Genetic mechanism of low resistance in shale analyzed via triaxial compression tests
-
摘要:
川南地区五峰−龙马溪组页岩气储层在多个地区出现低电阻异常现象。统计显示,低阻页岩(<10 Ω·m)与构造断裂带在空间分布上存在叠合关系。为揭示页岩电阻率与构造断裂带之间的关联机制,基于薄片鉴定、X射线衍射分析、激光拉曼光谱分析、全岩沥青反射率测定以及常规物性分析等手段,确定了页岩试样的岩石学特征和地球化学特征;基于三轴压缩物理模拟试验确定了变形过程中页岩试样电阻率的变化特征,明确了裂缝发育及盐水的侵入对页岩低阻现象的影响。结果表明:黏土矿物、黄铁矿和高热演化程度有机质相对均一的页岩试样,在饱和不同浓度盐水后,电阻率显著降低,且电阻率降低幅度(95.07%~98.70%)与盐水质量浓度之间存在正相关关系;饱和盐水的页岩试样受压破裂后电阻率进一步降低,范围介于5.7~25.7 Ω·m之间(平均值为13.3 Ω·m),且页岩试样饱和盐水后的电阻率与其破裂后的电阻率符合正相关线性关系。页岩内部裂缝系统的发育后导电流体的侵入,是页岩电阻率降低的主要控制因素。页岩受压破裂后电阻率的降低幅度受到入侵溶液浓度和裂缝发育程度的双重影响。研究成果解释并补充了构造断裂带对页岩电阻率的影响机制,丰富了低阻页岩成因机制理论,对低阻页岩层段的勘探开发具有重要意义。
Abstract:Objective The gas-rich Wufeng-Longmaxi shale of the southern Sichuan Basin exhibits low-resistance anomalies in multiple areas. Statistical analysis reveals that the low-resistivity zone (<10 Ω·m) in the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale is spatially associated with tectonic faults. This study aims to reveal the coupling mechanism between shale resistivity and tectonic faults.
Methods This study determines the petrological and geochemical characteristics of outcrop samples obtained from the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in the southern Sichuan Basin through thin-section identification, X-ray diffraction, laser Raman spectroscopy, whole-rock asphalt reflectance, and conventional physical property analyses. The characteristics of resistivity change in the shale during deformation were analyzed through triaxial compression tests. The impacts of fracture system generation and conductive fluid intrusion on low-resistivity shale were also clarified.
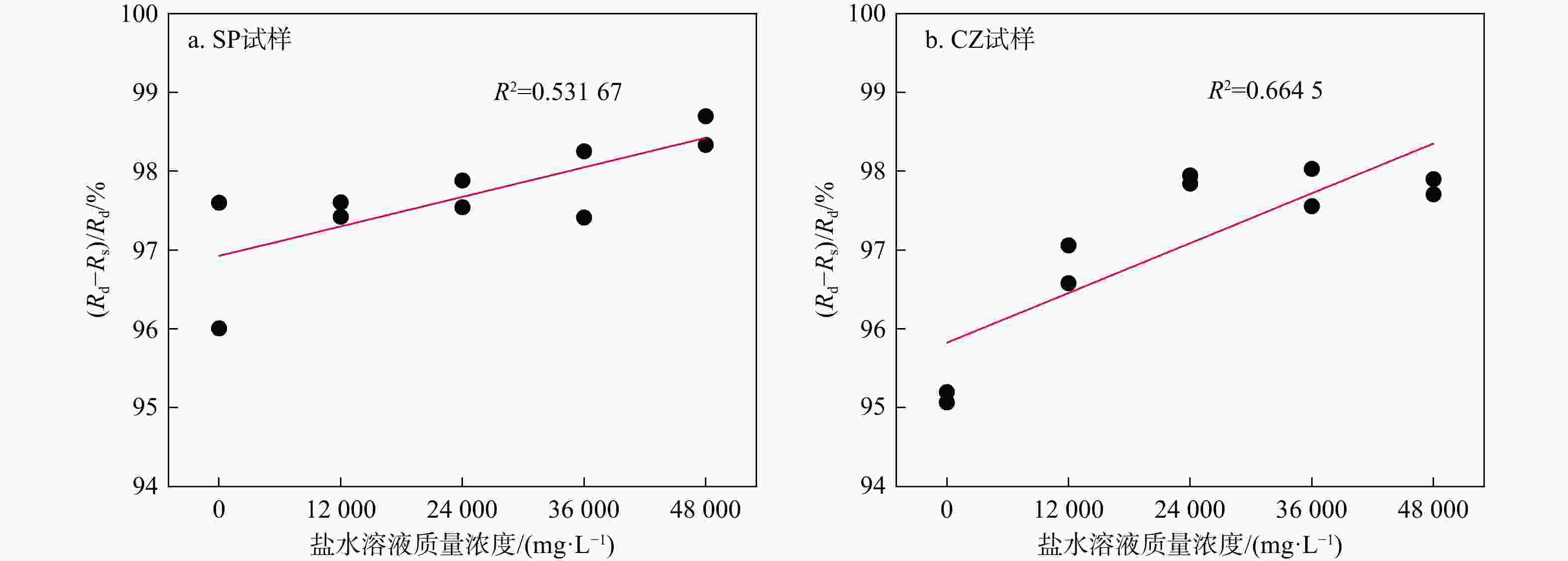
Results The results show that the resistivity of shale samples, which have similar characteristics of clay minerals, pyrite, organic matter content, and thermal maturity level, significantly decreased after saturation with brines of various salinities. A positive correlation was observed between the resistivity reduction (95.07%-98.70%) and brine salinity. After reaching the compressive strength, the resistivity reduction of the brine-saturated samples varies from 5.7 Ω·m to 25.7 Ω·m (average: 13.3 Ω·m). This reduction shows a linearly positive correlation with the resistivity observed post cracking. The intrusion of conductive fluid and the generation of the fracture system in shale are the primary controlling factors for resistivity reduction. The resistivity after cracking is influenced by both the intruded saltwater salinity and fracture density.
Conclusion This research elucidates the influence mechanism of tectonic fault zones on shale resistivity and enhances the theoretical framework for understanding the genesis of low-resistivity shale, with significant implications for the exploration and development of low-resistivity shale formations.
-
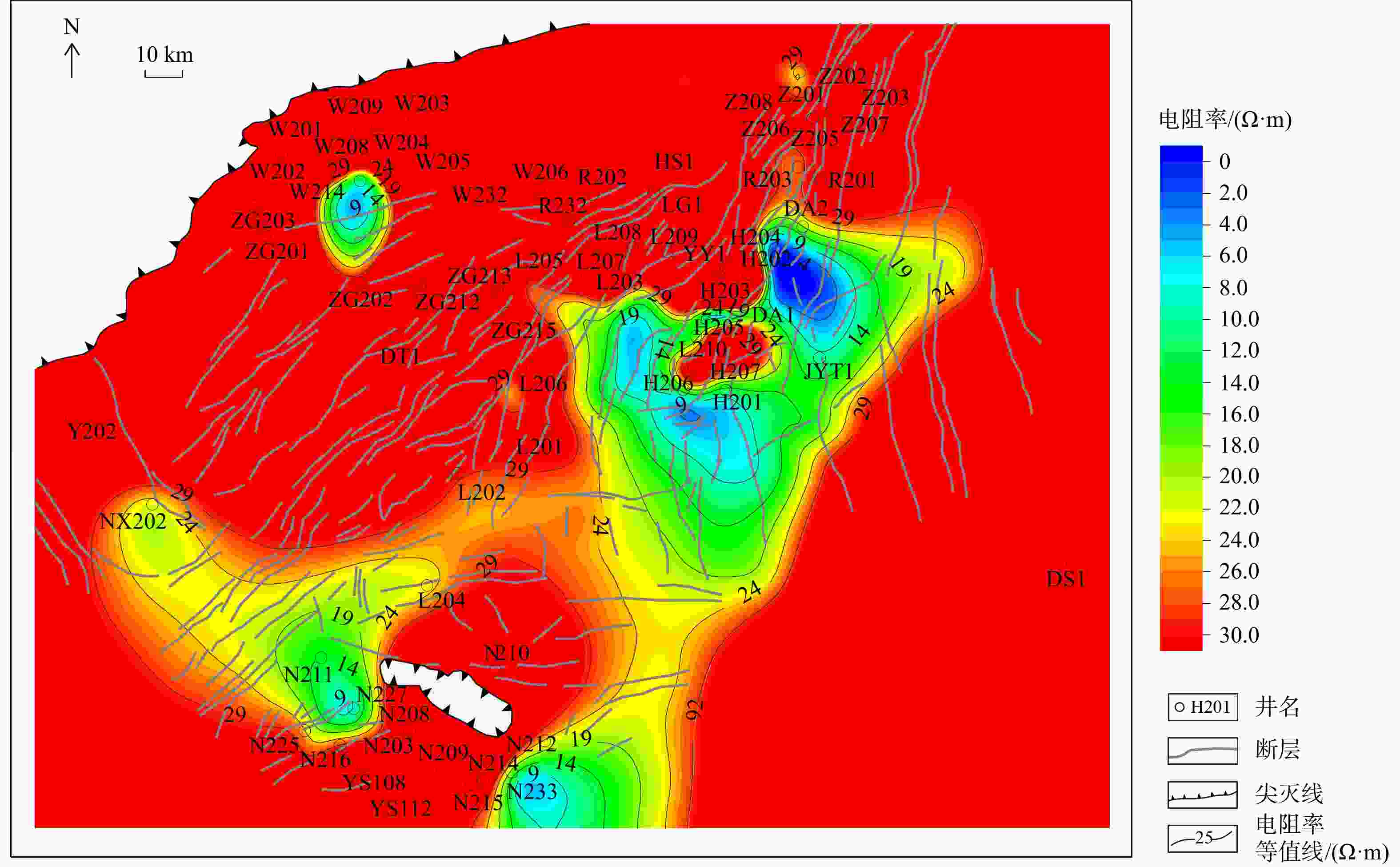
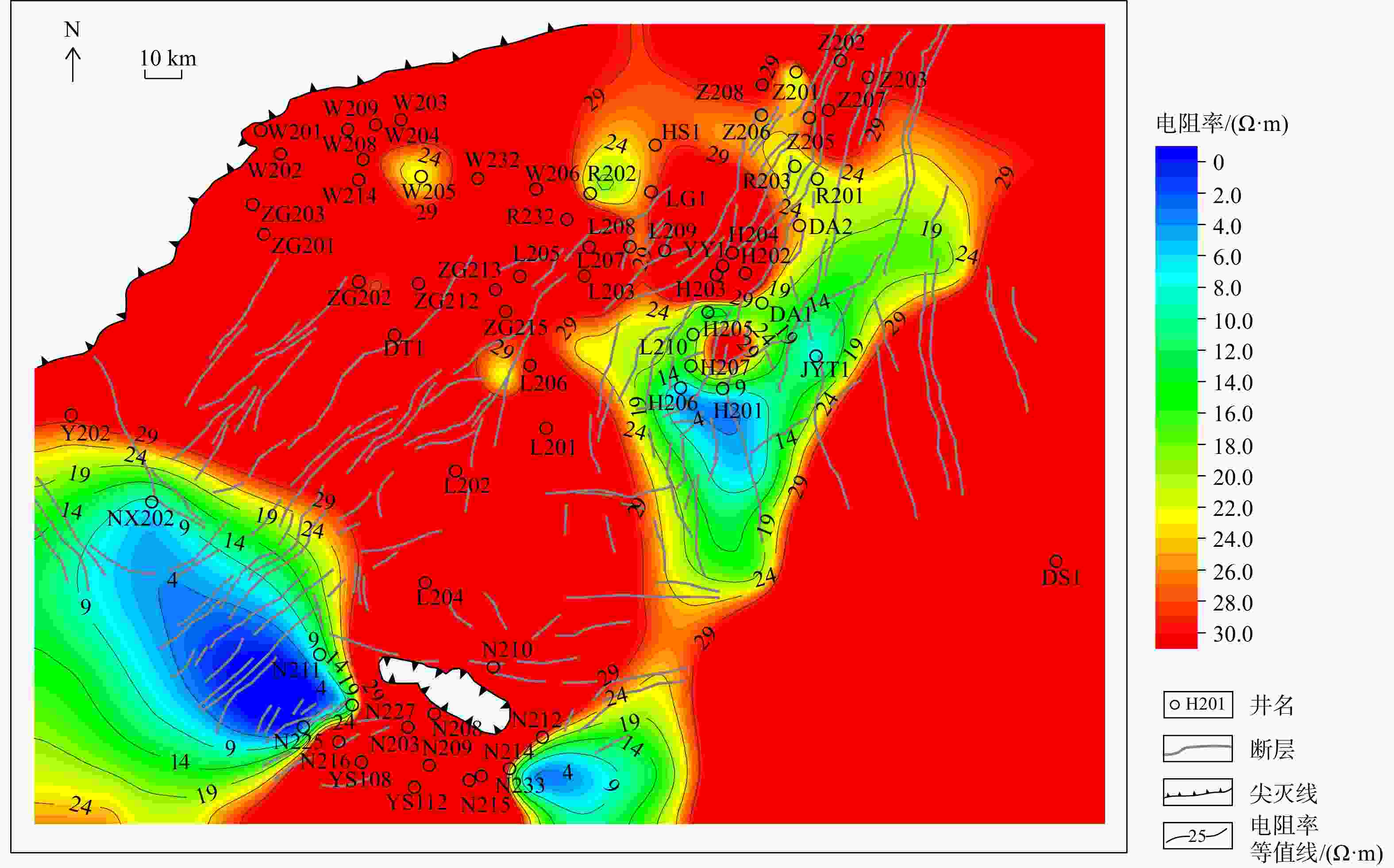
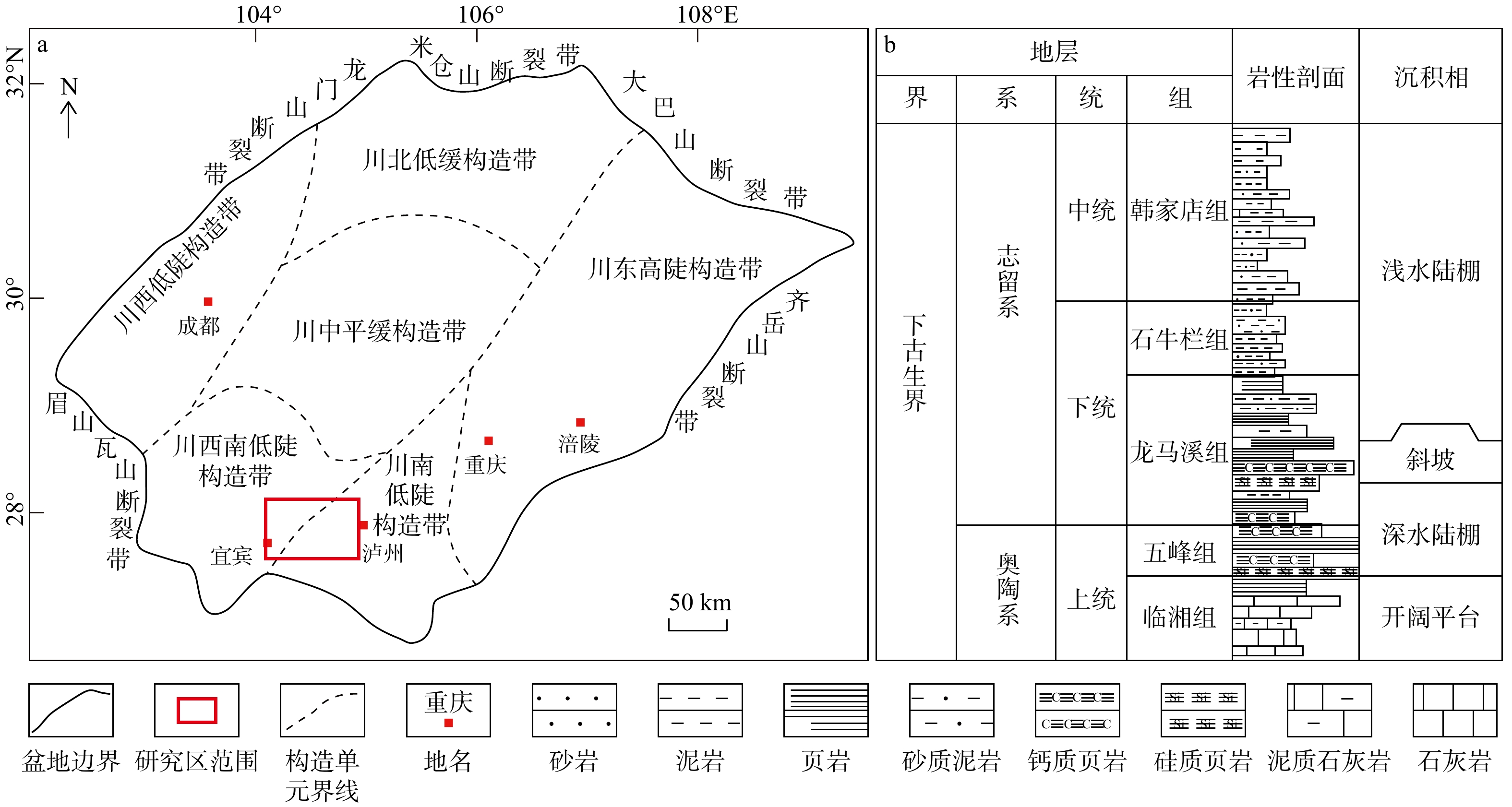
图 1 研究区构造位置图(a)及地层综合柱状图(b) [28]
Figure 1. Tectonic location (a) and stratigraphic column (b) of the study area
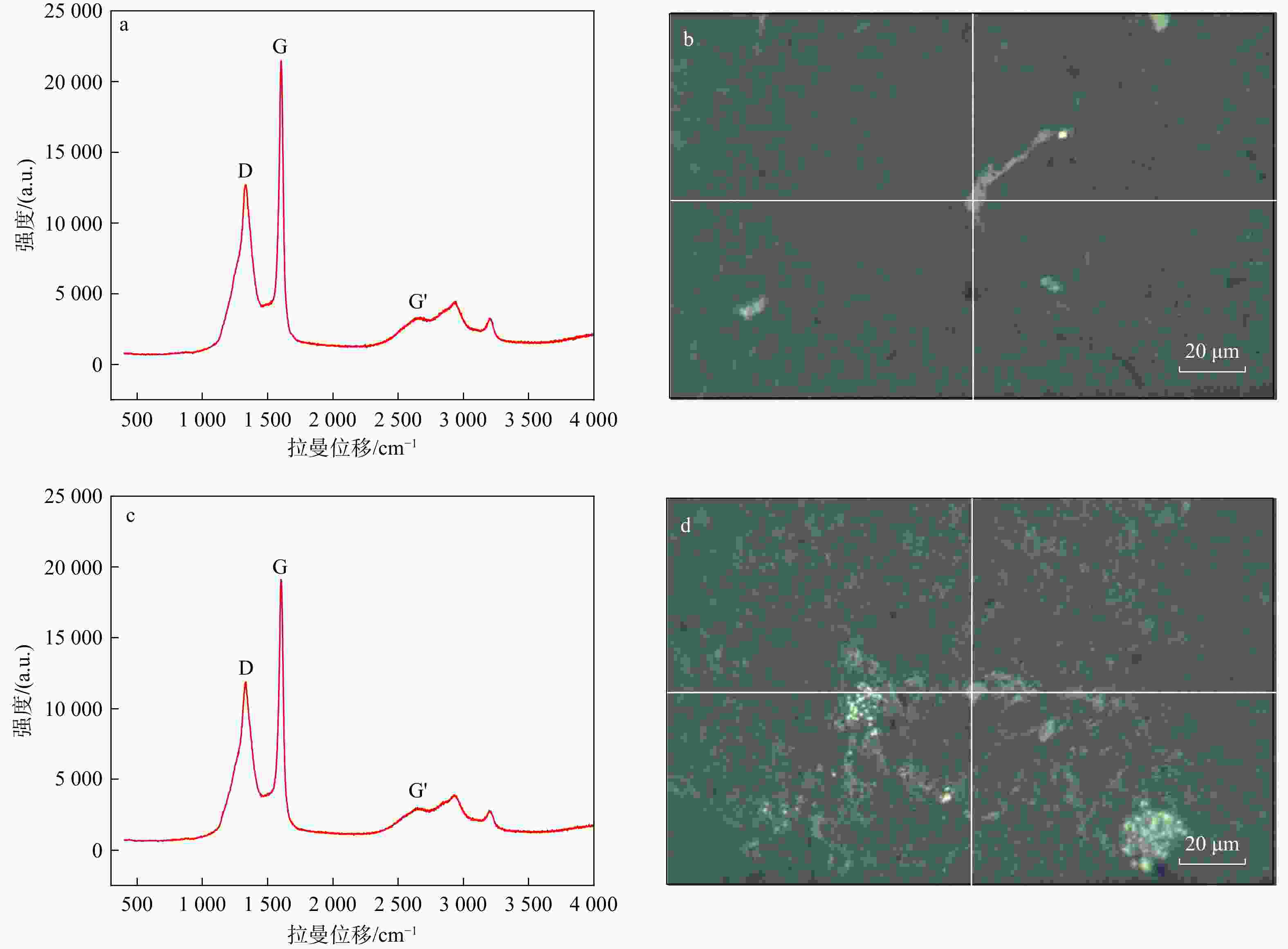
图 5 SP6试样部分测点激光拉曼图谱结果及测点位置
a,b. 测点1的测试结果及位置;c,d. 测点5的测试结果及位置;D. 位于拉曼位移
1300 ~1350 cm−1区间内的峰值,主要与沥青中碳质的无序结构和缺陷有关;G. 位于拉曼位移1580 ~1600 cm−1区间内的峰值,与芳香族碳−碳双键(C=C)的伸缩振动有关;G'. 位于拉曼位移2600 ~2700 cm−1区间内的峰值,为 G 峰的二阶倍频峰,可辅助判断沥青中碳质结构的有序性Figure 5. Raman spectra characteristics and measurement point positions of the SP6 sample
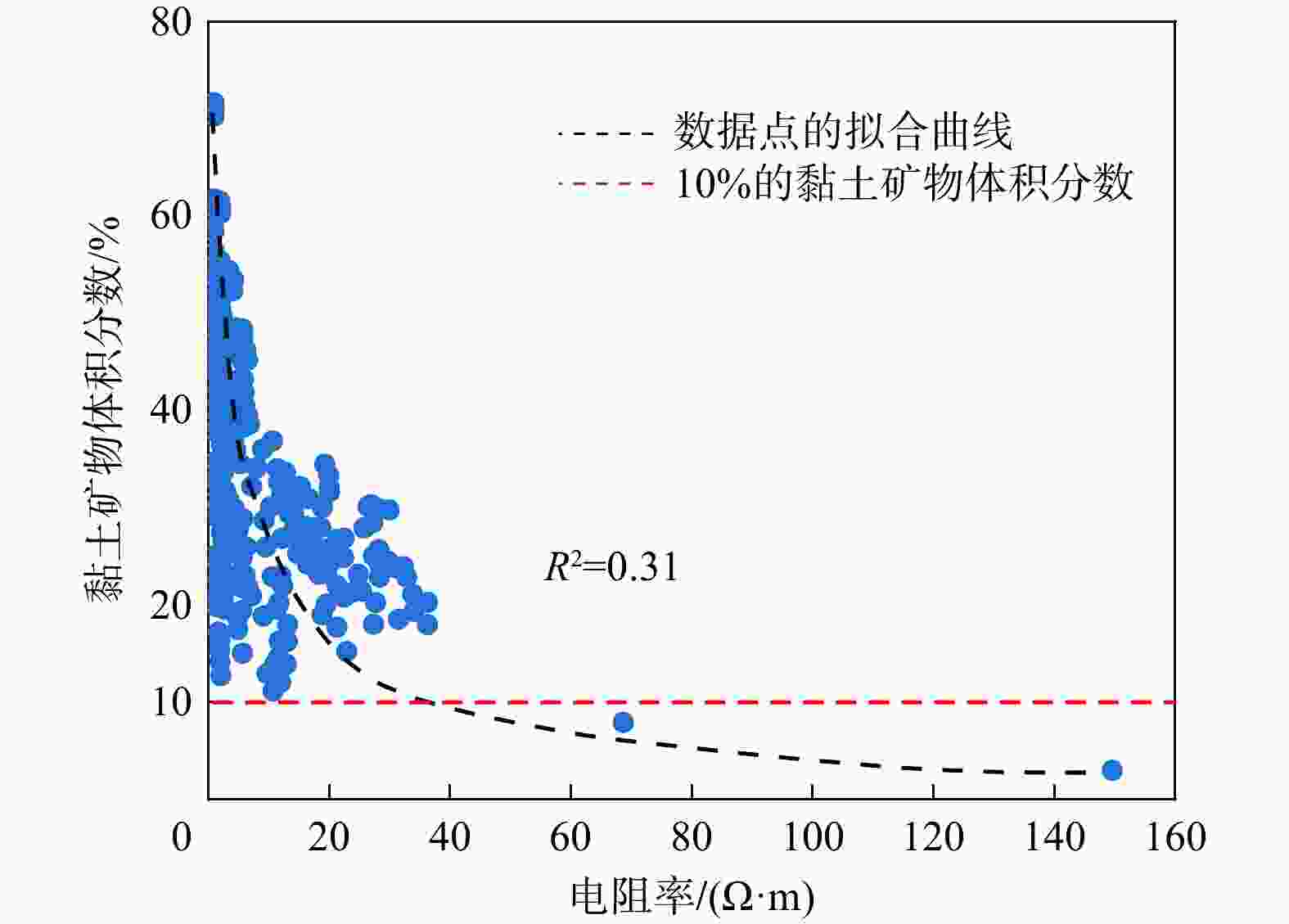
图 8 长宁地区五峰−龙马溪组页岩黏土矿物含量与电阻率间关系[6]
Figure 8. Relationship between clay mineral content and resistivity of shale of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Changning area
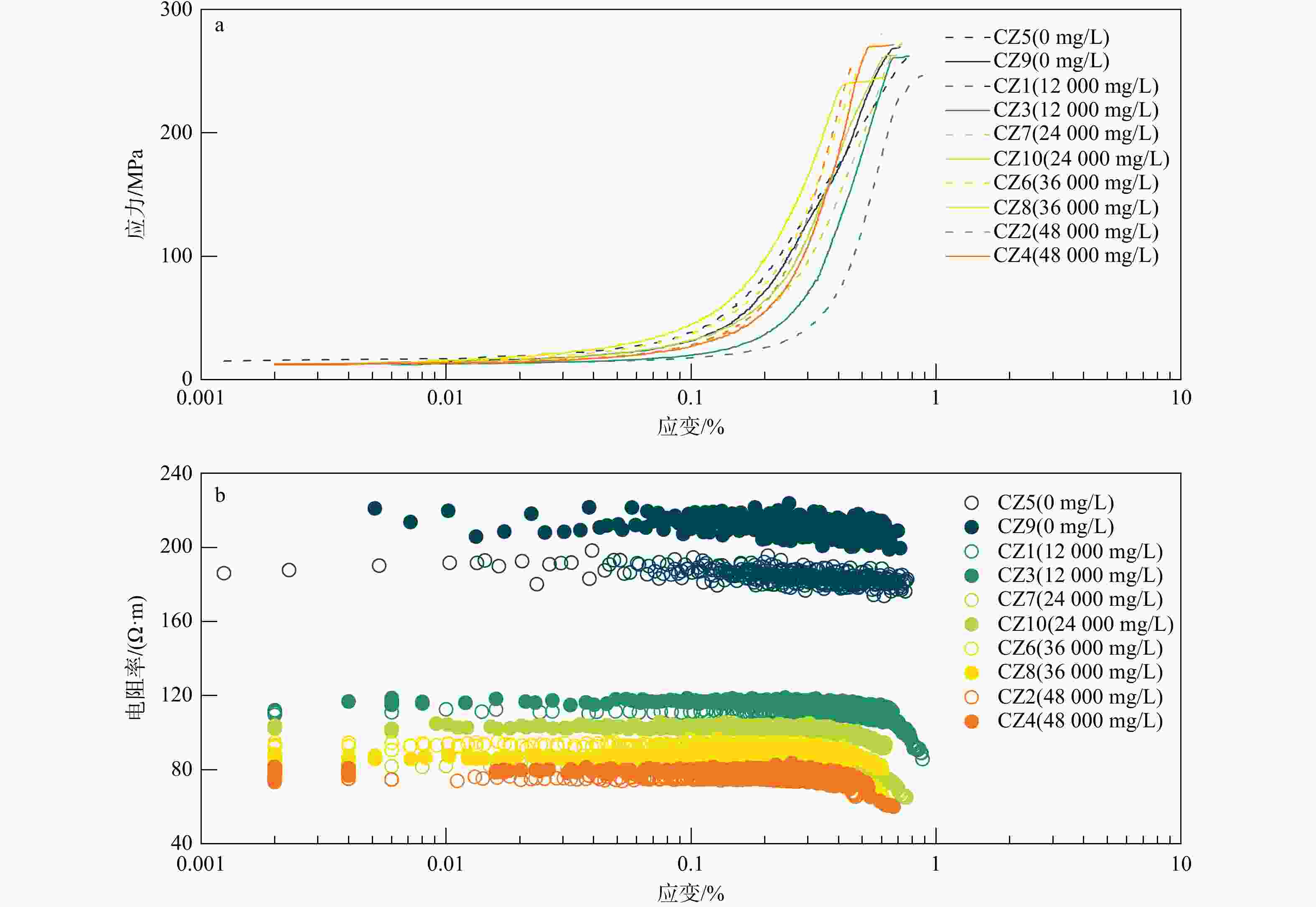
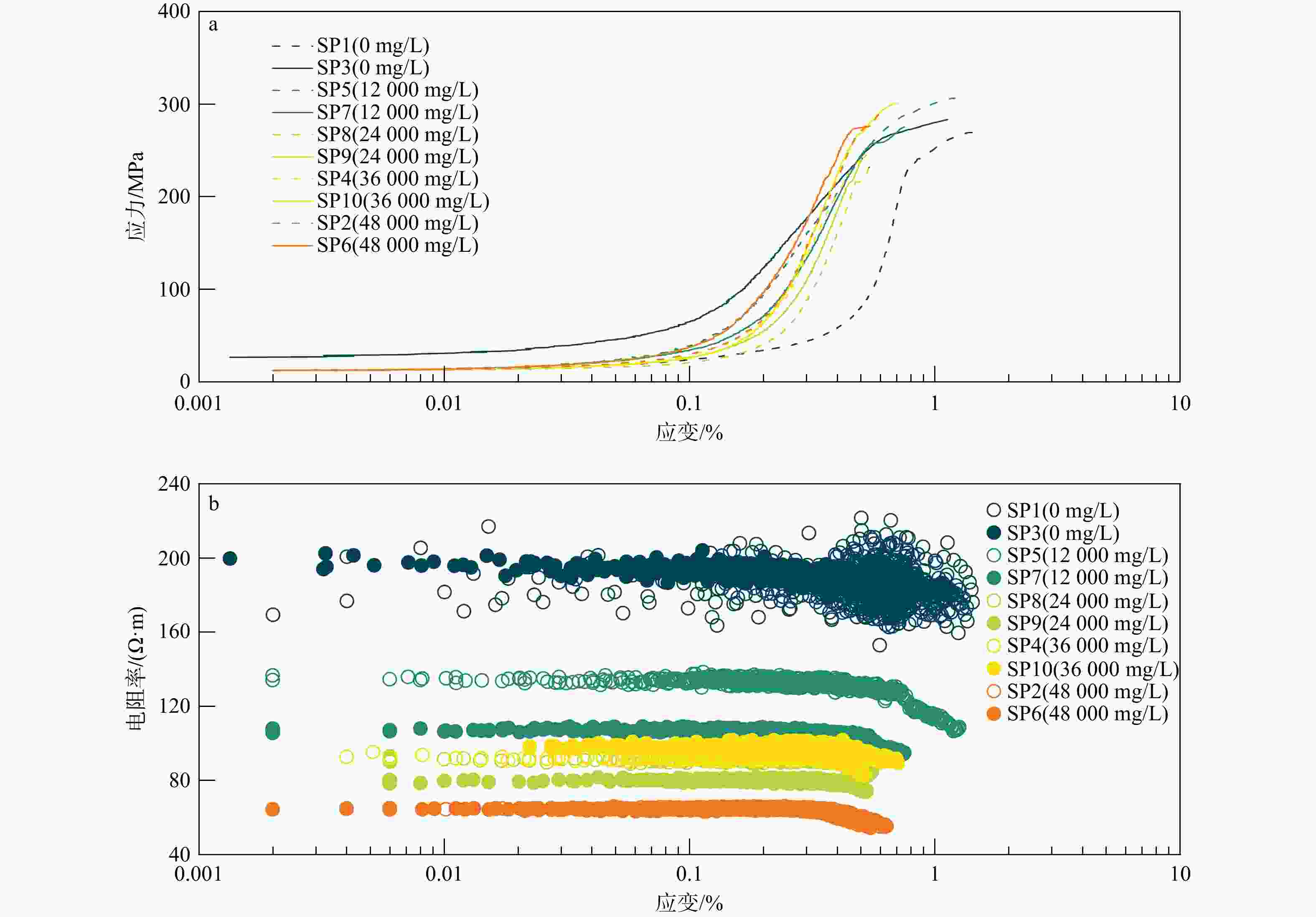
表 1 页岩试样测试结果数据汇总
Table 1. Test results of shale samples
分组编号 溶液质量浓度/
(mg·L−1)溶液电阻率*/
(Ω·m)试样编号 初始电阻率
Ri/(Ω·m)干燥电阻率
Rd/(Ω·m)饱和电阻率
Rs/(Ω·m)破裂电阻率
Rc/(Ω·m)破裂压力
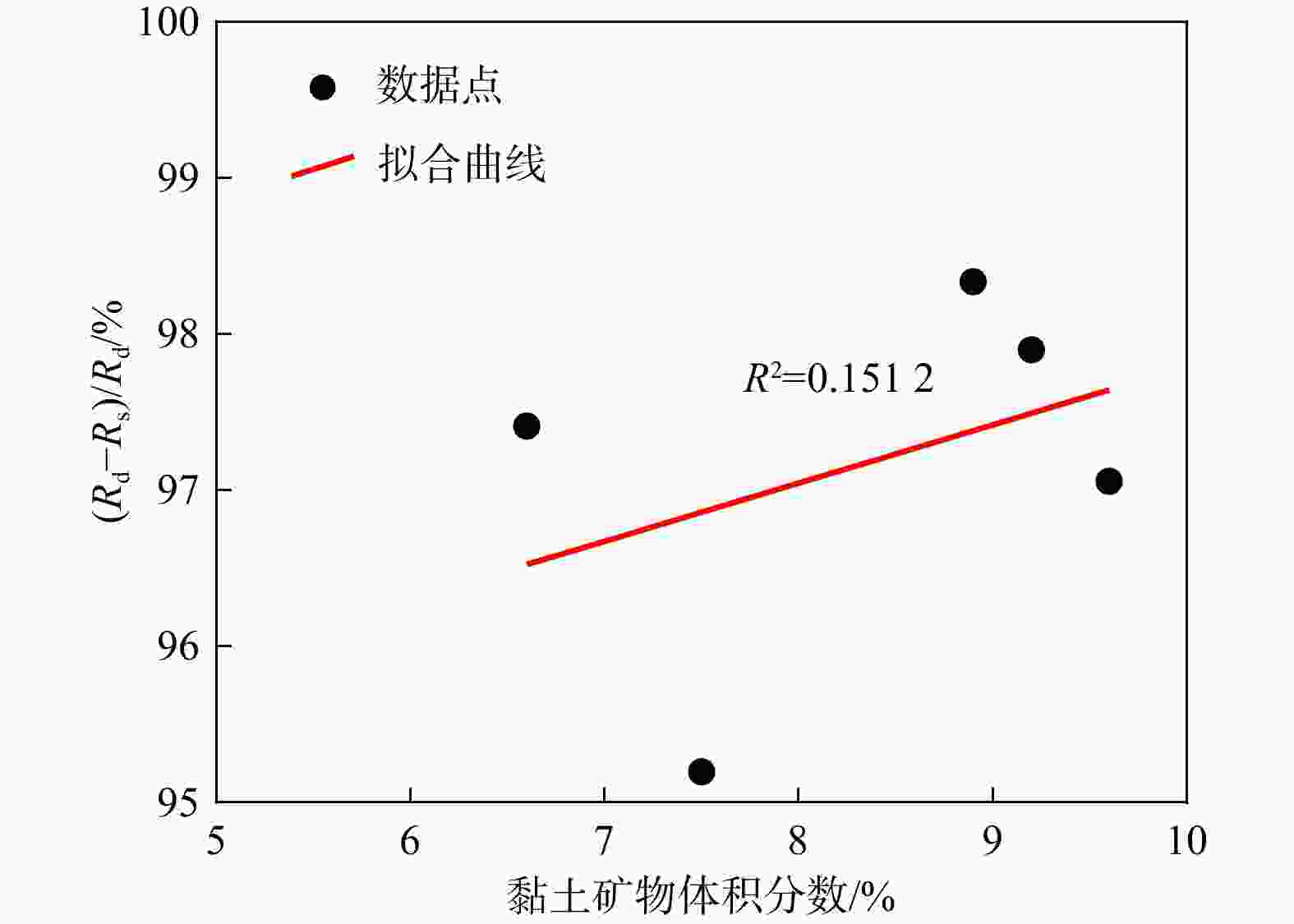
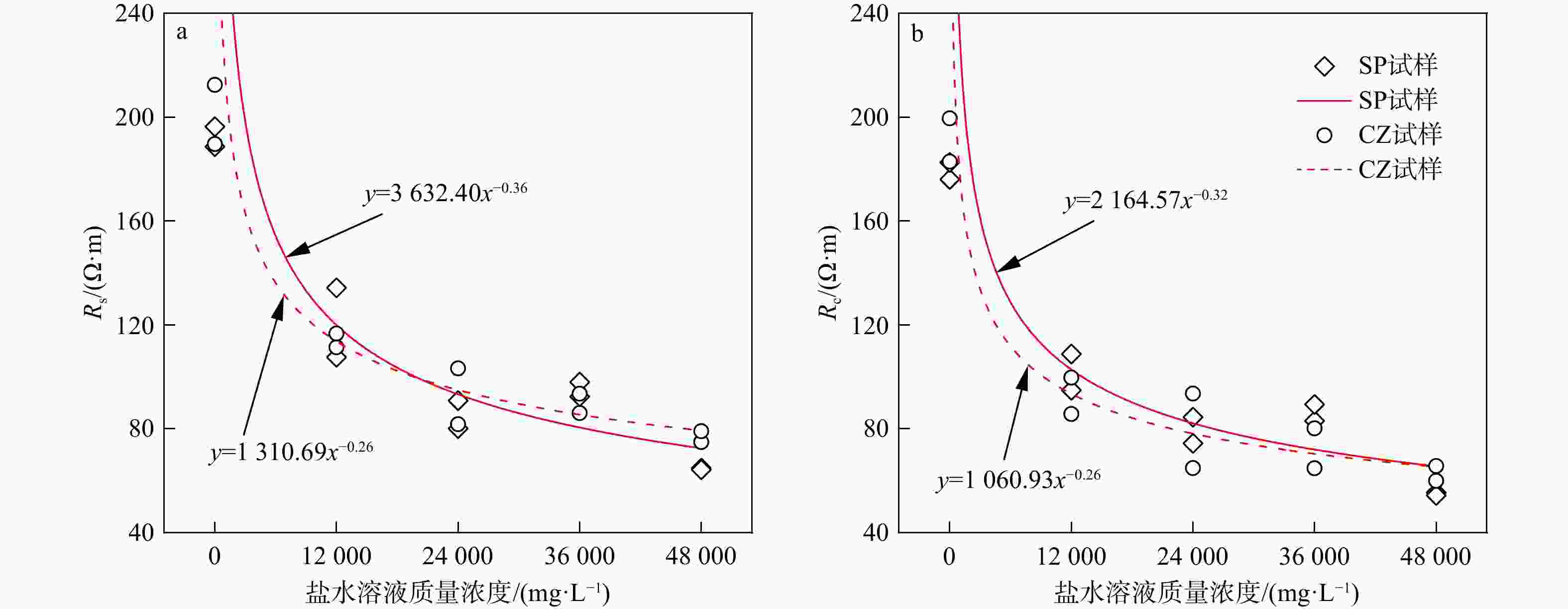
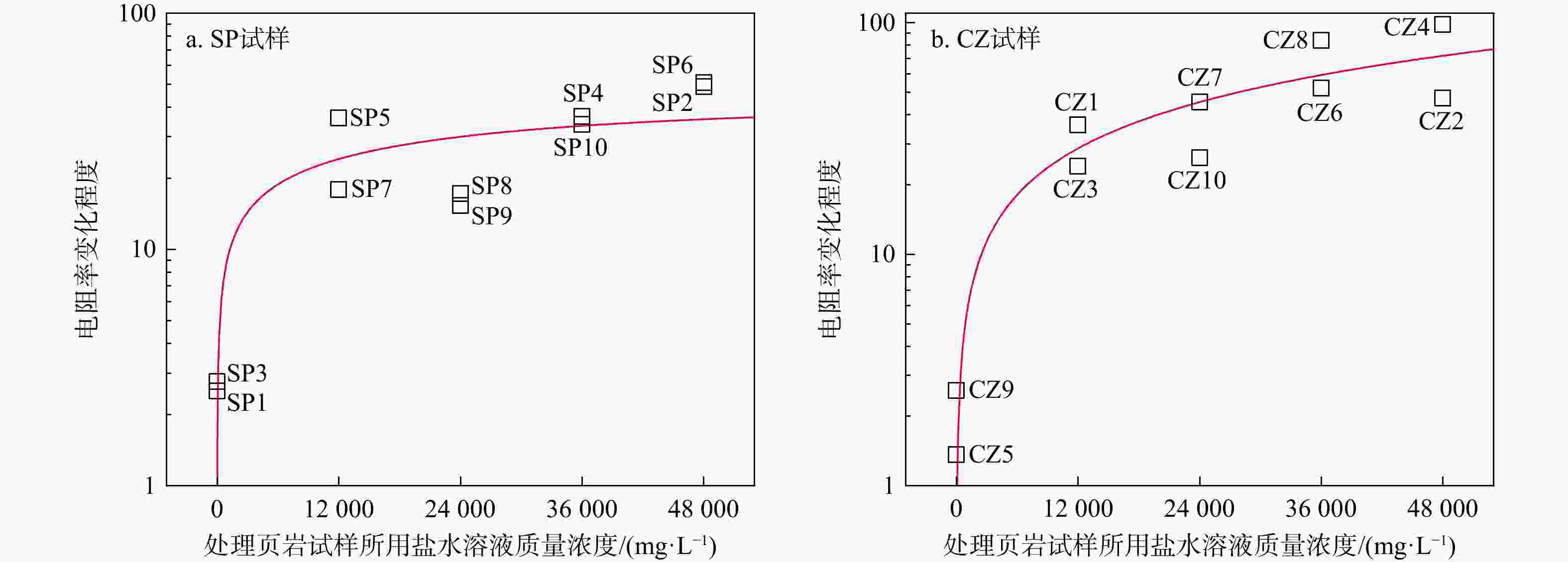
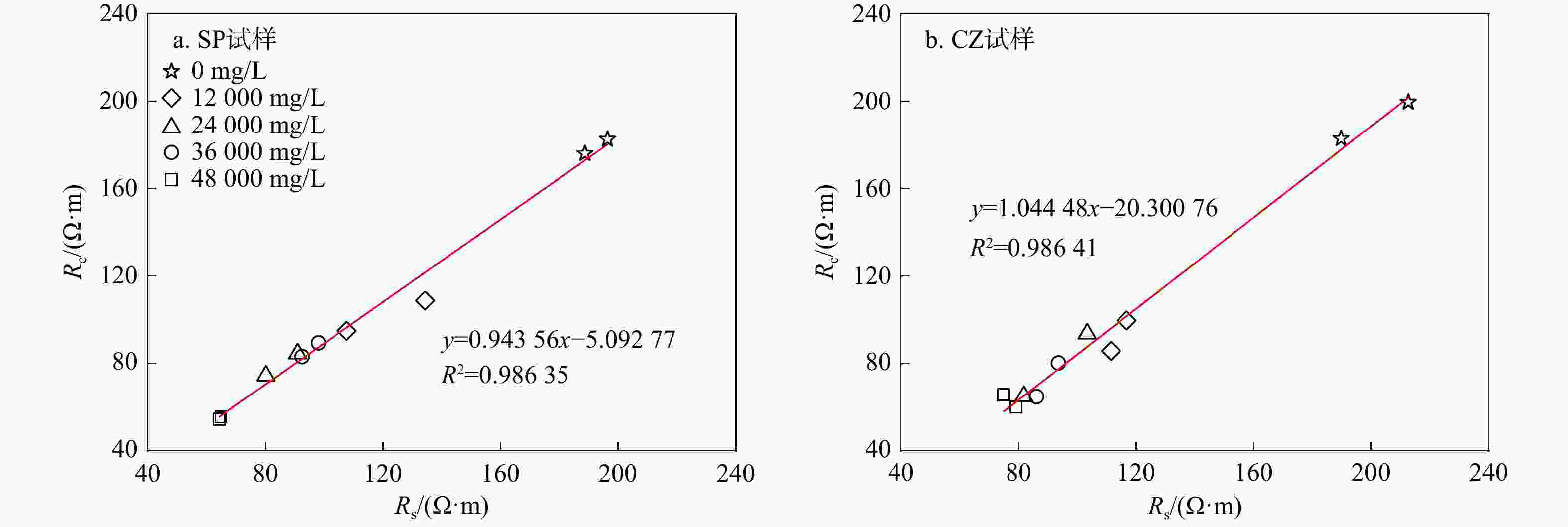
Pc/MPa孔隙度/% Ⅰ 0 / SP1 411.4 7862.6 188.7 176.1 269.3 4.26 SP3 600.9 4918.0 196.4 182.6 283.4 4.62 CZ5 435.2 3844.8 189.7 182.9 261.1 4.87 CZ9 424.5 4424.2 212.5 199.6 269.3 4.90 Ⅱ 12000 0.71 SP5 800.3 5206.8 134.3 108.8 308.1 4.71 SP7 470.4 4491.3 107.6 94.9 275.4 4.99 CZ1 808.6 3785.2 111.4 85.7 246.3 4.95 CZ3 266.4 3410.4 116.7 99.7 262.1 4.94 Ⅲ 24000 0.37 SP8 467.0 3697.4 90.9 84.5 232.0 5.02 SP9 456.4 3780.8 80.1 74.4 245.1 5.25 CZ7 477.6 3982.9 81.8 64.9 272.8 5.09 CZ10 791.7 4788.1 103.3 93.6 262.6 5.56 Ⅳ 36000 0.25 SP4 650.9 3568.4 92.4 83.1 242.6 5.37 SP10 913.4 5608.9 98.0 89.4 301.4 5.45 CZ6 576.6 3824.9 93.5 80.2 280.6 5.70 CZ8 663.4 4368.8 86.1 64.8 245.1 5.73 Ⅴ 48000 0.19 SP2 329.2 3896.0 64.9 55.4 295.9 5.54 SP6 474.6 4932.9 64.3 54.4 276.1 5.71 CZ2 492.8 3267.2 74.9 65.7 255.1 5.95 CZ4 595.7 3764.8 79.1 60.0 271.3 5.74 *据斯伦贝谢公司《NaCl溶液的电阻率与其浓度和温度关系》图版拟合得到试验条件下NaCl溶液浓度与电阻率之间函数关系:$ {y}=4\ 514.15{x}^{-0.93} $ 表 2 页岩试样矿物组成及热演化程度
Table 2. Mineral composition and clay mineral composition of shale samples
试样
编号全岩矿物体积分数/% 黏土矿物占比/% 伊/蒙混层占比/% 沥青反射率
Rb/%沥青等效镜质体
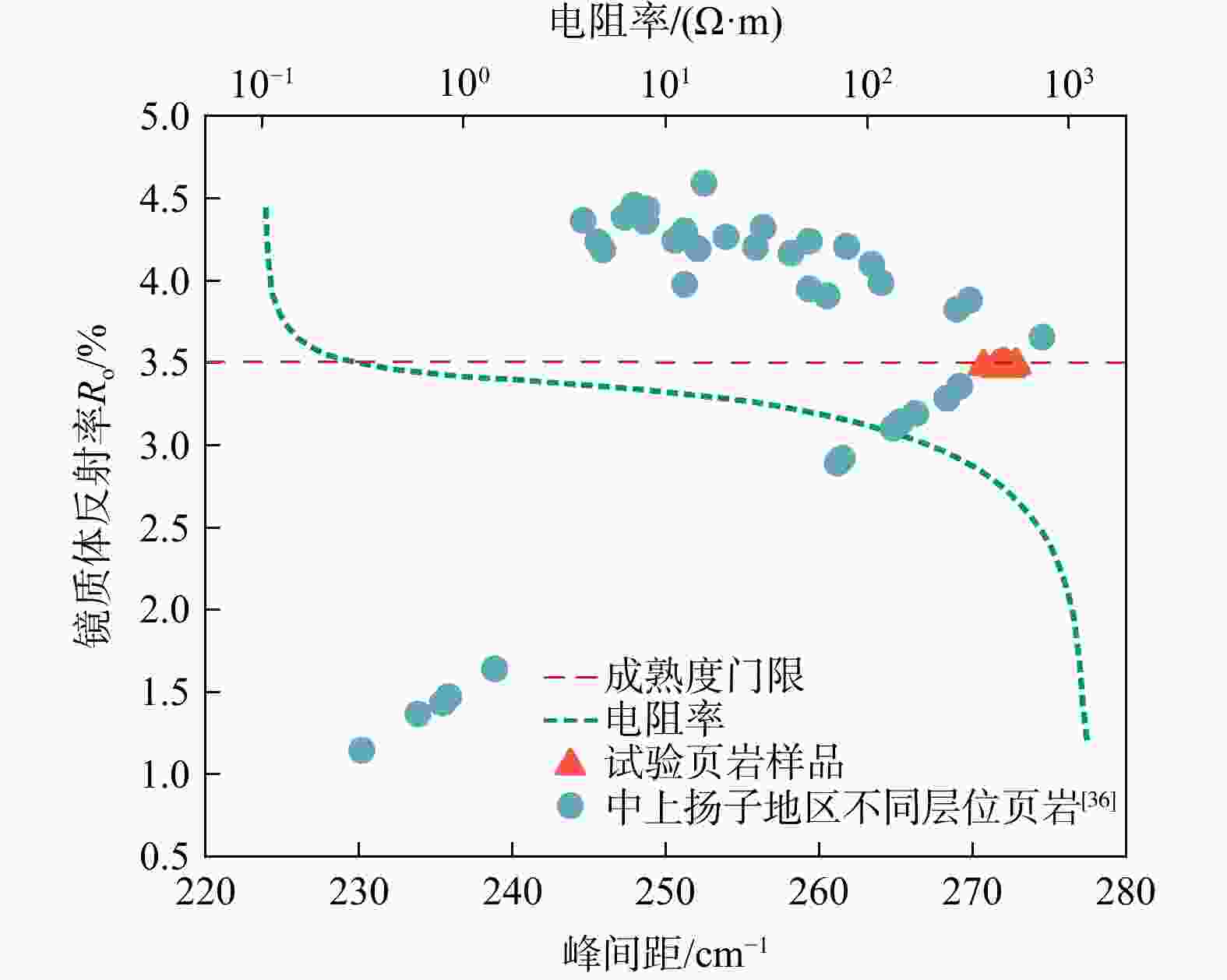
反射率bRoeq/%石英 斜长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 黏土矿物 伊利石 伊/蒙混层 蒙皂石层 伊利石层 SP2 55.7 1.3 20.5 12.7 0.9 8.9 97 3 5 95 3.83 2.92 SP4 52.8 0.8 22.7 15.9 1.2 6.6 97 3 5 95 / / CZ1 58.2 1.4 18.3 11.7 0.8 9.6 98 2 5 95 3.98 3.02 CZ4 53.8 0.7 18.4 16.7 1.2 9.2 99 1 5 95 4.06 3.08 CZ9 50.6 1.9 22.6 16.4 1.0 7.5 97 3 5 95 4.08 3.09 表 3 SP6试样激光拉曼光谱测试数据及等效镜质体反射率计算结果
Table 3. Laser Raman spectroscopy test results and equivalent vitrinite reflectance results of SP6 smaple
测点编号 D峰峰高 G峰峰高 峰间距/cm−1 峰高比 激光拉曼反射率RmcRo/% 拉曼等效镜质体反射率rRoeq/% 1 9415.60 18264.10 272.51 0.52 3.36 3.47 2 7856.00 14891.10 272.13 0.53 3.37 3.48 3 8082.24 15545.40 271.95 0.52 3.36 3.47 4 7271.43 13530.90 272.05 0.54 3.39 3.49 5 8829.71 16437.00 272.83 0.54 3.39 3.49 6 8250.88 15437.50 272.21 0.53 3.38 3.49 7 9002.58 16678.10 271.91 0.54 3.39 3.49 8 8522.53 16270.90 271.60 0.52 3.37 3.48 9 9150.72 17194.30 270.70 0.53 3.38 3.48 10 7612.25 14789.00 271.45 0.51 3.36 3.47 -
[1] 赵文智,贾爱林,位云生,等. 中国页岩气勘探开发进展及发展展望[J]. 中国石油勘探,2020,25(1):31-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.004ZHAO W Z,JIA A L,WEI Y S,et al. Progress in shale gas exploration in China and prospects for future development[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2020,25(1):31-44. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.004 [2] 李鹭光,王红岩,刘合,等. 天然气助力未来世界发展:第27届世界天然气大会(WGC)综述[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(9):1-9.LI L G,WANG H Y,LIU H,et al. Natural gas fueling the world's future:A brief summary from the 27th World Gas Conference(WGC)[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2018,38(9):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 熊亮,赵勇,魏力民,等. 威荣海相页岩气田页岩气富集机理及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(8):1365-1381.XIONG L,ZHAO Y,WEI L M,et al. Enrichment mechanisms and key exploration and development technologies of shale gas in Weirong marine shale gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2023,44(8):1365-1381. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 邹才能,潘松圻,荆振华,等. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(1):1-12. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0299-4ZOU C N,PAN S Q,JING Z H,et al. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2020,41(1):1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0299-4 [5] 黄莉莎,闫建平,胡兴中,等. 川南五峰组–龙马溪组低阻页岩特征分析及启示[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2024,46(2):26-40.HUANG L S,YAN J P,HU X Z,et al. Characteristics analysis and its enlightenment of shale of low resistivity in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition),2024,46(2):26-40. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] MA X H,WANG H Y,ZHOU T Q,et al. Geological controlling factors of low resistivity shale and their implications on reservoir quality:A case study in the southern Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Energies,2022,15(16):5801. doi: 10.3390/en15165801 [7] 邹辰,李德华,杨庆,等. 滇黔北地区龙马溪组有机质石墨化特征及成因[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(增刊1):67-72.ZOU C,LI D H,YANG Q,et al. Characteristics and genesis of organic matter graphitization in Longmaxi Formation,northern Yunnan and Guizhou[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2021,41(S1):67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 王伟庆,王学军,李政,等. 低演化陆相页岩孔缝特征及对页岩油赋存的意义:以济阳坳陷外围青南洼陷沙河街组为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):94-107.WANG W Q,WANG X J,LI Z,et al. Pore and fracture characteristics of low-maturity continental shale and its significance for shale oil occurrence: A case study of Shahejie Formation in Qingnan Sag,Jiyang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):94-107.(in Chinese with English abstract [9] KETHIREDDY N,CHEN H Y,HEIDARI Z. Quantifying the effect of kerogen on resistivity measurements in organic-rich mudrocks[J]. Petrophysics,2014,55(2):136-146. [10] YANG A Q,FIRDAUS G,HEIDARI Z. Electrical resistivity and chemical properties of kerogen isolated from organic-rich mudrocks[J]. Geophysics,2016,81(6):D643-D655. doi: 10.1190/geo2016-0071.1 [11] SENGER K,BIRCHALL T,BETLEM P,et al. Resistivity of reservoir sandstones and organic rich shales on the Barents Shelf:Implications for interpreting CSEM data[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(6):101063. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.08.007 [12] 杨小兵,张树东,张志刚,等. 低阻页岩气储层的测井解释评价[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2015,42(6):692-699.YANG X B,ZHANG S D,ZHANG Z G,et al. Logging interpretation and evaluation of low resistivity shale gas reservoirs[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2015,42(6):692-699. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] SUN F J,SUN J M,ZENG X,et al. Analysis of the influencing factors on electrical properties and evaluation of gas saturation in marine shales:A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022,10:824352. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.824352 [14] 崔瑞康,孙建孟,刘行军,等. 低阻页岩电阻率主控因素研究[J]. 物探与化探,2022,46(1):150-159.CUI R K,SUN J M,LIU X J,et al. Major controlling factors of low-resistance shale gas reservoirs[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2022,46(1):150-159. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 廖明光,苏崇华,唐洪,等. W油藏黏土矿物特征及油层低阻成因[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2010,32(5):70-74.LIAO M G,SU C H,TANG H,et al. Characteristics of clay minerals in W low resistivity reservoirs and the genesis of low resistivity[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2010,32(5):70-74. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] WANG X B,ZHANG B,HE Z X,et al. Electrical properties of Longmaxi organic-rich shale and its potential applications to shale gas exploration and exploitation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2016,36:573-585. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.10.027 [17] 孙建孟,熊铸,罗红,等. 扬子地区下古生界页岩气储层低阻成因分析及测井评价[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2018,42(5):47-56.SUN J M,XIONG Z,LUO H,et al. Mechanism analysis and logging evaluation of low resistivity in Lower Paleozoic shale gas reservoirs of Yangtze region[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2018,42(5):47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] ZHONG Z Q,REZAEE R,JOSH M,et al. The salinity dependence of electrical conductivity and Archie's cementation exponent in shale formations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2022,208:109324. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109324 [19] 高和群,丁安徐,蔡潇,等. 中上扬子海相页岩电阻率异常成因分析[J]. 断块油气田,2016,23(5):578-582.GAO H Q,DING A X,CAI X,et al. Genetic analysis of abnormal resistivity of Middle-Upper Yangtze marine shales[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,2016,23(5):578-582. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 文杰,徐尚,苟启洋,等. 页岩油微运移研究进展及意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):1-14.WEN J,XU S,GOU Q Y,et al. Research status and significance of shale oil micromigration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 梁霄,徐剑良,王滢,等. 川南地区渐变型盆—山边界条件下龙马溪组页岩气(藏)富集主控因素:构造—沉积分异与差异性演化[J]. 地质科学,2021,56(1):60-81.LIANG X,XU J L,WANG Y,et al. The shale gas enrichment factors of Longmaxi Formation under gradient basin-mountain boundary in South Sichuan Basin:Tectono-depositional differentiation and discrepant evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2021,56(1):60-81. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] JIANG Y Q,CHEN L,QI L,et al. Characterization of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in Changning area in the south Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Geological Journal,2018,53(5):1656-1664. doi: 10.1002/gj.2983 [23] 陈增裕,刘睿,谭秀成,等. 四川盆地南缘长宁地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩内多源石英对页岩气富集的意义[J]. 古地理学报,2023,25(4):920-930.CHEN Z Y,LIU R,TAN X C,et al. Implications of multi-source quartz on shale-gas enrichment in the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale of Changning area in southern margin of Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),2023,25(4):920-930. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 赵圣贤,杨跃明,张鉴,等. 四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组页岩小层划分与储层精细对比[J]. 天然气地球科学,2016,27(3):470-487.ZHAO S X,YANG Y M,ZHANG J,et al. Micro-layers division and fine reservoirs contrast of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale,Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2016,27(3):470-487. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] SHI Z S,WANG H Y,SUN S S,et al. Graptolite zone calibrated stratigraphy and topography of the Late Ordovician-Early Silurian Wufeng-Lungmachi shale in Upper Yangtze area,South China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2021,14(3):213. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-06517-5 [26] 张福,黄艺,蓝宝锋,等. 正安地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):49-56.ZHANG F,HUANG Y,LAN B F,et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale reservoir in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation of the Zheng'an area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):49-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 韦国栋,谭秀成,刘睿,等. 长宁地区龙马溪组页岩沉积古地貌与页岩气差异富集的耦合机制[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2024,44(2):253-266.WEI G D,TAN X C,LIU R,et al. The coupling mechanism between geomorphology of shale sedimentary and differential enrichment of shale gas in Longmaxi Formation in Changning area[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2024,44(2):253-266. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 张砚,惠栋,张鉴,等. 四川盆地海相页岩水蒸气吸附特征及其主控因素:以川南地区下志留统龙马溪组页岩为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(6):1431-1444.ZHANG Y,HUI D,ZHANG J,et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of water vapor adsorption in marine shale:A case study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shales in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2022,43(6):1431-1444. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 张晋言,李淑荣,王利滨,等. 页岩气测井电性解析及含气性评价:以四川盆地涪陵地区龙马溪组一段—五峰组为例[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2018,41(3):33-41.ZHANG J Y,LI S R,WANG L B,et al. Electrical-logging analysis and evaluation on gas-bearing property of shale gas:An example from Longmaxi 1 Member-Wufeng Formation,Fuling area,Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development,2018,41(3):33-41. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 谢青,王建民. 鄂尔多斯盆地志丹、安塞地区长6低阻油层成因机理及识别方法[J]. 岩性油气藏,2013,25(3):106-111.XIE Q,WANG J M. Genetic mechanism and identification methods of Chang 6 low resistivity reservoir in Zhidan and Ansai area,Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2013,25(3):106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 王立伟,李生杰,刘晓雪,等. 四川盆地五峰−龙马溪组低阻页岩含水饱和度测井评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(16):6456-6462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.16.010WANG L W,LI S J,LIU X X,et al. Water saturation of low resistance shale in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation of Sichuan Basin logging evaluation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2022,22(16):6456-6462. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.16.010 [32] 丰国秀,陈盛吉. 岩石中沥青反射率与镜质体反射率之间的关系[J]. 天然气工业,1988,8(3):20-25.FENG G X,CHEN S J. Relationship between the reflectance of bitumen and vitrinite in rock[J]. Natural Gas Industry,1988,8(3):20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 刘德汉,肖贤明,田辉,等. 固体有机质拉曼光谱参数计算样品热演化程度的方法与地质应用[J]. 科学通报,2013,58(13):1228-1241. doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-13-1228LIU D H,XIAO X M,TIAN H,et al. Sample maturation calculated using Raman spectroscopic parameters for solid organics:Methodology and geological applications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(13):1228-1241. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-13-1228 [34] SCHMIDT J,MENEZES T,SOUZA I,et al. Comments on empirical conversion of solid bitumen reflectance for thermal maturity evaluation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2018,201:44-50. [35] 曹涛涛,邓模,宋之光,等. 黄铁矿对页岩油气富集成藏影响研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(3):404-414.CAO T T,DENG M,SONG Z G,et al. Study on the effect of pyrite on the accumulation of shale oil and gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2018,29(3):404-414. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 侯宇光,张坤朋,何生,等. 南方下古生界海相页岩极低电阻率成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):80-89.HOU Y G,ZHANG K P,HE S,et al. Origin and geological significance of ultra-low resistivity in Lower Paleozoic marine shale, South China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):80-89. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 王玉满,李新景,王皓,等. 中上扬子地区下志留统龙马溪组有机质碳化区预测[J]. 天然气地球科学,2020,31(2):151-162.WANG Y M,LI X J,WANG H,et al. Prediction of organic matter carbonization zones for Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Middle-Upper Yangtze region[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2020,31(2):151-162. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 王玉满,李新景,陈波,等. 海相页岩有机质炭化的热成熟度下限及勘探风险[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(3):385-395.WANG Y M,LI X J,CHEN B,et al. Lower limit of thermal maturity for the carbonization of organic matter in marine shale and its exploration risk[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2018,45(3):385-395. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 李艺菲,辜海林,毕二平. 龙马溪组页岩组分在液−岩作用过程中的释放特征[J]. 环境化学,2021,40(11):3421-3431.LI Y F,GU H L,BI E P. Releasing characteristics of the Longmaxi Formation shale components during fluid-rock interactions[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2021,40(11):3421-3431. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] MOGOLLóN J L,PéREZ-DIAZ A,LO MONACO S. The effects of ion identity and ionic strength on the dissolution rate of a gibbsitic bauxite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2000,64(5):781-795. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00351-8 [41] RENOCK D,LANDIS J D,SHARMA M. Reductive weathering of black shale and release of Barium during hydraulic fracturing[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2016,65:73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.11.001 [42] 解经宇,陆洪智,陈磊,等. 龙马溪组层状页岩微观非均质性及力学各向异性特征[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):67-77.XIE J Y,LU H Z,CHEN L,et al. Micro scopic heterogeneity and mechanical anisotropy of the laminated shale in Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):67-77. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 沈金才. 页岩气井邻井压裂干扰响应特征及机理探讨:以涪陵页岩气田为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):87-97.SHEN J C. Response characteristics and mechanism for fracturing interference of adjacent wells of shale gas wells:A case study in the Fuling shale gas field[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):87-97. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] 李彦伟,朱超凡,曾壹坚,等. 层理特征对油页岩水力压裂裂缝扩展规律影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(11):44-54.LI Y W,ZHU C F,ZENG Y J,et al. Numerical simulations of the effects of bedding planes on hydraulic fracture propagation law in oil shale[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2023,51(11):44-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] 魏海峰. 非均质性页岩水力压裂裂缝扩展形态研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2023,30(4):156-166.WEI H F. Research progress on fracture propagation patterns of hydraulic fracturing in heterogeneous shale[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2023,30(4):156-166. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] 王元,杨恒林,黄浩勇,等. 四川盆地泸州区块深层页岩气地质力学研究及应用[J]. 中国石油勘探,2023,28(5):68-83.WANG Y,YANG H L,HUANG H Y,et al. Geomechanical study of deep shale gas and application in Luzhou block, Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2023,28(5):68-83. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: