Method for predicting formation buried depth based on regional geological maps and digital elevation model and its application
-
摘要:
对于页岩气、水溶气等非常规天然气资源早期选区评价,往往因为缺乏地震资料导致难以依赖地震构造解释获得目的层的埋深,故借助其他非地震资料有效预测目的层区域性埋深具有重要意义。区域地质图与数字高程模型(DEM)都是广泛覆盖且容易获取的基础性资料。利用区域地质图蕴含的地层产状、地下构造起伏趋势、地层埋深和地表出露地层年代的关系等信息,再叠合DEM地表高程,建立了一种有效预测目的层构造高度和埋深的新方法。利用四川盆地及周缘地区36幅1∶20万区域地质图和美国航空航天局(NASA)数字高程模型资料,预测了该区下志留统龙马溪组底界埋深,据此编制的龙马溪组底界埋深等值线图为该区页岩气保存条件评价提供了重要参数。该方法不仅可为页岩气早期选区评价提供有效支撑,还可应用于深部高压含水层中水溶气的资源评价、深部咸含水层CO2地质封存的构造优选。
Abstract:Objective For the early selection and evaluation of unconventional gas resources such as shale gas and dissolved gas, it is often difficult to obtain formation burial depth by seismic structural interpretation due to the lack of seismic data. Therefore, it is necessary to effectively predict the burial depth of the target layer using other non-seismic data.
Methods Both regional geological maps and digital elevation model (DEM) are widely covered and easily accessible basic data. In this study, a new method for predicting structural height and buried depth of target layer is established by superposing regional DEM information with geological map which contains the attitude of stratum, trend of underground structures, as well as the relation between buried depth of underground layer and age of surface layer.
Results This method is effective for predicting the burial depth of Marine strata with relatively stable sedimentary thickness. The buried depth of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its periphery is predicted based on 36 geological maps with scale of 1∶200 000 and DEM data, and then the contour map of the buried depth of Longmaxi Formation provides important parameters for the evaluation of shale gas preservation conditions in this area.
Conclusion The method of predicting the burial depth of Marine strata by using non-seismic data such as regional geological map and DEM can not only provide effective support for the early selection evaluation of shale gas, but also can be applied to the resource evaluation of water-soluble gas in deep high-pressure aquifers and the structural optimization of CO2 geological storage in deep saline aquifers.
-
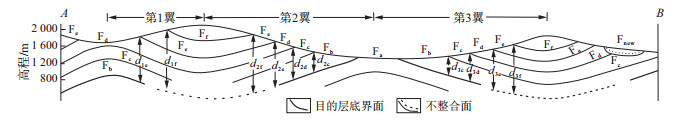
图 1 地质图图切剖面A-B构造起伏与目的层埋深示意图(剖面位置见图 3)
Fnew.新构造层; Ff.地层f组; Fe.地层e组; Fd.地层d组; Fc.地层c组; Fb.地层b组; Fa.地层a组。d1e,d1f.第1翼地层e, f组的埋深; d2f, d2e, d2d,d2c.第2翼地层f, e, d, c组的埋深; d3c, d3d, d3e, d3f.第3翼地层c, d, e, f组的埋深(下同)
Figure 1. Profile A-B of geological map showing the fold structures and buried depth of target stratum
图 5 1∶20万酉阳幅区域地质图A-B地质剖面及龙马溪组顶、底界面示意图(剖面位置见图 3)
∈2g.中寒武统高台组; ∈2p.中寒武统平井组; ∈3g.上寒武统耿家店组; ∈3m.上寒武统毛田组; O1n.下奥陶统南津关组; O1 f+h.下奥陶统分乡组、红花园组; O1d.下奥陶统大湾组; O2+3.中、上奥陶统;S1l.下志留统龙马溪组; S2lr.中志留统罗惹坪组; P1.下二叠统; P2.中二叠统; T1d.下三叠统大冶组; T1 j.下三叠统嘉陵江组; T2b.中三叠统巴东组;下同
Figure 5. Profile A-B showing top and bottom interface of Longmaxi Formation in 1∶200 000 geological map of Youyang
表 1 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组底界埋深预测误差分析
Table 1. Error analysis for the buried depth of Longmaxi Formation bottom in Sichuan Basin and its periphery
构造位置 川东断褶带 川东高陡褶皱带 川南低陡褶皱带 威远背斜 川东南断褶带 盆缘丁山构造 盆外安场向斜 盆外道真向斜 核部 翼部 井号 五科1 池7 座3 阳深2 隆32 威202 威203 东深1 临7 丁页1 安页1 道页1 龙马溪组底深/m 5 250 4 660 4 300 3 552 3 244.5 2 570 3 180 3 426 2 640.4 2 054 2 350 585 井位预测深度/m 5 641 4 753 4 392 3 740 3 100 2 445 3 338 3 386 2 562 2 076 2 327 706 绝对误差/m 391 93 92 188 -145 -125 158 -40 -78 22 -23 121 相对误差/% 7.5 2.0 2.1 5.3 -4.5 -4.9 5.07 -1.2 -3.0 1.17 -1.0 20.6 -
[1] 唐令, 宋岩, 陈晓智, 等. 页岩气选区评价关键参数及上下限: 以四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(1): 153-168.TANG L, SONG Y, CHEN X Z, et al. Key parameters and the upper-lower limits of shale gas selection evaluation: Case study from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(1): 153-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 李耀华, 宋岩, 姜振学, 等. 全球致密砂岩气盆地参数统计分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(6): 952-964.LI Y H, SONG Y, JIANG Z X, et al. Parameters statistic analysis of global tight sand gas basins[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(6): 952-964. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 路萍, 白勇, 刘伟刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地马家沟组二氧化碳地质封存有利区优选[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(3): 816-827.LU P, BAI Y, LIU W G, et al. Optimization of favorable areas for carbon dioxide geological storage in Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(3): 816-827. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 高志豪, 赵锐锐, 成建梅. 砂岩含水层CO2封存中考虑盐沉淀反馈作用的数值模拟: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073GAO Z H, ZHAO R R, CHENG J M. Numerical simulation of CO2 sequestration in sandstone aquifers with feedback effect of salt precipitation: A case study of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073 [5] 乔秀夫, 丁孝忠. 区域地质调查与编图综合研究: 写在新编《中国地质图集》出版之际[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(10): 769-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.10.004QIAO X F, DING X Z. A magnificent project of regional geological survey and integrated map-compilation study: A few words written at the time of the publication of the new 《Geological Atlias of China》[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2003, 22(10): 769-774. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.10.004 [6] 张宝一, 杨莉, 陈笑扬, 等. 基于图切地质剖面的区域成矿地质体三维建模与资源评价: 以桂西南地区锰矿为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(3): 933-948.ZHANG B Y, YANG L, CHEN X Y, et al. Regional metallogenic geo-bodies 3D modeling and mineral resource assessment based on geologic map cut cross-sections: A case study of manganese deposits in southwestern Guangxi, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(3): 933-948. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 常直杨, 孙伟红, 王建, 等. 数字高程模型在构造地貌形态分析中的应用现状及展望[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(4): 129-136.CHANG Z Y, SUN W H, WANG J, et al. Application of DEM in the morphological analysis of tectonic geomorphology: Status and prospect[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 38(4): 129-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 徐思煌, 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 等. 四川盆地及周缘复杂构造背景下页岩气保存条件研究[R]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉)资源学院, 2020: 172-173.XU S H, MEI L F, LIU Z Q, et al. Study on preservation conditions of shale gas under complex structural background of Sichuan Basin and its periphery[R]. Wuhan: School of Earth Resources of China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020: 172-173. (in Chinese) [9] 刘义生, 金吉能, 潘仁芳, 等. 渝东南盆缘转换带五峰组-龙马溪组常压页岩气保存条件评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 253-263.LIU Y S, JIN J N, PAN R F, et al. Preservation condition evaluation of normal pressure shale gas in the Wufeng and Longmaxi formations of basin margin transition zone, Southeast Chongqing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 2011, 46(3): 589-606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001HE D F, LI D S, ZHANG G W, et al. Formation and evolution of multi-cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology(Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2011, 46(3): 589-606. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001 [11] 董大忠, 施振生, 管全中, 等. 四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气勘探进展、挑战与前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(4): 67-76.DONG D Z, SHI Z S, GUAN Q Z, et al. Progress, challenges and prospects of shale gas exploration in the Wufeng-Longmaxi reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(4): 67-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 刘树根, 邓宾, 钟勇, 等. 四川盆地及周缘下古生界页岩气深埋藏-强改造独特地质作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 11-28.LIU S G, DENG B, ZHONG Y, et al. Unique geological features of burial and superimposition of the Lower Paleozoic shale gas across the Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 11-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: