Characterization method of pore throat structure in dense sandstone based on NMR and CMP experiments
-
摘要:
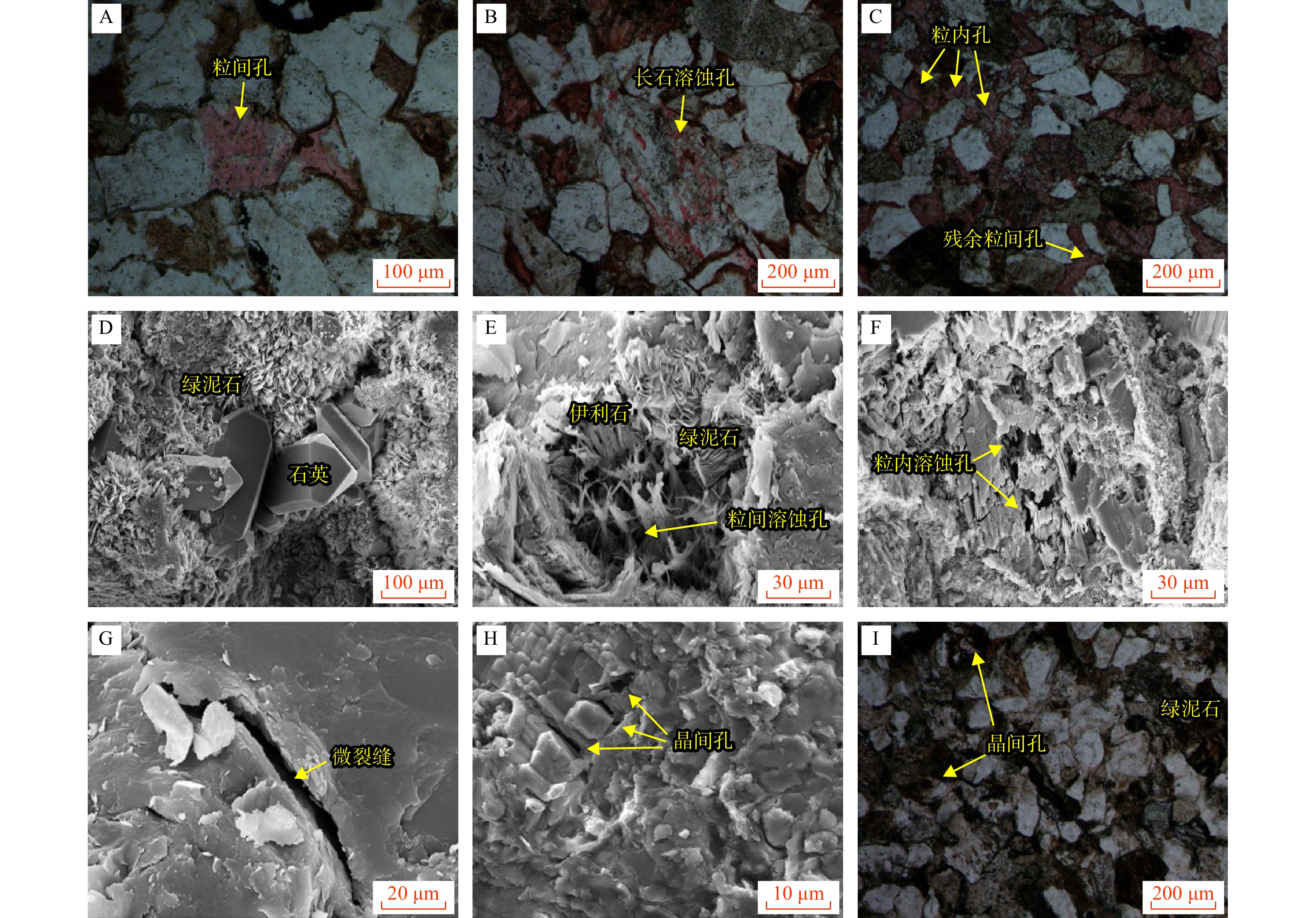
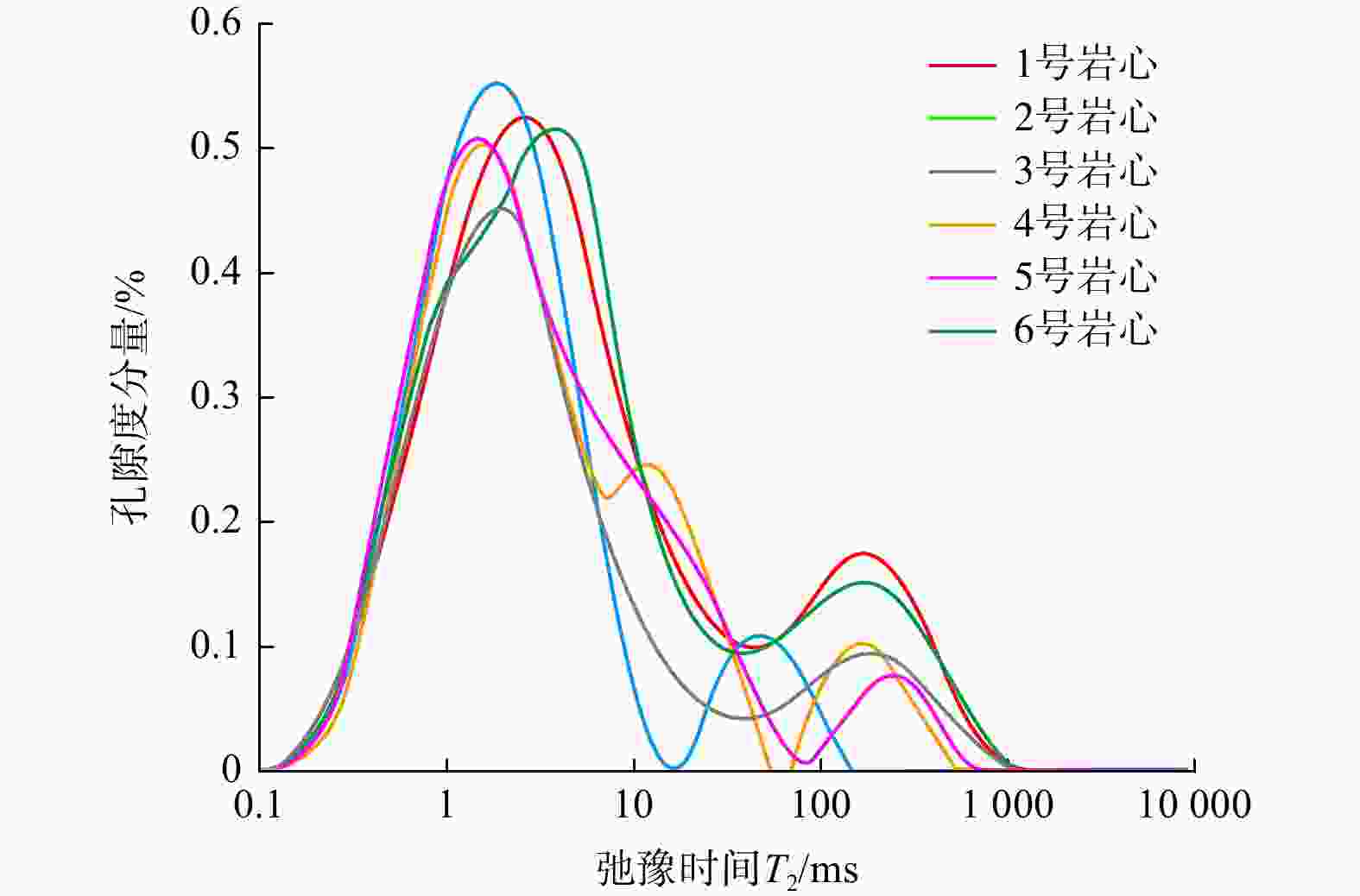
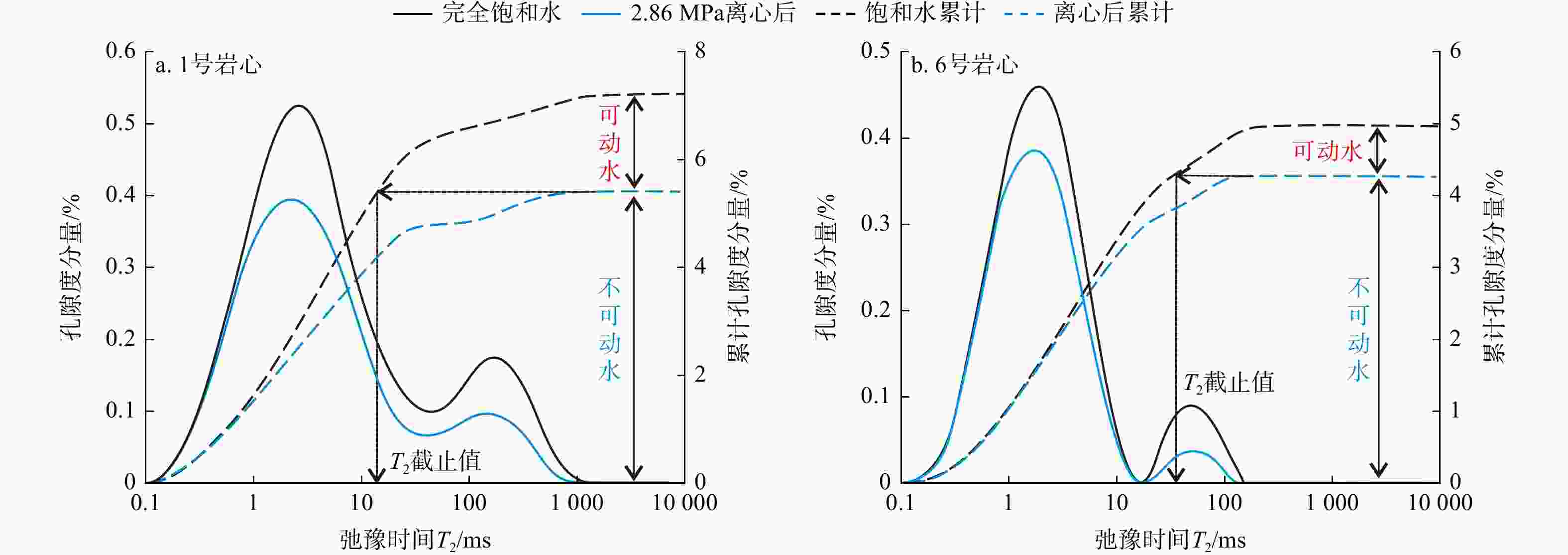
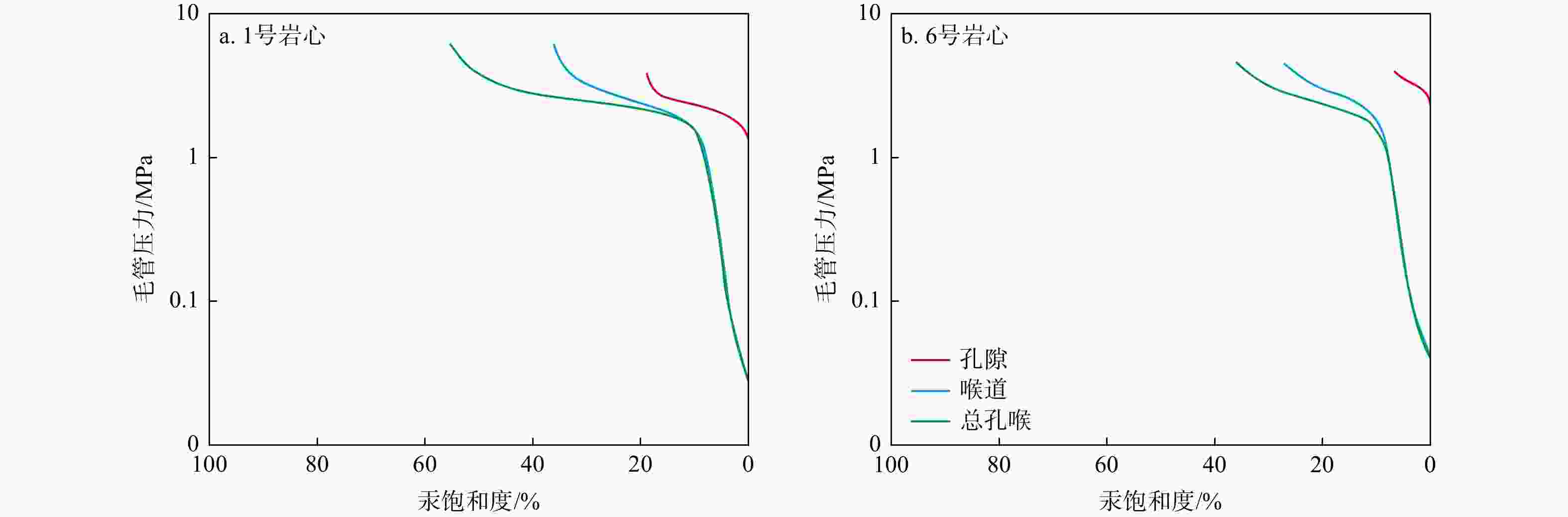
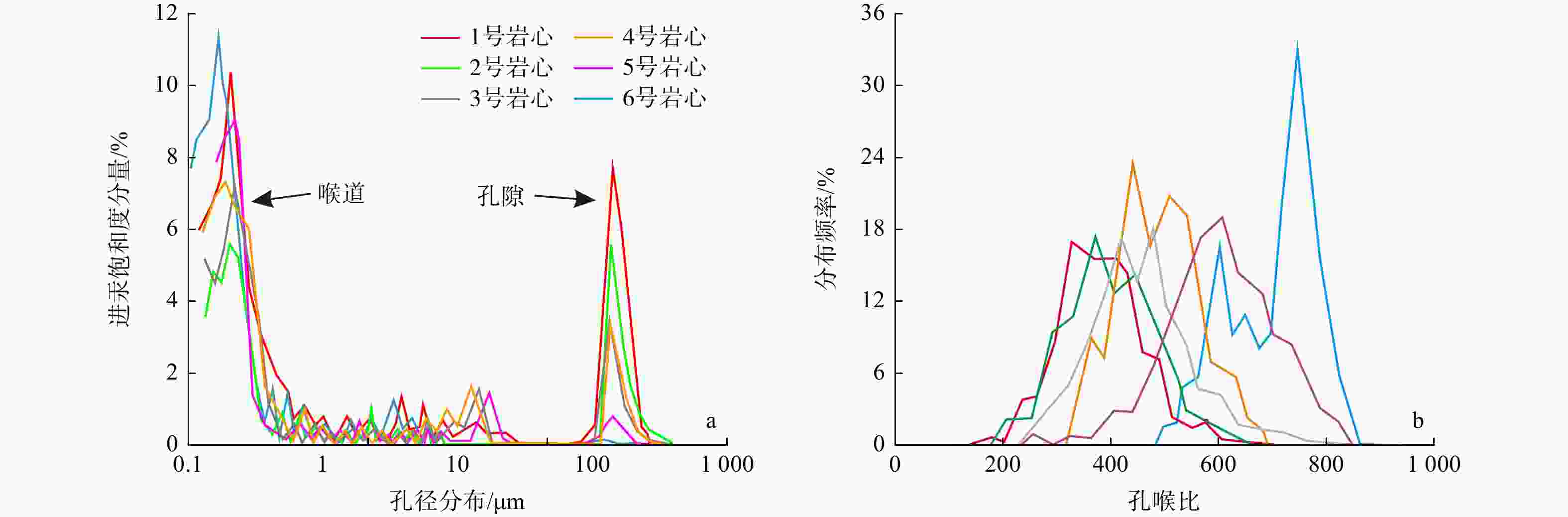
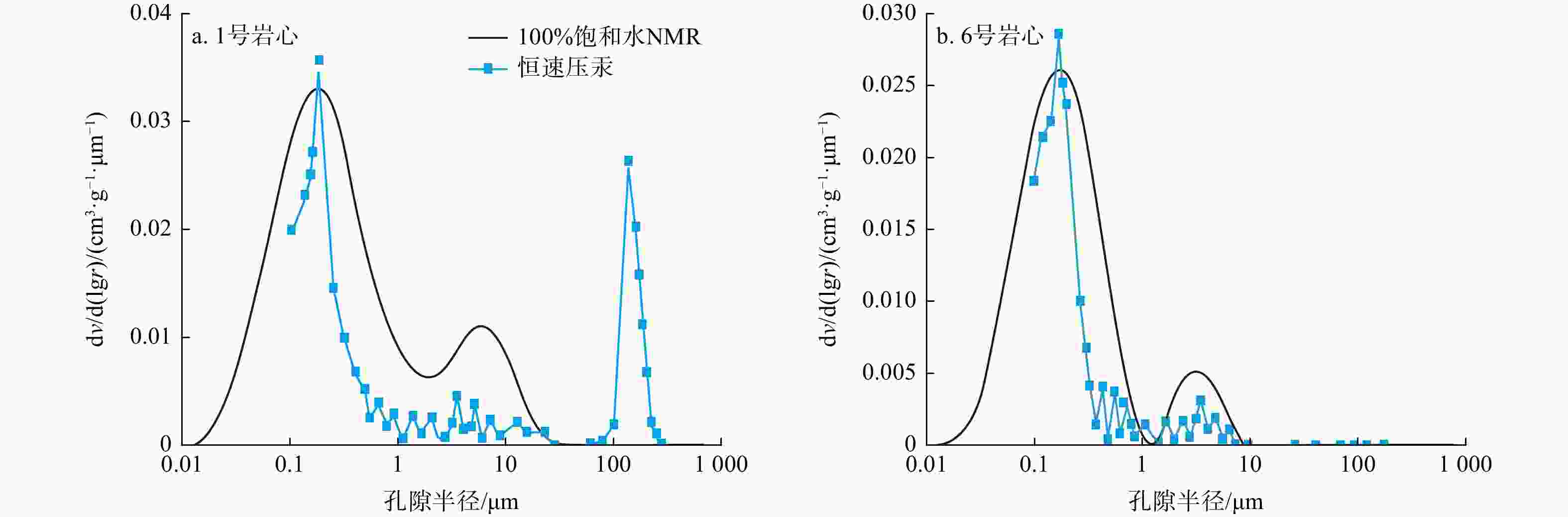
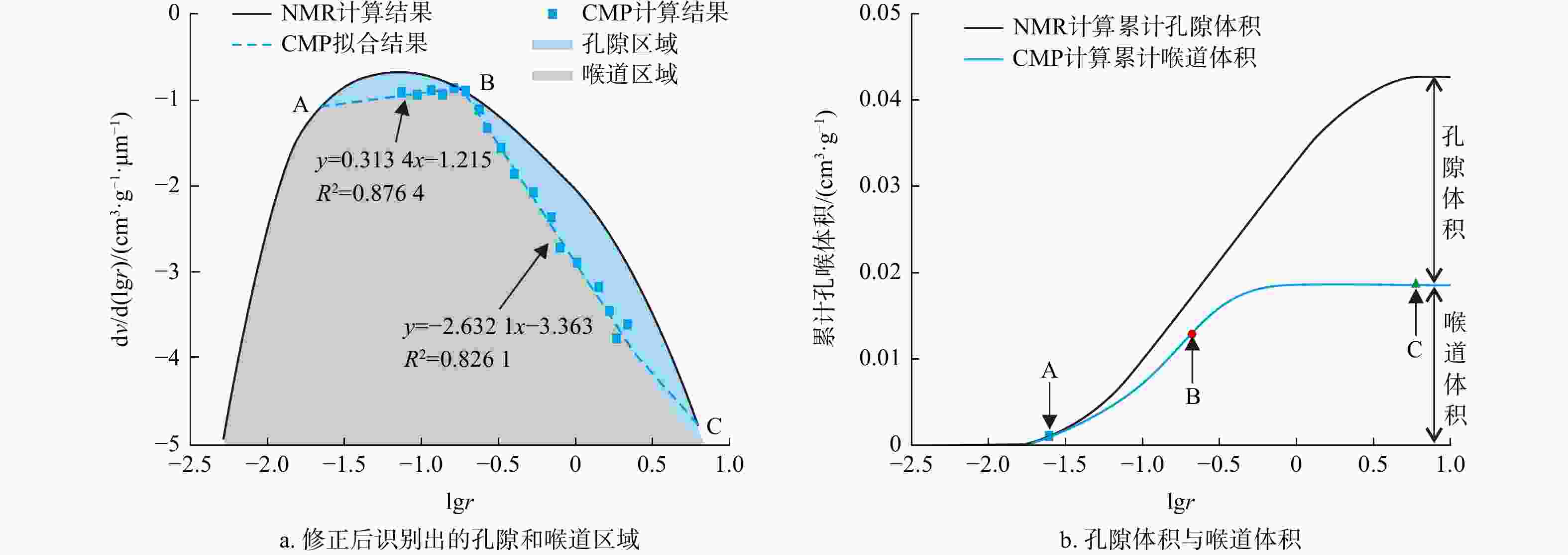
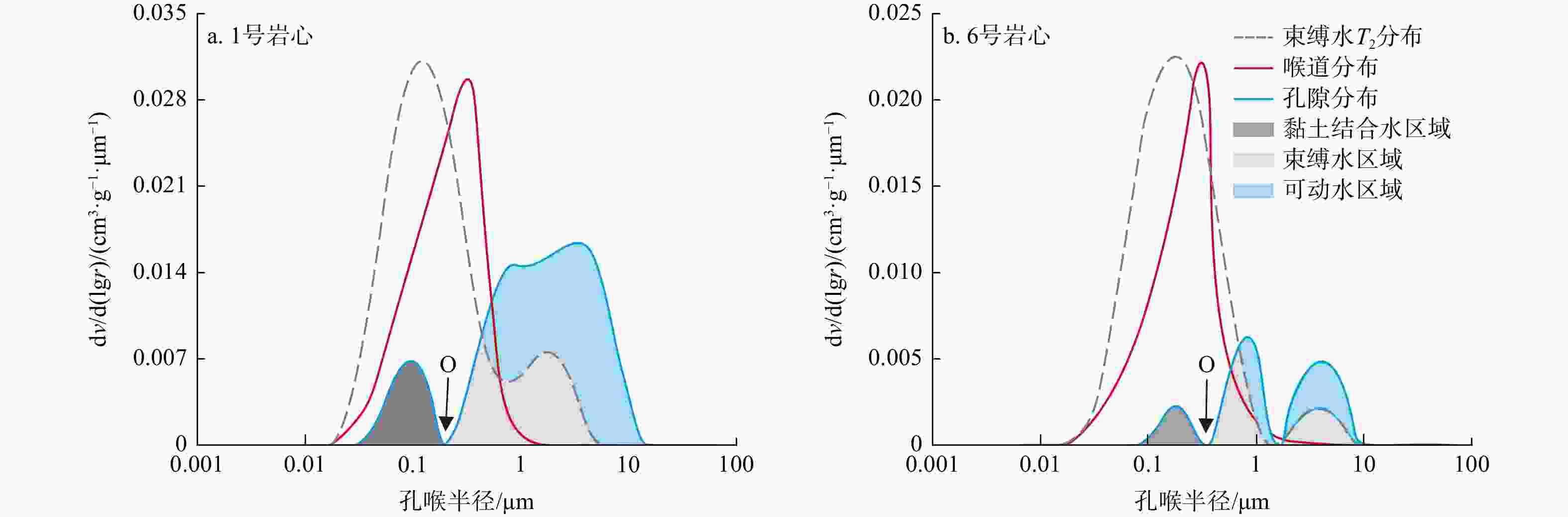
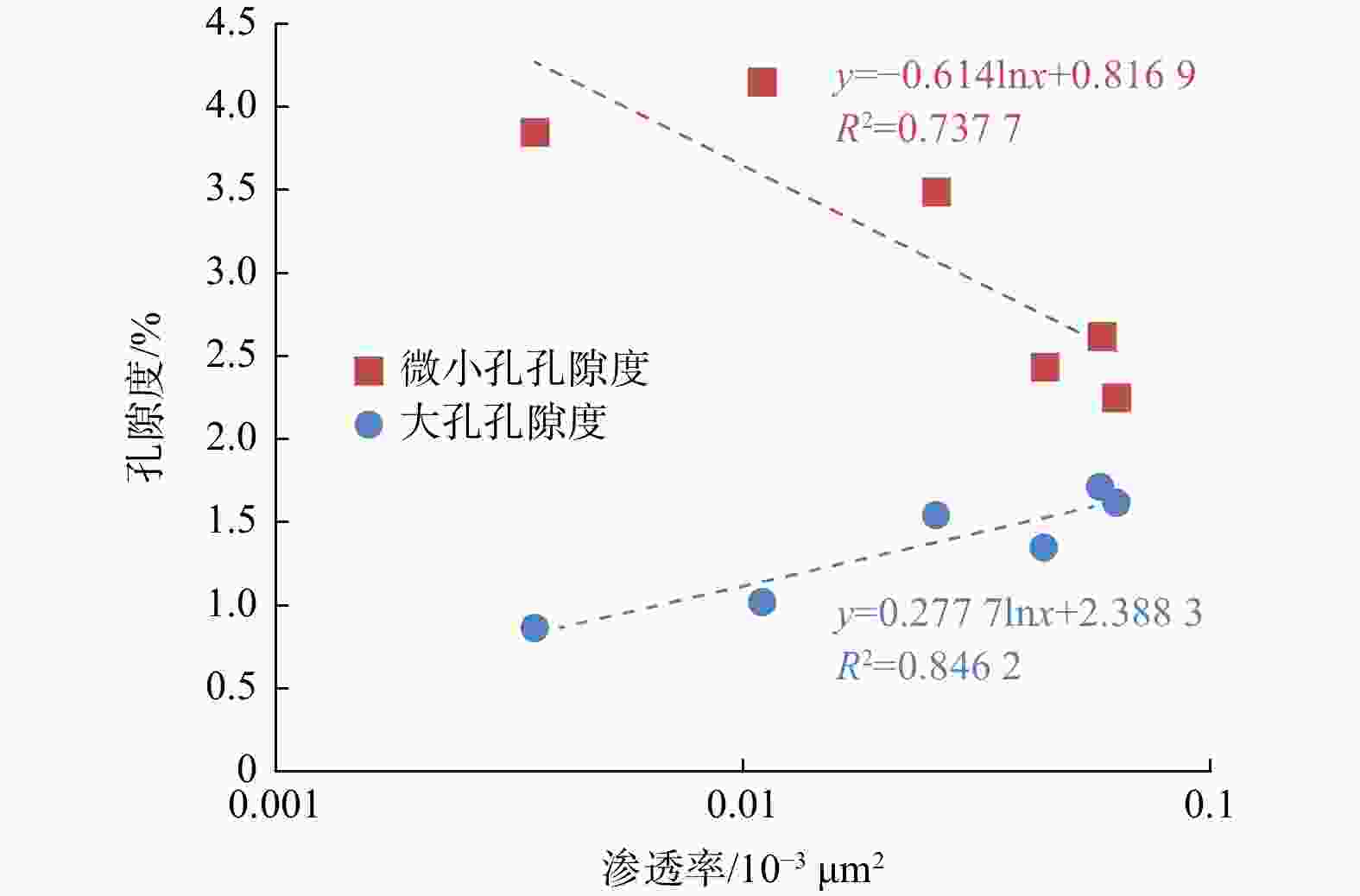
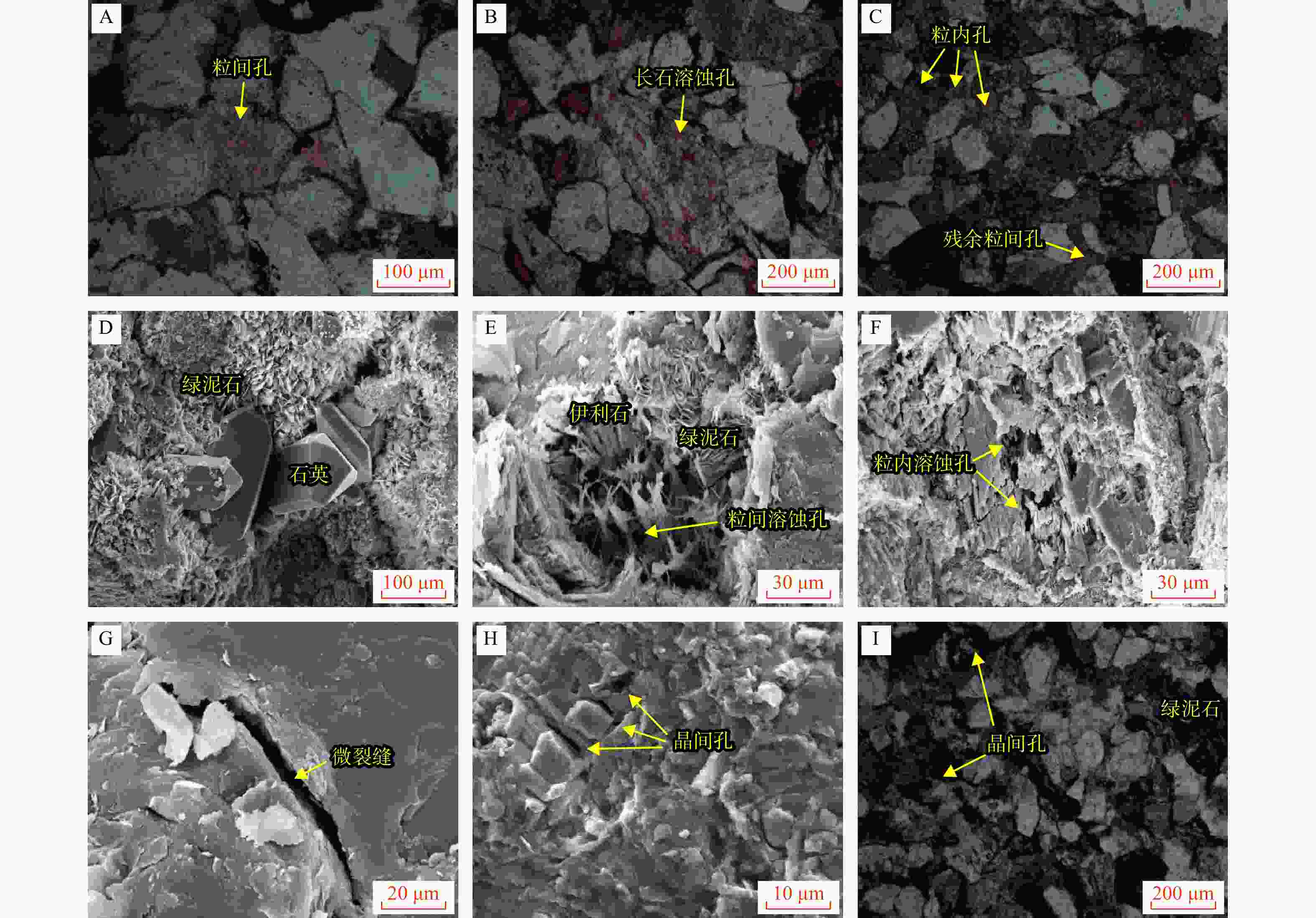
致密砂岩储层孔隙结构复杂、纳米孔隙发育,需集成多种技术对孔隙结构进行综合表征,以更好地认识储层。在优选6块延长组长71储层代表性岩心基础上,采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)、恒速压汞(CMP)和核磁共振(NMR)等方法,研究了岩心样品的孔隙类型及结构特征。采用CMP数据对NMR孔隙分布进行了修正,识别了喉道半径与孔隙半径的分布范围,建立了适用于致密砂岩的孔隙半径分类方法。研究结果表明,目标储层可动水与不可动水孔隙度之比仅为0.14~0.47,渗流能力差。将NMR与CMP数据相结合可精确识别出目标储层喉道半径中值为0.151~0.525 μm,孔隙半径中值为4.38~9.76 μm。孔隙内赋存水类型分为可动水、束缚水和黏土结合水,对应的饱和度平均值分别为23.4%、14.8%和9.4%。微小孔(
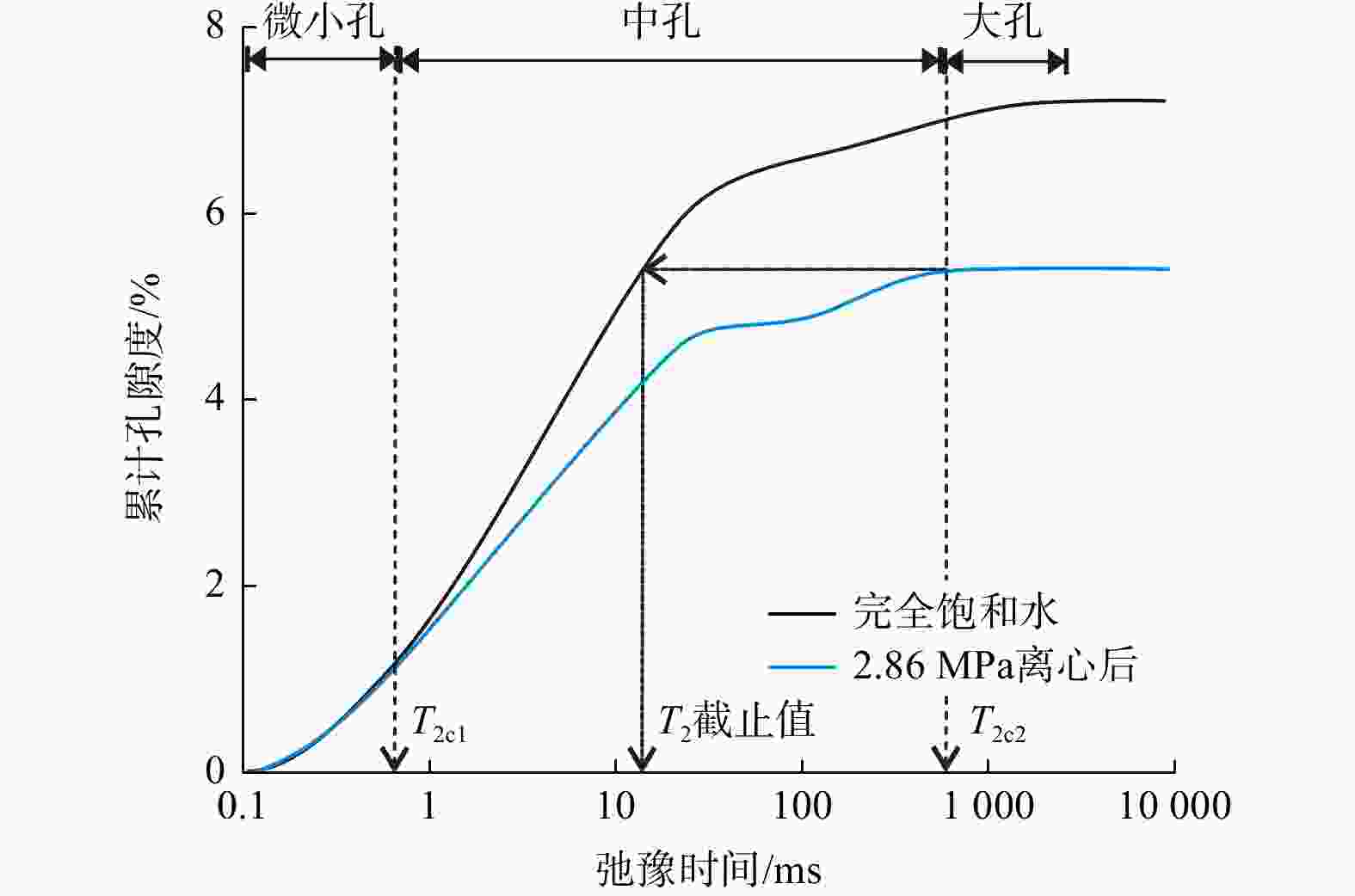
T 2<T 2c1)、中孔(T 2c1<T 2<T 2 c2)和大孔(T 2c2<T 2)的平均孔隙度分别为3.12%、3.42%和1.35%。孔喉半径r 2c1可作为储层渗流能力划分的评价指标,r 2c1的降低会导致微小孔(即吸附孔)孔隙度的降低,以及中孔和大孔(即渗流孔)孔隙度的增加。研究成果为优选致密砂岩优质储层,提高致密油采收率提供了参考和借鉴。Abstract:Objective The pore structure of tight sandstone reservoirs is complex, featuring the presence of nanopores, which is essential to integrate multiple technologies for a systematic characterization of the pore structure to enhance the understanding of these reservoirs.
Methods Six representative cores from the Chang 71 Chang Yanchang reservoir were selected for analysis. The pore types and structural characteristics of the core samples were examined using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), constant rate mercury injection (CMP), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The NMR pore distribution was adjusted based on CMP data, allowing for the identification of distribution ranges for the throat and pore radii, and a pore size classification method tailored for tight sandstone was developed.
Results Findings indicate that the ratio of the movable water porosity to the immovable water porosity of the target reservoir is only 0.14-0.47, indicating poor seepage capacity. The integration of NMR and CMP data enabled accurate characterization of the reservoir, identifying a median throat radius of 0.151-0.525 μm and a median pore radius of 4.38-9.76 μm. The pore types include mobile water, bound water, and clay-bound water, with average saturation values of 23.4%, 14.8%, and 9.4%, respectively. The average porosities of the small pores (
T 2 <T 2c1), medium pores (T 2c1 <T 2 <T 2c2), and large pores (T 2c2 <T 2) were found to be 3.12%, 3.42%, and 1.35%, respectively. The parameterr 2c1 serves as an evaluation index for the classification of reservoir seepage capacity. A decrease inr 2c1 leads to a decrease in the porosity of small pores (i.e., adsorption pores) and an increase in the porosity of medium and large pores (i.e., seepage pores).Conclusion The research findings offer valuable insights for the selection of high-quality tight sandstone reservoirs and the enhancement of tight oil recovery.
-
表 1 实验岩心物性参数及矿物组成
Table 1. Experimental core physical parameters and mineral composition
岩心编号 物性参数 主要矿物类型及质量分数wB/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10−3μm2 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 黏土矿物 其他矿物 1 7.89 0.0630 48.9 14.2 21.9 4.8 3.2 4.8 2.2 2 7.97 0.0580 40.3 17.4 21.2 8.2 2.2 7.3 3.4 3 9.32 0.0440 36.1 11.6 29.3 2.3 7.4 8.6 4.7 4 6.53 0.0260 26.2 21.1 18.4 8.8 11.1 10.8 3.6 5 8.58 0.0100 32.5 3.7 26.7 11.6 4.4 16.7 4.4 6 5.73 0.0036 34.0 9.1 27.3 0 6.3 23.3 0 均值 7.67 0.0340 36.3 12.9 24.1 6.0 5.8 11.9 3.1 注:孔隙度为氦气法测量;渗透率为脉冲衰减法测定;其他矿物包括黄铁矿、菱铁矿和金红石等 表 2 实验岩心NMR参数
Table 2. Experimental cores NMR parameters
岩心
编号T2截止值/
ms转换系数/
(μm·ms−1)可动水
孔隙度/%不可动水
孔隙度/%T2c1/
msT2c2/
ms孔隙度/% 贡饱和度/% 微小孔 中孔 大孔 可动水 束缚水 黏土
结合水1 13.2 0.083 1.94 5.28 0.86 684.52 2.24 4.04 1.61 33.5 11.2 13.4 2 17.2 0.072 2.26 4.86 1.32 232.18 2.61 3.57 1.71 29.3 19.1 7.7 3 9.4 0.088 2.42 5.81 1.15 368.35 2.42 4.13 1.34 24.4 15.7 10.3 4 20.6 0.059 1.37 4.46 2.68 164.43 3.48 2.87 1.54 18.8 20.2 7.7 5 24.4 0.036 1.28 5.49 5.12 89.63 4.14 2.73 1.02 18.4 13.5 5.8 6 32.8 0.052 0.62 4.32 4.67 113.23 3.84 3.18 0.87 15.7 8.8 11.6 均值 19.6 0.065 1.65 5.04 2.63 275.39 3.12 3.42 1.35 23.4 14.8 9.4 注:T2c1. 划分微小孔与中孔的弛豫时间;T2c2. 划分中孔与大孔的弛豫时间;下同 表 3 实验岩心CMP孔隙结构参数及结合NMR修正后的参数
Table 3. CMP pore structure parameters and NMR-corrected parameters of experimental cores
岩心编号 CMP孔隙结构参数 NMR修正后的参数 阈压/MPa 总进汞饱和度/% 孔隙进汞饱和度/% 喉道进汞饱和度/% 孔隙半径中值/μm 喉道半径中值/μm 孔喉比 孔隙半径中值/μm 孔喉比 1 1.37 54.89 19.20 35.68 156.22 0.525 312.7 9.76 18.61 2 1.14 54.84 22.83 32.00 141.18 0.380 389.8 7.43 19.54 3 1.45 46.81 15.25 31.57 128.61 0.370 365.1 6.43 17.39 4 1.63 42.29 13.86 28.43 120.84 0.317 399.9 6.04 19.04 5 2.17 35.79 11.86 23.93 115.65 0.226 537.8 4.63 20.49 6 2.43 34.62 7.01 27.61 109.61 0.151 764.2 4.38 29.11 均值 1.70 44.87 15.00 29.87 128.69 0.328 461.6 6.45 20.70 -
[1] 马永生, 黎茂稳, 蔡勋育, 等. 中国海相深层油气富集机理与勘探开发: 研究现状、关键技术瓶颈与基础科学问题[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(4):655-661.MA Y S, LI M W, CAI X Y, et al. Mechanisms and exploitation of deep marine petroleum accumulations in China: Advances, technological bottlenecks and basic scientific problems[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2020,41(4):655-661. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 卢双舫, 李俊乾, 张鹏飞, 等. 页岩油储集层微观孔喉分类与分级评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(3):436-444.LU S F, LI J Q, ZHANG P F, et al. Classification of microscopic pore-throats and the grading evaluation on shale oil reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(3):436-444. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 黄兴, 李天太, 王香增, 等. 致密砂岩储层可动流体分布特征及其影响因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油田延长组长8储层为例[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(5):557-567.HUANG X, LI T T, WANG X Z, et al. Distribution characteristics and its influence factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of Chang 8 oil layer of Yanchang Formation Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2019,40(5):557-567. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 李源流, 郭彬程, 杨兆平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地麻地沟油区三叠系延长组长 61 亚段致密砂岩储层特征及评价[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,35(5):38-46.LI Y L, GUO B C, YANG Z P, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of tight sandstone reservoir in Chang 61 submember of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Madigou oil area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi’ an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition),2020,35(5):38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 刘翰林, 杨友运, 王凤琴, 等. 致密砂岩储集层微观结构特征及成因分析:以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长6段和长8段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(2):225-231.LIU H L, YAN Y Y, WANG F Q, et al. Micro pore and throat characteristics and origin of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Triassic Chang 6 and Chang 8 members in Longdong area, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(2):225-231. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] ZHANG L C, LU S F, XIAO D S, et al. Pore structure characteristics of tight sandstones in the northern Songliao Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,88:170-180. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.08.005 [7] 肖佃师, 卢双舫, 陆正元, 等. 联合核磁共振和恒速压汞方法测定致密砂岩孔喉结构[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(6):1049-1059. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30122-7XIAO D S, LU S F, LU Z Y, et al. Combining nuclear magnetic resonance and rate-controlled porosimetry to probe the pore-throat structure of tight sandstones[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2016,43(6):1049-1059. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30122-7 [8] 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(3):419-427.TIAN H, ZHANG S C, LIU S B, et al. Determination of organic-rich shale pore features by mercury injection and gas adsorption methods[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(3):419-427. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学,2013,24(3):450-455.YANG F, NING Z F, KONG D T, et al. Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2013,24(3):450-455. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 贾连超, 刘鹏飞, 袁丹, 等. 注CO2提高页岩吸附气采收率实验:以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7页岩气为例[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2021,40(2):152-159.JIA L C, LIU P F, YUAN D, et al. Experiment of enhancing the recovery of the shale adsorbed gas by CO2 injection: Taking Yanchang Formation Chang 7 shale gas in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2021,40(2):152-159. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 郎东江, 伦增珉, 吕成远, 等. 页岩油注二氧化碳提高采收率影响因素核磁共振实验[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(3):1-10.LANG D J, LUN Z M, LÜ C Y, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance experimental study of CO2 injection to enhanced shale oil recovery[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(3):1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] LYU C, NING Z, WANG Q, et al. Application of NMR T2 to pore size distribution and movable fluid distribution in tight sandstones[J]. Energy & Fuels,2018,32(2):1395-1405. [13] 夏玉磊, 兰建平, 姚伟. 致密储层微观孔喉结构及可动流体分布特征:以鄂尔多斯盆地东部神木地区盒8储层为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2):41-51.XIA Y L, LAN J P, YAO W. Micro pore structure and movable fluid distribution characteristics of tight sandstone reservoir: Taking He 8 reservoir in Shemu area of eastern Ordos Basin as an example [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2):41-51. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 孟昆, 王胜建, 薛宗安, 等. 利用核磁共振资料定量评价页岩孔隙结构[J]. 波谱学杂志,2021,38(2):215-226.MENG K, WANG S J, XUE Z A, et al. Quantitative evaluation of shale pore structure using nuclear magnetic resonance data[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance,2021,38(2):215-226. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 杜佳, 刘彦成, 白洁玢, 等. 基于波形指示模拟的致密砂岩储层预测[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(5):94-100.DU J, LIU Y C, BAI J B, et al. Prediction of tight sandstone reservoirs based on waveform indication simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(5):94-100. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 刘永. 基于核磁共振流态分析的页岩微纳米孔隙类型划分方法[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.LIU Y. A study of shale pore size classification by using low field nuclear magnetic resonance fluid typing method [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):57-68.LIU K, SHI W Z, WANG R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with reservoir properties of the First Member of Lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):57-68. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] WU H, ZHANG C, JI Y, et al. An improved method of characterizing the pore structure in tight oil reservoirs: Integrated NMR and constant-rate-controlled porosimetry data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2018,166:778-796. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.065 [19] 汪新光, 张冲, 张辉, 等. 基于微观孔隙结构的低渗透砂岩储层分类评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(4):93-103.WANG X G, ZHANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Classification and evaluation of low-permeability sand reservoir based on micro-pore structure[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(4):93-103. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] DONG X, SHEN L W, LIU X, et al. NMR characterization of a tight sand's pore structures and fluid mobility: An experimental investigation for CO2 EOR potential[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,118:104460. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104460 [21] ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids: Technical report[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry,1994,66(8):1739-1758. [22] LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock porse[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2012,96(6):1071-1098. [23] 代全齐, 罗群, 张晨, 等. 基于核磁共振新参数的致密油砂岩储层孔隙结构特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段为例[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(7):887-897.DAI Q Q, LUO Q, ZHANG C, et al. Pore structure characteristics of tight-oil sandstone reservoir based on a new parameter measured by NMR experiment: A case study of Seven Member in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2016,37(7):887-897. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 王晓雯. 致密油藏储层敏感性评价及主控因素研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2021,28(1):103-110.WANG X W. Study on reservoir sensitivity evaluation and key control factors of tight oil reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2021,28(1):103-110. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载: