Landslide mechanism of metamorphic sandstone area containing weak interlayers in Shuangqiaoshan Group
-
摘要:
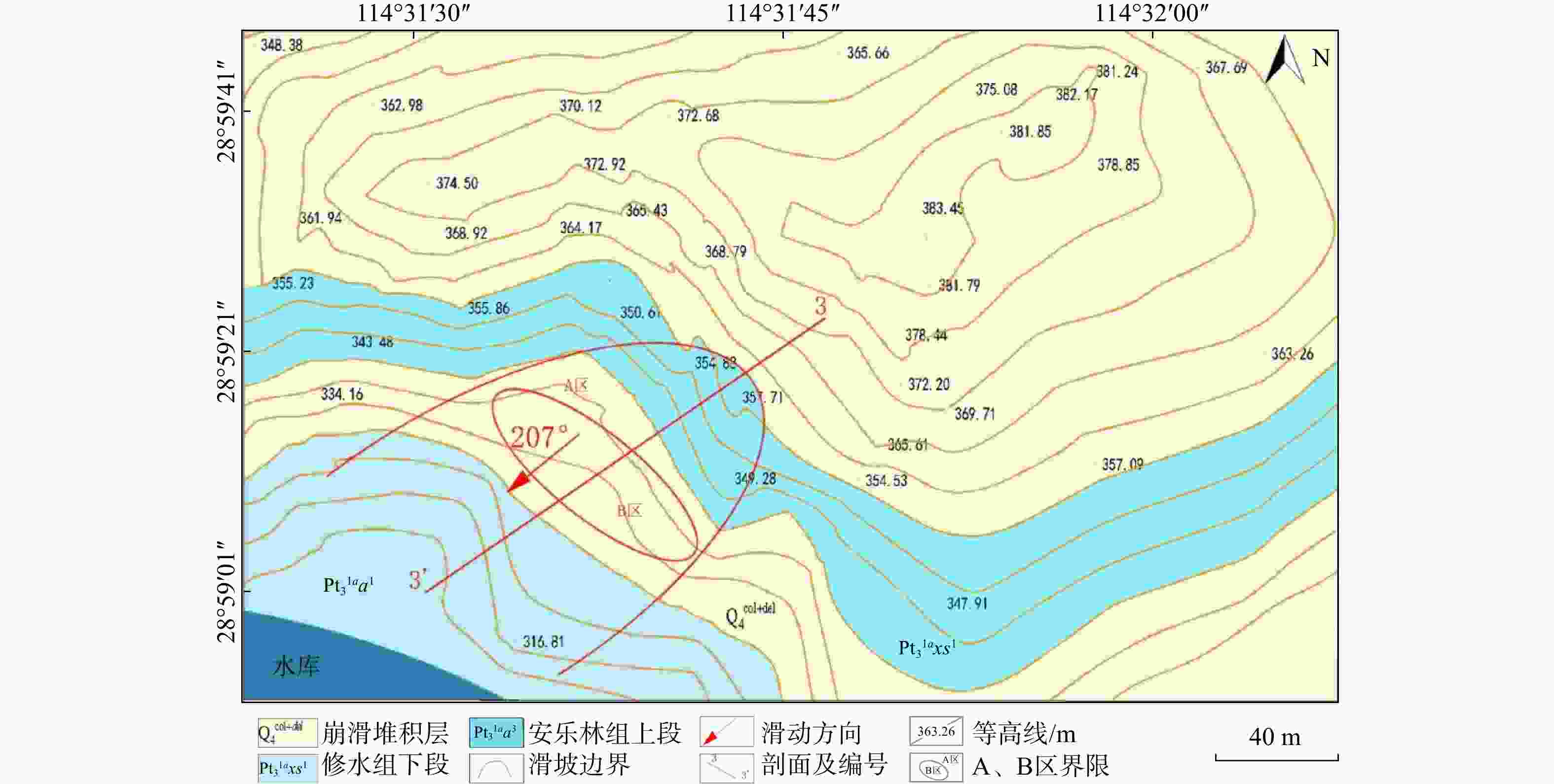
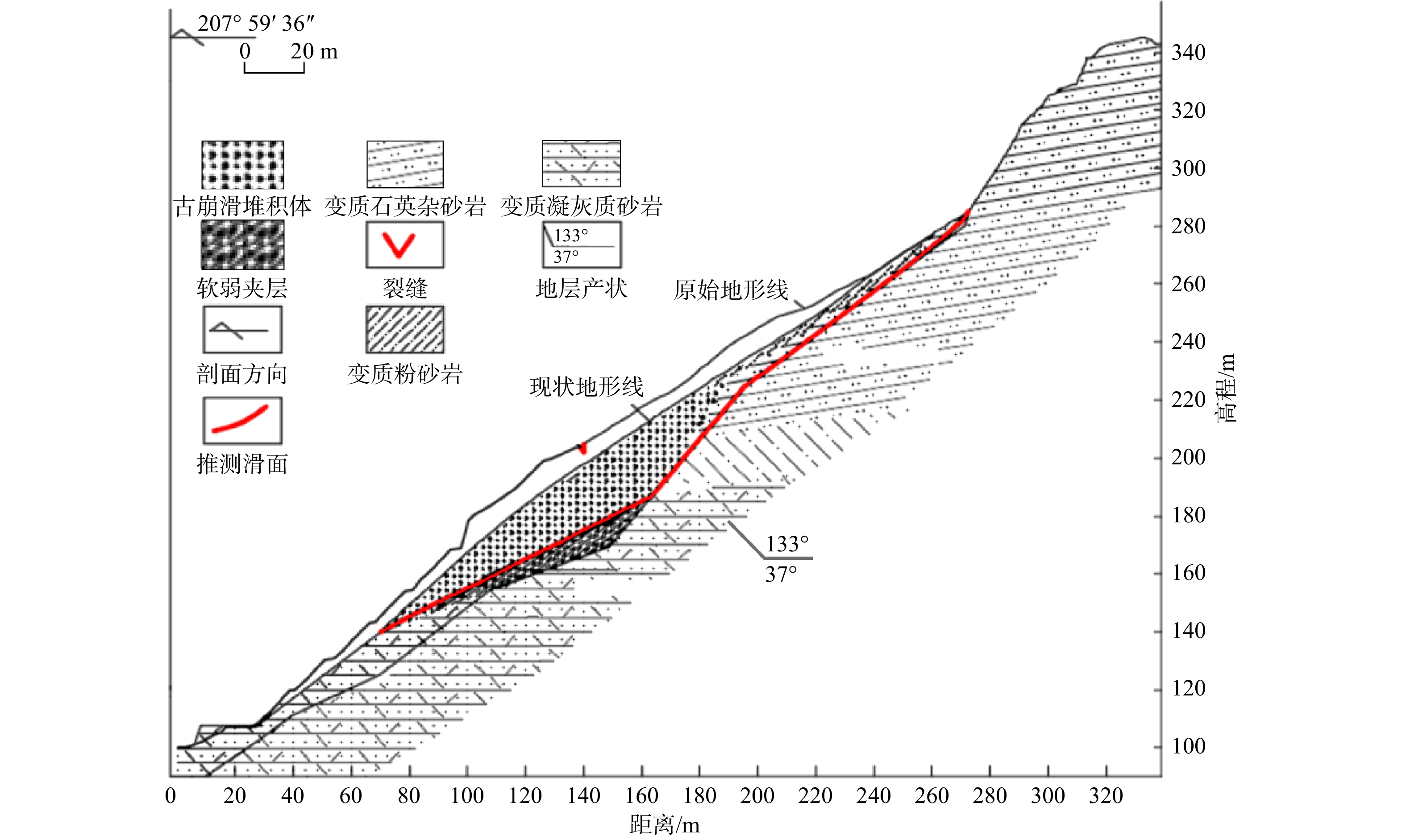
双桥山群地层在华东地区广泛揭露,岩性与地层复杂,断层及褶皱发育,常形成软弱夹层斜坡,在降雨入渗的作用下极易发生滑坡。为揭示其在降雨条件下变形演化机理,以江西省修水县一典型含粉质黏土软弱夹层堆积体滑坡为例,分析了该软弱夹层滑坡的形成原因和变形破坏特征,建立了堆积体滑坡的地质力学模型,采用GeoStudio数值分析软件模拟了该滑坡在不同降雨强度条件下的形成机理。研究结果表明:(1)滑坡后缘EW向断层与韧性断裂带共同作用,发育了4组控制坡体稳定性的裂隙,在滑床之上形成厚达8.8 m的船形软弱夹层。(2)降雨入渗到碎屑和黏土物质组成的滑带,使滑体经历前期蠕变-中期滑动面贯通-后期剪切变形3个变形破坏阶段。(3)当降雨强度达9.9 mm/d时,滑坡坡体开始蠕变;当降雨强度增加到40 mm/d时,坡体沿着软弱结构面剪切变形增大;当降雨强度上升至120 mm/d时,坡体沿着软层结构面产生贯通性破碎面,最终加速失稳破坏。研究结果对今后该类似岩群的滑坡灾害的防治具有一定的参考价值。
Abstract:Objective The Shuangqiaoshan Group strata are widely exposed in East China, with complex lithology and stratigraphy, developed faults and folds, often forming weak interlayer slopes. These characteristics often create weak interlayer slopes that are prone to landslides under rainfall infiltration.
Methods This study aims to reveal the deformation and evolution mechanisms of such slopes under rainfall conditions. Taking a typical silty clay-bearing soft interlayer landslide in Xiushui County as an example, the formation reasons and failure characteristics of the weak interlayer landslide were analyzed. A geomechanical model of accumulation landslides was established, and the landslide's response under different rainfall intensities was simulated using GeoStudio numerical analysis software.
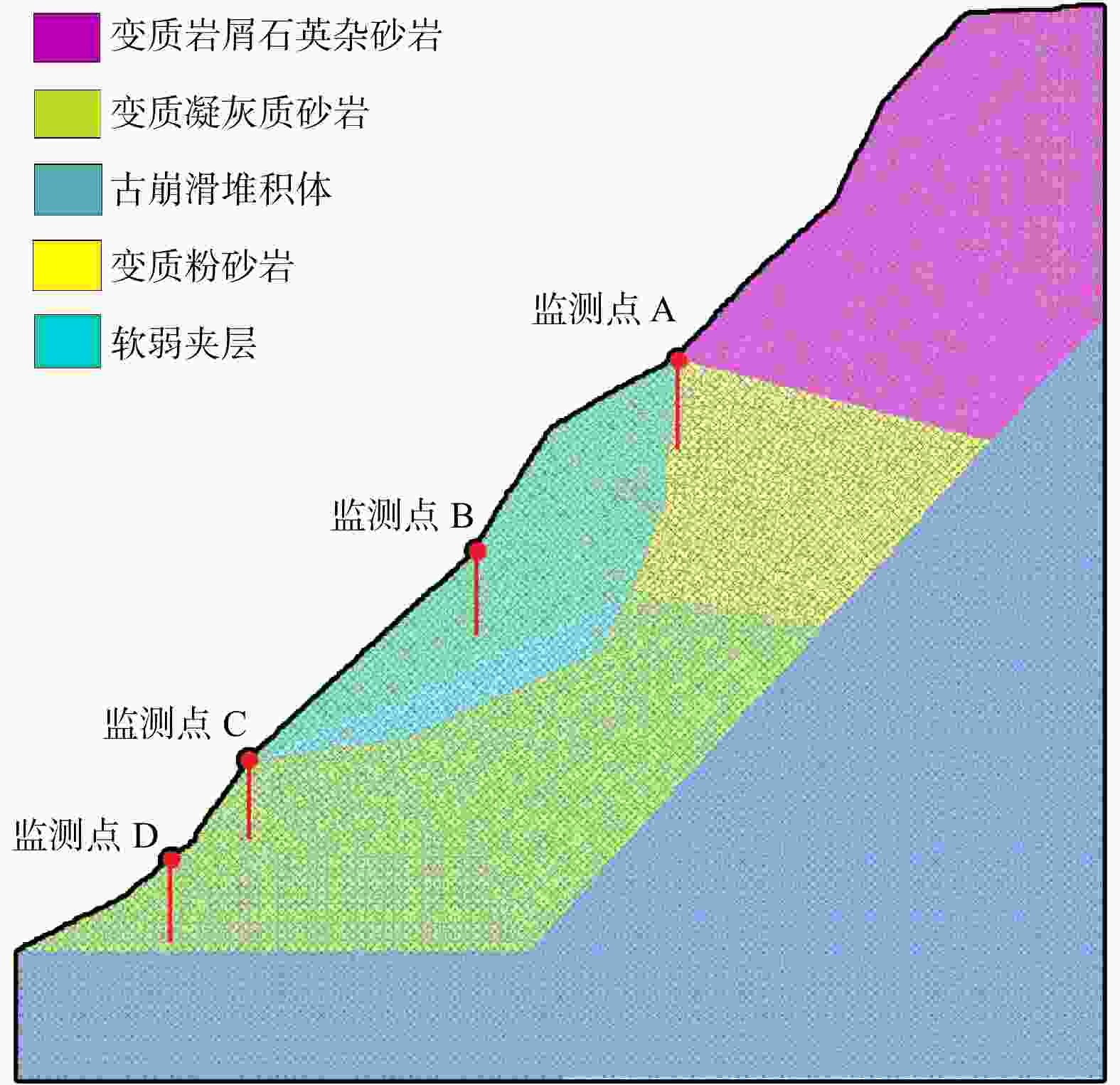
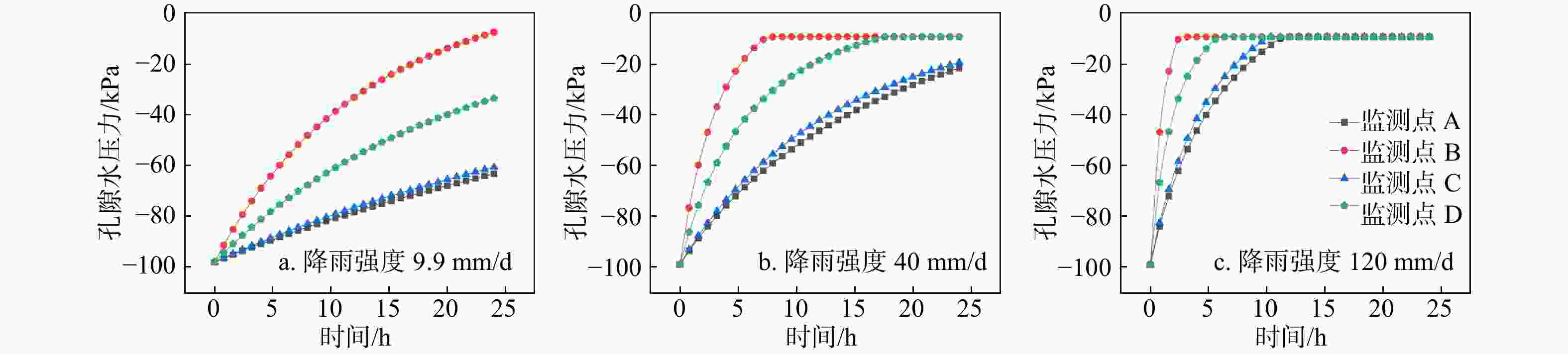
Results The findings are as follows: (1) An EW-trending fault zone and ductile fault zone at the landslide's rear edge combine to form four groups of cracks that control slope stability, forming a boat-shaped weak interlayer approximately 8.8 m thick in the sliding bed; (2) Rainfall infiltrates into the sliding zone composed of debris and clay, triggering the sliding body to undergo three deformation stages: early creep, mid-stage sliding surface penetration, and late-stage shear deformation; (3) Creep deformation begins when rainfall intensity reaches 9.9 mm/d. At 40 mm/d, shear deformation increases along the weak structural plane and progressively intensifies. At 120 mm/d, a connected fracture surface forms along the weak interlayer structure, ultimately accelerating instability and landslide failure.
Conclusion These findings provide valuable insights into the prevention and management of landslide disasters in similar lithological settings.
-
表 1 滑坡A区物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of landslide in Area A
工况 岩层 γ/(kg·m3) E/GPa 泊松比 C/kPa φ/(°) 工况一 变质岩屑石英杂砂岩 26.8 4.3 0.2 22.0 37.0 变质凝灰质砂岩 26.8 4.3 0.2 22.0 37.0 变质粉砂岩 26.8 4.2 0.25 22.0 37.0 工况二 变质岩屑石英杂砂岩 27.0 2.2 0.24 17.5 33.7 变质凝灰质砂岩 27.0 2.2 0.24 17.5 33.7 变质粉砂岩 27.0 2.1 0.28 17.5 33.7 工况三 变质岩屑石英杂砂岩 27.3 1.1 0.30 13.0 28.0 变质凝灰质砂岩 27.3 1.1 0.30 13.0 28.0 变质粉砂岩 27.3 1.05 0.35 13.5 28.0 表 2 滑坡B区物理力学参数
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of landslide in Area B
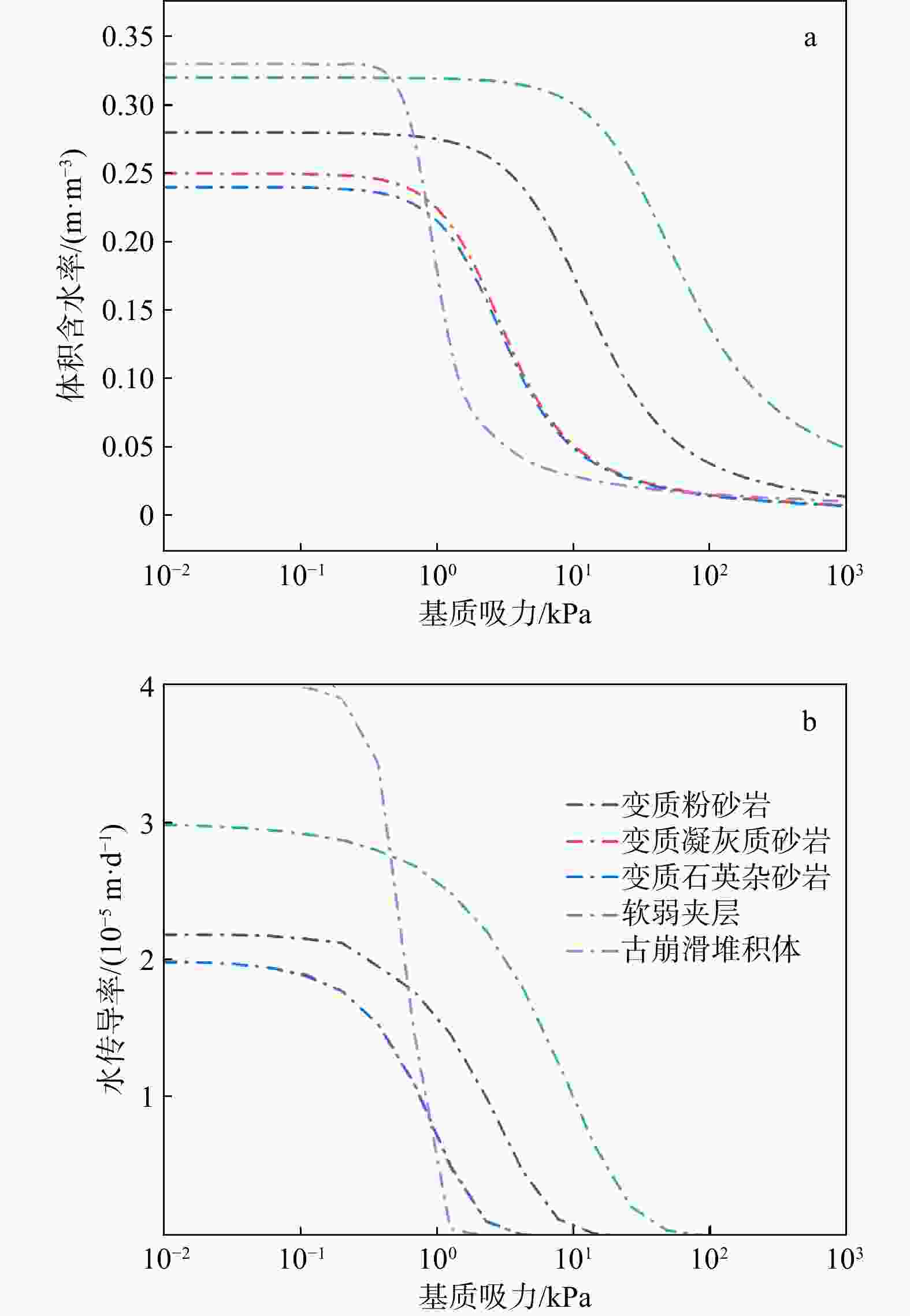
工况 岩层 γ/(kg·m3) E/GPa 泊松比 C/kPa φ/(°) 工况一 古崩滑堆积体 26.8 4.3 0.18 22 37 软弱夹层 16.2 0.16 0.3 17.6 25.4 工况二 古崩滑堆积体 27 2.2 0.23 17.5 33.7 软弱夹层 19.8 0.09 0.34 14.2 24.6 工况三 古崩滑堆积体 27.2 1.1 0.28 13.2 28 软弱夹层 21.4 0.075 0.4 11.1 23.8 表 3 岩土层的持水曲线和渗透曲线相关参数
Table 3. Related parameters of water retention curve and permeability curve of rock and soil layer
岩土层 材料模型 饱和含水率θs/
(m3·m−3)残余含水率θr/
(m3·m−3)饱和渗透系数Ks/
(10−5 m·s−1)变质粉砂岩 饱和/非饱和 0.28 0.028 2.2 变质凝灰
质砂岩饱和/非饱和 0.25 0.025 2.0 变质岩屑石
英杂砂岩饱和/非饱和 0.24 0.024 2.0 软弱夹层 饱和/非饱和 0.32 0.032 0.3 基岩 饱和 0.005 0.0005 0.1 堆积体 饱和/非饱和 0.33 0.033 4.0 表 4 不同降雨工况下降雨1 d监测点位移
Table 4. Displacement of monitoring points under different rainfall conditions after one day
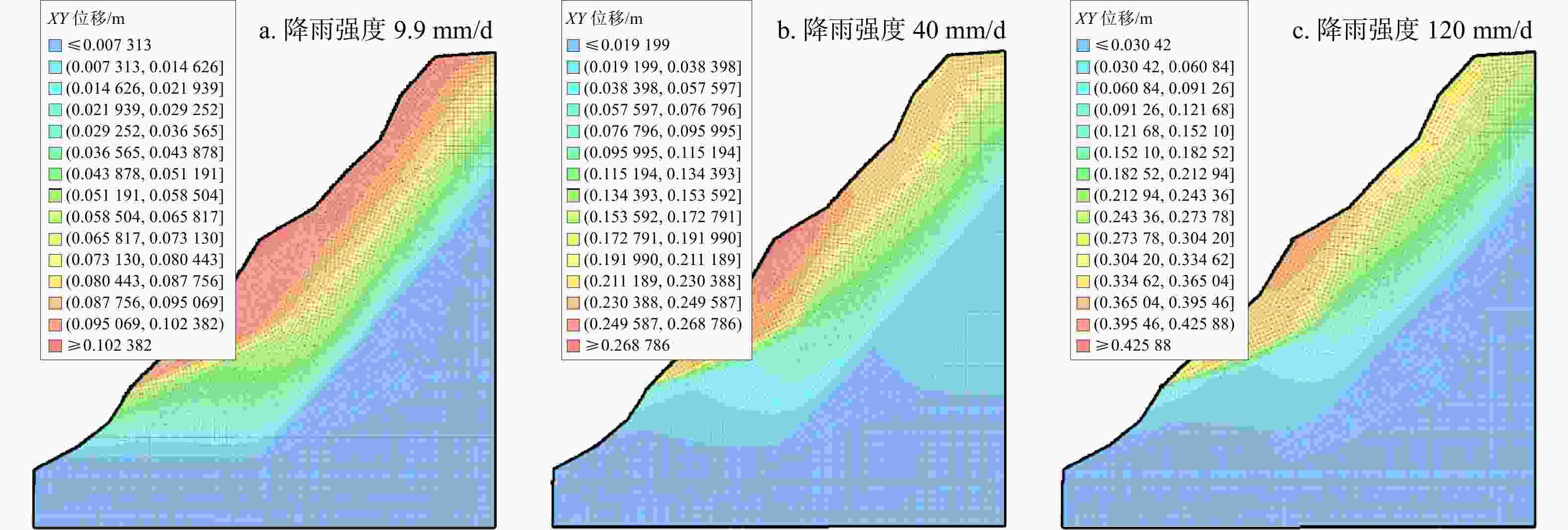
工况 降雨类型 降雨强度/(mm·d−1) 后缘位移/m 中部位移/m 前缘位移/m 坡脚位移/m 工况一 小雨 9.9 0.102 0.096 0.090 0.039 工况二 大雨 40 0.229 0.234 0.203 0.153 工况三 大暴雨 120 0.386 0.426 0.390 0.324 -
[1] 马雪,高天山,周效华,等. 江南造山带东段新元古代双桥山群沉积环境分析[J]. 地层学杂志,2019,43(3):295-305.MA X,GAO T S,ZHOU X H,et al. Sedimentary environment analysis of Neoproterozoic Shuangqiao Mountain Group in eastern Jiangnan Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2019,43(3):295-305. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 刘冰琪,于津海,蒋威,等. 赣北双桥山群变沉积岩的地球化学特征及与钨多金属成矿的关系[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(2):433-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.02.009LIU B Q,YU J H,JIANG W,et al. Geochemical characteristics of metamorphic sedimentary rocks of Shuangqiaoshan Group in northern Jiangxi and their relationship with tungsten polymetallic mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(2):433-447. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.02.009 [3] 荣冠,张伟,周创兵. 降雨入渗条件下边坡岩体饱和非饱和渗流计算[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(10):24-29.RONG G,ZHANG W,ZHOU C B. Calculation of saturated and unsaturated seepage of slope rock mass under rainfall infiltration[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics,2005,26(10):24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 杨背背,殷坤龙,梁鑫,等. 三峡库区麻柳林滑坡变形特征及演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2):122-129.YANG B B,YIN K L,LIANG X,et al. Deformation characteristics and evolution simulation of Maliulin landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(2):122-129. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] YU H,LI C,ZHOU J Q,et al. A semi-analytical model for transient infiltration into inclined soil interlayer considering varying water head and stratified water content[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,614:128627. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128627 [6] 李秀珍,张小红. 基于Mein-Larson入渗模型的降雨滑坡失稳破坏概率研究[J]. 水土保持通报,2017,37(1):219-223.LI X Z,ZHANG X H. Study on failure probability of rainfall landslide based on Mein-Larson infiltration model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2017,37(1):219-223. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] YU P,LIU H,YU H,et al. Study on fluid-solid coupling numerical simulation and early warning of weathered granite landslides induced by extreme rainfall[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(15):11738. doi: 10.3390/su151511738 [8] 王旋,胡新丽,周昌,等. 基于物理模型试验的滑坡-抗滑桩位移场变化特征[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(4):103-108.WANG X,HU X L,ZHOU C,et al. Variation characteristics of displacement field of landslide-anti-slide pile based on physical model test[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(4):103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] ISMAIL M A M,HAMZAH N H. Study on the response of unsaturated soil slope based on the effects of rainfall intensity and slope angle[C]//Anon. AIP Conference Proceedings. [S. l. ]:AIP Publishing,2017. [10] 霍志涛,李高,王力,等. 降雨型滑坡浅层滑动对土体含水率变化的响应[J]. 长江科学院院报,2022,39(7):110-117. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20210211HUO Z T,LI G,WANG L,et al. Response of shallow sliding of rainfall landslide to soil moisture content change[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2022,39(7):110-117. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20210211 [11] FAN X M,YANG F,SRIKRISHNAN S S,et al. Prediction of a multi-hazard chain by an integrated numerical simulation approach:The Baige landslide,Jinsha River,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(1):147-164. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01313-5 [12] JIANG S,Li J Y,ZHANG S,et al. Landslide risk prediction by using GBRT algorithm:Application of artificial intelligence in disaster prevention of energy mining[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2022,166:384-392. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.08.043 [13] SALAHUDEEN A B,SADEEQ J A. Investigation of shallow foundation soil bearing capacity and settlement characteristics of Minna City Centre Development Site using Plaxis 2D software and empirical formulations[J]. Nigerian Journal of Technology,2017,36(3):663-670. doi: 10.4314/njt.v36i3.1 [14] JI J,ZHANG T,CUI H,et al. Numerical investigation of post-earthquake rainfall-induced slope instability considering strain-softening effect of soils[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2023,171:107938. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.107938 [15] 豆红强,谢森华,王浩,等. 降雨条件下球状风化花岗岩类土质边坡渗流特性与稳定性分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(2):638-649.DOU H Q,XIE S H,WANG H,et al. Seepage characteristics and stability analysis of spherical weathered granite soil slope under rainfall[J]. Acta Geologica Engineering,2023,31(2):638-649. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 朱志男,李慧亭,陈羽,等. 基于PFC-GeoStudio耦合的边坡降雨变形破坏研究[J]. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2022,39(4):92-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2022.04.013ZHU Z N,LI H T,CHEN Y,et al. Study on slope deformation and failure due to rainfall based on PFC-GeoStudio coupling[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2022,39(4):92-99. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2022.04.013 [17] 刘帅,朱杰勇,杨得虎,等. 不同降雨工况条件下的崩滑地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):253-267.LIU S,ZHU J Y,YANG D H,et al. Risk assessment of collapsible and sliding geohazards under different rainfall conditions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):253-267. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] CHEN Y ,YE Y ,HU R ,et al. Modeling unsaturated flow in fractured rocks with scaling relationships between hydraulic parameters[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2022,14(6):1697-1709. [19] 周少伟,边小卫,李卫波,等. 考虑降雨条件陕北Q2黄土斜坡稳定性的非线性劣化研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):218-226.ZHOU S W,BIAN X W,LI W B,et al. Study on nonlinear deterioration of slope stability in Q2 loess of northern Shaanxi under rainfall conditions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):218-226. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 查新元,童富果,薛松,等. 三峡库区降雨型滑坡体型特征分析[J]. 水电能源科学,2023,41(6):142-145.CHA X Y,TONG F G,XUE S,et al. Analysis of the shape characteristics of the rainfall-type landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydropower and Energy Science,2023,41(6):142-145. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: