Pore and fracture characteristics of low-maturity continental shale and its significance for shale oil occurrence: A case study of Shahejie Formation in Qingnan Sag, Jiyang Depression
-
摘要:
济阳坳陷低演化页岩油资源潜力巨大, 是继中高成熟页岩油成功突破后的重要领域之一。为了明确低演化陆相页岩孔缝特征及对页岩油赋存的意义, 以济阳坳陷外围青南洼陷沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段为例, 综合运用薄片观察、有机碳测试、X射线衍射(XRD)分析、溶剂抽提、低温N2吸附、高压压汞、扫描电镜、能谱元素等多种技术, 在划分页岩岩相基础上, 探讨了低演化页岩孔隙类型、大小、分形特征及影响因素, 明确了裂缝发育特征, 阐明了页岩孔缝对页岩油赋存的重要意义。结果表明: 研究区页岩总有机碳质量分数
w (TOC)多在1.0%~4.0%, 矿物组分以长英质矿物为主, 其次为黏土矿物和碳酸盐矿物。孔隙类型以墨水瓶孔、平板狭缝孔为主, 包括石英粒间孔、黏土矿物片间孔、白云石晶间孔等, 孔径多小于200 nm, 呈多峰分布, 主要集中在2~50, 50~80, 100~200 nm。页岩储层发育较多的水平层理缝、高角度缝和网状缝, 多被沥青充填或浸染, 裂缝有利于页岩油的赋存和运移。富长英质矿物岩相通常比富黏土矿物岩相具有更高的孔体积和比表面积, 长英质矿物对孔隙有积极贡献, 且随热演化程度的增加, 孔体积和比表面积呈先降低后增加的趋势。当镜质体反射率R o>0.6%时, 页岩油含量显著增加, 主要与有机质开始大量生烃有关。水平层理缝、石英颗粒粒间孔、白云石和方解石晶间孔是页岩油有利的储集和赋存空间。Abstract:Low-maturity shale oil has great resource potential in Jiyang Depression and has become an important field after the successful breakthrough of medium- to high-maturity shale oil.
Objective The purpose of this paper is to clarify the pore and fracture characteristics of low-maturity continental shale and their significance to shale oil occurrence.
Methods By studying the E
s 3x and Es 4scs members in Qingnan Depression, Jiyang Depression, this study combines thin section observation, TOC content, XRD analysis, solvent extraction, low-temperature N2 adsorption, high-pressure mercury injection, scanning electron microscope observation and EDS analysis to classify the shale lithofacies, characterize the pore and fracture development, and illustrate the importance of shale pores and fractures for shale oil occurrence.Results The TOC content is mostly in the range of 1.0%-4.0%, and the mineral composition mainly includes felsic minerals, followed by clay and carbonate minerals. The major pore types are ink-bottle-shaped pores and plate-parallel-shaped pores, including quartz intergranular pores, clay mineral interlamellar pores, and dolomite intercrystalline pores. The major pore sizes are mostly less than 200 nm and exhibit a multipeak distribution, which is concentrated in the ranges of 2-50 nm, 50-80 nm and 100-200 nm. Horizontal bedding fractures, vertical fractures and network fractures developed in the studied shales and were mostly filled or contacted by bitumen.Felsic-rich shale lithofacies usually have a greater pore volume and specific surface area than clay-rich lithofacies, and felsic minerals positively contribute to pore development. The pore volume and specific surface area first decreased and then increased with increasing thermal maturity. When
R o>0.6%, the shale oil content increases significantly, which is mainly related to the large amount of hydrocarbon generation in organic matters.Conclusion Horizontal bedding fractures, quartz intergranular pores, and dolomite and calcite intercrystalline pores are favourable storage and occurrence spaces for shale oil.
-
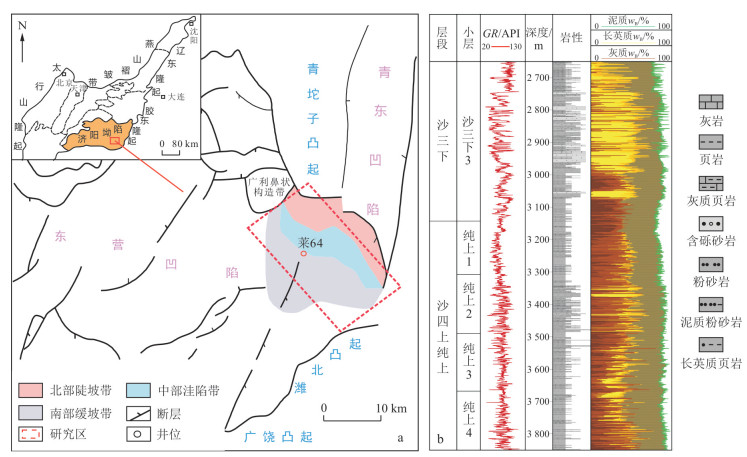
图 1 济阳坳陷青南洼陷区域构造(a)与地层发育特征(b)(图a自文献[16]修改)
Figure 1. Structural (a) and stratigraphic development characteristics (b) of Qingnan Sag in Jiyang Depression
图 3 青南洼陷莱64井沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段典型页岩沉积构造
a. 2 709.6 m,沙三下亚段,层状构造,单偏光;b. 3 664.0 m,沙四上纯上亚段,纹层状构造,单偏光;c. 3 818.7 m,沙四上纯上亚段,纹层状构造,单偏光;d. 2 710.6 m,沙三下亚段,块状构造,单偏光;e. 3 152.8 m,沙四上纯上亚段,块状构造,单偏光;f. 3 460.1 m,沙四上纯上亚段,块状构造,单偏光
Figure 3. Typical shale sedimentary structures in the Es3x and Es4scs members in Well Lai 64, Qingnan Sag
图 5 青南洼陷莱64井沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段页岩孔隙类型
a. 2 709.0 m,粒间孔和黏土矿物片间孔;b. 3 664.0 m,粒间孔;c. 3 664.0 m,粒内孔和边缘溶蚀孔;d. 3 664.0 m,黏土矿物片间孔;e. 3 664.0 m,有机质内部孔隙不发育;f. 3 746.8 m,白云石晶间孔;g. 3 746.8 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩纹层内部;h. 3 746.8 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩纹层界面处;i. 3 818.7 m,有机质内部孔隙不发育
Figure 5. Shale pore types of the Es3x and Es4scs members in Well Lai 64, Qingnan Sag
图 6 青南洼陷莱64井沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段典型页岩N2吸附孔径分布特征
a. 2 709.6 m, 富有机质层状长英质页岩;b. 3 155.3 m,富有机质块状泥质混合页岩;c. 3 664.0 m, 含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩;d. 3 746.8 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩;e. 3 747.7 m,富有机质层状泥质混合页岩;f. 3 818.7 m,富有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩
Figure 6. Typical pore size distribution of the Es3x and Es4scs members in Well Lai 64, Qingnan Sag
图 12 青南洼陷莱64井沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段裂缝发育特征
a. 3 664.0 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩, 单偏光;b. 3 746.8 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩,单偏光;c. 3 664.0 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩,单偏光;g. 3 818.7 m,富有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩;h. 图g中黄色方框视域;d、e、f、i分别为a、b、c、h同视域荧光图像
Figure 12. Fracture development characteristics of the Es3x and Es4scs members in Well Lai 64, Qingnan Sag
图 13 青南洼陷莱64井沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段页岩洗油前后氮气吸附-脱附曲线
a. 2 709.6 m,富有机质层状长英质页岩;b. 3 155.3 m,富有机质块状泥质混合页岩;c. 3 347.0 m,含有机质纹层状泥质粉砂岩;d. 3 664.0 m,含有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩;e. 3 747.7 m,富有机质层状泥质混合页岩;f. 3 818.7 m,富有机质纹层状泥质混合页岩;蓝色箭头指未洗油页岩氮气吸附-脱附曲线回滞环(2条蓝色线之间所夹的区域),红色箭头指洗油后页岩氮气吸附-脱附曲线回滞环(2条红色线之间所夹的区域)
Figure 13. Nitrogen adsorption-desorption curves before and after oil washing in the Es3x and Es4scs members in Well Lai 64, Qingnan Sag
表 1 青南洼陷沙河街组沙三下-沙四上纯上亚段页岩分形维数汇总
Table 1. Fractal dimension of the Es3x and Es4scs members in Qingnan Sag
样品深度/m P/Po<0.45 P/Po>0.45 拟合公式 R2 D1 拟合公式 R2 D2 2 709.6 y=-0.383 6x+2.438 5 0.995 3 2.616 y=-0.141 9x+0.255 09 0.969 9 2.858 3 155.3 y=-0.628 5x+0.972 7 0.999 2 2.371 y=-0.328 2x+1.106 2 0.980 4 2.671 3 664.0 y=-0.643 0x+0.957 6 0.999 8 2.357 y=-0.247 1x+1.198 4 0.947 7 2.753 3 746.8 y=-0.729 3x-0.301 7 0.995 3 2.27 y=-0.380 6x-0.181 8 0.977 7 2.619 3 747.7 y=-0.906 2x-0.151 5 0.996 6 2.093 y=-0.297 7x+0.126 1 0.957 9 2.702 3 818.7 y=-0.764 6x-0.414 7 0..994 1 2.235 y=-0.381 6x-0.311 0 0.978 8 2.618 -
[1] 付金华, 刘显阳, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段页岩油勘探发现与资源潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(5): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.05.001FU J H, LIU X Y, LI S X, et al. Discovery and resource potential of shale oil of Chang 7 Member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(5): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.05.001 [2] 何文渊, 蒙启安, 张金友. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油富集主控因素及分类评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202105001.htmHE W Y, MENG Q A, ZHANG J Y. Controlling factors and their classification-evaluation of Gulong shale oil enrichment in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202105001.htm [3] 刘惠民, 李军亮, 刘鹏, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系页岩油富集条件与勘探战略方向[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(12): 1717-1729. doi: 10.7623/syxb202212004LIU H M, LI J L, LIU P, et al. Enrichment conditions and strategic exploration direction of Paleogene shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(12): 1717-1729. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb202212004 [4] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 甘华军, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段页岩形成环境及页岩油潜力综合评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233ZHOU L H, CHEN C W, GAN H J, et al. Shale formation environment and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233 [5] 辛红刚, 田杨, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地典型夹层型页岩油地质特征及潜力评价: 以宁228井长7段为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 114-124. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220224XIN H G, TIAN Y, FENG S B, et al. Geological characteristics and potential evaluation of typical interlayer shale oil in the Ordos Basin: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Well Ning 228[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 114-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220224 [6] 蔚远江, 王红岩, 刘德勋, 等. 中国陆相页岩油示范区发展现状及建设可行性评价指标体系[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(1): 191-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202301013.htmYU Y J, WANG H Y, LIU D X, et al. Development status and feasibility evaluation index system of continental shale oil demonstration area in China[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(1): 191-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202301013.htm [7] 宋明水, 刘惠民, 王勇, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系页岩油富集规律认识与勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 225-235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002003.htmSONG M S, LIU H M, WANG Y, et al. Enrichment rules and exploration practices of Paleogene shale oil in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 225-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002003.htm [8] 张顺, 刘惠民, 张鹏飞, 等. 东营凹陷中低成熟度富碳酸盐页岩地质特征: 以牛庄洼陷沙四段上亚段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(6): 1138-1151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202206010.htmZHANG S, LIU H M, ZHANG P F, et al. Geological characteristics of shale oil enrichment in Niuzhuang Sag, Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(6): 1138-1151. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202206010.htm [9] 杨勇. 济阳陆相断陷盆地页岩油富集高产规律[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(1): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202301001.htmYANG Y. Enrichment and high production regularities of shale oil reservoirs in continental rift basin: A case study of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(1): 1-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202301001.htm [10] 张善文. 转变观念在老区勘探中的重要性: 以胜利油田东部探区青南油田的发现为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(4): 441-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201404001.htmZHANG S W. Importance of unconventional mindsets in further fine exploration of mature blocks: A case study of Qingnan oilfield, eastern Dongying Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(4): 441-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201404001.htm [11] SANG Q, ZHANG S J, LI Y J, et al. Determination of organic and inorganic hydrocarbon saturations and effective porosities in shale using vacuum-imbibition method[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 200: 123-134. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.10.010 [12] LI J B, WANG M, JIANG C Q, et al. Sorption model of lacustrine shale oil: Insights from the contribution of organic matter and clay minerals[J]. Energy, 2022, 260: 125011. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125011 [13] YUAN Y J, REZAEE R, AL-KHDHEEAWI E A, et al. Impact of composition on pore structure properties in shale: Implications for micro-/ mesopore volume and surface area prediction[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(10): 9619-9628. [14] CURTIS M E, CARDOTT B J, SONDERGELD C H, et al. Development of organic porosity in the Woodford Shale with increasing thermal maturity[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 103: 26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.08.004 [15] MILLIKEN K L, RUDNICKI M, AWWILLER D N, et al. Organic matter-hosted pore system, Marcellus Formation (Devonian), Pennsylvania[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 177-200. doi: 10.1306/07231212048 [16] 李继岩. 局限湖盆滨浅湖滩坝砂体沉积特征: 以东营凹陷青南洼陷沙四上亚段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2): 160-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002006.htmLI J Y. Sedimentary characteristics of shore-shallow lake-beach bar in limited lacustrine basin: Taking upper part of Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation of Qingnan Sag in Dongying Depression as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(2): 160-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002006.htm [17] 姜亦栋, 周李军, 许建华, 等. 青南洼陷沉积特征、成藏条件及勘探潜力分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2003, 10(3): 44-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2003.03.015JIANG Y D, ZHOU L J, XU J H, et al. Analysis of sedimentary characteristics, reservoir forming conditions and exploration potential in Qingnan low land[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2003, 10(3): 44-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2003.03.015 [18] 罗阳, 王永诗, 吴智平, 等. 青南洼陷构造特征及对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(2): 55-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.02.010LUO Y, WANG Y S, WU Z P, et al. Structural features of Qingnan subsag and control factors on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(2): 55-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.02.010 [19] 姜在兴, 梁超, 吴靖, 等. 含油气细粒沉积岩研究的几个问题[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6): 1031-1039. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201306001.htmJIANG Z X, LIANG C, WU J, et al. Several issues in sedimentological studies on hydrocarbon-bearing fine-grained sedimentary rocks[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(6): 1031-1039. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201306001.htm [20] HICKEY J J, HENK B. Lithofacies summary of the Mississippian Barnett Shale, Mitchell 2 T.P. Sims well, Wise County, Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 437-443. [21] CHALMERS G R, BUSTIN R M, POWER I M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses: Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig units[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1099-1119. doi: 10.1306/10171111052 [22] ROSS D J K, MARC BUSTIN R. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 916-927. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.06.004 [23] LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061 [24] CLARKSON C R, SOLANO N, BUSTIN R M, et al. Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 606-616. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.06.119 [25] KUILA U, PRASAD M. Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2013, 61(2): 341-362. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12028 [26] MASTALERZ M, SCHIMMELMANN A, DROBNIAK A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany Shale across a maturation gradient: Insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(10): 1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194 [27] 曾宏斌, 王芙蓉, 罗京, 等. 基于低温氮气吸附和高压压汞表征潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 242-252. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022ZENG H B, WANG F R, LUO J, et al. Characteristics of pore structure of intersalt shale oil reservoir by low temperature nitrogen adsorption and high pressure mercury pressure methods in Qianjiang Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 242-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022 [28] VALENZA J J, DRENZEK N, MARQUES F, et al. Geochemical controls on shale microstructure[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(5): 611-614. doi: 10.1130/G33639.1 [29] 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htmYANG F, NING Z F, KONG D T, et al. Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htm [30] MANDELBROT B. Fractal Geometry of Nature[M]. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Company, 1982. [31] 汪虎, 何治亮, 张永贵, 等. 四川盆地海相页岩储层微裂缝类型及其对储层物性影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1): 41-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901006.htmWANG H, HE Z L, ZHANG Y G, et al. Microfracture types of marine shale reservoir of Sichuan Basin and its influence on reservoir property[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 41-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901006.htm [32] 袁玉松, 周雁, 邱登峰, 等. 泥页岩非构造裂缝形成机制及特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1): 155-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201601016.htmYUAN Y S, ZHOU Y, QIU D F, et al. Formation mechanism and characteristics of non-tectonic fractures in shales[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(1): 155-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201601016.htm [33] 王濡岳, 胡宗全, 刘敬寿, 等. 中国南方海相与陆相页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素对比: 以黔北岑巩地区下寒武统为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(4): 631-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804002.htmWANG R Y, HU Z Q, LIU J S, et al. Comparative analysis of characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in marine and continental shales: A case study of the Lower Cambrian in Cengong area, northern Guizhou Province[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(4): 631-640. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804002.htm [34] 刘庆, 张林晔, 沈忠民, 等. 东营凹陷富有机质烃源岩顺层微裂隙的发育与油气运移[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(6): 593-597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.06.010LIU Q, ZHANG L Y, SHEN Z M, et al. Microfracture occurrence and its significance to the hydrocarbons expulsion in source rocks with high organic matter abundance, Dongying Depression[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(6): 593-597. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.06.010 [35] 王学军, 宁方兴, 郝雪峰, 等. 古近系页岩油赋存特征: 以济阳坳陷为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(29): 39-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201729006.htmWANG X J, NING F X, HAO X F, et al. Paleogene shale oil occurrence features: A case of Jiyang Depression[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(29): 39-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201729006.htm [36] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 魏祥峰, 等. 四川盆地焦石坝地区页岩裂缝发育主控因素及对产能的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6): 799-808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201606002.htmGUO X S, HU D F, WEI X F, et al. Main controlling factors on shale fractures and their influences on production capacity in Jiaoshiba area, the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(6): 799-808. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201606002.htm [37] ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739-1758. doi: 10.1351/pac199466081739 [38] 王民, 马睿, 李进步, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组湖相页岩油赋存机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 789-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904020.htmWANG M, MA R, LI J B, et al. Occurrence mechanism of lacustrine shale oil in the Paleogene Shahejie Formation of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 789-802. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904020.htm [39] DISTEFANO V H, MCFARLANE J, ANOVITZ L M, et al. Extraction of organic compounds from representative shales and the effect on porosity[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 35: 646-660. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.08.064 -





 下载:
下载: