Intelligent identification methods for shale lithology based on the coupling deeply of logging curves
-
摘要:
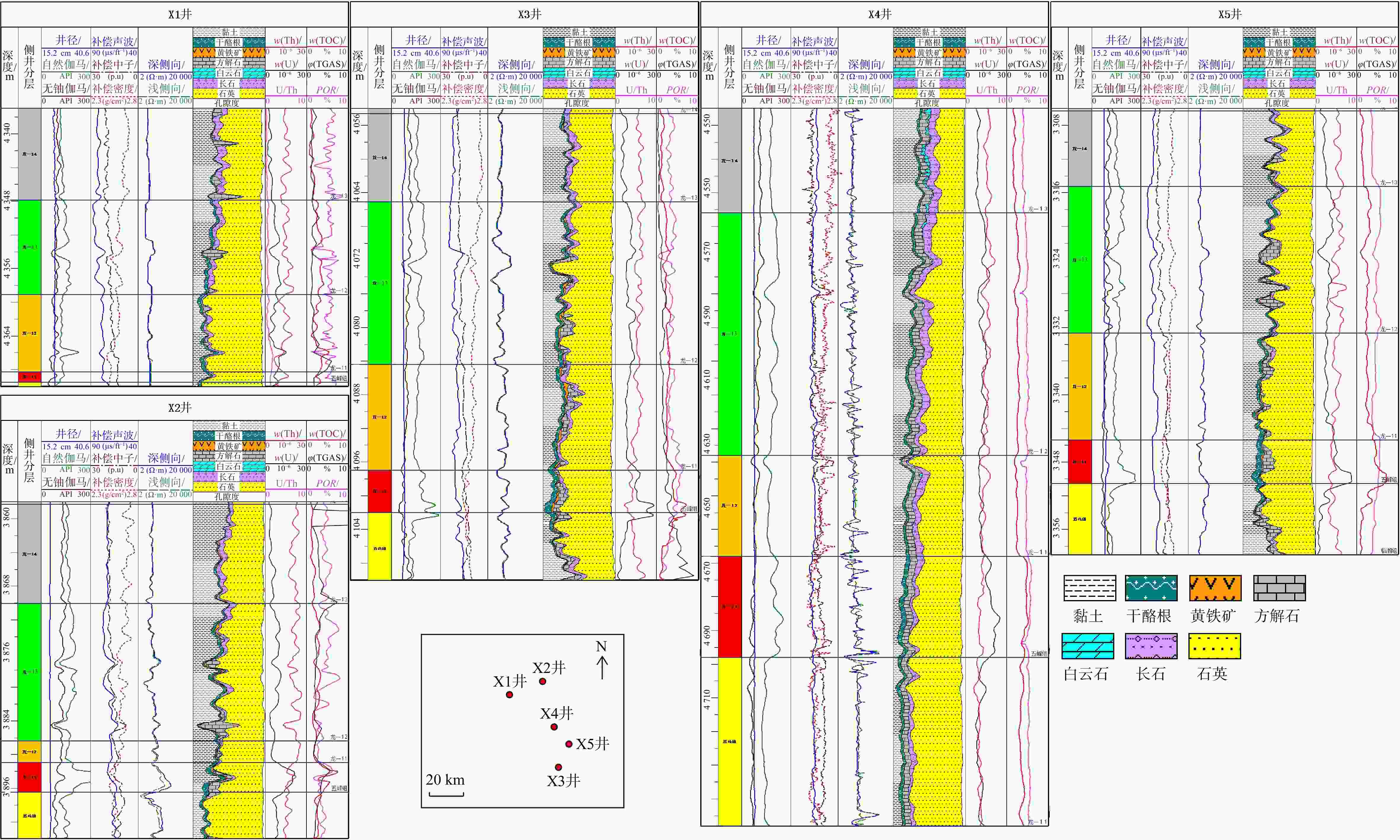
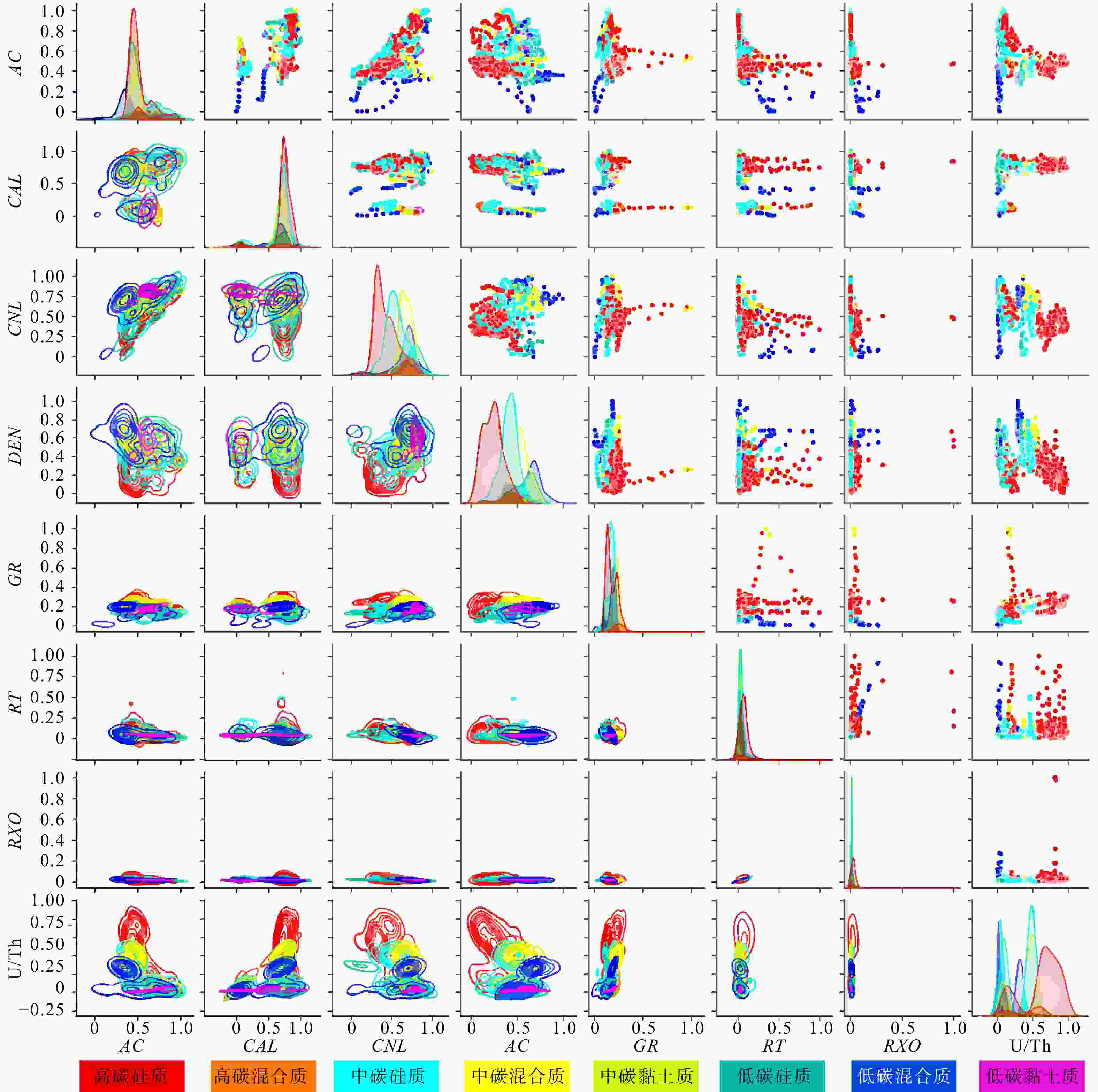
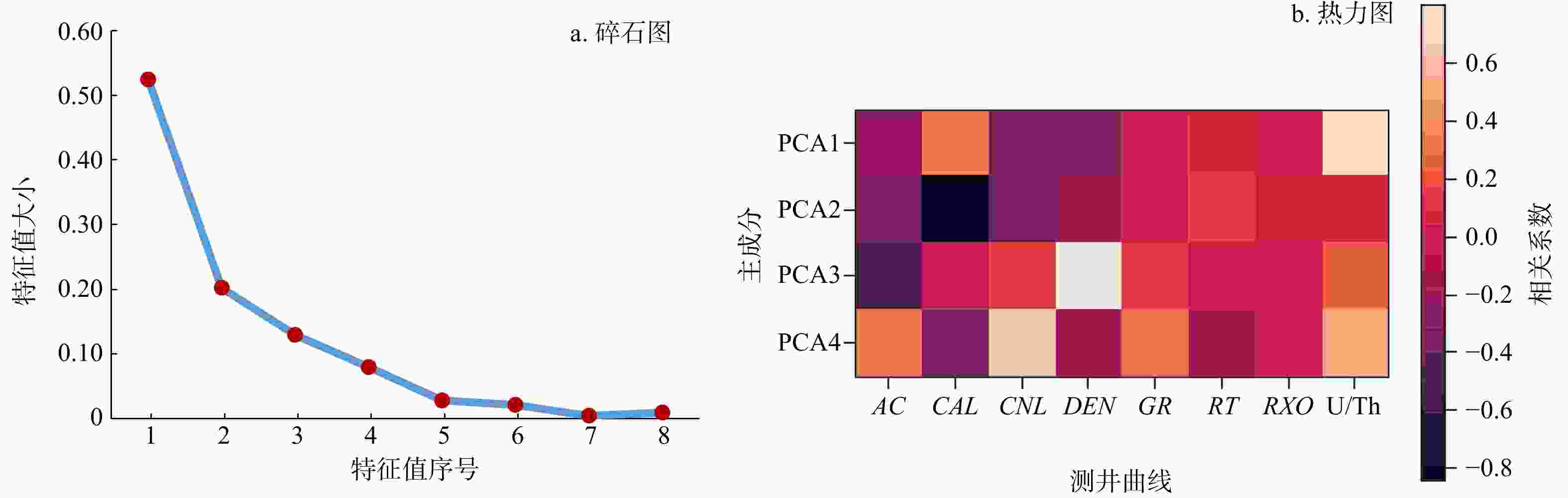
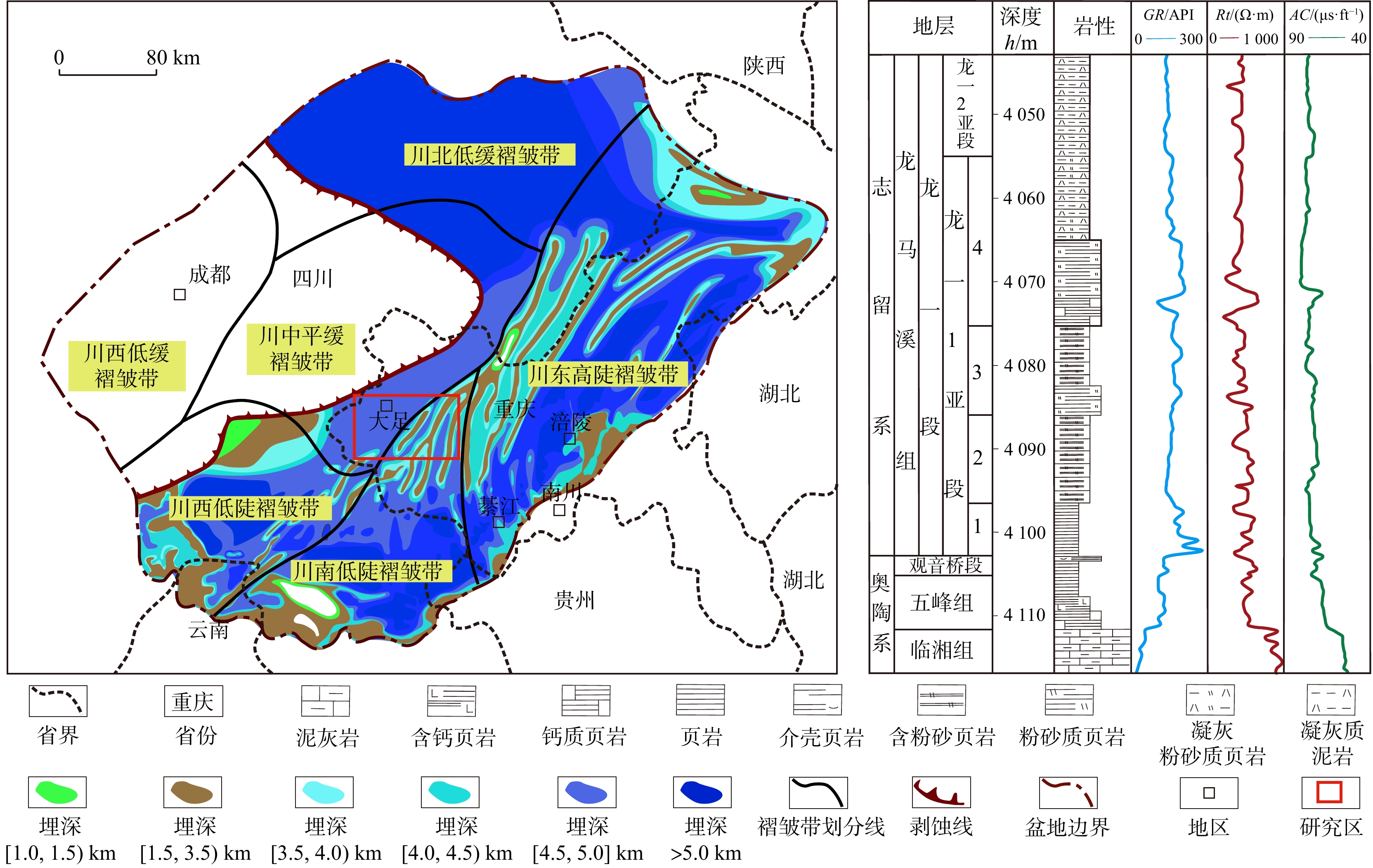
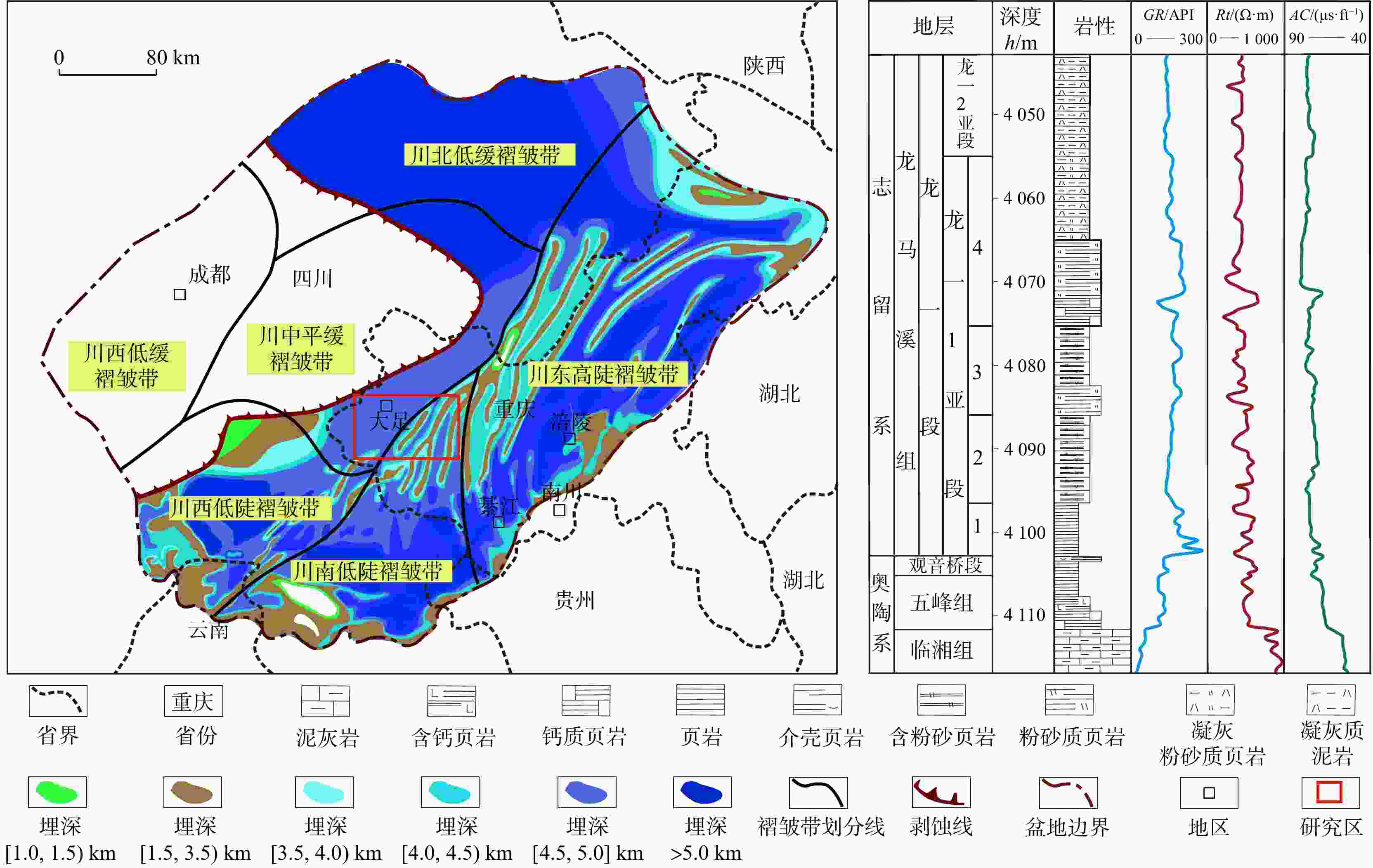
四川盆地渝西区块五峰组-龙马溪组是国内典型的页岩气储层,其层间强非均质性,导致采集的测井曲线信息存在大量冗余且曲线间耦合关系复杂,岩相测井识别难度高、精度低,亟需技术方法创新。本文在岩相划分与分析的基础上,联合主成分分析法与随机森林算法构建了一种岩相智能识别方法。研究结果表明:①利用主成分分析法对测井曲线进行优化,可以使测井曲线深度耦合,削减测井信息冗余及曲线间复杂耦合关系等因素对岩相识别的影响,可得到更加科学有效的数据信息;②向原始数据添加不改变其岩相的微量变化,可以达到数据增强的效果,在一定程度上解决随机森林算法由于数据集比较小或者不平衡时,模型的泛化能力和稳定性差的问题;③联合主成分分析法与随机森林算法构建的岩相智能识别方法运用识别准确率达83%以上,适用性强,准确率高。该方法不仅在一定程度上克服了研究区岩相识别困难的问题,也极大地提高了岩相识别效率,对促进研究区页岩气经济高效开发具有重要意义。
Abstract:Objective The Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the Yuxi Block of the Sichuan Basin, China are typical shale gas reservoirs. The strong heterogeneities of these formations leads to both information redundancy and complex coupling relationships of logging curves, which is challenging and inaccurate for traditional lithofacies identification.
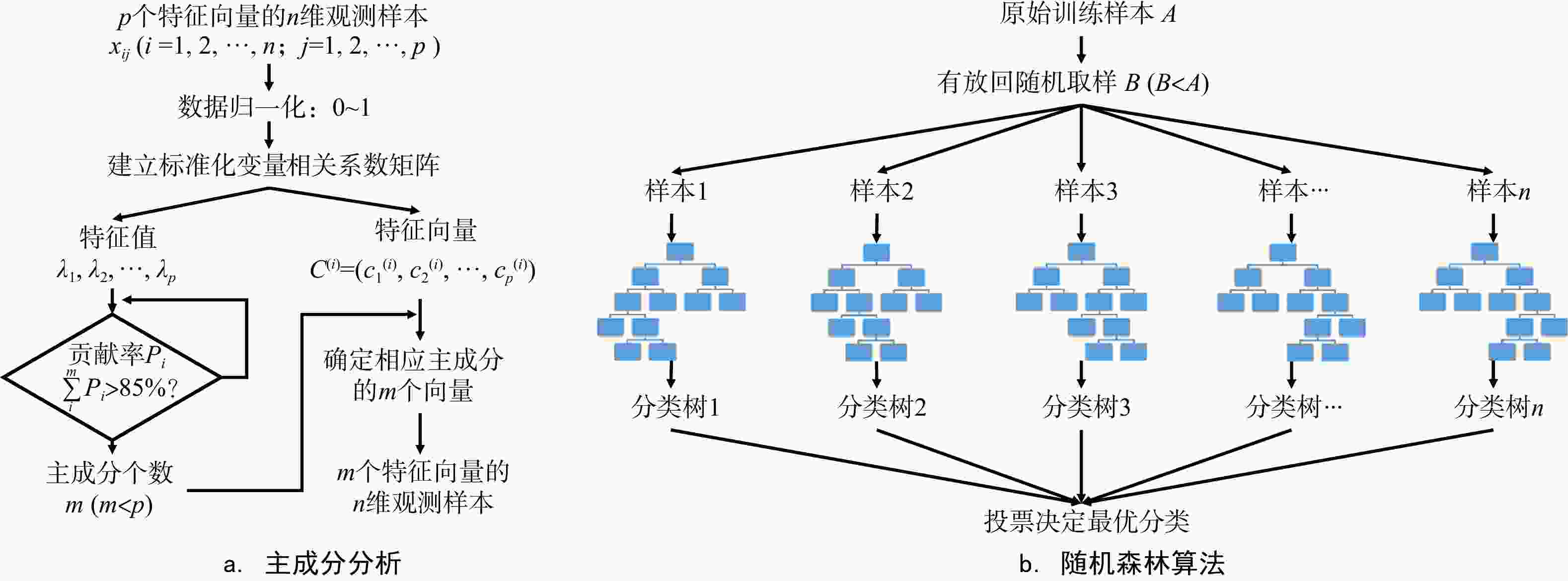
Methods This study developed an intelligent lithofacies identification method that integrated with both principal component analysis (PCA) and the random forest algorithm based on lithofacies classification and analysis.
Results Research findings were given as follows: First, PCA optimization can strengthen the coupling of logging curves, reducing the impact of lithofacies identification such as logging curve information redundancy and complex relationships . Second, data augmentation was achieved by including minor changes to the original data without impacting lithofacies, improving model generalization and stability during handling small or imbalanced datasets. Finally, lithofacies identification accuracy based on PCA with the random forest algorithm achievedabove 83%, with a high precision and a strong applicability.
Conclusion This method not only overcomes the difficulty of lithofacies identification in the study area, but also greatly improves the efficiency of lithofacies identification, which is of great significance for promoting the economic and efficient development of shale gas in the study area.
-
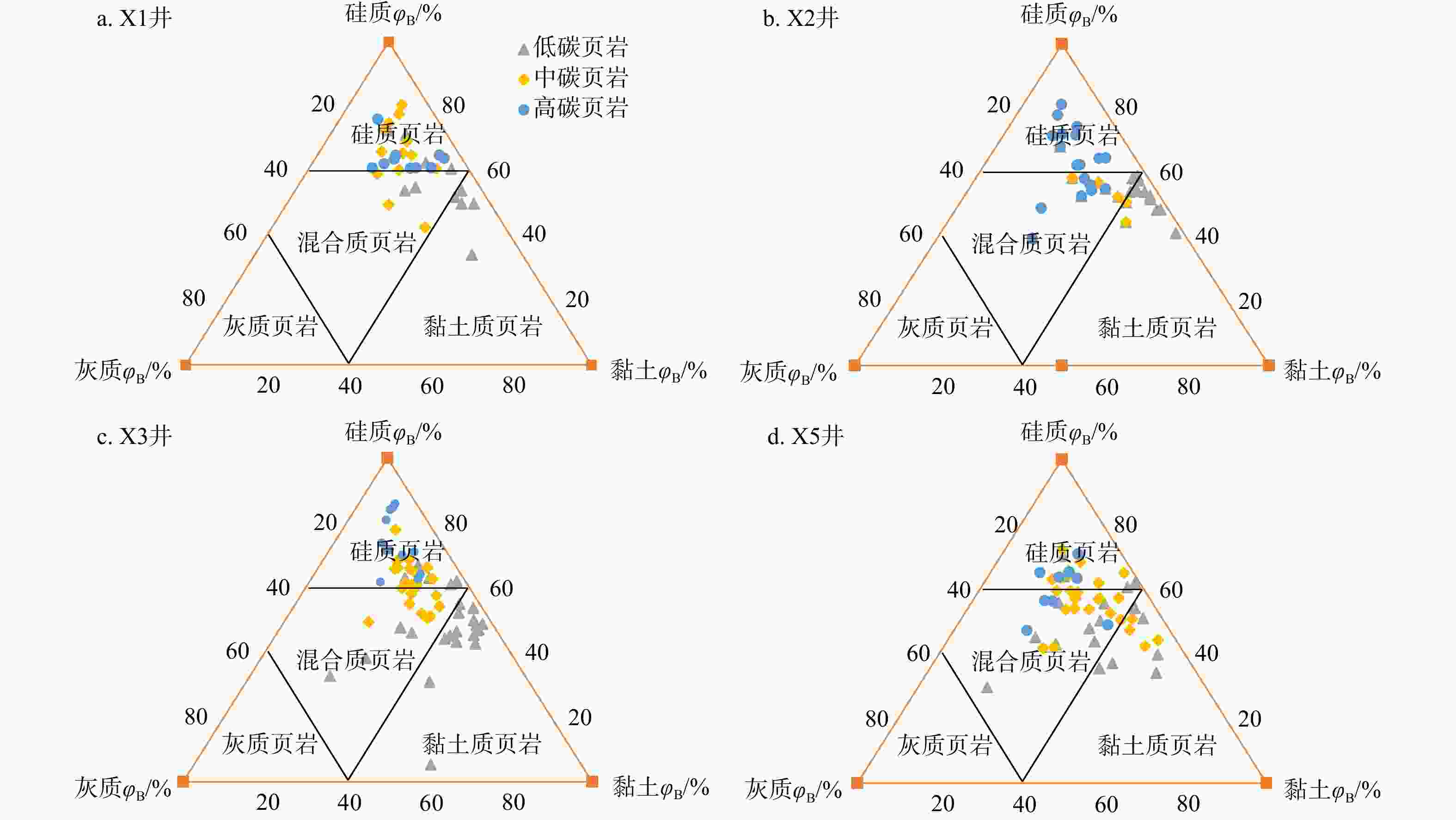
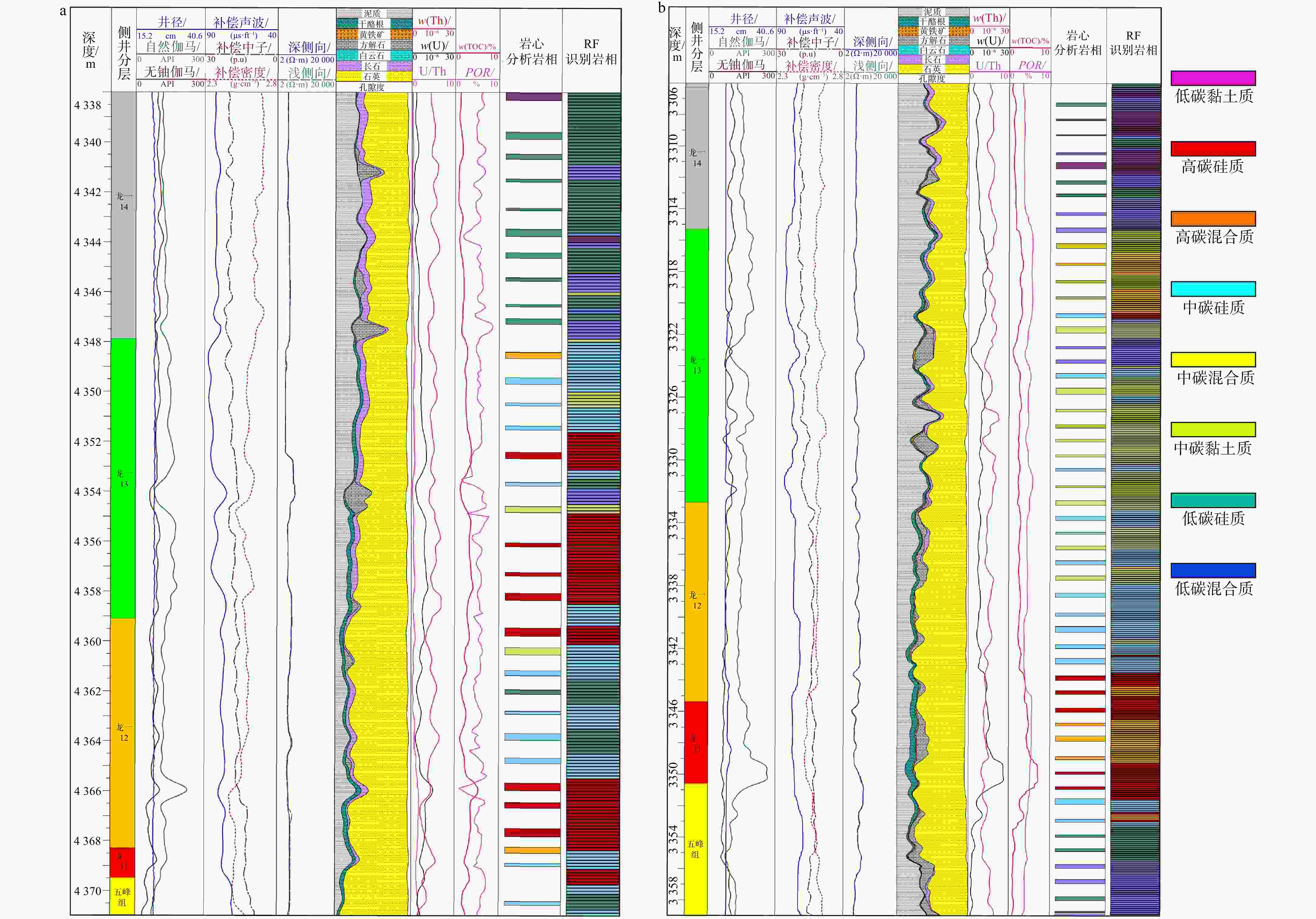
表 1 研究区页岩岩相类型发育特征
Table 1. Development characteristics of lithofacies types in the study area
岩相类型 高碳硅质 中碳混合质 中碳硅质 低碳黏土质 低碳混合质 矿物体积分数
φB/%




岩心照片 









铸体薄片 




扫描电镜 




w(TOC)/% 3.9(1.8~6.7) 2.8(1.9~4.5) 2.8(1.6~3.5) 1.5(0.4~2.9) 0.9(0.1~2.9) POR/% 3.9(2.6~5.5) 3.8(0.4~6.3) 3.4(2.9~4.3) 3.351(1.081~4.616) 1.8(0.1~4.6) φ(TGAS)/% 4.1(1.7~8.2) 3.9(2.7~6.4) 3.8(2.4~5.4) 2.2(0.8~5.1) 1.3(0.2~5.5) 总体评价 优质 较优等 中等 差 最差 注:POR为孔隙度;φ(TGAS)为总含气量 表 2 数据增强与样本集划分
Table 2. Data augmentation and sample division
页岩岩相 高碳硅质 高碳混合质 中碳硅质 中碳混合质 中碳黏土质 低碳硅质 低碳混合质 低碳黏土质 统计 原始数据 训练集数据/个 639 73 546 408 26 222 252 46 2212 2766 测试集数据/个 167 16 147 88 7 52 67 10 554 识别准确率/% 89 77 88 91 58 67 85 62 平均77 增强数据 训练集数据/个 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 5600 7200 测试集数据/个 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 1600 识别准确率/% 92 88 92 93 87 90 91 89 平均90 表 3 随机森林算法参数调优
Table 3. Parameter tuning of the random forest algorithm
参数 搜索范围 步长 最优值 决策树的个数 200~ 2000 200 1000 决策树最大深度 10~100 10 100 叶子节点含有的最少样本 1~4 2 4 节点可分的最小样本数 1~10 1 2 -
[1] 邹才能,赵群,丛连铸,等. 中国页岩气开发进展、潜力及前景[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(1):1-14.ZOU C N,ZHAO Q,CONG L Z,et al. Development progress,potential and prospect of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(1):1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] LE M T,DO H T,NGUYEN T T,et al. What prospects for shale gas in Asia? Case of shale gas in China[J]. The Journal of World Energy Law & Business,2021,13(5/6):426-440. [3] 舒红林,何方雨,李季林,等. 四川盆地大安区块五峰组-龙马溪组深层页岩地质特征与勘探有利区[J]. 天然气工业,2023,43(6):30-43.SHU H L,HE F Y,LI J L,et al. Geological characteristics and favorable exploration areas of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation deep shale in the Da' an Block,Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2023,43(6):30-43. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 汤济广,汪凯明,秦德超,等. 川东南南川地区构造变形与页岩气富集[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(5):11-21.TANG J G,WANG K M,QIN D C,et al. Tectonic deformation and its constraints to shale gas accumulation in Nanchuan area,southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(5):11-21. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] SUN N L,CHEN T Y,GAO J B,et al. Lithofacies and reservoir characteristics of saline lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the northern Dongpu Sag,Bohai Bay Basin:Implications for shale oil exploration[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2023,252:105686. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105686 [6] BIAN C S,GUO B C,PU X G,et al. Lithofacies characteristics and their effects on shale oil enrichment:A case study from Shahejie Formation of the Qibei Sag,Bohai Bay Basin,China[J]. Energies,2023,16(5):2107-2107. doi: 10.3390/en16052107 [7] 王民,杨金路,王鑫,等. 基于随机森林算法的泥页岩岩相测井识别[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(1):130-142.WANG M,YANG J L,WANG X,et al. ldentification of shale lithofacies by well logs based on random forest algorithm[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(1):130-142. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 李宁,冯周,武宏亮,等. 中国陆相页岩油测井评价技术方法新进展[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(1):28-44.LI N,FENG Z,WU H L,et al. New advances in methods and technologies for well logging evaluation of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(1):28-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 曾棒,刘小平,刘国勇,等. 陆相泥页岩层系岩相测井识别与预测:以南堡凹陷拾场次洼为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):69-79.ZENG B,LIU X P,LIU G Y,et al. Logging identification and prediction of lithofacies of lacustrine shale system in Shichang Sub-sag,Nanpu Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):69-79. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 李跃纲,周安富,谢伟,等. 四川盆地南部泸州地区五峰组-龙一1亚段页岩岩相划分及储层发育主控因素[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(8):112-123. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.009LI Y G,ZHOU A F,XIE W,et al. Lithofacies division and main controlling factors of reservoir development in Wufeng Formation-Long11 sub-member shale in the Luzhou region,south Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2022,42(8):112-123. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.009 [11] 陈玉林,李戈理,杨智新,等. 基于KNN算法识别合水地区长7储层岩性岩相[J]. 测井技术,2020,44(2):182-185.CHEN Y L,LI G L,YANG Z X,et al. ldentification of lithology and lithofacies of Chang 7 reservoir in Heshui area by KNN algorithm[J]. Well Logging Technology,2020,44(2):182-185. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] TEWARI S,DWIVEDI U D. A comparative study of heterogeneous ensemble methods for the identification of geological lithofacies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology,2020,10:1-20. [13] KIM J K. Lithofacies classification integrating conventional approaches and machine learning technique[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2022,100:104500. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2022.104500 [14] 赖锦,韩能润,贾云武,等. 基于测井资料的辫状河三角洲沉积储层精细描述[J]. 中国地质,2018,45(2):304-318.LAI J,HAN N R,JIA Y W,et al. Detailed description of the sedimentary reservoir of a braided delta based on well logs[J]. Geology in China,2018,45(2):304-318. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] TEWARI S,DWIVEDI D U. A comparative study of heterogeneous ensemble methods for the identification of geological lithofacies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology,2020,10(5):1-20. [16] 刘宏坤,艾勇,王贵文,等. 深层、超深层致密砂岩储层成岩相测井定量评价:以库车坳陷博孜-大北地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):299-310.LIU H K,AI Y,WANG G W,et al. Quantitative well logging evaluation of diagenetic facies of deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs:A case study of Bozi-Dabei area in Kuqa Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):299-310. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 王濡岳,胡宗全,董立,等. 页岩气储层表征评价技术进展与思考[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2021,42(1):54-65. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210105WANG R Y,HU Z Q,DONG L,et al. Advancement and trends of shale gas reservoir characterization and evaluation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2021,42(1):54-65. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20210105 [18] FENG R H. Improving uncertainty analysis in well log classification by machine learning with a scaling algorithm[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2020,196:107995. [19] HALL M,HALL B. Distributed collaborative prediction:Results of the machine learning contest[J]. The Leading Edge,2017,36(3):267-269. doi: 10.1190/tle36030267.1 [20] OHWOGHERE-ASUMA O,AWETO K E,UGBE C F. Lithofacies identification and multivariate analysis of groundwater chemistry in coastal aquifers in Koko area of the western Niger Delta[J]. Hydrology,2019,6(2):1-9. [21] 杨洋,石万忠,张晓明,等. 页岩岩相的测井曲线识别方法:以焦石坝地区五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏,2021,33(2):135-146.YANG Y,SHI W Z,ZHANG X M,et al. ldentification method of shale lithofacies by logging curves:A case study from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Jiaoshiba area,SW China[J]. Lithologic Reservoir,2021,33(2):135-146. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LIU Y J,LAI F Q,ZHANG H J,et al. A novel mineral composition inversion method of deep shale gas reservoir in western Chongqing[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,202:108528. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108528 [23] 王濡岳,胡宗全,龙胜祥,等. 四川盆地上粤陶统五峰组-下去留统龙马溪组页岩储层特征与演化机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(2):353-364. doi: 10.11743/ogg20220209WANG R Y,HU Z Q,LONG S X,et al. Reservoir characteristics and evolution mechanisms of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng-Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale,Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2022,43(2):353-364. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20220209 [24] MGIMBA M M,JIANG S,MWAKIPUNDA G C. The identification of normal to underpressured formations in the southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2022,219:111085. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.111085 [25] 王濡岳,胡宗全,周彤,等. 四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及其控储意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2021,42(6):1295-1306. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210605WANG R Y,HU Z Q,ZHOU T,et al. Characteristics of fractures and their significance for reservoirs in Wufeng-Longmaxi shale,Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2021,42(6):1295-1306. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20210605 [26] REN Q,ZHANG H B,ZHANG D L,et al. Lithology identification using principal component analysis and particle swarm optimization fuzzy decision tree[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2023,220:111233. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.111233 [27] LUBO-ROBLES D,BEDLE H,MARFURT K J,et al. Evaluation of principal component analysis for seismic attribute selection and self-organizing maps for seismic facies discrimination in the presence of gas hydrates[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2023,150:106097. [28] MARZIEH Z,ALI K. Prediction of hydraulic conductivity of porous granular media by establishment of random forest algorithm[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,366:130065. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.130065 [29] 聂云丽,高国忠. 基于随机森林的页岩气“甜点”分类方法[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2023,13(3):358-367.NIE Y L,GAO G Z. Classification of shale gas "sweet spot" based on random forest machine learning[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development,2023,13(3):358-367. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] ZHANG Z,CAI Z X. Permeability prediction of carbonate rocks based on digital image analysis and rock typing using random forest algorithm[J]. Energy & Fuels,2021,35(14):11271-11284. [31] HONG H Y. Assessing landslide susceptibility based on hybrid best-first decision tree with ensemble learning model[J]. Ecological Indicators,2023,147:109968. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109968 [32] Al-MUDHAFAR W J,ABBAS M A,WOOD D A. Performance evaluation of boosting machine learning algorithms for lithofacies classification in heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2022,145:105886. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105886 [33] 于洲,黄正良,李维岭,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中奥陶统乌拉力克组海相页岩岩相类型及优质储层发育特征[J]. 天然气工业,2023,43(3):23-33.YU Z,HUANG Z L,LI W L,et al. Lithofacies types and high-quality reservoir development characteristics of marine shale in the Middle Ordovician Wulalike Formation,Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2023,43(3):23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] CUI Q Y,YANG H F,LI X Q,et al. Identification of lithofacies and prediction of mineral composition in shales:A case study of the Shahejie Formation in the Bozhong Sag[J]. Unconventional Resources,2022,2:72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.uncres.2022.09.002 [35] 刘义生,金吉能,潘仁芳,等. 渝东南盆缘转换带五峰组-龙马溪组常压页岩气保存条件评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):253-263.LIU Y S,JIN J N,PAN R F,et al. Preservation condition evaluation of normal pressure shale gas in the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations of basin margin transition zone,southeast Chongging[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: