Nonlinear degradation of stability of Q2 loess slopes in northern Shaanxi considering rainfall conditions
-
摘要:
降雨致灾是陕北黄土斜坡最常见的灾害之一, 揭示降雨对黄土斜坡稳定性影响特征有利于预防滑坡灾害的发生。通过一系列室内试验研究了降雨条件下陕北Q2黄土的力学特性变化特征, 并结合数值模拟分析了其对陕北黄土斜坡稳定性的影响。首先设计干湿循环试验(循环路径和次数)以模拟降雨条件(如强度、频次等); 其次通过三轴剪切试验获取陕北Q2黄土的力学性质的变化规律; 最后以陕北地区某黄土斜坡为例, 利用有限元计算并分析不同降雨条件下斜坡安全系数和塑性区的变化特征。结果表明: (1)干湿循环作用后Q2黄土的抗剪强度存在非线性劣化特征。当干湿循环次数超过一定范围后, 黄土物理力学性质参数劣化的边际效应减弱, 并趋于稳定。(2)降雨作用下黄土斜坡的稳定性呈现出随着降雨频次或降雨强度的增加而降低的趋势。(3)Q2黄土斜坡的塑性区范围随着Q2黄土力学性能的不断劣化而增大, 体现了降雨条件对黄土斜坡稳定性影响的非线性特征。研究结果为降雨型滑坡预防提供参考。
Abstract:Objective Rainfall disasters are one of the most common disasters on loess slopes in northern Shaanxi, and revealing the effects of rainfall on loess slope stability is beneficial for preventing and controlling such disasters.
Methods This research studied the mechanical properties of Q2 loess in northern Shaanxi under rainfall conditions through a series of tests. Combined with numerical simulation technology, the influence of these changes on the stability of loess slopes in northern Shaanxi was analyzed.Firstly, the drying-wetting cycles test (cyclic path and the number of cycles) was designed to simulate rainfall conditions (such as intensity, frequency, etc.).Secondly, a triaxial shear test was performed to obtain the variation law of the mechanical properties of the Q2 loess in northern Shaanxi.Finally, taking a loess slope in northern Shaanxi region as an example, finite element calculations were carried out, by which the change characteristics of the slope safety coefficients and plasticity zones under different rainfall conditions were analyzed.
Results The results show that (1) the shear strength of Q2 loess after the action of drying-wetting cycles has nonlinear deterioration characteristics. When the number of drying-wetting cycles exceeds a specific range, the marginal effect of the deterioration of the physical and mechanical property parameters of loess is weakened and tends to stabilize. (2) The stability of loess slopes decreases under the effect of rainfall, and it decreases with the increase of rainfall frequency or intensity. (3) The plastic zone of Q2 loess slopes in northern Shaanxi increases with the continuous deterioration of the mechanical properties of the Q2 loess, which reveals a nonlinear characteristic of the influence of rainfall on the stability of the loess slopes.
Conclusion The research results can provide a reference for preventing rainfall-induced landslide.
-
图 4 不同干湿循环作用下Q2黄土的应力-应变关系(n为干湿循环次数,路径信息见表 4,下同)
Figure 4. Stress-strain relationship of Q2 loess under different drying-wetting cycles
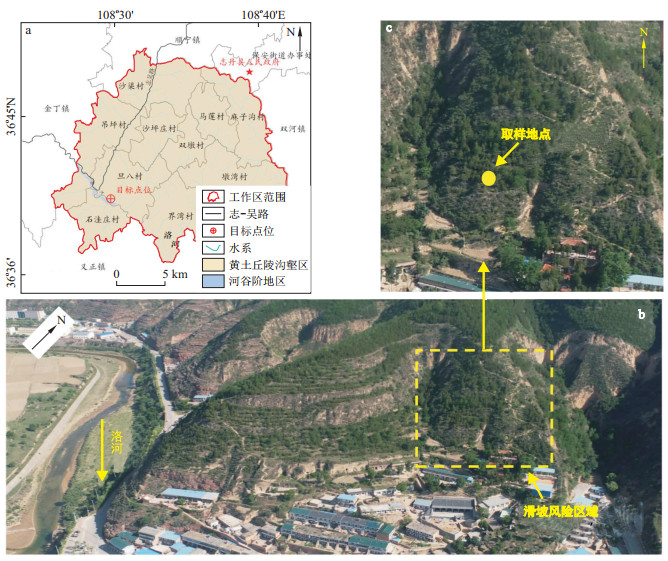
表 1 DBXP088斜坡中Q2黄土物理性质
Table 1. Physical propeities of Q2 loess in DBXP088 slope
指标 含水率/% 天然密度/(g·cm-3) 干密度/(g·cm-3) 比重 孔隙比/% 饱和度/% 液限/% 塑限/% 值 10.30 1.88 1.36 2.71 0.69 74.7 29.37 16.55 表 2 DBXP088斜坡中Q2黄土粒径分布特征
Table 2. Distribution of Q2 loess particles in DBXP088 slope
粒径种类 粗粒 细粒 粉粒组 黏粒组 粒径/mm ≥0.075 0.075~0.005 ≤0.005 质量分数/% 3.72 67.62 28.66 表 3 DBXP088斜坡中黄土力学参数
Table 3. Main mechanical parameters in DBXP088 slope
地层 变形模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗剪强度/kPa Q2黄土 18.09 0.29 87.38 27.90 612.33 地层 天然密度/(g·cm-3) 变形模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 地层厚度/m Q3黄土 1.58 5.62 0.31 31.73 23.60 5.00 表 4 干湿循环作用路径试验设计方案
Table 4. Experimental design scheme of drying-wetting cycles action path
路径编号 下限质量含水率/% 上限质量含水率/% 质量含水率幅度(上限-下限)/% 停止后质量含水率/% 路径1 4.0 18.0 14.0 10.3 路径2 4.0 24.0 20.0 路径3 4.0 30.0 26.0 表 5 Q2黄土试样编号及不同干湿循环作用下主要物理力学参数
Table 5. Number of Q2 loess samples and main physical and mechanical parameters under different drying-wetting cycles
试样标号 循环路径 循环次数/次 天然密度/(g·cm-3) 泊松比 变形模量/MPa 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) N-0 无干湿循环作用 0 1.88 0.29 18.09 87.38 27.9 N1-1 路径1 1 1.88 0.29 17.43 80.40 25.8 N1-2 3 1.88 0.29 16.52 74.36 23.7 N1-3 7 1.88 0.29 14.24 69.90 22.3 N1-4 10 1.88 0.29 10.17 58.66 21.7 N1-5 14 1.88 0.29 13.55 66.96 22.1 N1-6 18 1.88 0.29 10.21 70.11 22.2 N1-7 21 1.88 0.29 10.15 70.79 21.9 N2-1 路径2 1 1.88 0.29 16.69 75.72 23.7 N2-2 3 1.88 0.29 11.17 65.38 20.5 N2-3 7 1.88 0.29 10.32 51.48 19.9 N2-4 10 1.88 0.29 9.07 54.62 20.4 N2-5 14 1.88 0.29 8.23 61.81 21.1 N2-6 18 1.88 0.29 8.73 64.71 21.3 N2-7 21 1.88 0.29 8.66 60.60 21.3 N3-1 路径3 1 1.88 0.29 15.24 63.81 21.9 N3-2 3 1.88 0.29 9.82 31.73 19.8 N3-3 7 1.88 0.29 8.47 26.59 19.6 N3-4 10 1.88 0.29 6.84 38.24 20.2 N3-5 14 1.88 0.29 6.75 49.01 20.9 N3-6 18 1.88 0.29 7.43 55.09 21.2 N3-7 21 1.88 0.29 7.54 58.66 21.0 -
[1] 彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等. 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(4): 684-691. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201404018.htmPENG J B, LIN H Z, WANG Q Y, et al. The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(4): 684-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201404018.htm [2] LI Y R, SHI W H, AYDIN A, et al. Loess genesis and worldwide distribution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 201: 102947. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102947 [3] 李泽坤, 马鹏辉, 彭建兵, 等. 黑方台地区马兰黄土渗透特性及结构损伤试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 200-210. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0251LI Z K, MA P H, PENG J B, et al. Experimental study on the permeability characteristics and structure damage of Malan loess in Heifangtai area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 200-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0251 [4] ZHUANG J Q, PENG J B. A coupled slope cutting: A prolonged rainfall-induced loess landslide: A 17 October 2011 case study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2014, 73(4): 997-1011. doi: 10.1007/s10064-014-0645-1 [5] 卢永兴, 陈剑, 霍志涛, 等. 降雨与开挖作用下黄土滑坡失稳过程分析: 以关中地区长武县杨厂村老庙滑坡为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0249LU Y X, CHEN J, HUO Z T, et al. Analysis of instability process of the loess landslides under rainfall and excavation actions: A case study of Laomiao landslide at Yangchang Village in Changwu County, Guanzhong area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 95-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0249 [6] QI T J, ZHAO Y, MENG X M, et al. AI-based susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides induced by heavy rainfall in Tianshui, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(9): 1819. doi: 10.3390/rs13091819 [7] 李同录, 李颖喆, 赵丹旗, 等. 对水致黄土斜坡破坏模式及稳定性分析原则的思考[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(2): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202202004.htmLI T L, LI Y Z, ZHAO D Q, et al. Thoughts on modes of loess slope failure triggered by water infiltration and the principals for stability analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202202004.htm [8] LENG Y Q, PENG J B, WANG Q Y, et al. A fluidized landslide occurred in the Loess Plateau: A study on loess landslide in South Jingyang Tableland[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 236: 129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.05.006 [9] GUO Z Y, HUANG Q B, LIU Y, et al. Model experimental study on the failure mechanisms of a loess-bedrock fill slope induced by rainfall[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 313: 106979. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106979 [10] CUI S H, PEI X J, WU H Y, et al. Centrifuge model test of an irrigation-induced loess landslide in the Heifangtai loess platform, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2018, 15(1): 130-143. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4490-0 [11] 同霄, 彭建兵, 朱兴华, 等. 黄土地区降雨的优势入渗深度[J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(3): 231-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201703039.htmTONG X, PENG J B, ZHU X H, et al. Advantage infiltration depth of rainfall in loess area[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 37(3): 231-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201703039.htm [12] 马鹏辉, 彭建兵, 朱兴华, 等. 黄土浅层降雨入渗规律研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(4): 248-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201704042.htmMA P H, PENG J B, ZHU X H, et al. Regularities of rainfall infiltration in shallow loess[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 37(4): 248-253. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201704042.htm [13] SUN P, WANG H J, WANG G, et al. Field model experiments and numerical analysis of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 295: 106411. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106411 [14] 韩幽铭, 桂蕾, 朱兴华, 等. 滑坡张拉变形区砌体房屋变形破坏特征数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 55-62. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220718HAN Y M, GUI L, ZHU X H, et al. Numerical simulation of masonry building deformation and failure characteristics in landslide tension areas[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 55-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220718 [15] 邵生俊, 罗爱忠, 于清高, 等. 加荷增湿作用下Q3黏黄土的结构损伤特性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(12): 2077-2081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200612005.htmSHAO S J, LUO A Z, YU Q G, et al. Structural damage characteristics of Q3 clay loess under loading and humidification[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(12): 2077-2081. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200612005.htm [16] 陈存礼, 高鹏, 胡再强. 黄土的增湿变形特性及其与结构性的关系[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(7): 1352-1360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.07.009CHEN C L, GAO P, HU Z Q. Moistening deformation characteristic of loess and its relation to structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(7): 1352-1360. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.07.009 [17] 王飞, 李国玉, 穆彦虎, 等. 干湿循环条件下压实黄土变形特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(8): 2306-2312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201608024.htmWANG F, LI G Y, MU Y H, et al. Experimental study of deformation characteristics of compacted loess subjected to drying-wetting cycle[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(8): 2306-2312. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201608024.htm [18] 袁志辉, 倪万魁, 唐春, 等. 干湿循环下黄土强度衰减与结构强度试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(7): 1894-1902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201707007.htmYUAN Z H, NI W K, TANG C, et al. Experimental study of structure strength and strength attenuation of loess under wetting-drying cycle[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(7): 1894-1902. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201707007.htm [19] LI P, VANAPALLI S, LI T L. Review of collapse triggering mechanism of collapsible soils due to wetting[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 8(2): 256-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.12.002 [20] 郝延周, 王铁行, 汪朝, 等. 干湿循环作用下压实黄土三轴剪切特性试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2021, 52(3): 359-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202103012.htmHAO Y Z, WANG T X, WANG Z, et al. Experimental study on triaxial shear characteristics of compacted loess under drying and wetting cycles[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 52(3): 359-368. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202103012.htm [21] YE W J, ZHANG Y Y. Effect of dry-wet cycle on the formation of loess slope spalling hazards[J]. Civil Engineering Journal, 2018, 4(4): 785. doi: 10.28991/cej-0309133 [22] ZHANG F Y, WANG G H, KAMAI T, et al. Undrained shear behavior of loess saturated with different concentrations of sodium chloride solution[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 155: 69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.12.018 [23] LIAN B Q, WANG X G, ZHAN H B, et al. Creep mechanical and microstructural insights into the failure mechanism of loess landslides induced by dry-wet cycles in the Heifangtai platform, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 300: 106589. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106589 [24] 刘禹阳, 安驰, 来弘鹏, 等. 不同干湿循环路径下Q2原状黄土强度与微观结构演化试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(12): 168-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202212014.htmLIU Y Y, AN C, LAI H P, et al. Experimental research on strength and microstructure evolution of Q2 undisturbed loess under different wetting-drying cycle paths[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(12): 168-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202212014.htm [25] 朱彦鹏, 杨晓宇, 马孝瑞, 等. 边坡稳定性分析双折减法的几个问题[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(1): 331-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201801041.htmZHU Y P, YANG X Y, MA X R, et al. Several questions of double reduction method for slope stability analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 331-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201801041.htm [26] 黄俊, 党发宁, 覃源, 等. 高地应力黄土公路隧道稳定性储备[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 36(3): 33-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201603006.htmHUANG J,DANG F N,QIN Y,et al. Stability reserve of loess highway tunnel under high ground stress[J]. Journal of Chang′an University (Natural Science Edition),2016,36(3):33-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201603006.htm -





 下载:
下载: