Threshold model of landslide rainfall in Chongqing based on different geological environment zones
-
摘要:
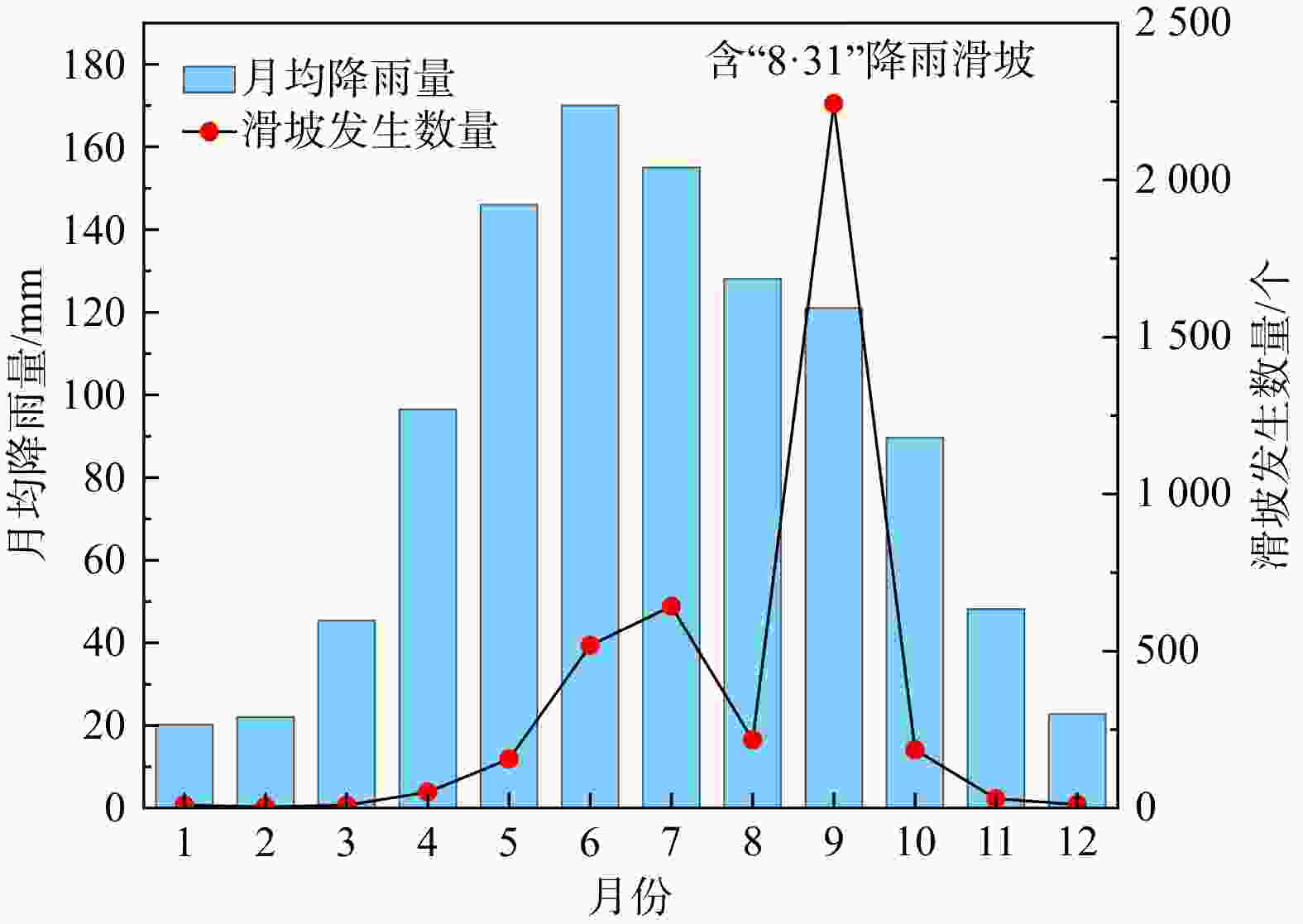
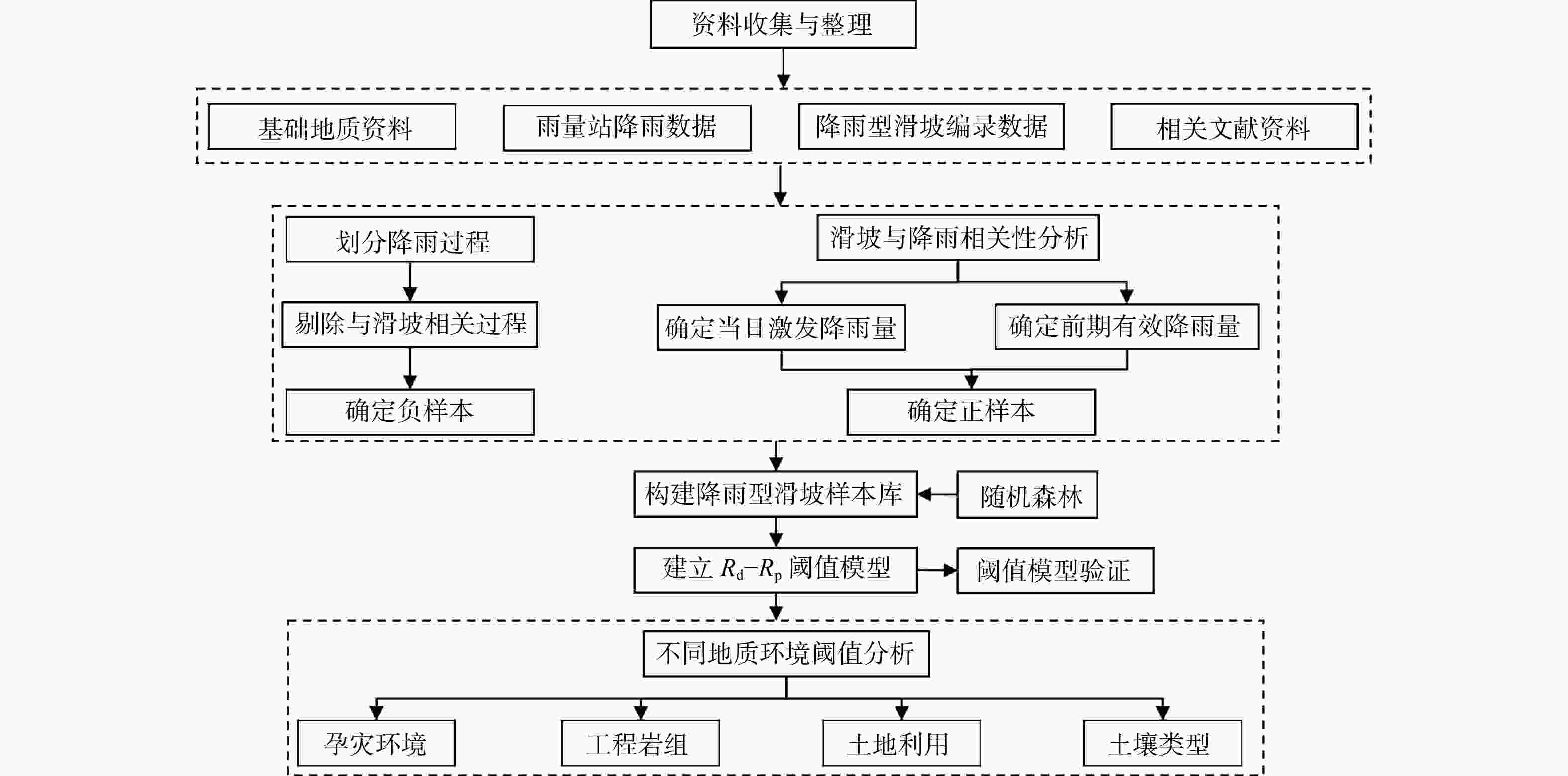
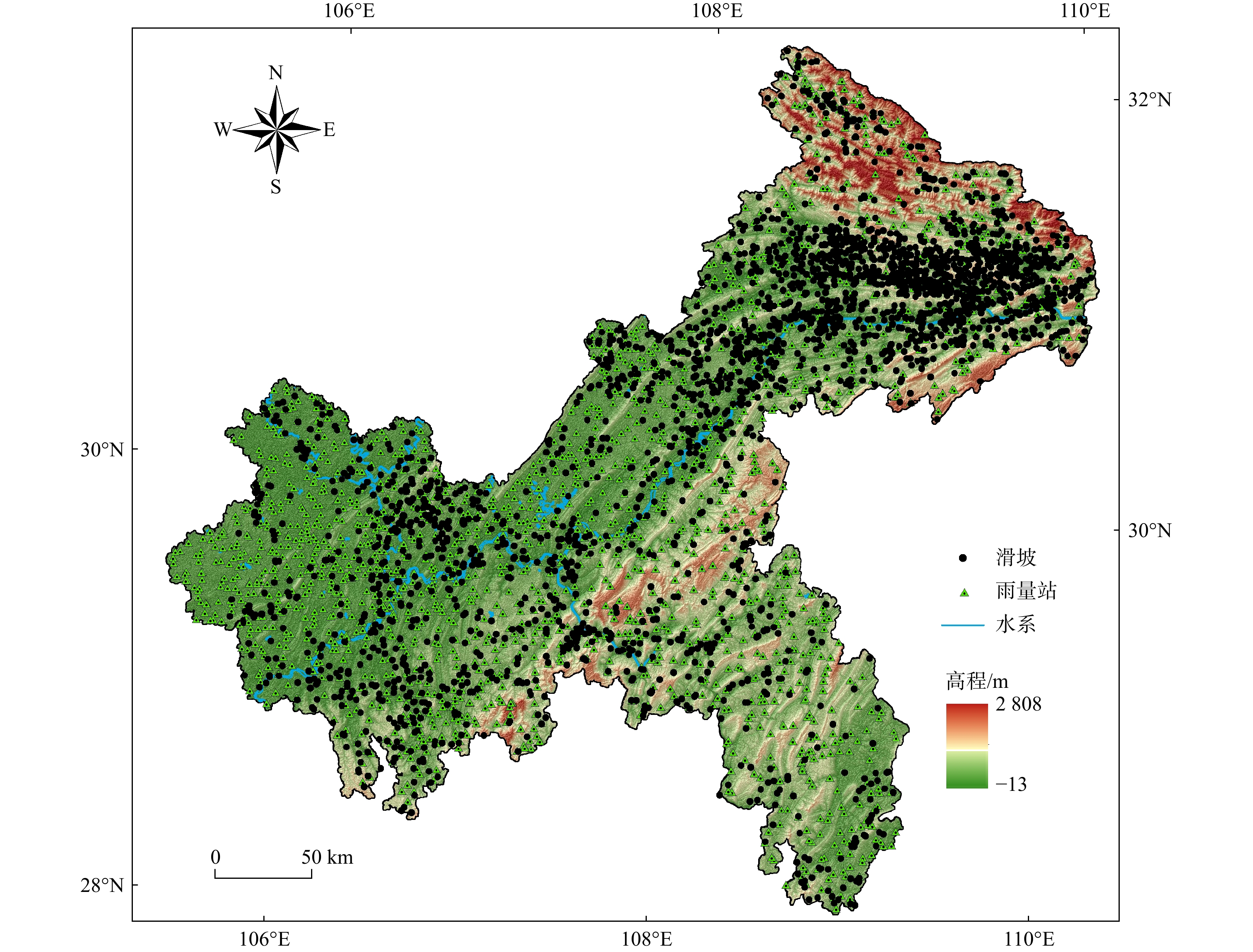
考虑区域历史滑坡的降雨特征与地质环境,构建合理的降雨阈值模型,对区域滑坡灾害的预测预报十分重要。以重庆市2013-2021年的
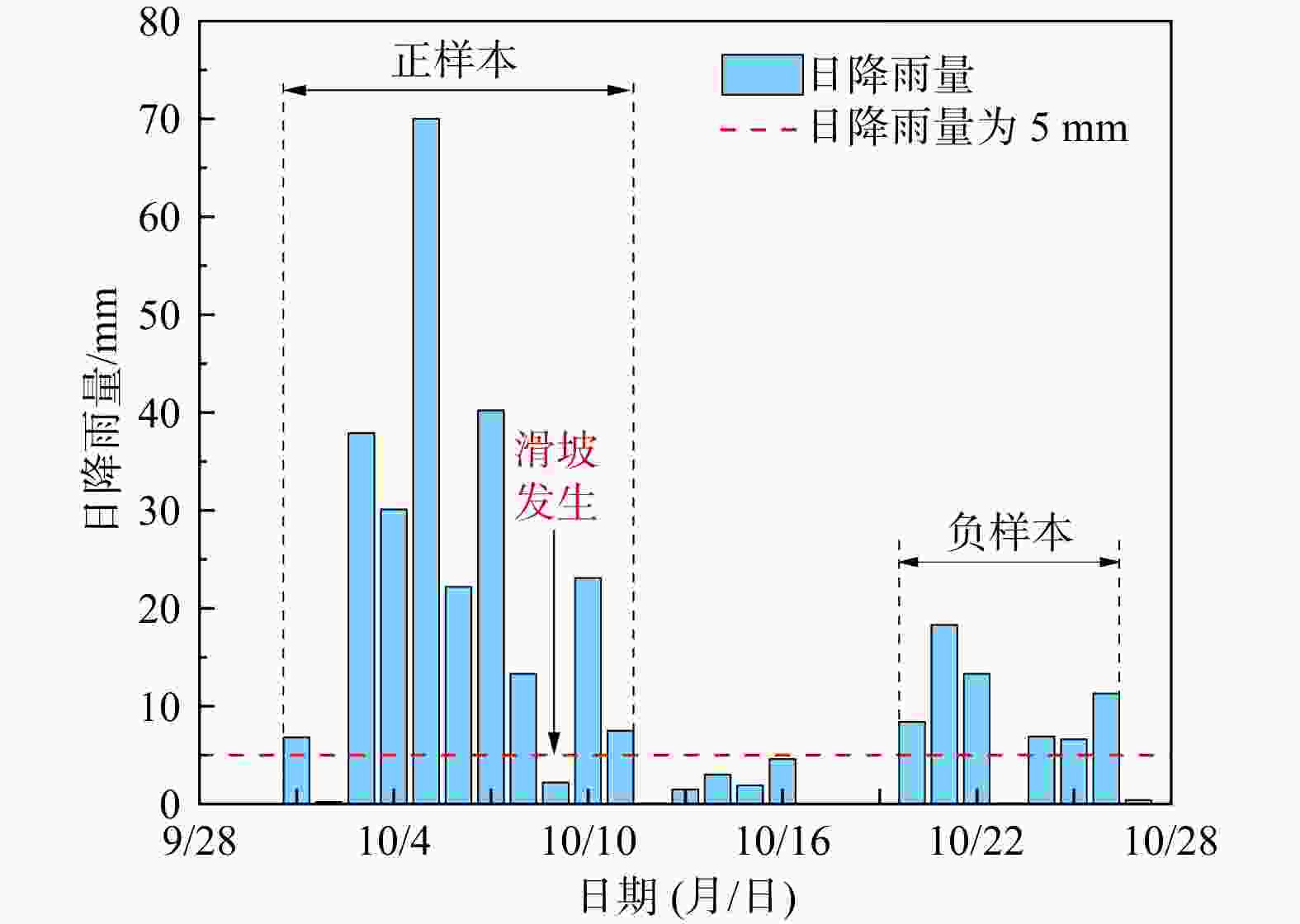
1368 个降雨型滑坡为研究对象,基于详细的滑坡编录数据和区域地质环境资料,划分降雨事件,构建滑坡样本库。利用随机森林(RF)算法,建立了当日激发降雨量-前期有效降雨量(R d-R p)降雨阈值模型,基于概率分级划分了不同预警等级。以中等预警概率按孕灾环境、工程岩组、土地利用和土壤类型4种地质环境分别构建了19个临界降雨阈值判据。结果表明:R d-R p阈值模型能够很好地反映当日激发降雨量和前期有效降雨量对滑坡发育的影响,且前期有效降雨量在滑坡诱发中占主导作用。不同的地质环境类型对降雨因子的敏感性不同,地质构造、岩土体工程性质、植被覆盖以及土壤性质等对滑坡发育有重要影响。以坚硬岩为主的岩组阈值高于以软弱岩为主的岩组,林地的阈值大于耕地,受人类工程活动破坏严重的区域阈值会降低。利用随机森林方法为重庆市不同地质环境分区建立了降雨阈值判据,本研究可为重庆市降雨型滑坡的气象预警管理提供新的思路与借鉴依据。Abstract:Objective Considering the rainfall characteristics and geological environment of regional landslides, constructing a reasonable rainfall threshold model is crucial for the prediction and forecasting regional landslide disasters.
Methods This study takes
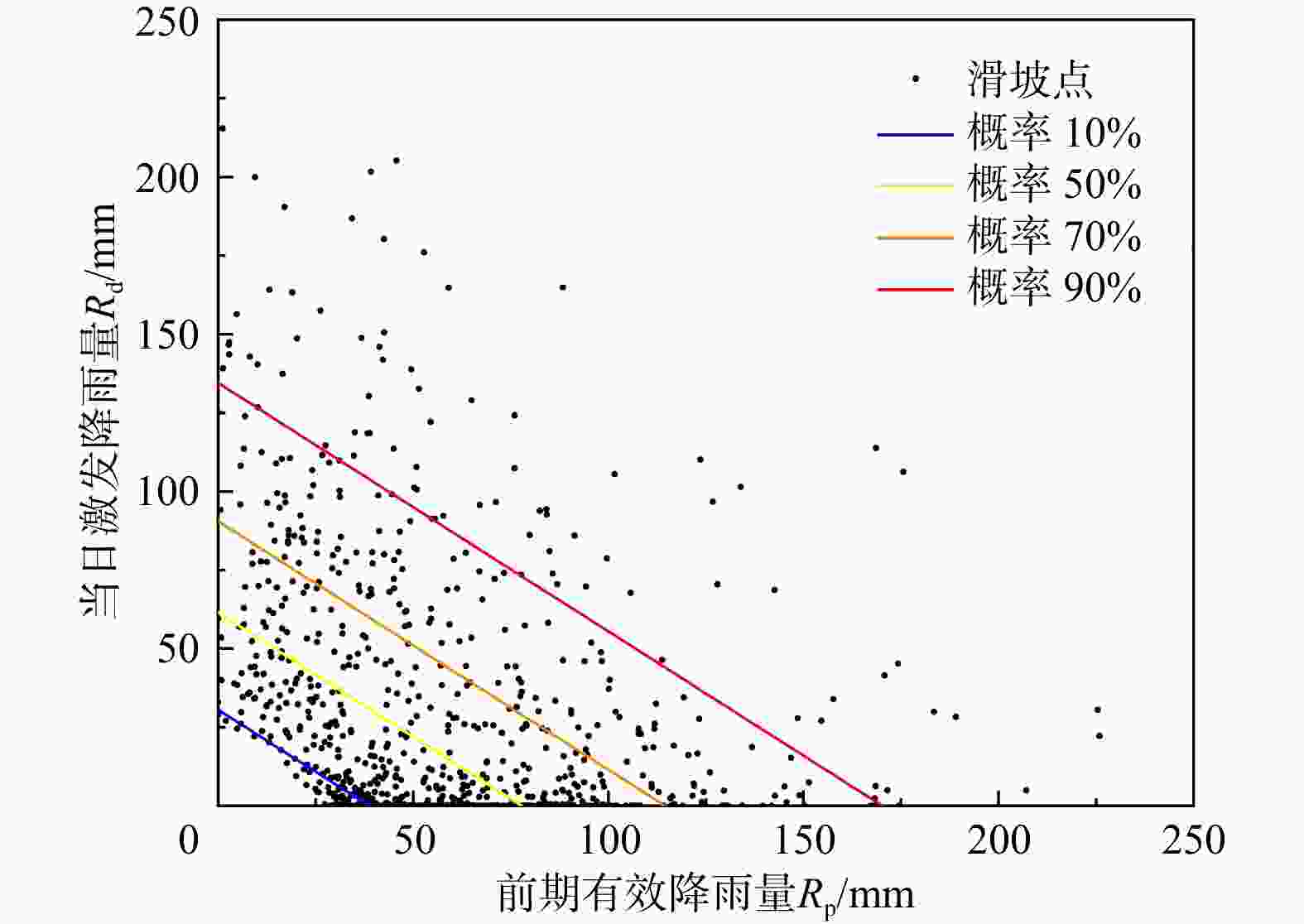
1368 rain-induced landslides in Chongqing from 2013 to 2021 as the research object. Based on detailed landslide data and regional geological environment information, rainfall events were divided and a landslide sample database was constructed. Using the random forest (RF) algorithm, a rainfall threshold model of the day's triggered rainfall-previous rainfall-previous effective rainfall (R d-R p) was established, and different warning levels were classified based on probability grading. Based on the medium early warning probability, 19 threshold criteria for critical rainfall were constructed according to four geological environments: the disaster-prone environment, engineering rock group, land use, and soil type.Results The results show that the
R d-R p threshold model can effectively reflect the impact of the daily excitation rainfall and the early effective rainfall on landslide development, and that early effective rainfall plays a dominant role in landslide induction. Different geological environment types show different sensitivities to rainfall factors, and geological structures, engineering properties of rock and soil masses, vegetation coverage, and soil properties have significant effects on landslide development. The threshold of rock formations dominated by hard rocks is higher than that dominated by weak rocks, and the threshold of forest land is greater than that of cultivated land. The threshold of areas severely damaged by human engineering activities will decrease.Conclusion This study can provide new ideas and references for the meteorological early warning management of rainfall-related landslide disasters in Chongqing.
-
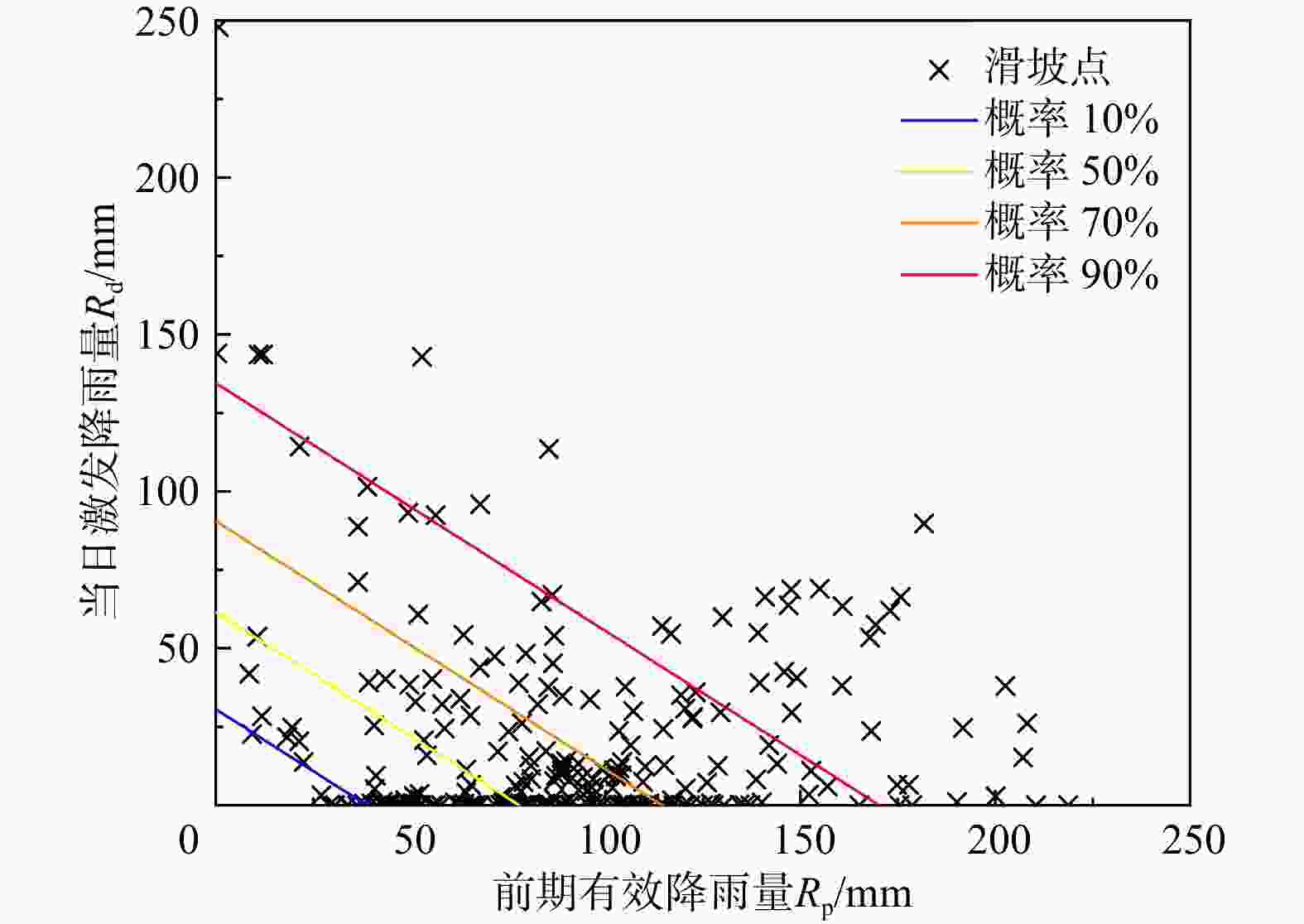
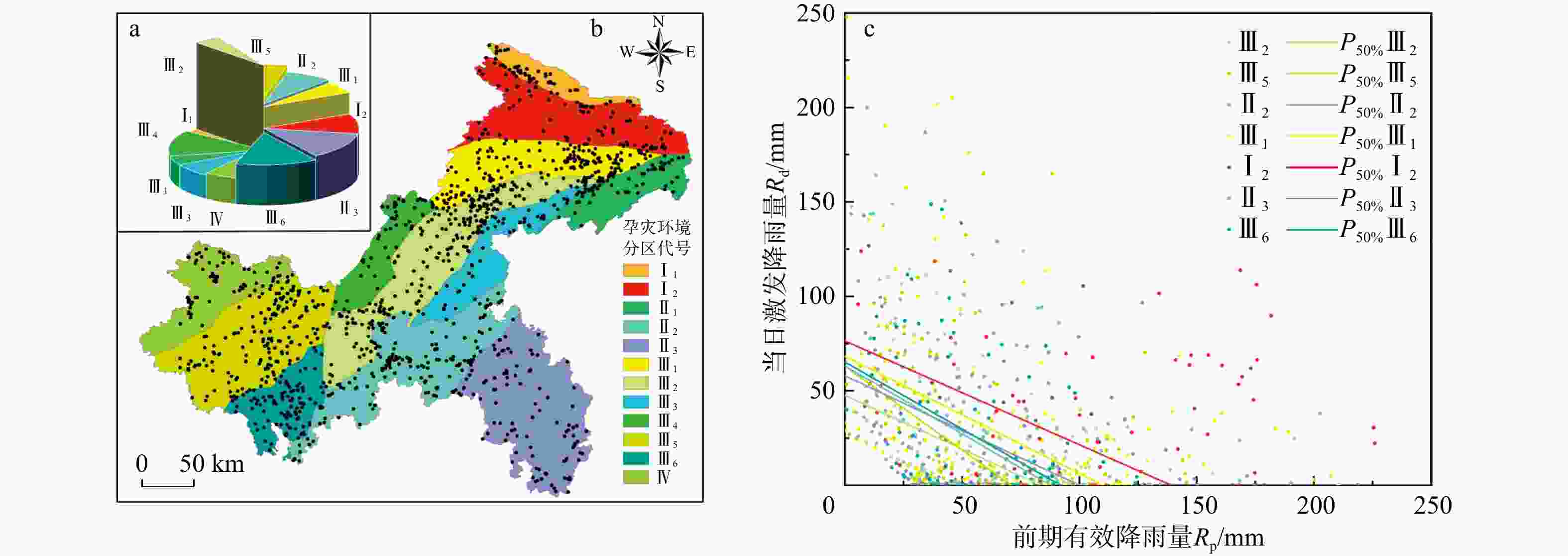
图 7 研究区不同孕灾环境下的滑坡分布及降雨阈值曲线(孕灾环境分区代号Ⅰ1~Ⅳ同表2;P50%为滑坡发生的中等概率;下同)
Figure 7. Landslide distributions and rainfall threshold curves under different disaster prone environments in the study area
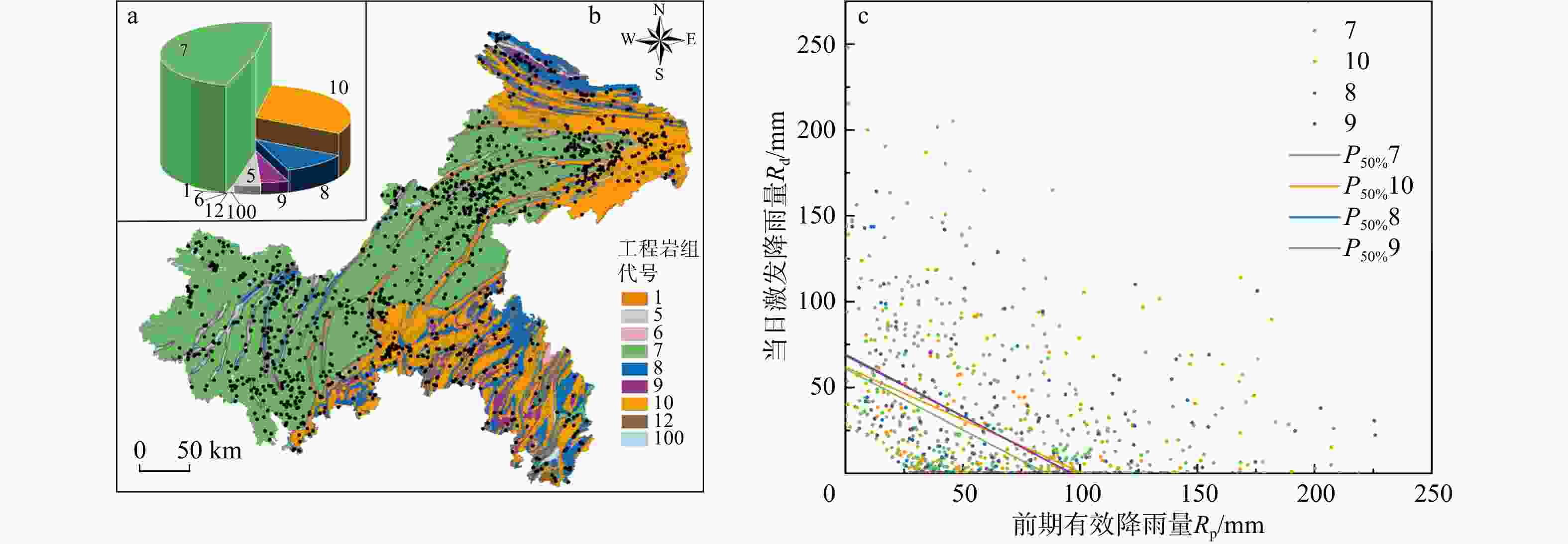
图 8 研究区不同工程岩组下的滑坡分布及降雨阈值曲线(工程岩组代号同表3)
Figure 8. Landslide distributions and rainfall threshold curves for different engineering rock formations in the study area
图 9 研究区不同土地利用下的滑坡分布及降雨阈值曲线(土地利用代号同表4)
Figure 9. Landslide distributions and rainfall threshold curves for different land uses in the study area
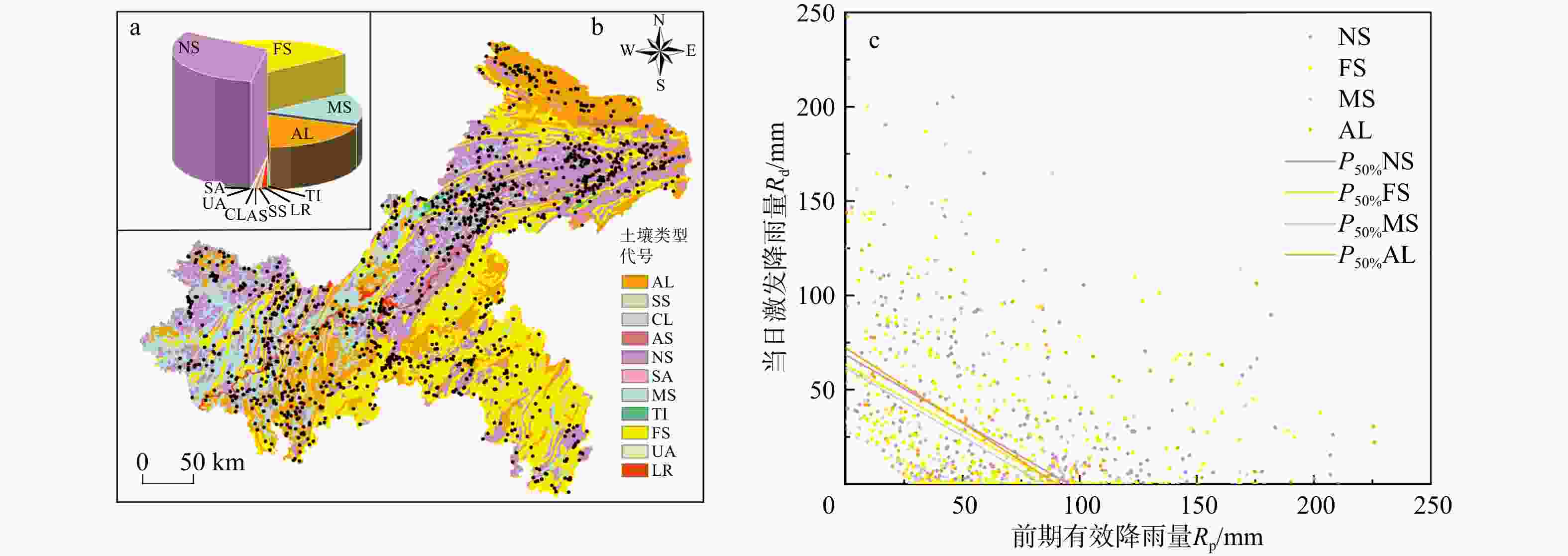
图 10 研究区不同土壤类型下的滑坡分布及降雨阈值曲线(土壤类型代号同表5)
Figure 10. Landslide distributions and rainfall threshold curves for different soil types in the study area
表 1 不同的有效降雨量系数与滑坡相关性分析
Table 1. Correlation analysis between different effective rainfall coefficients and landslides
有效降雨量系数α 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 相关性系数 0.677﹡﹡ 0.709﹡﹡ 0.714﹡﹡ 0.697﹡﹡ 0.665﹡﹡ 注:﹡﹡表示在0.01显著性水平下,显著相关 表 2 研究区不同孕灾环境下的中等概率降雨阈值判据
Table 2. Medium probability rainfall threshold criteria for different disaster prone environments in the study area
孕灾环境分区名称 分区代号 面积占比S/% 滑坡数量NL 滑坡事件NE 滑坡点分布密度/% 阈值方程 AUT/mm2 Rp截距/mm 北大巴山弱岩溶化中山崩滑流孕灾亚区 Ⅰ1 2.62 50 46 3.65 南大巴山强岩溶化中山滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅰ2 9.99 108 94 7.89 Rd=76.5−0.55Rp 5320 139.1 七曜山-巫山中山峡谷崩塌滑坡孕灾亚区 Ⅱ1 4.74 56 38 4.09 七曜山-金佛山中山峡谷崩塌滑坡孕灾亚区 Ⅱ2 7.97 168 148 12.28 Rd=63.2−0.72Rp 2773 87.78 黔江-酉阳岩溶化中山峡谷崩塌滑坡孕灾亚区 Ⅱ3 13.16 108 84 7.89 Rd=58−0.58Rp 2900 100 开州-奉节北深丘、低山滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ1 5.76 160 123 11.70 Rd=68.3−0.62Rp 3761 110.16 云阳-南川北深丘、低山滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ2 4.57 260 199 19.01 Rd=47.6−0.57Rp 1994 83.8 方斗山-七曜山中低山滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ3 6.86 57 51 4.17 梁平-垫江平行岭谷滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ4 13.01 56 55 4.09 重庆市区四山平行岭谷滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ5 11.92 184 164 13.45 Rd=63.1−0.89Rp 2237 70.9 江津-綦江平行岭谷滑坡崩塌孕灾亚区 Ⅲ6 13.89 98 87 7.16 Rd=65.3−0.71Rp 3003 91.97 渝西红层浅丘孕灾区 Ⅳ 5.50 63 52 4.61 注:AUT为曲线下面积,用以衡量阈值大小;Rp为前期有效降雨量;Rd为当日激发降雨量;下同 表 3 研究区不同工程岩组下的中等概率降雨阈值判据
Table 3. Medium probability rainfall threshold criteria for different engineering rock formations in the study area
工程岩组名称 工程岩组代号 面积占比S/% 滑坡数量NL 滑坡事件NE 滑坡点分布密度/% 阈值方程 AUT/mm2 Rp截距/mm 坚硬块状各类侵入岩岩组 1 0.03 0 0 0 以坚硬层状碎屑岩为主的岩组 5 4.45 61 58 4.46 以较坚硬层状碎屑岩为主的岩组 6 0.16 0 0 0 以软弱层状碎屑岩为主的岩组 7 47.84 744 619 54.39 Rd=60.8−0.71Rp 2603 85.63 碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩岩组 8 11.26 156 142 11.40 Rd=68.6−0.71Rp 3314 96.62 以坚硬层状碳酸盐岩为主的岩组 9 4.71 81 77 5.92 Rd=69.3−0.72Rp 3335 96.25 碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩岩组 10 30.34 308 261 22.51 Rd=61.8−0.61Rp 3130 101.31 坚硬块状变质岩岩组 12 0.23 5 5 0.37 水系 100 0.98 13 13 0.95 表 4 研究区不同土地利用下的中等概率降雨阈值判据
Table 4. Mediun probability rainfall threshold criteria under different land uses in the study area
土地利用名称 土地利用代号 面积占比S/% 滑坡数量NL 滑坡事件NE 滑坡点分布密度/% 阈值方程 AUT/mm2 Rp截距/mm 耕地 CR 46.64 797 666 58.26 Rd=66.5−0.75Rp 2949 88.7 林地 FO 41.90 369 331 26.97 Rd=67.6−0.68Rp 3360 99.4 草地 GR 6.03 85 83 6.21 Rd=56.1−0.60Rp 2623 93.5 灌木地 SH 0.65 8 8 0.58 湿地 WE 0.02 0 0 0.00 水体 WA 1.57 14 14 1.02 人造地表 IS 3.20 95 93 6.94 Rd=67.6−0.91Rp 2508 74.2 裸地 BA 0.01 0 0 0.00 表 5 研究区不同土壤类型下的中等概率降雨阈值判据
Table 5. Medium probability rainfall threshold criteria under different soil types in the study area
土壤类型名称 土壤类型代号 面积占比S/% 滑坡数量NL 滑坡事件NE 滑坡点分布密度/% 阈值方程 AUT/mm2 Rp截距/mm 淋溶土 AL 18.81 200 184 14.62 Rd=72.2−0.80Rp 3258 90.25 半淋溶土 SS 0.54 5 5 0.37 钙层土 CL 0.40 4 4 0.29 干旱土 AS 0.58 4 4 0.29 初育土 NS 31.23 508 419 37.13 Rd=68.6−0.72Rp 3268 95.28 半水成土 SA 0.14 0 0 0 人为土 MS 15.38 214 194 15.64 Rd=61.6−0.73Rp 2599 84.38 高山土 TI 0.36 16 15 1.17 铁铝土 FS 31.37 400 352 29.24 Rd=63.3−0.70Rp 2856 90.23 城区 UA 0.09 4 3 0.29 湖泊、水库 LR 1.11 13 10 0.95 -
[1] SHIBIAO B,JIAN W,BENNI T,et al. Analysis of the relationship of landslide occurrence with rainfall:A case study of Wudu County,China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2014,7(4):1277-1285. [2] 晏同珍,伍法权,殷坤龙. 滑坡系统静动态规律及斜坡不稳定性空时定量预测[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),1989,14(2):117-133.YAN T Z,WU F Q,YIN K L. Static and dynamic regularity of landslides and space-time prognosis of slope instability[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences),1989,14(2):117-133. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 刘传正,陈春利. 中国地质灾害防治成效与问题对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):375-383.LIU C Z,CHEN C L. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):375-383. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):1-13.TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 吴益平,张秋霞,唐辉明,等. 基于有效降雨强度的滑坡灾害危险性预警[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2014,39(7):889-895. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.083WU Y P,ZHANG Q X,TANG H M,et al. Landslide hazard warning based on effective rainfall intensity[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences),2014,39(7):889-895. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.083 [6] KIM S W,CHUN K W,KIM M,et al. Effect of antecedent rainfall conditions and their variations on shallow landslide-triggering rainfall thresholds in South Korea[J]. Landslides,2021,18(2):569-582. [7] 郭子正,殷坤龙,刘庆丽,等. 基于位移比模型的三峡库区云阳县域内蠕变型滑坡降雨预警[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(2):672-684.GUO Z Z,YIN K L,LIU Q L,et al. Rainfall warning of creeping landslide in Yunyang County of Three Gorges Reservoir region based on displacement ratio model[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(2):672-684. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CAMPBELL R H. Debris floes originating from soil slips during rains forms in southern California[J]. Engineering Geology,1974,43(7):339-349. [9] CAINE N. The rainfall intensity:Durationcontrol of shallow landslides and debris flows[J]. Geografiska Annaler,1980,62(1/2):23-27. [10] PIETRO A. A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,73(3):247-265. [11] GUZZETTI F,PERUCCACCI S,ROSSI M,et al. Rainfall thresholds for the initiation of landslides in central and southern Europe[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics,2007,98(3/4):239-267. [12] 谢剑明,刘礼领,殷坤龙,等. 浙江省滑坡灾害预警预报的降雨阀值研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2003,22(4):101-105.XIE J M,LIU L L,YIN K L,et al. Study on the threshold valves of rainfall of landslide hazards for early-warning and prediction in Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2003,22(4):101-105. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] SEGONI S,ROSSI G,ROSI A,et al. Landslides triggered by rainfall:A semi-automated procedure to define consistent intensity-duration thresholds[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2014,63:123-131. [14] VESSIA G,PISANO L,VENNARI C,et al. Mimic expert judgement through automated procedure for selecting rainfall events responsible for shallow landslide:A statistical approach to validation[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2016,86:146-153. [15] PARK J,LEE S,LEE D,et al. A regional-scale landslide early warning methodology applying statistical and physically based approaches in sequence[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,260:105193. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105193 [16] 朱文慧,晏鄂川,邹浩,等. 湖北省黄冈市降雨型滑坡气象预警判据[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):45-53.ZHU W H,YAN E C,ZOU H,et al. Meteorological early warning criterion for rainfall-induced landslides in Huanggang City,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):45-53. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LEE M L,NG K Y,HUANG Y F,et al. Rainfall-induced landslides in Hulu Kelang area,Malaysia[J]. Natural Hazards,2014,70(1):353-375. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0814-8 [18] ROSI A,PETERNEL T,JEMEC A M,et al. Rainfall thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Slovenia[J]. Landslides,2016,13(6):1571-1577. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0733-3 [19] 孙金山,陈明,左昌群,等. 降雨型浅层滑坡危险性预测模型[J]. 地质科技情报,2012,31(2):117-121.SUN J S,CHEN M,ZUO C Q,et al. A model for predicting rainfall-induced shallow landslides[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2012,31(2):117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 唐扬,殷坤龙,夏辉. 前期含水率对浅层滑坡降雨入渗及稳定性影响研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(5):204-208.TANG Y,YIN K L,XIA H. Effects of initial water content on the rainfall infiltration and stability of shallow landslide[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(5):204-208. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] YANG H J,WEI F Q,MA Z F,et al. Rainfall threshold for landslide activity in Dazhou,southwest China[J]. Landslides (Journal of the International Consortium on Landslides),2020,17(2):61-77. [22] 周剑,汤明高,许强,等. 重庆市滑坡降雨阈值预警模型[J]. 山地学报,2022,40(6):847-858.ZHOU J,TANG M G,XU Q,et al. Early warning model of rainfall-induced landslide in Chongqing of China based on rainfall threshold[J]. Mountain Research,2022,40(6):847-858. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] SEGONI S,ROSI A,ROSSI G,et al. Analysing the relationship between rainfalls and landslides to define a mosaic of triggering thresholds for regional-scale warning systems[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2014,14(9):2637-2648. doi: 10.5194/nhess-14-2637-2014 [24] SILVIA P,MARIA T B,STEFANO L G,et al. Rainfall thresholds for possible landslide occurrence in Italy[J]. Geomorphology,2017,290:39-57. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.03.031 [25] 吴杰,陈冠,孟兴民,等. 白龙江流域滑坡降雨临界值[J]. 山地学报,2022,40(6):875-886.WU J,CHEN G,MENG X M,et al. Rainfall threshold of landslides in the Bailong River Basin,China[J]. Mountain Research,2022,40(6):875-886. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 刘书豪. 降雨条件下的输电线路滑坡风险评估与预警技术研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2021.LIU S H. Research on risk assessment and early warning of landslides triggered by rainfall along electrical power transmission line[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] BERTI M,MARTINA M,FRANCESCHINI S,et al. Probabilistic rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence using a Bayesian approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research( Earth Surface),2012,117(F4):1-20. [28] 赵玉,陈丽霞,梁梦姣. 基于LSTM-TCN模型的降雨型滑坡时间概率预测及气象预警建模[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):201-214.ZHAO Y,CHEN L X,LIANG M J. Temporal probability prediction and meteorological early warning modeling of rainfall-induced landslide based on LSTM-TCN model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):201-214. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 黄发明,曹中山,姚池,等. 基于决策树和有效降雨强度的滑坡危险性预警[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(3):472-482.HUANG F M,CAO Z S,YAO C,et al. Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2021,55(3):472-482. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 周国兵,马力,廖代强,等. 重庆市山体滑坡等级预报研究[J]. 气象科学,2005,25(1):105-109.ZHOU G B,MA L,LIAO D Q,et al. The research of landslide grade forecast in Chongqing[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences,2005,25(1):105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 孙德亮. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性区划与降雨诱发滑坡预报预警研究[D]. 上海:华东师范大学,2019.SUN D L. Mapping landslide susceptibility based on machine learning and forecast warning of landslide induced by rainfall[D]. Shanghai:East China Normal University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] CROZIER M J. Landslides:Causes,consequences & environment[M]. London:Croom Helm,1986. [33] 林巍,李远耀,徐勇,等. 湖南慈利县滑坡灾害的临界降雨量阈值研究[J]. 长江科学院院报. 2020,37(2):48-54.LIN W,LI Y Y,XU Y,et al. Rainfall thresholds of rainfall-triggered landslides in Cili County ,Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(2):48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 宋宇飞,范文,左琛,等. 基于敏感性分析的最优降雨阈值选择[J]. 工程地质学报,2024,32(2):529-544.SONG Y F,FAN W,ZUO C,et al. The optimal rainfall thresholds selection based on sensitivity analysis[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2024,32(2):529-544. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 龚泉冰,殷坤龙,肖常贵,等. 基于I-D阈值的滑坡气象预警双指标模型[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):262-274.GONG Q B,YIN K L,XIAO C G,et al. Double-index model of landslide meteorological warning based on the I-D threshold[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):262-274. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 刘艳辉,董力豪,黄俊宝,等. 基于RF和概率分级的滑坡临界降水阈值的确定方法[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文),2022,53(10):177-185.LIU Y H,DONG L H,HUANG J B,et al. A method of landslide critical precipitation threshold based on RF and probability grading classification[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2022,53(10):177-185. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 刘谢攀,殷坤龙,肖常贵,等. 基于I-D-R阈值模型的滑坡气象预警[J]. 地球科学,2024,49(3):1039-1051.LIU X P,YIN K L,XIAO C G,et al. Meteorological early warning of landslide based on I-D-R threshold model[J]. Earth Science,2024,49(3):1039-1051. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: