Failure probability simulation of passive protection net for collapses and rockfalls in typical karst area
-
摘要:
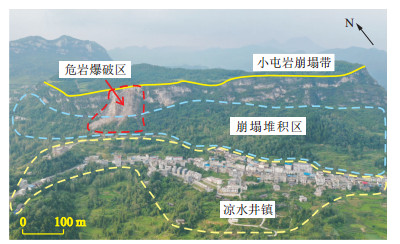
贵州省位于我国西南地区, 多山地丘陵, 是典型的喀斯特地形地貌区, 崩塌、滑坡等地质灾害频发。思南县小屯岩崩塌带上现存危岩体方量大, 裂隙、凹岩腔、溶蚀孔洞等发育。为研究岩溶典型区崩塌落石被动防护网失效概率, 通过高精度实景建模技术, 构建崩塌带三维模型, 进行崩塌落石运动过程模拟, 根据现场调查、无人机航拍和数值模拟结果, 选择合适的位置布设落石被动防护网。基于落石粒径大小识别, 选取不同粒径大小的落石, 进行落石被动防护网拦截效果模拟, 计算落石被动防护网失效概率。结果表明: 13种粒径落石突破概率各不相同, (0.25, 2.25] m粒径落石拦截效果良好, 但落石被动防护网拦截率不能达到百分之百; 落石粒径大于2.25 m, 被动防护网出现失效现象, 故将2.25 m粒径的落石为小屯岩崩塌带下被动防护网的设计上限。根据计算, 所有粒径落石经被动防护网拦截后的失效概率低于5%, 属可接受范畴。研究成果为小屯岩崩塌带的落石防护措施提供了有力的参考依据, 对保护岩溶地区山区人民的生命安全和财产安全具有重要意义。
Abstract:Guizhou Province is located in Southwest of China, with many mountains and hills, and is a typical karst topography and geomorphology area with frequent geological disasters such as collapses and landslides. The existing dangerous rock mass in the Xiaotunyan collapse zone in Sinan County has large range and volume, and fissures, concave cavities, and solution caves have developed.
Objective In order to study the failure probability of passive protection nets for rockfalls in typical karst areas.
Methods A three-dimensional model of the collapse zone through high-precision realistic modeling technology was constructed, by which the movement process of collapsed falling rocks was simulated. According to the results of the field investigation, aerial photography of the unmanned aerial vehicle and numerical simulation, an appropriate rockfall location layout for the passive protection net was selected. And based on the identification of the rockfall particle size, the different rockfall particle sizes were selected to simulate the interception effect of the passive protection net, then the failure probability of the passive protective net can be calculated.
Results The results show that the rockfall breakthrough rates of 13 particle sizes vary: the interception effect of small to medium sized falling rocks with particle sizes ranging from 0.25 m to 2.25 m is effective, but the interception rate of passive protection net cannot reach 100%. When the particle size is larger than 2.25 m, the passive protection net fails, that is the upper limit of the design of the passive protection net under the Xiaotunyan collapse zone is the 2.25 m particle size of rockfall. According to the calculation, the failure probability of all rockfall particle sizes intercepted by the passive protection net is less than 5%, which is within the acceptable scope.
Conclusion The research results provide a reference for rockfall protection measures in the Xiaotunyan collapse zone and are of great significance for the protection of life and property safety for people in karst mountainous areas.
-
表 1 坡面计算参数赋值
Table 1. Slope calculation parameter assignment
坡面变型 法向恢复系数 切向恢复系数 滑动或滚动摩擦系数 裸岩-灰岩 0.65 0.88 0.35 碎石堆积区 0.45 0.75 0.70 覆土区 0.35 0.60 0.55 道路住房区 0.50 0.80 0.55 -
[1] 胡厚田. 崩塌与落石[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1989.HU H T. Collapse and falling rocks[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 1989. (in Chinese) [2] CHAU K T, WONG R H C, WU J J. Coefficient of restitution and rotational motions of rockfall impacts[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002, 39(1): 69-77. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00016-3 [3] AZZONI A, LA BARBERA G, ZANINETTI A. Analysis and prediction of rockfalls using a mathematical model[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1995, 32(7): 709-724. [4] BOZZOLO D, PAMINI R. Simulation of rock falls down a valley side[J]. Acta Mechanica, 1986, 63(1): 113-130. [5] 张路青, 杨志法, 许兵. 滚石与滚石灾害[J]. 工程地质学报, 2004, 12(3): 225-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.03.001ZHANG L Q, YANG Z F, XU B. Rock falls and rock fall hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004, 12(3): 225-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.03.001 [6] 丁斌, 孟永旭, 裴晓东. 尼泊尔某项目滚石灾害的工程地质调查与评价[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(2): 554-563. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202102025.htmDING B, MENG Y X, PEI X D. Engineering geological investigation and assessment on rockfall hazard of one project in Nepal[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(2): 554-563. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202102025.htm [7] WYLLIE D C, MAH C W. Rock slope engineering: Civil and mining[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. [8] CHEN T J, ZHANG G C, XIANG X. Research on rockfall impact process based on viscoelastic contact theory[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 173: 104431. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104431 [9] PALMA B, PARISE M, REICHENBACH P, et al. Rockfall hazard assessment along a road in the Sorrento Peninsula, Campania, southern Italy[J]. Natural Hazards, 2012, 61(1): 187-201. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9899-0 [10] 何宇航, 裴向军, 梁靖, 等. 基于Rockfall的危岩体危险范围预测及风险评价: 以九寨沟景区悬沟危岩体为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(4): 24-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202004003.htmHE Y H, PEI X J, LIANG J, et al. Risk assessment and range prediction of dangerous rockmass based on rockfall: A case study of the Xuangou collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(4): 24-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202004003.htm [11] SCHILIRÒ L, ROBIATI C, SMERAGLIA L, et al. An integrated approach for the reconstruction of rockfall scenarios from UAV and satellite-based data in the Sorrento Peninsula (southern Italy)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 308: 106795. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106795 [12] YAN J H, CHEN J P, TAN C, et al. Rockfall source areas identification at local scale by integrating discontinuity-based threshold slope angle and rockfall trajectory analyses[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 313: 106993. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.106993 [13] 王军义, 梁风, 彭雄武, 等. 基于GIS技术的单体崩塌危险范围评价方法研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2023, 31(1): 188-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202301019.htmWANG J Y, LIANG F, PENG X W, et al. Study on assessment method of single collapse risk range based on GIS technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(1): 188-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202301019.htm [14] FANOS A M, PRADHAN B. A novel rockfall hazard assessment using laser scanning data and 3D modelling in GIS[J]. CATENA, 2019, 172: 435-450. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.012 [15] 王东坡, 何启维, 刘彦辉, 等. 滚石冲击改进型开口帘式网耗能机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(12): 3356-3365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202112015.htmWANG D P, HE Q W, LIU Y H, et al. Research on the energy dissipation mechanism of rockfall impacts on the improved rockfall attenuator barrier[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(12): 3356-3365. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202112015.htm [16] THOENI K, GIACOMINI A, LAMBERT C, et al. A 3D discrete element modelling approach for rockfall analysis with drapery systems[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2014, 68: 107-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.008 [17] 刘冀昆, 杨晓琳, 王成虎. S-SARⅡ技术的崩塌临灾应急监测原理及其应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 42-51. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220495LIU J K, YANG X L, WANG C H. Principle and application of S-SARⅡ technology for collapse emergency monitoring[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 42-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220495 [18] 庞鑫, 袁明, 卢渊, 等. 基于无人机LiDAR仿地飞行技术的高陡边坡危岩体快速识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 21-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220427PANG X, YUAN M, LU Y, et al. Rapid identification method for the dangerous rock mass of a high-steep slope based on UAV LiDAR and ground imitation flight[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220427 [19] 马显东, 周剑, 张路青, 等. 基于崩塌滚石运动特征的防护网动态响应规律[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(12): 4559-4573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202212017.htmMA X D, ZHOU J, ZHANG L Q, et al. Dynamic response laws of flexible rockfall barriers based on movement characteristics of rockfall[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(12): 4559-4573. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202212017.htm [20] SARRO R, RIQUELME A, GARCÍA-DAVALILLO J, et al. Rockfall simulation based on UAV photogrammetry data obtained during an emergency declaration: Application at a cultural heritage site[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(12): 1923. doi: 10.3390/rs10121923 [21] 彭双麒, 柯灵, 郑体, 等. 基于图像识别的碎屑流颗粒分布特征及碎屑流与房屋相互作用探究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 226-235. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0622PENG S Q, KE L, ZHENG T, et al. Particle distribution characteristics of rock avalanche and the interaction between rock avalanche and houses based on image recognition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 226-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0622 [22] 王颂, 张路青, 周剑, 等. 青藏铁路设兴村段崩塌特征分析与运动学模拟[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(4): 784-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202004012.htmWANG S, ZHANG L Q, ZHOU J, et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along Shexing village section of Qinghai-Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(4): 784-792. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202004012.htm [23] SINGH A K, KUNDU J, SARKAR K, et al. Impact of rock block characteristics on rockfall hazard and its implications for rockfall protection strategies along Himalayan highways: A case study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(7): 5347-5368. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02288-1 [24] WANG D, BI Y, ZHOU L, et al. Experimental study on physical model of waste tennis ball-sand composite shed cushion under rockfall impact[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(5): 193. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02643-w [25] YAN P, ZHANG J H, KONG X Z, et al. Numerical simulation of rockfall trajectory with consideration of arbitrary shapes of falling rocks and terrain[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 122: 103511. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103511 [26] JIANG N, LI H B, LIU M S, et al. Quantitative hazard assessment of rockfall and optimization strategy for protection systems of the Huashiya cliff, Southwest China[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2020, 11(1): 1939-1965. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2020.1819445 [27] 阳友奎, 周迎庆, 姜瑞琪, 等. 坡面地质灾害柔性防护的理论与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.YANG Y K, ZHOU Y Q, JIANG R Q, et al. Theory and practice of flexible protection against slope geological hazards[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: