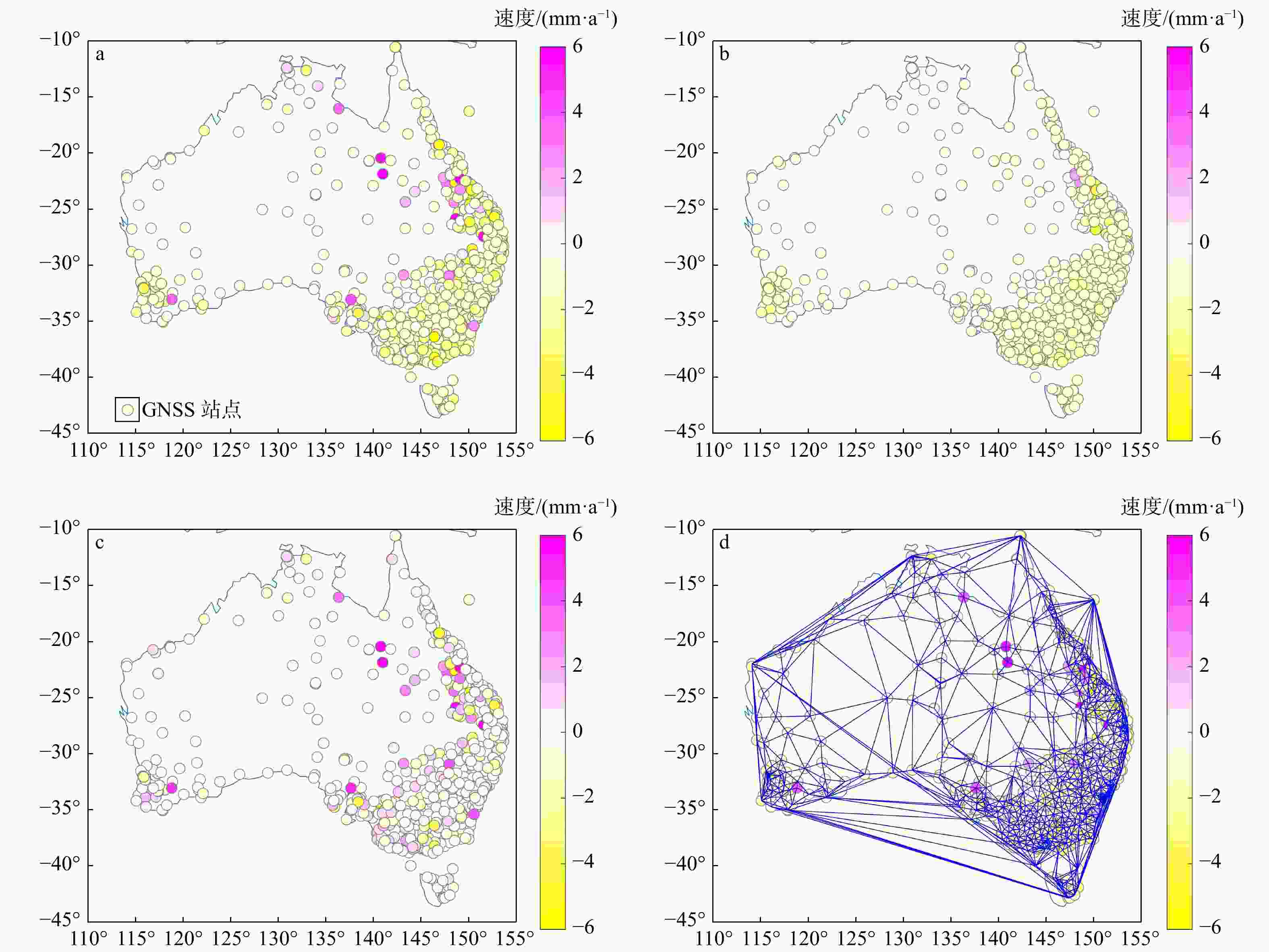
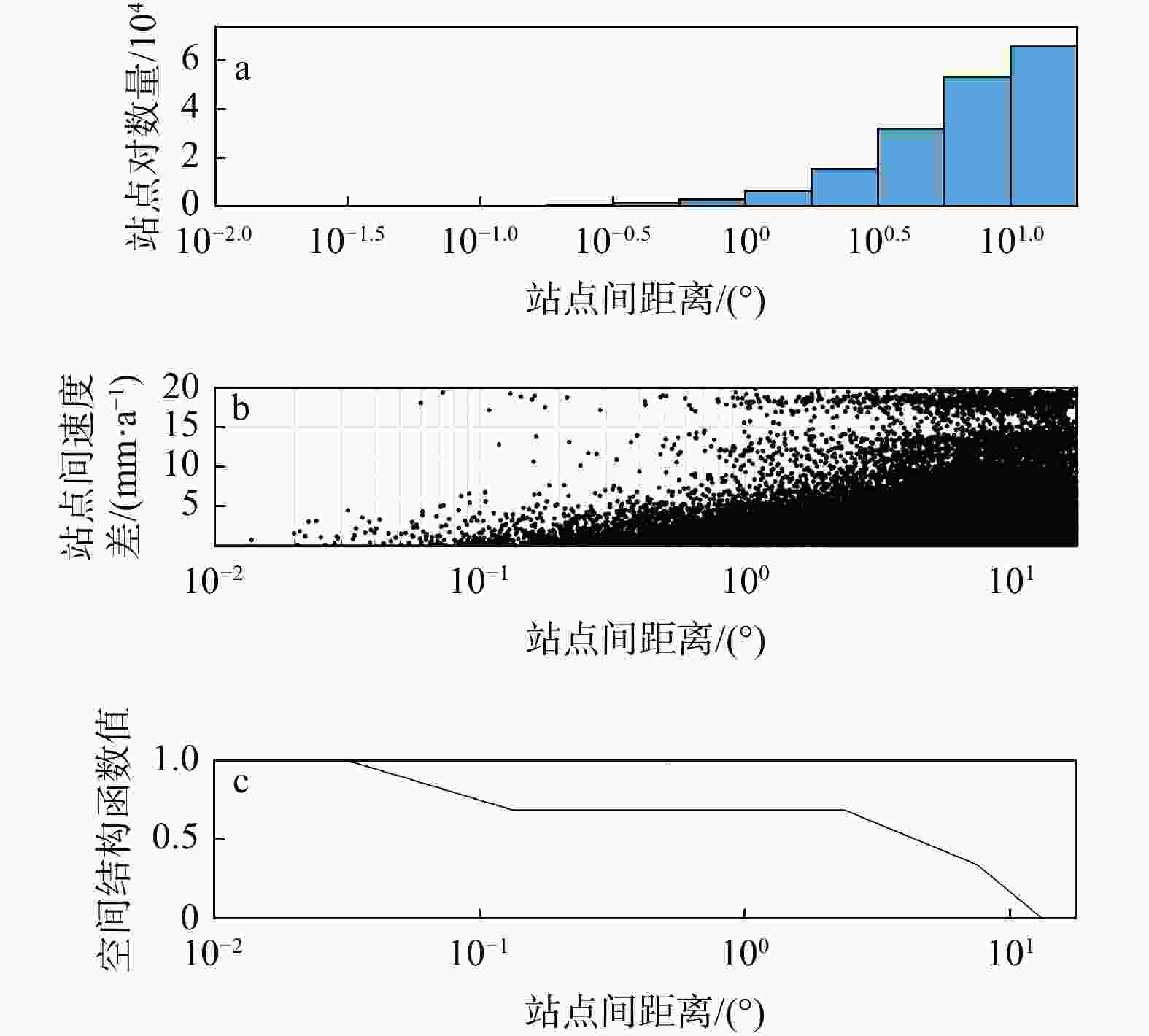
-
摘要:
在地壳垂向形变监测中全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)技术和合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)技术分别存在空间分辨率和时间分辨率不足的问题,而GNSS影像学方法基于离散的GNSS站点速度生成地壳垂直运动的图像,可以直接揭示地壳垂直运动的连续空间特性。使用GNSS影像学方法,研究了澳大利亚大陆地壳垂向形变,并通过棋盘格检验和交叉检验的方法对GNSS地壳垂直运动影像的可靠性进行了分析。结果表明GNSS影像学方法可以有效地剔除一些粗差的影响,并减少GNSS地壳垂直运动影像中出现零碎图斑和规则圆弧形突变边缘的问题,但同时也会剔除掉一些峰值和突变值,从而使生成的影像出现过度平滑的问题。GNSS地壳垂直运动影像表明澳大利亚将近98%的地区正在沉降,只有在澳大利亚北部部分地区和东部极小部分地区地壳呈上升运动,沉降和上升的量级基本在−3~1 mm/a之间。所有地区的垂直运动平均值为−0.76 mm/a,中值为−0.72 mm/a。本研究证实GNSS影像学方法具有合理性与正确性,GNSS地壳垂直运动影像能够准确获取大范围、高时空分辨率的地壳垂向形变,有助于揭示区域地壳垂向形变时空变化的细节特征。
Abstract:Objective In the study of vertical crustal deformation, the GNSS technique and InSAR technique have insufficient spatial and temporal resolutions, respectively. To better explore the continuous spatial characteristics of crustal vertical deformation, images of crustal vertical motion can be generated based on discrete GNSS station velocities; thus, the continuous spatial characteristics of crustal vertical motion can be directly revealed.
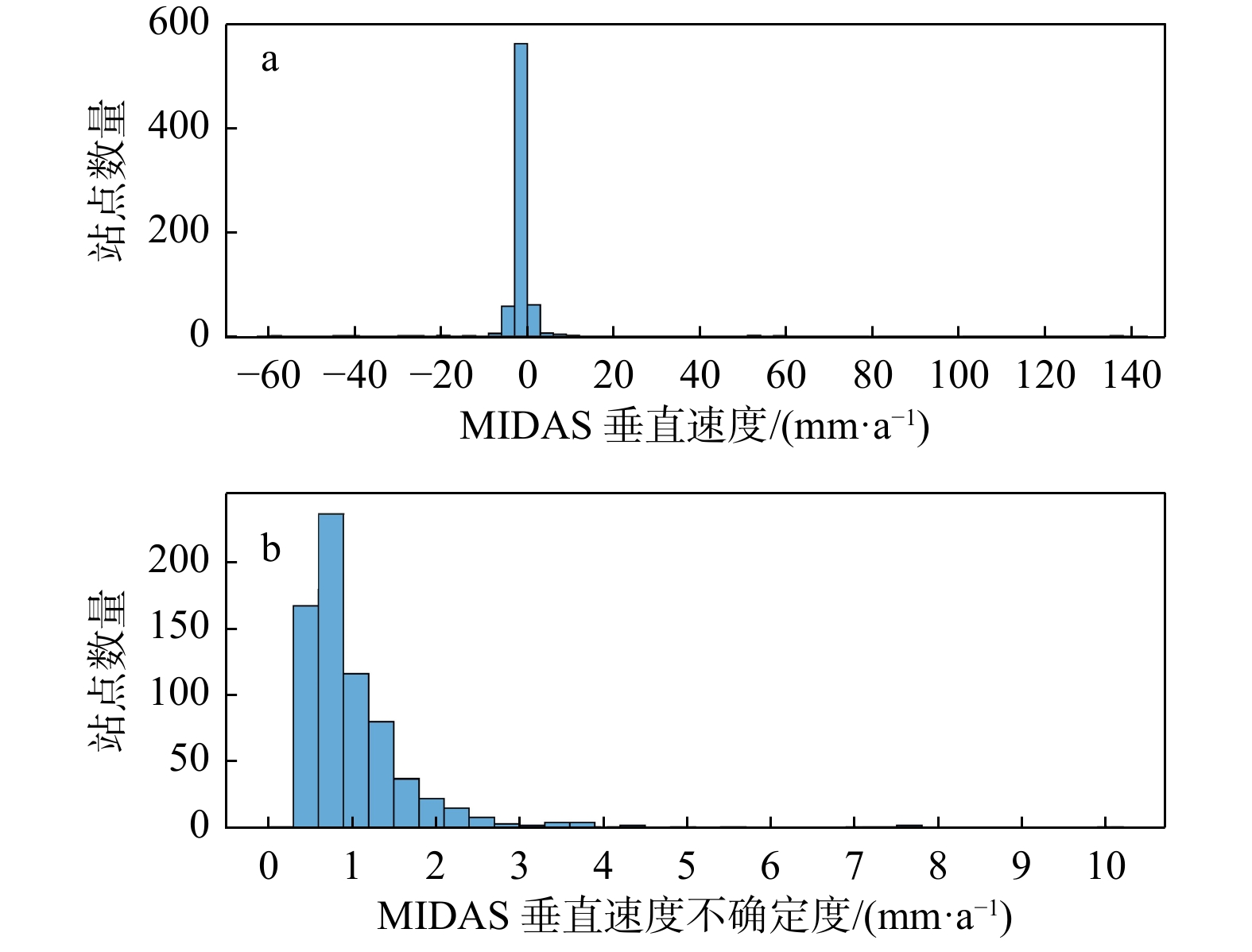
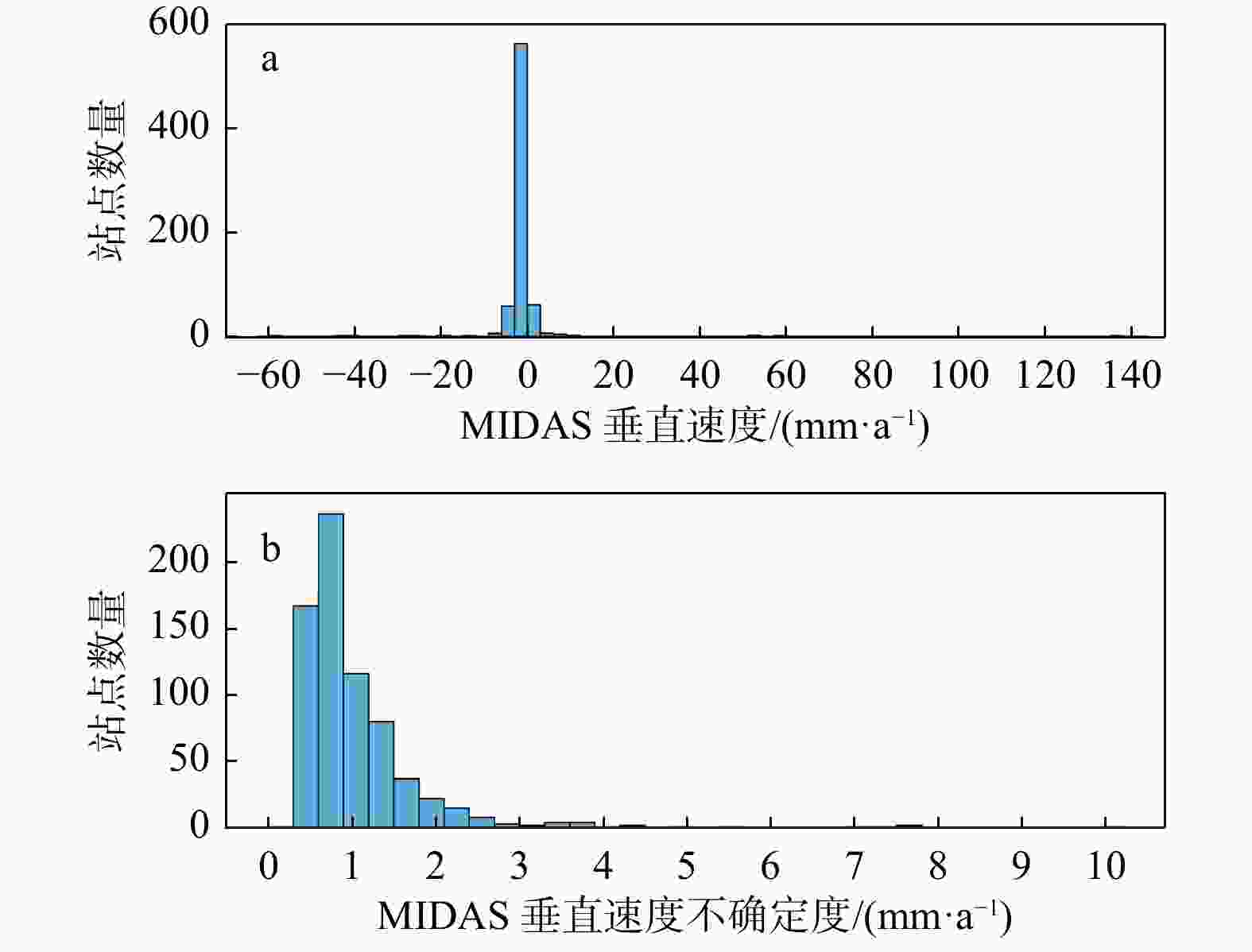
Methods In this work, the vertical deformation of the Australian continental crust is studied via GNSS imaging. GNSS imaging was first proposed by Professor Hammond of the Nevada Geodesy Laboratory, who used this method to obtain high-resolution images of crustal vertical deformation (GNSS images) in California and Nevada, USA. As a method to obtain images of continuous crustal vertical deformation with the help of image processing technology, it can automatically eliminate the influence of abnormal observations in the study area and reveal the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of crustal vertical deformation. First, the coordinate time series of the GNSS station in Australia are used to obtain the station velocities and uncertainties via a robust nonparametric estimation method, namely, the median interannual difference adjusted for skewness (MIDAS); second, the relationships between stations with the spatial structure function (SSF) are constructed; third, a median spatial filter (MSF) is constructed and applied to eliminate velocity outliers and enhance regional common characteristics; finally, the velocity field is densified using image processing technology, and spatially continuous GNSS images in the study areas are generated. In addition, checkerboard tests and cross-checks are carried out to verify the reasonability of GNSS imaging and the reliability of the GNSS images generated with the stations in these areas. Moreover, when the velocities before and after MSF were compared, the necessity of MSF in GNSS imaging was verified, and the causes of oversmoothing and the formation of arcuate abrupt boundaries were analyzed.
Results The findings of this study indicated that 98% of the Australian continent and its surrounding regions experienced subsidence. In contrast, only certain areas in northern Australia and a small portion of eastern Australia exhibited an increase in crustal deformation. Notably, the subsidence rate in the eastern part of the region was higher than that observed in the central and western areas. This pattern aligns with certain impacts from climate-related load sources but contradicts the effects associated with glacial isostatic adjustment.The mean and median values of vertical deformation in and around Australia are −0.76 mm/a and −0.72 mm/a, respectively, and the vertical deformation ranges from −3 mm/a to 1 mm/a. Moreover, through checkerboard tests and cross-checks, we can conclude that MSF for sites can effectively eliminate some effects of gross errors and effectively reduce the problems of fragmentary pattern spots and regular circular abrupt edges in GNSS images. However, gross errors cannot be well identified with peak and mutation values in the filtering process when sites are sparse. In the filtering process, some peaks and mutation values may be eliminated, which makes the generated image too smooth.
Conclusion Based on the research in this paper, it is concluded that GNSS images from the Australian continent accurately capture the overarching trends across extensive areas, demonstrating their reliability and correctness. Furthermore, these images effectively represent the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of crustal vertical deformation. This method is helpful for studying the temporal and spatial distributions of crustal vertical deformation.
-
Key words:
- GNSS imaging /
- vertical deformation /
- Australia /
- imaging analysis
-
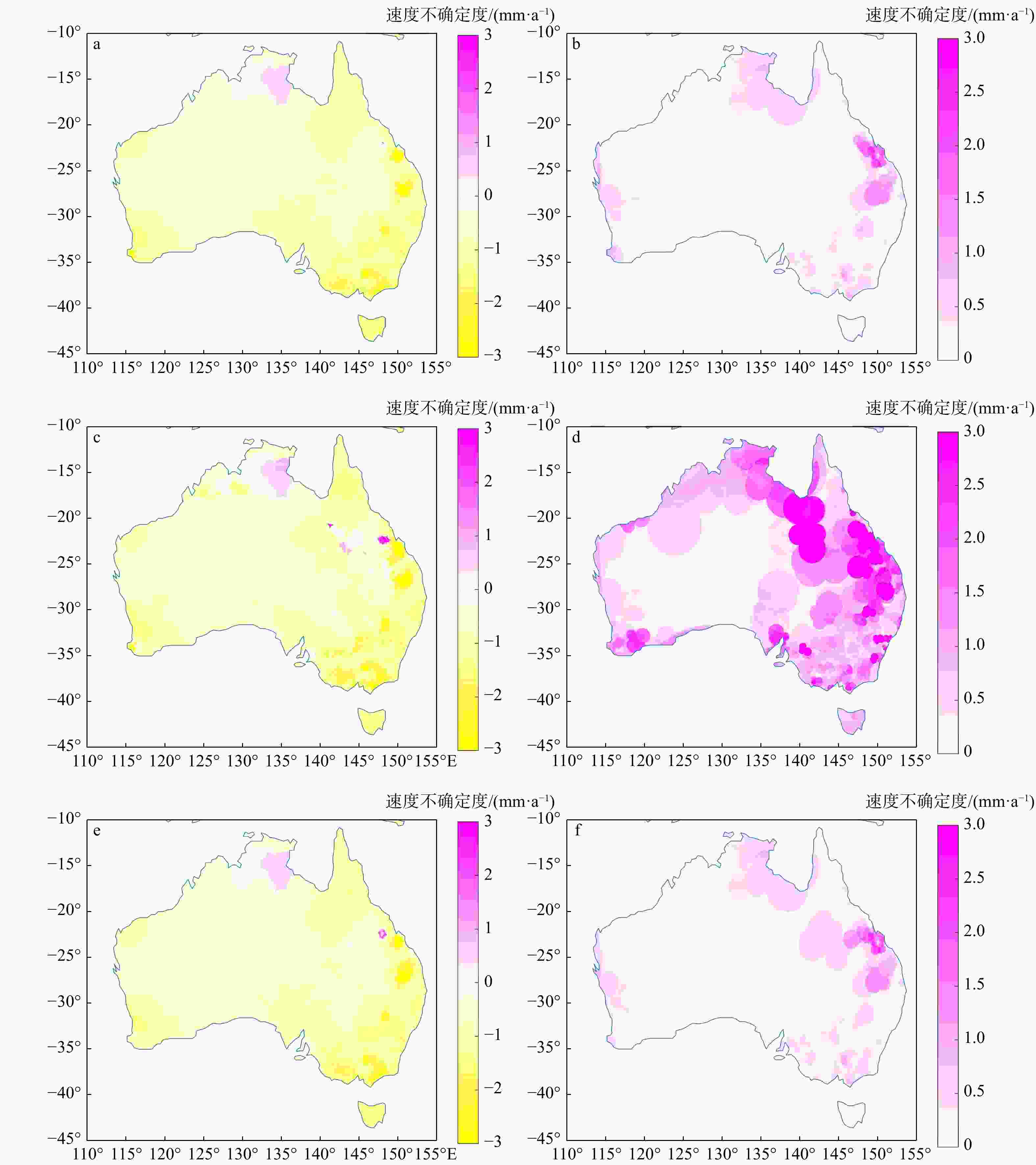
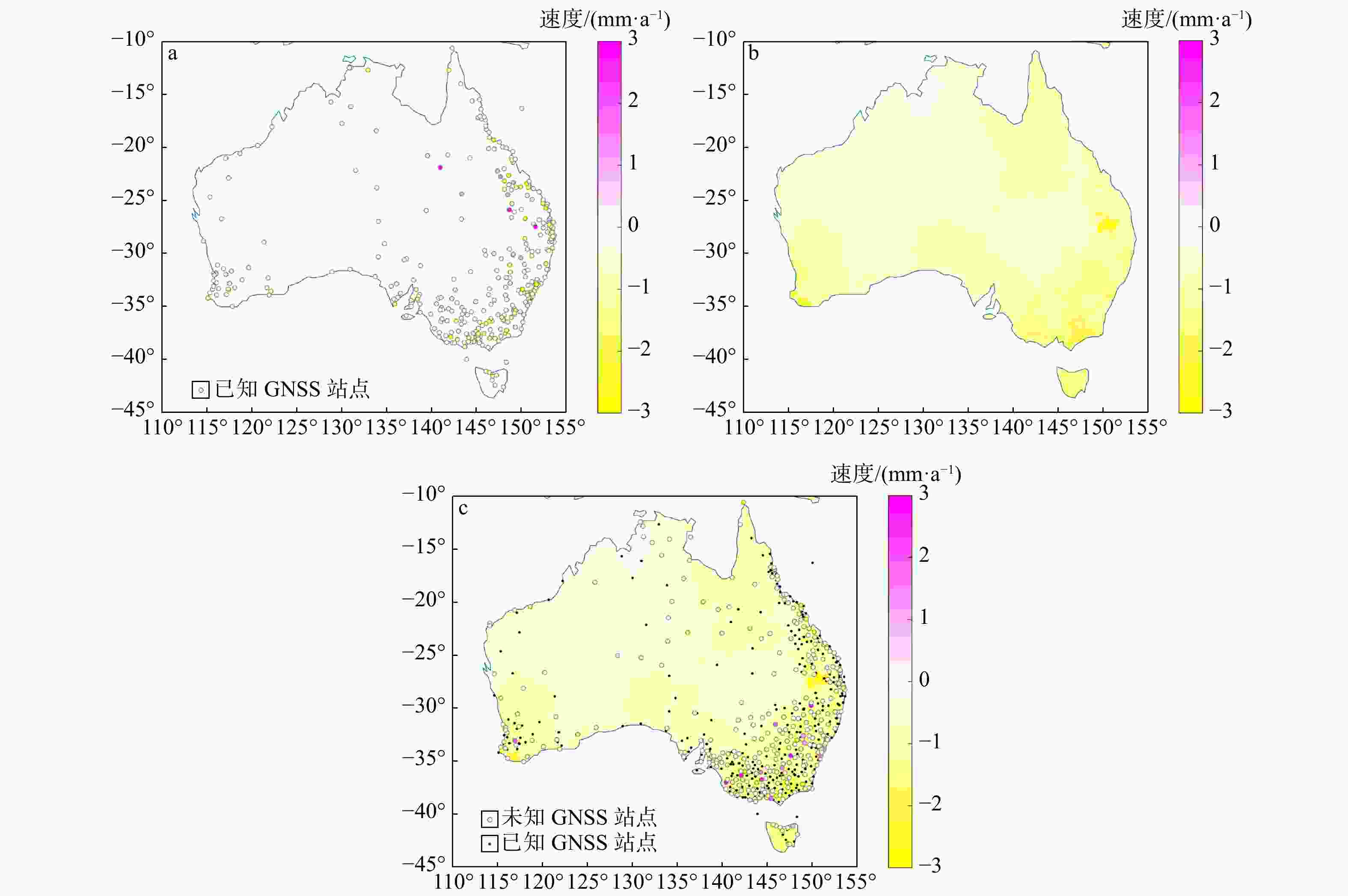
图 4 使用GNSS成像方法生成的地壳垂直运动影像(a)和相应的不确定度影像(b)、未经过MSF滤波生成的地壳垂直运动影像(c)和相应的不确定度影像(d)、采用非球面三角网生成的地壳垂直运动影像(e)和相应的不确定度影像(f)
Figure 4. Vertical crustal movement image (a) and corresponding uncertainty image (b) generated by GNSS imaging method, vertical crustal movement image (c) and corresponding uncertainty image (d) generated without MSF filtering, and vertical crustal movement image (e) and corresponding uncertainty image (f) generated by aspherical triangulation network
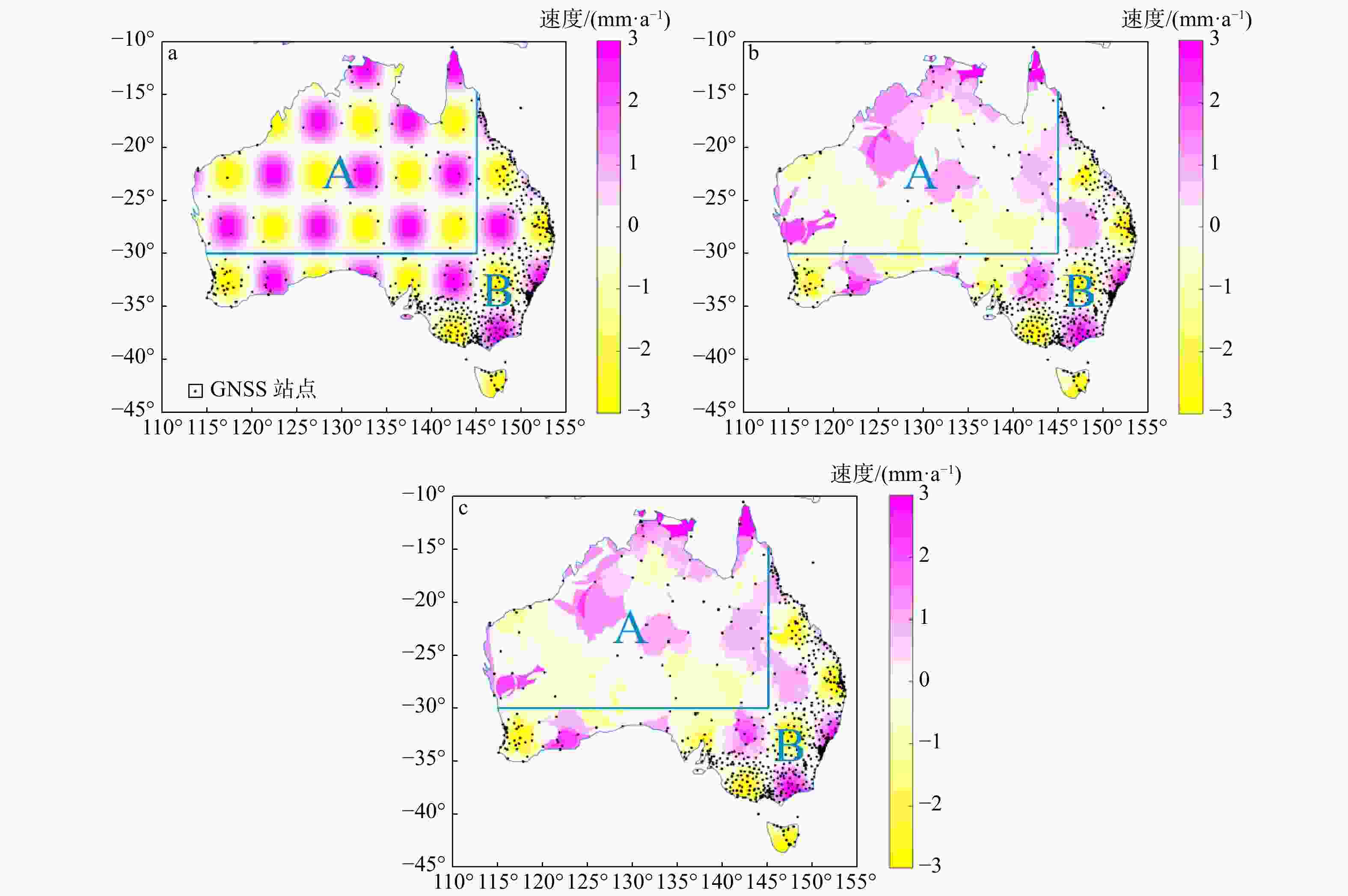
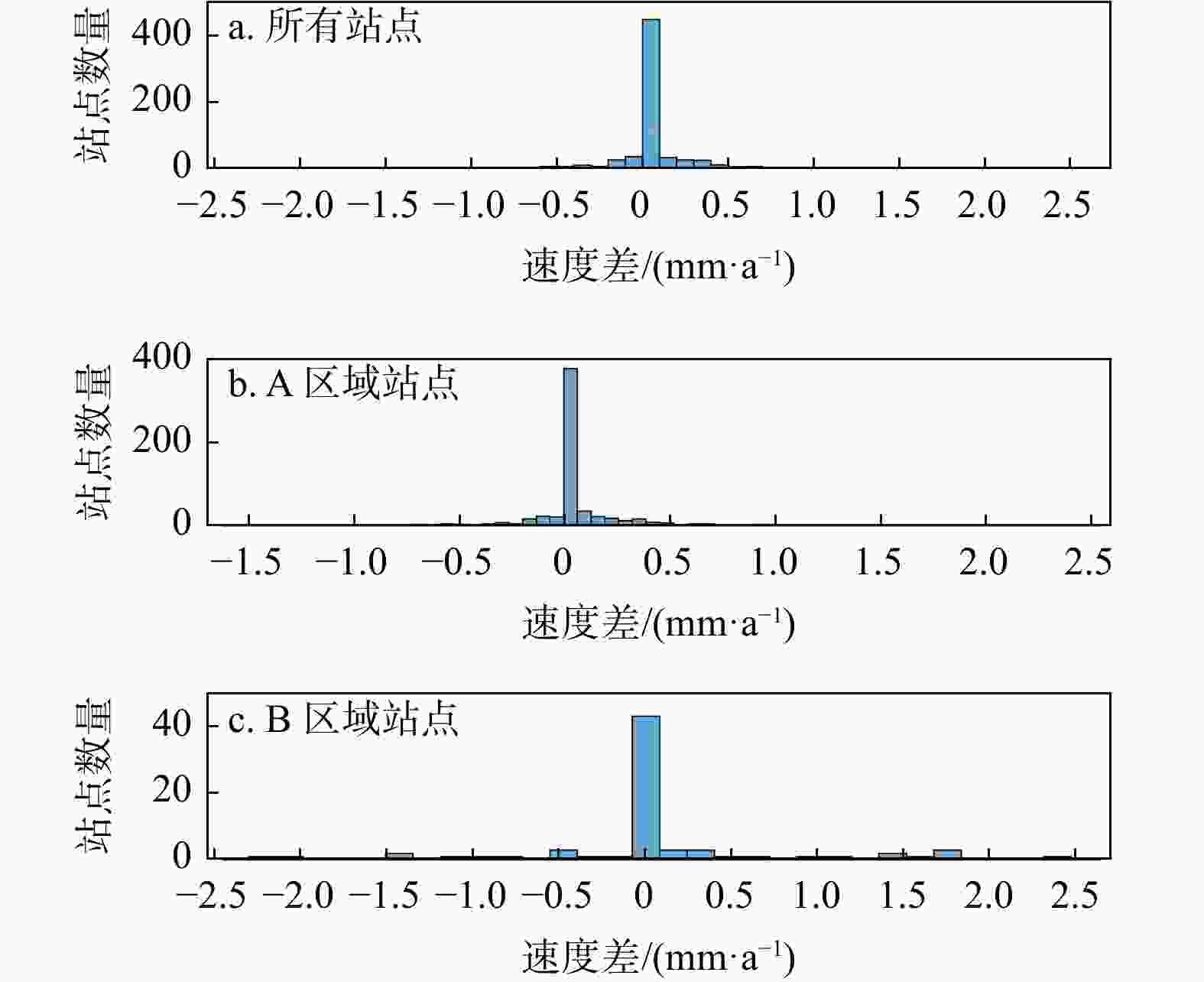
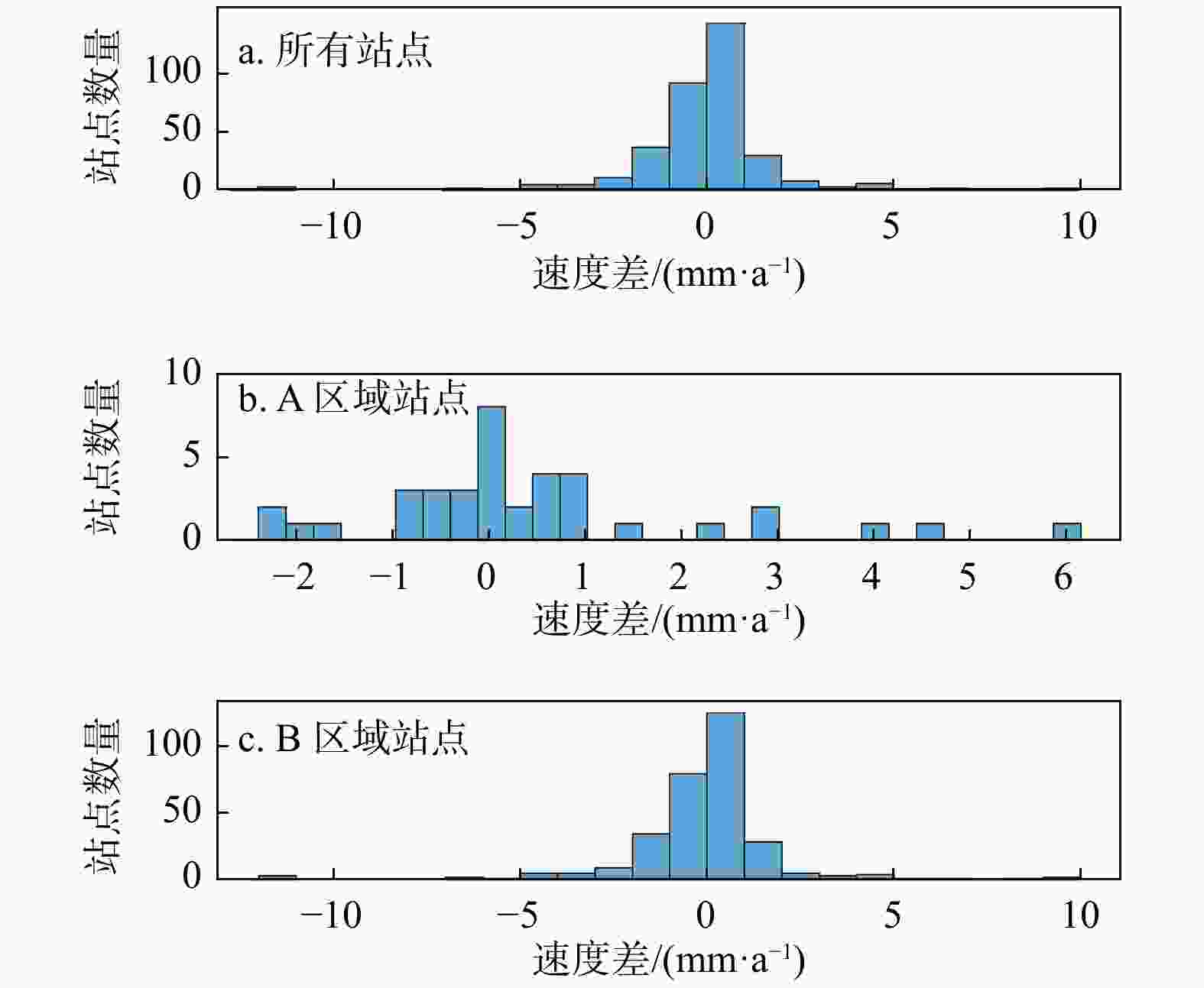
图 6 所有站点恢复速度与原棋盘速度的差值(a)、A区域站点恢复速度与原棋盘速度的差值(b)和B区域站点恢复速度与原棋盘速度的差值(c)的统计结果
Figure 6. Statistical results of the difference between the recovery speed of all sites and the original board speed (a), the difference between the recovery speed of sites in Zone A and the original board speed (b), and the difference between the recovery speed of sites in Zone B and the original board speed (c)
-
[1] LARSON K M,FREYMUELLER J T,PHILIPSEN S. Global plate velocities from the Global Positioning System[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),1997,102:9961-9981. [2] HUANG H,MENG L S,BURGMANN R,et al. Early aftershocks and afterslip surrounding the 2015 Mw 8.4 Illapel rupture[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2017,457:282-291. [3] 张占忠,陈富强,刘亚林,等. 基于遥感技术的嘉黎江巴变形体稳定性评价与分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):28-37.ZHANG Z Z,CHEN F Q,LIU Y L,et al. Stability evaluation and analysis of the Jiangba deformed body in Jiali County based on remote sensing technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):28-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 董佳慧,牛瑞卿,亓梦茹,等. InSAR技术和孕灾背景指标相结合的地灾隐患识别[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):187-196.DONG J H,NIU R Q,QI M G,et al. Identification of geological hazards based on the combination of InSAR technology and disaster background indicators[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):187-196. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] SHEN Z K,JACKSON D D,GE B X. Crustal deformation across and beyond the Los Aangeles Basin from geodetic measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research( Solid Earth),1996,101:27957-27980. [6] WANG M,SHEN Z K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GNSS and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2020,125:e2019JB018774. [7] 谭凯,赵斌,张彩红,等. GPS和InSAR同震形变约束的尼泊尔Mw7.9和Mw7.3地震破裂滑动分布[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(6):2080-2093. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160614TAN K,ZHAO B,ZHANG C H,et al. Rupture models of the Nepal Mw7.9 earthquake and Mw7.3 aftrershock constrained by GPS and InSAR coseismic deformations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(6):2080-2093. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg20160614 [8] 许才军,何平,温扬茂,等. InSAR技术及应用研究进展[J]. 测绘地理信息,2015,40(2):1-9.XU C J,HE P,WEN Y M,et al. Recent advances InSAR interferometry and its applications[J]. Journal of Geomatics,2015,40(2):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 黄宇,杨荣森,韩晓东,等. 基于定向半变异函数的裂隙网络空间变异性分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):186-193.HUANG Y,YANG R S,HAN X D,et al. Analysis of the spatial variability on a fracture network based on an oriented semivariogram[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] HAMMOND W C,BLEWITT G,KREEMER C. GPS imaging of vertical land motion in California and Nevada:Implications for Sierra Nevada uplift[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research( Solid Earth),2016,121:7681-7703. [11] PAN Y,HAMMOND W C,DING H,et al. GPS imaging of vertical bedrock displacements:Quantification of two-dimensional vertical crustal deformation in China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2021,126:e2020JB020951. [12] XIANG Y,YUE J,LIU G,et al. Characterizing the spatial patterns of vertical crustal deformations over the South American Continent based on GNSS imaging[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics,2022,179:3569-3587. [13] 周晓慧,杨艺林,姜卫平,等. GNSS影像及其时空特征初探[J]. 地球物理学报,2020,63(1):155-171. doi: 10.6038/cjg2020M0473ZHOU X H,YANG Y L,JIANG W P,et al. Preliminary spatial temporal pattern of vertical deformation revealed by GNSS imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2020,63(1):155-171. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2020M0473 [14] BLEWITT G,KREEMER C,HAMMOND W C,et al. MIDAS robust trend estimator for accurate GPS station velocities without step detection[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2016,121:2054-2068. [15] THEIL H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis[J]. Indagationes Mathematicae,1950,12:85-91. [16] SEN P K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau[J]. American Statistical Association,1968,63:1379-1389. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1968.10480934 [17] DELAUNAY B. Sur la sphère vide[J]. Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR,1934,7:793-800. [18] RIDDELL A R,KING M A,WATSON C S. Present-day vertical land motion of Australia from GPS observations and geophysical models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2020,125:e2019JB018034. [19] HAMMOND W C,BLEWITT G,KREEMER C,et al. GPS imaging of global vertical land motion for studies of sea level rise[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),2021,126:e2021JB022355. -




 下载:
下载: