Ore-bearing discrimination of granite rock masses in the Nanling area via data-driven models
-
摘要:
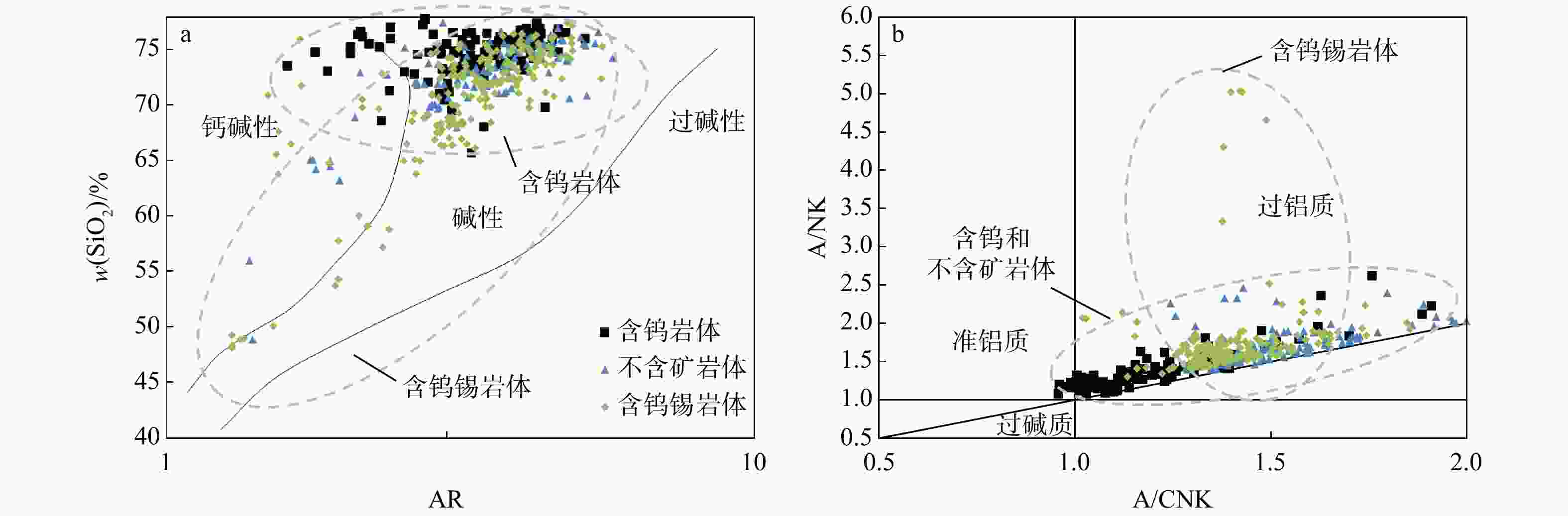
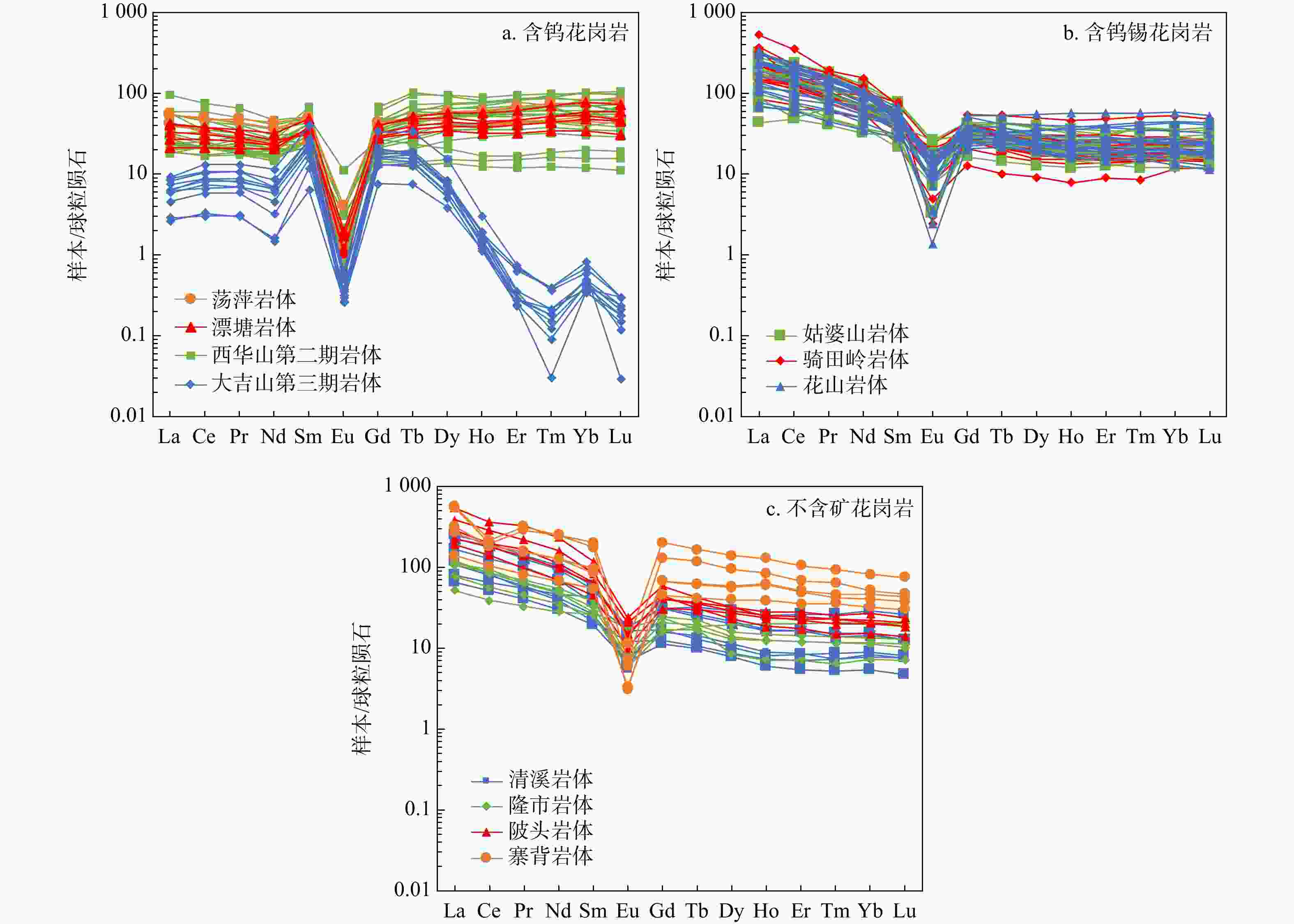
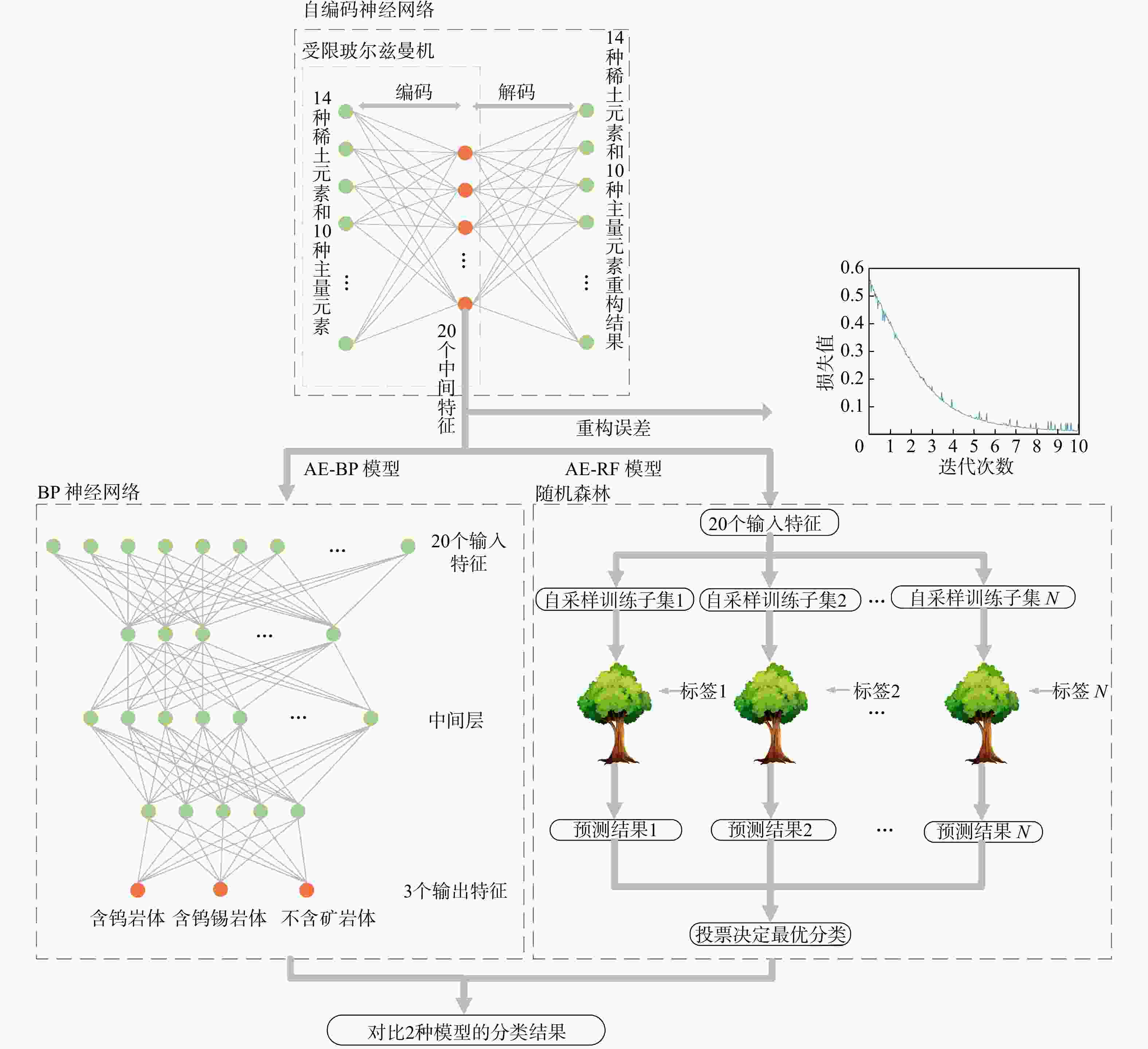
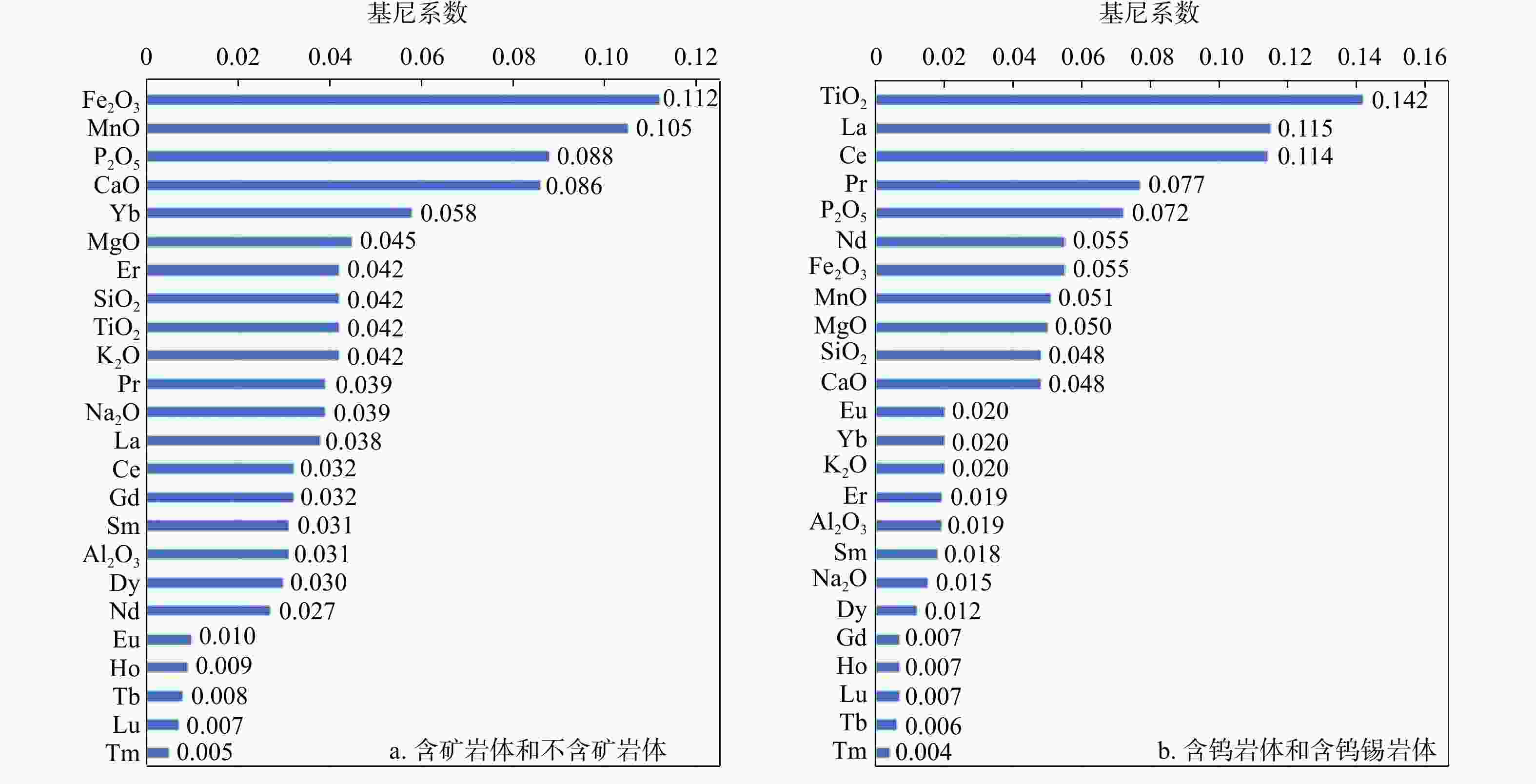
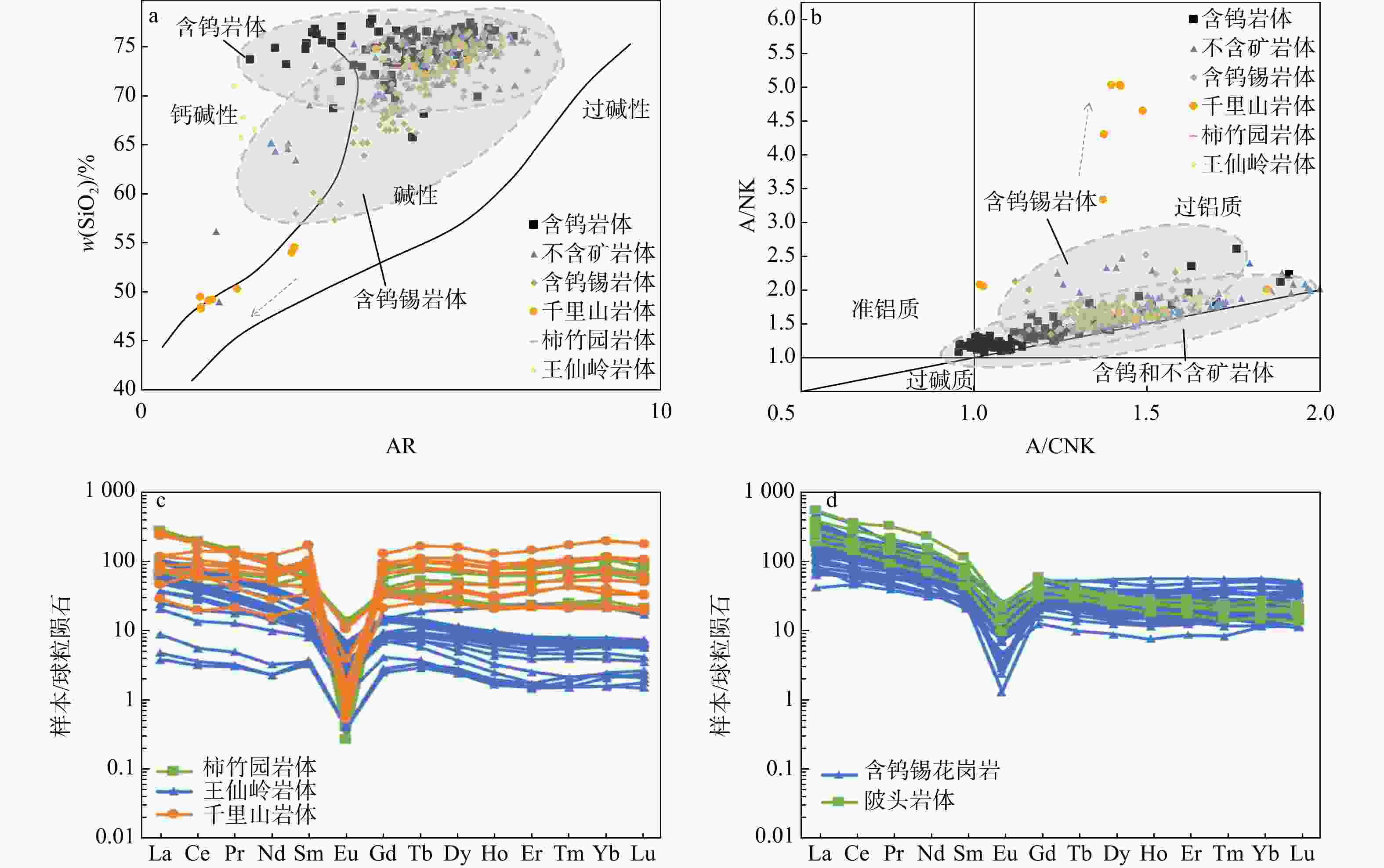
花岗岩作为成矿作用的重要参与者,对它的研究有利于了解钨锡成矿作用的地球化学过程并区分岩体的含矿性。收集了南岭地区含钨花岗岩、含钨锡花岗岩和不含矿花岗岩的主量元素和稀土元素数据,共42个岩体466组数据。总结对比了3类岩体的地球化学特征,从数据驱动和机器学习的角度区分了3类岩体的含矿性和岩石地球化学特征之间的关联,运用受限玻尔兹曼机来训练自编码神经网络以消除主量元素和稀土元素之间量级的差别,并且提取中间特征,再将中间特征输入随机森林和多层BP神经网络,建立AE-RF和AE-BP岩体含矿性分类模型。通过随机森林输出了分类特征重要性。结果表明,含钨花岗岩的演化程度最高,含钨锡花岗岩次之,不含矿花岗岩最低。2种模型在测试集上都有很高的正确率(平均>90%),并且在盲测试集上AE-BP模型的实际运用效果更好。随机选择了6组岩体作为盲测试集,20个岩体中有13个岩体正确率>80%,有2个岩体正确率为[70%,80%],有2个岩体正确率为[50%,70%)。还有4个岩体正确率<50%。铁锰磷钙镁等主量元素和轻重稀土元素是区分3类岩体的重要特征。机器学习能够很好地反映出3类花岗岩的含矿性。地球化学特征的相似性会导致模型错误分类,陂头岩体有一定的成矿潜力。铁锰磷钙镁等主量元素决定了岩体能否含矿,而轻稀土元素是区分含钨岩体和含钨锡岩体的重要指标,表明岩浆的分异演化程度决定了岩体能否含矿,而幔源物质的加入是区别岩体含钨还是含钨锡的特征。
Abstract:Objective As a significant component of mineralization, granite plays a critical role in understanding the geochemical processes of tungsten-tin mineralization and distinguishing the ore-bearing of rock masses.
Methods This study collected both major and rare earth element data from tungsten-bearing granite, tungsten-tin-bearing granite, and non-ore-bearing granite in the Nanling area, with 466 groups of datasets of 42 rock masses in total. The geochemical characteristics among three types of rock masses were summarized and compared. A data-driven approach integrating with machine learning techniques was used to explore the relationship between ore-bearing properties and geochemical characteristics. The restricted Boltzmann model was employed to train an autoencoder neural network to eliminate dimensional differences between major and rare earth elements, allowing for feature extraction. Then, these features were subsequently input into random forests and multilayer BP neural networks to develop AE-RF and AE-BP classification models for ore-bearing evaluation. The importance of classification features was derived from random forests.
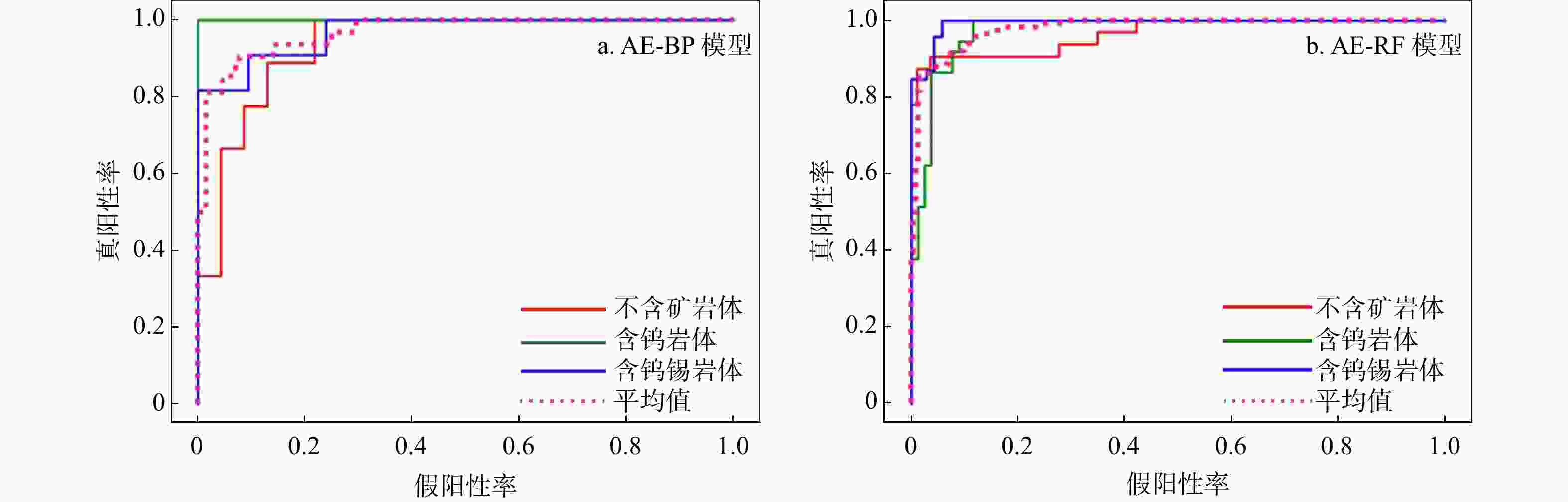
Results Results indicate that tungsten-bearing granite exhibits a slightly higher evolution degree compared against tungsten-tin-bearing granite, and non-ore-bearing granite displays the lowest evolution degree. Both two models achieved high accuracy (>90%) on testing datasets, with the better application performance of AE-BP model on the blind testing set. Six rock masses were randomly selected as the blind test set, 13 out of 20 groups of rock masses had an accuracy rate above 80%, two of them had accuracy between 70% and 80%, and two had accuracy between 50% and 70%, while rest four rock masses showed accuracy below 50%. Major elements such as iron, manganese, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium, along with light and heavy rare earth elements, were important for distinguishing the three rock mass types. Machine learning effectively identified the ore-bearing properties of these granite types.
Conclusion Results reveal that geochemical characteristic similarities and tungsten-tin type differences can lead to incorrect classifications, with the Beitou rock mass showing metallogenic potential. The major elements are pivotal in determining the ore-bearing potential, while the light rare earth content can distinguish tungsten-bearing from tungsten-tin-bearing rock masses. The differentiation and evolution degree of magma is related to ore potential, while mantle-derived material can better distinguish characteristics between tungsten and tungsten-tin contents.
-
表 1 岩体数据来源
Table 1. Rock mass data sources
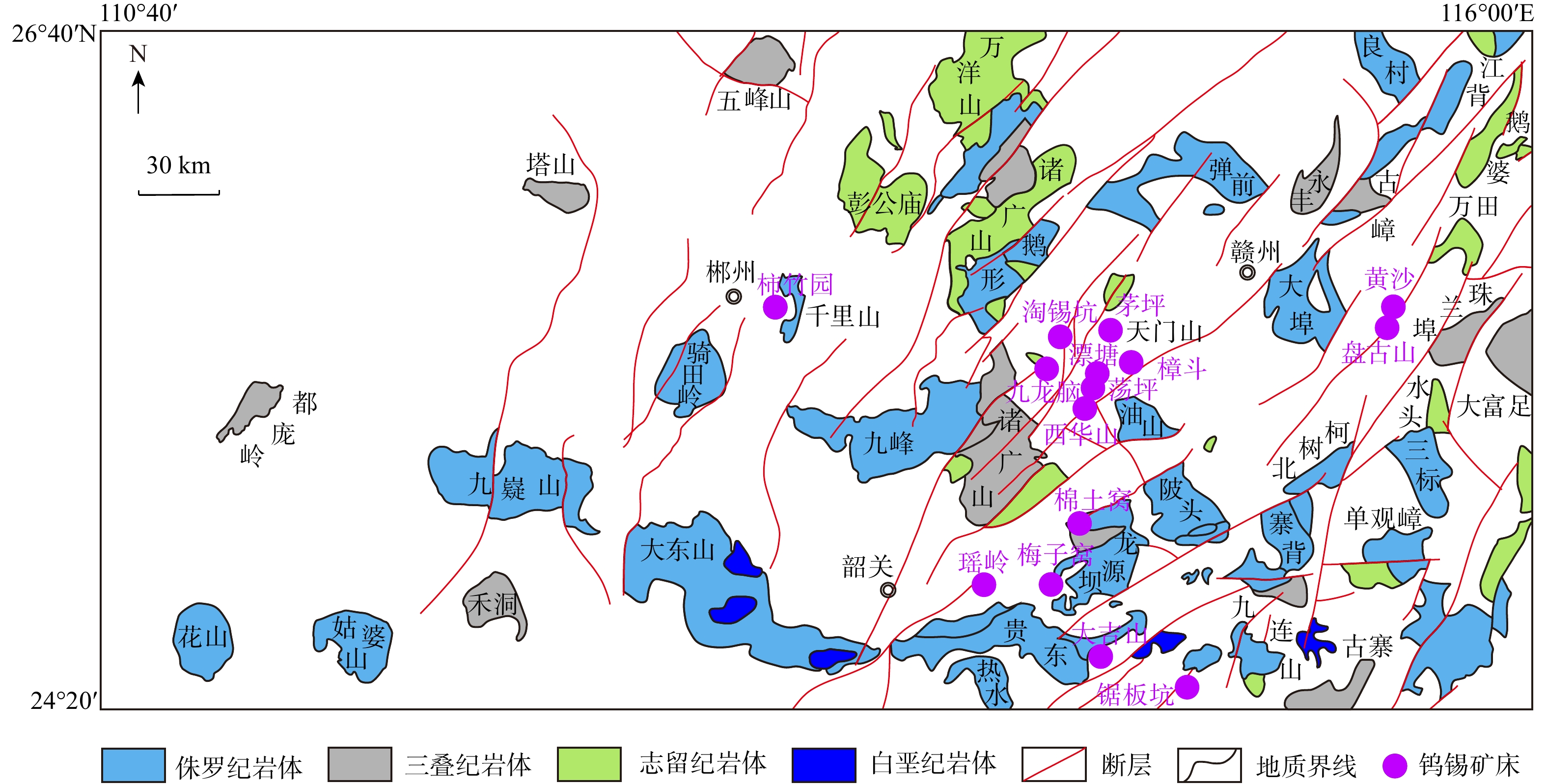
岩体名称 样本数量 岩体类型 来源 彭公庙 14 不含矿岩体 于玉帅等[38] 万洋山 13 不含矿岩体 季文兵[39] 寨背 5 不含矿岩体 陈培荣[40] 水头 2 不含矿岩体 于扬等[41] 单观嶂 4 不含矿岩体 张庆林等[42] 大富足 10 不含矿岩体 张万良[43] 广平 5 不含矿岩体 王泰山等[44] 塔山 16 不含矿岩体 杜云等[45] 摩天岭 12 不含矿岩体 徐争启等[46] 五团 16 不含矿岩体 吴疆[47] 乐洞 6 不含矿岩体 曹豪杰等[2] 鹅婆 5 不含矿岩体 郭娜欣等[48] 大吉山第一期 5 不含矿岩体 蒋国豪[49] 富城 18 不含矿岩体 任海涛[50] 永丰 5 不含矿岩体 杨世文等[51] 杨村 4 不含矿岩体 邓必荣等[52] 陂头 5 不含矿岩体 范春方等[53] 清溪 7 不含矿岩体 王丽丽[54] 隆市 5 不含矿岩体 杨世文等[51] 古嶂 3 不含矿岩体 吴兴星等[55] 西华山 11 含钨岩体 李光来[56] 牛岭-樟斗 12 含钨岩体 丰成友等[57] 九龙脑 19 含钨岩体 郭春丽等[58] 西华山第二期 11 含钨岩体 吕科等[59] 荡坪 4 含钨岩体 杨競红等[60] 漂塘 5 含钨岩体 华仁民等[61] 盘古山 7 含钨岩体 方贵聪等[62] 黄沙 11 含钨岩体 李光来[56] 大吉山第二期 2 含钨岩体 蒋国豪[49] 淘锡坑 21 含钨岩体 蔡运花等[63]、邹欣[3]、杨帆等[64] 铁山垅-生龙口 3 含钨岩体 李光来[56] 茅坪 6 含钨岩体 朱明波等[65] 红岭 13 含钨岩体 吴剑[66]、刘红娜[67] 梅子窝 16 含钨岩体 姜海等[68] 瑶岭 13 含钨岩体 李社宏等[69] 大吉山第三期 11 含钨岩体 华仁民等[61] 千里山 18 含钨锡岩体 仝立华[70] 柿竹园 7 含钨锡岩体 甘秋玲[71] 姑婆山 28 含钨锡岩体 刘风雷[72]、冯佐海[73] 花山 50 含钨锡岩体 顾晟彦等[74]、张雪峰等[75]、
姚巍等[76]、秦拯纬等[77]骑田岭 19 含钨锡岩体 李晓敏等[78]、李超[79] 王仙岭 19 含钨锡岩体 徐慢[80] 表 2 2种模型测试集分类正确率
Table 2. Classification accuracy of the two model test sets
模型 AE-BP AE-RF 准确率/% 90.51 89.57 精准率/% 88.33 89.05 召回率/% 82.83 89.33 表 3 盲测试集分类结果
Table 3. Blind test set classification results
实验编号 岩体名称 样本数量 岩体类别 AE-BP正确率/% AE-RF正确率/% BP正确率/% 实验一 彭公庙 14 不含矿岩体 100.0 71.4 85.0 西华山 11 含钨岩体 90.9 90.9 81.8 柿竹园 7 含钨锡岩体 42.9 14.3 57.1 实验二 万洋山 13 不含矿岩体 84.6 69.2 76.9 牛岭-樟斗 12 含钨岩体 100.0 100.0 58.3 姑婆山超单元 13 含钨锡岩体 76.9 0 76.9 实验三 鹅婆 5 不含矿岩体 80.0 80.0 100.0 永丰 5 不含矿岩体 100.0 40.0 80.0 大吉山第二、三期 13 含钨岩体 100.0 100.0 83.3 花山超单元 10 含钨锡岩体 70.0 0 70.0 实验四 五团 16 不含矿岩体 68.8 93.8 62.5 黄沙 11 含钨岩体 90.9 100.0 100.0 千里山 18 含钨锡岩体 11.1 0 77.8 实验五 摩天岭 12 不含矿岩体 83.3 0 91.6 红岭 13 含钨岩体 53.8 100.0 30.8 王仙岭 19 含钨锡岩体 21.1 0 0 实验六 陂头 5 不含矿岩体 40.0 40.0 0 古嶂 3 不含矿岩体 100.0 100.0 100.0 瑶岭 13 含钨岩体 84.6 84.6 61.5 骑田岭 19 含钨锡岩体 84.2 54 84.2 -
[1] 赵旭辰. 赣南东固花岗岩体的年代学、成因及构造背景研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2017.ZHAO X C. Chronology,genesis and tectonic setting of Donggu granite in southern Jiangxi Province[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 曹豪杰,黄乐真,刘国安,等. 诸广山南体乐洞花岗岩的地球化学特征与成因研究[J]. 矿物岩石,2018,38(3):19-27.CAO H J,HUANG L Z,LIU G A,et al. Studies on the geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Ledong granite batholiths in southern Zhuguang Mountians[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,2018,38(3):19-27. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 邹欣. 江西淘锡坑钨矿地球化学特征及成因研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2006.ZOU X. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Taoxikeng tungsten mine in Jiangxi Province[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2006. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 邵飞,许健俊,张展适,等. 江西于都马岭岩体地球化学特征及其找矿意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2014,33(4):19-23.SHAO F,XU J J,ZHANG Z S,et al. Geochemical characteristics and prospecting significance of Maling intrusion in Yudu County,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2014,33(4):19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] JIANG S Y,YU J M,LU J J. Trace and rare-earth element geochemistry in tourmaline and cassiterite from the Yunlong tin deposit,Yunnan,China:Implication for migmatitic-hydrothermal fluid evolution and ore genesis[J]. Chemical Geology,2004,209(3/4):193-213. [6] LECUMBERRI-SANCHEZ P,VIEIRA R,HEINRICH C A,et al. Fluid-rock interaction is decisive for the formation of tungsten deposits[J]. Geology,2017,45(7):579-582. doi: 10.1130/G38974.1 [7] LI X,ZHAO K D,JIANG S Y,et al. In-situ U-Pb geochronology and sulfur isotopes constrain the metallogenesis of the giant Neves Corvo deposit,Iberian Pyrite Belt[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2019,105:223-235. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.023 [8] NI P,WANG X D,WANG G G,et al. An infrared microthermometric study of fluid inclusions in coexisting quartz and wolframite from Late Mesozoic tungsten deposits in the Gannan metallogenic belt,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2015,65:1062-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.007 [9] WOLF M,ROMER R L,FRANZ L,et al. Tin in granitic melts:The role of melting temperature and protolith composition[J]. Lithos,2018,310/311:20-30. [10] YANG Y F,LI N,CHEN Y J. Fluid inclusion study of the Nannihu giant porphyry Mo-W deposit,Henan Province,China:Implications for the nature of porphyry ore-fluid systems formed in a continental collision setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2012,46:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.02.003 [11] 王硕儒,葛宗侠. 鄂东南中酸性小岩体含矿性评价的模糊聚类法[J]. 物探与化探,1990,14(1):63-68.WANG S R,GE Z X. The application of fuzzy cluster method to the evaluation of ore potentialitt for intermediate-acid small rock bodies in southeastern Hubei[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,1990,14(1):63-68. (in Chinese). (in Chinese with English abstract [12] BALLOUARD C,BRANQUET Y,TARTÈSE R,et al. Nb-Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites:A marker of the magmatic-hydrothermal transition:Reply[J]. Geology,2016,44(7):e395. doi: 10.1130/G38169Y.1 [13] CHEN J F,SHENG D,SHAO Y J,et al. Silurian S-type granite-related W-(Mo) mineralization in the Nanling Range,South China:A case study of the Pingtan W-(Mo) deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2019,107:186-200. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.020 [14] LINNEN R L,KEPPLER H. Melt composition control of Zr/Hf fractionation in magmatic processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2002,66(18):3293-3301. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00924-9 [15] YUAN S D,WILLIAMS-JONES A E,ROMER R L,et al. Protolith-related thermal controls on the decoupling of Sn and W in Sn-W metallogenic provinces:Insights from the Nanling region,China[J]. Economic Geology,2019,114(5):1005-1012. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4669 [16] 陈骏,陆建军,陈卫锋,等. 南岭地区钨锡铌钽花岗岩及其成矿作用[J]. 高校地质学报,2008,14(4):459-473.CHEN J,LU J J,CHEN W F,et al. W-Sn-Nb-Ta-bearing granites in the Nanling Range and their relationship to metallogengesis[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2008,14(4):459-473. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 吴福元,郭春丽,胡方泱,等. 南岭高分异花岗岩成岩与成矿[J]. 岩石学报,2023,39(1):1-36. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.01.01WU F Y,GUO C L,HU F Y,et al. Petrogenesis of the highly fractionated granites and their mineralizations in Nanling Range,South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2023,39(1):1-36. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.01.01 [18] 赵禹. 花岗岩体钨锡成矿能力的地质地球化学判别标志:以湘东南地区为例[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2015.ZHAO Y. Geological and geochemical criteria of tungsten-tin mineralization ability of granite bodies:A case study of southeastern Hunan[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 柏道远,贾宝华,李金冬,等. 区域构造体制对湘东南印支期与燕山早期花岗岩成矿能力的重要意义:以千里山岩体和王仙岭岩体为例[J]. 矿床地质,2007,26(5):487-500.BAI D Y,JIA B H,LI J D,et al. Important significance of regional tectonic regime to metallogenic capacity of Indosinian and Early Yanshanian granites in southeastern Hunan:A case study of Qianlishan and Wangxianling plutons[J]. Mineral Deposits,2007,26(5):487-500. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 王汝成,谢磊,陈骏,等. 南岭中段花岗岩中榍石对锡成矿能力的指示意义[J]. 高校地质学报,2011,17(3):368-380.WANG R C,XIE L,CHEN J,et al. Titanite as an indicator mineral of tin mineralizing potential of granites in the middle Nanling Range[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2011,17(3):368-380. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 王怀涛,罗建民,王金荣,等. 基于大数据的基性-超基性岩定量分类及成矿预测研究:以北山地区为例[J]. 岩石学报,2018,34(11):3195-3206.WANG H T,LUO J M,WANG J R,et al. Quantitative classification and metallogenic prognosis of basic-ultrabasic rocks based on big data:Taking the Beishan area as an example[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2018,34(11):3195-3206. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 肖毅,董方灵. 多元统计分析在超基性岩体含矿性评价中的应用[J]. 科技信息,2009(7):336-337.XIAO Y,DONG F L. The application of multivariate statistical analysis in mineralization assessment of ultrabasic rocks[J]. Science & Technology Information,2009(7):336-337. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] GE C,HUO J J,GU H O,et al. Tectonic discrimination and application based on convolution neural network and incomplete big data[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2021,220:106662. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106662 [24] PETRELLI M,PERUGINI D. Solving petrological problems through machine learning:The study case of tectonic discrimination using geochemical and isotopic data[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2016,171(10):81. doi: 10.1007/s00410-016-1292-2 [25] UEKI K,HINO H,KUWATANI T. Geochemical discrimination and characteristics of magmatic tectonic settings:A machine-learning-based approach[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2018,19(4):1327-1347. [26] WANG Y,QIU K F,MÜLLER A,et al. Machine learning prediction of quartz forming-environments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2021,126(8):e2021JB021925. doi: 10.1029/2021JB021925 [27] ZHONG R C,DENG Y,YU C. Multi-layer perceptron-based tectonic discrimination of basaltic rocks and an application on the Paleoproterozoic Xiong'er volcanic province in the North China Craton[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2021,149:104717. [28] 第鹏飞,王金荣,张旗,等. 玄武岩构造环境判别图评估:全体数据研究的启示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2017,36(6):891-896.DI P F,WANG J R,ZHANG Q,et al. The evaluation of basalt tectonic discrimination diagrams:Constraints on the research of global basalt data[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2017,36(6):891-896. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 韩帅,李明超,任秋兵,等. 基于大数据方法的玄武岩大地构造环境智能挖掘判别与分析[J]. 岩石学报,2018,34(11):3207-3216. HAN S,LI M C,REN Q B,et al. Intelligent determination and data mining for tectonic settings of basalts based on big data methods[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2018,34(11):3207-3216. (in Chinese with English abstract). [30] 张旗,王金荣,陈万峰,等. 利用大数据方法研究玄武岩构造环境判别图[C]. 西安:[出版社不详],2017.ZHANG Q,WANG J R,CHEN W F,et al. The discriminant map of basalt tectonic environment is studied by big data method[C]// China Society of Mineral Geochemistry . The 9th National Member Congress and the 16th Annual Conference of Chinese Society for Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry. Xi'an:[S. n. ],2017. (in Chinese) [31] HASTEROK D,GARD M,BISHOP C M B,et al. Chemical identification of metamorphic protoliths using machine learning methods[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2019,132:56-68. [32] GREGORY D D,CRACKNELL M J,LARGE R R,et al. Distinguishing ore deposit type and barren sedimentary pyrite using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry trace element data and statistical analysis of large data sets[J]. Economic Geology,2019,114(4):771-786. [33] HU B,ZENG L P,LIAO W,et al. The origin and discrimination of high-Ti magnetite in magmatic-hydrothermal systems:Insight from machine learning analysis[J]. Economic Geology,2022,117(7):1613-1627. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4946 [34] LI X M,ZHANG Y X,LI Z K,et al. Discrimination of Pb-Zn deposit types using sphalerite geochemistry:New insights from machine learning algorithm[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2023,14(4):101580. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101580 [35] ZHONG R C,DENG Y,LI W B,et al. Revealing the multi-stage ore-forming history of a mineral deposit using pyrite geochemistry and machine learning-based data interpretation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,133:104079. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104079 [36] 卢友月,付建明,程顺波,等. 南岭成矿带钨锡矿找矿远景区划分[J]. 矿物学报,2015,35(增刊1):907.LU Y Y,FU J M,CHENG S B,et al. Division of prospecting areas for tungsten-tin deposits in Nanling metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2015,35(S1):907. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 华仁民,陈培荣,张文兰,等. 南岭与中生代花岗岩类有关的成矿作用及其大地构造背景[J]. 高校地质学报,2005,11(3):291-304.HUA R M,CHEN P R,ZHANG W L,et al. Metallogeneses and their geodynamic settings related to Mesozoic granitoids in the Nanling Range[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2005,11(3):291-304. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 于玉帅,周云,牛志军,等. 湖南彭公庙岩体地球化学特征、时代及钨锡成矿潜力[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2022,41(4):695-713.YU Y S,ZHOU Y,NIU Z J,et al. Geochemical characteristics,age and W-Sn metallogenic potential of Penggongmiao pluton,Hunan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2022,41(4):695-713. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 季文兵. 南岭地区万洋山岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 湖北荆州:长江大学,2017.JI W B. Chronological and geochemical characteristics of Wanyangshan rock mass in Nanling area and its geological significance[D]. Jingzhou Hubei:Yangtze University,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 陈培荣,章邦桐,孔兴功,等. 赣南寨背A型花岗岩体的地球化学特征及其构造地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,1998,14(3):289-298.CHEN P R,ZHANG B T,KONG X G,et al. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic implication of Zhaibei A-type granitic intrusives in south Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,1998,14(3):289-298.(in Chinese with English abstract [41] 于扬,陈振宇,陈郑辉,等. 赣南燕山期水头岩体的锆石铀-铅年代学研究及其含矿性评价[J]. 岩矿测试,2012,31(4):736-744.YU Y,CHEN Z Y,CHEN Z H,et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and ore-bearing properties evaluation of Yanshanian Shuitou pluton in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2012,31(4):736-744. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 张庆林,田幽军. 江西南部单观嶂复式岩体岩石谱系单位划分及其特征[J]. 东华理工学院学报(自然科学版),2006,29(增刊1):172-176.ZHANG Q L,TIAN Y J. Genealogy division and geological characteristics of complex rock body in Danguanzhang,south Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science),2006,29(S1):172-176. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 张万良. 赣南大富足岩体岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境判别[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2006,30(1):98-107.ZHANG W L. Petrogeochemistry and tectonic environment of Dafuzu rock mass in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2006,30(1):98-107. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] 王泰山,杨启军,鲁海峰,等. 广西佛子冲广平岩体成因及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石,2016,36(4):86-94.WANG T S,YANG Q J,LU H F,et al. The genesis and geological implication of the Guangping syenogranite in Fozichong,Guangxi[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,2016,36(4):86-94. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] 杜云,罗小亚,黄革非,等. 湖南塔山岩体岩石学、地球化学、U-Pb年代学特征及其形成构造背景[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(6):50-61.DU Y,LUO X Y,HUANG G F,et al. Petrological,geochemical,and U-Pb geochronological characteristics and tectonic setting of Tashan pluton formation in Hunan Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(6):50-61. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] 徐争启,宋昊,尹明辉,等. 华南地区新元古代花岗岩铀成矿机制:以摩天岭花岗岩为例[J]. 岩石学报,2019,35(9):2695-2710.XU Z Q,SONG H,YIN M H,et al. Uranium metallogenic mechanism of Neoproterozoic granites in South China:A case study from the Motianling granite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2019,35(9):2695-2710. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] 吴疆. 南岭湘桂交界地区印支期花岗岩成因及其地质意义[D]. 广西桂林:桂林理工大学,2022.WU J. Genesis of Indosinian granites in the border area of Hunan and Guangxi of Nanling,South China and their geological significance[D]. Guilin Guangxi:Guilin University of Technology,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [48] 郭娜欣,赵正,陈振宇,等. 赣南鹅婆岩体的年代学和岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩矿测试,2014,33(4):589-597.GUO N X,ZHAO Z,CHEN Z Y,et al. Chronology,geochemistry and geological significance of Epo granite intrusion,southern Jiangxi[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2014,33(4):589-597. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 蒋国豪. 氟、氯对热液钨、铜成矿的制约:以江西德兴铜矿、大吉山钨矿为例[D]. 贵阳:中国科学地球化学研究所,2004.JIANG G H. Chlorine and fluorine control on copper and tungsten mineralization in hydrothermal deposits[D]. Guiyang:Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2004. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] 任海涛. 江西会昌富城花岗岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[D]. 南京:南京大学,2016.REN H T. Geochronology,geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Fucheng granite from Huichang County,Jiangxi Province[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] 杨世文,楼法生,张芳荣,等. 赣南晚侏罗世铝质A型花岗岩带及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(3):12-29.YANG S W,LOU F S,ZHANG F R,et al. Late Jurassic aluminum A-type granite belt in southern Jiangxi and its geological significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(3):12-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] 邓必荣,石鉴东. 兴国杨村岩体特征及侵位机制探讨[J]. 华东地质学院学报,2000,23(2):141-145.DENG B R,SHI J D. The inquisition of character and emplacement mechanism of rock mass in Xingguo Yang Village[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute,2000,23(2):141-145. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] 范春方,陈培荣. 赣南陂头A型花岗岩的地质地球化学特征及其形成的构造环境[J]. 地球化学,2000,29(4):358-366.FAN C F,CHEN P R. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic implication of Beitou A type grantic intrusive in south Jiangxi Province[J]. Geochimica,2000,29(4):358-366. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] 王丽丽. 华南赣州地区早古生代晚期-中生代花岗岩类地球化学与岩石成因[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2015.WANG L L. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Early Paleozoic-Mesozoic granites in Ganzhou,Jiangxi Province,South China Block[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2015. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] 吴兴星,鞠鹏. 赣中早古生代古嶂花岗岩体的岩石学特征及其成因[J]. 四川地质学报,2019,39(4):546-549.WU X X,JU P. Petrology and genesis of the Early Paleozoic Guzhang granite intrusive in central Jiangxi[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2019,39(4):546-549. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] 李光来. 赣南及邻区燕山期花岗岩演化与钨成矿作用[D]. 南京:南京大学,2011.LI G L. The evolution of Yanshanian granite and tungsten mineralization in southern Jiangxi Province and adjacent region[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2011. (in Chinese with English abstract [57] 丰成友,许建祥,曾载淋,等. 赣南天门山-红桃岭钨锡矿田成岩成矿时代精细测定及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报,2007,81(7):952-963.FENG C Y,XU J X,ZENG Z L,et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating in Tianmenshan-Hongtaoling tungsten-tin orefield,southern Jiangxi Province,China,and its geological implication[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2007,81(7):952-963. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] 郭春丽,陈毓川,黎传标,等. 赣南晚侏罗世九龙脑钨锡铅锌矿集区不同成矿类型花岗岩年龄、地球化学特征对比及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报,2011,85(7):1188-1205.GUO C L,CHEN Y C,LI C B,et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating,geochemistry,Sr-Nd isotopic analysis of the Late Jurassic granitoids in the Jiulongnao W-Sn-Pb-Zn ore-concentrated areas in Jiangxi Province and their geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2011,85(7):1188-1205. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] 吕科,王勇,肖剑. 西华山复式花岗岩株地球化学特征及构造环境探讨[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,34(2):117-128.LV K,WANG Y,XIAO J. Geochemistry characteristics of Xihuashan granite and structural environment discussion[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science),2011,34(2):117-128. (in Chinese with English abstract [60] 杨競红,陈欣阳,王旭东. 江西荡萍钨矿花岗岩年代学与成矿流体地球化学研究[J]. 矿物学报,2009,29(增刊1):339-340.YANG J H,CHEN X Y,WANG X D. Study on granite chronology and ore-forming fluid geochemistry in Dangping tungsten deposit,Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2009,29(S1):339-340. (in Chinese with English abstract [61] 华仁民,张文兰,陈培荣,等. 赣南大吉山与漂塘花岗岩及有关成矿作用特征对比[J]. 高校地质学报,2003,9(4):609-619.HUA R M,ZHANG W L,CHEN P R,et al. Comparison in the characteristics,origin,and related metallogeny between granites in Dajishan and Piaotang,southern Jiangxi,China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2003,9(4):609-619. (in Chinese with English abstract [62] 方贵聪,陈毓川,陈郑辉,等. 赣南盘古山钨矿隐伏花岗岩体岩石学与地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质,2016,43(5):1558-1568.FANG G C,CHEN Y C,CHEN Z H,et al. Petrology and geochemistry of granite in the Pangushan tungsten deposit,south Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China,2016,43(5):1558-1568. (in Chinese with English abstract [63] 蔡运花,蔡永丰. 赣南淘锡坑花岗岩地球化学特征及其对钨成矿作用的意义[J]. 地质与资源,2016,25(3):275-280.CAI Y H,CAI Y F. Geochemical characteristics and mineralization significance of the Taoxikeng granite in southern Jiangxi Province,China[J]. Geology and Resources,2016,25(3):275-280. (in Chinese with English abstract [64] 杨帆,肖荣阁,白凤军,等. 江西赣州淘锡坑钨矿床稀土地球化学研究[J]. 地质与勘探,2013,49(6):1139-1152.YANG F,XIAO R G,BAI F J,et al. REE geochemistry of the Taoxikeng tungsten deposit in Ganzhou,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology and Exploration,2013,49(6):1139-1152. (in Chinese with English abstract [65] 朱明波,谭红艳,何登华,等. 江西茅坪钨锡矿床花岗岩地球化学特征[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分),2012,64(5):34-39.ZHU M B,TAN H Y,HE D H,et al. Geochemical characteristics of Maoping tungsten-tin deposit granite in Jiangxi Province[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section),2012,64(5):34-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [66] 吴剑. 广东红岭岩体型钨矿床热液蚀变过程中元素的活动性研究[J]. 矿产与地质,2018,32(1):48-59.WU J. Study on the element activity during hydrothermal alteration process of Hongling tungsten deposit in Guangdong[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2018,32(1):48-59. (in Chinese with English abstract [67] 刘红娜. 红岭钨矿区花岗岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 西部探矿工程,2021,33(5):165-169.LIU H N. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of granite in Hongling tungsten deposit[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2021,33(5):165-169. (in Chinese with English abstract [68] 姜海,李文铅. 粤北梅子窝钨矿二长花岗岩的发现及其地球化学特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2014,38(1):197-207.JIANG H,LI W Q. Geochemistry of the Meiziwo monzogranite,northern Guangdong[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2014,38(1):197-207. (in Chinese with English abstract [69] 李社宏,李文铅,丁玉进,等. 瑶岭钨矿白基寨花岗岩地质特征及成矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2010,34(1):139-146.LI S H,LI W Q,DING Y J,et al. Geological characteristics of the Baijizhai granite and its metallogenetic significance in the Yaoling tungsten deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2010,34(1):139-146. (in Chinese with English abstract [70] 仝立华. 湖南郴州千里山含钨锡金属花岗岩岩石成因及成矿模式探讨[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2013.TONG L H. The petrogenesis and metallogenetic model of Qianlishan tin-tungsten bearing granite in Hunan,China[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [71] 甘秋玲. 湖南宝山、黄沙坪及柿竹园花岗质岩石岩石学特征及成矿研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2014.GAN Q L. The comparative study of granitic rocks petrological characteristic and metallogenic in Baoshan,Huangshaping and Shizhuyuan[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing ),2014. (in Chinese with English abstract [72] 刘风雷. 广西姑婆山花岗岩暗色包体年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 广西桂林:桂林理工大学,2021.LIU F L. The chronological and geochemical characteristics of the dark enclave of the Guposhan granite in Guangxi and its geological significances[D]. Guilin Guangxi:Guilin University of Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [73] 冯佐海. 广西姑婆山-花山花岗岩体侵位过程及构造解析[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2003.FENG Z H. Emplacement process and structural analysis of Guposhan-Huashan granitic pluton,Guangxi[D]. Changsha:Central South University,2003. (in Chinese with English abstract [74] 顾晟彦,华仁民,戚华文. 广西花山-姑婆山燕山期花岗岩的地球化学特征及成因研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2006,25(2):97-109.GU S Y,HUA R M,QI H W. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Yanshanian Huashan-Guposhan granites in Guangxi[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2006,25(2):97-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [75] 张雪峰,刘晓东,刘剑钊. 广西花山花岗岩体地球化学特征及产铀潜力分析[J]. 地质与勘探,2011,47(6):1051-1058.ZHANG X F,LIU X D,LIU J Z. Geochemical characteristics of the Huashan granites in Guangxi Province and their uranium-bearing potential[J]. Geology and Exploration,2011,47(6):1051-1058. (in Chinese with English abstract [76] 姚巍,陈珲,马明杰. 粤北花山岩体地球化学特征及成因研究[J]. 四川地质学报,2016,36(2):217-220.YAO W,CHEN H,MA M J. A study of geochemistry and genesis of the Huashan rock mass in north Guangdong[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2016,36(2):217-220. (in Chinese with English abstract [77] 秦拯纬,付建明,卢友月,等. 粤北早古生代花山岩体的成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(3):1-12.QIN Z W,FU J M,LU Y Y,et al. Petrogenesis and geological significance of the Early Paleozoic Huashan pluton in northern Guangdong[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(3):1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract [78] 李晓敏,胡瑞忠,毕献武,等. 湘南骑田岭花岗岩岩体地球化学特征及锡成矿潜力[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2010,40(1):80-92.LI X M,HU R Z,BI X W,et al. Geochemistry and tin metallogenic potential for Qitianling granite mass in southern Hunan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2010,40(1):80-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [79] 李超. 湖南骑田岭花岗岩体岩石学、岩石地球化学及其大地构造意义[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2019.LI C. Petrology,petro-geochemistry and tectonic significance of the Qitianling granite body,Hunan Province[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [80] 徐慢. 南岭地区王仙岭复式岩体地球化学及岩石成因[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学,2020.XU M. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Wangxianling compound granitoid in Nanling area[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [81] SHUKI R,林磊. 人工神经网络在非线性特征标定中的应用[J]. 石油物探译丛,1994(6):10-16.SHUKI R,LIN L. Application of artificial neural network in nonlinear feature calibration[J]. Geophysical Exploration of Petroleum,1994(6):10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [82] 黄庭. 基于多目标优化的矿产资源经济评价模型及其实证研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2010.HUANG T. Multi-objective optimize mineral resources economic assessment models and their applications[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geoscienses (Wuhan). (in Chinese with English abstract [83] GORDON A D,BREIMAN L,FRIEDMAN J H,et al. Classification and regression trees[J]. Biometrics,1984,40(3):874. [84] LOUPPE G. Understanding random forests:From theory to practice[D]. 2014. [85] 陈培荣,周新民,张文兰,等. 南岭东段燕山早期正长岩-花岗岩杂岩的成因和意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2004,34(6):493-503.CHEN P R,ZHOU X M,ZHANG W L,et al. The genesis and significance of the Early Yanshanian syenite-granite complex in the eastern section of Nanling Mountains[J]. Chinese Science (Earth Science),2004,34(6):493-503. (in Chinese with English abstract [86] 章邦桐,吴俊奇,凌洪飞,等. 南岭寨背和陂头花岗岩基属印支期侵位的岩浆动力学证据及构造意义[J]. 地质找矿论丛,2011,26(2):119-130.ZHANG B T,WU J Q,LING H F,et al. Magma-dynamic evidence for Indosinian cycle emplacement of the Zhaibei and Pitou granite batholith of Nanling Range in South China and the tectonic implication[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research,2011,26(2):119-130. (in Chinese with English abstract [87] 莫柱孙,叶伯丹,潘维祖,等. 南岭花岗岩地质学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1980.MO Z S,YE B D,PAN W Z,et al. Granite geology of Nanling[M]. Beijing :Geological Publishing House,1980. (in Chinese [88] 朱年方. 红岭钨矿成矿岩体及周边岩体地球化学特征[J]. 西部资源,2021(6):133-134.ZHU N F. Geochemical characteristics of ore-forming rock mass and surrounding rock mass in Hongling tungsten deposit[J]. Western Resourses,2021(6):133-134. (in Chinese [89] 苏慧敏,蒋少涌. 赣南和赣北-皖南钨成矿带含钨花岗岩及其成矿作用特征对比研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2017,47(11):1292-1308. doi: 10.1360/N072016-00304SU H M,JIANG S Y. A comparison study of tungsten-bearing granite and related mineralization in the northern Jiangxi-southem Anhui provinces and southern Jiangxi Province in South China[J]. Chinese Science (Earth Science),2017,47(11):1292-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/N072016-00304 [90] WATSON E B. Apatite saturation in basic to intermediate magmas[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,1979,6(12):937-940. doi: 10.1029/GL006i012p00937 [91] WATSON E B,CAPOBIANCO C J. Phosphorus and the rare earth elements in felsic magmas:An assessment of the role of apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1981,45(12):2349-2358. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90088-0 [92] GREEN T H,WATSON E B. Crystallization of apatite in natural magmas under high pressure,hydrous conditions,with particular reference to 'Orogenic' rock series[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1982,79(1):96-105. [93] HARRISON T M,WATSON E B. The behavior of apatite during crustal anatexis:Equilibrium and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1984,48(7):1467-1477. [94] WOLF M B,LONDON D. Apatite dissolution into peraluminous haplogranitic melts:An experimental study of solubilities and mechanisms[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1994,58(19):4127-4145. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90269-0 [95] 李献华,李武显,李正祥. 再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意义[J]. 科学通报,2007,52(9):981-991. doi: 10.1360/csb2007-52-9-981LI X H,LI W X,LI Z X. On the genetic types and tectonic significance of Early Yanshan granite in Nanling[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2007,52(9):981-991. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/csb2007-52-9-981 [96] 吴堑虹,周厚祥,刘飚,等. 华南与花岗岩有关的稀有金属矿床和钨锡矿床的时空分布规律及其成因联系[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):78-88.WU Q H,ZHOU H X,LIU B,et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of granite-related rare metal deposits and W-Sn deposits in South China and their genetic relationship[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):78-88. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: