Analysis of the formation conditions of Mesozoic secondary oil and gas reservoirs in Halahatang-Hade area of the Tabei Uplift
-
摘要:
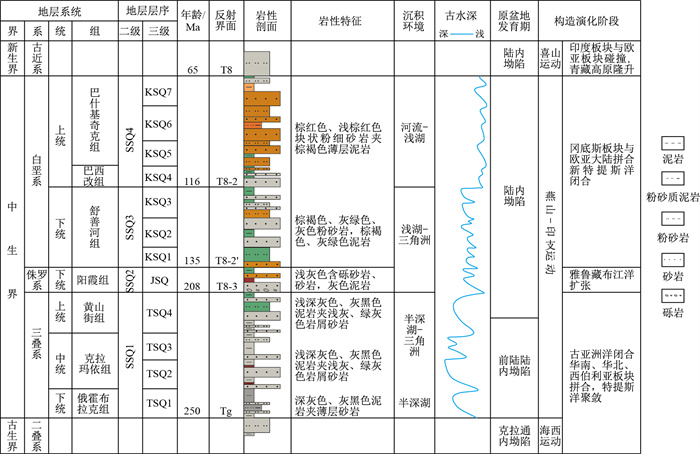
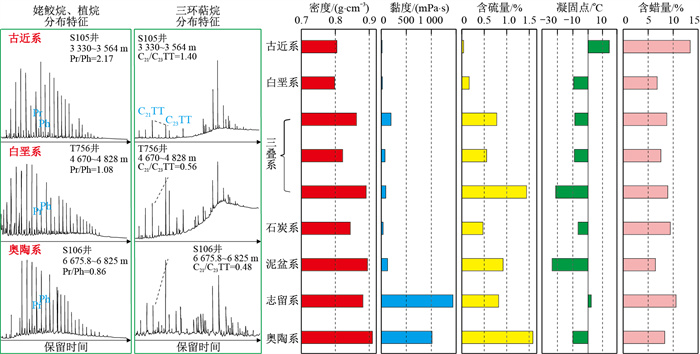
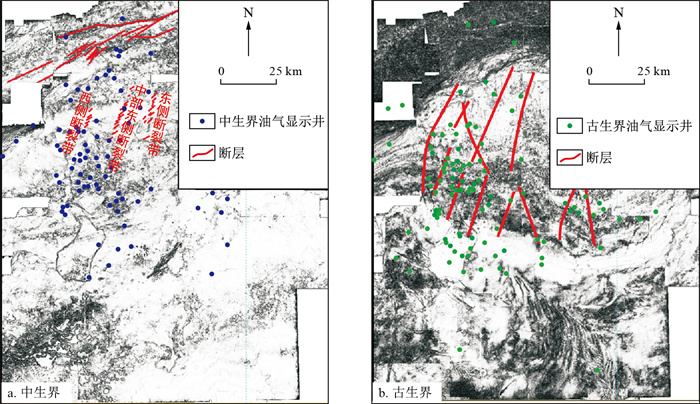
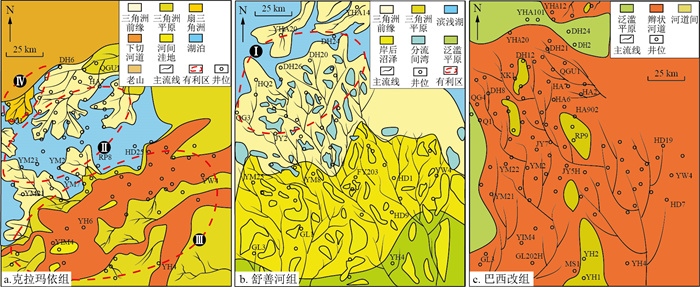
塔里木盆地塔北隆起带哈拉哈塘-哈得地区中生界面积超3万km2, 处于大型单斜背景, 油气显示活跃, 具有较大的勘探潜力, 但多年来未有勘探突破。邻区中石化矿区的发现使得该区的勘探再次提上了日程。基于新处理的三维地震资料, 在分析区域地质概况的基础上, 系统分析了油源条件、走滑断裂的构造及演化特征和岩性圈闭的形成及封堵条件, 明确了该区的成藏模式及有利勘探方向。研究区中生界发育河流-三角洲沉积体系, 其中三叠系发育NE-SW向条带状三角洲砂体, 侏罗系和白垩系下部发育SE-NW向展布的叠覆浅水三角洲砂体, 白垩系上部发育大面积连片状的辫状河砂体。该区经历了3期隆升, 发育5期断层, 其中中生界的三叠系-侏罗系断层是古生界断层的伴生断层, 受古生界断层的发育控制, 雁列状NE-SW向展布。白垩系和侏罗系浅水三角洲前缘单一朵体或多个朵体披覆泥岩拼接形成了侧向遮挡, 与上倾方向断层联合形成岩性-断层圈闭, 三叠系条带状SE方向展布的三角洲砂体和大型河道弯曲部位河道外泥岩遮挡形成岩性圈闭。油气源于古生界古油藏, 通过古生界奥陶系断层泄漏后, 经中生界伴生断层直接进入中生界圈闭或经中生界断层接替输运进入圈闭而成藏。基于此, 认为本区勘探潜力区主要有北部走滑带的侏罗系-白垩系舒善河组三角洲前缘岩性油气藏、三叠系北侧的三角洲前缘砂体和南部河道砂体岩性油气藏和三叠系北部隆起区披覆小型扇体岩性油气藏。断裂组合、砂体展布及披覆泥岩遮挡3个关键控藏要素及其有效配置是塔北隆起带大型斜坡区形成有利岩性、岩性-断层复合圈闭油气藏的重要前提, 该认识为该区油气的深化勘探指明了方向, 对其他地区岩性、岩性-断层复合圈闭油气藏勘探具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:Objective The Mesozoic strata in the Halahatang-Hade area of the Tabei Uplift belt, Tarim Basin, cover an area of more than 30 000 km2. It has a large monoclinic background, with active hydrocarbon displays and great exploration potential, but no exploration breakthrough have been made for many years. The discovery of the adjacent SINOPEC mining area promoted exploration in the area.
Methods Based on the newly obtained 3D seismic data and a regional geological overview, the oil source conditions, structural and evolutionary characteristics of strike-slip faults, and formation and sealing conditions of lithologic traps were systematically analysed, and the reservoir formation pattern and favourable exploration directions in this area were clarified.
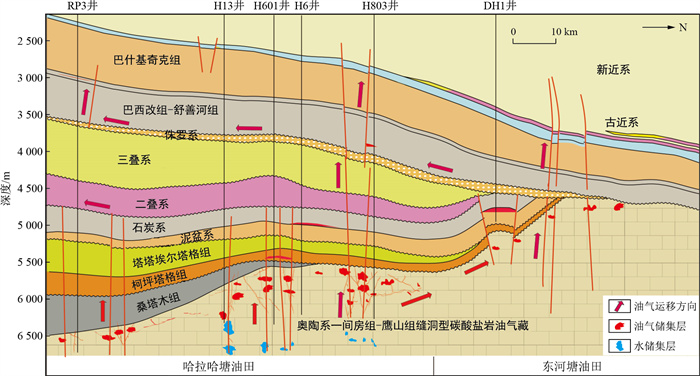
Results In this area, fluvial-delta sedimentary systems developed in the Mesozoic, including a NE-SW-trended delta sand-body developed during the Triassic, the SE-NW-directed shallow water delta sand-bodies developed during the Early Jurassic and Cretaceous, and a large scale of continuous braided river sand-body developed during Late Cretaceous. The study area had experienced three uplift episodes and five faulting episodes. The Triassic-Jurassic fault system accompanied by the Palaeozoic fault system show NE-SW-striked in echelon. The front edge of the Cretaceous and Jurassic shallow water deltas was spliced with a single body or multiple bodies covered with mudstone to form lateral occlusion, which combined with an upwards-dipping fault to form a lithology-fault trap. The Triassic striped sand-body spread in the southeast direction and formed lithology, and the mudstone shading outside the channel at the bend of the large river channel formed a lithological trap. Hydrocarbon sourced from Palaeozoic palaeo-accumulations, migrated through Palaeozoic-Ordovician faults, and directly or successively charged into the Mesozoic trap through the Mesozoic fault.
Conclusion Based on the hydrocarbon accumulation model, it is believed that the potential exploration areas in the study area mainly include the Jurassic-Cretaceous Shushan River formation Delta front lithological reservoir of the northern strike-slip zone, the delta front sand-body on the north side of the Triassic, and the southern channel sand-body lithological trap, and the northern Triassic descending area covered with small fan lithological traps. The three controlling factors, fault assemblage, sand-body distribution, and mantled mudstone shielding, and their effective allocation are important for guaranteeing the formation of favourable lithologic and lithologic fault combination traps in the large slope areas of the Tabei Uplift belt. The research results point out the direction of further hydrocarbon exploration in this area and are important for guiding hydrocarbon reservoir exploration of lithologic and lithologic fault combination traps in other areas.
-
Key words:
- secondary oil and gas reservoir /
- lithologic trap /
- Mesozoic /
- Halahatang-Hade area /
- Tabei Uplift
-
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
-
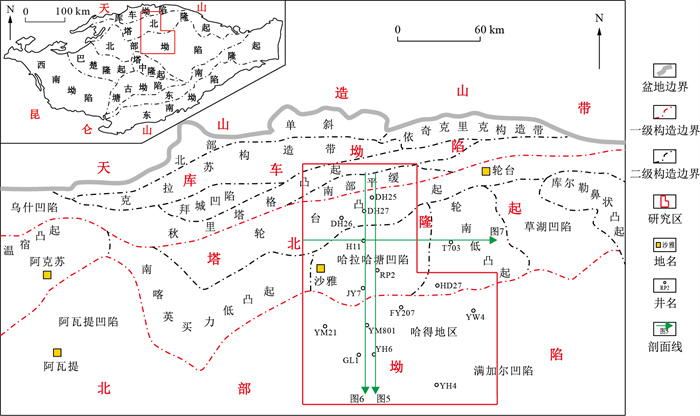
图 1 塔北隆起构造单元划分及研究区位置图(据文献[12]修改)
Figure 1. Subdivision of tectonic units in the Tabei Uplift and location of the study area
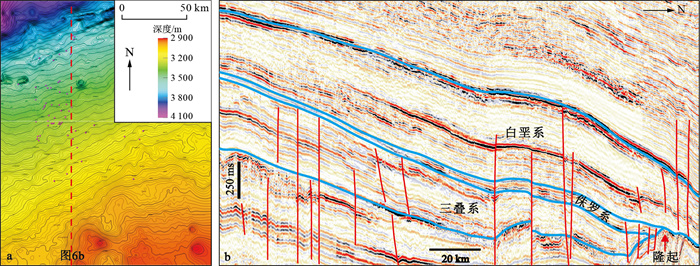
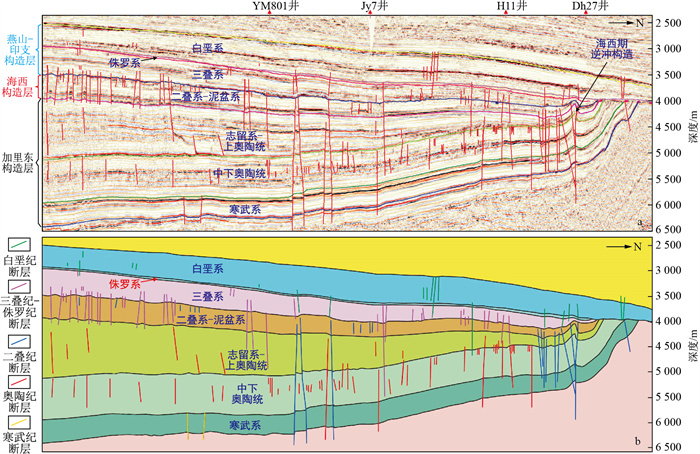
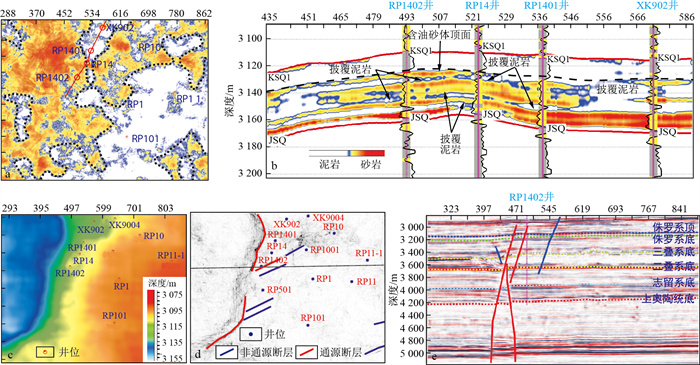
图 5 哈拉哈塘-哈得地区侏罗系顶面构造图(a)及典型剖面特征(b) (剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 5. Structural map of the Jurassic top interface (a) and typical profile characteristics (b) in the Halahatang-Hade area
图 6 哈拉哈塘-哈得地区不同时期断层发育特征(剖面位置见图 1)
a.地层及断层解释;b.不同时期断层
Figure 6. Characteristics of fault development during different periods in the Halahatang-Hade area
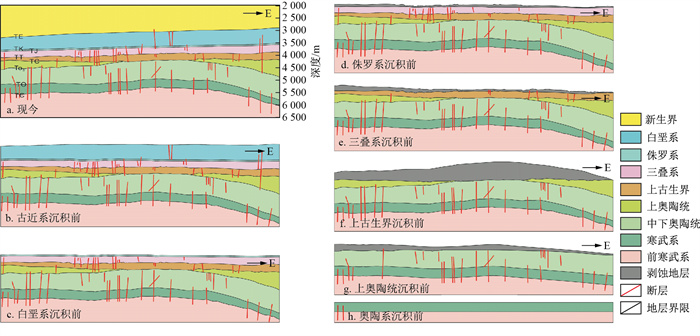
图 7 哈拉哈塘-哈得地区构造演化恢复(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 7. Restoration of tectonic evolution in the Halahatang-Hade area
-
[1] HORSTAD I, LARTER S R. Petroleum migration, alteration, and remigration within Troll Field, Norwegian North Sea[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(2): 222-248. [2] UNDERDOWN R, REDFERN J. Petroleum generation and migration in the Ghadames Basin, North Africa: A two-dimensional basin-modeling study[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(1): 53-76. doi: 10.1306/08130706032 [3] 平宏伟, 陈红汉. 次生油气藏成藏研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(9): 990-1000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.09.005PING H W, CHEN H H. Advances in the research of secondary petroleum reservoirs forming[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2009, 24(9): 990-1000. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.09.005 [4] 赵靖舟, 郭德运, 阎红军, 等. 塔北轮南地区油气成藏年代与成藏模式[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 19(6): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200406000.htmZHAO J Z, GUO D Y, YAN H J, et al. Geological age and mode of hydrocarbon accumulation in Lunnan region north Talimu Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 19(6): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200406000.htm [5] 麻伟娇, 卫延召, 李霞, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部中浅层远源、次生油气藏成藏过程及主控因素[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(6): 1195-1204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201806008.htmMA W J, WEI Y Z, LI X, et al. Accumulation process and control factors of Jurassic-Cretaceous distant source and secondary-filled reservoirs in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2018, 54(6): 1195-1204. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201806008.htm [6] HIGLEY D K, LEWAN M D, LAURA N R, et al. Timing and petroleum sources for Lower Cretaceous Mannville Group oil sands of northern Alberta based on 4-D modeling[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(2): 203-230. doi: 10.1306/09150808060 [7] 陶士振, 李建忠, 柳少波, 等. 远源/次生油气藏形成与分布的研究进展和展望[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(4): 699-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201704003.htmTAO S Z, LI J Z, LIU S B, et al. Formation condition, distribution law and exploration potential of far-source secondary oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Journal of China University of Mining&Technology, 2017, 46(4): 699-714. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201704003.htm [8] 贾承造, 马德波, 袁敬一, 等. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造特征、形成演化与成因机制[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(8): 81-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108012.htmJIA C Z, MA D B, YUAN J Y, et al. Structural characteristics, formation&evolution and genetic mechanisms of strike-slip faults in the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(8): 81-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108012.htm [9] 曹自成, 唐大卿, 骆满嵩, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中新生界断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 226-238. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176CAO Z C, TANG D Q, LUO M S, et al. Structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 226-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176 [10] 刘永福, 赵建华, 范秋海, 等. 塔北隆起中部白垩系卡普沙良群层序地层格架及沉积体系研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(6): 1113-1122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406013.htmLIU Y F, ZHAO J H, FAN Q H, et al. Study on the sequence stratigraphy and depositional systems of the Kapushaliang Group of Cretaceous in the central Tabei Uplift[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(6): 1113-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406013.htm [11] YANG F L, WANG T G, LI M J. Oil filling history of the Mesozoic oil reservoir in the Tabei Uplift of Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 142: 129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.02.005 [12] 刘永福, 夏辉, 孙琦, 等. 塔里木盆地塔北隆起西部巴什基奇克组层序地层及沉积演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(1): 62-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901006.htmLIU Y F, XIA H, SUN Q, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and depositional evolution of the Bashijiqike Formation in the western Tabei Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(1): 62-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901006.htm [13] 李丕龙. 塔里木盆地中央隆起带油气突破领域与勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(5): 576-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705008.htmLI P L. Potential areas and exploration direction in the central uplift belt of the Tarim Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2007, 28(5): 576-583. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705008.htm [14] YANG S, WU G H, ZHU Y F, et al. Key oil accumulation periods of ultra-deep fault-controlled oil reservoir in northern Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(2): 285-299. [15] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htmMA Y S, CAI X Y, YUN L, et al. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htm [16] 贾承造. 中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997.JIA C Z. Tectonic characteristics and petroleum in Tarim Basin of China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997. (in Chinese) [17] 贾承造, 王祖纲, 姜林, 等. 中国油气勘探开发成就与未来潜力: 深层、深水与非常规油气: 专访中国科学院院士、石油地质与构造地质学家贾承造[J]. 世界石油工业, 2023, 30(3): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SSYY202303001.htmJIA C Z, WANG Z G, JIANG L, et al. Achievements and future potential for oil&gas exploration and development in China: Deep-formation, deep-water and unconventional reservoirs: Interview with JIA Chengzao, Academician of the CAS, Geologist in Petroleum Geology and Structure[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2023, 30(3): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SSYY202303001.htm [18] 张光亚, 赵文智, 王红军, 等. 塔里木盆地多旋回构造演化与复合含油气系统[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(5): 653-663. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705019.htmZHANG G Y, ZHAO W Z, WANG H J, et al. Multicycle tectonic evolution and composite petroleum systems in the Tarim Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2007, 28(5): 653-663. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705019.htm [19] 邬光辉, 邓卫, 黄少英, 等. 塔里木盆地构造-古地理演化[J]. 地质科学, 2020, 55(2): 305-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202002001.htmWU G H, DENG W, HUANG S Y, et al. Tectonic-paleogeographic evolution in the Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2020, 55(2): 305-321. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202002001.htm [20] 张银涛, 邓兴梁, 邬光辉, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区走滑断裂带油气分布与油藏模式[J]. 地质科学, 2020, 55(2): 382-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202002006.htmZHANG Y T, DENG X L, WU G H, et al. The oil distribution and accumulation model along the strike-slip fault zones in Halahatang area, Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2020, 55(2): 382-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202002006.htm [21] 王新新, 崔德育, 孙崇浩, 等. 哈拉哈塘油田A地区断裂特征及其控油作用[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(6): 1058-1067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201906023.htmWANG X X, CUI D Y, SUN C H, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip fault and its controlling on oil in Block A of Halahatang Oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(6): 1058-1067. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201906023.htm [22] 吴高奎, 张忠民, 林畅松, 等. 塔里木盆地塔北隆起区中生界沉积演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4): 845-858. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202204009.htmWU G K, ZHANG Z M, LIN C S, et al. Evolution of Mesozoic sedimentary fill in the Tabei Uplift region, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 845-858. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202204009.htm [23] 范秋海, 肖中尧, 张海祖, 等. 塔里木盆地北部坳陷及周缘下寒武统烃源岩特征及分布[J]. 地球化学, 2021, 50(3): 251-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX202103003.htmFAN Q H, XIAO Z Y, ZHANG H Z, et al. Characteristics and distribution of the Lower Cambrian source rocks in the Northern Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2021, 50(3): 251-260. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX202103003.htm [24] 张科, 苏劲, 陈永权, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武系-奥陶系烃源岩油源特征与超深层油气来源[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(6): 2026-2041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202306018.htmZHANG K, SU J, CHEN Y Q, et al. The biogeochemical features of the Cambrian-Ordovician source rocks and origin of ultra-deep hydrocarbons in the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(6): 2026-2041. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202306018.htm [25] 吕海涛, 耿锋, 伍齐乔. 塔里木盆地阿瓦提地区阿北1井三叠系高含有机碳泥岩的发现意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(6): 587-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201106008.htmLÜ H T, GENG F, WU Q Q. Discovery significance of Triassic dark mudstone rich in organic carbon, Well AB1, Avat area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2011, 33(6): 587-591. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201106008.htm [26] 张坦, 齐育楷, 姚威, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷南斜坡三叠系烃源岩热演化特征及油气地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 1018-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202206009.htmZHANG T, QI Y K, YAO W, et al. Thermal evolution characteristics of Triassic source rocks and their petroleum geological significance on the southern slope of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 1018-1027. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202206009.htm [27] 张俊, 庞雄奇, 刘洛夫, 等. 塔里木盆地志留系沥青砂岩的分布特征与石油地质意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2004, 34(增刊1): 169-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2004S1019.htmZHANG J, PANG X Q, LIU L F, et al. Distribution characteristics and petroleum geological significance of Silurian bituminous sandstone in Tarim Basin[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2004, 34(S1): 169-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2004S1019.htm [28] 程斌, 王铁冠, 常象春, 等. 塔北哈6井油砂及沥青砂岩抽提物的地球化学特征及对比[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6): 736-743. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406014.htmCHENG B, WANG T G, CHANG X C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and correlation of extracts from Silurian bituminous sandstones and Carboniferous oil sands in well Ha6, northern Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2014, 36(6): 736-743. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406014.htm [29] 邓卫龙. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区跃满区块成藏地球化学研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.DENG W L. Reservoir geochemical study of Yueman Block in Halahatang region, Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 刘军, 龚伟, 黄超, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断裂带北段超深层裂缝储层的地震属性表征方法研究及应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 1-11. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0112LIU J, GONG W, HUANG C, et al. Seismic attribute characteristics of an ultradeep fractured-reservoir in the northern section of Shunbei No. 5 strike-slip fault zone in Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0112 -





 下载:
下载: