Distribution, sources and transport of HCHs and DDTs in the Yuquandong spring system from Zigui County, Hubei Province
-
摘要:
岩溶区特殊的地形地貌, 使得地表环境中的有机氯农药(OCPs)很容易进入地下环境, 对地下水的安全构成威胁。采用气相色谱-电子捕获检测器(GC-ECD)对湖北秭归鱼泉洞泉域系统中的典型OCPs——六六六(HCHs)和滴滴涕(DDTs)进行了检测, 探究了其时空分布特征、潜在污染来源和迁移特征。结果表明: 水体中HCHs质量浓度范围为0.09~5.17 ng/L, 土壤和泉沉积物中HCHs质量分数范围分别为0.36~3.67, 0.11~2.53 ng/g; 水体中DDTs质量浓度范围为0.13~7.16 ng/L, 土壤和泉沉积物中DDTs质量分数范围分别为0.22~19.13, 0.73~11.53 ng/g, 呈现出以DDTs为主的污染特征。水体中HCHs和DDTs质量浓度在冬季最高; 土壤中HCHs和DDTs质量分数分别在夏季和冬季达到最高; 泉沉积物中HCHs和DDTs质量分数分别在夏季和春季达到峰值。特征比值结果显示, 水体、土壤和泉沉积物中HCHs主要源于林丹的使用; 水体中DDTs主要源于历史残留, 而土壤和泉沉积物中DDTs主要来源于近期使用。相关性分析结果表明, HCHs和DDTs可从补给区地表水和补给区土壤分别向排泄区泉水和泉沉积物中迁移。HCHs和DDTs在介质中的快速迁移证实了岩溶区地下水的脆弱性。本研究成果可以为岩溶地下水资源和环境的保护提供参考。
Abstract:The special topography of karst areas allows organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) from the surface environment to easily infiltrate the underground environment, posing a threat to groundwater security.
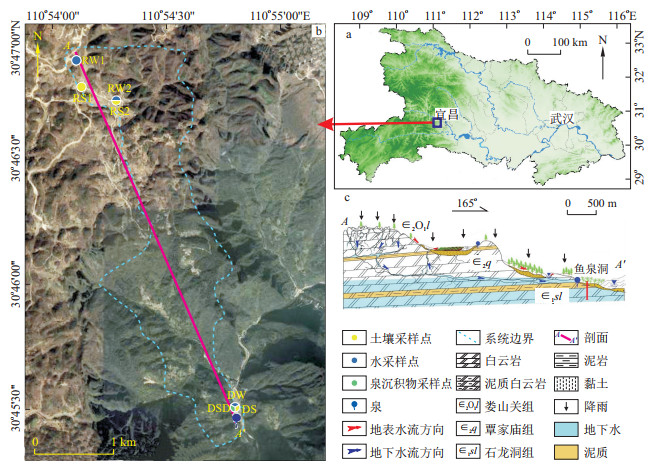
Methods In this study, a gas chromatography-electron capture detector (GC-ECD) was used to detect two typical OCPs, namely, HCHs and DDTs, in the Yuquandong spring system in Zigui, Hubei.
Objective This study investigated spatial and temporal distribution characteristics, sources and transport of HCHs and DDTs.
Results The results showed that the mass concentrations of HCHs in the water ranged from 0.09 to 5.17 ng/L, and the mass fractions of HCHs in the soils and spring sedimentsranged from 0.36 to 3.67, 0.11 to 2.53 ng/g, respectively, mass concentrations of DDTs in the water ranged from 0.13 to 7.16 ng/L, and the mass fractions of DDTs in the soils and spring sedimentsranged from 0.22 to 19.13, 0.73 to 11.53 ng/g, indicating that the pollution was dominated by DDTs. The highest mass concentrations of HCHs and DDTs in water were observed in winter; the highest mass fractions of HCHs and DDTs in the soils were observed in summer and winter, respectively; and the mass fractions of HCHs and DDTs in the spring sediments peaked in summer and spring, respectively. Characteristic ratios showed that HCHs in water, soils and spring sediments mainly originated from lindane usage, DDTs in water mainly originated from historical residues, and DDTs in the soils and spring sediments mainly originated from recent usage. Correlation analysis indicated that HCHs and DDTs could be transported from the surface water and the soils in the recharge area to the spring water and spring sediments in the discharge area, respectively. The rapid transport of HCHs and DDTs across multiple media confirmed groundwater vulnerability in karst areas.
Conclusion The study can provide a reference for the protection of karst groundwater resources and the environment.
-
Key words:
- karst area /
- HCHs /
- DDTs /
- source /
- transport /
- organochlorine pesticides(OCPs) /
- Yuquandong spring system /
- Zigui County, Hubei Province
-
表 1 鱼泉洞泉域水体中HCHs和DDTs的质量浓度及检出率
Table 1. Mass concentrations and detection rates of HCHs and DDTs in water from the Yuquandong spring system
物质 补给区地表水 排泄区泉水 范围/(ng·L-1) 均值/(ng·L-1) 检出率/% 范围/(ng·L-1) 均值/(ng·L-1) 检出率/% α-HCH <MDL~0.99 0.26 63 <MDL~0.70 0.18 25 β-HCH <MDL~1.19 0.27 88 0.03~0.72 0.26 100 γ-HCH <MDL~1.44 0.22 75 <MDL~1.00 0.26 50 δ-HCH 0.03~2.02 0.64 100 0.03~1.12 0.34 100 Σ4HCHs 0.09~5.17 1.39 100 0.12~3.55 1.04 100 o, p′-DDE 0.02~0.51 0.17 100 0.02~0.39 0.17 100 p, p′-DDE 0.01~0.51 0.13 100 0.02~0.41 0.12 100 o, p′-DDD 0.02~0.33 0.14 100 0.02~0.27 0.10 100 p, p′-DDD 0.01~0.73 0.17 100 0.02~0.59 0.16 100 o, p′-DDT 0.03~2.30 0.49 100 <MDL~0.04 0.02 75 p, p′-DDT 0.02~2.78 0.61 100 <MDL~2.36 0.61 75 Σ6DDTs 0.21~7.16 1.71 100 0.13~4.03 1.19 100 注:Σ4HCHs表示α-HCH、β-HCH、γ-HCH和δ-HCH的和;Σ6DDTs表示o, p′-DDE、p, p′-DDE、o, p′-DDD、p, p′-DDD、o, p′-DDT和p, p′-DDT的和;<MDL表示低于检出限(下同) 表 2 鱼泉洞泉域土壤中HCHs和DDTs的质量分数及检出率
Table 2. Mass fractions and detection rates of HCHs and DDTs in soils from the Yuquandong spring system
物质 补给区土壤 排泄区土壤 范围/(ng·g-1) 均值/(ng·g-1) 检出率/% 范围/(ng·g-1) 均值/(ng·g-1) 检出率/% α-HCH 0.13~2.98 1.05 100 0.13~2.04 0.61 100 β-HCH <MDL~0.57 0.21 100 0.13~0.26 0.18 100 γ-HCH <MDL~0.28 0.19 88 0.12~1.23 0.43 100 δ-HCH 0.13~0.27 0.21 100 0.12~1.04 0.38 100 Σ4HCHs 0.36~3.67 1.67 100 0.49~2.71 1.60 100 o, p′-DDE <MDL~0.23 0.15 88 0.04~2.01 0.82 100 p, p′-DDE 0.07~0.29 0.12 100 0.08~0.94 0.42 100 o, p′-DDD 0.03~0.78 0.17 100 0.03~0.08 0.05 100 p, p′-DDD <MDL~0.07 0.05 88 0.07~10.49 2.70 100 o, p′-DDT <MDL~1.86 0.73 88 0.23~7.20 3.29 100 p, p′-DDT <MDL~1.30 0.51 63 0.31~5.83 2.24 100 Σ6DDTs 0.22~3.53 1.73 100 0.75~19.13 9.52 100 表 3 鱼泉洞泉域中HCHs和DDTs含量的皮尔逊相关系数(r)
Table 3. Spearman correlation coefficients (r) of HCHs and DDTs concentrations from the Yuquandong spring system
地表水 泉水 补给区土壤 排泄区土壤 泉沉积物 地表水 1 泉水 0.78** 1 补给区土壤 0.09 -0.05 1 排泄区土壤 0.22 0.17 0.15 1 泉沉积物 -0.15 -0.12 0.43** 0.24 1 ** 在0.01水平,相关性显著 -
[1] HARTMANN A, GOLDSCHEIDER N, WAGENER T, et al. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2014, 52(3): 218-242. doi: 10.1002/2013RG000443 [2] 郑小康, 杨志兵. 岩溶含水层饱和-非饱和流动与污染物运移数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 357-366. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211ZHENG X K, YANG Z B. Numerical simulation of saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and contaminant transport in a karst aquifer[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 357-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211 [3] WANG Z J, LI S L, YUE F J, et al. Rainfall driven nitrate transport in agricultural karst surface river system: Insight from high resolution hydrochemistry and nitrate isotopes[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 291: 106787. [4] ZHU J F, NOLTE A M, JACOBS N, et al. Using machine learning to identify karst sinkholes from LiDAR-derived topographic depressions in the Bluegrass region of Kentucky[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 588: 125049. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125049 [5] QIAN Z, MAO Y, XIONG S, et al. Historical residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a flood sediment profile from the Longwang cave in Yichang, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 196: 110542. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110542 [6] HUANG H F, LIU H F, XIONG S, et al. Rapid transport of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in multimedia environment from karst area[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 775: 145698. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145698 [7] 邢立亭, 于苗, 宿庆伟, 等. 地下工程建设对岩溶水流场的影响及其修复[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 242-254. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0190XING L T, YU M, SU Q W, et al. Influence and repair of underground engineering construction on karst flow field[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 242-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0190 [8] 郭蕾蕾, 魏良帅, 黄安邦, 等. 乌蒙山地区岩溶地下水流系统结构及其找水应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 146-157. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0025GUO L L, WEI L S, HUANG A B, et al. Structure of karst groundwater system and its water exploration in Wumeng Mountain area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 146-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0025 [9] HU L M, ZHANG G, ZHENG B H, et al. Occurrence and distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 77(5): 663-672. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.070 [10] CHEN C, LUO J H, SHU X Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variations and ecological risks of organochlorine pesticides in surface waters of a plateau lake in China[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 303: 135029. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135029 [11] CAO F M, LI Z Z, HE Q, et al. Occurrence, spatial distribution, source, and ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in Dongting Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(24): 30841-30857. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12743-x [12] JONES K C, DE VOOGT P. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs): State of the science[J]. Environmental Pollution, 1999, 100(1/3): 209-221. [13] BHUTTO S U A, XING X L, SHI M M, et al. Occurrence and distribution of OCPs and PAHs in water, soil and sediment of Daye lake[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 226: 106769. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106769 [14] WANG Y Z, ZHANG S L, CUI W Y, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in surface water from the Yongding River basin, China: Seasonal distribution, source apportionment, and potential risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618: 419-429. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.066 [15] CHEN C, ZOU W B, CHEN S S, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in an urbanized river network of Shanghai, China[J]. Environmental Sciences Europe, 2020, 32(1): 42. doi: 10.1186/s12302-020-00322-9 [16] DVORŠĈAK M, FINGLER S, MENDAŠ G, et al. Distribution of organochlorine pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl residues in lake sediment cores from the plitvice Lakes National Park (croatia)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2019, 77(4): 537-548. doi: 10.1007/s00244-019-00668-z [17] 张俊鹏, 祁士华, 姚慧丽. 广西岩溶地下河水体中有机氯农药浓度分布特征研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(4): 54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2011.04.013ZHANG J P, QI S H, YAO H L. The distribution characteristics of OCPs residues in karst underground river of Guangxi[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2011, 33(4): 54-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2011.04.013 [18] ALAM M J, YUAN D X, JIANG Y J, et al. Sources and transports of organochlorine pesticides in the Nanshan underground river, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(4): 1977-1987. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2919-5 [19] 叶凯, 孙玉川, 贾亚男, 等. 岩溶地下水水体中有机氯农药和多氯联苯的残留特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012028.htmYE K, SUN Y C, JIA Y N, et al. Residual characteristics and health assessment analysis of OCPs and PCBs in karst groundwater[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202012028.htm [20] 谢正兰, 孙玉川, 张媚, 等. 岩溶地下河流域表层土壤有机氯农药分布特征及来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(3): 900-909. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201603017.htmXIE Z L, SUN Y C, ZHANG M, et al. Distribution characteristics and source identification of organochlorine pesticides in surface soil in karst underground river basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(3): 900-909. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201603017.htm [21] CHEN W, ZENG F M, LIU W, et al. Organochlorine pesticides in karst soil: Levels, distribution, and source diagnosis[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(21): 11589. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111589 [22] 孙玉川, 王永啟, 梁作兵, 等. 有机氯农药在岩溶区上覆土壤中的垂直迁移特征及对地下水的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(5): 1605-1614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201505014.htmSUN Y C, WANG Y Q, LIANG Z B, et al. Vertical migration characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in overlying soil in karst terranes and its impact on groundwater[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(5): 1605-1614. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201505014.htm [23] CHENG C, HU T P, LIU W J, et al. Modern lake sedimentary record of PAHs and OCPs in a typical karst wetland, South China: Response to human activities and environmental changes[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 291: 118173. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118173 [24] ZHOU T, HUANG F Y, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of hydrogeochemical conditions on the distribution of pesticides in the karst river system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(24): 30468-30478. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09262-6 [25] PERERA-RIOS J, RUIZ-SUAREZ E, BASTIDAS-BASTIDAS P D, et al. Agricultural pesticide residues in water from a karstic aquifer in Yucatan, Mexico, pose a risk to children's health[J]. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 2022, 32(10): 2218-2232. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2021.1950652 [26] LIU W, WANG Z J, CHEN Q L, et al. An interpretation of water recharge in karst trough zone as determined by high-resolution tracer experiments in western Hubei, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(14): 357. doi: 10.1007/s12665-020-09056-6 [27] CHEN W, JING M M, BU J W, et al. Organochlorine pesticides in the surface water and sediments from the Peacock River Drainage basin in Xinjiang, China: A study of an arid zone in central Asia[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2011, 177(1): 1-21. [28] 余悦, 邢新丽, 程铖, 等. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地水体与沉积物中有机氯农药污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(3): 1387-1396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202303018.htmYU Y, XING X L, CHENG C, et al. Pollution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in water and sediments of Huixian karst wetland in Guilin[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(3): 1387-1396. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202303018.htm [29] 张坤锋, 付青, 涂响, 等. 武汉典型饮用水水源中典型POPs污染特征与健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5836-5847. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202112027.htmZHANG K F, FU Q, TU X, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of typical POPs in typical drinking water sources in Wuhan[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(12): 5836-5847. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202112027.htm [30] 符鑫, 梁延鹏, 覃礼堂, 等. 桂林会仙岩溶湿地水体中有机氯农药分布特征及混合物环境风险评估[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 974-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201805017.htmFU X, LIANG Y P, QIN L T, et al. Distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the water body of Huixian karst wetland of Guilin and environmental risk assessment of OCP mixtures[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 974-983. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201805017.htm [31] 师阳, 孙玉川, 徐昕, 等. 重庆老龙洞地下河不同部位水体、表层沉积物有机氯农药含量及组成研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(2): 238-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201402017.htmSHI Y, SUN Y C, XU X, et al. Distribution of OCPs in underground water and surface sediment of underground river in Chongqing's Laolongdong[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(2): 238-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201402017.htm [32] 胡英, 祁士华, 兰兰, 等. 岩溶地下河中HCHs和DDTs的分布特征与健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(6): 802-807. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201006025.htmHU Y, QI S H, LAN L, et al. Distribution and health risk assessment of HCHs and DDTs in underground river of karst, Southwest China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(6): 802-807. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201006025.htm [33] ADEYINKA G C, MOODLEY B, BIRUNGI G, et al. Evaluation of organochlorinated pesticide (OCP) residues in soil, sediment and water from the Msunduzi River in South Africa[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(6): 223. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8227-y [34] SUN J T, PAN L L, TSANG D C W, et al. Phthalate esters and organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils and vegetables from fast-growing regions: A case study from eastern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(1): 34-42. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7725-7 [35] HUANG H F, DING Y, CHEN W, et al. Two-way long-range atmospheric transport of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) between the Yellow River source and the Sichuan Basin, western China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 3230-3240. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.133 [36] 王帆, 王平. 土壤中有机氯农药残留研究[J]. 大连大学学报, 2020, 41(3): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2395.2020.03.011WANG F, WANG P. A study on the residue of organochlorine pesticides in the soil[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 2020, 41(3): 41-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2395.2020.03.011 [37] 朱彬, 江忠远, 齐玉. 滴滴涕对人类的贡献及其危害[J]. 遵义师范学院学报, 2022, 24(2): 85-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYSF202202019.htmZHU B, JIANG Z Y, QI Y. Contribution and harm of DDT to human beings[J]. Journal of Zunyi Normal University, 2022, 24(2): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYSF202202019.htm [38] 杨梅, 蒲俊兵, 张俊鹏, 等. 重庆典型岩溶区地下河表层沉积物OCPs初步研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(7): 1340-1344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ200907041.htmYANG M, PU J B, ZHANG J P, et al. A preliminary study of OCPs in underground river surface sediments from Chongqing typical karst areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(7): 1340-1344. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ200907041.htm [39] 韦丽丽. 岩溶地下河系统持久性有机污染物分布与迁移研究: 以鸡喇地下河及龙寨地下河为例[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2011.WEI L L. Distribution and migration of persistent organic pollutants in Karst subterranean river system: A case of Jila subterranean river and Longzhai subterranean river[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] 孙倩倩, 吴克. 巢湖表层水中有机氯农药的时空分布及健康风险[J]. 安庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 23(3): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQSX201703020.htmSUN Q Q, WU K. Temporal and spatial distribution and human health risk of rganochlorine pesticides in surface water from Chaohu Lake[J]. Journal of Anqing Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 23(3): 76-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQSX201703020.htm [41] NASEEM S, TABINDA A B, BAQAR M, et al. Organochlorines in the riverine ecosystem of Punjab Province, Pakistan: Contamination status, seasonal variation, source apportionment, and ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(14): 40340-40355. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24528-x [42] SYED J H, MALIK R N, LIU D, et al. Organochlorine pesticides in air and soil and estimated air-soil exchange in Punjab, Pakistan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444: 491-497. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.018 [43] BOSCH C, GRIMALT J O, FERNÁNDEZ P. Enantiomeric fraction and isomeric composition to assess sources of DDT residues in soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.047 [44] 孙玉川. 有机氯农药和多环芳烃在表层岩溶系统中的迁移、转化特征研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2012.SUN Y C. Study on migration and transformation characteristics of OCPs and PAHs in epikarst system[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 李军. 珠江三角洲有机氯农药污染的区域地球化学研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2005.LI J. Regional geochemistry of organochlorine pesticides in the Pearl River Delta[D]. Guangzhou: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] KNÖLL P, SCHEYTT T. A tracer test to determine a hydraulic connection between the Lauchert and Danube karst catchments (Swabian Alb, Germany)[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(2): 429-437. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1678-x [47] KAĈAROĜLU F. Review of groundwater pollution and protection in karst areas[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1999, 113(1): 337-356. -





 下载:
下载: