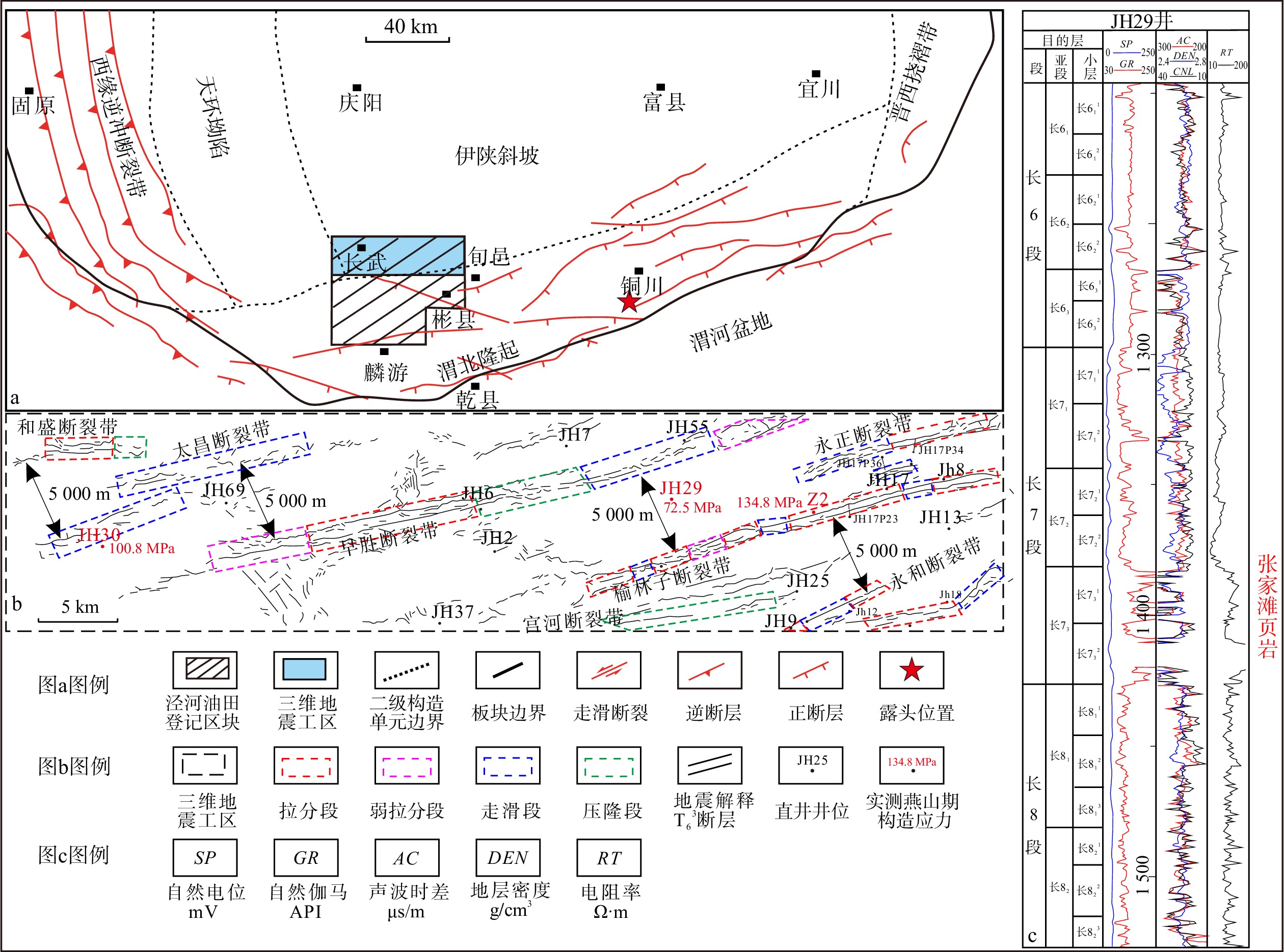
Structural diagenesis and reservoir control analysis of tight sandstone in the strike-slip fault zones of the Chang 8 to Chang 6 Members in the Jinghe Oilfield
-
摘要:
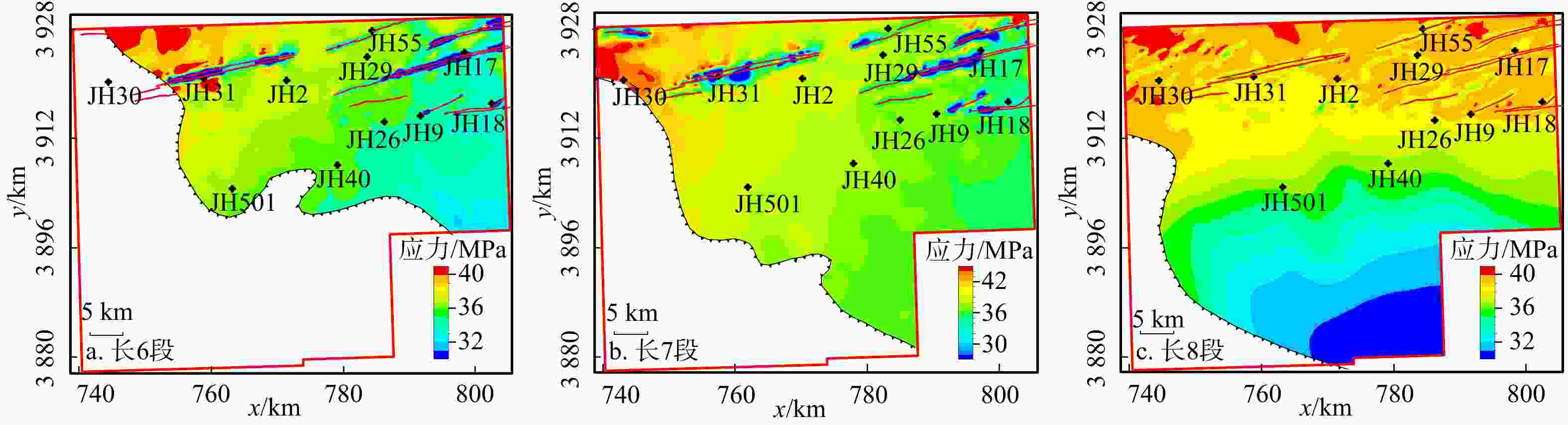
泾河油田长8-长6段致密砂岩“甜点”储层受走滑断裂带及内部结构模式控制,且分布非均质性极强,表明构造成岩作用是主要控制因素。综合多种资料,开展了断裂带构造成岩成储分析,为致密砂岩油藏高效开发提供了依据。研究表明:受构造应力应变差异控制,走滑断裂带与走滑断裂带之间区域的构造成岩作用及控储特征存在差异,主要表现在:(1)走滑断裂带的构造应力应变具有簇状分布特点。走滑断裂带为高应力应变区(HSSZ),走滑断裂带之间的区域为低应力应变区(LSSZ)。走滑断裂带沿走向可划分为张扭段、压扭段和走滑段;垂直于断层走向可概括出三大类八小类侧向分带结构模式。(2)走滑断裂带的构造成岩作用包括:变形条带、胶结作用、溶蚀及交代作用、微裂缝、碎裂作用、构造涂抹。(3)构造应力应变差异控制了构造成岩差异,进而控制了储层物性:① HSSZ区域和LSSZ区域的压实减孔作用均强于胶结作用。但是HSSZ区域的构造成岩减孔作用强于LSSZ区域,而LSSZ区域的胶结减孔作用强于HSSZ区域。②分段控储作用由好到差依次为:张扭段、断层端部、弱张扭段、走滑段、压扭段。
Abstract:Objective The distribution of tight sandstone sweet spots in the Chang 8 to Chang 6 members of the Jinghe Oilfield is primarily influenced by strike-slip fault zones and their internal structural patterns, which demonstrate significant heterogeneity. This finding indicates that tectonic diagenesis is the main controlling factor of reservoir heterogeneity.
Methods This paper integrates various datasets to analyze structural diagenesis and reservoir formation within fault zones, thereby providing a foundation for the efficient development of tight sandstone reservoirs.
Results and Conclusions Variations in structural stress and strain lead to differing structural diagenesis and reservoir characteristics between and within strike-slip fault zones. The key findings include the following: (1) The structural stress and strain in strike-slip fault zones show clustered distribution characteristics. The zones are categorized into high-stress–strain zones (HSSZs) and low-stress–strain zones (LSSZs). Additionally, within strike-slip faults, transtensional, transpressional, and strike-slip segments can be distinguished along the fault strike, while three major categories and eight secondary categories of lateral zoning structural patterns are summarized along the fault dip. (2) Structural diagenesis within strike-slip fault zones includes deformation bands, cementation, dissolution and replacement, microfracturing, cataclasis, and smearing. (3) The differences in structural stress and strain govern the variations in structural diagenesis and, consequently, reservoir physical properties: (a) Both the HSSZ and LSSZ experienced more significant compaction and porosity reduction compared to cementation. However, the porosity reduction caused by structural diagenesis in the HSSZ was more intense than that in the LSSZ, whereas cementation in the HSSZ was greater than that in the LSSZ. (b) Under the influence of structural diagenesis, the physical properties of different segments decrease in the following sequence: transtensional segments, fault tips, weak transtensional segments, strike-slip segments, and transpressional segments.
-
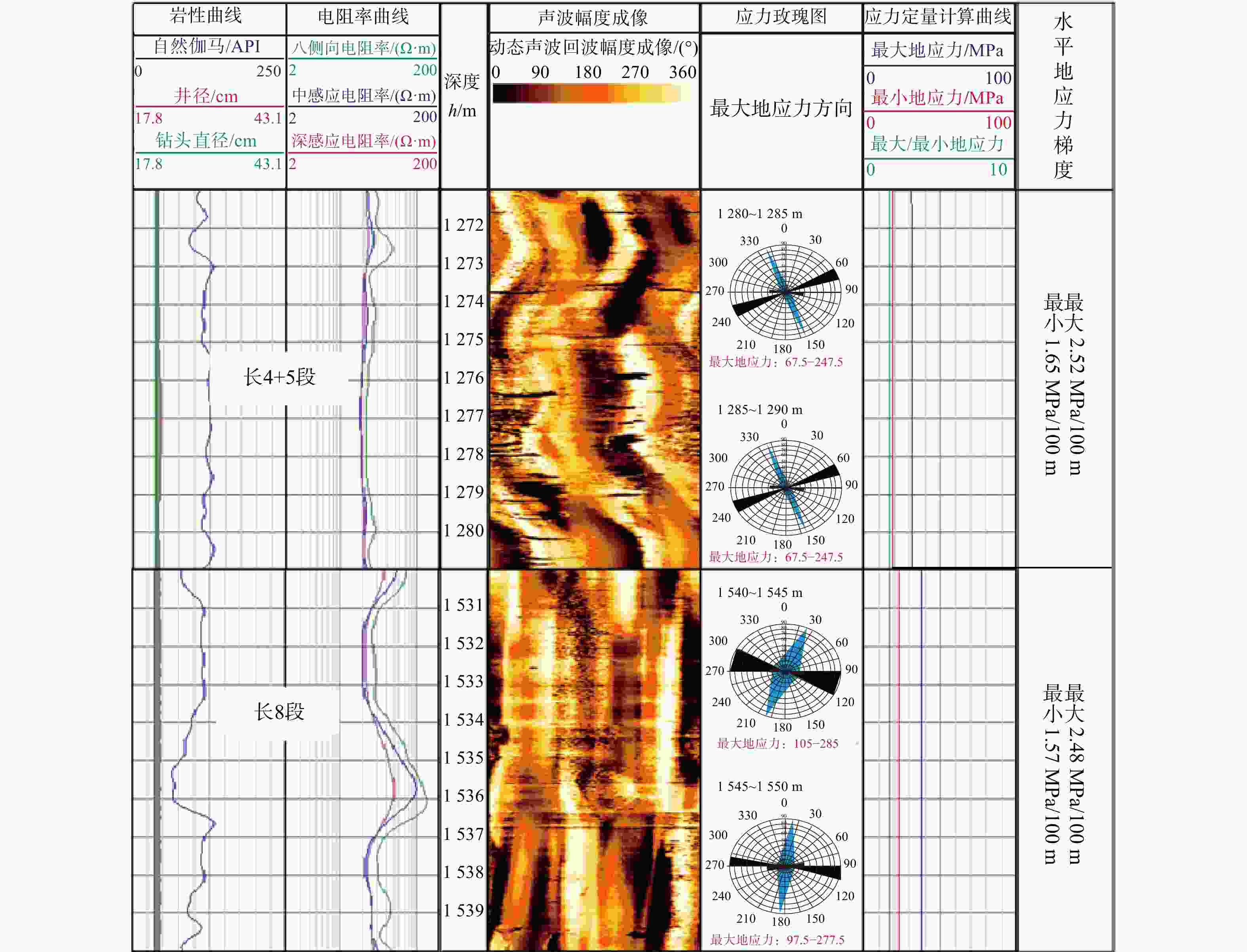
表 1 泾河油田长6-长8段不同构造期的最大主应力值(声发射AE测试)
Table 1. Maximum principal stress values of the Chang 6- Chang 8 Members across different tectonic stages of the Jinghe Oilfield (AE test)
井号 岩性 声波时差/
(μs·m−1)深度/m 最大主应力σ1/MPa 燕山期 喜马拉雅期 现今 JH29 细砂岩 256 1312.07 72.5 62.7 35.8 JH30 细砂岩 214 1588.50 100.8 58.9 30.7 Z2 细砂岩 211 1406.56 134.8 57.6 42.8 平均 / / 102.7 59.7 36.4 表 2 泾河油田长6-长8段走滑断层侧向分带结构模式特征
Table 2. Characteristics of the lateral zonal structure of strike-slip faults in the Chang 6-Chang 8 Members of the Jinghe Oilfield
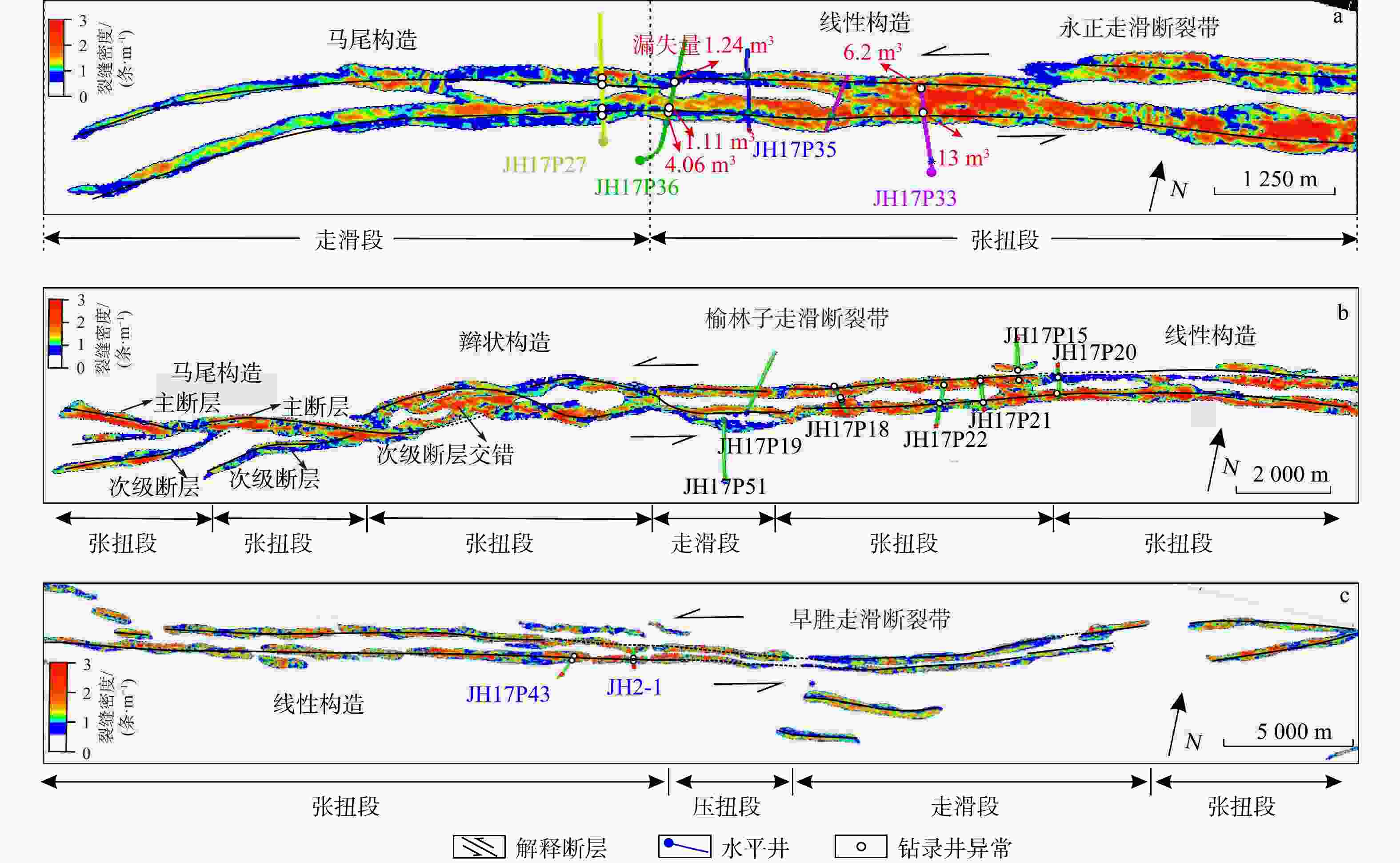
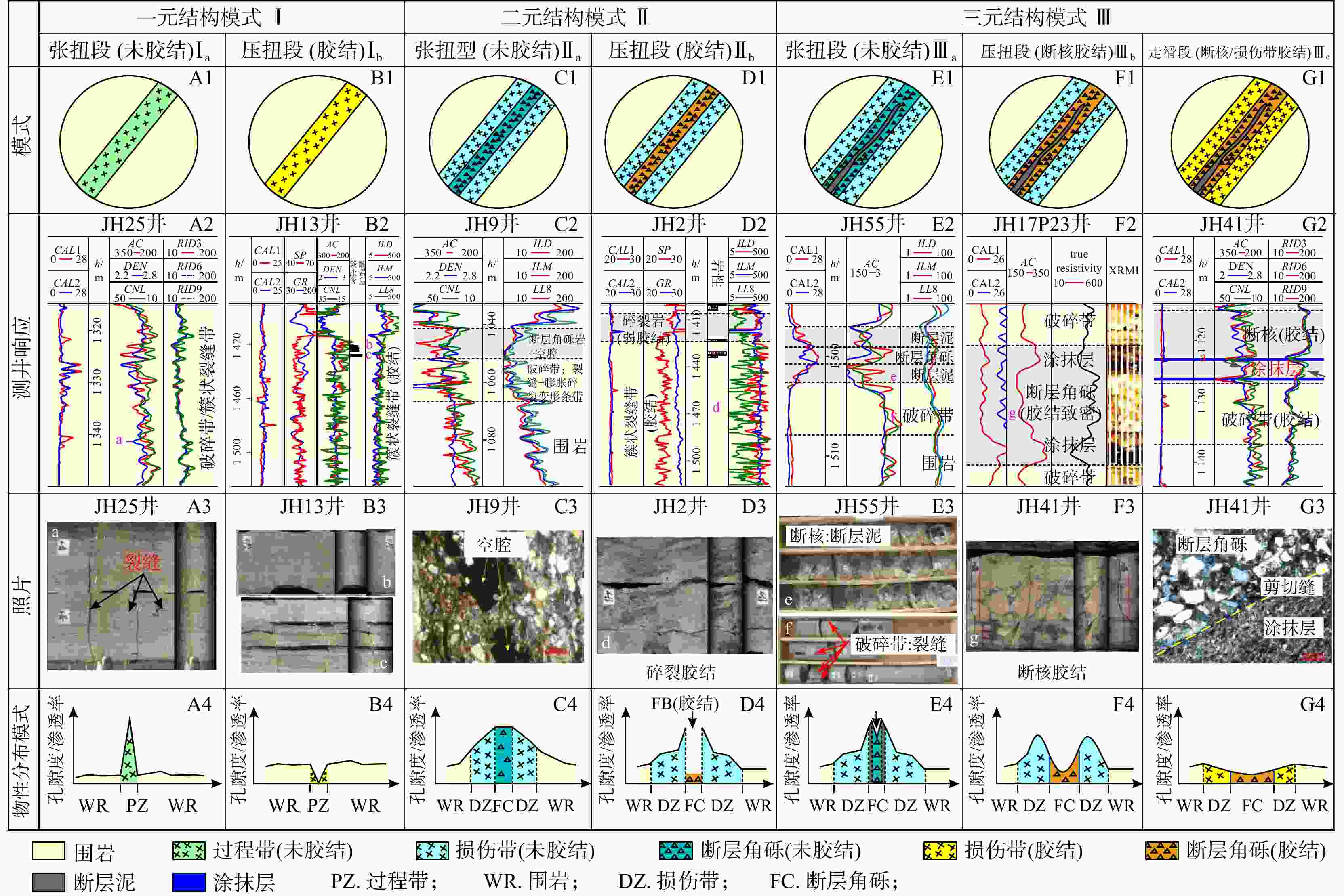
侧向分带结构模式 特 征 类型 亚类 Ⅰ型 Ⅰa 位于走滑断层张扭性端部,主要发育张开型微裂缝和膨胀型变形条带,溶蚀作用较发育 Ⅰb 主要发育走滑断层压扭性端部,多发育闭合型微裂缝及压实型变形条带,胶结作用较发育 Ⅱ型 Ⅱa 断核常见断层角砾及空腔,溶蚀作用发育,破碎带多由剪切解聚和膨胀碎裂变形条带及张开缝等组成 Ⅱb 断核多由胶结角砾岩及闭合缝组成,胶结作用发育,破碎带多由压性闭合缝及压实碎裂变形带等组成 Ⅱc 断核多由剪切碎裂岩及高角度剪切缝密集带组成,破碎带以剪切缝及胶结剪切变形带为主 Ⅲ型 Ⅲa 断核多为断层角砾+断层泥,破碎带为张裂缝密集带及膨胀碎裂带 Ⅲb 断核见胶结碎裂角砾、断层泥,具有页理化组构糜棱岩。破碎带见密集闭合微裂缝及压溶变形条带 Ⅲc 断核见剪切碎裂岩、断层泥及涂抹层,偶见糜棱岩。破碎带见密集剪切微裂缝带及剪切碎裂变形条带 表 3 成岩早-中期阶段解聚变形条带的成因及识别特征
Table 3. Genesis and identification characteristics of disaggregation bands during the early-middle diagenetic stages
变形构造 识别特征 实例 解
聚
变
形
条
带压实
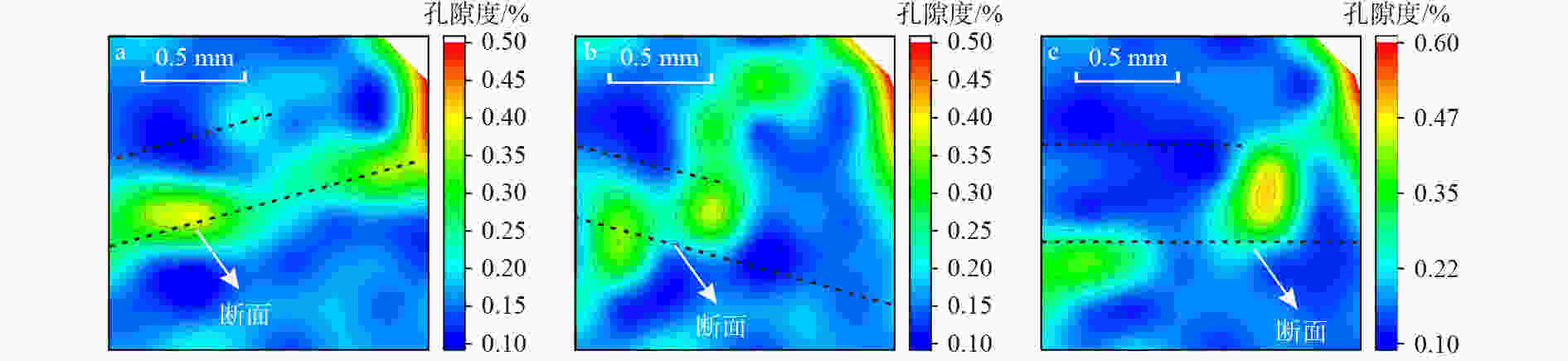
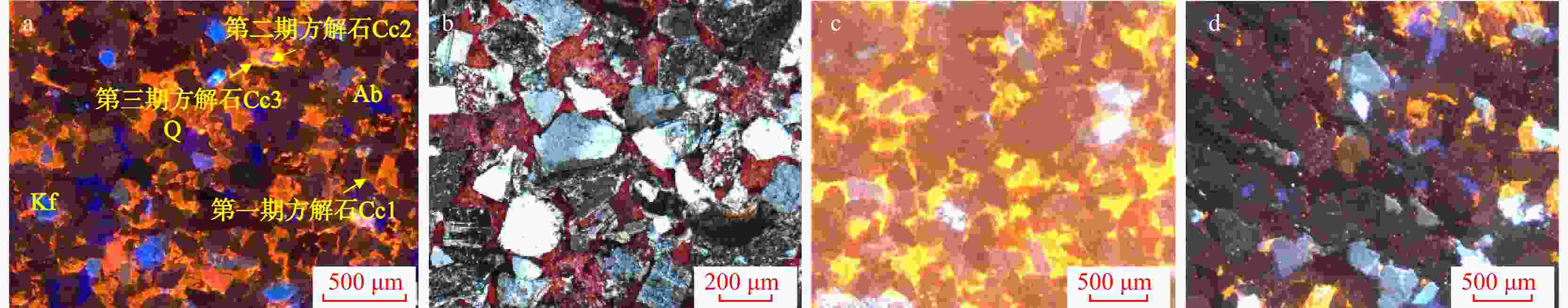
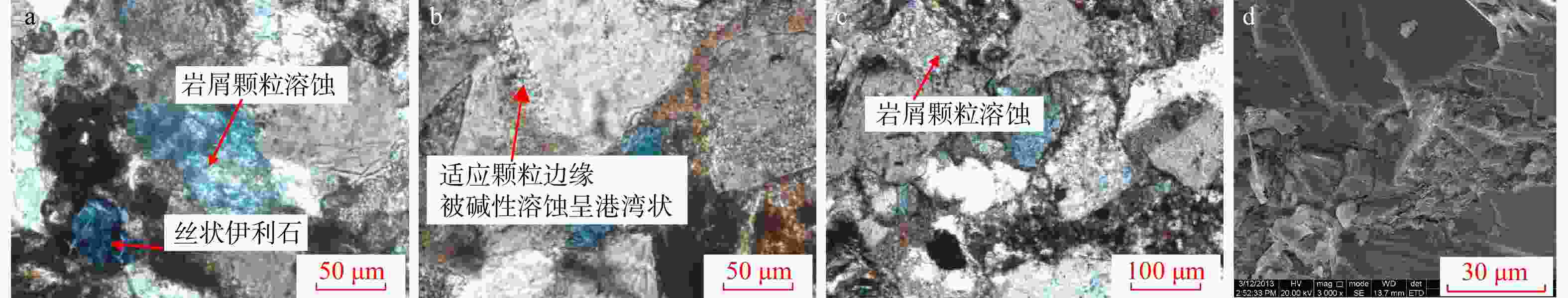
解聚成岩早-中期,碎屑颗粒间存在孔隙空间(后期钙质胶结),颗粒旋转与颗粒间错动发生重组,形成颗粒顺层排列。变形条带中颗粒呈线接触;变形条带之间颗粒呈点接触。后期铁方解石胶结,图像处理面孔率估算变形带面孔率为2%,变形条带之间面孔率为17%,两者孔隙度相差15%(红色为硒素红染色,代表后期钙质胶结,统计时不考虑胶结物面积),反映了局部变形导致储层硬化 
JH2井,长812小层,细砂岩,早胜断裂带,压扭段(单偏光) 剪切
解聚剪切应力作用下,颗粒平移-旋转-滑动发生重组,形成颗粒长轴顺层排列。变形条带之间,发育线状微裂缝。颗粒线接触。由于剪切解聚作用,粒间孔明显发育(蓝色面积),变形带有储层“软化”现象。变形条带面孔率为17.2%;变形条带之间面孔率为1.6%,两者相差15.6%(蓝色为铸体孔隙),正交,铸体薄片 
JH25井,长823小层,细砂岩,宫河断裂带,端部张扭马尾段 表 4 成岩中-晚期阶段碎裂变形条带的成因及识别特征
Table 4. Genesis and identification characteristics of the cataclasite band in the middle-late diagenetic stages
变形构造 识别特征 实例 碎
裂
变
形
条
带膨胀
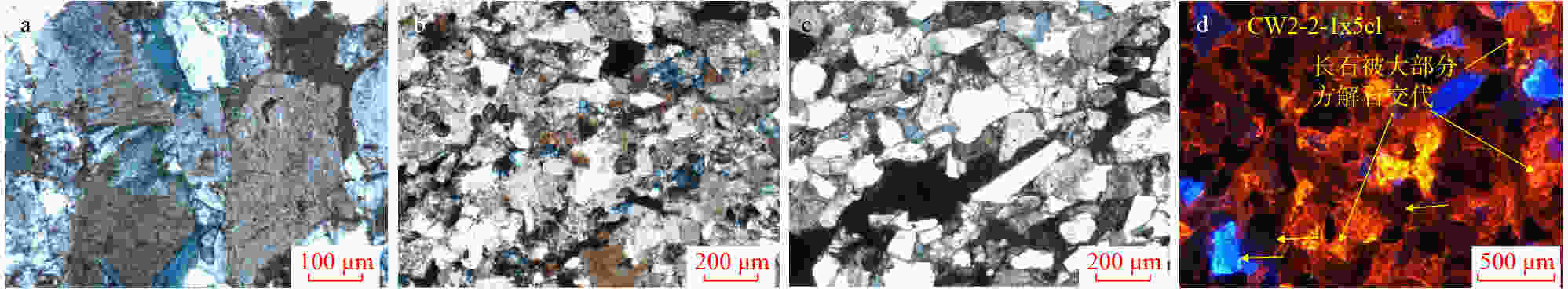
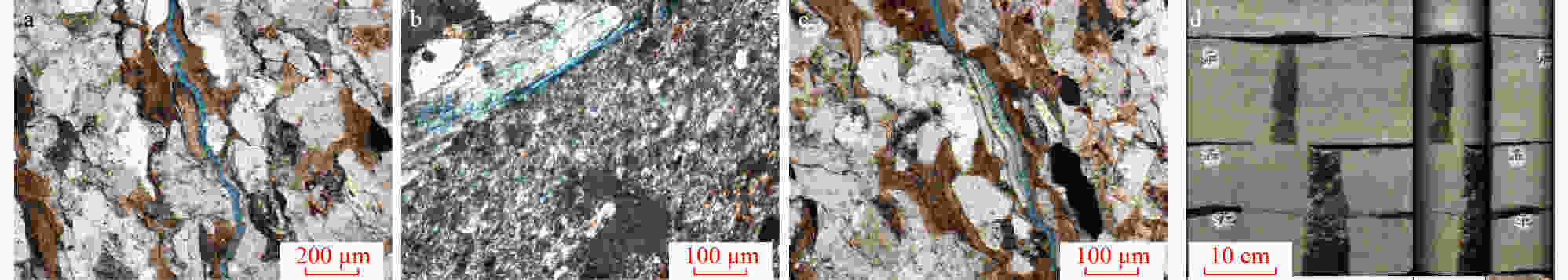
碎裂颗粒碎裂,大小不一,角砾状,构造角砾岩,颗粒呈点接触;中-细晶方解石斑状充填于砾间,裂缝发育,空腔发育,方解石、沥青充填,缝洞型储层。物性好,岩心实测孔隙度为9.42%,渗透率为16.7×10−3 μm2 
JH9井, 1047 m,长811小层,正交光。宫河断裂带,张扭段压实
碎裂颗粒碎裂,分选差,棱角-次棱角状,颗粒定向明显,呈紧密连接状(interlocking)的压实条带,偶见微裂缝,颗粒以线接触为主,微显位移,钙质胶结,物性较差,孔隙度为4.4%,渗透率为0.05×10−3 μm2 
JH41井, 1126 m,长81亚段,细砂岩,正交光。芋圆走滑断裂带压扭段剪切
碎裂见剪切缝,微裂缝一侧为角砾岩,另外一侧为断层泥,反映较强的剪切碎裂作用,由于微裂缝发育,因此,孔隙度较低,为4.9%,渗透率较好,可达0.26×10−3 μm2 
JH13井, 1422 m,长81亚段,灰色细砂岩;宫河走滑断裂带东北走滑段表 5 泾河油田长6-长8段走滑断裂带不同分段砂岩的钙质胶结物
Table 5. Calcareous cement of sandstone in different segments of the strike-slip fault zone of the Chang 6-Chang 8 Members, Jinghe Oilfield
分段 钙质胶结物体积分数/% 样品数 代表井号 最大 最小 平均 张扭段 49.0 1 8.87 78 JH8、JH17、JH18、JH25、JH9 压扭段 48.0 1 11.94 58 JH11、JH22、JH23、JH13、JH26 走滑段 20.5 4 12.15 11 JH16、JH33 表 6 泾河油田长6-长8段不同应力应变带视压实率与视胶结率计算结果统计
Table 6. Statistical data of the calculated compaction and cementation rates of the Chang 6, Chang 7 and Chang 8 Members in high and low stress, strain zones in the Jinghe Oilfield
层位 走滑断裂带间低应力应变带(LSSZ) 走滑断裂带内高应力应变带(HSSZ) 视压实率CR/% 视胶结率CE/% 视压实率CR/% 视胶结率CE/% 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 长6段 29~49 39.0 18~63 33.00 26~81 49.6 2.6~53 25.80 长7段 25~63 47.0 18~54 28.00 28~65 56.2 2.59~78 27.00 长8段 10~70 51.1 9~75 33.36 31~88 65.0 1~72 18.64 -
[1] 彭伟,舒逸,陈绵琨,等. 四川盆地复兴地区侏罗系凉高山组致密砂岩储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):102-113.PENG W,SHU Y,CHEN M K,et al. Tight sandstone reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation in Fuxing area,Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):102-113. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] MORAD S,AL-RAMADAN K,KETZER J M,et al. The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs:A review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2010,94(8):1267-1309. doi: 10.1306/04211009178 [3] 何发岐,梁承春,陆骋,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘过渡带致密-低渗油藏断缝体的识别与描述[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(4):710-718.HE F Q,LIANG C C,LU C,et al. Identification and description of fault-fracture bodies in tight and low permeability reservoirs in transitional zone at the south margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology,2020,41(4):710-718. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 陈红汉. 我国大型克拉通叠合盆地的走滑构造与油气聚集研究进展[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(6):2039-2066.CHEN H H. Advances on relationship between strike-slip structures and hydrocarbon accumulations in large superimposed craton basins,China[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(6):2039-2066. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] FOSSEN H,BALE A. Deformation bands and their influence on fluid flow[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2007,91(12):1685-1700. doi: 10.1306/07300706146 [6] AYDIN A. Small faults formed as deformation bands in sandstone[J]. Rock Friction and Earthquake Prediction,1978,116:913-930. [7] AYDIN A,JOHNSON A M. Analysis of faulting in porous sandstones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,1983,5(1):19-31. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(83)90004-4 [8] 张荣虎,曾庆鲁,王珂,等. 储层构造动力成岩作用理论技术新进展与超深层油气勘探地质意义[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(10):1278-1292.ZHANG R H,ZENG Q L,WANG K,et al. New progress in the theory and technology of tectonic diagenesis on reservoir and the geological significance of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2020,41(10):1278-1292. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 刘志达,付晓飞,孟令东,等. 高孔隙性砂岩中变形带类型、特征及成因机制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2017,46(6):1267-1281.LIU Z D,FU X F,MENG L D,et al. Types,characteristics and genetic mechanism of deformation bands in high-porous sandstone[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2017,46(6):1267-1281. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 付晓飞,尚小钰,孟令东. 低孔隙岩石中断裂带内部结构及与油气成藏[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,44(6):2428-2438.FU X F,SANG X Y,MENG L D. Internal structure of fault zone and oil/gas reservior in low-porosity rock[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2013,44(6):2428-2438. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 付晓飞,肖建华,孟令东. 断裂在纯净砂岩中的变形机制及断裂带内部结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(1):25-37.FU X F,XIAO J H,MENG L D. Fault deformation mechanisms and internal structure characteristics of fault zone in pure sandstone[J]. Journal of Jilin University( Earth Science Edition),2014,44(1):25-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 邬光辉,陈志勇,郭群英. 碳酸盐岩变形带特征及其与油气关系:以塔里木盆地下古生界为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2014,38(3):580-589.WU G H,CHEN Z Y,GUO Q Y. Characteristics of carbonate deformation band and its significance for hydrocarbon exploration:An example from the Lower Paleozoic in the Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2014,38(3):580-589. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 张新乐,平宏伟,杨鑫,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘泾河油田长7段烃源岩生、排烃期与油气成藏期对比[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):108-121.ZHANG X L,PING H W,YANG X,et al. Comparison of hydrocarbon generation,expulsion periods,and accumulation periods of source rocks in Member 7 of the Yanchang Formation in the Jinghe Oilfield,southern Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):108-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 王朝,黄雷,刘池洋,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部走滑断-缝体分布规律及其主控因素[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2024,53(4):793-807.WANG C,HUANG L,LIU C Y,et al. Distribution of strike-slip fault-fracture volume and its controlling factors in the southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2024,53(4):793-807. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LIU H P,ZHAO Y C,LUO Y,et al. Origin of the reservoir quality difference between Chang 8 and Chang 9 Member sandstones in the Honghe Oil Field of the southern Ordos Basin,China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2020,185:106668. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106668 [16] 吉园园. 鄂尔多斯盆地泾河油田长81油层沉积相研究[J]. 辽宁化工,2017,46(7):657-658.JI Y Y. Study on the sedimentary facies of Chang 8_1 oil reservoir in Jinghe Oilfield,Ordos Basin[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry,2017,46(7):657-658. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 王振,张元福,张娜,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部旬邑地区延长组长7段深水牵引流的发现及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(2):9-16.WANG Z,ZHANG Y F,ZHANG N,et al. Discovery and significance of deep-water tractive current deposits in Member 7 of Yanchang Formation in Xunyi area of southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(2):9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] FUDOL Y A,ZHAO Y C,LIU H P,et al. Origin and reservoir properties of deep-water gravity flow sediments in the Upper Triassic Ch6-Ch7 members of the Yanchang Formation in the Jinghe Oilfield,the southern Ordos Basin,China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation,2019,37(4):1227-1252. [19] 夏东领,邹敏,庞雯,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾地区长8致密砂岩储层孔喉组合分类及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(4):120-126.XIA D L,ZOU M,PANG W,et al. Classification and significance of pore throat combination of Chang 8 tight sandstone reservoir in Zhenjing area,Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(4):120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 唐大卿,陈红汉,耿锋,等. 板内小位移走滑断裂特征解析:以塔里木、四川及鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(6):2067-2086.TANG D Q,CHEN H H,GENG F,et al. Characteristics of intraplate small-displacement strike-slip faults:A case study of Tarim,Sichuan and Ordos Basins[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(6):2067-2086. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] YIN A,ZUZA A V,PAPPALARDO R T. Mechanics of evenly spaced strike-slip faults and its implications for the formation of tiger-stripe fractures on Saturn's moon Enceladus[J]. Icarus,2016,266:204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2015.10.027 [22] ZUZA A V,YIN A,LIN J,et al. Spacing and strength of active continental strike-slip faults[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2017,457:49-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.09.041 [23] ZENG L,MAO Z,LIU G,et al. Controls of strike-slip fault on fractures:Insight from 3D discrete element simulation[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences),2024,67(1):146-164. doi: 10.1007/s11430-022-1142-4 [24] 徐黎明,周立发,张义楷,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造应力场特征及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2006,30(4):455-462.XU L M,ZHOU L F,ZHANG Y K,et al. Characteristics and tectonc setting of tectono-stress field of ordos basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2006,30(4):455-462. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 丁健民,梁国平. 水力压裂应力测量及其在油气田开发中的应用[J]. 地质力学学报,1989,12(1):185-195.DING J M,LIANG G P. Hydrofracturing stress measurement and its application in exploitation of oil and gas field[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,1989,12(1):185-195. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 曹金凤,孔亮,王旭春. 水压致裂法地应力测量的数值模拟[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2012,8(1):148-153.CAO J F,KONG L,WANG X C. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing technique in geostress measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2012,8(1):148-153. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 郭鹏,李元昊,段祎乐,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地彬长地区长7油层组软沉积物变形构造空间分布规律及其触发机制[J]. 中外能源,2022,27(5):50-54.GUO P,LI Y H,DUAN W L,et al. Spatial distribution pattern of soft sediment deformation structure and lts triggering mechanism in Chang 7 Oil Formation in Binchang area of Ordos Basin[J]. Sino-Global Energy,2022,27(5):50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 夏青松,田景春. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部上三叠统延长组震积岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2007,25(2):246-252.XIA Q S,TIAN J C. Characteristics and geological significance of seismites of the Yanchang Formation,Upper Triassic,Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2007,25(2):246-252. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 李文厚,庞军刚,曹红霞,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚三叠世延长期沉积体系及岩相古地理演化[J]. 西北大学学报 :自然科学版,2009,39(3):501-506.LI W H,PANG J G,CAO H X,et al. Depositional system and paleogeographic evolution of the Late Triassic Yanchang Stage in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2009,39(3):501-506. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 孟玉净,陈红汉,赵彦超,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部泾河油田延长组板内走滑断裂内部结构刻画[J]. 地球科学,2023,48:2281-2293.MENG Y J,CHEN H H,ZHAO Y C,et al. Characterization of architecture of intraplate strike-slip faults in Yanchang Formation of Jinghe Oilfield in southern Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science,2023,48:2281-2293. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] MENG Y J,CHEN H H,LUO Y,et al. Architecture of intraplate strike-slip fault zones in the Yanchang Formation,southern Ordos Basin,China:Characterization and implications for their control on hydrocarbon enrichment[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2023,170:104851. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2023.104851 [32] 袁静,俞国鼎,钟剑辉,等. 构造成岩作用研究现状及展望[J]. 沉积学报,2018,36(6):1177-1189.YUAN J,YU G D,ZHONG J H,et al. An overview of structural diagenesis[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2018,36(6):1177-1189. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] FOSSEN H. Structural geology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,2010:139-148. [34] 杨鑫,平宏伟,雷涛,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地泾河油田走滑断裂带油气成藏特征及控藏机制[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(6):2324-2341.YANG X,PING H W,LEI T,et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and controlling mechanism of strike-slip faults in Jinghe Oilfield,Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(6):2324-2341. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 李凌川,徐文玺,邓虎成,等. 泾河油田三叠系长8段天然裂缝特征与预测[J]. 新疆石油地质,2016,37(3):291-296.LI L C,XU W X,DENG H C,et al. Characteristis and prediction of natural fractures in Triassic Chang-8 Member,Jinghe Oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2016,37(3):291-296. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] LUO Y,WANG Y Z,LIU H P,et al. Overpressure controlling factors for tectonic fractures in near-source tight reservoirs in the southwest Ordos Basin,China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2020,188:106818. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106818 [37] 陈贺贺,朱筱敏,陈纯芳,等. 致密砂岩储层致密化与成藏史耦合关系研究:以鄂尔多斯南部镇原—泾川地区延长组长8油层组为例[J]. 沉积学报,2018,36(2):401-414.CHEN H H,ZHU X M,CHEN C F,et al. The coupling relationship of reservoir densification history and hydrocarbon emplacement in tight sandstone reservoir:A case study of the Chang8 Oil Member,Yanchang Formation,southern Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2018,36(2):401-414. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] BEARD P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1973,57(2):349-369. -




 下载:
下载: