647 [56] LIANG X Y, SHENG J J. Comparison of chemical-induced fracturing by Na2S2O8, NaClO, and H2O2 in Marcellus shale[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(12): 15905-15919. [57] LIANG C J, GUO Y Y, CHIEN Y C, et al. Oxidative degradation of MTBE by pyrite-activated persulfate: Proposed reaction pathways[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(18): 8858-8864. [58] ZHANG Y Q, TRAN H P, DU X D, et al. Efficient pyrite activating persulfate process for degradation of p-chloroaniline in aqueous systems: A mechanistic study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 308: 1112-1119. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.104 [59] DO S H, KWON Y J, KONG S H. Effect of metal oxides on the reactivity of persulfate/Fe(Ⅱ)in the remediation of diesel-contaminated soil and sand[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182(1/2/3): 933-936. [60] PENG H, SHANG Q, CHEN R H, et al. Highly efficient oxidative-alkaline-leaching process of vanadium-chromium reducing residue and parameters optimization by response surface methodology[J]. Environmental Technology, 2022, 43(14): 2167-2176. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1869317 [61] PENG H, GUO J, LIU Z H, et al. Direct advanced oxidation process for chromium(Ⅲ)with sulfate free radicals[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2018, 1(1): 14. [62] NAVIAUX J D, SUBHAS A V, ROLLINS N E, et al. Temperature dependence of calcite dissolution kinetics in seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 246: 363-384. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.11.037 [63] SJÖBERG E L, RICKARD D T. Temperature dependence of calcite dissolution kinetics between 1 and 62 ℃ at pH 2.7 to 8.4 in aqueous solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(3): 485-493. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90276-X [64] 杜佰松, 朱光有, 刘舒飞, 等. 浅析影响方解石生长和溶解的动力学因素及机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 335-351.DU B S, ZHU G Y, LIU S F, et al. Key factors and mechanisms affecting calcite growth and dissolution: A critical review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4): 335-351. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: