Structural features of the southern Hubei Province along the northern of the Mufushan pluton structural ore-controlling of polymetallic deposits
-
摘要:
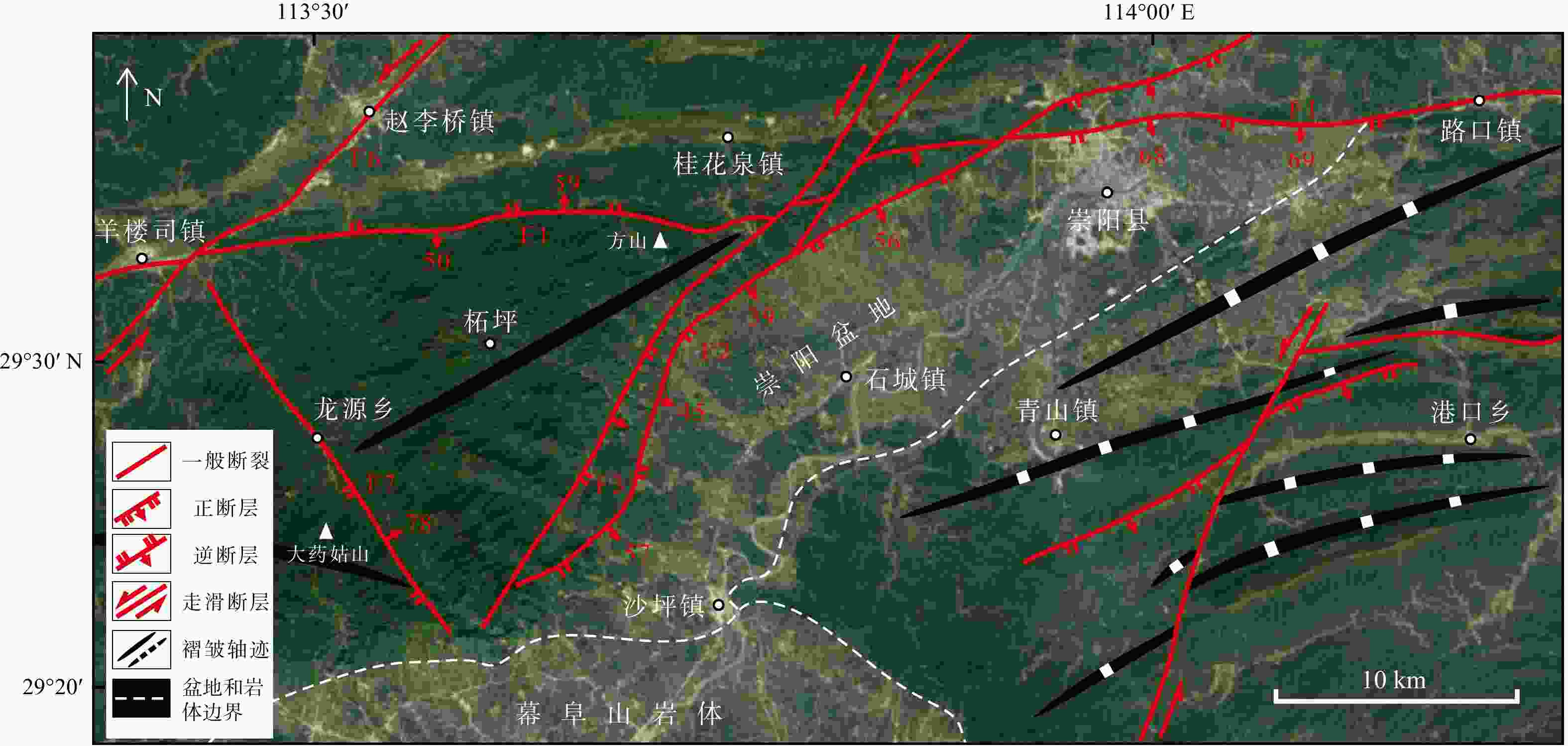
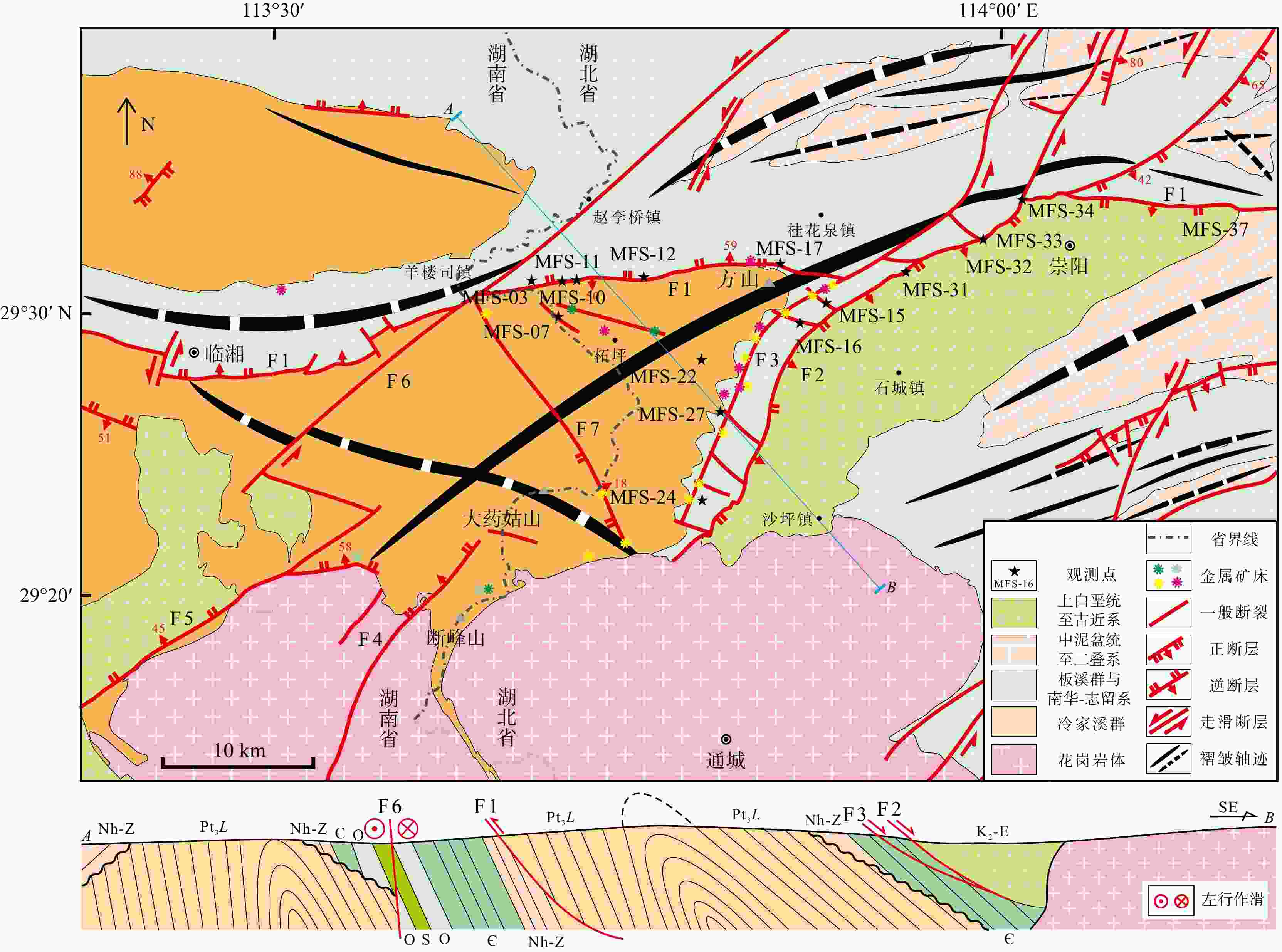
江南造山带中段幕阜山地区发育规模巨大的早白垩世Li-Be-Cs-Nb-Ta等稀有金属和Pb-Zn-Cu-Au-Sb等有色金属岩浆−热液成矿系统。幕阜山岩体南、北缘的湘东北和鄂南地区具有相同的成矿物质基础,但现有矿产勘探成果差距明显,可能是构造变形差异所致。本研究通过构造解析、古应力场反演以及矿床分布规律,探讨了鄂南地区的构造控矿作用。构造解析表明E-W走向江南断裂形成于新元古代,保存了三叠纪由S向N的逆冲作用、晚白垩世断层上盘向SE的正断作用和古近纪E-W走向左行剪切作用;而NE-SW走向长坪断裂形成于中侏罗世燕山运动,记录了早白垩世晚期左行走滑、晚白垩世正断作用和古近纪晚期右行走滑。基于断层滑移矢量反演的古应力场揭示鄂南地区经历了早白垩世晚期走滑(近N-S向最大主应力)、晚白垩世NW-SE走向伸展、古近纪早期走滑(NE-SW向最大主应力)和古近纪中−晚期NE-SW走向伸展的应力场演化历史。结合研究区的金属矿床分布特征,认为鄂南地区NE-SW走向主干断裂的次级近平行断裂或与其相交的NW-SE走向和近E-W走向断裂具有较好的金属矿产勘探潜力。
Abstract:Objective An intensive Early Cretaceous magmatic-hydrothermal metallogenic system developed in the Mufushan area of the central Jingnan Orogen. This orogenic belt in the South China Block formed through the accretion and subsequent collision of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks during the early Neoproterozoic, resulting in the formation of rare metal deposits (Li-Be-Cs-Nb-Ta) and nonferrous metal deposits (Pb-Zn-Cu-Au-Sb).
Methods This study investigates the structural control of polymetallic deposits in southern Hubei Province utilizing structural analysis, paleostress inversions of fault-slip data, and the spatial distribution of polymetallic ore deposits.
Results Structural analysis revealed that the Jiangnan fault, striking E-W and originating in the Neoproterozoic, exhibits Triassic top-to-the-north thrusting, Late Cretaceous oblique normal faulting, and Paleogene left-lateral strike-slip motion. The NE-striking Changping fault, formed during the Middle Jurassic Yanshanian orogeny, shows evidence of late Early Cretaceous left-lateral strike-slip motion, late Cretaceous normal faulting, and late Paleogene right-lateral strike-slip motion. Paleostress inversions indicate that southern Hubei Province experienced a series of paleostress fields, including a strike-slip stress field (with maximum principal stress oriented N-S and minimum principal stress oriented N-S) during the late Early Cretaceous, an NW-SE extensional stress field during the late Cretaceous, another strike-slip stress field (with maximum principal stress oriented NE-SW and minimum principal stress oriented N-S) during the early Paleogene, and a NE-SW extensional stress field during the late Paleogene.
Conclusion Based on the polymetallic deposits in the study area, we conclude that secondary faults subparallel to the primary NE-SW trending fault, along with NW-SE and E-W trending faults intersecting with the primary NE-SW fault, present substantial potential for polymetallic mineral exploration.
-
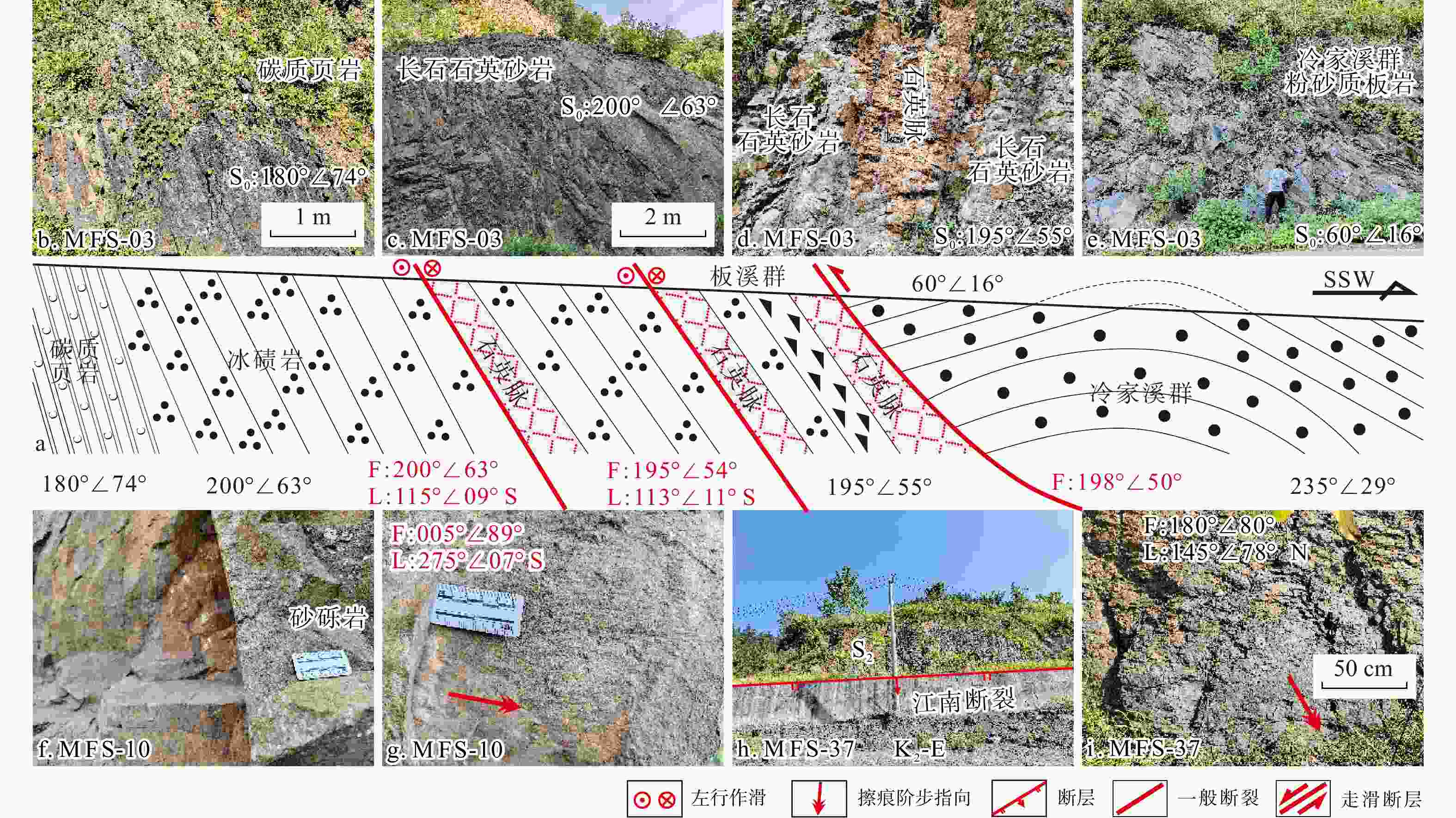
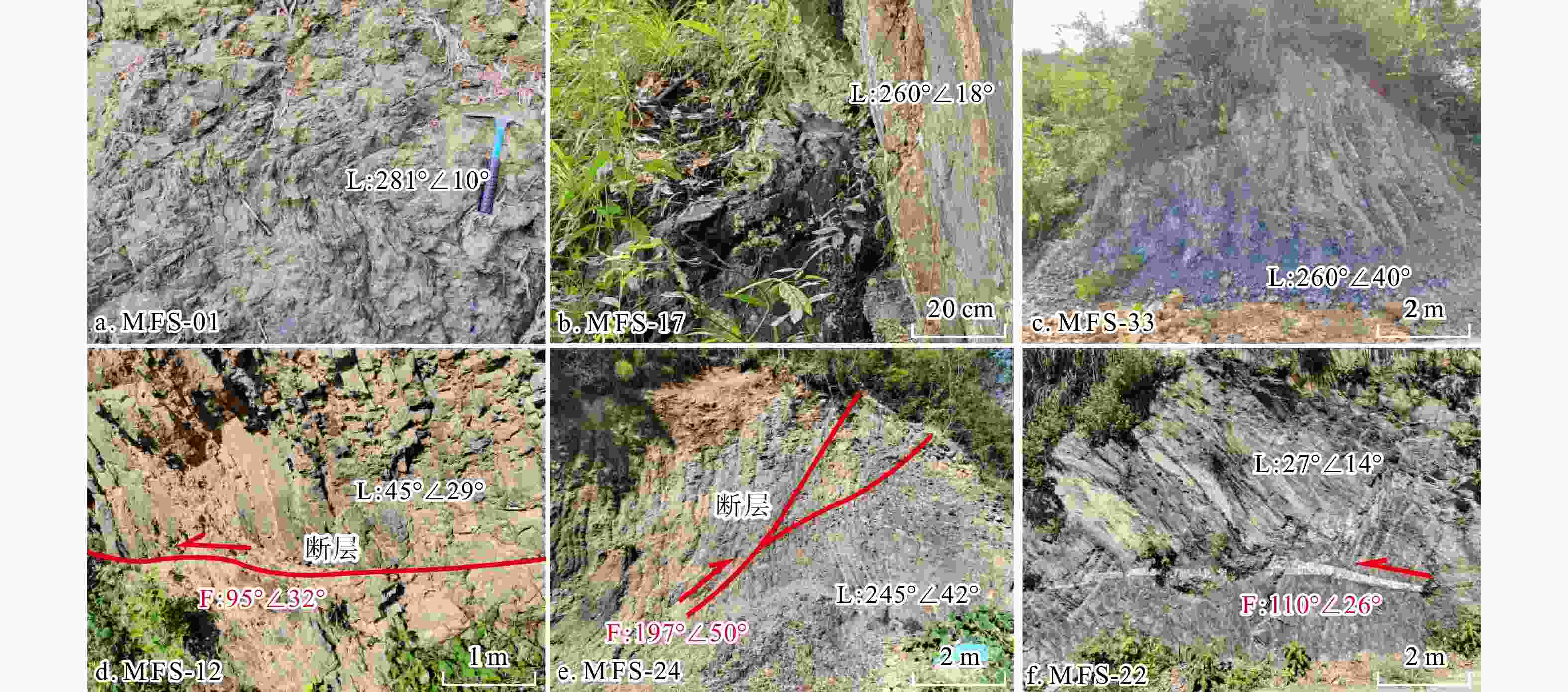
图 3 江南断裂野外露头素描与野外照片
a. 江南断裂野外露头素描;b. 层序倒转的碳质页岩;c. 层序倒转的长石石英砂岩;d. 层序倒转的长石石英砂岩与沿层面侵入的石英脉;e. 层序正常的冷家溪群粉砂质板岩;f. 层序正常的砂砾岩;g. 石英砂岩中发育的E-W走向左行走滑断层;h. 志留系和上白垩统至古近系呈正断层接触;i. 志留系中发育的E-W走向正断层;S0. 岩层产状;F. 断层面;L. 擦痕线理;K2-E. 上白垩统−古近系;S2. 中志留统
Figure 3. Sketch and field photographs of outcrops along the Jiangnan fault
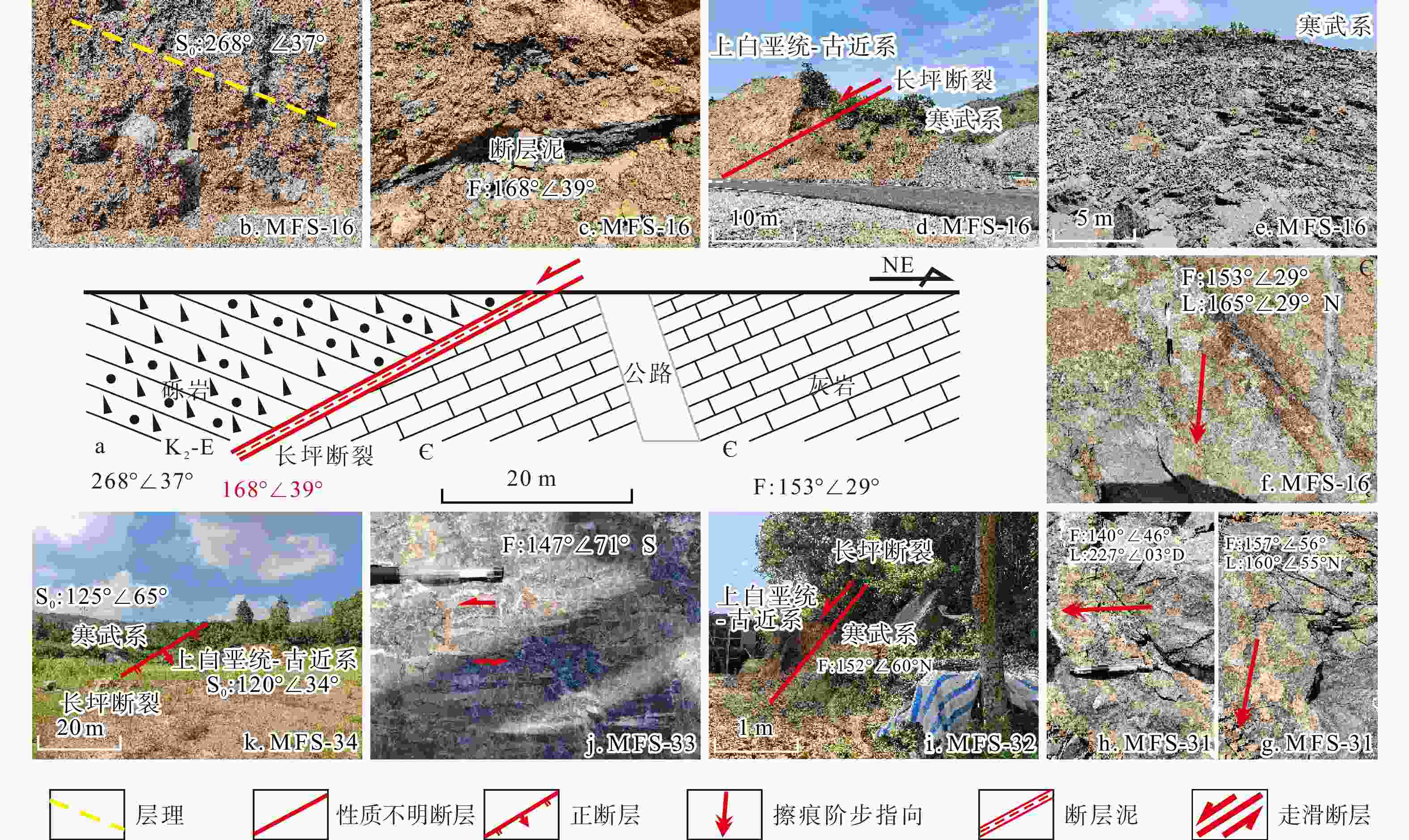
图 4 长坪断裂野外露头素描与野外照片
a. 长坪断裂野外露头素描;b. 断层上盘上白垩统至古近系紫红色砾岩;c. 断层泥;d. 上覆上白垩统至古近系紫红色砾岩与下伏寒武系灰岩呈断层接触;e. 断层下盘寒武系灰岩;f. 寒武系灰岩层面上发育的阶步和擦痕指示正断作用;g. 寒武系灰岩层面上发育的阶步和擦痕指示正断作用;h. 寒武系灰岩层面上发育的阶步和擦痕指示右行剪切;i. 上覆上白垩统至古近系紫红色砾岩与下伏寒武系灰岩呈断层接触;j. 寒武系灰岩中白云岩旋转碎斑指示左行走滑;k. 上覆上白垩统至古近系紫红色砾岩与下伏寒武系灰岩呈断层接触
Figure 4. Sketch and field photographs of outcrops along the Changping fault
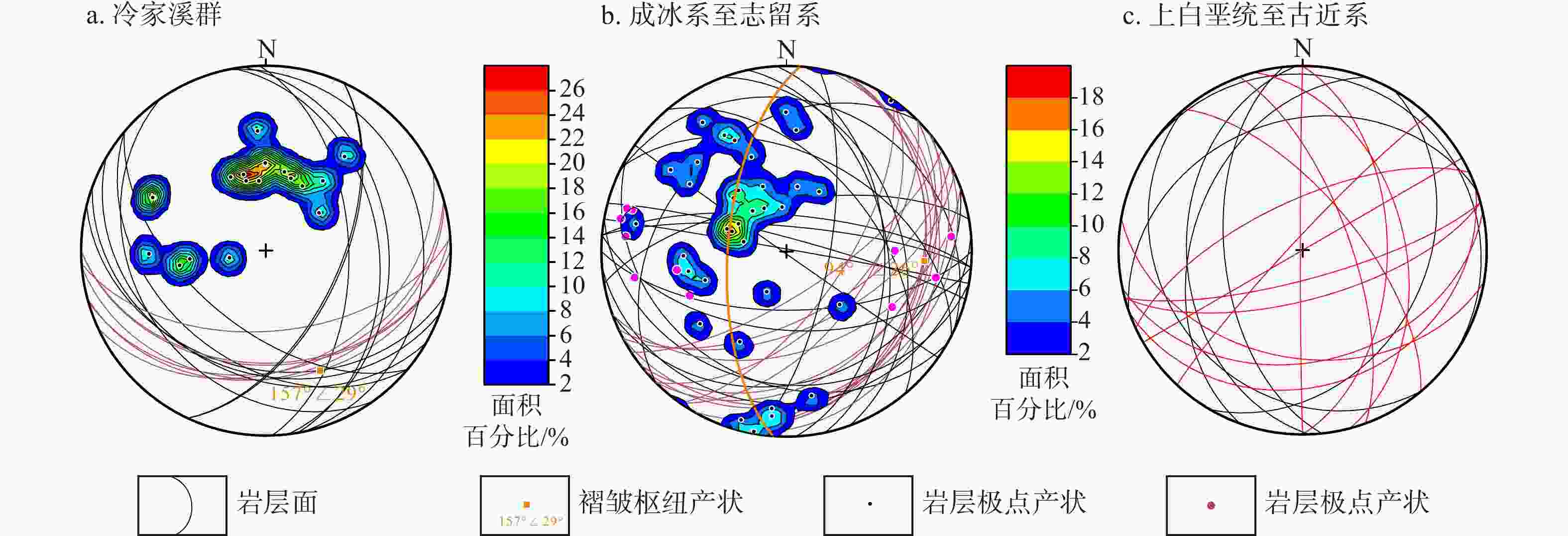
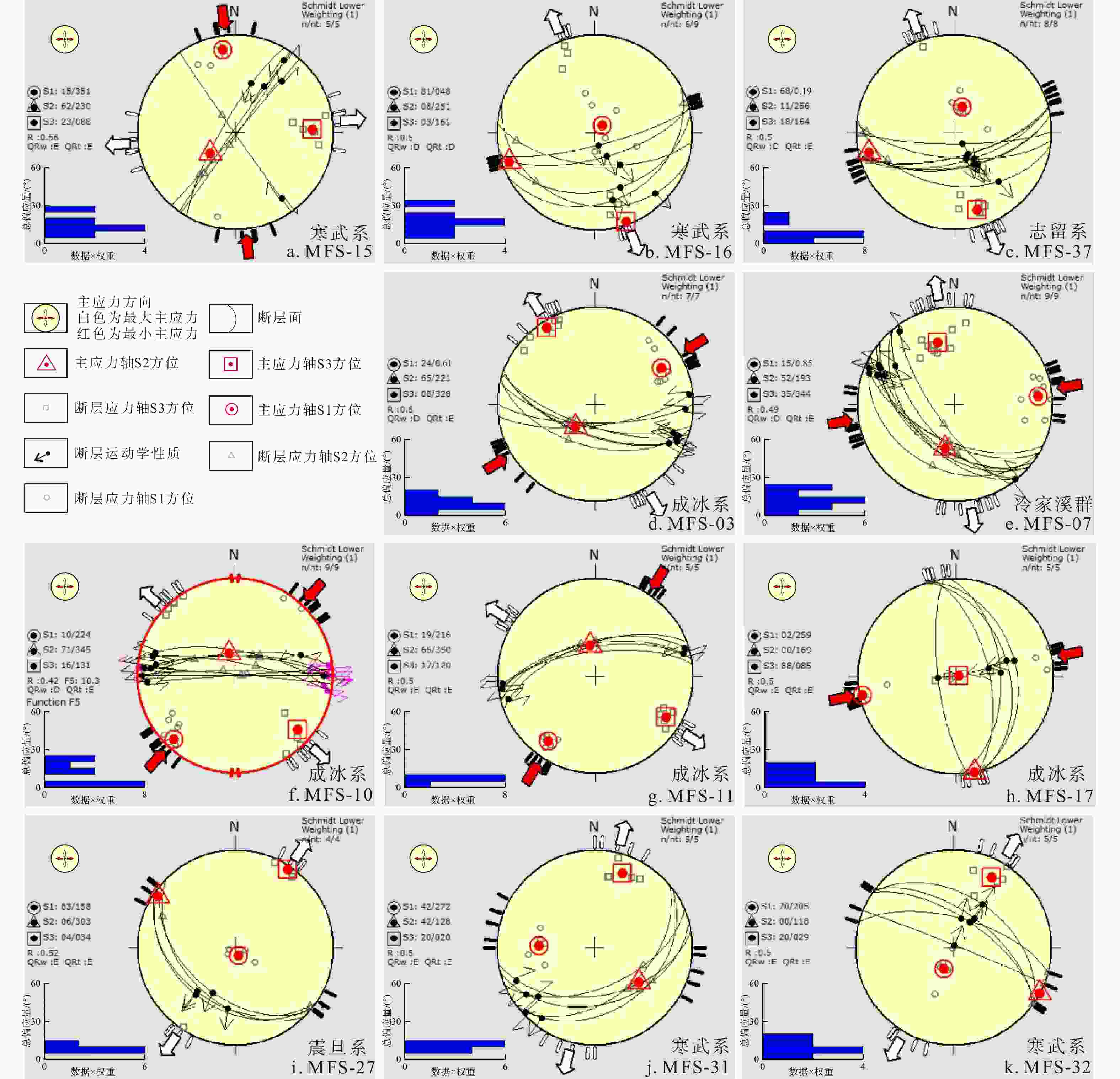
图 7 幕阜山岩体北缘鄂南地区构造应力场反演
a. 第一期走滑应力场,N-S向水平的最大主应力,E-W向水平的最小主应力;b,c. 第二期NW-SE向伸展应力场,NW-SE向水平的最小主应力,中间主应力直立;d,e,f,g,h. 第三期走滑应力场,NE-SW向水平的最大主应力,NW-SE向水平的最小主应力;i,j,k. 第四期NE-SW向伸展应力场,NE-SE向水平的最小主应力,中间主应力直立;Schmidt Lower. 施密特网下半球投影;Weighting. 权重;n. 数据个数;S1. 最大主应力轴方位;S2. 中间主应力轴方位;S3. 最小主应力轴方位;R. 应力比;Function. 函数;QRw. WSM(世界地应力图)定义的质量等级;QRt. TENSOR程序中定义的质量等级;QRw. 世界应力图WSM规定的质量登记;QRt. 应力反演程序Win_Tensor规定的质量等级
Figure 7. Paleostress inversions in the southern Hubei Province, northern margin of the Mufushan pluton
表 1 幕阜山岩体北缘鄂南地区用于应力场反演的断层滑移矢量数据
Table 1. Fault-slip data for stress inversion analysis in the southern Hubei Province, northern margin of the Mufushan pluton
观测点 MFS-15 MFS-16 MFS-37 编号 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 1 305 88 032 44 S 197 26 135 13 N 188 44 138 32 N 2 300 79 018 46 S 165 68 153 68 N 180 80 145 78 N 3 124 88 034 12 S 168 39 155 38 N 185 68 156 65 N 4 131 89 042 30 S 166 79 165 79 N 165 64 143 62 N 5 235 89 145 18 D 185 63 142 55 N 170 60 149 58 N 6 190 82 142 78 N 170 59 144 56 N 7 166 69 149 68 N 8 165 69 148 68 N 观测点 MFS-03 MFS-07 MFS-10 编号 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 1 195 54 113 11 S 220 54 292 23 S 002 74 278 19 S 2 193 70 110 16 S 230 51 141 01 S 010 69 286 16 S 3 198 71 111 10 S 230 61 303 28 S 000 86 090 10 S 4 200 63 115 09 S 205 59 290 07 S 000 73 275 14 S 5 200 64 118 16 S 217 52 297 13 S 010 79 283 15 S 6 173 72 084 04 S 220 49 296 16 S 005 89 275 07 S 7 180 74 093 09 S 210 58 290 16 S 000 90 270 05 S 8 210 33 293 05 S 355 71 073 30 S 9 235 73 323 07 S 356 90 266 10 S 观测点 MFS-11 MFS-17 MFS-27 编号 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 1 345 61 073 04 S 263 75 263 75 I 225 44 187 37 N 2 350 63 262 04 S 077 62 077 62 I 217 37 220 37 N 3 340 63 255 09 S 075 38 075 38 I 220 48 206 47 N 4 350 66 076 08 S 073 45 073 45 I 214 40 221 40 N 5 353 70 265 05 S 086 52 086 52 I 观测点 MFS-31 MFS-32 编号 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾伏向/(°) 倾伏角/(°) 运动学 1 157 56 56 229 D 022 88 022 88 N 2 143 35 35 217 N 034 65 034 65 N 3 165 41 41 236 N 015 65 015 65 N 4 140 46 46 227 D 034 46 034 46 N 5 170 49 49 247 D 036 60 036 60 N 注:N,I,S,D分别代表正断层,逆断层,左行平移断层和右行平移断层 表 2 幕阜山岩体北缘鄂南地区早白垩世晚期至古近纪应力场
Table 2. Paleostress fields from Late Early Cretaceous to Paleogene in the southern Hubei Province, northern margin of the Mufushan pluton
观测点 地层时代 数据个数 主应力轴方位(倾伏向/倾伏角) 主应力相对大小R 应力场期次 应力场形成时代 S1 S2 S3 MFS-15 寒武纪 5 351/15 230/62 088/23 0.56 第一期 早白垩世晚期 MFS-16 寒武纪 6 048/81 251/08 161/03 0.50 第二期 晚白垩世 MFS-37 志留纪 8 0.19/68 256/11 164/18 0.50 第二期 晚白垩世 MFS-03 成冰纪 7 0.61/24 221/65 328/08 0.50 第三期 古近纪中期 MFS-07 拉伸纪 9 0.85/15 193/52 344/35 0.49 第三期 古近纪中期 MFS-10 成冰纪 9 224/10 345/71 131/16 0.42 第三期 古近纪中期 MFS-11 成冰纪 5 216/19 350/65 120/17 0.50 第三期 古近纪中期 MFS-17 成冰纪 5 259/02 169/00 085/88 0.50 第三期 古近纪中期 MFS-27 埃迪卡拉纪 4 158/83 303/06 034/04 0.52 第四期 古近纪晚期 MFS-31 寒武纪 5 272/42 128/42 020/20 0.50 第四期 古近纪晚期 MFS-32 寒武纪 5 205/70 118/00 029/20 0.50 第四期 古近纪晚期 -
[1] 李鹏,李建康,裴荣富,等. 幕阜山复式花岗岩体多期次演化与白垩纪稀有金属成矿高峰:年代学依据[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(10):1684-1696.LI P,LI J K,PEI R F,et al. Multistage magmatic evolution and Cretaceous peak metallogenic epochs of Mufushan composite granite mass:Constrains from geochronological evidence[J]. Earth Science,2017,42(10):1684-1696. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 郭唯明,王登红,李鹏,等. Sb-Li组合:罕见的矿化组合及锂的赋存状态[J]. 地质学报,2019,93(6):1296-1308.GUO W M,WANG D H,LI P,et al. Sb-Li assemblages:Rare assemblages of mineralization and the occurrence of lithium[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2019,93(6):1296-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 尹近,吴金昊,李源,等. 湖北赤壁金银山锂矿赋存状态及矿床成因[J]. 地质论评,2024,70(4):1558-1570.YIN J,WU J H,LI Y,et al. The occurrence status and genesis of the Jinyinshan lithium deposit in Chibi,Hubei[J]. Geological Review,2024,70(4):1558-1570. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 祝明明,邹建林,王闯,等. 幕阜山地区断峰山铌钽矿的矿物学、年代学和赋存状态[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(6):55-69.ZHU M M,ZOU J L,WANG C,et al. Mineralogy,geochronology and occurrence state of the Duanfengshan Nb-Ta deposit in Mufushan area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(6):55-69. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] XU D R,YU D S,WANG Z L,et al. Zircon U-Pb and muscovite 40Ar/39Ar dating of Pb-Zn-(Cu) polymetallic deposits in northeastern Hunan Province,Jiangnan Orogen:Evidence for large-scale mineralization in South China at Ca. 150-120 Ma[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,150:105200. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105200 [6] 李胜虎. 华南典型花岗岩型稀有金属矿床的成矿机制与找矿模式研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2015.LI S H. Study on metallogenic mechanism and prospecting model of typical granite-type rare metal deposits in South China[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2015. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 吴堑虹,周厚祥,刘飚,等. 华南与花岗岩有关的稀有金属矿床和钨锡矿床的时空分布规律及其成因联系[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):78-88.WU Q H,ZHOU H X,LIU B,et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of granite-related rare metal deposits and W-Sn deposits in South China and their genetic relationship[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):78-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] LI P,LI J K,LIU X,et al. Geochronology and source of the rare-metal pegmatite in the Mufushan area of the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt:A case study of the giant Renli Nb-Ta deposit in Hunan,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,116:103237. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103237 [9] 李乐广,王连训,朱煜翔,等. 华南幕阜山北缘含稀有金属伟晶岩成矿时代及成矿过程[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(9):3221-3244.LI L G,WANG L X,ZHU Y X,et al. Metallogenic age and process of rare metal-bearing pegmatites from the northern margin of Mufushan complex,South China[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(9):3221-3244. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] CHEN J F,WEN C H,LV Z H,et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic Li-,Cs-,and Ta-rich (LCT) pegmatites from the Neoproterozoic Jiangnan Orogenic Belt,South China:An alternative origin model for the LCT type pegmatite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,153:105276. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105276 [11] MADAYIPU N,LI H,ALGEO T J,et al. Long-lived Nb-Ta mineralization in Mufushan,NE Hunan,South China:Geological,geochemical,and geochronological constraints[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2023,14(1):101491. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101491 [12] MADAYIPU N,LI H,GHADERI M,et al. Contrasting Nb-Ta mineralization between the Mufushan and Lianyunshan granites,South China:Evidence from whole-rock and zircon geochemistry and geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,158:105487. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105487 [13] XU D R,DENG T,CHI G X,et al. Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China:Geological,geochemical and geochronological characteristics,ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2017,88:565-618. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.004 [14] ZHANG L,YANG L Q,GROVES D I,et al. An overview of timing and structural geometry of gold,gold-antimony and antimony mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen,southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2019,115:103173. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103173 [15] SHAN L,LI Y J,JIANG J S,et al. Magmatism and mineralization of the Taolin Pb-Zn-Cu deposit in the Mufushan area,central Jiangnan Orogen (South China):Insightfvs from zircon U-Pb and sphalerite Rb-Sr geochronology,and H-O-S-Pb isotope geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,153:105266. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105266 [16] XIONG Y Q,JIANG S Y,WEN C H,et al. Granite–pegmatite connection and mineralization age of the giant Renli Ta Nb deposit in South China:Constraints from U-Th-Pb geochronology of coltan,monazite,and zircon[J]. Lithos,2020,358:105422. [17] YU D S,XU D R,ZHAO Z X,et al. Genesis of the Taolin Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China:Constraints from trace elements and oxygen-sulfur-lead isotopes of the hydrothermal minerals[J]. Mineralium Deposita,2020,55(7):1467-1488. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00947-8 [18] 李建康,李鹏,黄志飚,等. 湘北仁里伟晶岩型稀有金属矿田的地质特征及成矿机制概述[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(5):1-25.LI J K,LI P,HUANG Z B,et al. Geological features and formation mechanism of pegmatite-type rare-metal deposits in the Renli orefield,northern Hunan,China:An overview[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2023,30(5):1-25. ( in Chinese with English abstract [19] ZHAO J H,ZHOU M F,YAN D P,et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the Grenvillian Orogeny[J]. Geology,2011,39(4):299-302. doi: 10.1130/G31701.1 [20] XIN Y J,LI J H,DONG S W,et al. Neoproterozoic post-collisional extension of the central Jiangnan Orogen:Geochemical,geochronological,and Lu-Hf isotopic constraints from the Ca. 820-800 Ma magmatic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research,2017,294:91-110. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.018 [21] 杨志坚. 横贯中国东南部的一条古断裂带[J]. 地质科学,1987,22(3):221-230.YANG Z J. A paleo-fault zone traversing southeastern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,1987,22(3):221-230. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 牛志军,宋芳,何垚砚,等. 中南地区南华纪地层序列及对重大地质事件的响应[J]. 华南地质,2023,39(2):173-185.NIU Z J,SONG F,HE Y Y,et al. Nanhuan(cryogenian) stratigraphic sequence in central-south China and its response for major geological events[J]. South China Geology,2023,39(2):173-185. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 陈家驹,徐先兵,梁承华,等. 湘东南中泥盆统石英砂砾岩物源分析及其大地构造意义[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(10):3421-3434.CHEN J J,XU X B,LIANG C H,et al. Provenance analysis and tectonic implications of Middle Devonian quartzose conglomerate and sandstone in southeastern Hunan Province,South China[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(10):3421-3434. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] WANG L X,MA C Q,ZHANG C,et al. Genesis of leucogranite by prolonged fractional crystallization:A case study of the Mufushan complex,South China[J]. Lithos,2014,206:147-163. [25] JIN W,WAN L,TIAN Y,et al. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous granites in Mufushan complex,northeastern Hunan Province:Insights on Middle-Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of eastern South China[J]. Lithos,2023,456:107296. [26] WAN L,JIN W,TIAN Y,et al. Petrogenesis of Late Jurassic Mufushan high-Mg diorites and Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern South China Block[J]. Gondwana Research,2023,121:118-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2023.04.001 [27] 章泽军,张雄华,易顺华. 赣西北幕阜山—九岭山一带前震旦纪构造变形[J]. 高校地质学报,2003,9(1):81-88.ZHANG Z J,ZHANG X H,YI S H. Intraplate tectonic deformation of the Precambrian in the Mufu and Jiuling Mountains area,north-west Jiangxi[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2003,9(1):81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 翟文建,齐小兵,章泽军. 江南断裂构造属性及成生环境初探[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2009,33(3):372-380.ZHAI W J,QI X B,ZHANG Z J. A preliminary study of tectonic attribute and formation environment of Jiangnan fault[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2009,33(3):372-380. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 丁道桂,郭彤楼,刘运黎,等. 对江南−雪峰带构造属性的讨论[J]. 地质通报,2007,26(7):801-809.DING D G,GUO T L,LIU Y L,et al. Structural attribute of the Jiangnan-Xuefengshan belt,China:A discussion[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2007,26(7):801-809. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 陈世悦,李聪,张鹏飞,等. 江南—雪峰地区加里东期和印支期不整合分布规律[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(5):1212-1219.CHEN S Y,LI C,ZHANG P F,et al. The unconformable distribution of Caledonian and Indosinian strata in Jiangnan-Xuefeng area[J]. Geology in China,2011,38(5):1212-1219. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 柏道远,文春华,黄建中,等. 湘东北幕阜山地区中生代构造−岩浆特征及其对稀有金属伟晶岩的控制[J]. 地质论评,2023,69(3):855-880.BAI D Y,WEN C H,HUANG J Z,et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic characteristics and their control on rare metal pegmatites in Mufushan area,northeastern Hunan[J]. Geological Review,2023,69(3):855-880. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] LI Z H,ZHENG H,LI H,et al. Polyphase deformation-controlled giant Renli Nb-Ta deposit,South China:Constraints from systematic structural analysis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,153:105286. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105286 [33] HE C S,DONG S W,SANTOSH M,et al. Seismic evidence for a geosuture between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks,South China[J]. Scientific Reports,2013,3:2200. doi: 10.1038/srep02200 [34] GUO L H,GAO R,SHI L,et al. Crustal thickness and Poisson's ratios of South China revealed from joint inversion of receiver function and gravity data[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2019,510:142-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.12.039 [35] CHEN C X,Lü Q T,CHEN L,et al. Crustal thickness and composition in the South China Block:Constraints from earthquake receiver function[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences),2022,65(4):698-713. doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9858-x [36] ANGELIER J. Tectonic analysis of fault slip data sets[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),1984,89(B7):5835-5848. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB07p05835 [37] DELVAUX D,SPERNER B. New aspects of tectonic stress inversion with reference to the TENSOR program[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,2003,212(1):75-100. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.212.01.06 [38] YAO J L,CAWOOD P A,SHU L S,et al. Jiangnan Orogen,South China:A ~970-820 Ma Rodinia margin accretionary belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2019,196:102872. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.05.016 [39] 徐先兵,汤帅,梁承华. 江南东段新元古代至中生代构造演化:盆地物源分析和区域构造解析的制约[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,2020.XU X B,TANG S,LIANG C H. Tectonic evolution from Neoproterozoic to Mesozoic in eastern Jiangnan:Constraints of basin provenance analysis and regional tectonic analysis[M]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,2020. (in Chinese) [40] SHU L S,YAO J L,WANG B,et al. Neoproterozoic plate tectonic process and Phanerozoic geodynamic evolution of the South China Block[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2021,216:103596. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103596 [41] LI J H,DONG S W,ZHANG Y Q,et al. New insights into Phanerozoic tectonics of South China:Part 1,Polyphase deformation in the Jiuling and Lianyunshan domains of the central Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2016,121(4):3048-3080. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012778 [42] XU X B. Late Triassic to Middle Jurassic tectonic evolution of the South China Block:Geodynamic transition from the Paleo-Tethys to the Paleo-Pacific regimes[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2023,241:104404. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2023.104404 [43] 徐先兵,张岳桥,贾东,等. 华南早中生代大地构造过程[J]. 中国地质,2009,36(3):573-593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.007XU X B,ZHANG Y Q,JIA D,et al. Early Mesozoic geotectonic processes in South China[J]. Geology in China,2009,36(3):573-593. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.007 [44] 徐先兵,汤帅,李源,等. 江南造山带东段新元古代至早中生代多期造山作用特征[J]. 中国地质,2015,42(1):33-50.XU X B,TANG S,LI Y,et al. Characteristics of Neoproterozoic-Early Mesozoic multiphase orogenic activities of eastern Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Geology in China,2015,42(1):33-50. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] 张岳桥,徐先兵,贾东,等. 华南早中生代从印支期碰撞构造体系向燕山期俯冲构造体系转换的形变记录[J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(1):234-247. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.01.026ZHANG Y Q,XU X B,JIA D,et al. Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2009,16(1):234-247. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.01.026 [46] WANG Z H,LU H F. Ductile deformation and 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Changle-Nanao ductile shear zone,southeastern China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2000,22(5):561-570. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00179-0 [47] ZHU G,WANG Y S,LIU G S,et al. 40Ar/39Ar dating of strike-slip motion on the Tan-Lu fault zone,East China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2005,27(8):1379-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2005.04.007 [48] XU X B,TANG S,LIN S F. Paleostress inversion of fault-slip data from the Jurassic to Cretaceous Huangshan Basin and implications for the tectonic evolution of southeastern China[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,2016,98:31-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2016.03.013 [49] XU X B,LIANG C H,XU Y D. Kinematic analysis of fault-slip data in the Nanling Tectonic Belt and Cretaceous to Paleogene tectonic evolution of the Central South China Block[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021,221:104951. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104951 [50] QIU E K,ZHANG Y Q,LARSON K P,et al. Dating strike-slip ductile shear through combined zircon-,titanite- and apatite U-Pb geochronology along the southern Tan-Lu fault zone,East China[J]. Tectonics,2023,42(4):e2022TC007734. doi: 10.1029/2022TC007734 [51] LI J H,ZHANG Y Q,DONG S W,et al. Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China:A preliminary synthesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2014,134:98-136. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.008 [52] LI J H,CAWOOD P A,RATSCHBACHER L,et al. Building Southeast China in the Late Mesozoic:Insights from alternating episodes of shortening and extension along the Lianhuashan fault zone[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,201:103056. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103056 [53] LI J H,DONG S W,CAWOOD P A,et al. Cretaceous long-distance lithospheric extension and surface response in South China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2023,243:104496. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2023.104496 [54] 石红才,施小斌,杨小秋,等. 江南隆起带幕阜山岩体新生代剥蚀冷却的低温热年代学证据[J]. 地球物理学报,2013,56(6):1945-1957.SHI H C,SHI X B,YANG X Q,et al. The exhumation process of Mufushan granite in Jiangnan uplift since Cenozoic:Evidence from low temperature thermochronology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2013,56(6):1945-1957. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] SHEN C B,HU D,MIN K,et al. Post-orogenic tectonic evolution of the Jiangnan-Xuefeng Orogenic Belt:Insights from multiple geochronometric dating of the Mufushan massif,South China[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2020,31(5):905-918. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1346-2 [56] YIN A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia:A preliminary synthesis[J]. Tectonophysics,2010,488(1/2/3/4):293-325. [57] XIA Y,XU X B,CHEN J J,et al. Polyphase deformation and geochronology of Late Triassic volcano-sedimentary rocks in the Yidun Terrane,eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,and implications for tectonic evolution of the Paleo- and NeoTethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2023,242:105492. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105492 [58] YU D S,XU D R,WANG Z L,et al. Trace element geochemistry and O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic systematics of the Lishan Pb-Zn-Cu hydrothermal deposit,NE Hunan,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,133:104091. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104091 [59] LI P,LI J K,CHEN Z Y,et al. Compositional evolution of the muscovite of Renli pegmatite-type rare-metal deposit,northeast Hunan,China:Implications for its petrogenesis and mineralization potential[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,138:104380. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104380 [60] 姜忠正,唐大卿,沙旭光,等. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起中北部地区断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):120-132.JIANG Z Z,TANG D Q,SHA X G,et al. Structure and evolution of faults in central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):120-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [61] 张浩,李伟,李丽梅,等. 郯庐断裂带江苏段山左口-泗洪断裂活动特征变化及成因分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(12):29-37.ZHANG H,LI W,LI L M,et al. Activity variations of the Shanzuokou-Sihong fault within the Jiangsu segment of the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone and their origins[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(12):29-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [62] 蒋佳兵,陈如鹤,李小刚,等. 火山岩内幕型储层特征与主控因素——以准噶尔盆地滴南凸起滴水泉西断裂下盘为例[J]. 中国石油勘探,2023,28(2):119-132.JIANG J B,CHEN R H,LI X G,et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of inner volcanic reservoir: A case study of the footwall of West Dishuiquan Fault in Dinan Bulge, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2023,28(2):119-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [63] 徐先兵,邓飞,王墩,等. 基岩区断层泥的物质组成、定年方法与地震断层弱化机制研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(5):122-131.XU X B,DENG F,WANG D,et al. Advances in composition and dating methods of fault gouge and weakening mechanisms of earthquake faults in bedrock area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(5):122-131. (in Chinese with English abstract [64] ZHOU X M,LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics,2000,326(3/4):269-287. [65] LI Z X,LI X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology,2007,35(2):179. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1 [66] XU X B,ZHANG Y Q,JIA D,et al. U-Pb dating of volcanic rocks and granites along the Wuyishan Belt:Constraints on tuning of late Mesozoic tectonic events in southeast China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition),2011,85(1):130-144. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00385.x [67] MAO J W,LIU P,GOLDFARB R J,et al. Cretaceous large-scale metal accumulation triggered by post-subductional large-scale extension,East Asia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,136:104270. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104270 [68] 刘俊民,张关龙,赵乐强,等. 胜利探区油气共/伴生资源综合利用前景[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2024,31(4):207-216.LIU J M,ZHANG G L,ZHAO L Q,et al. Prospects for comprehensive utilization of symbiotic/associated oil and gas resources in exploration area of Shengli oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2024,31(4):207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: