Paleoenvironmental controls on organic-rich lithofacies of Eocene saline lacustrine in the Chentuokou Depression, Jianghan Basin
-
摘要:
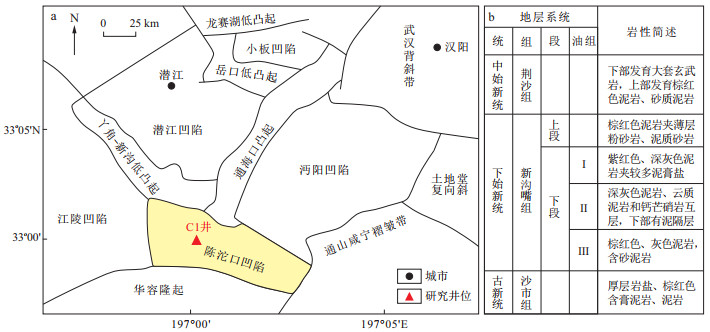
江汉盆地新沟嘴组下段Ⅱ油组广泛发育页岩与白云岩互层的烃源岩, 近期该层系页岩油勘探获得了重大突破, 但盐湖沉积背景下沉积的膏盐对于孔隙的影响制约了页岩油的勘探开发, 明确低膏盐富有机质岩相发育的控制因素对页岩油勘探具有重要意义。选取陈沱口凹陷的C1系统取心井作为研究对象, 通过岩心及岩石薄片的观察鉴定, 全岩矿物组成质量分数、有机碳及地球化学元素含量测定, 对C1井新沟嘴组下段Ⅱ油组的岩相类型、沉积环境和有机质富集主控因素进行了系统研究, 建立了适合江汉盆地新沟嘴组盐湖相岩相划分方案和沉积模式。结果表明: C1井新沟嘴组下段Ⅱ油组共发育4类7种岩相, 分别为富碳细纹层状白云岩、富碳粗纹层状白云岩、含碳块状白云岩; 富碳细纹层状混合质页岩、富碳粗纹层状混合质页岩; 含碳粗纹层状粉砂岩; 贫碳块状膏盐岩。古气候、古盐度与古氧化还原协同演化控制了岩相发育的多样性, 有机质富集的主控因素为还原性古水介质环境。页岩油勘探有利岩相为富碳(含碳)粗纹层(细纹层)状白云岩(混合质页岩), 有利岩相的沉积环境为咸水、还原的半深湖环境。陈沱口凹陷新沟嘴组下段Ⅱ油组富有机质岩相发育控制因素及其沉积环境的揭露, 可为江汉盆地相关凹陷新沟嘴组页岩油勘探提供借鉴和参考。
Abstract:Source rocks characterized by shale-dolomite interbeds were widely developed in oil group Ⅱ, the lower Member of Xingouzui Formation in Jianghan Basin. A breakthrough has been made recently in shale oil exploration of shale-dolomite interbeds, while the presence of gypsum and salt deposites in saline lake on shale porosity restrains the process of shale oil exploration.
Objective It is of great significance for shale oil exploration to clarify the controlling factors of the organic-rich shale lithofacies with low content of gypsum and salt.
Methods Well C1 penetrated stratigraphic unit of the Xingouzui Formationin the Chentuokou Depression, Jianghan Basin was studied. Based on the core and thin section observations and the analyses of whole rock mineral compositions, organic carbon contents (TOC), and geochemical elements, a systematic study on lithofacies, sedimentary environment, and main controlling factors of organic matter accumulation were conducted.
Results The classification of fine-grained sediments and the saline lacustrine sedimentary model in Jianghan Lake Basin were established. Lithofacies of oil group Ⅱ, the lower Member of Xingouzui Formation Xingouzui Formation in Well C1 can subdivided into seven types: organic-rich laminated dolomite facies, organic-rich layered dolomite facies, organic-contain massive dolomite facies, organic-rich laminated mixed shale facies, organic-rich layered mixed shale facies, organic-contain layered siltstone, and organic-poor massive gypsum-salt rock facies. The co-evolution of paleoclimate, paleosalinity, and paleoredox resulted in the diversity of lithofacies development, and the main controlling factor of organic matter accumulation was the anoxic palaeo-water body. The favorable lithofacies for shale oil exploration are organic-rich/organic-contain laminated/layered dolomite/mixed shale, which deposited in semi-deep lake with brackish water, anoxic condition.
Conclusion This study reveals the controlling factors for the development of organic-rich lithofacies and its depositional environment of oil group Ⅱ, the lower Member of Xingouzui Formation in the Chentuokou Depression, which can provide valuable insights for shale oil exploration of Xingouzui Formation in related Depression in Jianghan Saline Basin.
-
表 1 江汉盆地盐湖细粒沉积岩岩相划分方案
Table 1. Lithofacies classification criterion of fine-grained rocks in saline lacustrine of Jianghan Basin
划分依据 标准 命名 有机碳质量分数 w(TOC)≤0.5%
0.5% < w(TOC) < 1%
w(TOC)≥1%贫碳
含碳
富碳沉积构造 纹层厚度≤1 mm
纹层厚度>1 mm
无纹层状构造细纹层状
粗纹层状
块状矿物成分 w(岩盐+膏类) < 50%
(10% < w(岩盐+膏类) < 50%)碳酸盐矿物、长英质矿物、黏土矿物 含膏盐 碳酸盐岩、长英质碳酸盐岩、泥质碳酸盐岩、粉砂岩、钙质粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、黏土质泥(页)岩、长英质泥(页)岩、钙质泥(页)岩、混合质页岩 w(岩盐+膏类)
≥50%
(排除后期脉状)钙质膏盐岩
长英质膏盐岩
黏土质膏盐岩
混合质膏盐岩表 2 陈沱口凹陷C1井新下段Ⅱ油组1小层主要岩相类型及特征
Table 2. Main lithofacies and features of oil group Ⅱ of Lower Member of Xingouzui Formation in Well C1, Chentuokou Depression

-
[1] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 韩元佳, 等. 潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构分形表征与评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 125-137. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0063SUN Z L, WANG F R, HAN Y J, et al. Characterization and evaluation of fractal dimension of intersalt shale oil reservoirs in Qianjiang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 125-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0063 [2] 李文浩, 卢双舫, 薛海涛, 等. 江汉盆地新沟嘴组页岩油储层物性发育主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(1): 56-61.LI W H, LU S F, XUE H T, et al. Major controlling factors of poroperm characteristics of shale oil reservoirs in the Xingouzui Formation, Jianghan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(1): 56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] ZACHOS J, PAGANI M, SLOAN L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present[J]. Science, 2001, 292: 686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412 [4] TENG X H, FANG X M, KAUFMAN A J, et al. Sedimentological and mineralogical records from drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin, Central China, and their implications for Late Cretaceous-Early Eocene climate change[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 182: 103936. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103936 [5] 黎茂稳, 马晓潇, 金之钧, 等. 中国海、陆相页岩层系岩相组合多样性与非常规油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 1-25.LI M W, MA X X, JIN Z J, et al. Diversity in the lithofacies assemblages of marine and lacustrine shale strata and significance for unconventional petroleum exploration in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 1-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 刘鑫, 尚婷, 田景春, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇北地区延长组长4+5段沉积期古环境条件及意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(11): 3501-3518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.11.023LIU X, SHANG T, TIAN J C, et al. Paleo-sedimentary environmental conditions and its significance of Chang 4+5 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Zhenbei area, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(11): 3501-3518. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.11.023 [7] 文华国, 郑荣才, 唐飞, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地耿湾地区长6段古盐度恢复与古环境分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2008, 28(1): 114-120.WEN H G, ZHENG R C, TANG F, et al. Reconstruction and analysis of paleosalanity and paleoenvironment of the Chang 6 Member in the Gengwan region, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 28(1): 114-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 阳宏, 刘成林, 王飞龙, 等. 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 339-349. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0077YANG H, LIU C L, WANG F L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of source rocks of the Dongying Formation in Southwest Subsag of Bozhong Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 339-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0077 [9] 査光煜, 乐乐, 周晓, 等. 江汉盆地陈沱口凹陷新沟嘴组下段沉积相分析[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(6): 41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2013.06.008ZHA G Y, LE L, ZHOU X, et al. Analysis on sedimentary facies of the Lower Member of Xingouzhui Formation in Chentuokou Depression of Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(6): 41-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2013.06.008 [10] 马存飞, 黄文俊, 杜争利, 等. 陆相湖盆页岩岩相分类方案及其意义: 以沧东凹陷孔二段为例[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3287-3300.MA C F, HUANG W J, DU Z L, et al. Shale lithofacies classification scheme of continental lake basin and its significance: A case of E2 Member of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong Sag[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3287-3300. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 李维, 朱筱敏, 段宏亮, 等. 苏北盆地高邮-金湖凹陷古近系阜宁组细粒沉积岩纹层特征与成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(3): 469-482.LI W, ZHU X M, DUAN H L, et al. Characteristics and forming mechanism of laminae fine-grained sedimentary rock of the Paleogene Funing Formation in Gaoyou and Jinhu sags, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2020, 22(3): 469-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 姜在兴, 梁超, 吴靖, 等. 含油气细粒沉积岩研究的几个问题[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6): 1031-1039.JIANG Z X, LIANG C, WU J, et al. Several issues in sedimentological studies on hydrocarbon-bearing fine-grained sedimentary rocks[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(6): 1031-1039. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 朱如凯, 李梦莹, 杨静儒, 等. 细粒沉积学研究进展与发展方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2): 251-264.ZHU R K, LI M Y, YANG J R, et al. Advances and trends of fine-grained sedimentology[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 251-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 刘惠民, 杨怀宇, 张鹏飞, 等. 古湖泊水介质条件对混积岩相组合沉积的控制作用: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系沙河街组三段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2): 297-306.LIU H M, YANG H Y, ZHANG P F, et al. Control effect of paleolacustrine water conditions on mixed lithofacies assemblages: A case study of the Palaeogene Es3, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 297-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 邹才能, 张国生, 杨智, 等. 非常规油气概念、特征、潜力及技术: 兼论非常规油气地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4): 385-399.ZOU C N, ZHANG G S, YANG Z, et al. Geological concepts, characteristics, resource potential and key techniques of unconventional hydrocarbon: On unconventional petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(4): 385-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] DEMICCO R V, HARDIE L A. Sedimentary structures and early diagenetic features of shallow marine carbonate deposits[M]. Tulsa, Okla, USA: SEPM(Society of Sedimentary Geology), 1994. [17] FLVGEL E. Microfacies of carbonate rocks: Analysis, interpretation and application[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2004. [18] ORTÍ F, ROSELL L. Evaporative systems and diagenetic patterns in the Calatayud Basin(Miocene, central Spain)[J]. Sedimentology, 2000, 47(3): 665-685. [19] WEI W, ALGEO T J. Elemental proxies for paleosalinity analysis of ancient shales and mudrocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 287: 341-366. [20] 熊小辉, 肖加飞. 沉积环境的地球化学示踪[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 39(3): 405-414.XIONG X H, XIAO J F. Geochemical indicators of sedimentary environments: A summary[J]. Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(3): 405-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] WILDE P, QUINBY-HUNT M S, ERDTMANN B D. The whole-rock cerium anomaly: A potential indicator of eustatic sea-level changes in shales of the anoxic facies[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1996, 101(1/2): 43-53. [22] RIMMER S M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian-Mississippian black shales, Central Appalachian Basin(USA)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 373-391. [23] 王敏芳, 黄传炎, 徐志诚, 等. 综述沉积环境中古盐度的恢复[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2006, 2(1): 9-12.WANG M F, HUANG C Y, XU Z C, et al. Review on paleosalinity recovery in sedimentary environment[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2006, 2(1): 9-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 滕晓华, 王春连, 沈立建, 等. 江汉盆地SKD1深钻记录的古新世-始新世极热事件时期的古气候[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(1): 65-72.TENG X H, WANG C L, SHEN L J, et al. Paleoclimate during the Paleocene-Eocene extreme thermal event recorded by the deep drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 65-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 刘惠民, 王勇, 李军亮, 等. 济阳坳陷始新统页岩岩相发育主控因素及分布特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2023, 25(4): 752-767.LIU H M, WANG Y, LI J L, et al. Main controlling factors and distribution characteristics of shale lithofacies in the Eocene of Jiyang Depression[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2023, 25(4): 752-767. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] MURPHY A E, SAGEMAN B B, HOLLANDER D J, et al. Black shale deposition and faunal overturn in the Devonian Appalachian Basin: Clastic starvation, seasonal water-column mixing, and efficient biolimiting nutrient recycling[J]. Paleoceanography, 2000, 15(3): 280-291. [27] 郑克涛, 李吉君, 张春林, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部奥陶系盐下烃源岩有机质富集机制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2023, 52(1): 128-144.ZHENG K T, LI J J, ZHANG C L, et al. Organic matter enrichment mechanism of Ordovician pre-salt source rocks in the eastern-central Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2023, 52(1): 128-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] MORT H, JACQUAT O, ADATTE T, et al. The Cenomanian/Turonian anoxic event at the Bonarelli Level in Italy and Spain: Enhanced productivity and/or better preservation?[J]. Cretaceous Research, 2007, 28(4): 597-612. [29] 李艳芳, 邵德勇, 吕海刚, 等. 四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组海相页岩元素地球化学特征与有机质富集的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12): 1470-1483.LI Y F, SHAO D Y, LV H G, et al. A relationship between elemental geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment in marine shale of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12): 1470-1483. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] TYSON R V. Sedimentation rate, dilution, preservation and total organic carbon: Some results of a modelling study[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2001, 32(2): 333-339. [31] ZENG S Q, WANG J, FU X G, et al. Geochemical characteristics, redox conditions, and organic matter accumulation of marine oil shale from the Changliang Mountain area, northern Tibet, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 64: 203-221. [32] YAN D, WANG H, FU Q L, et al. Geochemical characteristics in the Longmaxi Formation(Early Silurian) of South China: Implications for organic matter accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65: 290-301. [33] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 甘华军, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段页岩形成环境及页岩油潜力综合评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233ZHOU L H, CHEN C W, GAN H J, et al. Shale formation environment and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233 -





 下载:
下载: