Chemical clogging pattern of hot reservoir tailwater recharge in the Guantao Formation, northern Shandong, China
-
摘要:
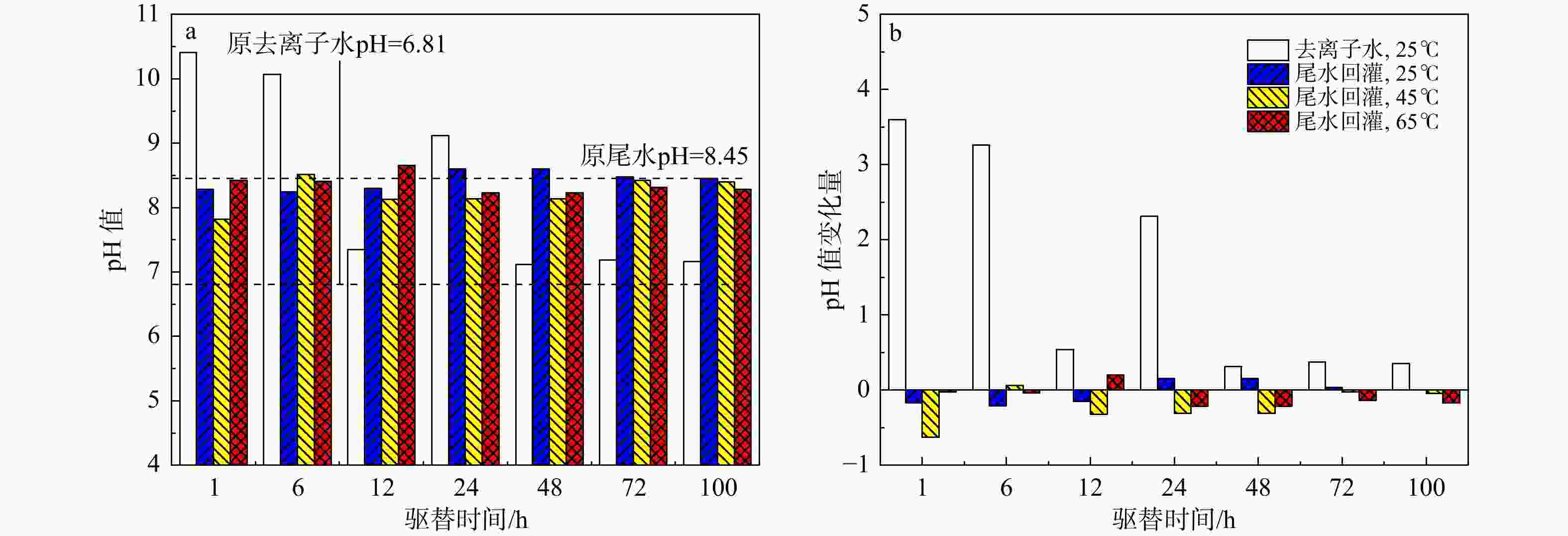
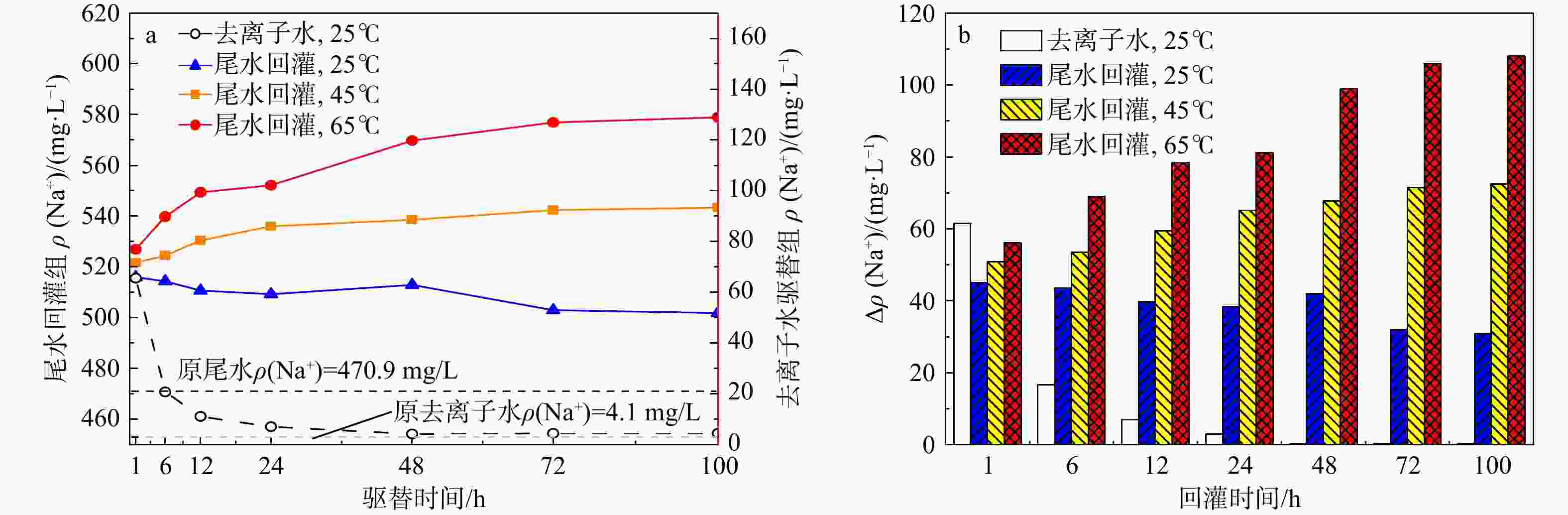
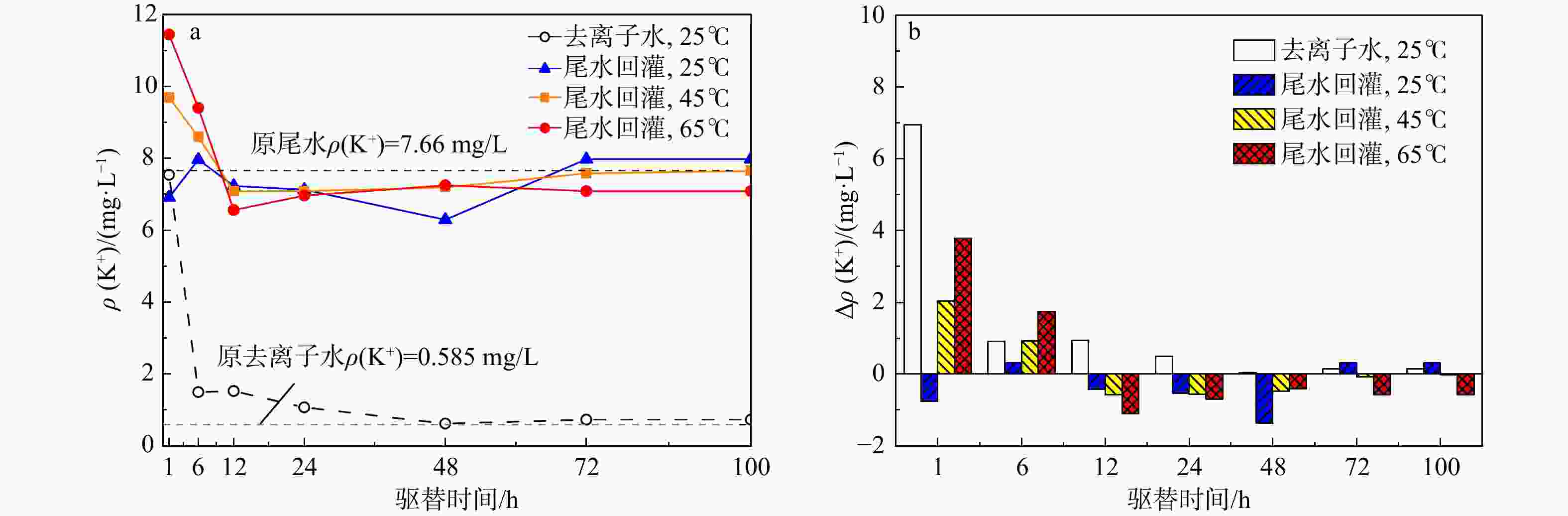
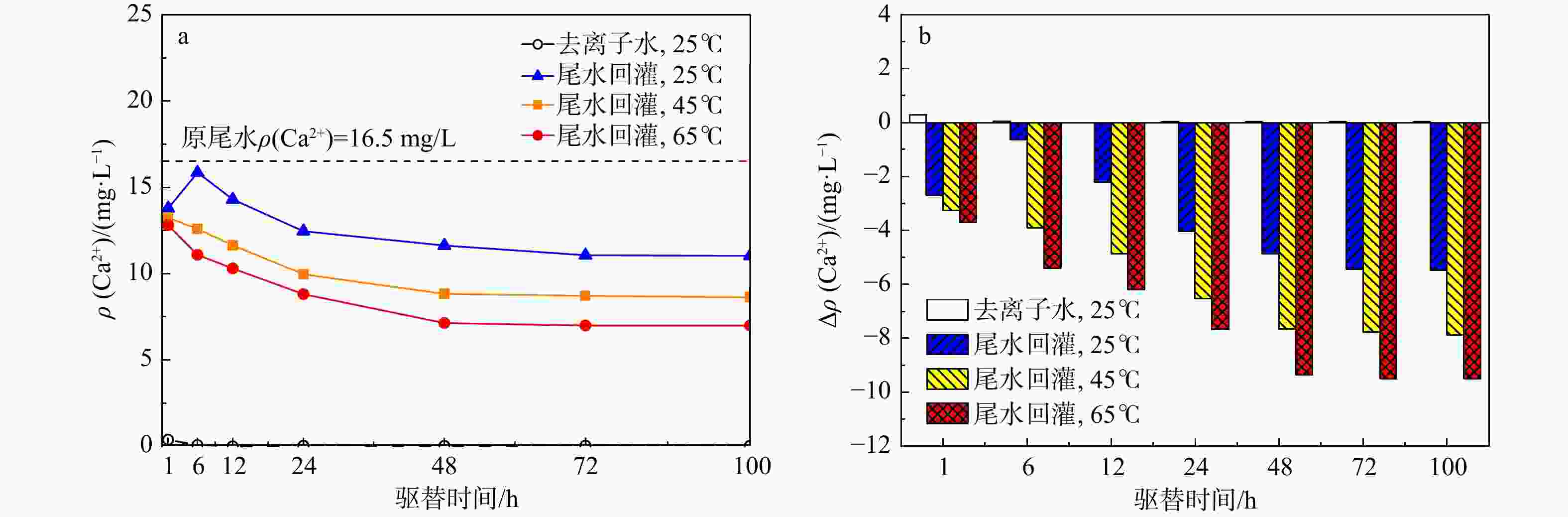
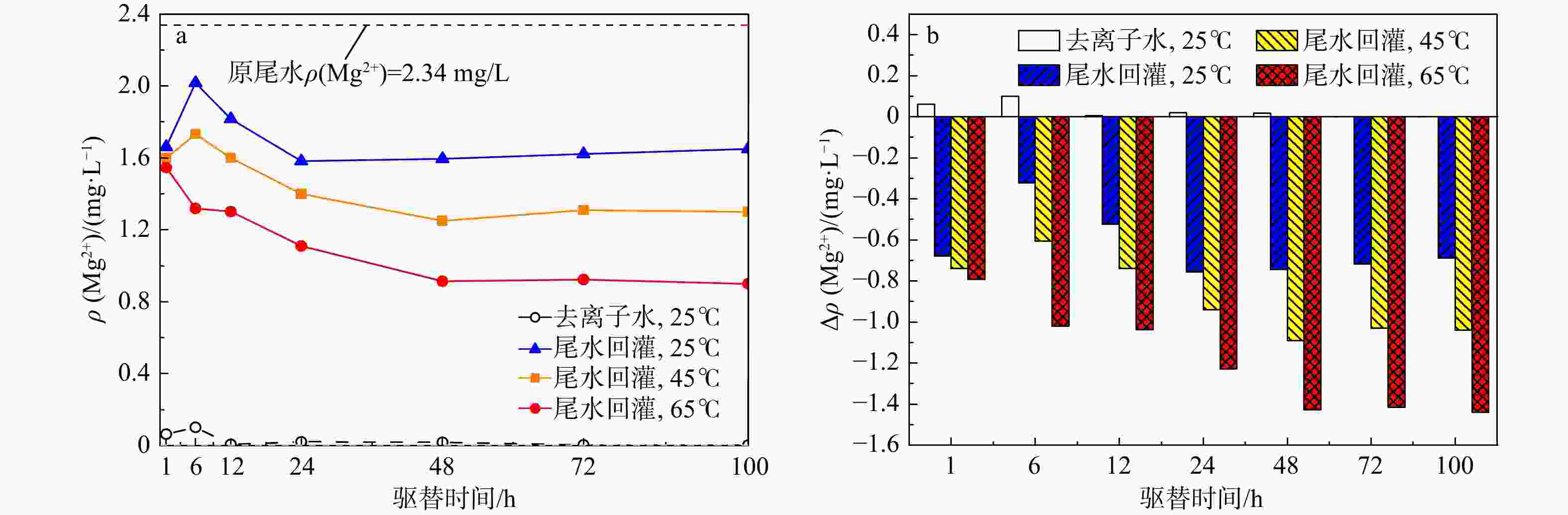
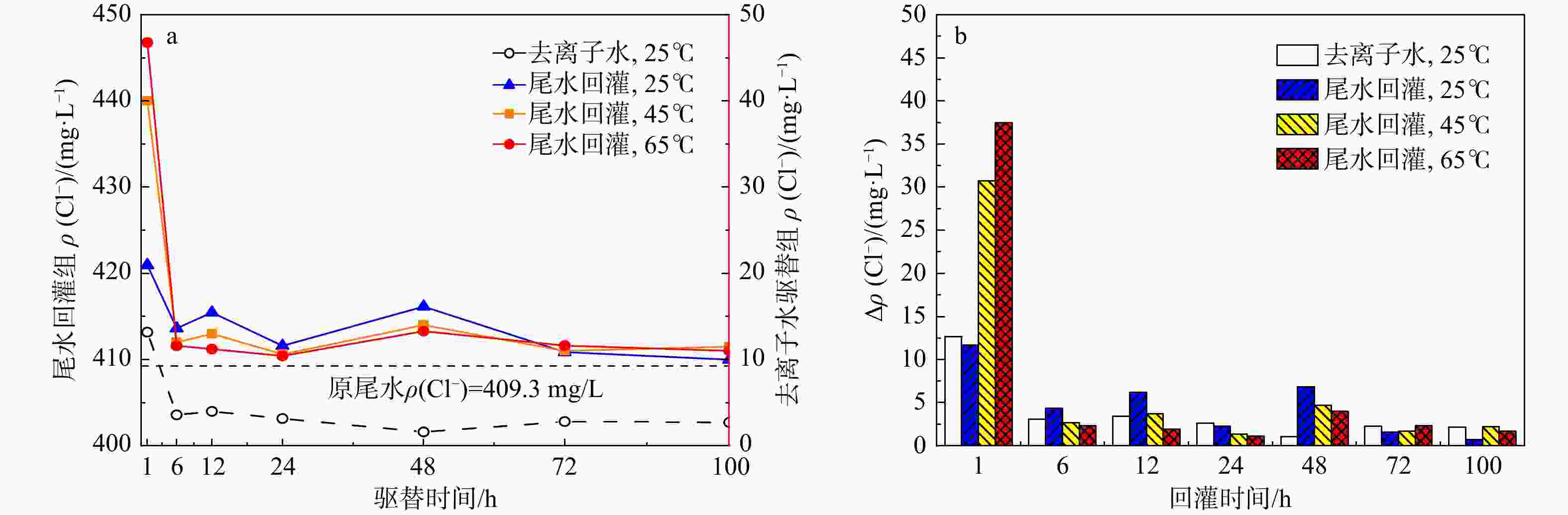
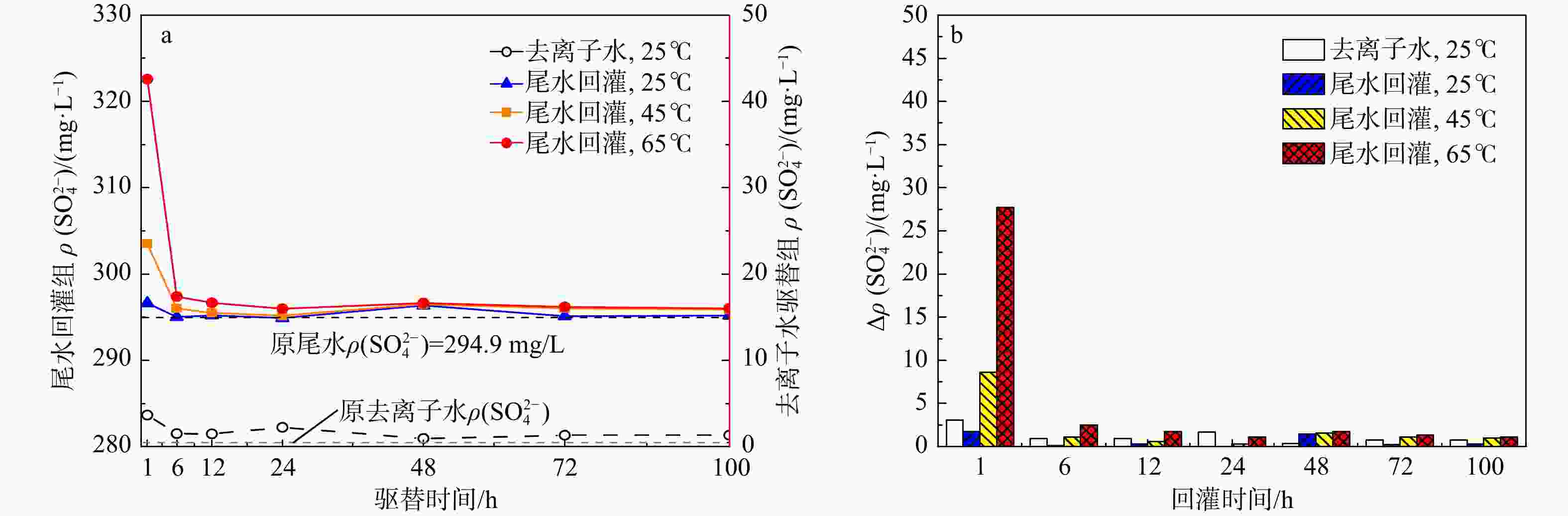
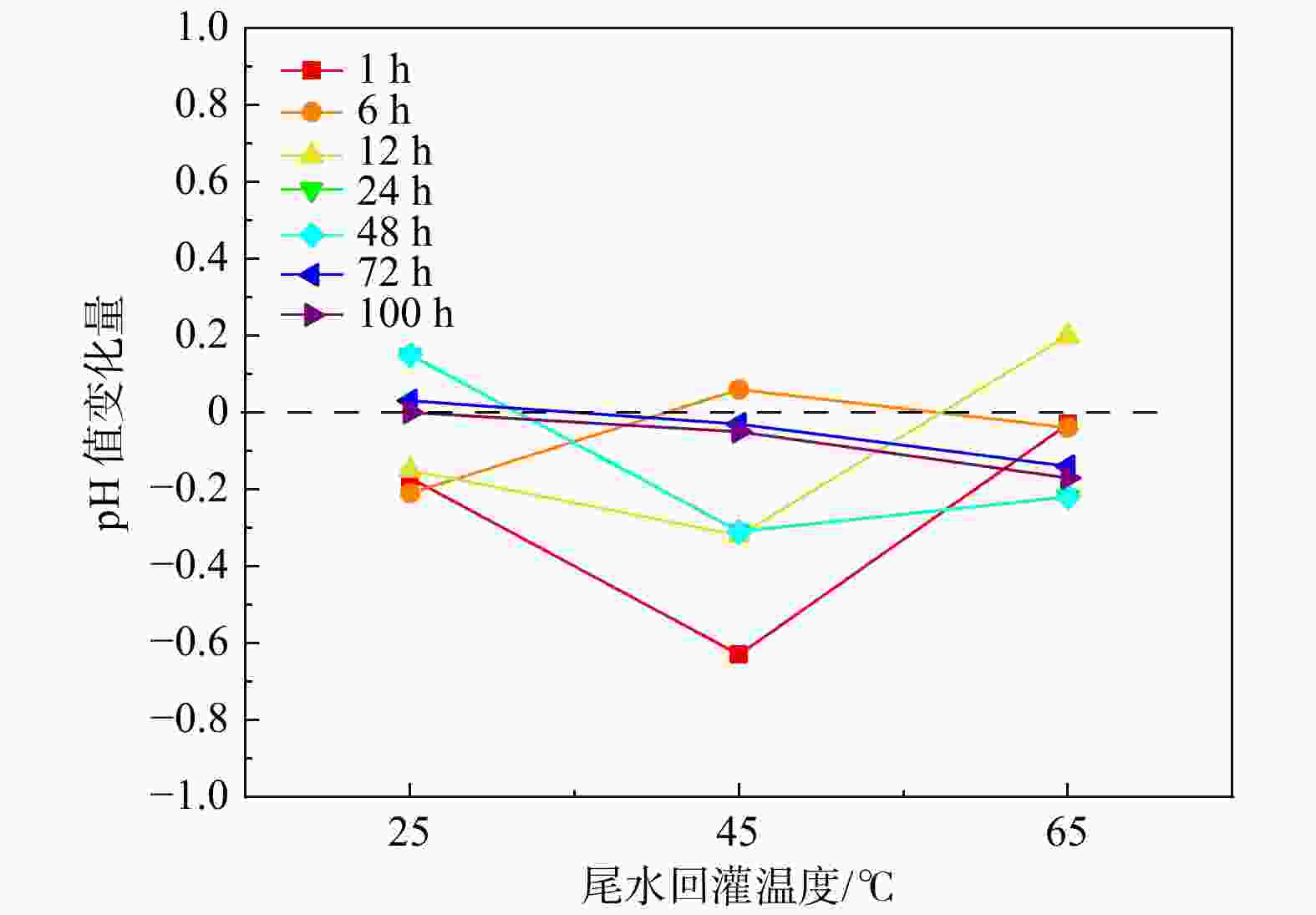
地热尾水回灌是实现地热能绿色环保可持续利用的关键,但在地热尾水回灌过程中产生的堵塞问题已成为亟待攻克的难题,严重制约了砂岩热储的开发利用。为了更好地了解不同温度和时间对水化学的影响,以鲁北馆陶组砂岩热储为研究对象,利用高温高压渗流溶蚀实验平台,分别对岩样于25,45,65℃温度下开展了为期100 h的砂岩热储回灌实验,探究了回灌过程中尾水的离子浓度和pH值的演化规律,揭示了砂岩热储尾水回灌中化学堵塞过程和机理。研究结果表明,随着温度的升高,Na+浓度逐渐上升,而Ca2+和Mg2+浓度稳步下降,且随着回灌时间的延长或温度的升高,Ca2+和Mg2+浓度的减少量逐渐增加。在65℃温度下,堵塞主要由Ca2+和Mg2+与重碳酸根和碳酸根发生反应所生成的沉淀造成,因此Ca2+和Mg2+的浓度与岩石样品的渗透率和化学堵塞率呈正相关。温度越高,化学堵塞程度越高,且快速增长阶段和快速下降阶段时间越久,化学反应越强烈,化学堵塞越严重。在实际工程中,可以利用降低回灌尾水的温度,或者通过在回灌前降低尾水的pH值,降低尾水中的Ca2+、Mg2+和HCO3−浓度来减轻化学堵塞的影响。
Abstract:Objective Geothermal brine reinjection is crucial for the sustainable and environmentally friendly utilization of geothermal energy. However, reinjection blockage presents a significant challenge, particularly hindering the development of sandstone reservoirs. This study explores the impact of temperature and reinjection duration on water chemistry, with a specific focus on the Guantao Formation sandstone reservoir in northern Shandong.
Methods We employed a high-temperature and high-pressure core flow apparatus to conduct flow-through dissolution tests on rock samples at temperatures of 25℃, 45℃, and 65℃ over a period of 100 hours. By analyzing changes in ion concentration and pH in the brine during reinjection, we aimed to uncover the mechanisms of chemical blockage in sandstone reservoirs.
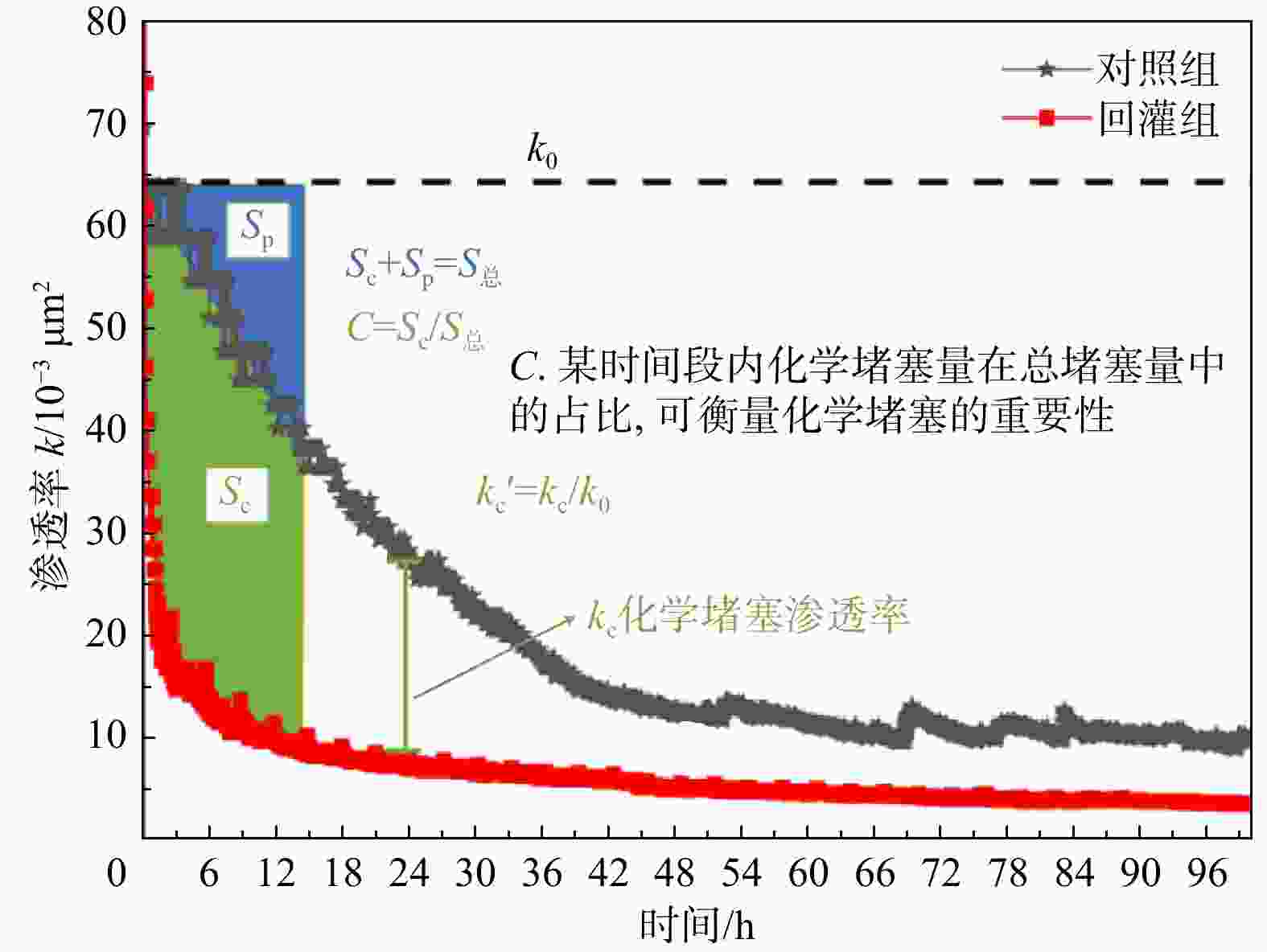
Results The results indicated that as the temperature rose, the concentration of Na+ ion gradually increased, while the concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions steadily declined. Prolonged reinjection time or elevated temperatures further reduced Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations. At 65℃, reactions involving Ca2+, Mg2+, bicarbonate, and carbonate ions led to precipitation, which significantly contributed to blockage. Thus, Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations were positively correlated with the permeability and chemical blockage rate of the rock samples. Longer reinjection durations and higher temperatures resulted in more severe chemical blockages.
Conclusion In practical applications, reducing the pH of the brine before reinjection or lowering temperature could alleviate chemical blockage by decreasing Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− concentrations.
-
Key words:
- tailwater recharge /
- sandstone thermal reservoir /
- ion concentration /
- chemical clogging
-
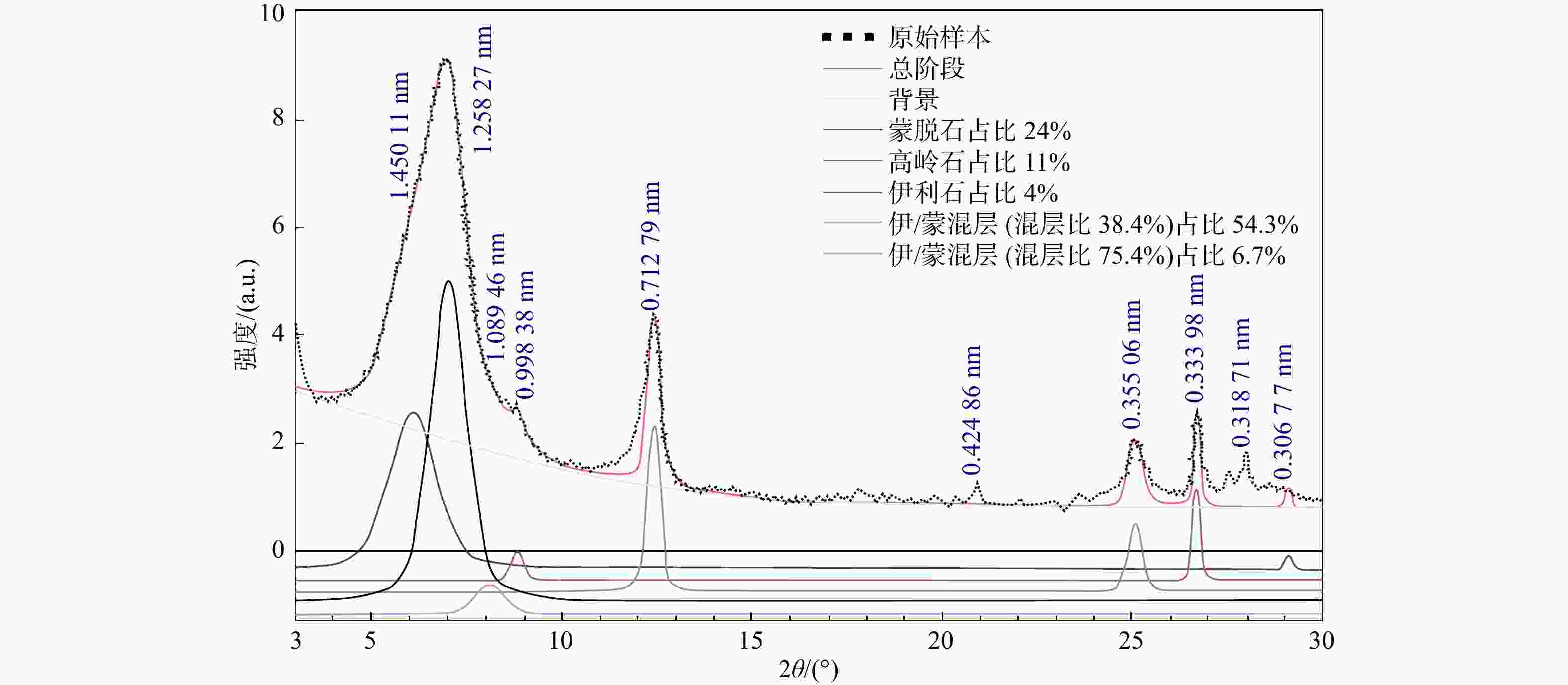
表 1 岩样XRD分析结果
Table 1. XRD analysis results of the rock samples
矿物成分 质量分数/% 黏土成分 质量分数/% 黏土矿物占比/% 钠长石 32.49 伊/蒙混层 9.85 61 钾长石 24.62 蒙脱石 3.88 24 石英 24.26 高岭石 1.78 11 透闪石 2.47 伊利石 0.65 4 黏土矿物 16.16 表 2 实验条件
Table 2. Experimental conditions
围压/MPa 流速/(mL·min−1) 回灌时间/h 流体介质 温度/℃ 10 0.5 100 去离子蒸馏水 25 回灌尾水 25 回灌尾水 35 回灌尾水 45 回灌尾水 55 回灌尾水 65 表 3 各组岩样尺寸及密度参数平均值
Table 3. Average values of size and density parameters for each group of rock samples
参数 去离子水
25℃尾水回灌25℃ 尾水回灌35℃ 尾水回灌45℃ 尾水回灌55℃ 尾水回灌65℃ 直径D/cm 2.501 2.517 2.513 2.523 2.521 2.519 长度L/cm 4.985 4.987 4.988 4.992 4.995 4.989 质量m/g 41.911 42.072 43.453 43.625 42.122 42.521 横截面积
A/cm24.912 4.976 4.959 4.999 4.991 4.983 体积V/cm3 24.486 24.815 24.735 24.957 24.930 24.860 密度ρ/
(g·cm−3)1.712 1.695 1.757 1.748 1.689 1.710 表 4 25℃下尾水回灌组相关性
Table 4. Correlation between ions in the tailwater reinjection group at 25°C
皮尔逊相关性 Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− pH Na+ 1 K+ 0.043 1 Ca2+ −0.108 0.002 1 Mg2+ 0.864** 0.374 0.220 1 Cl− −0.252 −0.654 0.508 −0.326 1 SO42− −0.187 −0.734* 0.039 −0.425 0.848** 1 pH −0.021 −0.337 −0.773* −0.368 −0.408 −0.048 1 kc 0.728 0.065 0.952** 0.763* 0.586 0.110 −0.880** $ {{k}}_{{{\mathrm{c}}}}{'} $ 0.729 0.064 0.952** 0.762* 0.587 0.110 −0.880** C 0.820* −0.151 0.923** 0.611 0.664 0.168 −0.728 Ch −0.774* 0.087 −0.812* −0.536 −0.759* −0.376 0.810* 注:**. 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性极显著;*. 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著,kc,kc',C,Ch的含义见正文,下同 表 5 45℃下尾水回灌组相关性
Table 5. Correlation between ions in the tailwater reinjection group at 45°C
皮尔逊相关性 Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− pH Na+ 1 K+ −0.378 1 Ca2+ −0.047 0.683 1 Mg2+ 0.658 0.210 0.612 1 Cl− −0.434 0.818* 0.549 −0.045 1 SO42− −0.454 0.843** 0.496 −0.088 0.993** 1 pH 0.343 −0.315 −0.304 0.255 −0.787* −0.737* 1 kc −0.359 0.593 0.968** 0.993** 0.411 0.363 −0.188 $ {{k}}_{{{\mathrm{c}}}}{'} $ −0.359 0.593 0.968** 0.993** 0.411 0.363 −0.188 C −0.261 0.558 0.973** 0.931** 0.508 0.446 −0.413 Ch 0.358 −0.740 −0.991** −0.898** −0.681 −0.639 0.468 表 6 65℃回灌水驱替组离子相关性
Table 6. Correlation between ions in the tailwater reinjection group at 65°C
皮尔逊相关性 Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− pH Na+ 1 K+ −0.399 1 Ca2+ −0.263 0.707* 1 Mg2+ 0.060 0.306 0.765* 1 Cl− −0.378 0.854** 0.549 0.147 1 SO42− −0.404 0.869** 0.586 0.167 0.998** 1 pH −0.246 0.113 0.626 0.495 0.110 0.142 1 kc −0.285 0.482 0.858* 0.844* 0.217 0.268 0.679 $ {{k}}_{{{\mathrm{c}}}}{'} $ −0.285 0.482 0.859* 0.845* 0.217 0.269 0.679 C −0.180 0.506 0.892** 0.885** 0.311 0.356 0.638 Ch 0.242 −0.728 −0.978** −0.972** −0.594 −0.631 −0.588 -
[1] 李俊峰,李广. 中国能源、环境与气候变化问题回顾与展望[J]. 环境与可持续发展,2020,45(5):8-17.LI J F,LI G. Review and outlook on energy,environment and climate change in China[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development,2020,45(5):8-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 邹晶莹. 砂岩热储地热尾水回灌化学堵塞机理研究[D]. 山东青岛:山东科技大学,2020.ZOU J Y. Research on chemical plugging mechanism of geothermal tailwater recharge in sandstone thermal storage[D]. Qingdao Shandong:Shandong University of Science and Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 崔圆圆. 关于山东省地热尾水回灌试验的应用研究[J]. 山东国土资源,2019,35(7):64-71. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.07.010CUI Y Y. Application research on geothermal brine reinjection experiment in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2019,35(7):64-71. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.07.010 [4] 李尧,齐玉峰,黄烜,等. 兰考县新近系热储赋存规律及开发适宜性研究[J]. 河南科学,2021,39(10):1615-1623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2021.10.012LI Y,QI Y F,HUANG X,et al. Study on the occurrence regularity and development suitability of Neogene geothermal reservoir in Lankao County[J]. Henan Science,2021,39(10):1615-1623. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2021.10.012 [5] 赵振,秦光雄,罗银飞,等. 西宁盆地地热水特征及回灌结垢风险[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):193-204.ZHAO Z,QIN G X,LUO Y F,et al. Geothermal water characteristics and reinjection scaling risk in Xining Basin[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):193-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 罗璐,朱霞,何春艳,等. 陕西咸阳地热田地热流体成因研究[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1422-1430.LUO L,ZHU X,HE C Y,et al. Study on the genesis of geothermal fluid in Xianyang geothermal field,Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(6):1422-1430. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 许勇. 西安三桥地区孔隙型地热尾水回灌模拟及前景展望[D]. 西安:长安大学,2018.XU Y. Simulation and prospects of porous geothermal brine reinjection in Sanqiao area,Xi'an [D]. Xi'an :Chang'an University,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 李泽威,袁飞,李明龙,等. 水化学特征在恩施盆地地热资源调查中的指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):83-94.LI Z W,YUAN F,LI M L,et al. Indicative significance of hydrochemical characteristics in geothermal resource investigations in the Enshi Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):83-94. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 刘杰,宋美钰,田光辉. 天津地热资源开发利用现状及可持续开发利用建议[J]. 地质调查与研究,2012,35(1):67-73.LIU J,SONG M Y,TIAN G H. Current status and sustainable development suggestions for geothermal resource development and utilization in Tianjin[J]. Geological Survey and Research,2012,35(1):67-73. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 阮传侠. 天津地区雾迷山组热储地热回灌研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018.RUAN C X. Geothermal reinjection study of Wumishan Formation in Tianjin area [D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing). 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 蔺文静,刘志明,王婉丽,等. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质,2013,40(1):312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021LIN W J,LIU Z M,WANG W L,et al. Assessment of geothermal resources and their potential in China[J]. Geology of China,2013,40(1):312-321. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021 [12] DU X,YE X,LU Y,et al. Research progress on artificial groundwater recharge blockage[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2009,24(9):973-980. [13] PORTIER S,VUATAZ F,NAMI P,et al. Chemical stimulation techniques for geothermal wells:Experiments on the three-well EGS system at Soultz-sous-Forêts,France[J]. Geothermics,2009,38(4):349-359. [14] JEONG H Y,JUN S C,CHEON J Y,et al. A review on clogging mechanisms and managements in aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) applications[J]. Geosciences Journal,2018,22(4):667-679. [15] GUNNARSSON I,ARNÓRSSON S. Impact of silica scaling on the efficiency of heat extraction from high-temperature geothermal fluids[J]. Geothermics,2005,34(3):320-329. [16] MACKAY E J. Modelling of in-situ scale deposition:The impact of reservoir and well geometries and kinetic reaction rates[C]//Anon. International Symposium on Oilfield Scale. [S. l. ]:OnePetro,2002. [17] 闫志为,刘辉利,张志卫. 温度及CO2对方解石、白云石溶解度影响特征分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2009,28(1):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.01.002YAN Z W,LIU H L,ZHANG Z W. Influences of temperature and Pco2 on the solubility of calcite and dolomite[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2009,28(1):7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.01.002 [18] 闫志为. 硫酸根离子对方解石和白云石溶解度的影响[J]. 中国岩溶,2008,27(1):24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.005YAN Z W. Effect of sulfate ions on the solubility of calcite and dolomite[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2008,27(1):24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.005 [19] 徐国芳,马致远,周鑫,等. 地压型热储流体尾水回灌化学堵塞机理研究:以咸阳回灌一号井为例[J]. 工程勘察,2013,41(7):40-44.XU G F,MA Z Y,ZHOU X,et al. Study on chemical plugging mechanism of ground-pressure type thermal storage fluid tailwater recharge:A case study of Xianyang recharge Well No. 1[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2013,41(7):40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 潘俊,姜明岑,冯许阳. 地下水中铁锰离子对地下水地源热泵回灌影响的试验研究[J]. 暖通空调,2014,44(8):80-84.PAN J,JIANG M C,FENG X Y. Experimental study on the effect of iron and manganese ions in ground water on groundwater ground source heat pump recharge[J]. Journal of HV& AC,2014,44(8):80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 周鑫. 沉积盆地孔隙型地下热水回灌堵塞机理研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2013.ZHOU X. Study of pore-type groundwater recharge plugging mechanism in sedimentary basins[D]. Xi'an:Chang'an University,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 刘久荣. 地热回灌的发展现状[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2003,30(3):100-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.03.025LIU J R. The status of geothermal reinjection[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2003,30(3):100-104. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.03.025 [23] 祁翠婷,詹红兵,郝永红. 包气带井回灌引起的非饱和-饱和流分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):118-129.QI C T,ZHAN H B,HAO Y H. Analysis of unsaturated-saturated flow induced by a vadose zone well injection[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):118-129. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] JANSE R J. Conducting correlation analysis:Important limitations and pitfall[J]. Clinical Kidney Journal,2021,14(11):2332-2337. -




 下载:
下载: