-
摘要:
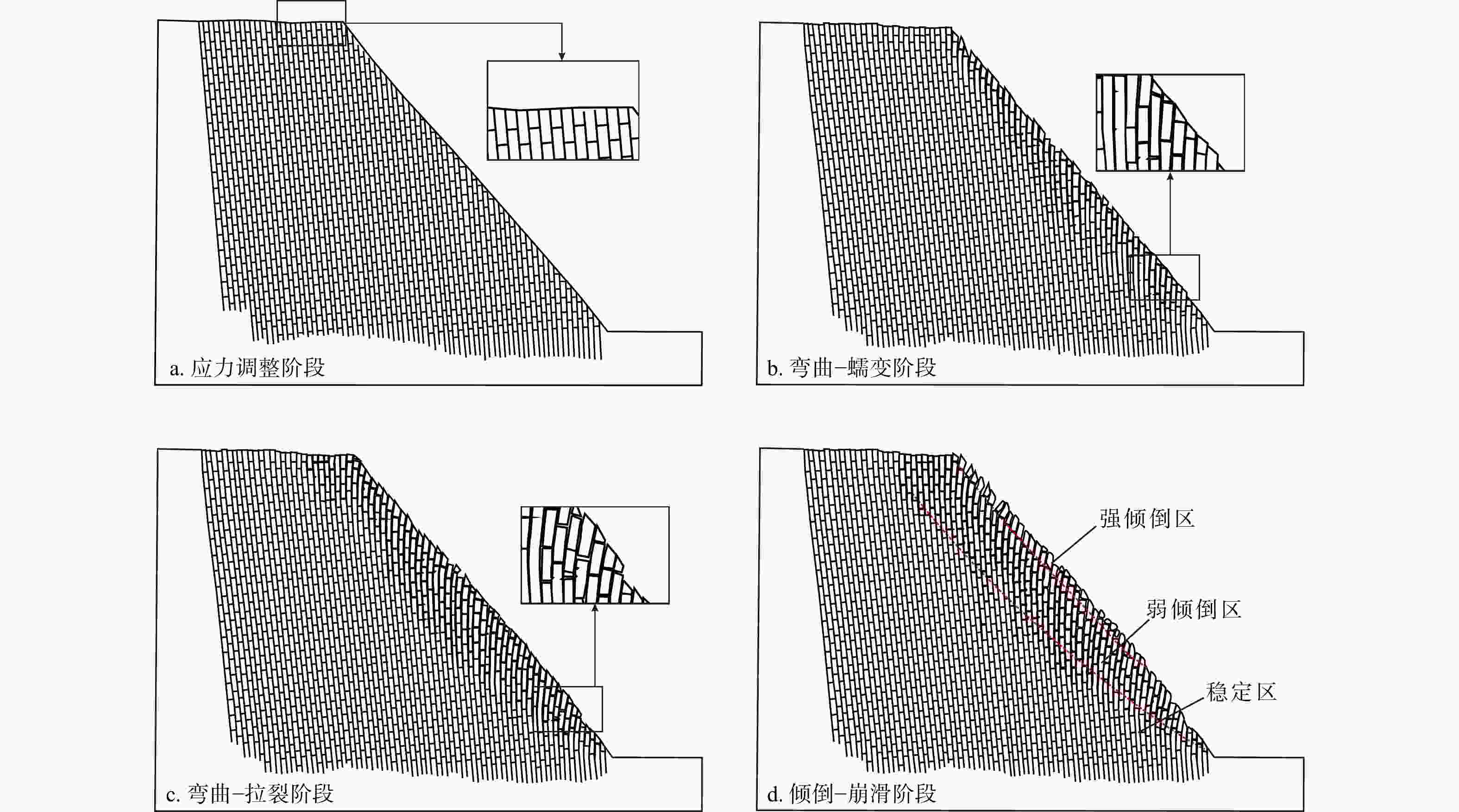
在澜沧江中上游大华桥水电站的左岸分布着大量顺层陡倾岩质边坡,库区独特的工程地质条件为其提供了良好的变形孕育环境,因倾倒变形体失稳崩落形成的滑坡堆积物在库区分布广泛,这对水电工程的运行和维护造成了极大困难。为了研究顺层陡倾岩质边坡的演化过程、倾倒模式以及倾倒变形破坏机理,以库区左岸微风化板岩为参照原型配置相似材料,采用室内底摩擦模型试验方法,分析不同坡角、层面倾角、结构面产状条件下边坡的变形破坏特征。结果表明:①顺层陡倾岩质边坡主要倾倒破坏模式为拉裂−倾倒式,在演化初期坡脚处岩体由于应力集中最先发生弯曲变形,并由坡体前缘逐渐向中后部发展,坡表中部的岩体也逐渐由顺倾转变为直立至反倾状态,并在重力作用下加速向临空面方向弯曲倾倒,当变形到达一定程度时将沿着最大弯曲部位或结构面发生拉裂折断,最终岩块将会沿着拉裂面产生滑移甚至崩落。②通过对比试验模型的坡体参数及变形特征,将7组模型边坡大致分为3类:近直立顺层岩质缓坡、陡倾角顺层岩质陡坡、近直立顺层岩质陡坡。相较于坡角,岩层倾角对顺层陡倾岩质边坡倾倒变形破坏的影响更大;非垂直于层面的缓倾结构面比垂直于层面的结构面更容易引起顺层陡倾边坡的倾倒变形破坏,且相较于外倾结构面,当坡体发育内倾结构面时发生倾倒变形破坏的规模更大。③从变形阶段的角度将斜坡的变形演化过程划分为初始变形阶段、倾倒变形阶段、倾倒破坏阶段。④从机理上将顺层陡倾岩质边坡发生倾倒变形破坏的过程划分为应力调整阶段、弯曲−蠕变阶段、弯曲−拉裂阶段、倾倒−崩滑阶段;根据倾倒区的变形程度将变形破坏后的斜坡划分为强倾倒区、弱倾倒区和稳定区。研究成果可为顺层陡倾岩质边坡的演化过程、倾倒模式以及倾倒变形破坏机理的研究提供参考。
Abstract:There are a large number of steep bedding rock slopes along the left bank of Dahuaqiao Hydropower Station in the middle and upper reaches of Lancang River. The unique engineering geological conditions in the reservoir area provide a good breeding environment for deformation. The landslide deposits formed by the collapse of the toppling deformed body are widely distributed in the reservoir area, which causes great difficulties for the operation and maintenance of the hydropower project.
Objective In this paper, in order to study the evolution process, toppling mode, toppling deformation and failure mechanism of steep bedding rock slope,
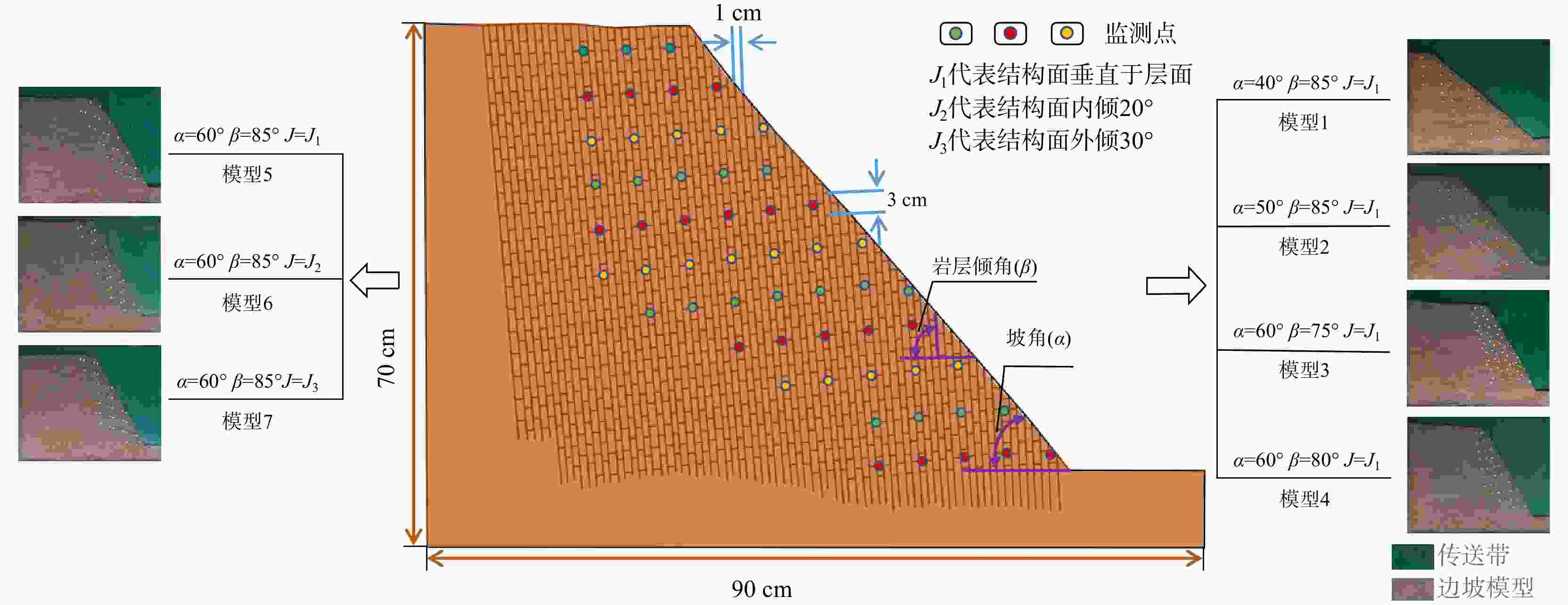
Methods we used the slightly weathered slate on the left bank of the reservoir as a reference prototype for the similar material material, then we choose to use the bottom friction test method to analyze the deformation and failure characteristics of slope under different condition of slope angles, plane inclination angles and structural plane occurrences.
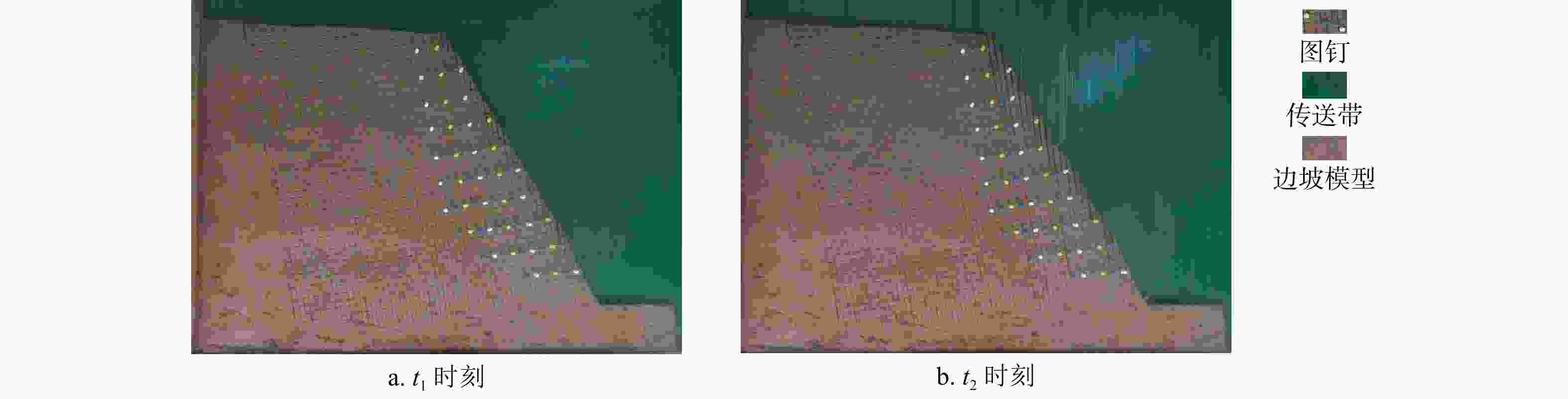
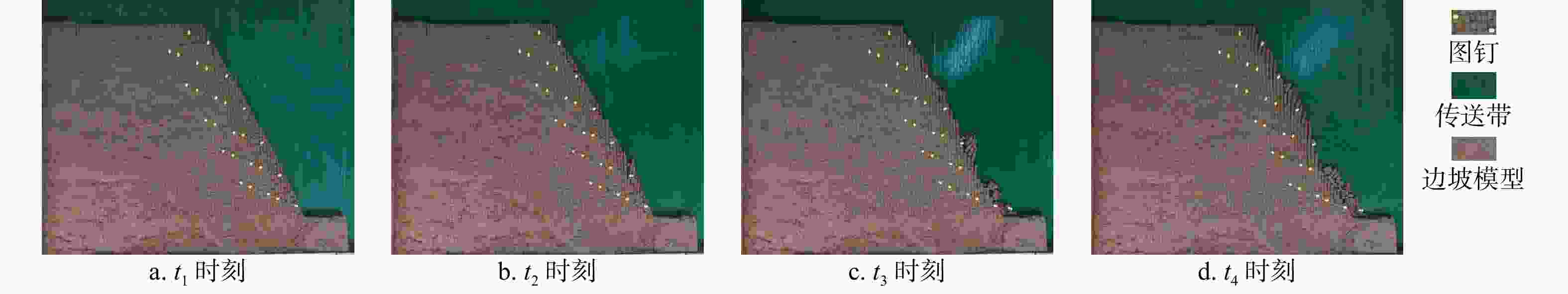
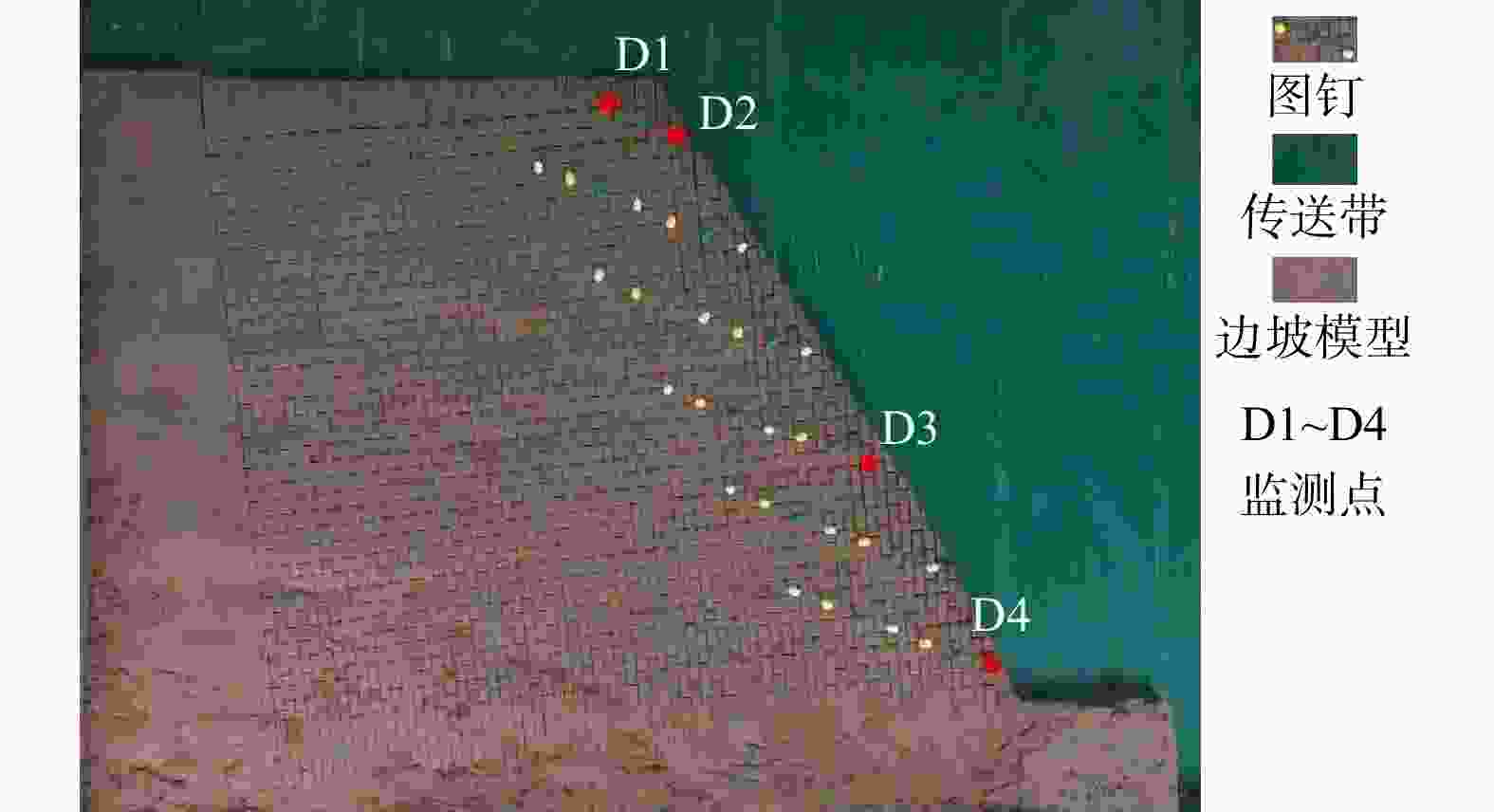
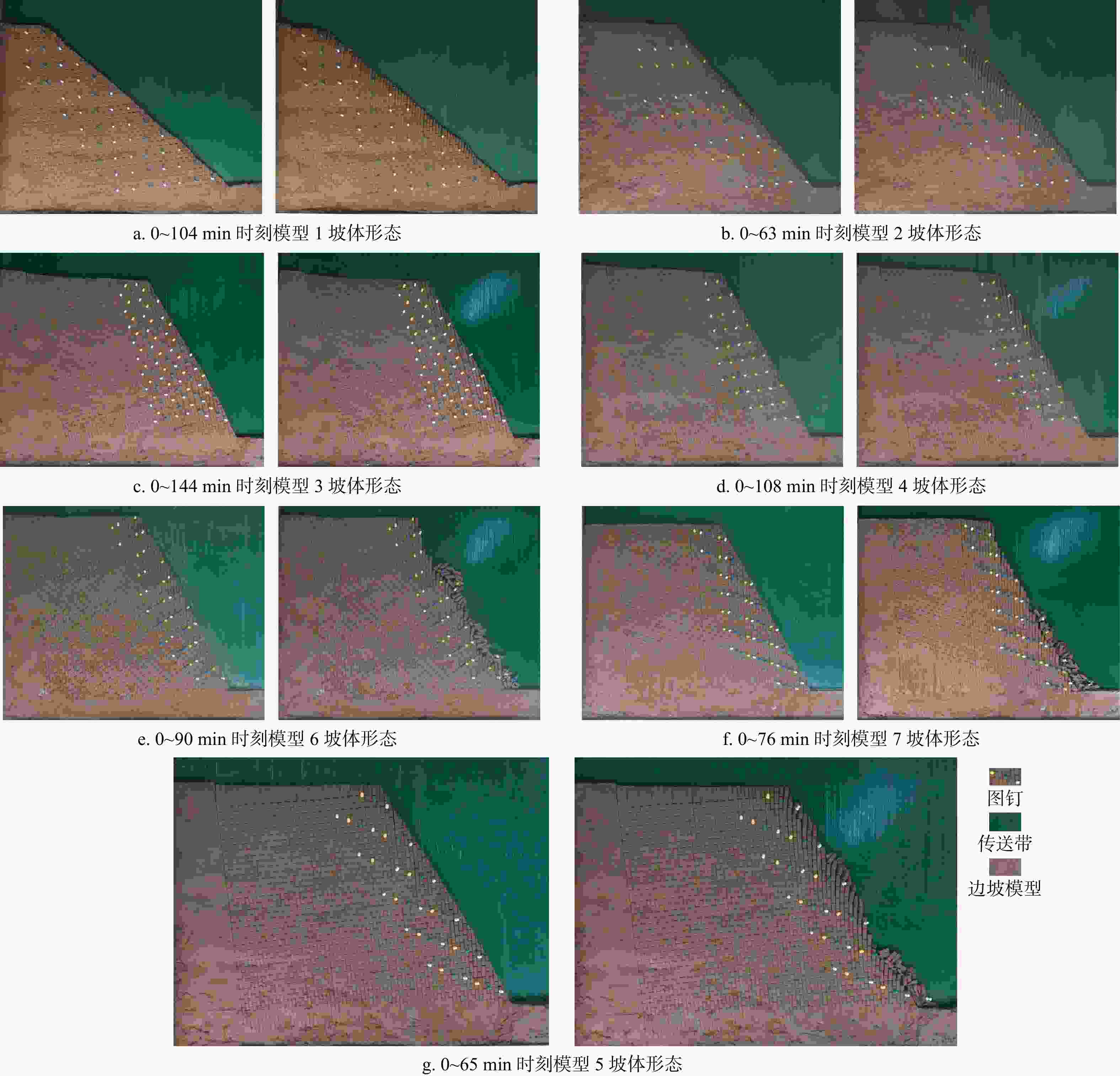
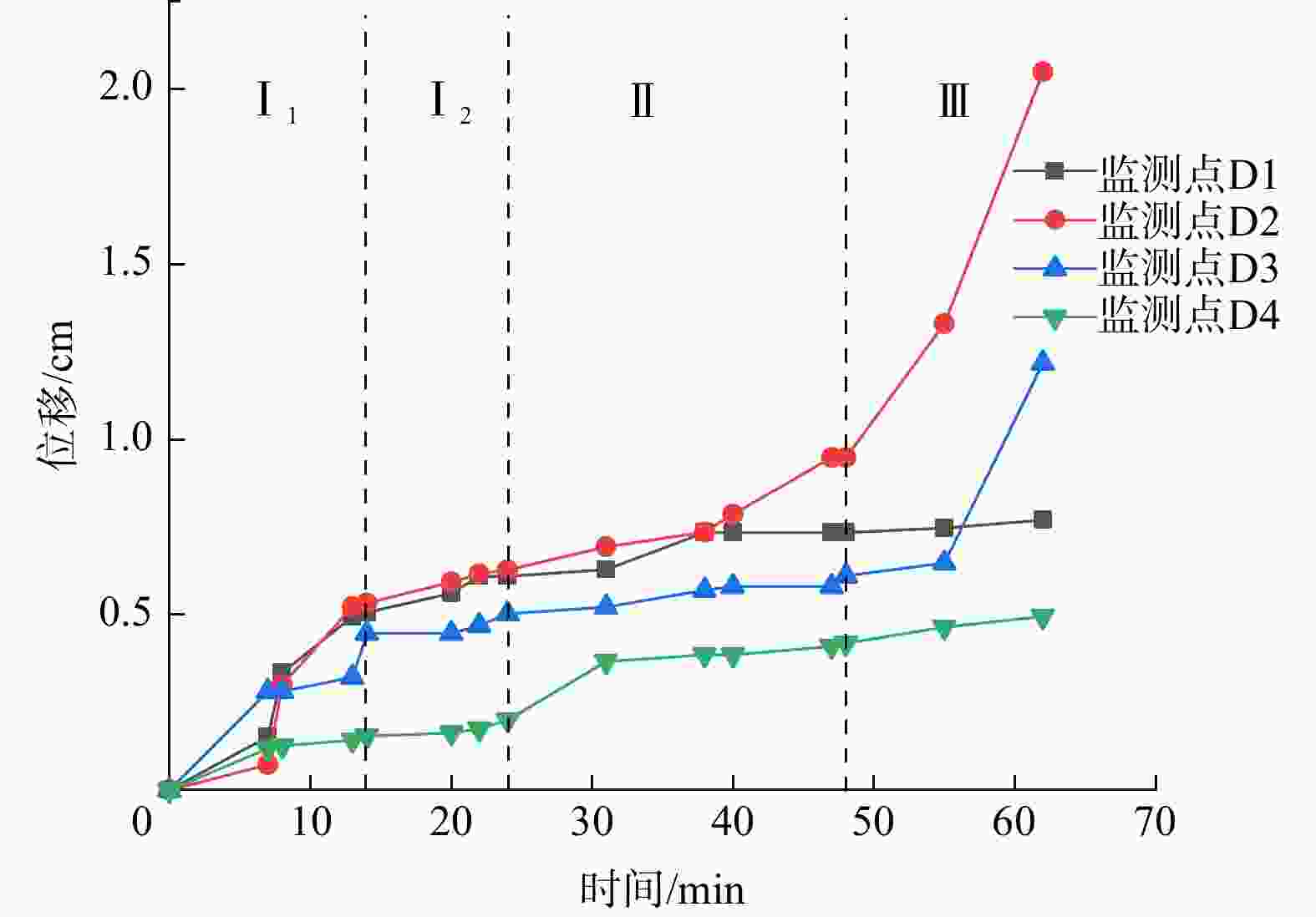
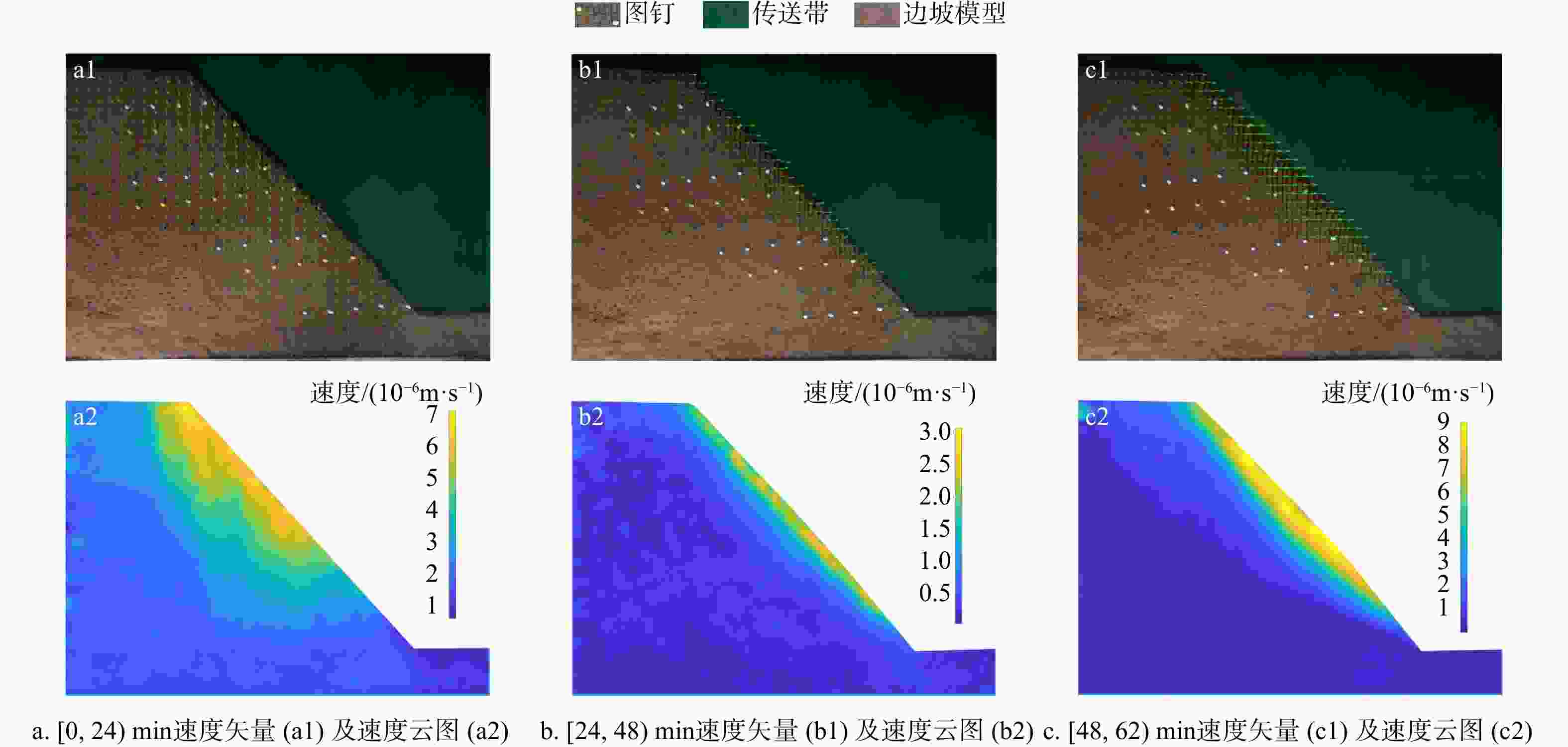
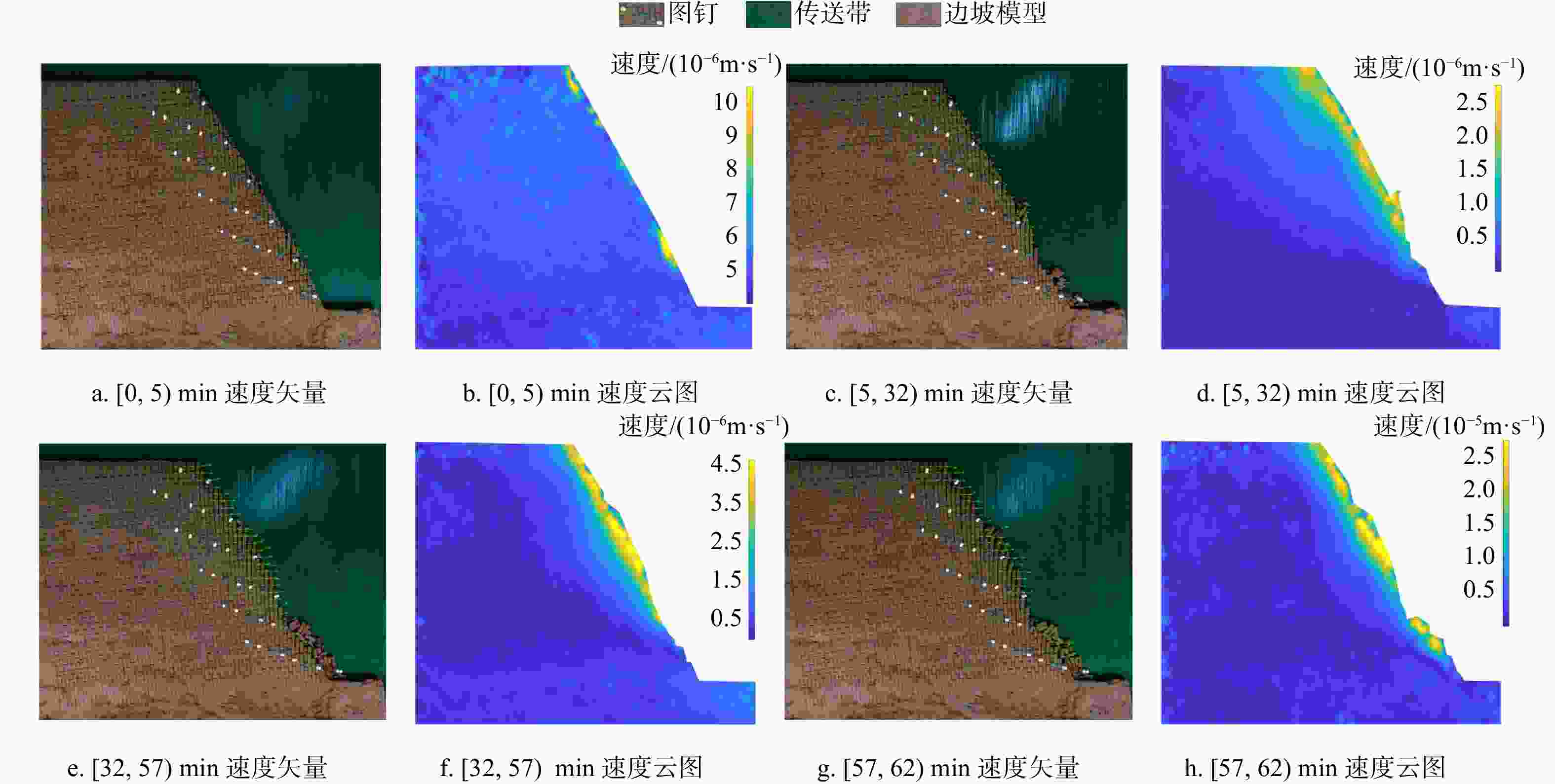
Results The results show that: ①The main toppling failure mode of the steep bedding rock slope is the tensile-toppling type. In the early stage of evolution, the rock mass at the foot of the slope is the first to topple due to stress concentration, and gradually develops from the front edge of the slope body to the middle and back. The rock mass in the middle of the slope surface also gradually changes from the forward dip to the upright to the reverse dip state, and accelerates to bend and topple towards the free surface under the action of gravity. When the deformation of rock mass reaches a certain extent, it will fracture along the maximum bending part or structural plane, and eventually slip along the tensile fracture plane or even collapse directly. ②By comparing the slope parameters and deformation characteristics of the test models, the 7 groups of model slopes are roughly divided into 3 categories: near-vertical bedding rock gentle slope, steep dip bedding rock steep slope, near-vertical bedding rock steep slope. Compared with slope Angle, the rock layer dip Angle has more influence on the toppling deformation and failure of the steep bedding rock slope. The gently inclined structural plane that is not perpendicular to the plane is more likely to cause the toppling deformation and failure of the steep bedding slope than the one perpendicular to the plane, and the scale of toppling deformation and failure is larger when the slope body develops the inward structural plane compared with the outward inclined structural plane. ③From the perspective of deformation stage, the deformation evolution process of slope is divided into initial deformation stage, toppling deformation stage and toppling failure stage. ④The toppling deformation and failure process of steep bedding rock slope is divided into stress adjustment stage, flexural-creep stage, flexural-sliding stage and toppling-sliding-collapse fracture stage from the mechanism. According to the deformation degree of the toppling area, the deformed slope can be divided into three zones: a strong toppled zone, a weak toppled zone, and a stable zone.
Conclusion The research results can provide reference for the research of the evolution process, toppling mode, toppling deformation and failure mechanism of steep bedding rock slope.
-
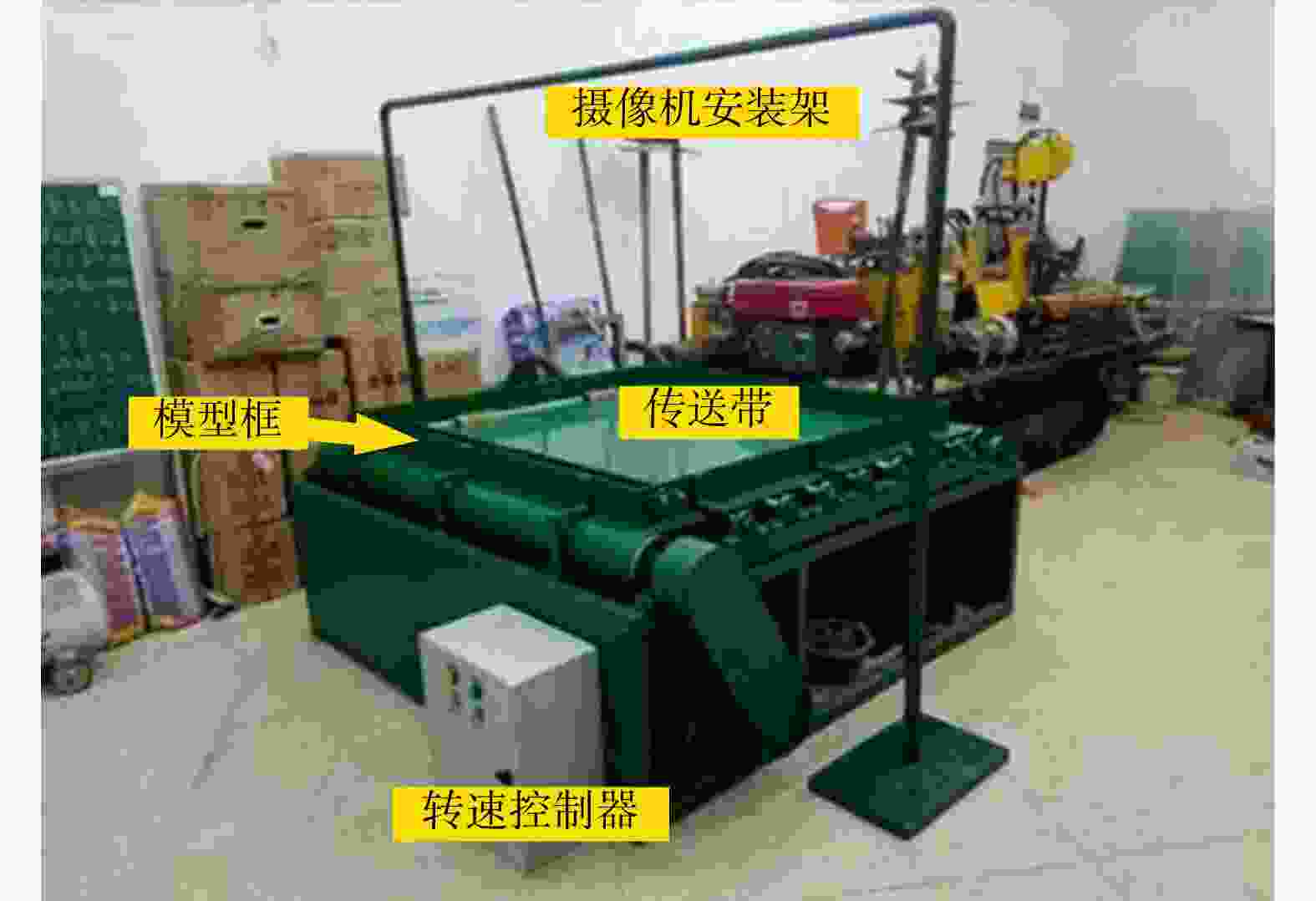
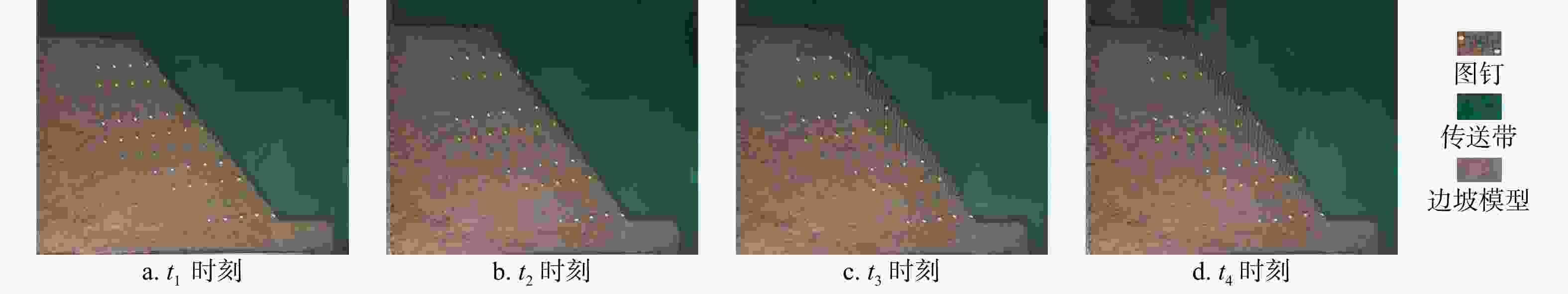
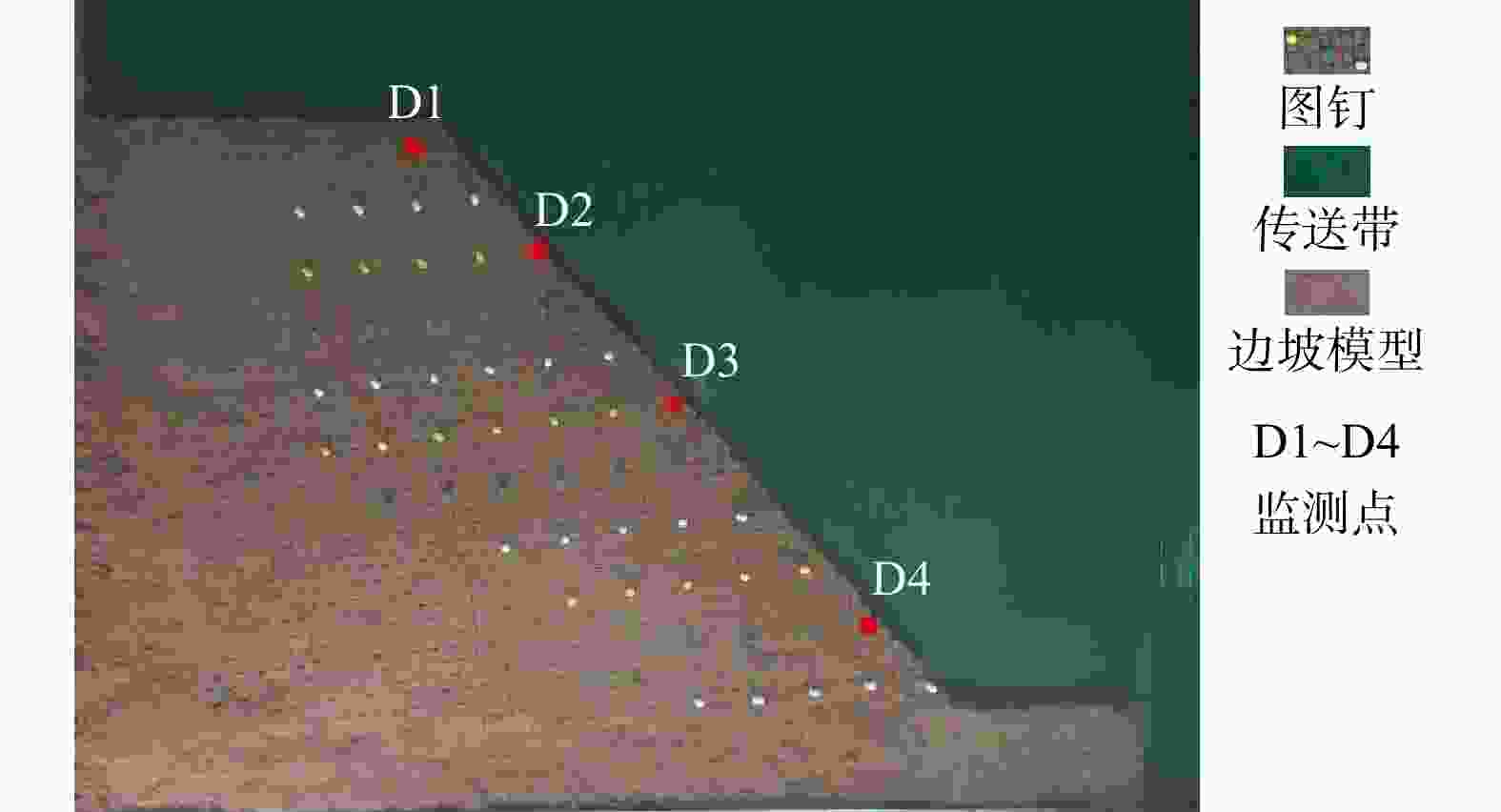
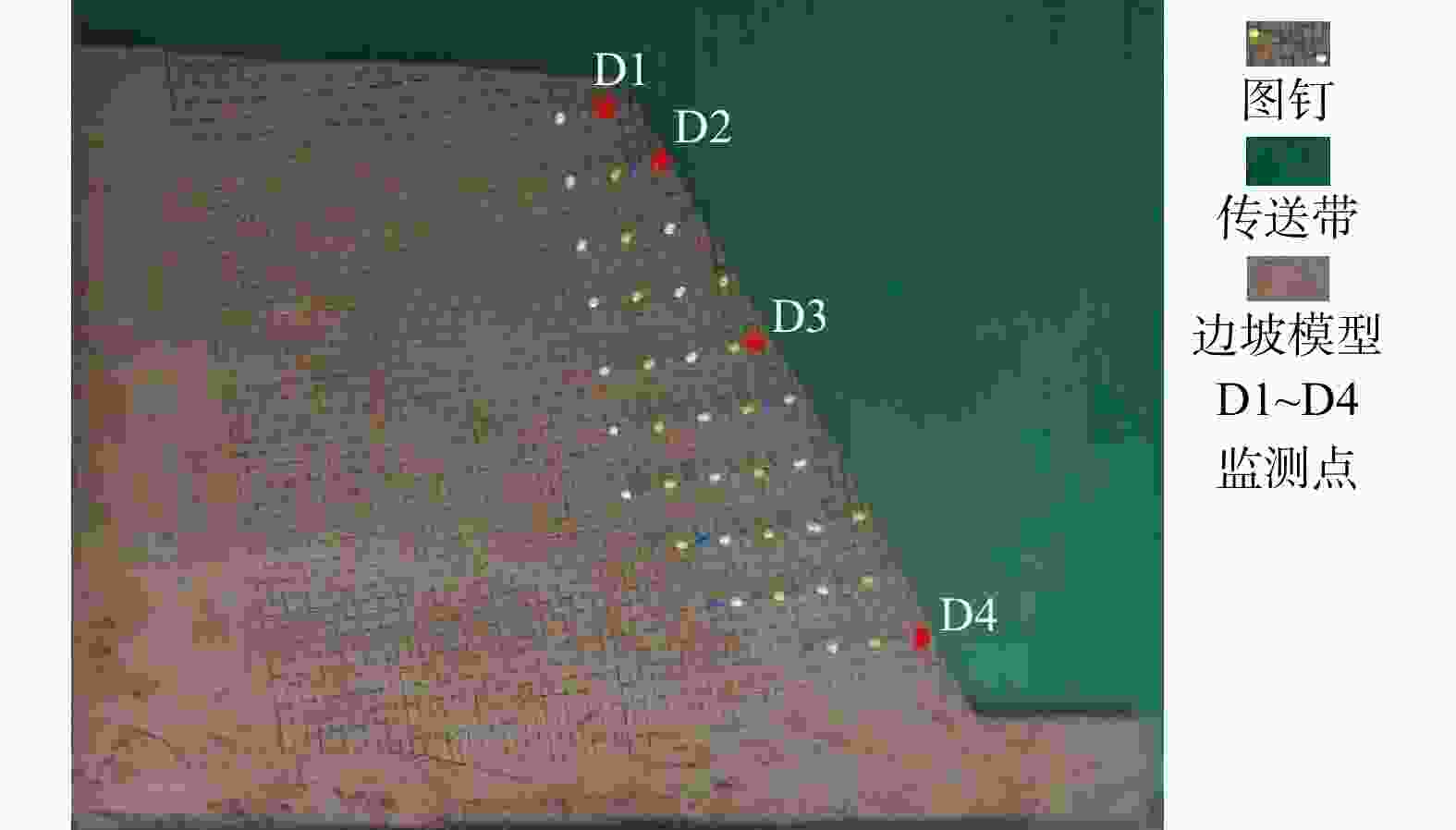
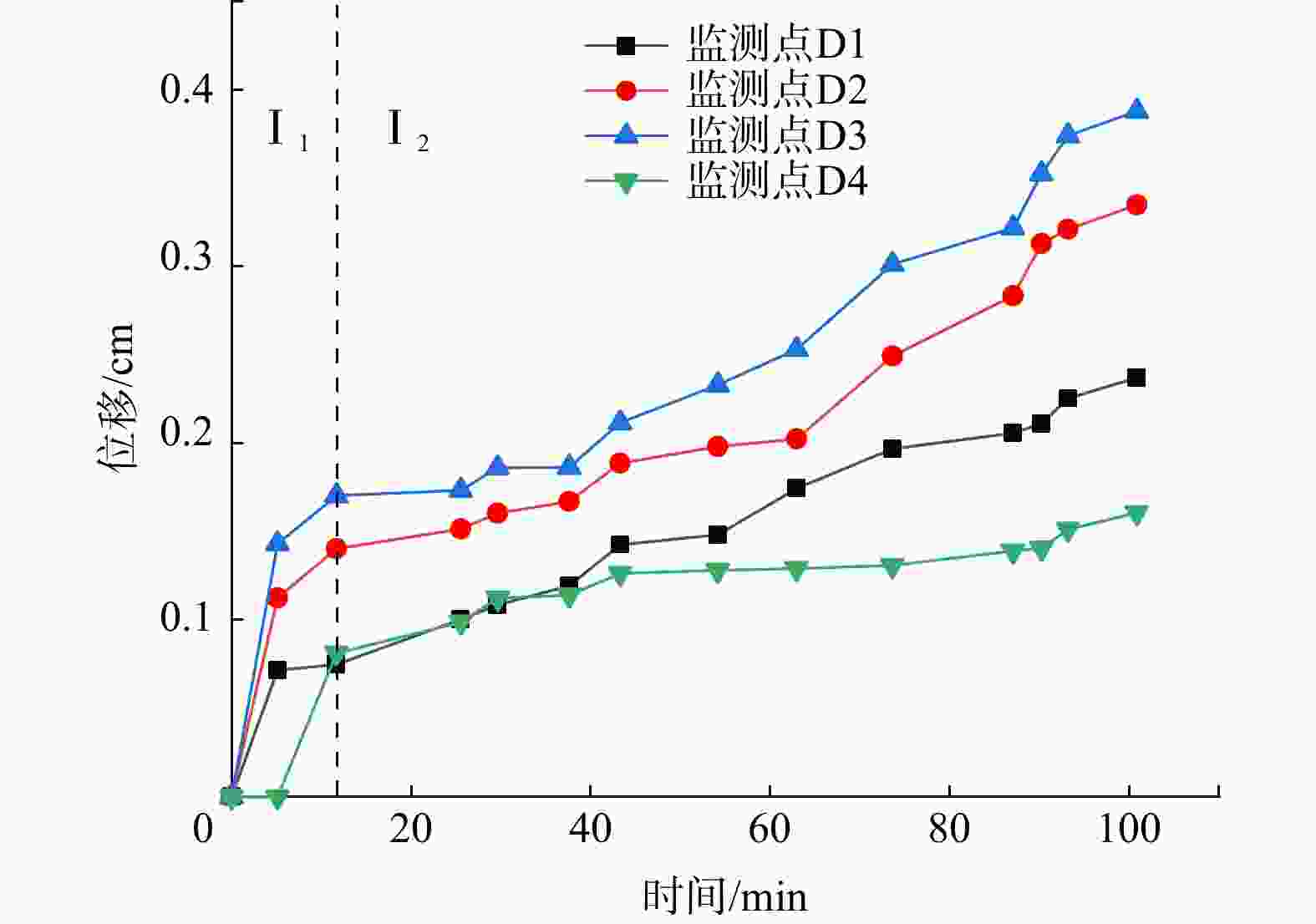
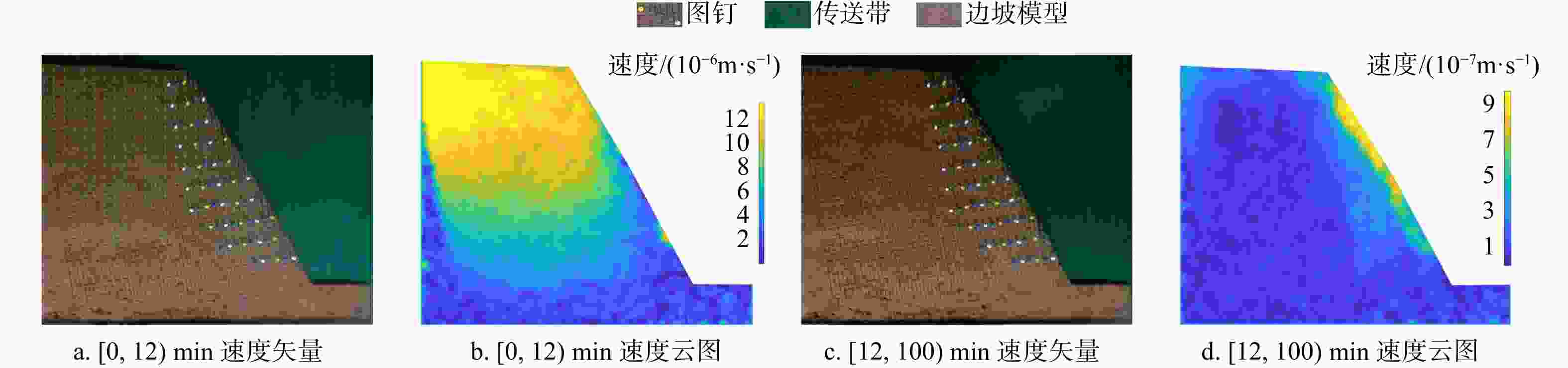
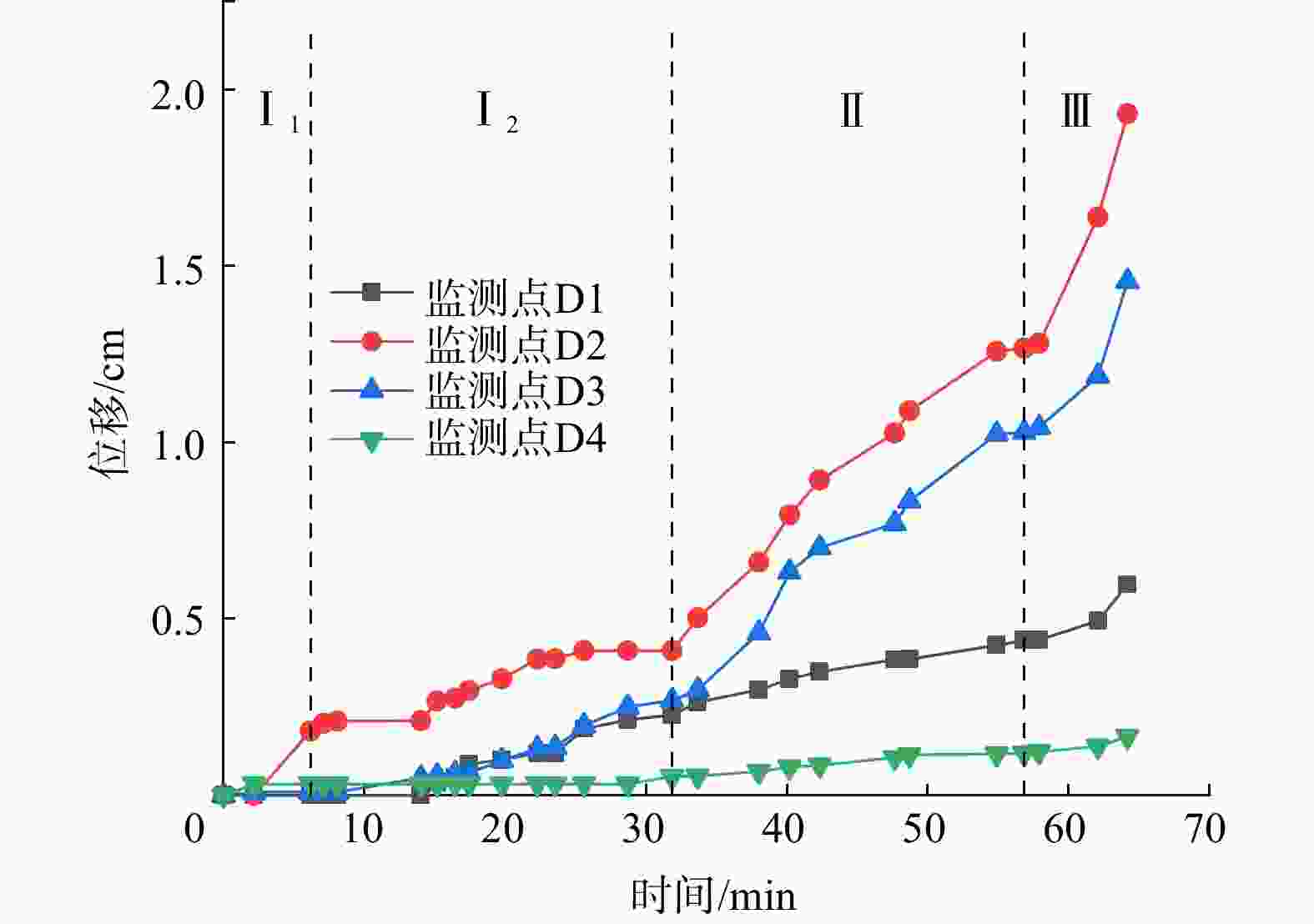
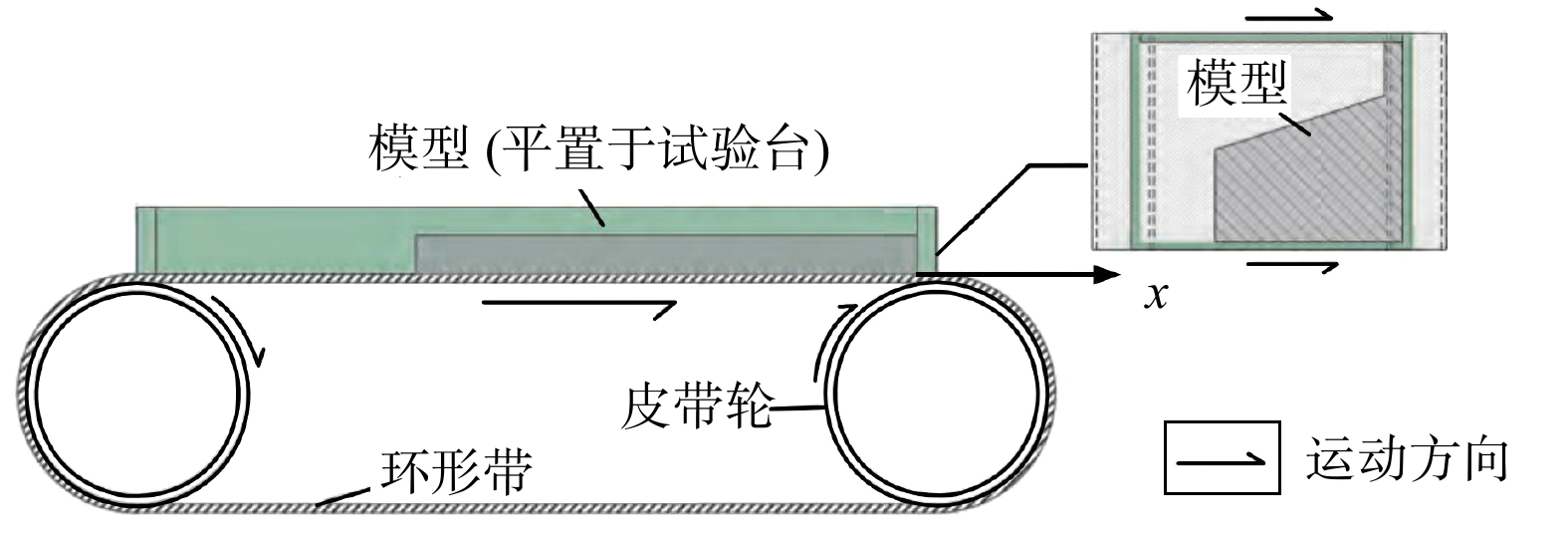
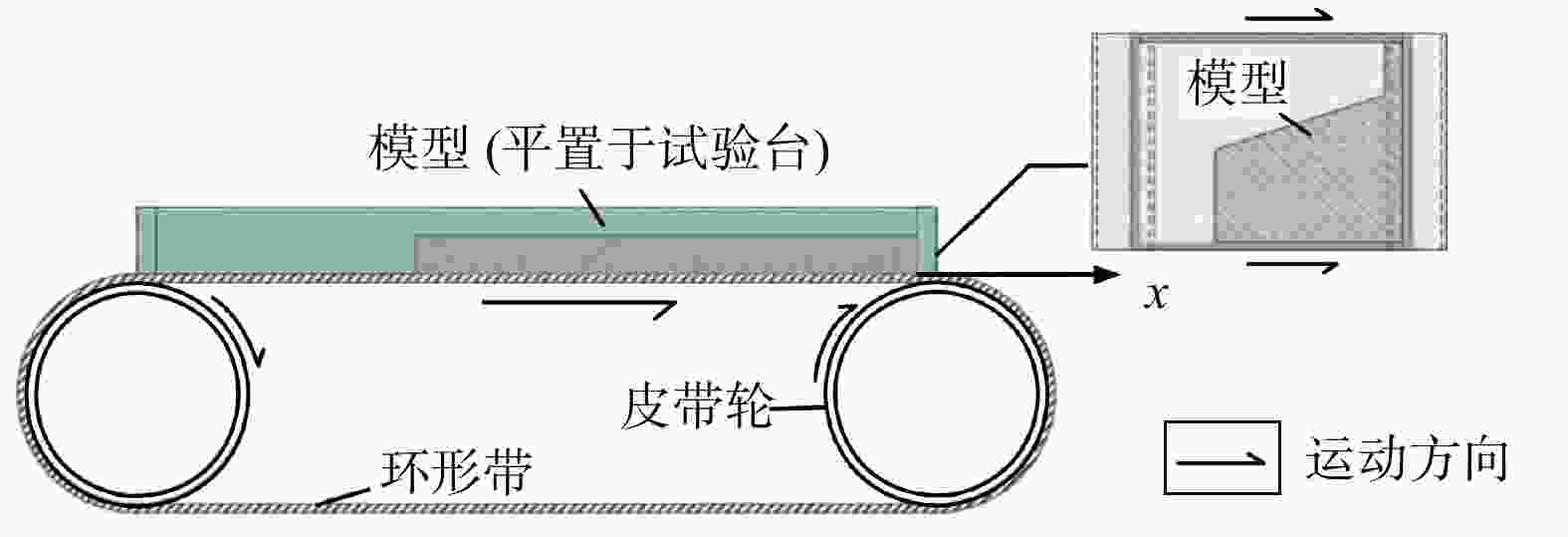
图 1 底摩擦试验原理图[30]
Figure 1. Principle of bottom friction test
表 1 相似材料配比试验设计
Table 1. Experimental design of proportioning ratio of similar materials
试验组号 黏土∶石英砂质量比 黏土∶石膏质量比 1 1∶2 2∶1 2 1∶2 3∶1 3 1∶2 4∶1 4 1∶1 2∶1 5 1∶1 3∶1 6 1∶1 4∶1 7 2∶1 2∶1 8 2∶1 3∶1 9 2∶1 4∶1 表 2 模型材料与原型材料相似关系
Table 2. Similarity relationship between model materials and prototype materials
物理量 相似系数 比例因子 几何尺寸 CL(控制量) 500 密度 Cγ(控制量) 1.2 黏聚力 Cc = CLCγ 600 内摩擦角 Cφ(无次因量) 1 抗拉强度 $ C_{\sigma_{\mathrm{t}}} $ = CLCγ 600 弹性模量 CE = CLCγ 600 泊松比 Cμ(无次因量) 1 表 3 相似材料目标值与实际值
Table 3. Target values and actual values of similar materials
参数 密度
r/(g·cm−3)黏聚力
c/MPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)抗拉强度
σt/MPa弹性模量
E/GPa泊松比
μ板岩 2.60 1.55 30.1 3.4 8.08 0.27 目标值 2.17 0.0026 30.1 0.0057 0.0135 0.27 最佳相似材料 2.15 0.0029 29.1 0.0053 0.0107 0.30 理论相似比 1.20 600 1 600 600 1 实际相似比 1.21 534.5 1.03 641.5 755.1 0.9 表 4 研究区顺层倾倒变形体发育基本特征
Table 4. Basic characteristics of the development of toppling bedding deformation bodies in the study area
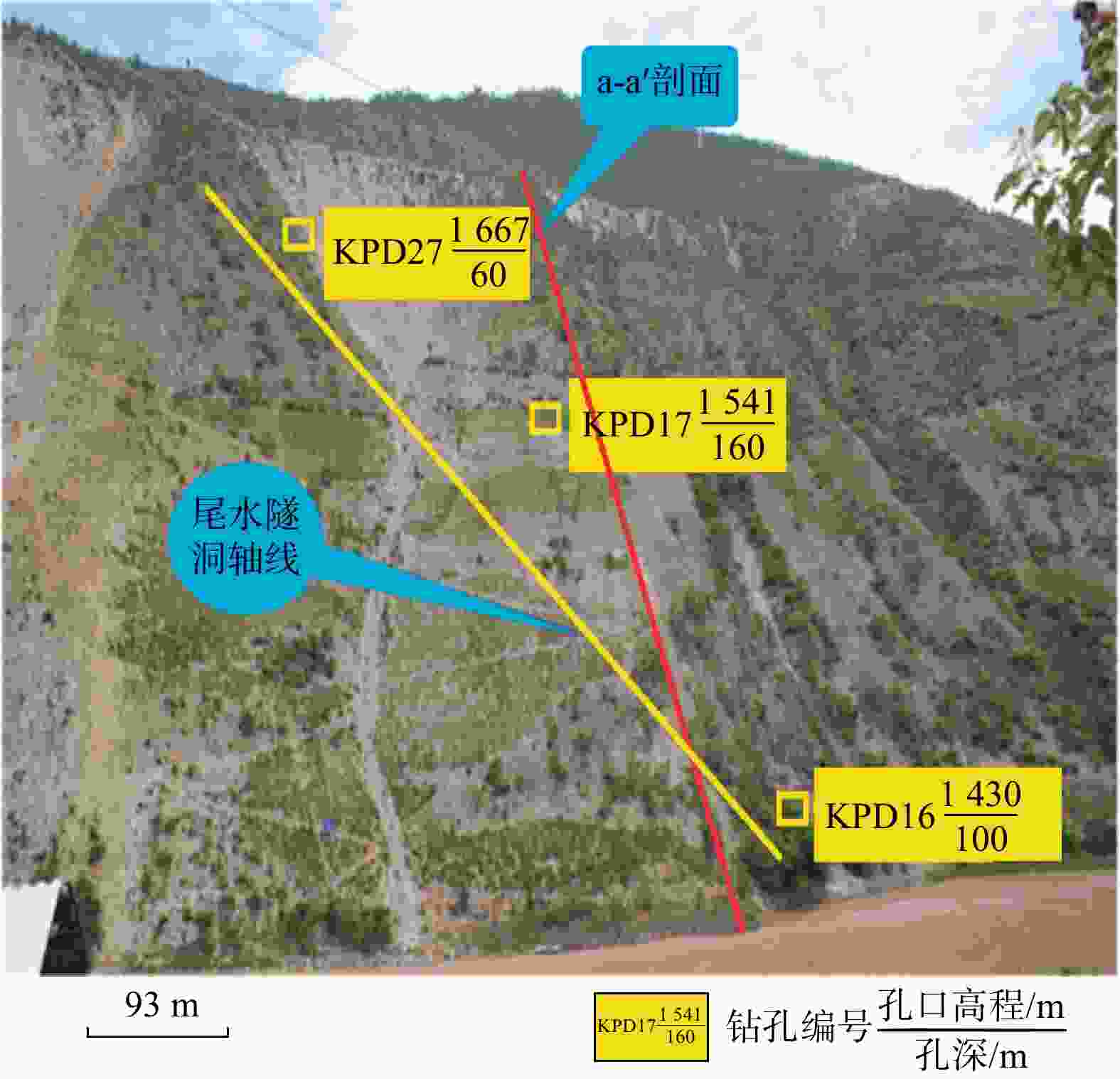
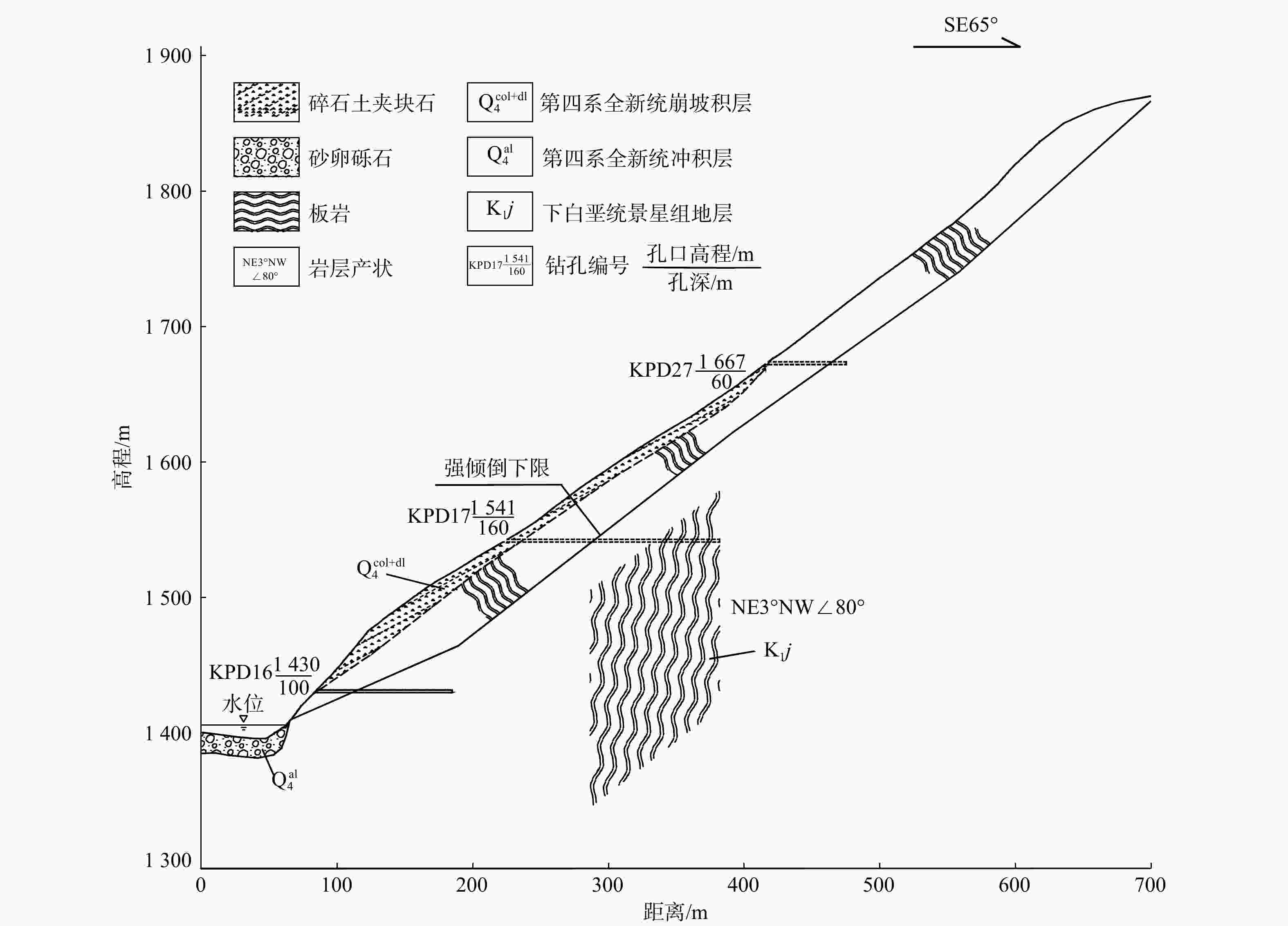
编号 灾害点或边坡 地质体状态 岩性组合 坡度α/(°) 岩层倾角β/(°) 坡高/m 倾倒深度/m 1 沧江桥滑坡体 滑坡 K1j板岩夹砂岩 30~40 70~85 >300 40~50 2 下坝址左岸堆积体 倾倒变形 K1j紫红色板岩、灰绿色板岩 40~50 75~80 300 60~80 3 上坝线左岸边坡 倾倒变形 K1j板岩、石英砂岩 50~60 80~85 400 50-80 4 中坝线左岸边坡 倾倒变形 K1j板岩、石英砂岩 48~56 80~85 >300 40~60 5 地面厂房后边坡 倾倒变形 K1j紫红色、灰绿色绢云母板岩 38~45 80~85 460 40~80 6 尾水隧洞出口边坡 倾倒变形 K1j板岩、石英砂岩 35~45 75~85 250~300 60~80 注:K1j为下白垩统景星组 表 5 研究区主要结构面分组及特征
Table 5. Groups and characteristics of the main rock discontinuities in the study area
类型 产状 宽度/cm 充填物、胶结情况及分布特征 层面 NW350°~NE10°SE(NW)∠75°~85° 多闭合 延伸长,广泛分布于坝址区 陡倾角裂隙 NW280°~290°NE(SW)∠75°~80° 0.1~0.3 多数充填岩屑,少量为泥质充填,面平直,延伸较长 缓倾角裂隙 NE5°~20°NW(SE)∠5°~25° 0.2~0.3 数量多,充填岩屑,少量泥质,泥钙质胶结,面平直,延伸短 缓倾角裂隙 NW275°~300°SW(NE)∠5°~25° 0.1~0.3 充填岩屑,少量泥质,泥钙质胶结,面平直,延伸短 -
[1] 丁戈媛,胡新丽. 大奔流顺层岩质滑坡溃屈型破坏力学机制研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2):186-190.DING G Y,HU X L. Mechanical mechanism of buckling failure of Dabenliu consequent bedding rockslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(2):186-190. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 王禹,冯霄,杜娟,等. 建设区顺层岩质滑坡地质力学演化模型:以万州铁峰乡麦地坪滑坡为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(5):43-51.WANG Y,FENG X,DU J,et al. Geomechanical evolution model of bedding rock landslides in construction areas:A case study of the Maidiping landslide in Tiefeng Town,Wanzhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(5):43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 黄润秋,李渝生,严明. 斜坡倾倒变形的工程地质分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(5):1165-1181.HUANG R Q,LI Y S,YAN M. The implication and evaluation of toppling failure in engineering geology practice[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(5):1165-1181. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] CRUDËN D M. Limits to common toppling:Reply[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1991,28(3):465. doi: 10.1139/t91-058 [5] 邱俊,任光明,王云南. 层状反倾−顺倾边坡倾倒变形形成条件及发育规模特征[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(增刊2):513-524.QIU J,REN G M,WANG Y N. Characteristics of forming conditions and development scale of toppling in anti-dip and dip stratified slopes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(S2):513-524. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] SAGASETA C,SáNCHEZ J M,CAñIZAL J. A general analytical solution for the required anchor force in rock slopes with toppling failure[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2001,38(3):421-435. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00011-9 [7] LIU C H,JAKSA M B,MEYERS A G. Improved analytical solution for toppling stability analysis of rock slopes[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2008,45(8):1361-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.01.009 [8] ZHENG Y,CHEN C X,LIU T T,et al. Study on the mechanisms of flexural toppling failure in anti-inclined rock slopes using numerical and limit equilibrium models[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,237:116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.02.006 [9] ZHAO W H,ZHANG C Q,JU N P. Identification and zonation of deep-seated toppling deformation in a metamorphic rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(3):1981-1997. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-02027-y [10] XIA M,REN G M,TIAN F. Mechanism of an ancient river-damming landslide at Batang Hydropower Station,Jinsha River Basin,China[J]. Landslides,2023,20(10):2213-2226. doi: 10.1007/s10346-023-02124-5 [11] TAMRAKAR N K,YOKOTA S,OSAKA O. A toppled structure with sliding in the Siwalik Hills,midwestern Nepal[J]. Engineering Geology,2002,64(4):339-350. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00095-3 [12] 王飞,唐辉明. 雅砻江上游互层斜坡倾倒变形破坏机制与演化[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(6):1501-1508.WANG F,TANG H M. Mechanism and evolotion of toppling in interbedded slopes at upstream of Yalong River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(6):1501-1508. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 周洪福,聂德新,李树武. 澜沧江某水电工程大型倾倒变形体边坡成因机制[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2012,32(3):48-52.ZHOU H F,NIE D X,LI S W. Integrated analysis of formation mechanism for large-scale toppling rock mass of a hydropower station on Lancangjiang River[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2012,32(3):48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 李长冬,唐辉明,胡新丽,等. 岩石相似材料变形与强度特性及数值模拟研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2008,27(6):98-101.LI C D,TANG H M,HU X L,et al. Deformation and strength characteristics and numerical simulation of rock similar material[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2008,27(6):98-101. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 许艺林,李远耀,李思德,等. 库水位下降叠加降雨作用时堆积层滑坡渗流−变形机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):216-228.XU Y L,LI Y Y,LI S D,et al. Seepage-deformation mechanism of colluvial landslides under the action of reservoir water level decline and rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):216-228. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] HE J X,QI S W,ZHAN Z F,et al. Seismic response characteristics and deformation evolution of the bedding rock slope using a large-scale shaking table[J]. Landslides,2021,18(8):2835-2853. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01682-w [17] LI L Q,JU N P,ZHANG S,et al. Shaking table test to assess seismic response differences between steep bedding and toppling rock slopes[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(1):519-531. doi: 10.1007/s10064-017-1186-1 [18] ZANG M D,YANG G X,DONG J Y,et al. Experimental study on seismic response and progressive failure characteristics of bedding rock slopes[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2022,14(5):1394-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.06.004 [19] ZHU C,HE M C,KARAKUS M,et al. Investigating toppling failure mechanism of anti-dip layered slope due to excavation by physical modelling[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2020,53(11):5029-5050. doi: 10.1007/s00603-020-02207-y [20] 谭明健,周春梅,孙东,等. 软硬互层顺层岩质边坡破坏试验[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):274-281.TAN M J,ZHOU C M,SUN D,et al. Failure experiment of soft-hard interlayer bedding rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):274-281. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] ZHANG B C,NING Y B,TANG H M,et al. Study on the evolutionary process of interbedded anti-inclined slope block-flexure toppling in the upper Yalong River[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(7):240. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03223-2 [22] DING B D,HAN Z Y,ZHANG G C,et al. Flexural toppling mechanism and stability analysis of an anti-dip rock slope[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2021,54(8):3721-3735. doi: 10.1007/s00603-021-02435-w [23] 杨登芳,胡新丽,徐楚,等. 基于物理模型试验的多层滑带滑坡变形演化特征[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):300-308.YANG D F,HU X L,XU C,et al. Deformation and evolution characteristics of landslides with multiple sliding zones based on physical model test[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):300-308. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 宋娅芬,陈从新,郑允,等. 缓倾软硬岩互层边坡变形破坏机制模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(2):487-494.SONG Y F,CHEN C X,ZHENG Y,et al. Model experimental study of deformation and failure mechanism of low-angled slopes with interbedding of soft and hard rocks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(2):487-494. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 李任杰,胡富杭,石豫川,等. 基于底摩擦试验的硬岩岩质边坡变形过程及破坏机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):145-152.LI R J,HU F H,SHI Y C,et al. A study of deformation process and failure mechanism of hard rock slope based on the bottom friction test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):145-152. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 孙书伟,李圆,杨晓锐,等. 不同岩层倾角顺倾层状岩质边坡破坏机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2024,43(7):1607-1620.SUN S W,LI Y,YANG X R,et al. Study on the failure mechanism of rock slopes with dipped layered structures under various rock dip conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2024,43(7):1607-1620. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 张令非,陈忠辉,唐岳松. 含弱层边坡分区滑动破坏模式及演化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(6):1145-1154.ZHANG L F,CHEN Z H,TANG Y S. Study on regional sliding failure modes and evolution regularity of slopes with weak layers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(6):1145-1154. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 宁奕冰,唐辉明,张勃成,等. 基于正交设计的岩石相似材料配比研究及底摩擦物理模型试验应用[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(6):2009-2020.NING Y B,TANG H M,ZHANG B C,et al. Investigation of the rock similar material proportion based on orthogonal design and its application in base friction physical model tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(6):2009-2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] ZHANG L F,CHEN Z H,NIAN G Q,et al. Base friction testing methodology for the deformation of rock masses caused by mining in an open-pit slope[J]. Measurement,2023,206:112235. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.112235 [30] 姚晔,章广成,陈鸿杰,等. 反倾层状碎裂结构岩质边坡破坏机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(2):365-381.YAO Y,ZHANG G C,CHEN H J,et al. Study on the failure mechanisms of counter-tilt rock slopes with layered cataclastic structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(2):365-381. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] BENG X T,ZHANG G C,YANG Y C,et al. Flexural toppling characteristics of anti-dip soft rock slope with base friction test[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-03037-8 [32] PATEL A,DHARPURE J K,SNEHMANI,et al. Estimating surface ice velocity on Chhota Shigri glacier from satellite data using particle image velocimetry (PIV) technique[J]. Geocarto International,2019,34(4):335-347. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2017.1404142 [33] 阮博阳,杨盼瑞,郭会荣,等. 基于PIV技术研究不连通孔隙中残余DNAPL的溶解速率影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):241-249.RUAN B Y,YANG P R,GUO H R,et al. Factors influencing the dissolution rate of residual DNAPL in unconnected pores based on PIV technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):241-249. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] CHEN G Q,LI L,ZHAO C,et al. Acceleration characteristics of a rock slide using the particle image velocimetry technique[J]. Journal of Sensors,2016,2016(1):2650871. [35] KANG S,ZHAO Q H,LIU C W. Calculative width of pile foundation on slope based on particle image velocimetry (PIV)[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2020,2020(1):7084791. doi: 10.1155/2020/7084791 [36] TERWISSCHA VAN SCHELTINGA R C,COCO G,FRIEDRICH H. Sand particle velocities over a subaqueous dune slope using high-frequency image capturing[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2019,44(10):1881-1894. doi: 10.1002/esp.4617 [37] WANG D Y,ZHU H H,WANG B J,et al. Performance evaluation of buried pipe under loading using fiber Bragg grating and particle image velocimetry techniques[J]. Measurement,2021,186:110086. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110086 [38] WANG Z,LI C,DING X M. Application of transparent soil model tests to study the soil-rock interfacial sliding mechanism[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(4):935-943. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-5083-2 [39] 王东, 刘金尧, 李广贺, 等. 露天矿顺倾软岩边坡内排追踪压帮治理工程:以贺斯格乌拉南露天煤矿首采区南帮为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(3):80-87.WANG D, LIU J Y, LI G H, et al. Open-pit mine soft rock slope internal row tracking pressure side control engineering: A case study at the south side of the first mining area of Hesigewula south open-pit coal mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(3):80-87. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 程雨柯, 李亚虎, 夏金梧, 等. 无人机技术在超高陡边坡危岩体半自动识别中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(1):143-154.CHENG Y K, LI Y H, XIA J W, et al. Application UAV technology semi-automatic identification dangerous rock masses on ultra-high steep slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(1):143-154. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 曾启强, 王立朝, 刘伟, 等. 广州地区岩质边坡崩塌影响范围计算方法初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(5):159-168.ZENG Q Q, WANG L C, LIU W, et al. Calculation methods of the collapse influence range of a simple rock slope in the Guangzhou area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(5):159-168. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 汪鸣飞,章广成,包刘磊,等. 顺层陡倾岩质边坡变形机理探究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2021,28(5):107-120.WANG M F,ZHANG G C,BAO L L,et al. Research on deformation mechanism of steep bedding rock slope[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2021,28(5):107-120. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] LIU M,LIU F Z,HUANG R Q,et al. Deep-seated large-scale toppling failure in metamorphic rocks:a case study of the Erguxi slope in southwest China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2016,13(12):2094-2110. doi: 10.1007/s11629-015-3803-4 -




 下载:
下载: