-
摘要:
通过解读蕴含在地球物理测井资料中的地质信息,可拓展测井曲线在地质学领域的应用范围。对几个测井资料在地质领域应用的经典案例进行了解析,以期更好地为油气勘探开发提供指导。案例解析表明:测井资料通过拾取单井构造产状及其组合特征变化,能用于指导侧钻井部署工作。测井资料还能运用至古水流方向拾取及双向物源供给识别工作中,并与地质认识相互佐证从而得到科学精细的解释结果。作为地质学家的“眼睛”,测井资料在识别与评价孔隙、洞穴和裂缝方面具明显优势,测井资料可用于油气层发现以及储量参数连续、精确计算。测井曲线中泥岩电阻率和声波时差与地应力耦合关系可间接用于超深层储层品质和油气产能预测。将地质、测井与地震资料结合,可用于油气圈闭刻画,并指导油气勘探开发工作。以上典型案例解析有助于地质人员更好地解读蕴含在测井曲线中的地质信息,并拓展地球物理测井资料应用领域与范围。
Abstract:Objective To better interpret the geological information contained in geophysical logging data and expand the application scope of well logs in geology,
Methods several typical cases of representative logging data are analyzed. This analysis seeks to enhance the use of well logs in geological research. Logging data can aid in the deployment of sidetracking wells by identifying tectonic occurrences and variations in their combination characteristics. Image log data also enable determintion of palaeocurrent directions and the identification of bidirectional provenance supply, thus providing refined and scientifically calibrated interpretations in alignment with geological understanding.
Results Logging data, often regarded as the "eyes" of geologists, are advantageous for identifying and evaluating pores, caves, fractures, and other subsurface features. These data are crucial for discovering hydrocarbon reservoirs and facilitating the fine and continuous calculation of reserve parameters. The coupling relationships between mudstone resistivity, acoustic interval transit time, and in situ stress in logging curves can also be used to indirectly predict the quality of ultradeep reservoirs and hydrocarbon productivity. Moreover, combining geology, logging, and seismic activity allows for the delineation of hydrocarbon traps and supports oil and gas exploration and production.
Conclusion The analysis of these typical cases assists geologists in better interpreting the geological information in logging curves and further broadens the application field and scope of geophysical logging data.
-
Key words:
- geophysical well logs /
- geological application /
- typical case /
- well logging geology
-
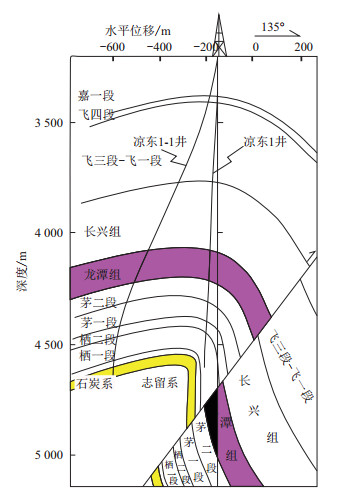
图 1 四川盆地东部凉东1井、凉东1-1井井旁构造剖面图[26]
Figure 1. Structures in the vicinity of boreholes around the Wells Liangdong 1 and Liangdong 1-1 in the eastern Sichuan Basin
图 3 诱导缝及其地应力测井判别(DN201井)
CAL.井径;AC.声波时差;CNL.补偿中子;DEN.体积密度;M2R1, M2R2, M2R3, M2R6, M2R9, M2RX.纵向分辨率为2 ft(1 ft=0.304 8 m),探测深度分别为10,20,30,60,90,120 in(1 in=2.54 cm)时的Baker Atlas公司测井系列高分辨率阵列感应测井电阻率;LLD.深侧向测井;LLS.浅侧向测井;RMSL.微球聚焦电阻率测井,下同
Figure 3. Induced fracture and related in situ stress determination using well logs(Well DN201)
-
[1] 刘光鼎, 李庆谋, 刘少华. 全球变化的地球物理测井研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1999, 14(4): 1-8.LIU G D, LI Q M, LIU S H. Geophysical well log in global change[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1999, 14(4): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] IQBAL O, AHMAD M, KADIR A A. Effective evaluation of shale gas reservoirs by means of an integrated approach to petrophysics and geomechanics for the optimization of hydraulic fracturing: A case study of the Permian Roseneath and Murteree shale gas reservoirs, Cooper Basin, Australia[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 58: 34-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.07.017 [3] 李宁, 徐彬森, 武宏亮, 等. 人工智能在测井地层评价中的应用现状及前景[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(4): 508-522.LI N, XU B S, WU H L, et al. Application statusand prospects of artificial intelligence in well logging and formation evaluation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 508-522. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] AMOSU A, IMSALEM M, SUN Y F. Effective machine learning identification of TOC-rich zones in the Eagle Ford Shale[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2021, 188: 104311. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104311 [5] 赖锦, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 测井地质学前世、今生与未来: 写在《测井地质学·第二版》出版之时[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828.LAI J, WANG G W, PANG X J, et al. The past, present and future of well logging geology: To celebrate the publication of second edition of "Well Logging Geology"[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 李红斌, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组页岩工程品质测井评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692LI H B, WANG G W, PANG X J, et al. Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of the Paleogene Funing Formation oil shales in the Subei Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692 [7] PASSEY Q R, CREANEY S, KULLA J B, et al. A practical model for organic richness from porosity and resistivity logs[J]. AAPG Bulletin 1990, 74: 1777-1794. [8] 欧阳健. 加强岩石物理研究提高油气勘探效益[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2001, 28(2): 1-5.OUYANG J. Strengthening petrophysical study to raise exploration benefit[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(2): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] CLARKSON C R, JENSEN J L, CHIPPERFIELD S. Unconventional gas reservoir evaluation: What do we have to consider?[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2012, 8: 9-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2012.01.001 [10] 王贵文, 邓清平, 唐为清. 测井曲线谱分析方法及其在沉积旋回研究中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(1): 93-95.WANG G W, DENG Q P, TANG W Q. The application of spectral analysis of logs in depositional cycle studies[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(1): 93-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 李国欣, 刘国强, 赵培华. 中国石油天然气股份有限公司测井技术的定位、需求与发展[J]. 测井技术, 2004, 28(1): 1-6.LI G X, LIU G Q, ZHAO P H. On orientation, requirements and development for log evaluation technology of PetroChina[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2004, 28(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] AVANZINI A, BALOSSINO P, BRIGNOLI M, et al. Lithologic and geomechanical facies classification for sweet spot identification in gas shale reservoir[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(3): 21-31. [13] YARMOHAMMADI S, KADKHODAIE A, HOSSEINZADEH S. An integrated approach for heterogeneity analysis of carbonate reservoirs by using image log based porosity distributions, NMR T2 curves, velocity deviation log and petrographic studies: A case study from the South Pars gas field, Persian Gulf Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 192: 107283. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107283 [14] 刘宏坤, 艾勇, 王贵文, 等. 深层、超深层致密砂岩储层成岩相测井定量评价: 以库车坳陷博孜-大北地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 299-310. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0256LIU H K, AI Y, WANG G W, et al. Quantitative well logging evaluation of diagenetic facies of deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Bozi-Dabei area in Kuqa Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 299-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0256 [15] LAI J, WANG G W, FAN Q X, et al. Toward the scientific interpretation of geophysical well logs: Typical misunderstandings and countermeasures[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2023, 44(2): 463-494. doi: 10.1007/s10712-022-09746-9 [16] 赖锦, 庞小娇, 赵鑫, 等. 测井地质学研究中的典型误区与科学思维[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(7): 31-44.LAI J, PANG X J, ZHAO X, et al. Typical misunderstandings and scientific ideas in well logging geology research[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(7): 31-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 赖锦, 肖露, 赵鑫, 等. 深层-超深层优质碎屑岩储层成因与测井评价方法: 以库车坳陷白垩系巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(4): 612-625.LAI J, XIAO L, ZHAO X, et al. Genesis and logging evaluation of deep to ultra-deep high-quality clastic reservoirs: A case study of the Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(4): 612-625. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 王立新, 唐明远, 李浩, 等. 基于测井曲线分析的沉积事件精准识别[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(11): 50-57.WANG L X, TANG M Y, LI H, et al. Precise identification of sedimentary events based on logging curve analysis[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(11): 50-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 李浩, 刘双莲, 柴公权, 等. 基于岩石成因的测井地质属性研究方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(2): 707-712.LI H, LIU S L, CHAI G Q, et al. Method about the geological attribution research of well logging based on lithogenesis[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(2): 707-712. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 李浩, 刘双莲, 魏修平, 等. 隐性测井地质信息的识别方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(1): 195-202.LI H, LIU S L, WEI X P, et al. Method exploration of implicit logging geological information research[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(1): 195-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 徐风, 司兆伟, 白松涛, 等. 基于测井地质"四性" 关系谱的储层评价方法[J]. 测井技术, 2017, 41(2): 183-188.XU F, SI Z W, BAI S T, et al. Reservoir evaluation based on four characters spectrum of geological logging[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2017, 41(2): 183-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] RADWAN A E, TRIPPETTA F, KASSEM A A, et al. Multi-scale characterization of unconventional tight carbonate reservoir: Insights from October oil filed, Gulf of Suez Rift Basin, Egypt[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 197: 107968. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107968 [23] 王华, 张雨顺. 测井资料人工智能处理解释的现状及展望[J]. 测井技术, 2021, 45(4): 345-356.WANG H, ZHANG Y S. Research status and prospect of artificial intelligence in logging data processing and interpretation[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2021, 45(4): 345-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 曾文冲. 关于我国测井技术发展的几点意见[J]. 测井技术, 2002, 26(1): 1-5.ZENG W C. On China's logging technology developments[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2002, 26(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] MUKHAMETDINOVA A, HABINA-SKRZYNIARZ I, KAZAK A, et al. NMR relaxometry interpretation of source rock liquid saturation: A holistic approach[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 132: 105165. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105165 [26] 苏明军, 卫平生, 陈启林. 测井资料在石油地震地质学中的作用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(3): 112-117.SU M J, WEI P S, CHEN Q L. Application of well logging data in petroleum seismogeology[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(3): 112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] LAI J, WANG G W, WANG S, et al. A review on the applications of image logs in structural analysis and sedimentary characterization[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 95: 139-166. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.04.020 [28] 赖锦, 肖露, 白天宇, 等. 成像测井解释评价方法及其地质应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 323-340. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220701LAI J, XIAO L, BAI T Y, et al. Interpretation and evaluation methods of image logs and their geological applications[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 323-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220701 [29] 闫建平, 蔡进功, 赵铭海, 等. 电成像测井在砂砾岩体沉积特征研究中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(4): 444-451.YAN J P, CAI J G, ZHAO M H, et al. Application of electrical image logging in the study of sedimentary characteristics of sandy conglomerates[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(4): 444-451. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 杨玉卿, 崔维平, 王猛. 成像测井沉积学研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(3): 7-18.YANG Y Q, CUI W P, WANG M. A review on the research progress and development trend of imaging logging sedimentology[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(3): 7-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 张荣虎, 王俊鹏, 马玉杰, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷深层沉积微相古地貌及其对天然气富集的控制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(4): 667-678.ZHANG R H, WANG J P, MA Y J, et al. The sedimentary microfacies, palaeogeomorphology and their controls on gas accumulation of deep-buried Cretaceous in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(4): 667-678. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 赖锦, 韩能润, 贾云武, 等. 基于测井资料的辫状河三角洲沉积储层精细描述[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(2): 304-318.LAI J, HAN N R, JIA Y W, et al. Detailed description of the sedimentary reservoir of a braided delta based on well logs[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(2): 304-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 曾庆鲁, 莫涛, 赵继龙, 等. 7 000 m以深优质砂岩储层的特征、成因机制及油气勘探意义: 以库车坳陷下白垩统巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 38-47.ZENG Q L, MO T, ZHAO J L, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism and oil & gas exploration significance of high-quality sandstone reservoirs deeper than 7 000 m: A case study of the Bashijiqike Formation of Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 王珂, 张荣虎, 曾庆鲁, 等. 库车坳陷博孜-大北地区下白垩统深层-超深层储层特征及成因机制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(2): 311-328.WANG K, ZHANG R H, ZENG Q L, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of Lower Cretaceous deep and ultra-deep reservoir in Bozi-Dabei area, Kuqa Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(2): 311-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 杨学文, 王清华, 李勇, 等. 库车前陆冲断带博孜-大北万亿方大气区的形成机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(6): 175-187.YANG X W, WANG Q H, LI Y, et al. Formation mechanism of the Bozi-Dabei trillion cubic natural gas field, Kuqa foreland thrust belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(6): 175-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] 史彪, 吴丰, 李树新, 等. 海陆过渡相优质页岩测井识别: 以鄂尔多斯盆地大宁-吉县地区山2段为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 115-126.SHI B, WU F, LI S X, et al. Logging identification of high-quality shale of the marine-continent transitional facies: An example of the Shan 2 Member of the Daning-Jixian area in the Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 115-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 张尚华, 司马立强, 颜其彬, 等. 复杂碳酸盐岩储层测井有效性评价[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(2): 84-88.ZHANG S H, SIMA L Q, YAN Q B, et al. The logging effectiveness evaluation of complex carbonate reservoirs[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2011, 33(2): 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 谭廷栋. 测井解释发现油气层[J]. 天然气工业, 2000, 20(6): 47-50.TAN T D. Oil and gas reservoirs discovered by log interpretation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2000, 20(6): 47-50. (in Chinese with Englishabstract) [39] WOOD D A. Predicting porosity, permeability and water saturation applying an optimized nearest-neighbour, machine-learning and data-mining network of well-log data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 184: 106587. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106587 [40] 吴丰, 罗莹莹, 李昱翰, 等. 四川盆地公山庙油田大安寨段湖相灰岩-页岩裂缝特征与测井识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 55-67.WU F, LUO Y Y, LI Y H, et al. Fracture characteristics and logging identification of lacustrine limestone-shale reservoirs in Da'anzhai Member, Gongshanmiao oilfield, Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 55-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] 谭廷栋. 测井解释发现油气层的典型案例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1997, 32(1): 16-25.TAN T D. Typical example of hydrocarbon reservoir discovery by logging data interpretation[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1997, 32(1): 16-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] 李国欣, 欧阳健, 周灿灿, 等. 中国石油低阻油层岩石物理研究与测井识别评价技术进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2006, 11(2): 43-50.LI G X, OUYANG J, ZHOU C C, et al. Advancement of petrophysics research and well-logging recognition and evaluation for low-resistivity oil-layer by PetroChina[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2006, 11(2): 43-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [43] LAI J, LI D, WANG G W, et al. Earth stress and reservoir quality evaluation in high and steep structure: The Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.036 [44] 李宁, 闫伟林, 武宏亮, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油测井评价技术现状、问题及对策[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(3): 117-128.LI N, YAN W L, WU H L, et al. Current situation, problems and countermeasures of the well-logging evaluation technology for Gulong shale oil[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(3): 117-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 刘国强. 非常规油气勘探测井评价技术的挑战与对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(5): 891-902.LIU G Q. Challenges and countermeasures of log evaluation in unconventional petroleum exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(5): 891-902. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] 杨小兵, 姚梦麟, 王思静, 等. 页岩气测井地质工程技术新需求及解决方案[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(2): 20-27.YANG X B, YAO M L, WANG S J, et al. Shale gas logging, geology and engineering technologies: New requirements and solutions[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(2): 20-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] LAI J, WANG G W, FAN Q X, et al. Geophysical well-log evaluation in the era of unconventional hydrocarbon resources: A review on current status and prospects[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2022, 43(3): 913-957. doi: 10.1007/s10712-022-09705-4 [48] 赵军, 张莉, 王贵文, 等. 一种基于测井信息的山前挤压构造区地应力分析新方法[J]. 地质科学, 2005, 40(2): 284-290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.02.012ZHAO J, ZHANG L, WANG G W, et al. A new method for analyzing crustal stress in foreland structural comprssive area based on logging data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology(Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2005, 40(2): 284-290. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.02.012 [49] 赵继勇, 周新桂, 雷启鸿, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地马岭油田长7致密储层古今构造应力研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2017, 23(6): 810-820.ZHAO J Y, ZHOU X G, LEI Q H, et al. Study on paleo-tectonic and present tectonic stress in Chang 7 tight reservoir of Maling oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(6): 810-820. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] 赖锦, 白天宇, 肖露, 等. 地应力测井评价方法及其地质与工程意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 1033-1043.LAI J, BAI T Y, XIAO L, et al. Well-logging evaluation of in situ stress fields and its geological and engineering significances[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 1033-1043. (in Chinese with English abstract) [51] 李军, 王贵文, 欧阳健. 利用测井信息定量研究库车坳陷山前地区地应力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2001, 28(5): 93-95.LI J, WANG G W, OUYANG J. Using logging data to quantitatively study terrestrial-stress of Kuqa field[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(5): 93-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) [52] 曾联波, 王贵文. 塔里木盆地库车山前构造带地应力分布特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(3): 59-60.ZENG L B, WANG G W. Distribution of earth stress in Kuche thrust belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(3): 59-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) [53] LAI J, WANG G W, CHAI Y, et al. Deep burial diagenesis and reservoir quality evolution of high-temperature, high-pressure sandstones: Examples from Lower Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Keshen area, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin of China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(6): 829-862. doi: 10.1306/08231614008 [54] 赖锦, 李红斌, 张梅, 等. 非常规油气时代测井地质学研究进展[J]. 古地理学报, 2023, 25(5): 1118-1138.LAI J, LI H B, ZHANG M, et al. Advances in well logging geology in the era of unconventional hydrocarbon resources[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2023, 25(5): 1118-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract) [55] 韩登林, 李忠, 寿建峰. 背斜构造不同部位储集层物性差异: 以库车坳陷克拉2气田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(3): 282-286.HAN D L, LI Z, SHOU J F. Reservoir property difference between structural positions in the anticline: A case study from Kela-2 gas field in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(3): 282-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) [56] 王珂, 杨海军, 李勇, 等. 库车坳陷克深气田致密砂岩储层构造裂缝形成序列与分布规律[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(1): 30-46.WANG K, YANG H J, LI Y, et al. Formation sequence and distribution of structural fractures in compact sandstone reservoir of Keshen gas field in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(1): 30-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) [57] 徐珂, 田军, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷超深层现今地应力对储层品质的影响及实践应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(1): 13-23.XU K, TIAN J, YANG H J, et al. Effects and practical applications of present-day in situ stress on reservoir quality in ultra-deep layers of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(1): 13-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) [58] 司马立强, 郑淑芬, 吴胜. 测井地震结合储层参数推广反演技术及应用[J]. 测井技术, 2001, 25(1): 12-15.SIMA L Q, ZHENG S F, WU S. Inversion technique for reservoir parameters by combining logs with seismic data and its application[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2001, 25(1): 12-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) [59] 孔祥宇, 于继崇, 李树峰. 复杂断块老油田精细地层对比综合方法的提出与应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(1): 120-124.KONG X Y, YU J C, LI S F. Fine stratigraphic correlation method and its application in complicated fault-block oilfield[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(1): 120-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) [60] 梁晓宇, 高树芳, 高志成, 等. 井震结合精细刻画英东油田断块油藏构造[J]. 测井技术, 2015, 39(2): 232-235.LIANG X Y, GAO S F, GAO Z C, et al. Finely describing fault oil reservoir construction with logging and seismic date in Yingdong oilfield[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2015, 39(2): 232-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: