U-Pb age characteristics of detrital zircon and provenance analysis of a Middle Miocene submarine fan in the Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
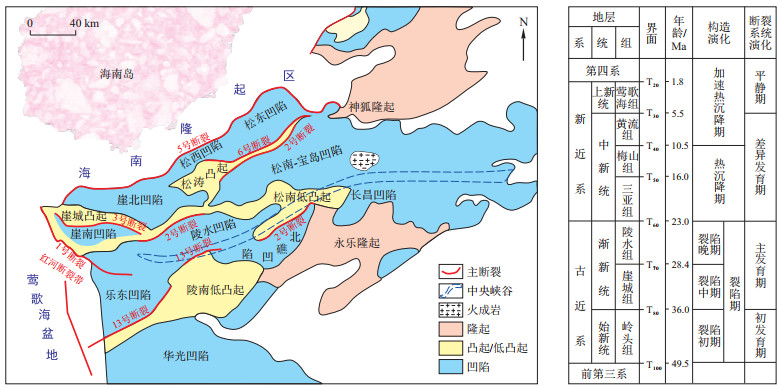
琼东南盆地中中新统海底扇是南海北部天然气勘探的重要目标, 但长期以来对该海底扇沉积物的物源并未达成共识, 因此, 物源分析对于该区天然气勘探有利目标优选具有重要意义。通过钻井取心开展了碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谱特征研究, 并与周缘潜在物源区锆石U-Pb年龄进行了对比分析, 示踪了研究区中中新统海底扇物源。结果表明: ①盆地北部N-1、N-2、N-3、N-4等4口井碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄表现为燕山期(160, 157, 133, 107, 102, 99 Ma)、印支期(249, 241, 239 Ma)、加里东期(466, 455 Ma)的年龄峰值特征, 且与中国海南岛碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄特征相似度高, 但与红河、越南中部碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄特征相似度低; ②盆地南部S-1、S-2、S-3等3口井碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄特征表现为印支期(242, 238, 237 Ma)、加里东期(435, 431, 425 Ma)、海西期(396, 392 Ma)以及燕山期(143 Ma)的年龄峰值特征, 且S-2井具有较年轻的喜马拉雅期(21 Ma)单峰年龄特征。琼东南盆地北部中中新统沉积物源主要来自海南岛, 红河及越南中部物源对其影响非常有限, 盆地南部中中新统为红河和海南岛双物源供给, 且以红河物源为主, 自西向东差异明显。
Abstract:Objective The middle Miocene submarine fan in the Qiongdongnan Basin is an important target for natural gas exploration in the northern South China Sea. However, there has been no consensus on the source of submarine fan sediments for a long time. Provenance analysis will be important for the optimization of natural gas exploration in this area.
Methods In this paper, the detrital zircon U-Pb age spectrum characteristics of drilling cores from the middle Miocene submarine fan in the Qiongdongnan Basin were analysed and compared with the U-Pb ages of zircons from potential provenance areas to determine the source of submarine fans in the study area.
Results The results show that ① the U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from the N-1, N-2, N-3 and N-4 wells in the northern part of the basin are characterized by Yanshanian (160, 157, 133, 107, 102, 99 Ma), Indosinian (249, 241, 239 Ma) and Caledonian (466, 455 Ma) age peaks and have high similarity with the U-Pb age characteristics of detrital zircons from Hainan Island sediments but low similarity with the U-Pb age characteristics of detrital zircons from Red River and central Vietnam sediments. ② The detrital zircon U-Pb ages of three wells (S-1, S-2, and S-3) in the southern part of the basin show peak ages of Caledonian (435, 431, 425 Ma), Hercynian (396, 392 Ma), Indosinian (242, 238, 237 Ma), and Yanshanian (143 Ma). The S-2 well has a younger unimodal Himalayan (21 Ma) age peak.
Conclusion The provenance of the middle Miocene in the northern part of the basin is Hainan Island. The influence of the provenance on the Red River and Central Vietnam is very limited. The provenance of the middle Miocene in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin was a double-source supply from the Red River and Hainan Island and was dominated by the former, with an obvious difference from west to east.
-
Key words:
- zircon U-Pb age /
- provenance /
- submarine fan /
- Middle Miocene /
- Qiongdongnan Basin /
- detrital
-
-
[1] 朱继田, 杨希冰, 胡向阳, 等. 琼东南盆地北部中生代凹陷特征及油气成藏条件初探[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 83-93. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0219ZHU J T, YANG X B, HU X Y, et al. Characteristic and petroleum geology of the Mesozoic sags of the northern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 83-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0219 [2] 解习农, 陈志宏, 孙志鹏, 等. 南海西北陆缘深水沉积体系内部构成特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 37(4): 627-634.XIE X N, CHEN Z H, SUN Z P, et al. Depositional architecture characteristics of deepwater depositional systems on the continental margins of northwestern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2012, 37(4): 627-634. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 李建平, 闫琢玉, 徐微, 等. 琼东南盆地中央坳陷西北部梅山组浊积扇源-汇分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(3): 53-67.LI J P, YAN Z Y, XU W, et al. Source-to-sink system analysis of the Meishan Formation turbidite fans in the northwest of the Central Depression in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(3): 53-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 尤丽, 江汝锋, 徐守立, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区乐东-陵水凹陷梅山组天然气成藏特征与勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(5): 24-31.YOU L, JIANG R F, XU S L, et al. Accumulation characteristics and exploration potential of Meishan Formation gas in Ledong-Lingshui Sag, deep water area of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(5): 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 甘军, 梁刚, 李兴, 等. 琼东南盆地梅山组海底扇天然气成因类型及成藏模式[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(3): 1069-1078. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.03.021GAN J, LIANG G, LI X, et al. Genetic types and accumulation model of submarine fan gas in the Meishan Formation, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(3): 1069-1078. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.03.021 [6] 王华, 陈思, 刘恩涛, 等. 南海北部莺-琼盆地典型重力流沉积特征与物源体系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 5-18. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0245WANG H, CHEN S, LIU E T, et al. Typical gravity flow sedimentary features and provenance system in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 5-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0245 [7] 姚根顺, 袁圣强, 吴时国, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区双物源沉积模式及勘探前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(6): 685-691. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.06.008YAO G S, YUAN S Q, WU S G, et al. Double provenance depositional model and exploration prospect in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(6): 685-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.06.008 [8] 王永凤, 王英民, 李冬, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷早上新世沉积物稀土元素特征及物源分析[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(6): 50-52.WANG Y F, WANG Y M, LI D, et al. Features and source analysis on Early Pliocene sedimentary rare earth element(REE) in Central Canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2011, 33(6): 50-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 李冬, 徐强, 王永凤. 琼东南盆地上新世中央峡谷物源分析及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(4): 659-664.LI D, XU Q, WANG Y F. Provenance analysis of the Pliocene Central Canyon in Qiongdongnan Basin and its implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(4): 659-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 张道军, 张迎朝, 邵磊, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积物源探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10): 1574-1581.ZHANG D J, ZHANG Y Z, SHAO L, et al. Sedimentary provenance in the Central Canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(10): 1574-1581. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 尹娜, 杨海长, 马明, 等. 琼东南盆地上中新统-上新统中央峡谷沉积物来源[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10): 1582-1592.YIN N, YANG H C, MA M, et al. Provenance of Central Canyon in the Upper Miocene to the Pliocene in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(10): 1582-1592. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 罗泉源, 焦祥燕, 刘昆, 等. 乐东-陵水凹陷梅山组海底扇识别及沉积模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2): 90-99.LUO Q Y, JIAO X Y, LIU K, et al. Identification of submarine fan in the Meishan Formation of the Ledong-Lingshui Sag in the Qiongdongnan Basin and its depositional model[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 90-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 李安琪, 胡林, 王真真, 等. 琼东南盆地乐东凹陷梅山组海底扇沉积演化及油气地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(2): 76-84.LI A Q, HU L, WANG Z Z, et al. Sedimentary evolution of Meishan Formation submarine fan in Ledong Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance in hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(2): 76-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 周俊燊, 邵磊, 乔培军, 等. 南海北部深海盆地上中新统浊积砂体物源分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(4): 775-784.ZHOU J S, SHAO L, QIAO P J, et al. Provenance analysis of the Upper Miocene turbidite sand-bodies in Deep-sea Basin of northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2020, 22(4): 775-784. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 周凤娟, 丁琳, 李晓艳, 等. 珠一坳陷文昌组锆石定年物源示踪及其对储层的影响[J]. 非常规油气, 2023, 10(3): 46-54.ZHOU F J, DING L, LI X Y, et al. Provenance tracing of zircon dating from Wenchang Formation in Zhu Ⅰ Depression and its influence on reservoir[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2023, 10(3): 46-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 王策, 梁新权, 付建刚, 等. 莺歌海盆地莺歌海组二段碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源意义[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(增刊1): 716-717.WANG C, LIANG X Q, FU J G, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of the Second Member of Yinggehai Formation in Yinggehai Basin and its provenance significance[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1): 716-717. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 杜晓东, 彭光荣, 吴静, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江东凹始新统的源汇过程: 碎屑锆石定年及物源示踪[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(6): 124-137.DU X D, PENG G R, WU J, et al. Tracing source-to-sink process of the Eocene in the Eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Evidence from detrital zircon spectrum[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6): 124-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 杨甫, 陈刚, 陈强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘上奥陶统平凉组碎屑岩锆石U-Pb年龄及物源分析[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(1): 172-182.YANG F, CHEN G, CHEN Q, et al. U-Pb dating of detrital zircon from Middle Ordovician Pingliang Formation in southwest margin of the Ordos Basin and provenance analysis[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(1): 172-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 闫义, 林舸, 李自安. 利用锆石形态、成分组成及年龄分析进行沉积物源区示踪的综合研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(2): 184-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.02.012YAN Y, LIN G, LI Z A. Provenance tracing of sediments by means of synthetic study of shape, composition and chronology of zircon[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2003, 27(2): 184-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.02.012 [20] BELOUSOVA E A, REID A J, GRIFFIN W L, et al. Proterozoic rejuvenation of the Archean Crust tracked by U-Pb and Hf-isotopes in detrital zircon[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(18): A44. [21] BELOUSOVA E A, GRIFFIN W L, O'REILLY S Y. Zircon crystal morphology, trace element signatures and Hf isotope composition as a tool for petrogenetic modelling: Examples from eastern Australian granitoids[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(2): 329-353. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi077 [22] 雷玮琰, 施光海, 刘迎新. 不同成因锆石的微量元素特征研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 273-284.LEI W Y, SHI G H, LIU Y X. Research progress on trace element characteristics of zircons of different origins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 273-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 焦鹏, 郭建华, 王玺凯, 等. 珠江口盆地韩江-陆丰凹陷珠江组下段碎屑锆石来源与储层物源示踪[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 239-253.JIAO P, GUO J H, WANG X K, et al. Detrital zircon genesis and provenance tracing for reservoirs in the Lower Zhujiang Formation in Hanjiang-Lufeng Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 239-253. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 邵磊, 李昂, 吴国瑄, 等. 琼东南盆地沉积环境及物源演变特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(4): 548-552.SHAO L, LI A, WU G X, et al. Evolution of sedimentary environment and provenance in Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(4): 548-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 李绪宣, 刘宝明, 赵俊青. 琼东南盆地古近纪层序结构、充填样式及生烃潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2007, 19(4): 217-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.04.001LI X X, LIU B M, ZHAO J Q. Paleogene sequence configuration, depositional filling pattern and hydrocarbon-generation potential in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2007, 19(4): 217-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.04.001 [26] 龚再升. 中国近海含油气盆地新构造运动与油气成藏[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2004, 29(5): 513-517.GONG Z S. Neotectonics and petroleum accumulation in offshore Chinese basins[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2004, 29(5): 513-517. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 谢玉洪, 童传新, 范彩伟, 等. 琼东南盆地断裂系统特征与演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(5): 795-807.XIE Y H, TONG C X, FAN C W, et al. Characteristics and evolution of fault system in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2015, 39(5): 795-807. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 王亚辉, 张道军, 陈杨, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷梅山组深水扇特征及控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2014, 35(6): 664-667.WANG Y H, ZHANG D J, CHEN Y, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of Meishan deep-water fans in Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2014, 35(6): 664-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 谢玉洪, 范彩伟, 周家雄, 等. 琼东南盆地中中新世重力流海底扇沉积特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(2): 220-228.XIE Y H, FAN C W, ZHOU J X, et al. Sedimentary features and controlling factors of the gravity flows in submarine fan of Middle Miocene in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(2): 220-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 谢玉洪, 李绪深, 范彩伟, 等. 琼东南盆地上中新统黄流组轴向水道源汇体系与天然气成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 521-528.XIE Y H, LI X S, FAN C W, et al. The axial channel provenance system and natural gas accumulation of the Upper Miocene Huangliu Formation in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 521-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 范彩伟, 李绪深, 刘昆, 等. 琼东南盆地乐东、陵水凹陷中新统岩性地层圈闭成藏条件[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(2): 53-59.FAN C W, LI X S, LIU K, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation condition of Miocene litho-stratigraphic trap in Ledong & Lingshui sags, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(2): 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 何家雄, 陈胜红, 刘海龄, 等. 南海北部边缘莺-琼盆地油气资源前景及有利勘探方向分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(4): 492-498.HE J X, CHEN S H, LIU H L, et al. Petroleum resource potential and advantageous exploration targets in Ying-Qiong Basin, northern margin of South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(4): 492-498. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 许怀智, 蔡东升, 孙志鹏, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积充填特征及油气地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(4): 641-650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.010XU H Z, CAI D S, SUN Z P, et al. Filling characters of Central Submarine Canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance of petroleum geology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(4): 641-650. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.010 [34] 谭建财, 范彩伟, 宋鹏, 等. 琼东南盆地中中新统古沟谷和坡折带特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2017, 24(3): 30-36.TAN J C, FAN C W, SONG P, et al. Characteristics of the mid-Miocene paleo ravine-slope break zones in Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance for oil-gas exploration[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017, 24(3): 30-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 王亚辉, 张道军, 陈杨, 等. 琼东南盆地三亚组陆架边缘三角洲的发现及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5): 30-36.WANG Y H, ZHANG D J, CHEN Y, et al. Discovery of shelf-edge delta in the Neogene Sanya Formation in the Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance for oil and gas exploration[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(5): 30-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] 赵燚林, 马遵青, 陈国俊, 等. 琼东南盆地松南-宝岛凹陷梅山组碎屑岩储集性及成岩作用研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2019, 39(4): 14-26.ZHAO Y L, MA Z Q, CHEN G J, et al. Physical properties and diagenesis of the clastic rocks from the Meishan Formation in the Songnan-Baodao Depression, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2019, 39(4): 14-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 樊隽轩, 王向东, 陈中强, 等. 国际地层委员会动态与《国际年代地层表》(2021/07版)[J]. 地层学杂志, 2021, 45(3): 460-466.FAN J X, WANG X D, CHEN Z Q, et al. Advances of the international commission on stratigraphy and the 《International Chronostratigraphic Chart》(v 2021/07)[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2021, 45(3): 460-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] SHAO L, CAO L C, PANG X, et al. Detrital zircon provenance of the Paleogene syn-rift sediments in the northern South China Sea[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2016, 17(2): 255-269. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006113 -





 下载:
下载: