A methodology for determining the optimal well spacing in sandstone geothermal reservoirs through production-reinjection equilibrium simulation
-
摘要:
为实现地热能可持续开发利用的目标, 需要明确不同采灌条件下合理的采灌井间距。为此, 以鲁北馆陶组热储为研究对象, 建立了层状热储开发的概念模型及数学模型, 采用COMSOL Multiphysics多场耦合模拟软件建立了地热对井采灌井距计算器。通过参数拟合及模拟结果对比, 验证了模型的准确性; 进而以软件APP编译功能为基础, 以普通用户使用为导向, 简化相关参数输入, 建立了地热采灌井距计算APP。为适应实际生产需求, 计算了不同采灌量条件下对应的合理采灌井距。计算结果表明: 鲁北地区馆陶组热储采灌量分别为40, 60, 80, 100 m3/h时, 不发生热突破的合理采灌井距分别为290, 330, 360, 390 m。研究表明: (1)在鲁北层状传导型砂岩热储地区, 对概念模型进行简化处理后, 数值模拟计算结果可靠, 可以在该地区建立合理采灌井距计算APP; (2)水热数值模拟是合理采灌井距计算的有力手段, 能够确定开采量、回灌量、回灌温度、采灌井距等地热开发利用工程的关键参数, 有利于实现地热资源可持续开发利用。
Abstract:Objective In order to accomplish the objective of sustainable development and utilization of geothermal energy, it is imperative to elucidate the optimal production-reinjection well spacing considering varying quantities and temperatures of reinjection.
Methods The thermal reservoir of the Guantao Formation in northern Shandong Province is selected as the research subject, and a conceptual model and mathematical model for layered thermal reservoir development are established. COMSOL Multiphysics multifield coupling simulation software is employed to develop a geothermal production-reinjection well spacing calculator. The accuracy of the model is validated through parameter fitting and simulation results.
Results Based on the software APP development function, which is guided by the input of ordinary users, the relevant parameter input was simplified for ease of use, leading to the establishment of an application for calculating geothermal production-reinjection well spacing. In contrast to previous studies that solely focused on production-reinjection well spacing, this study calculates optimal spacings under various conditions to meet real-world operational needs. The results indicate that the optimal production-reinjection well spacings, without experiencing thermal breakthrough are 290, 330, 360 m and 390 m at flow rates of 40, 60, 80 and 100 m3/h respectively.
Conclusion In the layered conductive sandstone thermal reservoir area of northern Shandong, a reliable geothermal production-reinjection well-spacing calculator was developed through simplification of the conceptual model and credible numerical simulation results. Hydrothermal numerical simulation serves as a robust approach to determine rational production-reinjection well spacings, which are crucial parameters for geothermal development and utilization projects including exploitation quantity, recharge quantity, injection temperature, and production-reinjection well spacing. These determinations contribute to the sustainable development and utilization of geothermal resources.
-
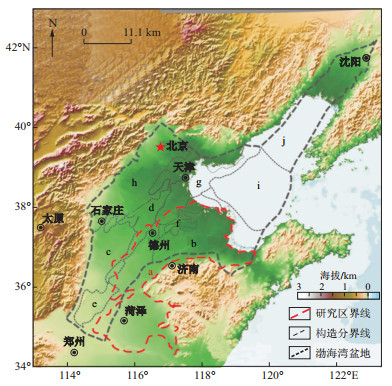
图 1 鲁北地质构造图(据文献[15]修改)
a.鲁西北平原; b.济阳坳陷; c.临清坳陷; d.沧县隆起; e.内黄凸起; f.埕宁凸起; g.黄骅坳陷; h.冀中坳陷; i.渤中坳陷; j.辽河坳陷
Figure 1. Geological structure map of northern Shandong
表 1 德州市水文家园回灌井地层层序
Table 1. Stratigraphic sequence of reinjection well at the hydrological site in Dezhou
地层 深度/m 厚度/m 岩性 第四系(Q) 0 260 黏土、粉砂岩、中细砂岩 新近系 明化镇组(N2m) 260 890 泥岩、中细砂岩 馆陶组(N1g) 上段 1 150 169 泥岩与细砂岩互层 下段 1 319 217 砂砾岩 古近系 东营组(E3d) 1 536(未揭穿) 8.5 泥岩 表 2 模型参数取值列表
Table 2. List of model parameter values
参数 取值 描述 参数 取值 描述 din/mm 177.8 回灌井井径 Qin/(m3·h-1) 60 回灌量 dpro/mm 177.8 开采井井径 Qout/(m3·h-1) 60 开采量 L/m 180 采灌井间距 Hm/m -80 水位标高 qc/(W·m-2) 0.062 9 大地热流密度 cp/(J·kg-1·K-1) 909 热储层比热容 htop/m 1 319 储层顶板埋深 kc/(W·m-1·K-1) 2.1 储层热导率 H/m 217 热储层厚度 ρden/(kg·m-3) 2 000 热储层密度 Kk/10-3 μm2 1 000 储层渗透率 Th/℃ 35 回灌尾水温度 kr 0.22 孔隙率 Tout/℃ 54.4 井口温度 t/a 100 计算时长 t1/Ms 1 输出时间间隔 -
[1] 康凤新, 赵季初, 黄迅, 等. 华北盆地梁村古潜山岩溶热储聚热机制及资源潜力[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(3): 1080-1092.KANG F X, ZHAO J C, HUANG X, et al. Heat accumulation mechanism and resources potential of the karst geothermal reservoir in Liangcun buried uplift of Linqing Depression[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(3): 1080-1092. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 窦斌, 肖鹏, 郑君, 等. 二氧化碳爆破致裂激发干热岩储层作用效果[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 150-159. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0194DOU B, XIAO P, ZHENG J, et al. Effect of stimulation in hot dry rock reservoirs from carbon dioxide blasting-induced cracking[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 150-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0194 [3] KANG F X, ZHAO J C, TAN Z R, et al. Geothermal power generation potential in the eastern Linqing Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2021, 95(6): 1870-1881. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14877 [4] KANG F X. Sustainable development of geothermal resources in China[C]//Anon. Proceedings world geothermal congress. Bali, Indonesia: [s. n.], 2010. [5] ZHENG X, SI G, XIA B. The sustainable development of geothermal resources in China[J]. Transactions - Geothermal Resources Council, 2005, 29: 321-323. [6] 杨询昌, 康凤新, 王学鹏, 等. 砂岩孔隙热储地温场水化学场特征及地热水富集机理: 鲁北馆陶组热储典型案例[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(3): 738-750.YANG X C, KANG F X, WANG X P, et al. Hydrochemical features of geothermal reservoir geotemperature field in sandstone porosity and enrichment mechanism of geothermal water: A case study of geothermal reservoir of Guantao Formation in the Lubei[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(3): 738-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 吴立进, 赵季初, 李艾银, 等. 鲁北坳陷区地热资源开发利用关键性问题研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(2): 300-306.WU L J, ZHAO J C, LI A Y, et al. Key issues of geothermal resource exploitation and utilization in the depression area of northern Shandong Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(2): 300-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 党书生, 马致远, 郑磊. 咸阳地区地热采灌井最佳井距分析[J]. 地下水, 2016, 38(1): 56-58.DANG S S, MA Z Y, ZHENG L. An optimization of the distance between geothermal fluid in Xiangyang area[J]. Ground Water, 2016, 38(1): 56-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 刘帅, 冯守涛, 刘志涛, 等. 层状热储地热井权益保护半径计算探讨[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(3): 104-108.LIU S, FENG S T, LIU Z T, et al. Discussion on the calculation of the rights protection radius of the geothermal well for stratified thermal reservoir[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(3): 104-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 朱家玲, 朱晓明, 雷海燕. 地热回灌井间压差补偿对回灌效率影响的分析[J]. 太阳能学报, 2012, 33(1): 56-62.ZHU J L, ZHU X M, LEI H Y. Analysis of impact of pressure compensation between geothermal wells on reinjection effeciency[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 段忠丰, 李福来, 巩亮, 等. 基于水热耦合模拟的油气区地热开发井网布局[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(10): 156-162.DUAN Z F, LI F L, GONG L, et al. Geo-thermal development well spacing patterns based on hydrothermal coupled modeling in oil-gas bearing areas[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(10): 156-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] XU T F, ZHAO Y A, ZHAO J C, et al. Heat extraction performance and optimization for a doublet-well geothermal system in Dezhou, China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2022, 40(2): 619-638. [13] 刘帅, 刘志涛, 冯守涛, 等. 采暖尾水回灌对砂岩热储地温场的影响: 以鲁北地区为例[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(5): 1507-1520.LIU S, LIU Z T, FENG S T, et al. Effect of heating tail water recharge on geothermal field of sandstone heat storage: A case study in northern Shandong Province[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(5): 1507-1520. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 陈墨香. 华北地热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1988.CHEN M X. Geothermal resources in North China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1988. (in Chinese) [15] 邱楠生, 许威, 左银辉, 等. 渤海湾盆地中-新生代岩石圈热结构与热-流变学演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 13-26.QIU N S, XU W, ZUO Y H, et al. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic thermal structure and thermal-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 13-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 宋晨, 杨兵, 张超谟, 等. 渤中19-6孔店组砂砾岩孔隙结构和渗透率估算模型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 274-285. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0093SONG C, YANG B, ZHANG C M, et al. Investigation of pore structure and permeability estimation models of Kongdian Formation glutenites in the Bozhong 19-6 gasfield[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 274-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0093 [17] 冯守涛, 王成明, 杨亚宾, 等. 砂岩热储回灌对储层影响评价: 以鲁西北坳陷地热区为例[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊1): 158-167.FENG S T, WANG C M, YANG Y B, et al. Inpact assessment of reinjection on sand stong geothermal reservoir: A case study of Northwest Shandong Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(S1): 158-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 秦耀军, 张平平. 山东省砂岩热储地热资源开发利用模式探讨[J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(10): 93-98.QIN Y J, ZHANG P P. Development and utilization of geothermal resources in the middle and deep layers of Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2018, 34(10): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 何丽娟. 沉积盆地地热学[M]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学出版社, 2019.QIU N S, HU S B, HE L J. Geothermics in sedimentary basins[M]. Qingdao Shandong: China University of Petroleum Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [20] 陈宗元, 祖甘霖, 牛智伟, 等. COMSOL Multiphysics在物理化学教学中的应用[J]. 大学化学, 2023, 38(5): 308-314.CHEN Z Y, ZU G L, NIU Z W, et al. Application of COMSOL Multiphysics in the teaching of physical chemistry[J]. University Chemistry, 2023, 38(5): 308-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 钟家伦. 空心通道与多孔介质圆管通道传热的理论分析和数值模拟[D]. 上海: 上海工程技术大学, 2017.ZHONG J L. Analytical and numerical analysis of heat transfer in hollow channeland circular channel filled with porous medium[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Engineering Science, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 朱喜, 张庆莲, 刘彦广. 基于热储法的鲁西平原地热资源评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4): 172-177.ZHU X, ZHANG Q L, LIU Y G. Evaluation of the geothermal resources in the plain of west Shandong Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4): 172-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 张保建. 鲁西北地区地下热水的水文地球化学特征及形成条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.ZHANG B J. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation conditions of the geothermal water in northwestern Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] KANG F X, JIN M G, QIN P R. Sustainable yield of a karst aquifer system: A case study of Jinan springs in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2011, 19(4): 851-863. [25] 康凤新, 隋海波, 郑婷婷. 山前岩溶热储聚热与富水机理: 以济南北岩溶热储为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5): 1606-1624.KANG F X, SUI H B, ZHENG T T. Heat accumulation and water enrichment mechanism of piedmont karstic geothermal reservoirs: A case study of northern Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(5): 1606-1624. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 施亦做, 王社教, 肖红平, 等. 基于三维地质建模的松辽盆地北部地温场模拟[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(4): 46-53.SHI Y Z, WANG S J, XIAO H P, et al. 3D GeoModeller-based simulation of the geothermal field in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(4): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 郑小康, 杨志兵. 岩溶含水层饱和-非饱和流动与污染物运移数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 357-366. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211ZHENG X K, YANG Z B. Numerical simulation of saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and contaminant transport in a karst aquifer[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 357-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211 [28] 高志豪, 赵锐锐, 成建梅. 砂岩含水层CO2封存中考虑盐沉淀反馈作用的数值模拟: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073GAO Z H, ZHAO R R, CHENG J M. Numerical simulation of CO2 sequestration in sandstone aquifers with feedback effect of salt precipitation: A case study of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073 -





 下载:
下载: