Influence of the sedimentary environment on the salt migration ability of ancient brine in the coastal plain of Laizhou Bay
-
摘要:
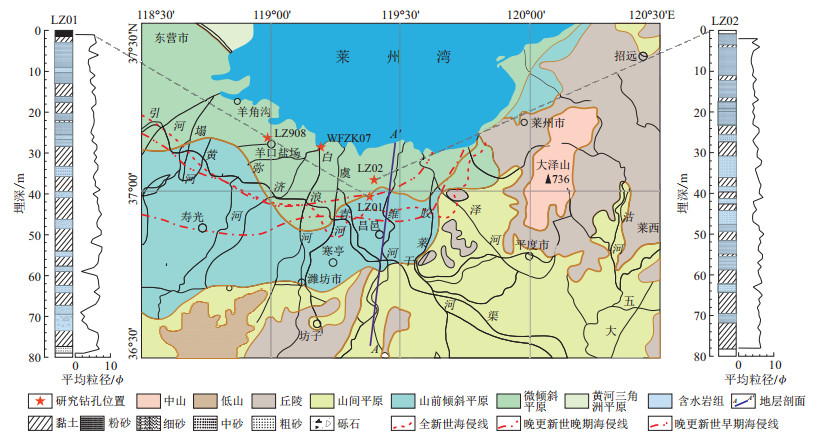
海岸带沉积环境是研究地下水演化与运移的基础。为探讨莱州湾南岸沉积环境对咸-淡地下水空间分布及迁移能力的影响,钻探采集了2个第四纪典型钻孔(LZ01和LZ02)样品,利用压榨法提取了孔隙水,测定了沉积物的粒度组成和孔隙水Cl-浓度。结果表明,2个钻孔均以细粒沉积物为主,平均粒径为5.5
ϕ 。根据沉积物岩性和粒度参数特征,得出LZ01与LZ02钻孔分别包含10、9个沉积相态交替,揭露了晚更新世以来的3套海相地层单元。孔隙水以卤(咸)水为主,Cl-浓度剖面形态呈现3个峰值,3个卤水层分别与3套海相地层对应,表明沉积物中残留海相古卤水,并向相邻沉积物中扩散。沉积物的水动力指数与Cl-浓度垂向变化率呈现明显的分区性;中等水动力条件下,孔隙水Cl-扩散迁移能力强。敏感粒径分析表明孔隙水迁移的优势粒径范围为45.61~111.47 μm。研究区古海侵事件控制了卤水的分布,而低渗透性及岩性组合对封存古卤水起着重要作用。研究结果可为莱州湾滨海平原卤水成因、地下水咸化及运移研究提供理论依据。Abstract:Objective The coastal sedimentary environment is fundamental to the comprehending the evolution and movement of groundwater. To investigate the impact of the distribution and mobility of brackish groundwater along the southern coast of Laizhou Bay,
Methods this study collected samples from two archetypal Quaternary boreholes (LZ01 and LZ02), extracted pore water using the mechanical squeezing technique, and measured the grain size composition of the sediments and the Cl- content of the pore water.
Results Both boreholes are dominated by fine-grained sediments with an average particle size of 5.5
ϕ . Based on the sediment lithology and grain size parameters, it was found that the LZ01 and LZ02 boreholes contained 10 and 9 alternating sedimentary facies, respectively, revealing three sets of marine stratigraphic units since the late Pleistocene. The porewater was found to be predominantly composed of brine (saline) water, with the Cl- profile displaying three peaks corresponding to the three sets of marine stratigraphic units. These results demonstrate the presence of residual ancient marine brine water in the sediment and its permeation into neighboring sediments. In this study, it was observed that the hydraulic index of sedimentary water exhibited a clear zonal pattern, with the vertical change rate of Cl- serving as a crucial indicator. Notably, under moderate hydraulic conditions, Cl- displayed a robust diffusion and migration capability in pore water, as confirmed by detailed particle size analysis. The dominant particle size range for pore water migration was 45.61-111.47 μm.Conclusion The paleo-marine transgression events in the study area controlled the distribution of brine, while low permeability and lithological combinations played a significant role in the preservation of ancient brine. The results of this study provide a theoretical basis for research on the origin of brine, groundwater salinization, and migration in the Laizhou Bay coastal plain.
-
图 2 莱州湾南A-A′(昌邑-青乡)地层剖面(据文献[10]修改)
Figure 2. A-A′(Changyi-Qingxiang) stratigraphic section in southern Laizhou Bay
图 4 LZ01(a)和LZ02(b)钻孔沉积物粒度参数特征及沉积相(岩性图例同图 1)
Figure 4. Grain size distribution parameters and sedimentary facies of boreholes LZ01(a) and LZ02(b)
图 6 钻孔沉积物孔隙水Cl-质量浓度及变化率(岩性图例同图 1)
Figure 6. Cl- concentration and variation rate of porewater borehole sediments
-
[1] 王焰新, 甘义群, 邓娅敏, 等. 海岸带海陆交互作用过程及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 1-10. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101WANG Y X, GAN Y Q, DENG Y M, et al. Land-ocean interactions and their eco-environmental effects in the coastal zone: Current progress and future perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101 [2] 韩有松, 孟广兰, 王少青. 渤海莱州湾滨海平原晚第四纪地质事件与古环境[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 1994(1): 87-96.HAN Y S, MENG G L, WANG S Q. The geological events and paleo-environment of the coastal plain of Laizhou Bay in Bohai Sea during Late Quaternary[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 1994(1): 87-96. (in Chinese) [3] 薛禹群, 吴吉春, 谢春红, 等. 莱州湾沿岸海水入侵与咸水入侵研究[J]. 科学通报, 1997, 42(22): 2360-2368.XUE Y Q, WU J C, XIE C H, et al. Study on sea water intrusion and salt water intrusion along the coast of Laizhou Bay[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(22): 2360-2368. (in Chinese) [4] 高茂生, 骆永明. 我国重点海岸带地下水资源问题与海水入侵防控[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(10): 1197-1203.GAO M S, LUO Y M. Change of groundwater resource and prevention and control of seawater intrusion in coastal zone[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(10): 1197-1203. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] HAN D M, KOHFAHL C, SONG X F, et al. Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(5): 863-883. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.007 [6] 陈鸿汉, 张永祥, 王新民, 等. 潍河下游地区海咸水入侵动态系统分析[J]. 地理科学, 1996, 16(3): 224-231.CHEN H H, ZHANG Y X, WANG X M, et al. Analysis of sea salt water intrusion dynamic system in the lower reaches of the Weihe River[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1996, 16(3): 224-231. (in Chinese) [7] 毕延凤, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 等. 莱州湾南岸平原地下水化学特征研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(3): 241-247.BI Y F, YU H J, XU X Y, et al. Study on the groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in the southern Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(3): 241-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 岳保静, 刘金庆, 刘健, 等. 渤海西缘YRD-1101孔晚更新世以来沉积物粒度特征及其环境变迁[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(3): 853-867.YUE B J, LIU J Q, LIU J, et al. Grain size distribution of sediment of core YRD-1101 in the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since the Latest Pleistocene and its environmental change[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(3): 853-867. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] YI L, YU H J, ORTIZ J D, et al. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the South Bohai Sea, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 329: 101-117. [10] 杨巧凤, 王瑞久, 徐素宁, 等. 莱州湾南岸卤水的稳定同位素与地球化学特征[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(2): 343-352.YANG Q F, WANG R J, XU S N, et al. Hydrogeochemical and stable isotopic characteristics of brine in Laizhou Bay[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(2): 343-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] HAN D M, SONG X F, CURRELL M J, et al. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 508: 12-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.040 [12] 李静, 梁杏, 毛绪美, 等. 水化学揭示的弱透水层孔隙水演化特征及其古气候指示意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 37(3): 612-620.LI J, LIANG X, MAO X M, et al. Hydro-geochemistry implications of evolution of pore water in low-penetrability aquifer and significance of paleoclimate[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2012, 37(3): 612-620. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 李静, 张亚年, 梁杏, 等. 江苏滨海平原弱透水层封存的古咸水及其运移过程[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 90-98. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0158LI J, ZHANG Y N, LIANG X, et al. Paleo-salt porewater trapped in the clayey aquitard and its transport processes in Jiangsu coastal plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 90-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0158 [14] 江欣悦, 李静, 郭林, 等. 豫北平原浅层地下水化学特征与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 290-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511JIANG X Y, LI J, GUO L, et al. Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 290-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511 [15] 刘宏伟, 胡云壮, 马震, 等. 莱州湾南岸浅层地下水咸化特征及其指示意义[J]. 节水灌溉, 2019(5): 71-76.LIU H W, HU Y Z, MA Z, et al. Characteristics of shallow groundwater salinization and its indication in southern Laizhou Bay area[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2019(5): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] TOLMAN C F, POLAND J F. Ground-water, salt-water infiltration, and ground-surface recession in Santa Clara Valley, Santa Clara County, California[J]. Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 1940, 21(1): 23-35. doi: 10.1029/TR021i001p00023 [17] 刘森. 莱州湾南岸地下咸水演化和咸水入侵过程机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.LIU S. The evolution of ground-saline water and process mechanism of saline water intrusion in southern Laizhou Bay[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 郑懿珉, 高茂生, 刘森, 等. 晚更新世以来莱州湾南岸地下卤水资源分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(5): 11-18.ZHENG Y M, GAO M S, LIU S, et al. Distribution characteristics of subsurface brine resources on the southern coast of Laizhou Bay since Late Pleistocene[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(5): 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 刘宏伟, 马震, 陈社明, 等. 基于水化学与地球物理法的莱州湾南岸海(咸)水入侵勘查[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 337-343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.017LIU H W, MA Z, CHEN S M, et al. Saltwater intrusion measurement in southern-area of Laizhou Bay based on hydro-chemical and geophysical methods[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 337-343. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.017 [20] 李倩, 易亮, 刘素贞, 等. 渤海南部莱州湾LZ908孔沉积物的岩石磁学性质[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(5): 1717-1728.LI Q, YI L, LIU S Z, et al. Rock magnetic properties of the LZ908 borehole sediments from the southern Bohai Sea, eastern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(5): 1717-1728. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 杨巧凤. 莱州湾沿海带浅层地下咸(卤)水的成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.YANG Q F. Origin of shallow salt(brine)water salinity in the coast of Laizhou Bay[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 于得芹, 蒙永辉. 莱州湾南岸地区表层土壤盐分离子分异规律[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(8): 29-35.YU D Q, MENG Y H. Spatial distribution of salt ions in surface soils in the south coast of Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(8): 29-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 冯晨馨, 邱隆伟, 高茂生, 等. 山东半岛北部泥质海岸带地下水水化学演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(12): 16-25.FENG C X, QIU L W, GAO M S, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in muddy coastal zone of the northern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(12): 16-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 侯国华, 高茂生, 郭飞, 等. 莱州湾海底地下水动态及影响机制研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(5): 124-132.HOU G H, GAO M S, GUO F, et al. Research on submarine groundwater dynamics and driving mechanism in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(5): 124-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 胡云壮, 李红, 李影, 等. 山东莱州湾南岸典型剖面海(咸)水入侵过程的水文地球化学识别[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2015, 38(1): 41-50.HU Y Z, LI H, LI Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical recognization of seawater intrusion process at the typical profile in Laizhou Bay[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2015, 38(1): 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 郭飞, 高茂生, 郑懿珉, 等. 我国北方沿海地区地下水库分类及综合对比[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(5): 35-40.GUO F, GAO M S, ZHENG Y M, et al. Classification and comparison of ground water reservoirs in coastal areas of northern China[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(5): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 王建, 张军强, 任寒寒, 等. 莱州湾南部沿海地区环境地质现状及成因研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2020, 38(2): 336-347. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.02.013WANG J, ZHANG J Q, REN H H, et al. Current situation and genesis of environmental geology in the coastal region of southern Laizhou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2020, 38(2): 336-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2020.02.013 [28] FOLK R L, WARD W C. Brazos River bar(Texas): A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [29] 王月玲, 王思成, 许浩, 等. 宁南黄土区植被恢复方式对土壤粒度特征的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(5): 83-91.WANG Y L, WANG S C, XU H, et al. Effects of vegetation restoration methods on soil particle size characteristics in loess region of southern Ningxia[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(5): 83-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 邹艳荣, 蔡玉兰. 水动力指数方法及其在沉积环境分析中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 1997, 22(2): 3-6.ZOU Y R, CAI Y L. Hydrodynamic index method and its application to depositional environment[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1997, 22(2): 3-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 孙立群. 江汉-洞庭典型区第四系含水系统无机氮素来源及富集机制[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.SUN L Q. Sources and enrichment mechanisms of inorganic nitrogen in Quaternary aquifer system in Jianghan and Dongting typical areas[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] LI J, LIANG X, JIN M G, et al. Geochemical signature of aquitard pore water and its paleo-environment implications in Caofeidian Harbor, China[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2013, 47(1): 37-50. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0238 [33] 李静. 黏性土弱透水层孔隙水地球化学特征及其环境指示: 以渤海湾西北岸滨海平原为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.LI J. Geochemistry of clayey aquitard pore water and its implication on environment: A case study in the coastal plain of northwest Bohai Bay[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] CLARKE D W, BOYLE J F, CHIVERRELL R C, et al. A sediment record of barrier estuary behaviour at the mesoscale: Interpreting high-resolution particle size analysis[J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 221: 51-68. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.05.029 [35] 刘乐军, 李培英, 王永吉. 鲁中黄土粒度特征及其成因探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1): 81-86.LIU L J, LI P Y, WANG Y J. The grain-size properties and genesis of the loess in central Shandong Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(1): 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] 王忱沛, 李琰, 商志文, 等. 渤海LZK06孔25万年沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2022, 40(1): 66-78.WANG C P, LI Y, SHANG Z W, et al. Grain-size characteristics and its environmental significance of sediments from core LZK06 in the North Bohai coast during the last 250 ka[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2022, 40(1): 66-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 李其华. 沉积物粒度在古环境重建中的应用[J]. 巢湖学院学报, 2003, 5(3): 26-28.LI Q H. Application of deposit's size to reconstruction of ancient environment[J]. Journal of Chaohu College, 2003, 5(3): 26-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9(1): 15-25.ZHAO S L, YANG G F, CANG S X, et al. On the marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the gulf of Bohai[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9(1): 15-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] 姜涛, 胡亦潘, 周从艳, 等. 海洋沉积物释光测年现状与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 31-54. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0192JIANG T, HU Y P, ZHOU C Y, et al. A review of luminescence dating on marine sediments[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 31-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0192 [40] 郭飞, 高茂生, 侯国华, 等. 莱州湾07钻孔沉积物晚更新世以来的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3): 145-155.GUO F, GAO M S, HOU G H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediment in Core 07 since the Late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(3): 145-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] YI L, DENG C L, XU X Y, et al. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary: Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from South Bohai Sea, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 319: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.01.005 [42] 李守军, 崔肖辉, 徐华, 等. 渤海莱州湾晚第四纪底栖有孔虫分布特征及古环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(2): 287-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.02.001LI S J, CUI X H, XU H, et al. Distribution characteristics of benthic foraminifera of the Late Quaternary in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China and its paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(2): 287-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.02.001 [43] 韩非, 薛禹群, 吴吉春, 等. 莱洲湾南岸咸水入侵条件下地下水的水化学特征与卤水形成[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(1): 102-108.HAN F, XUE Y Q, WU J C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in salt-water intrusion condition and genesis of brine along the south coast of the Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(1): 102-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] 李志威, 张晓影, 张明珠, 等. 海水入侵指标对比分析与评价: 以珠江口地下水含水层为例[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(1): 16-24.LI Z W, ZHANG X Y, ZHANG M Z, et al. Comparison of indicators for the assessment of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Taking aquifers in Pearl River Estuary as an example[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(1): 16-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 王珍岩, 孟广兰, 王少青. 渤海莱州湾南岸第四纪地下卤水演化的地球化学模拟[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(1): 49-53.WANG Z Y, MENG G L, WANG S Q. Geochemistry modeling of Quaternary subsurface brines in south coast of the Laizhou Bay, the Bohai Sea: Taking brines from core-Aoli501 in Changyi area as an example[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(1): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] 高茂生, 郑懿珉, 刘森, 等. 莱州湾地下卤水形成的古地理条件分析[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(2): 393-400.GAO M S, ZHENG Y M, LIU S, et al. Palaeogeographic condition for origin of underground brine in southern coast of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(2): 393-400. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] 李道高, 赵明华, 韩美, 等. 莱州湾南岸平原浅埋古河道带研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1): 23-29.LI D G, ZHAO M H, HAN M, et al. A study of the shallowly-buried paleochannel zones in the south coast plain of the Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(1): 23-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) [48] 左文喆, 徐叶净, 王英, 等. 东部沿海有咸区黏性原状土膜性能的试验研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(2): 69-72.ZUO W Z, XU Y J, WANG Y, et al. Experimental study on membrane performance of cohesive undisturbed soil salty area of eastern China[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(2): 69-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) [49] 田元, 范德江, 张喜林, 等. 东海内陆架沉积物敏感粒级构成及其地质意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2): 319-326.TIAN Y, FAN D J, ZHANG X L, et al. Sensitive grain size components and their geological implication in the inner shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(2): 319-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] 何继山, 梁杏, 李静, 等. 天津滨海平原区深孔沉积物环境敏感粒度提取及其意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2015, 40(7): 1215-1225.HE J S, LIANG X, LI J, et al. Environmentally sensitive grain-size extraction of deep hole sediment from Tianjin coastal plain and its significance[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2015, 40(7): 1215-1225. (in Chinese with English abstract) [51] LIU J G, LI A C, CHEN M H. Environmental evolution and impact of the Yellow River sediments on deposition in the Bohai Sea during the last deglaciation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 38(1/2): 26-33. [52] BOULAY S, COLIN C, TRENTESAUX A, et al. Sediment sources and East Asian monsoon intensity over the last 450 ky: Mineralogical and geochemical investigations on South China Sea sediments[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 228(3/4): 260-277. [53] 刘恩峰. 莱州湾南岸滨海平原沉积环境变化与咸水入侵关系研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2002.LIU E F. The relation research of the sedimentary environmental transformation and saline water encroachment in Laizhou Bay south sea shore plain[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2002. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: