Genesis of garnet in pegmatite and its implication for Nb-Ta mineralization in the northwestern margin of the Mufushan granite (central Jiangnan Orogen): Comparison from mineralized and unmineralized pegmatites
-
摘要:
江南造山带中段幕阜山地区已成为我国重要的稀有金属资源基地之一。断峰山地区伟晶岩型铌钽矿床是幕阜山复式花岗岩体西北缘唯一的大型矿床,其成因及物理化学条件不明确。新发现的微斜长石伟晶岩型铌钽矿化脉体中铌钽铁矿、石榴子石和电气石共生,其中石榴子石的成因研究可为该类型Nb-Ta成矿作用研究提供良好的制约。以断峰山地区成矿与未成矿2种微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石为研究对象,进行了背散射电子(BSE)和阴极发光(CL)微观结构观察、电子探针(EPMA)和激光电感耦合等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)原位微区主微量元素分析,探讨石榴子石成因及其对微斜长石伟晶岩成矿作用的指示。断峰山地区伟晶岩中的石榴子石均为岩浆成因,形成于中高温、中低压力环境,属于铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石(Alm48.61-Sps48.21)固溶体系列。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石以铁铝榴石为主(Sps42.56-Alm54.63),而未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石以锰铝榴石为主(Sps58.93-Alm37.18)。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石多与铌钽铁矿等共生,具有低的Mn、Nb和Ta元素含量,且由核部到边部Mn含量降低Fe含量增加,这可能是由于铌钽矿物的结晶导致,表明石榴子石中Nb、Ta、Fe、Mn等元素的演化关系可以指示幕阜山地区Nb-Ta成矿。
Abstract:Objective The Mufushan area, in the central Jiangnan Orogen, South China, has become one of the most significant rare metals resource bases in China. The Duanfengshan pegmatite-type Nb-Ta deposit is the only large-sized deposit in the northwestern margin of the Mufushan granitic batholith. However, its genesis and physicochemical conditions are still unclear. Niobium-tantalite, garnet and tourmaline coexist in the newly discovered Nb-Ta mineralized microcline pegmatite veins. Therefore, the study of garnet genesis can provide significant constraints for the Nb-Ta mineralization.
Methods This study focuses on garnets in the mineralized and unmineralized microcline pegmatite veins in the Duanfengshan area. Garnets were observed using cathodoluminescence (CL) and backscattered electron (BSE) imagery. The major and trace elements are determined by EPMA and LA-ICP-MS, and are used to discuss the genesis of garnet and the indication for Nb-Ta mineralization within microcline pegmatite veins.
Results These mineralogical and geochemical features suggest a magmatic origin for garnets within microcline pegmatite veins in the Duanfengshan area. Garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area formed in medium-high temperatures and medium-low pressures. Garnets in mineralized and unmineralized pegmatites both belong to the solid solution series of almandite-spssartite. Garnet in the mineralized pegmatites is dominated by almandite (Sps42.56 Alm54.63), whereas garnet in the unmineralized pegmatites is mainly characterized by spessartite (Sps58.93 Alm37.18).
Conclusion Garnets in mineralized pegmatites mostly coexist with columbite-tantalite, and have low Mn, Nb and Ta contents, as well as a decrease in Mn content and an increase in Fe content from the core to the rim. This mineralogical result is resulted by the crystallization of Nb-Ta minerals. It shows that the evolution relationship of Nb, Ta, Fe, Mn elements in garnet can indicate the pegmatite-type Nb-Ta mineralization in the Mufushan area.
-
石榴子石是一种成分和晶体都比较简单的等轴晶系岛状硅酸盐矿物,其化学通式为A3B2[SiO4]3,其中A位可由Fe2+,Mn2+,Ca2+和Mg2+占据,B位则由Al3+,Fe3+,Mn3+,Ti3+和Cr3+占据[1]。石榴子石存在着广泛的类质同象替代现象,主要是因为B位阳离子半径相近,易形成类质同象替代,而A位阳离子中Ca2+与Fe2+,Mn2+,Mg2+离子半径相差较大,很难发生类质同象。按照类质同象替代元素组合其可分为铁铝榴石和钙铁榴石两大系列[2],其中铁铝榴石系列包括镁铝榴石(Mg3Al2Si3O12)、铁铝榴石(Fe3Al2Si3O12)和锰铝榴石(Mn3Al2Si3O12);而钙铁榴石系列包括钙铝榴石(Ca3Al2Si3O12)、钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12)和钙铬榴石(Ca3Cr2Si3O12) [3]。伟晶岩是赋存稀有金属矿产的重要岩石类型之一[4],石榴子石作为花岗伟晶岩的典型副矿物之一,其主量和微量地球化学特征可以有效地反映成矿物质来源、岩浆演化及矿床成因等信息[5-7]。伟晶岩中石榴子石组分分带和包裹体组合可能是其生长历史和岩浆分异过程的指示物[8-9]。石榴子石地球化学特征及成因研究有助于了解伟晶岩演化过程,其富集的稀土元素丰度和配分模式被用作地质作用和地质年代学的地球化学示踪剂[10-11]。
我国最为重要的稀有金属矿床类型是花岗岩型和花岗伟晶岩型,其中花岗岩型又包括碱性花岗岩型和白云母花岗岩型[12-13],重要矿床包括巴尔哲和宜春414等大型Nb-Ta矿床。花岗伟晶岩型矿床主要分为Nb-Y-F(NYF)型和富含Li-Cs-Ta(LCT)型,特别是LCT型稀有金属矿床在我国广泛分布,如阿尔泰、甲基卡以及幕阜山地区均发育大型−超大型矿床。幕阜山地区是江南造山带中段重要组成部分,也是我国重要的稀有金属矿产资源基地之一[14-15]。目前已发现仁里−传梓源超大型、断峰山和虎形山等大型稀有金属矿床[14,16]。然而,前人工作主要集中在幕阜山南部的仁里−传梓源地区[16-21]。位于幕阜山复式岩体西北缘的断峰山铌钽矿床被确定为一大型伟晶岩型铌钽矿床[22],且被认为成矿潜力较大[23-25],但关于石榴子石成因及Nb-Ta等稀有金属成矿作用有待深入研究。李鹏等[26]报道断峰山钠长石伟晶岩白云母Ar-Ar坪年龄为(127.7 ± 0.9)Ma,祝明明等[27]测定了断峰山钠长石伟晶岩铌钽铁矿U-Pb年龄约为136 Ma。而新发现的铌钽矿化微斜长石伟晶岩型的锆石和独居石U-Pb年龄为(133 ± 2)~(131 ± 1)Ma [28]。此外,幕阜山复式岩体中也发育大量的未见稀有金属矿化的伟晶岩脉。成矿与未成矿伟晶岩脉中均发育不同粒径的石榴子石副矿物,石榴子石的成因研究可为对比研究稀有金属Nb-Ta成矿作用差异提供制约。因此,笔者选取断峰山地区成矿和未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石为研究对象,开展微观结构及微区主微量元素地球化学分析,确定其成因并对比分析其对稀有金属成矿作用的制约,为深入理解断峰山地区伟晶岩成矿机制提供矿物学依据。
1. 成矿地质背景
幕阜山复式花岗岩体位于湖北、湖南和江西三省交界处,大地构造位置上处于扬子地块与华夏地块过渡地区江南隆起带中段的幕阜山−九岭构造岩浆带(图1a)[29]。出露地层由老至新依次是新元古界、寒武系、奥陶系、志留系、白垩系−古近系和第四系。其中新元古界冷家溪群大面积出露于复式花岗岩体周缘,或呈孤立的残丘出露于花岗岩体中,其岩性主要为千枚状片岩和板岩[30]。幕阜山地区经历新元古代、晚侏罗世−早白垩世和早白垩世多期次岩浆活动。岩体出露面积约为
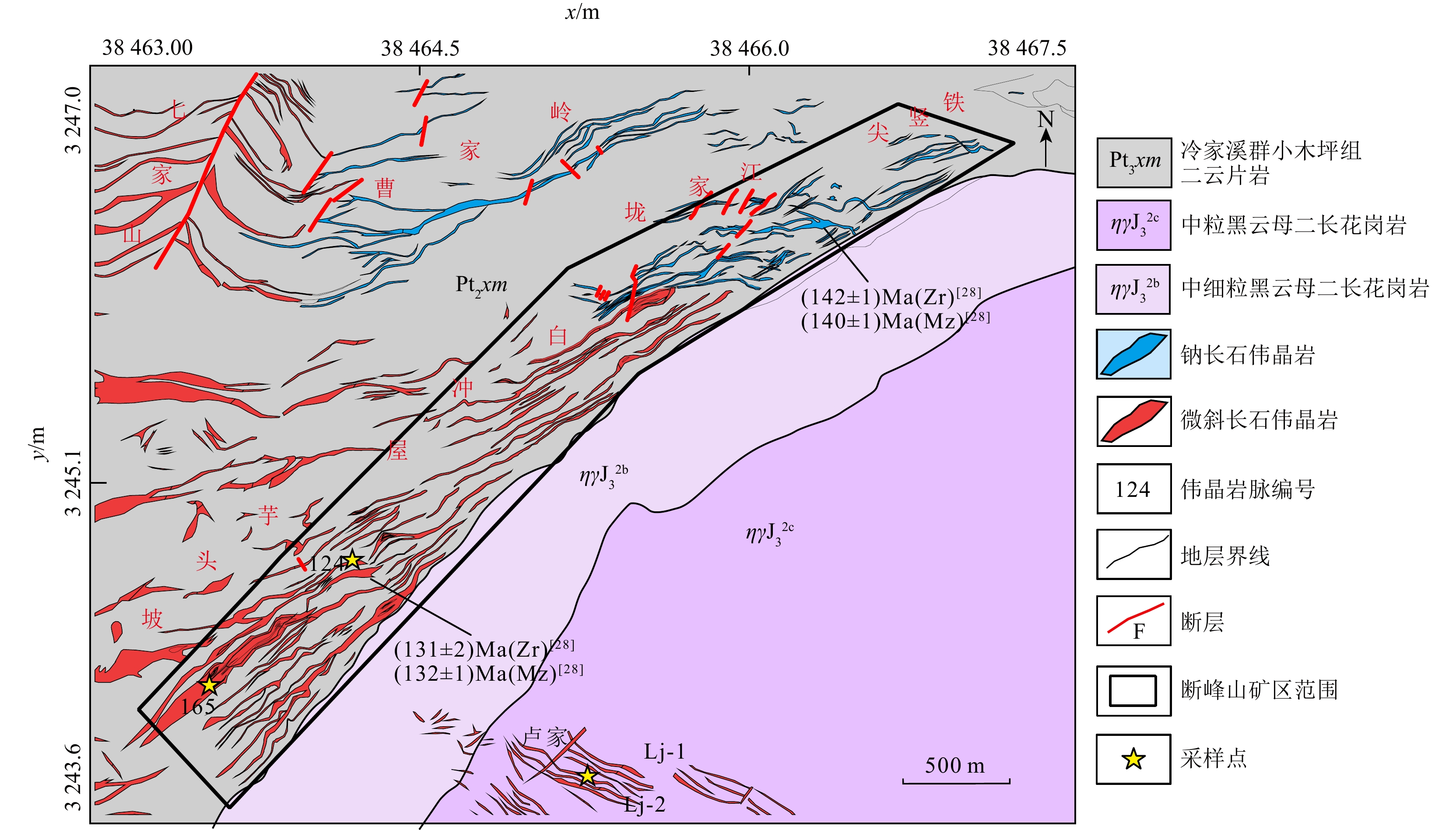
2360 km2,以中深成、中浅成侵入岩为主,一般为大规模的岩体或岩株 [23,26]。新元古代岩浆岩区域内分布较分散,大多发育于幕阜山复式岩体西南角(图1b),锆石U-Pb年龄为(839 ± 6)Ma[31]。燕山期岩浆活动相对强烈而集中,为幕阜山复式岩体主要组成部分,按照侵入顺序岩性为闪长岩(155~150 Ma)、花岗闪长岩(152~148 Ma)、黑云母二长花岗岩(156~139 Ma)、二云母二长花岗岩(145~125 Ma)[17,32-34]。幕阜山地区主要发育NE向、NNE向及NW向断裂(图1b)。NE向断裂控制着岩体和矿床的展布[18],NNE向次级断裂及一些小断裂也为伟晶岩脉提供储存空间。同时也可为富含挥发分和稀有金属的热液运移提供通道,使得稀有元素在该空间中富集[25]。 图 1 幕阜山地区大地构造 (a)及稀有金属矿床分布图 (b) [18]Figure 1. Geotectonic map (a) and distribution map of rare metal deposits (b) in the Mufushan area
图 1 幕阜山地区大地构造 (a)及稀有金属矿床分布图 (b) [18]Figure 1. Geotectonic map (a) and distribution map of rare metal deposits (b) in the Mufushan area幕阜山地区伟晶岩主要发育在岩体内部及围岩与岩体接触带内(图1b),部分伟晶岩脉富含Li-Nb-Ta-Be等元素形成伟晶岩型稀有金属矿体。幕阜山地区产出的稀有金属矿床呈现出空间分带特征,北部铌钽富集、东部铍富集、南部锂铍铌钽富集、中部偏东部铍铌钽富集,西部矿化较少(图1b)。文春华等[18]通过统计幕阜山稀有金属床(点)的分布发现其呈一定的分带规律,即花岗岩型和伟晶岩型铍矿带以岩体为中心分布;伟晶岩型铌钽矿带发育在岩体接触带向外围0~3 km;锂铌钽矿带发育在距离岩体3~5 km范围;石英脉型铍矿带距离岩体5~10 km(图1b)。
2. 断峰山地区伟晶岩及矿化特征
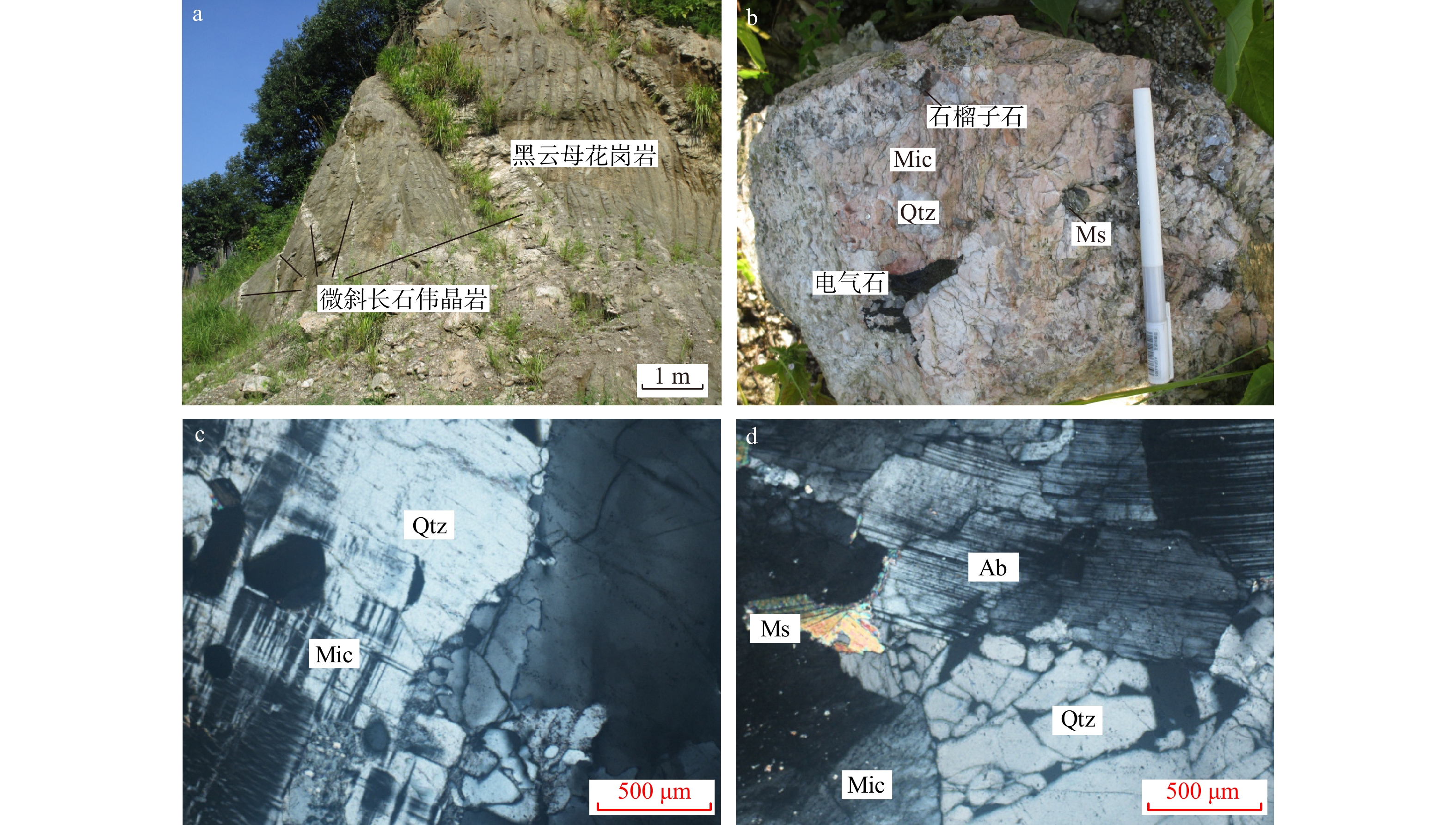
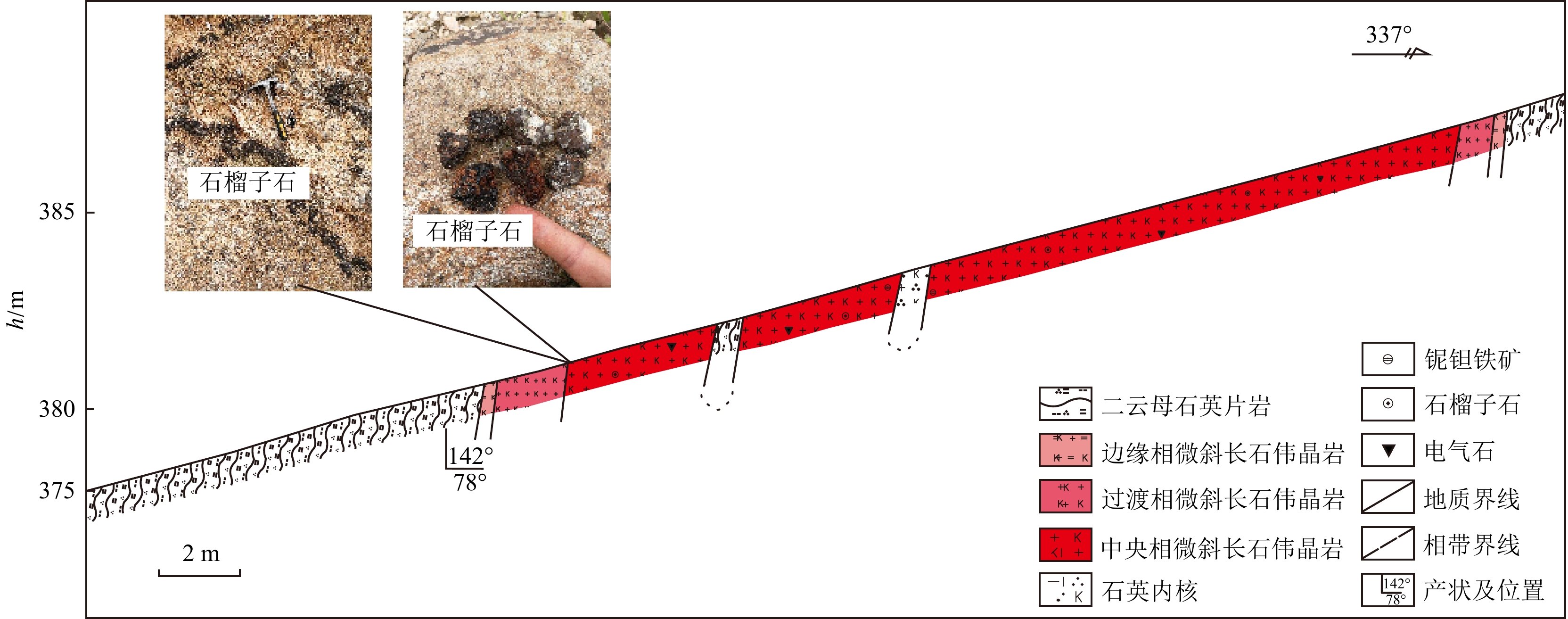
断峰山矿区伟晶岩脉十分发育,主要产出在黑云母二长花岗岩体和围岩接触带内(图2),而在远离岩体及接触带的千枚岩和千枚状板岩中发育很少的或几乎不发育伟晶岩脉[23]。矿区内已发现的伟晶岩脉高达266条,多呈不规则脉状、透镜状或条带状产出,规模差异很大,长度从几米到上千米,宽度由几厘米到百余米。伟晶岩脉多呈EN-WS或EW展布,可分为4个伟晶岩带: ①七家山−芋头坡带;②白冲屋带;③江家垅带;④铁竖尖带(图2)。断峰山矿区伟晶岩脉可分为微斜长石伟晶岩和钠长石伟晶岩2种类型。李艳军等[28]利用锆石和独居石LA-ICP-MS定年获得江家垅段钠长石伟晶岩年龄为(142 ± 1)~(140 ± 1)Ma,而白冲屋段微斜长石伟晶岩年龄为(132 ± 1)~(131 ± 2)Ma,证实了该地区发育2期伟晶岩成矿作用,且微斜长石伟晶岩型矿化晚于钠长石伟晶岩。
 图 2 断峰山地区伟晶岩型Nb-Ta 矿床地质图[22]Zr. 锆;Mz. 白云母Figure 2. Geological map of the pegmatite type Nb-Ta deposit in Duanfengshan area
图 2 断峰山地区伟晶岩型Nb-Ta 矿床地质图[22]Zr. 锆;Mz. 白云母Figure 2. Geological map of the pegmatite type Nb-Ta deposit in Duanfengshan area2.1 微斜长石伟晶岩矿化特征
微斜长石伟晶岩脉主要分布在矿区西部、西南部地层及花岗岩体内(图2),呈脉状或分枝状产出,长可达
1100 m,宽1~110 m。微斜长石伟晶岩往往具有较好的分带性,发育边缘相、过渡相、中央相和内核(图3)。边缘相颜色较深,块状构造,中细粒花岗伟晶结构,矿物粒径1~2 cm,主要矿物为石英和长石。过渡相为浅肉红色,中粒花岗伟晶结构(粒径2~3 cm),主要矿物为石英、长石和白云母。中央相呈肉红色,块状构造,中粗粒花岗伟晶结构,矿物粒径5~7 cm,主要矿物为石英、微斜长石和白云母,见石榴子石和电气石,偶见铌钽铁矿颗粒和锂云母(图4b~f)。内核主要由石英团块和白云母组成,石英团块大小13~16 cm,对比过渡相和边缘相,内核白云母含量高且粒径大。微斜长石伟晶岩矿化主要分布在白冲屋段和芋头坡段。白冲屋段矿脉长200~520 m,宽2.33~3.67 m,(Nb,Ta)2O5品位为0.018%~0.020%,其他脉体中也有一些够品位的样品[23]。芋头坡段伟晶岩脉体形态有板脉状、脉状和不规则状、扁豆状和透镜状,仅不规则状伟晶岩有铌钽矿化,个别脉体(Nb,Ta)2O5品位可达0.026% [23]。近年勘查中首次发现了与锂云母共生的铌钽铁矿及粗粒铌钽铁矿颗粒,如165#脉及124#脉及其东北部滚石中均发现了铌钽铁矿颗粒[28],说明断峰山地区微斜长石伟晶岩有巨大的找矿潜力。
2.2 未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩特征
未矿化微斜长石伟晶岩主要分布在断峰山南部花岗岩体内部,规模较小,长度仅有几米到几十米,宽度小于3 m,常呈脉群分布(图5a),无明显分带。未矿化微斜长石伟晶岩呈肉红色−浅肉红色,花岗伟晶结构,块状构造,主要矿物体积分数为微斜长石(45%左右),石英(30%左右),钠长石(15%左右)和白云母(10%左右),还可见电气石和石榴子石等副矿物(图5b)。微斜长石呈半自形−自形板状、柱状,粒径一般大于3 mm,可见格子双晶;石英呈它形−半自形柱状,粒径大小为0.5~3 mm;钠长石呈它形−半自形片状,粒径为1~2 mm,可见细小的聚片双晶;白云母呈它形−半自形片状,大小为0.5~2.5 mm (图5c,d)。
2.3 成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩地质特征差异
断峰山地区成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩在围岩类型、规模、矿物组合以及断裂构造有一定的差异(表1)。断峰山伟晶岩脉赋存于幕阜山复式花岗岩体及其围岩冷家溪群中,其片岩发育片理构造以及内部发育揉皱构造,渗透性和封闭性较好,有利于成矿流体的运移以及矿化的富集沉淀。幕阜山地区主要的伟晶岩型铌钽矿床如仁里和传梓源成矿伟晶岩均就位于冷家溪群板岩和片岩中。断峰山矿区成矿的钠长石伟晶岩和微斜长石伟晶岩脉也均位于岩体接触带外围的冷家溪群中。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩规模较大,受NE向断裂构造控制,长可达
1100 m,宽1~110 m,分带明显(图2,3)。而未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩规模较小(长度仅几米到几十米,宽度小于3 m),受控于岩体内部NW向断裂构造,大多数伟晶岩脉分带不明显。成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩主要成岩矿物组合相似,但成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中央相发育铌钽铁矿、锂云母、绿柱石等稀有金属矿物(图4b~g)。区域性的构造控制幕阜山地区花岗岩浆的多期侵入,而一些次级构造为成岩成矿作用提供了导矿、运矿和容矿通道,控制了伟晶岩脉及矿体的分布。仁里矿区成矿伟晶岩脉主要受NNW向断裂构造控制[29],传梓源矿区伟晶岩脉受NW向断裂构造控制[35],而断峰山矿区断裂构造以NE向断裂为主。这些断裂构造主要呈环形围绕幕阜山复式花岗岩体分布。但岩体内发育的次级断裂构造产状大多垂直接触带且规模较小。表 1 断峰山地区成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩差异对比Table 1. Comparison of differences between mineralized and unmineralized microcline pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area成矿微斜长石伟晶岩 未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩 围岩类型 新元古界冷家溪群片岩 黑云母二长花岗岩 与花岗岩的关系 岩体外的片岩内 岩体内部 展布方向 NE 向 NW向 规模及分带 数量较多,长度几百米至上千米,宽度几米至百余米,分带明显 数量较少,长度几米到几十米,宽度小于3 m,
分带不明显矿物组合 石英、斜长石、钾长石和白云母,副矿物石榴子石和电气石,
内带发育铌钽铁矿、锂云母、绿柱石石英、斜长石、钾长石和白云母,副矿物
石榴子石和电气石次级断裂构造 以NE向断裂为主,次为近NS向和近EW向断裂 以NW向断裂为主 3. 样品采集及分析
本研究共采集6件石榴子石样品,其中4件采集于124#、165#矿化微斜长石伟晶岩脉(124-1,124-2,165-1,165-2),另外2件采集于岭源村卢家组旁边的未矿化微斜长石伟晶岩脉(Lj-1,Lj-2),采样位置见图2。
将石榴子石样品在室内分别制作成环氧树脂镶嵌的圆靶和高精度抛光的探针片。先进行BES和CL拍照,以研究石榴子石形貌及微观结构,供微区主微量元素测试分析选点。使用电子探针(EPMA)和激光电感耦合等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)分别进行主量和微量元素含量分析。阴极发光和背散射拍照在武汉微束检测科技有限公司进行,使用JXA-8230电子探针中PCL全色阴极发光系统获得CL和BSE图像。EPMA使用日本电子EPMA-1600电子探针在中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心实验室完成,加速电压为20 kV,电流为15 nA,光束直径为1 μm。测试元素为Si、Al、Ti、Mn、K、Na、Fe、P、Ca和Mg共10种,标样为美国SPI 53种标准矿物。石榴子石端元组分计算方法和程序见LOCOCK[36]。
单矿物原位微区微量元素分析在武汉上谱科技分析有限公司利用LA-ICP-MS完成。激光剥蚀系统为 GeoLas Pro HD,ICP-MS为Agilent 7900。激光剥蚀系统配置了一个信号平滑装置,即使激光脉冲频率低于1 Hz,也能获得光滑的分析信号。每个时间分辨分析数据包括20 s空白信号和50 s样品信号。本次分析以美国地质勘探局(USGS)参考玻璃(BHVO-2G、BCR-2G、BIR-1G、SRM 610)为校正标准,并以对应样品EPMA测得的SiO2含量平均值为内标,对元素含量进行定量校正。这些USGS 玻璃中元素含量推荐值据GeoReM数据库。对分析数据离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量计算)采用软件ICPMSDataCal [37]完成。
4. 分析结果
4.1 石榴子石微观结构
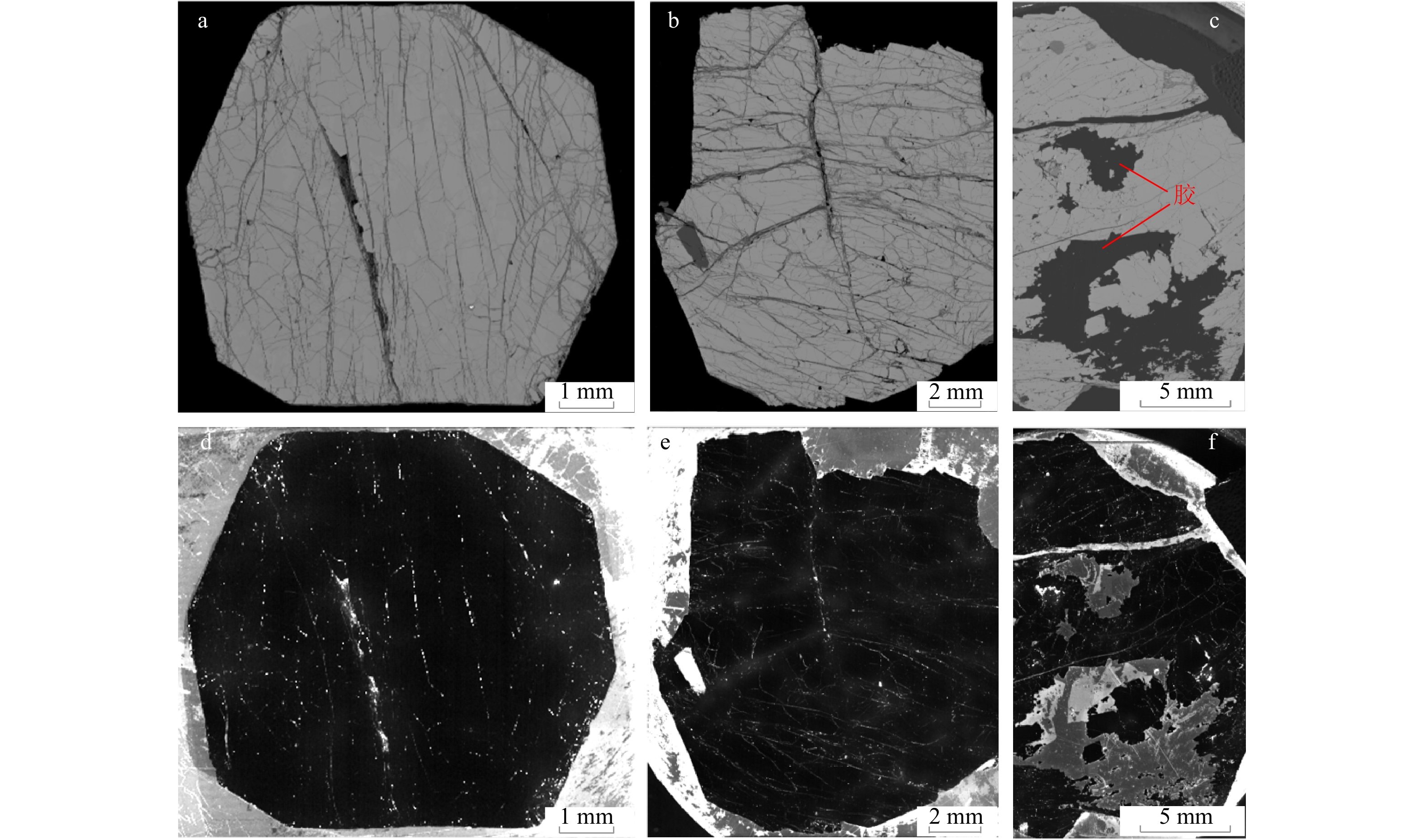
石榴子石呈带状分布,红棕色−棕色,自形程度较好,四角三八面体,颗粒较大(粒径0.5~2 cm)(图3)。不同产状石榴子石均晶型完整,局部含有石英或长石包裹体。BSE图像中显示均一的灰度,且CL图像也显示均一的深色调,均未显示明显的环带结构(图6),说明其结构均一。但是,成矿微斜长石伟晶岩和未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石均发育微观裂隙(图6)。
4.2 主量元素特征
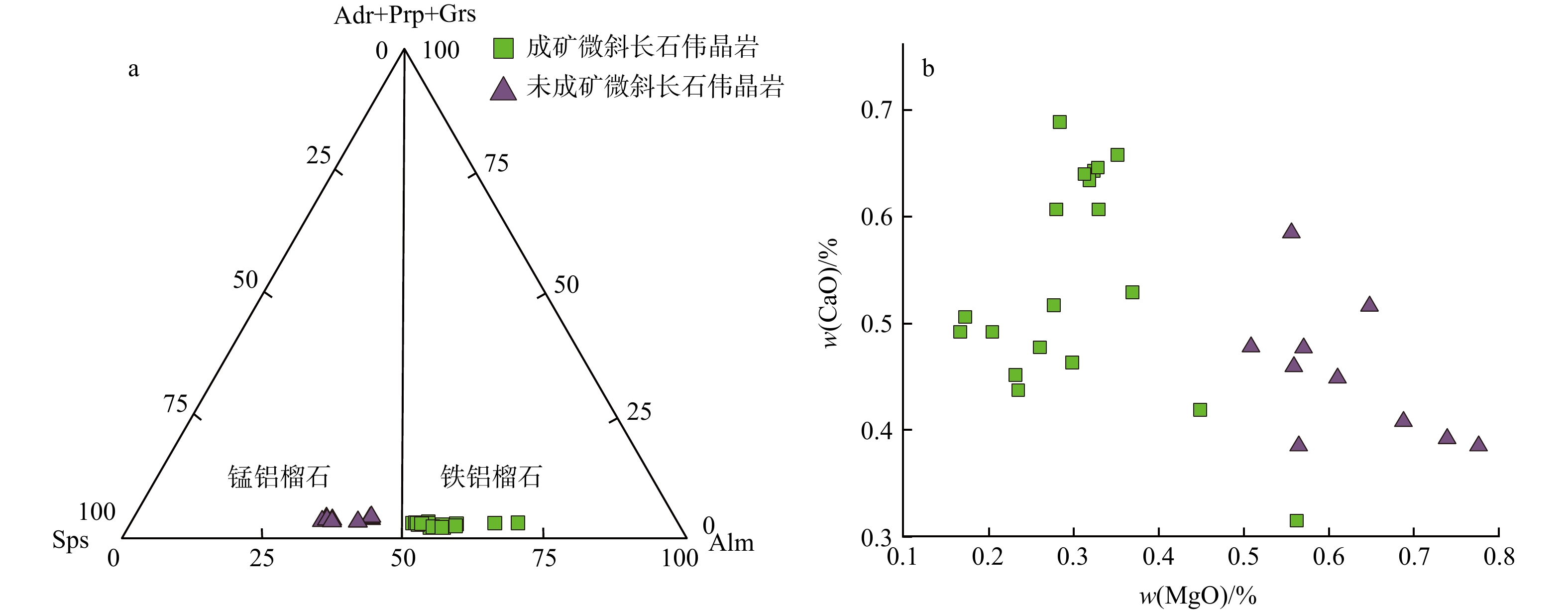
成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石EPMA主量元素分析结果见表2。w(SiO2)为34.13%~35.95%,w(Al2O3)为19.45%~20.88%,w(FeO)为17.17%~30.07%,w(MnO)为12.07%~25.50%,而w(MgO )(0.17%~0.78%)和w(CaO)(0.31%~0.69%)较低。计算结果表明(以12个氧原子为基准计算端元组分),成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石均属于铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石固溶体系列,以铁铝榴石(wB,下同)(33.59%~68.27%)为主,其次为锰铝榴石(28.54%~62.89%)和含量较低的镁铝榴石(0.73%~3.29%)、钙铝榴石(0~1.65%)和钙铁榴石(0~1.91%)。
表 2 断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石电子探针分析主量元素成分Table 2. EPMA major element compositions of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area样品号 成矿伟晶岩 未成矿伟晶岩 124-1 124-2 165-1 165-2 Lj-1 Lj-2 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 SiO2 wB/% 34.13 35.90 35.43 35.79 35.69 35.95 35.89 35.53 35.93 35.22 35.71 35.29 35.85 35.60 35.79 35.71 35.87 35.73 35.81 35.87 35.51 35.44 35.50 35.43 35.52 35.43 35.40 35.58 35.44 TiO2 0.04 0.02 0.01 bdl 0.09 0.11 0.03 0.07 bdl 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.04 0.06 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.01 0.05 0.03 0.08 0.10 0.05 0.05 Al2O3 19.83 19.99 19.90 19.62 19.54 19.87 19.58 19.75 20.12 20.55 19.45 20.33 20.68 20.52 20.58 20.76 20.71 20.88 20.74 20.43 19.93 19.93 20.35 20.03 20.01 19.82 19.76 20.06 20.04 FeO 26.88 27.13 26.32 27.55 25.26 25.25 24.75 24.47 22.99 25.35 24.55 23.14 30.07 25.91 24.63 23.86 24.32 25.64 28.48 19.89 20.09 17.55 20.01 19.22 17.49 17.43 17.17 17.23 17.62 MnO 17.34 17.56 17.65 16.96 18.94 18.80 19.00 18.92 18.77 18.36 18.85 18.82 12.07 16.55 17.81 18.49 17.95 16.79 13.82 22.71 22.20 25.22 22.35 23.30 25.13 25.27 25.50 25.49 25.14 MgO 0.17 0.21 0.17 0.28 0.33 0.33 0.33 0.28 0.35 0.32 0.29 0.31 0.56 0.37 0.23 0.26 0.24 0.30 0.45 0.69 0.74 0.65 0.78 0.57 0.57 0.56 0.56 0.61 0.51 CaO 0.51 0.49 0.49 0.52 0.64 0.65 0.61 0.61 0.66 0.63 0.69 0.64 0.31 0.53 0.45 0.48 0.44 0.46 0.42 0.41 0.39 0.52 0.39 0.39 0.48 0.59 0.46 0.45 0.48 Na2O 0.01 bdl 0.02 0.01 bdl bdl 0.02 bdl bdl bdl bdl 0.08 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 bdl bdl bdl 0.00 0.03 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 K2O 0.02 bdl 0.01 bdl bdl 0.01 bdl 0.01 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.02 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl bdl bdl bdl bdl bdl 0.00 bdl 0.00 bdl bdl bdl 0.01 0.00 总计 98.92 101.29 100.00 100.73 100.48 100.95 100.20 99.65 98.82 100.50 99.62 98.70 99.58 99.58 99.53 99.64 99.54 99.84 99.72 100.03 98.93 99.38 99.42 98.99 99.23 99.17 98.98 99.49 99.29 Si 原
子
数2.86 2.93 2.93 2.94 2.94 2.94 2.96 2.95 2.99 2.89 2.97 2.94 2.96 2.95 2.96 2.95 2.97 2.95 2.96 2.95 2.95 2.94 2.93 2.95 2.95 2.94 2.95 2.94 2.94 Ti 0.00 0.00 0.00 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 bdl 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 Al 1.82 1.86 1.87 1.84 1.84 1.86 1.87 1.88 1.97 1.88 1.87 1.94 1.98 1.95 1.97 1.97 1.99 1.98 1.97 1.93 1.91 1.88 1.92 1.91 1.90 1.88 1.89 1.90 1.90 Fe 1.88 1.85 1.82 1.89 1.74 1.73 1.71 1.70 1.60 1.74 1.70 1.61 2.08 1.79 1.71 1.65 1.68 1.77 1.97 1.37 1.40 1.22 1.38 1.34 1.21 1.21 1.20 1.19 1.22 Mn 1.23 1.22 1.24 1.18 1.32 1.30 1.33 1.33 1.33 1.28 1.33 1.33 0.84 1.16 1.25 1.29 1.26 1.17 0.97 1.58 1.56 1.77 1.56 1.64 1.77 1.78 1.80 1.79 1.77 Mg 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.07 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.10 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.06 Ca 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.03 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 Na 0.00 bdl 0.00 0.00 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 bdl bdl bdl 0.00 0.01 bdl 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Sps wB/% 44.49 42.94 43.35 42.00 47.16 45.92 46.61 46.38 44.25 44.43 46.38 45.62 28.54 39.51 42.16 43.97 42.46 39.83 32.70 54.06 54.09 61.77 53.80 56.64 60.97 61.98 62.89 61.90 61.19 Prp 0.78 0.89 0.73 1.22 1.42 1.42 1.43 1.21 1.46 1.37 1.24 1.34 2.34 1.55 0.97 1.10 0.98 1.25 1.88 2.88 3.17 2.80 3.29 2.42 2.44 2.40 2.43 2.62 2.18 Alm 53.23 54.70 54.42 55.16 49.69 51.01 50.18 50.75 52.32 52.45 50.47 51.34 68.27 57.56 55.64 53.69 55.26 57.62 64.17 41.96 41.70 34.02 41.76 39.92 35.21 34.08 33.59 34.27 35.32 Grs 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.66 0.00 0.00 1.65 0.85 0.86 1.14 1.24 1.30 1.30 1.26 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Adr 1.50 1.46 1.50 1.62 1.72 1.65 1.78 1.65 1.30 1.75 1.91 0.05 0.00 0.52 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.10 1.04 1.41 1.16 1.01 1.38 1.54 1.09 1.21 1.31 注:FeO为全铁含量;Sps. 锰铝榴石;Prp. 镁铝榴石;Alm. 铁铝榴石;Grs. 钙铝榴石;Adr. 钙铁榴石;bdl. 低于检测限;晶体化学式基于12个氧原子计算 成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石主要为铁铝榴石(Sps28.54-47.16Alm49.69-68.27,平均Sps42.56Alm54.63)(图7a),w(SiO2)为34.13%~35.95%,w(Al2O3)为19.45%~20.76%,w(FeO)为22.99%~30.07%,w(MnO)为12.07%~19.00%,w(CaO)为0.31%~0.69%,w(MgO)为0.17%~0.56%。与成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石相比,未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石以锰铝榴石为主(Sps53.80-62.89Alm33.59-41.96,平均Sps58.93Alm37.18),w(SiO2)(35.40%~35.87%)、w(Al2O3)(19.76%~20.43%),w(CaO)(0.39%~0.59%)和w(MgO)(0.51%~0.78%)无明显变化,但w(MnO)(22.20%~25.50%)增高,w(FeO)(17.17%~20.09%)降低。
 图 7 断峰山地区伟晶岩石榴子石三角分类图解(a,据文献[9]修改)和CaO−MgO图解(b)Sps. 锰铝榴石;Alm. 铁铝榴石;Adr. 钙铁榴石;Prp. 镁铝榴石;Grs. 钙铝榴石Figure 7. Triangle classification (a) and CaO-MgO (b) diagrams of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area
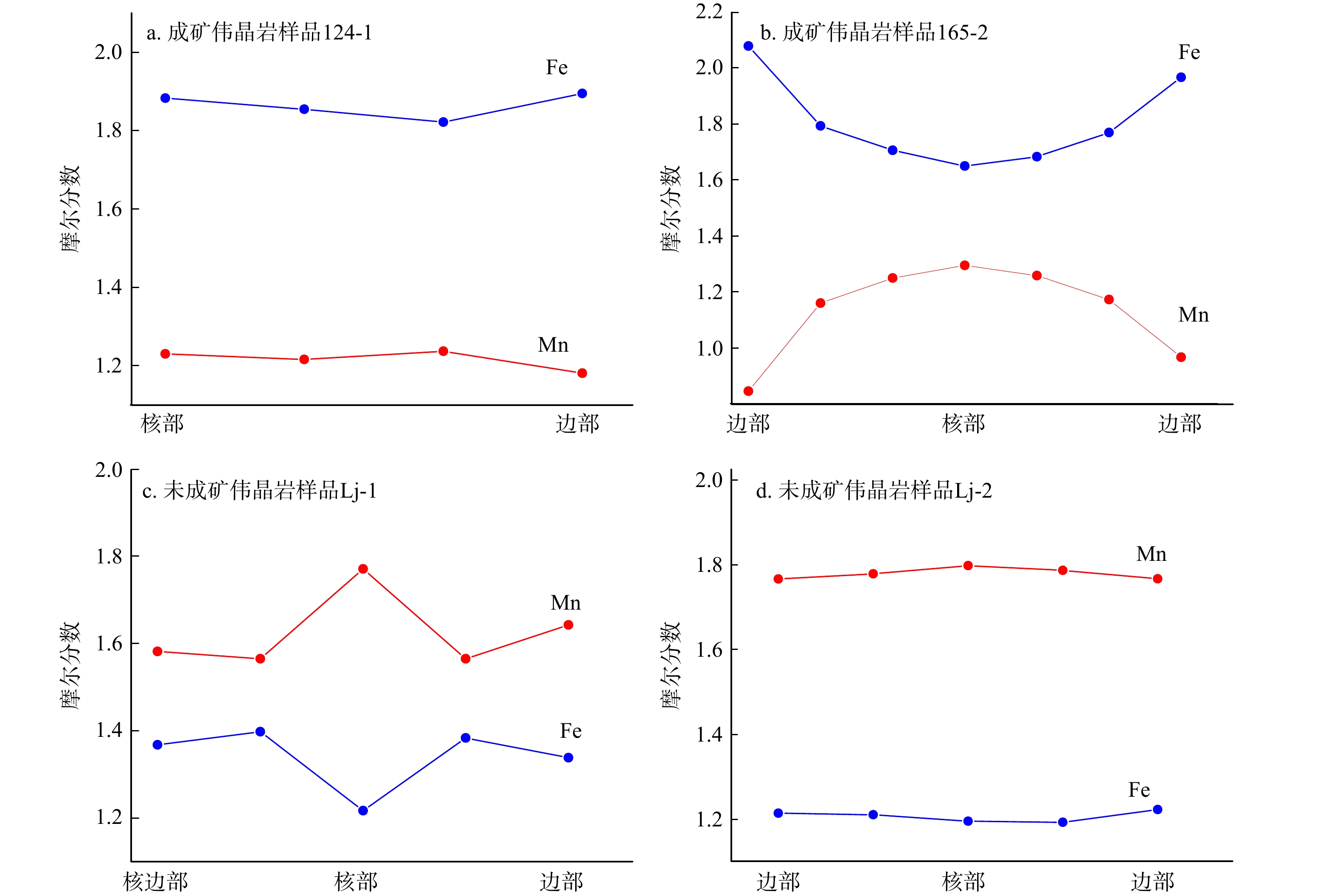
图 7 断峰山地区伟晶岩石榴子石三角分类图解(a,据文献[9]修改)和CaO−MgO图解(b)Sps. 锰铝榴石;Alm. 铁铝榴石;Adr. 钙铁榴石;Prp. 镁铝榴石;Grs. 钙铝榴石Figure 7. Triangle classification (a) and CaO-MgO (b) diagrams of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan areaw(MgO)和w(CaO)无明显相关性,成矿微斜长石伟晶岩表现出高钙低镁,而未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石表现出低钙高镁 (图7b)。此外,石榴子石中Fe-Mn质量分数显示出了明显的成分分带,成矿微斜长石伟晶岩和未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石的w(Mn)从核部到边部降低,w(Fe)则相反,且未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石Fe-Mn质量分数从核部到边部还呈现出了“震荡型”的成分分带(图8)。
4.3 微量元素特征
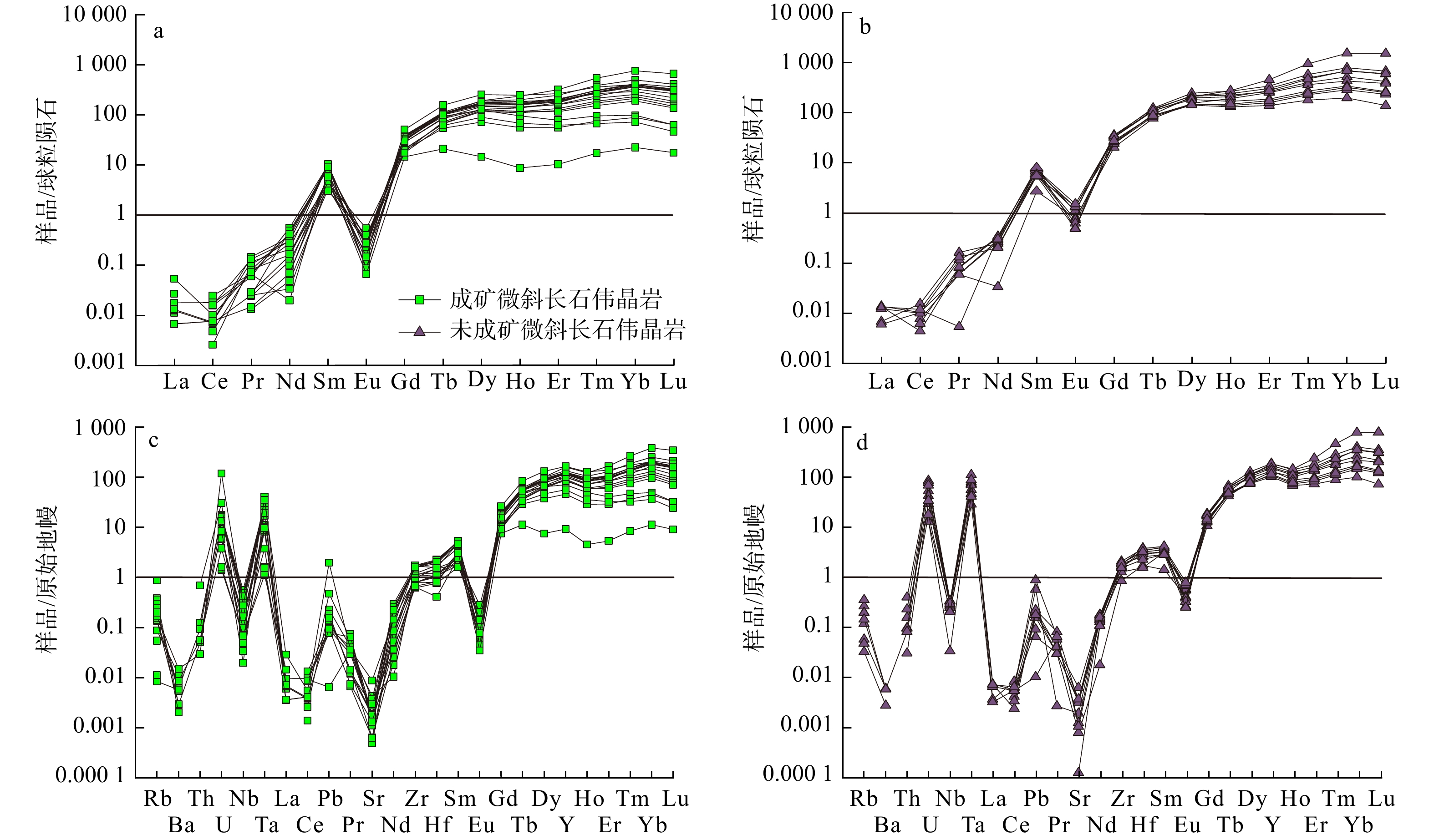
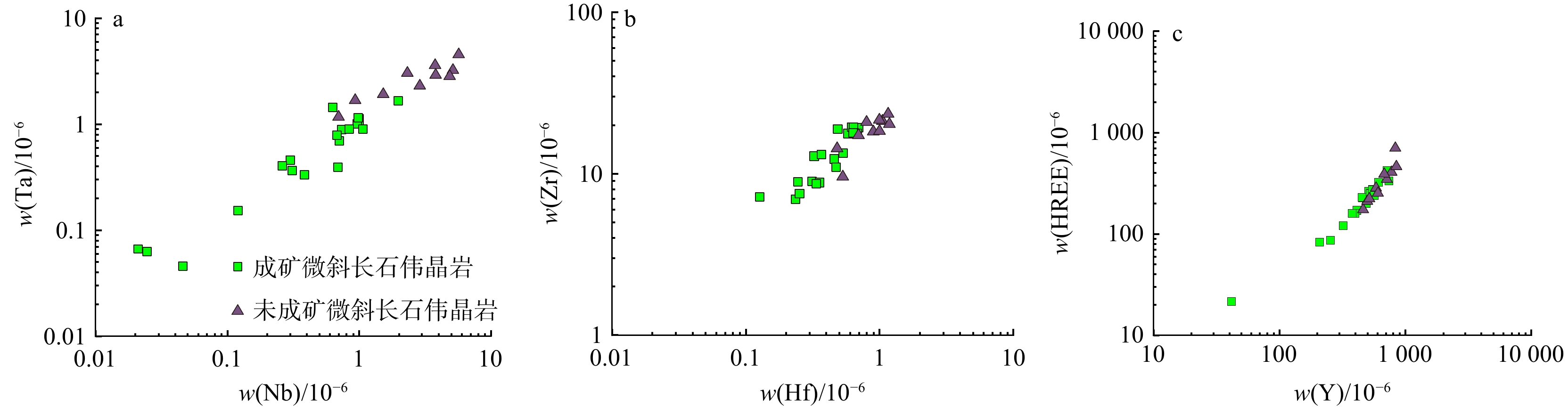
石榴子石LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析结果见表3,可以看出:断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石富集高场强元素(HFSE)和稀土元素(REE),大离子亲石元素(LILE)富集程度较低(图9)。成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石稀土元素组成和分布特征相似,稀土元素具有明显左倾趋势(图9a,b)。未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩石榴子石∑HREE明显高于成矿微斜长石伟晶岩石榴子石(图9a,b),(La/Sm)N比值<0.01,(Gd/Yb)N比值为0.02~0.67(表3),表现出轻稀土元素亏损重稀土元素富集特征。Eu/Eu*比值<0.09,表现为强烈的Eu负异常(表3)。成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石微量元素蛛网图总体上表现出较为相似的特征(图9c,d),U、Ta、Pb、Zr、Hf、Y、HREE质量分数较高,Ba、Sr质量分数相对较低。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石Y、Nb、Ta、Hf和Zr质量分数明显低于未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石,且Nb与Ta、Hf与Zr和Y与HREE等元素之间存在明显的正相关性(图10)。Y/Gd (成矿微斜长石伟晶岩为9.93~79.56;未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩为57.76~110.62)和Y/Dy(成矿微斜长石伟晶岩为6.81~9.76;未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩为8.54~10.44)值均较大。
表 3 断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石 LA-ICP-MS原位微区分析微量元素成分Table 3. LA-ICP-MS trace element compositions of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area样品号 成矿伟晶岩 未成矿伟晶岩 124-1 124-2 165-1 165-2 Lj-1 Lj-2 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 wB/10−6 Li 147.61 156.83 183.94 150.58 116.74 154.17 129.47 134.93 147.38 63.00 147.09 121.48 125.35 106.89 116.55 151.46 121.12 98.78 106.02 111.07 119.17 113.64 119.74 132.20 125.73 84.14 105.03 84.82 67.85 118.60 Be 0.00 0.20 0.18 0.13 0.10 0.19 0.05 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.31 0.31 0.32 0.00 0.00 0.32 0.06 0.00 0.25 0.51 0.05 0.05 0.26 0.13 0.11 0.11 0.00 0.24 0.00 B 1.81 0.03 1.88 0.27 0.47 4.36 0.00 1.67 0.00 1.44 1.76 1.21 0.00 0.14 2.36 0.00 0.35 1.06 0.74 1.37 2.15 1.38 1.46 1.37 0.12 0.96 2.92 0.94 0.00 0.51 Sc 4.22 6.83 11.64 5.98 20.17 20.60 16.57 15.56 14.77 4.91 14.79 13.24 14.29 7.31 5.65 7.73 11.94 9.27 8.61 7.92 4.48 5.37 5.25 4.82 2.53 6.83 4.75 2.60 2.46 2.64 V 0.03 0.00 0.12 0.04 0.04 0.11 0.13 0.00 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.06 0.09 0.00 0.10 0.01 0.04 1.41 0.86 1.19 0.14 0.07 0.12 0.79 0.06 0.15 0.09 1.48 0.74 0.99 Cr 2.64 0.81 2.06 0.99 0.00 0.00 0.58 0.00 0.00 0.70 2.23 0.19 1.52 0.00 0.00 0.97 0.06 0.97 0.00 0.88 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.46 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.88 0.00 0.21 Co 1.40 1.21 1.13 1.34 0.79 0.79 0.95 0.82 0.61 0.72 0.75 0.92 0.68 1.80 1.22 1.20 1.18 2.56 2.89 2.87 4.33 2.95 3.04 5.43 3.77 2.63 2.70 2.33 2.56 2.88 Ni 0.54 0.16 0.00 0.43 0.56 0.37 1.09 0.00 0.26 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.27 0.40 0.14 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.41 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.49 1.39 0.00 0.46 0.00 Cu 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.28 0.15 0.00 0.01 0.11 0.00 0.01 0.13 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.07 0.00 0.43 0.06 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.10 0.00 Zn 437.56 401.21 384.54 406.53 263.86 255.93 261.13 274.92 264.24 309.67 244.60 248.47 244.55 360.71 344.45 352.01 295.83 307.59 325.67 314.77 357.05 240.91 232.26 388.94 305.97 247.05 229.43 271.39 270.72 277.60 Ga 23.13 22.94 25.43 23.65 28.24 27.45 26.52 25.80 27.53 21.65 25.14 24.28 23.68 21.45 24.29 31.90 25.97 19.51 20.08 21.04 26.22 27.21 27.52 23.69 25.05 27.75 26.93 29.03 28.51 26.39 Rb 0.06 0.24 0.23 0.12 0.00 0.55 0.09 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.09 0.10 0.19 0.00 0.15 0.01 0.11 0.03 0.13 0.01 0.17 0.03 0.23 0.02 0.04 0.13 0.03 0.12 0.08 0.09 Sr 0.03 0.01 0.09 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.01 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.00 0.04 0.01 0.19 0.04 0.03 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.02 0.00 0.13 0.08 0.04 0.03 0.02 Y 412.70 491.11 719.37 399.24 613.71 551.78 514.67 457.63 549.46 41.67 532.36 527.06 549.03 321.23 379.42 454.46 208.79 254.55 568.45 742.88 712.33 775.60 849.18 585.37 462.66 831.41 679.86 606.30 497.87 517.41 Zr 12.82 13.11 13.36 12.34 17.74 19.41 17.95 18.90 19.33 8.91 19.34 17.76 17.85 8.96 8.80 8.67 10.93 6.93 7.17 7.52 21.13 18.18 18.33 9.55 14.29 20.84 20.26 23.40 21.48 17.26 Nb 0.30 0.38 0.74 0.31 1.00 1.00 0.96 0.84 0.98 0.26 1.07 0.71 0.68 0.12 0.69 1.97 0.63 0.02 0.02 0.05 5.14 2.88 3.81 1.52 0.70 2.32 4.86 5.70 3.77 0.93 Ag 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.05 0.01 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.00 0.00 Cd 11.24 10.41 12.40 10.70 7.62 10.55 9.05 8.47 6.06 6.94 6.79 6.91 6.97 8.31 7.89 10.14 6.55 7.93 10.09 7.23 6.90 6.14 5.43 8.10 6.81 7.97 6.19 8.64 9.66 10.15 Sn 6.61 6.79 7.38 5.64 6.29 6.22 6.98 6.57 7.03 1.68 7.69 7.12 6.67 3.89 4.31 6.49 6.35 1.63 1.18 0.91 11.41 12.10 11.42 6.11 7.88 12.94 12.87 9.85 9.67 9.44 Cs 0.04 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.03 1.36 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.06 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 Ba 0.08 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.06 0.00 0.04 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 La 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Ce 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Pr 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.02 Nd 0.11 0.11 0.01 0.09 0.31 0.15 0.26 0.22 0.40 0.12 0.22 0.35 0.30 0.07 0.02 0.03 0.20 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.17 0.19 0.20 0.02 0.15 0.23 0.24 0.24 0.21 0.15 wB/10−6 Sm 0.89 1.07 1.69 0.81 2.17 2.32 2.35 2.15 2.29 1.26 2.39 1.91 2.08 1.35 0.94 0.77 0.99 0.71 1.08 1.35 1.76 1.39 1.57 0.63 1.41 1.24 1.71 1.85 1.37 1.27 Eu 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.07 0.06 0.12 0.13 0.04 0.05 0.04 Gd 6.23 8.69 9.68 6.43 11.79 11.03 12.04 10.69 11.51 4.47 12.01 11.84 10.99 10.21 8.68 5.71 6.05 5.42 9.33 15.51 11.05 9.82 10.47 6.28 7.45 7.52 9.94 10.50 8.03 8.56 Tb 3.96 5.05 5.98 3.86 6.60 6.29 6.30 5.82 6.19 1.22 6.08 6.19 5.88 5.45 4.90 4.21 3.13 3.57 5.85 9.02 6.92 6.65 7.23 4.50 4.92 5.44 6.27 6.42 5.14 5.15 Dy 46.64 55.92 73.70 44.38 72.36 66.12 65.10 57.73 63.80 5.57 62.86 60.25 63.57 47.17 49.21 49.00 27.50 34.05 68.48 96.68 81.93 84.28 93.57 59.15 54.19 79.66 75.11 70.20 57.45 55.21 Ho 9.90 12.19 19.92 9.42 17.02 15.36 13.32 11.80 14.55 0.74 13.88 13.54 14.05 8.09 9.90 11.68 4.73 5.79 15.74 20.96 19.10 20.61 22.96 16.44 11.17 23.68 17.84 14.38 11.92 12.72 Er 33.20 39.76 79.42 30.52 61.37 51.80 47.58 40.31 50.85 2.57 46.29 44.72 49.46 19.37 28.69 43.56 13.91 15.51 48.30 66.16 66.28 76.52 85.58 63.21 34.77 113.59 69.14 46.86 39.66 43.41 Tm 6.76 7.74 19.50 6.22 13.84 10.98 10.32 8.58 11.15 0.62 9.87 9.99 11.15 3.44 5.53 10.22 2.68 2.40 9.53 12.84 14.53 17.87 20.85 13.09 6.45 34.21 17.01 9.78 8.22 8.81 Yb 57.11 63.16 187.59 52.81 122.96 99.92 96.19 81.37 98.13 5.56 89.30 89.26 103.69 24.38 46.96 92.96 22.01 17.89 72.94 100.04 128.98 169.54 196.62 106.20 49.22 381.86 171.94 84.68 71.18 79.36 Lu 6.37 7.10 25.15 5.63 15.52 12.40 12.36 10.10 12.38 0.67 11.22 11.49 13.68 2.40 5.21 11.81 2.41 1.77 8.34 11.82 16.01 22.40 25.85 14.69 5.32 57.98 22.96 10.11 8.90 9.59 Hf 0.32 0.37 0.53 0.46 0.58 0.62 0.66 0.49 0.70 0.24 0.64 0.68 0.63 0.31 0.36 0.34 0.47 0.23 0.13 0.25 1.05 0.90 1.00 0.53 0.48 0.80 1.18 1.16 1.00 0.70 Ta 0.46 0.34 0.89 0.37 1.13 1.07 1.01 0.90 1.15 0.40 0.90 0.69 0.79 0.15 0.39 1.66 1.44 0.07 0.06 0.05 3.24 2.30 2.90 1.92 1.17 3.03 2.83 4.54 3.58 1.68 Bi 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.04 0.01 0.09 0.08 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.07 Pb 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.36 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.03 0.11 0.00 0.16 Th 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.01 U 0.12 0.12 0.19 0.14 0.36 0.33 0.37 0.35 0.35 0.12 0.33 0.28 0.28 0.08 0.63 0.18 2.49 0.03 0.03 0.03 1.79 0.62 1.10 0.28 0.27 0.88 1.61 1.44 0.71 0.38 ∑REE 171.18 200.81 422.67 160.19 323.99 276.40 265.86 228.80 271.28 22.82 254.14 249.60 274.89 121.97 160.07 229.99 83.70 87.15 239.67 334.44 346.86 409.38 465.04 284.30 175.12 705.55 392.32 255.07 212.18 224.32 ∑LREE 1.02 1.20 1.74 0.92 2.52 2.50 2.65 2.40 2.71 1.41 2.65 2.30 2.41 1.46 0.99 0.83 1.27 0.75 1.17 1.42 2.07 1.70 1.90 0.74 1.63 1.62 2.10 2.14 1.67 1.50 ∑HREE 170.16 199.60 420.93 159.27 321.46 273.90 263.21 226.40 268.57 21.41 251.50 247.29 272.48 120.50 159.08 229.16 82.43 86.40 238.50 333.02 344.80 407.68 463.14 283.56 173.49 703.93 390.22 252.93 210.51 222.82 (La/Yb)N 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 (La/Sm)N 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 (Gd/Yb)N 0.09 0.11 0.04 0.10 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.10 0.66 0.11 0.11 0.09 0.35 0.15 0.05 0.23 0.25 0.11 0.13 0.07 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.13 0.02 0.05 0.10 0.09 0.09 Eu/Eu* 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.09 0.08 0.02 0.04 0.03 Y/Gd 66.27 56.54 74.35 62.10 52.05 50.01 42.73 42.82 47.75 9.33 44.33 44.51 49.94 31.46 43.72 79.56 34.50 46.93 60.93 47.91 64.48 78.96 81.08 93.27 62.14 110.62 68.37 57.76 61.96 60.45 Y/Dy 8.85 8.78 9.76 9.00 8.48 8.35 7.91 7.93 8.61 7.48 8.47 8.75 8.64 6.81 7.71 9.27 7.59 7.48 8.30 7.68 8.69 9.20 9.08 9.90 8.54 10.44 9.05 8.64 8.67 9.37  图 9 断峰山地区石榴子石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a,b)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(c,d)(标准化值据文献[38])Figure 9. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, b) and primitive mantle normalized spidergrams of trace elements (c, d) of garnets in the Duanfengshan area
图 9 断峰山地区石榴子石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a,b)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(c,d)(标准化值据文献[38])Figure 9. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, b) and primitive mantle normalized spidergrams of trace elements (c, d) of garnets in the Duanfengshan area5. 讨 论
5.1 石榴子石成因
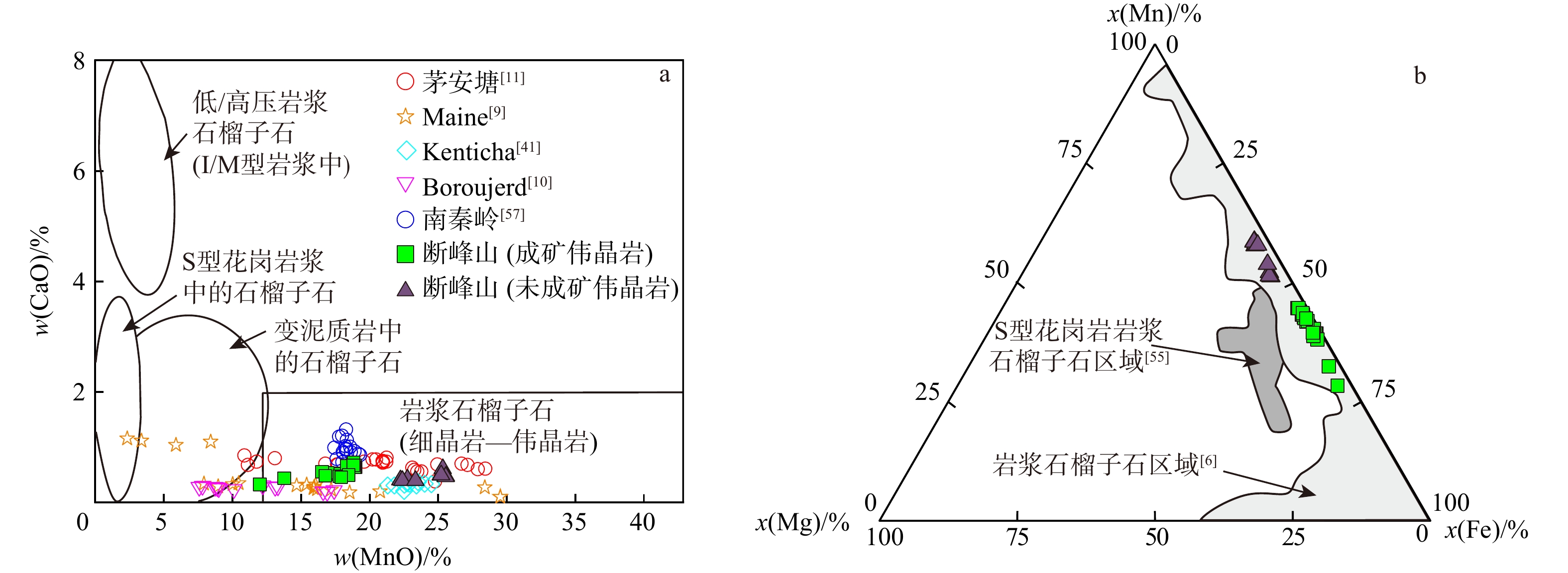
石榴子石结构、端元组分、成分环带以及包裹体的存在与否,可以用来判别石榴子石成因。石榴子石主要有3种成因类型:变质型、转熔型和岩浆型[39-42]。变质型石榴子石主要形成于不同岩石类型变质作用过程中,典型的有含石榴子石云母片岩和矽卡岩[42]。冷家溪群片岩形成时间为(839 ± 6)Ma[31],而断峰山地区微斜长石伟晶岩成岩时间约为130 Ma[28],伟晶岩的形成远远晚于区域变质作用。变质成因石榴子石具有高Mg和Ca,低Mn成分特征[8,11]。本研究的石榴子石富Mn (w(MnO)=12.07%~25.50%)和贫Mg(w(MgO)=0.17%~0.78%)和Ca(w(CaO)=0.31%~0.69%),明显不是变质成因。转熔型石榴子石是熔体捕获黑云母或角闪石等部分熔融形成的,该类石榴子石既具有源岩特征又有熔体特征[43-44],且多形成在源岩为片麻岩或麻粒岩的花岗岩中,岩相学上石榴子石也多与黑云母共生,化学成分也具富Fe和Mg和贫Mn和Ca特征[45-46]。断峰山地区围岩为冷家溪群片岩,含有很少的石榴子石,而伟晶岩中云母几乎均为白云母,不存在石榴子石与黑云母共生现象,石榴子石富Mn贫Mg特征,也不属转熔成因。岩浆型石榴子石可以是花岗质岩浆在高压条件下(>700 MPa)形成[47]、过铝质岩浆在中低压条件下结晶形成[5]或在贫锰矿物(石英、长石)形成后残留熔体中Mn含量升高促使其形成[6,48]。岩浆成因石榴子石多出现在伟晶岩及细晶岩中[49-50]。通过对比世界范围内岩浆成因伟晶岩中的石榴子石,断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石主体位于岩浆石榴子石(伟晶岩−细晶岩)中(图11a)。Mn-Mg-Fe三元图解也显示研究区石榴子石位于MILLER等[6]定义的岩浆石榴子石区域中(图11b)。此外,石榴子石主、微量元素地球化学特征表明,断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石为铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石固溶系列,具富锰、低镁、贫钙,富集HREE,亏损LREE,具显著的Eu负异常特征,属典型岩浆型石榴子石[11,39,42]。
前人研究表明富Mn铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石在花岗岩熔体中压力低于500 MPa时保持稳定状态[47,51]。断峰山地区伟晶岩中存在白云母,表明岩浆结晶时最大压力为0.38 GPa,最高温度约为710℃[52]。高压形成的石榴子石一般w(MnO)较低(<3%) [53-54],而断峰山地区石榴子石w(MnO)较高,显然不是形成于高压条件。石榴子石分带具有强烈的温度依赖性,在岩浆温度超过700℃时,扩散速率比较快,消除了成分分带,该温度下形成锰铝榴石−铁铝榴石固溶体系列且无明显成分分带[55]。BSE和CL图像显示两种伟晶岩脉中石榴子石均无明显分带(图6),说明断峰山地区石榴子石结晶于中高温、中低压力条件下。FITTON[56]和WHITWORTH[7]研究指出泥质沉积物部分熔融熔体中生长的石榴子石具自形结构,锰铝榴石组分小于10%。本研究的成矿与未成矿伟晶岩中石榴子石自形程度均较好,但锰铝榴石质量分数很高(28.54%~62.89%),这意味着它们的母熔体不是泥质沉积物部分熔融而成的,应与岩浆活动有关。
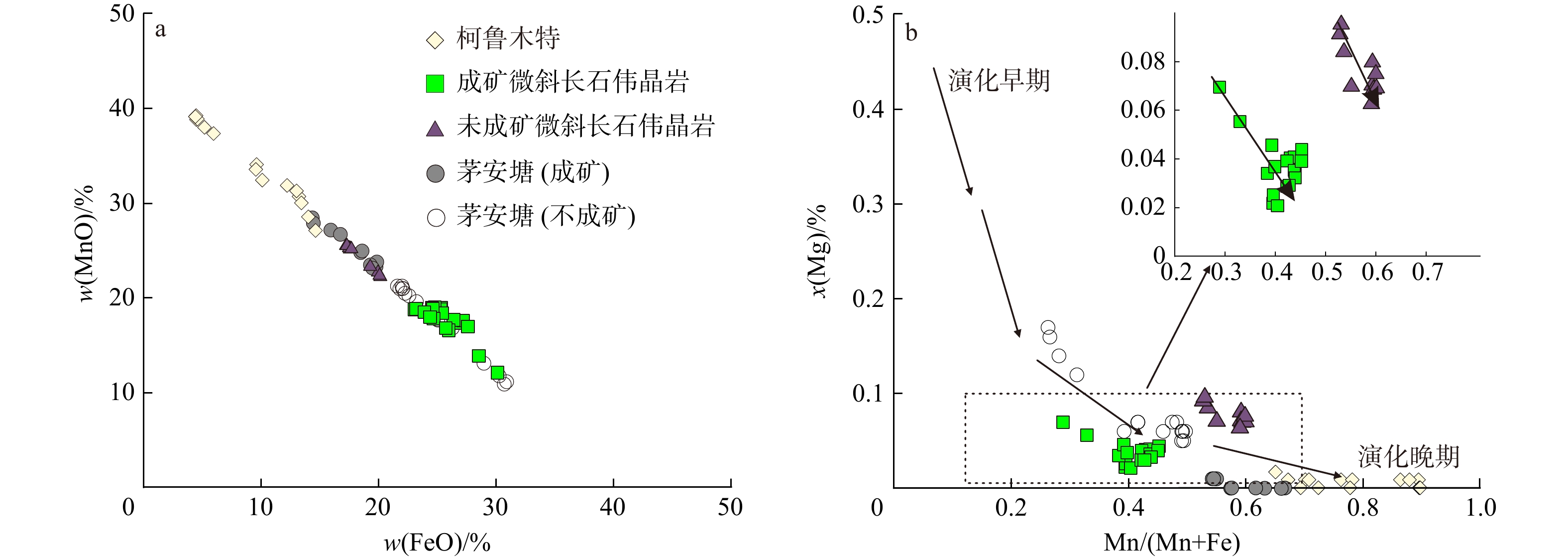
5.2 对稀有金属成矿作用的制约
形成于岩浆结晶分异晚期的石榴子石,通常以富含锰的铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石固熔体系列或富含锰铝榴石形式出现,而来自较低分馏伟晶岩的石榴子石通常富含铁[7,49,57-58]。MORETZ等[59]也认为来自演化程度较低的熔体中石榴子石含有较高的FeO含量,但MnO、MgO和CaO含量较低。如挪威南部 Froland和 EvjeIveland伟晶岩田中,从简单伟晶岩到白云母稀有金属伟晶岩,其石榴子石中MnO/(MnO+FeO)值显示增大的趋势[60]。茅安塘地区也显示出相似的规律,从不成矿伟晶岩到成矿伟晶岩,石榴子石中w(MnO)升高和w(FeO)降低(图11a)[11]。吕正航等[1]也指出稀有金属伟晶岩岩浆通常朝着富Mn和Ta的方向演化。石榴子石中Mn/(Fe+Mn) (摩尔分数)比值可以用作判别形成伟晶岩熔体的分异程度的指针[10],该比值增加反映了岩浆演化和分异程度的增强[6,58]。本研究的成矿微斜长石伟晶岩与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩均接近演化晚期[61],但不位于同一条演化线上(图12b)。未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩和成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石从核部到边部均表现为w(MnO)降低且w(FeO)增加趋势(图12)。石榴子石的这种微观成分变化环带在冈底斯东部的伟晶岩中也有报道,被解释为边部Ca含量的增加[62]。但是,吕正航等[1]提出对于具 Nb、Ta矿化伟晶岩,铌铁矿−钽锰矿系列的结晶对体系中 MnO和FeO质量分数影响较大。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石主要分布在中央相(图3),且该部位多分布有铌钽矿,根据与电气石和石榴子石的关系(图4),铌钽铁矿应与石榴子石共生。铌钽矿的类型主要为锰铌铁矿、锰钽铁矿和锰铌钽铁矿,其w(MnO)分别为7.95%~8.46%、5.47%~6.19%和7.00%~8.70%[28]。在花岗质岩浆演化过程中,长英质矿物(长石和石英)均贫Mn,而铌钽铁矿作为岩浆熔体中Mn、Fe组分的主要消耗矿物,导致残余岩浆熔体相对贫Mn富Fe,因此成矿伟晶岩中石榴子石中 Mn-Fe组成变化受到了铌钽矿物结晶的影响。目前幕阜山复式花岗岩体内部的大兴和麦埚伟晶岩脉被厘定形成于130~125 Ma[26,63],这与李艳军等[28]获得的本研究成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉形成时代一致,均为早白垩世岩浆活动的产物。尽管李乐广等[24]等认为幕阜山地区伟晶岩为复式岩体连续分离结晶形成,但更多研究者认为其是复式岩体的“体中体”模式 [17,21,29-30,64],即多个单一侵入体先后相继侵位构成“体中体”,而伟晶岩脉与每期较晚的高分异演化的岩体相关。因此,断峰山地区成矿与未成矿含石榴子石伟晶岩脉也可能是同时代不同来源的岩浆演化而成。
 图 12 断峰山地区石榴子石w(MnO)−w(FeO)(a) 和Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe)演化图解(b. 底图据文献[56])Figure 12. MnO content−FeO content (a) and Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe) diagrams (b) of garnets in the Duangfengshan area
图 12 断峰山地区石榴子石w(MnO)−w(FeO)(a) 和Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe)演化图解(b. 底图据文献[56])Figure 12. MnO content−FeO content (a) and Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe) diagrams (b) of garnets in the Duangfengshan area中酸性硅铝质熔浆体系从形成、迁移、冷却到到固结成岩大致需要经历3个阶段,即:岩浆阶段、岩浆−热液阶段以及热液阶段[65-66]。MULLER等[58]认为伟晶岩中石榴子石中Y和HREE含量变化与熔体和流体成分变化有关。随着岩浆分馏程度的增加,Nb、Ta、Y及HREE等元素在残余熔体中逐渐富集,这就导致了在残余熔体中结晶的石榴子石富集这些元素[67]。相对于未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩,断峰山地区成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石的Nb、Ta、Y及HREE等元素含量更低(图10)。成矿伟晶岩体系应进入了岩浆−热液阶段,热液流体的加入对岩浆环境造成了波动,不利于HREE和Y元素进入石榴子石[8,58]。在岩浆−热液体系中,Ta优先分配到硅酸盐熔体中,而Nb将优先分配在热液流体中,从而导致石榴子石Nb含量降低但Ta含量增加[68-69]。本研究的成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石Nb和Ta含量及变化关系明显不支持这一观点(图10a)。成矿伟晶岩中石榴子石中低的Nb和Ta含量可能与铌钽铁矿的结晶有关[70]。
挥发分对稀有金属元素富集有重要作用,岩浆侵位上升过程中,挥发分与稀有金属络合物快速迁移至岩体顶部逐渐富集[4,71]。从富含挥发分流体(熔体)中形成的石榴子石Y/Gd和Y/Dy值高于对应上地壳值,因富含高电负性配位体环境有利于络合物的形成,如F−、Cl−、SO42–和CO32–等 [10]。此外,BOGOCH等[60]认为富锰石榴子石是从富含挥发性成分熔体中结晶形成的。本研究的断峰山地区成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中富Mn石榴子石Y/Gd (9.93~111)和Y/Dy值 (6.81~9.76)均高于上地壳中Y/Gd和Y/Dy值(上地壳值Y/Gd=4.09和Y/Dy=4.00) [72]。且成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中常见电气石,少数成矿伟晶岩脉中可见锂云母,说明成岩过程中富含挥发组分 [73]。挥发组分起到助熔剂的作用,增加了熔体中铌钽等稀有金属含量[4,56,74],且挥发组分能增加熔体的流动性,致使了熔体能迁移较远距离,经济价值最大的伟晶岩脉(Li、Cs和Ta)与母岩花岗岩的距离最远(可达10 km)[61]。但对应复式岩体内部的伟晶岩脉,深部演化形成的伟晶岩岩浆就位时浅部岩浆−热液体系处于开放状态,高的过冷程度导致岩相分带不发育,且挥发分易逸出而不能与稀有金属组成络合物迁移富集成矿[75-76]。
6. 结 论
(1)断峰山地区伟晶岩中的石榴子石主要为岩浆成因,均具高铁锰、低钙镁、HREE富集、LREE亏损、显著的 Eu负异常特征,属于铁铝榴石−锰铝榴石固溶体系列。
(2)成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石以铁铝榴石为主(Sps42.56Alm54.63),而未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩脉中石榴子石以锰铝榴石为主(Sps58.93Alm37.18)。成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石Y、Nb、Ta、Zr和Hf含量低于未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石。
(3)成矿微斜长石伟晶岩中石榴子石具有低的Mn、Nb和Ta元素含量,且核部到边部Mn含量降低Fe含量增加,这可能是由于铌钽矿物的结晶导致,表明石榴子石中Nb,Ta,Fe,Mn等元素的演化关系可以指示幕阜山地区Nb-Ta成矿。
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
-
图 1 幕阜山地区大地构造 (a)及稀有金属矿床分布图 (b) [18]
Figure 1. Geotectonic map (a) and distribution map of rare metal deposits (b) in the Mufushan area
图 2 断峰山地区伟晶岩型Nb-Ta 矿床地质图[22]
Zr. 锆;Mz. 白云母
Figure 2. Geological map of the pegmatite type Nb-Ta deposit in Duanfengshan area
图 7 断峰山地区伟晶岩石榴子石三角分类图解(a,据文献[9]修改)和CaO−MgO图解(b)
Sps. 锰铝榴石;Alm. 铁铝榴石;Adr. 钙铁榴石;Prp. 镁铝榴石;Grs. 钙铝榴石
Figure 7. Triangle classification (a) and CaO-MgO (b) diagrams of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area
图 9 断峰山地区石榴子石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a,b)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(c,d)(标准化值据文献[38])
Figure 9. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, b) and primitive mantle normalized spidergrams of trace elements (c, d) of garnets in the Duanfengshan area
图 12 断峰山地区石榴子石w(MnO)−w(FeO)(a) 和Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe)演化图解(b. 底图据文献[56])
Figure 12. MnO content−FeO content (a) and Mg−Mn/(Mn+Fe) diagrams (b) of garnets in the Duangfengshan area
表 1 断峰山地区成矿与未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩差异对比
Table 1. Comparison of differences between mineralized and unmineralized microcline pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area
成矿微斜长石伟晶岩 未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩 围岩类型 新元古界冷家溪群片岩 黑云母二长花岗岩 与花岗岩的关系 岩体外的片岩内 岩体内部 展布方向 NE 向 NW向 规模及分带 数量较多,长度几百米至上千米,宽度几米至百余米,分带明显 数量较少,长度几米到几十米,宽度小于3 m,
分带不明显矿物组合 石英、斜长石、钾长石和白云母,副矿物石榴子石和电气石,
内带发育铌钽铁矿、锂云母、绿柱石石英、斜长石、钾长石和白云母,副矿物
石榴子石和电气石次级断裂构造 以NE向断裂为主,次为近NS向和近EW向断裂 以NW向断裂为主 表 2 断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石电子探针分析主量元素成分
Table 2. EPMA major element compositions of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area
样品号 成矿伟晶岩 未成矿伟晶岩 124-1 124-2 165-1 165-2 Lj-1 Lj-2 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 SiO2 wB/% 34.13 35.90 35.43 35.79 35.69 35.95 35.89 35.53 35.93 35.22 35.71 35.29 35.85 35.60 35.79 35.71 35.87 35.73 35.81 35.87 35.51 35.44 35.50 35.43 35.52 35.43 35.40 35.58 35.44 TiO2 0.04 0.02 0.01 bdl 0.09 0.11 0.03 0.07 bdl 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.04 0.06 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.01 0.05 0.03 0.08 0.10 0.05 0.05 Al2O3 19.83 19.99 19.90 19.62 19.54 19.87 19.58 19.75 20.12 20.55 19.45 20.33 20.68 20.52 20.58 20.76 20.71 20.88 20.74 20.43 19.93 19.93 20.35 20.03 20.01 19.82 19.76 20.06 20.04 FeO 26.88 27.13 26.32 27.55 25.26 25.25 24.75 24.47 22.99 25.35 24.55 23.14 30.07 25.91 24.63 23.86 24.32 25.64 28.48 19.89 20.09 17.55 20.01 19.22 17.49 17.43 17.17 17.23 17.62 MnO 17.34 17.56 17.65 16.96 18.94 18.80 19.00 18.92 18.77 18.36 18.85 18.82 12.07 16.55 17.81 18.49 17.95 16.79 13.82 22.71 22.20 25.22 22.35 23.30 25.13 25.27 25.50 25.49 25.14 MgO 0.17 0.21 0.17 0.28 0.33 0.33 0.33 0.28 0.35 0.32 0.29 0.31 0.56 0.37 0.23 0.26 0.24 0.30 0.45 0.69 0.74 0.65 0.78 0.57 0.57 0.56 0.56 0.61 0.51 CaO 0.51 0.49 0.49 0.52 0.64 0.65 0.61 0.61 0.66 0.63 0.69 0.64 0.31 0.53 0.45 0.48 0.44 0.46 0.42 0.41 0.39 0.52 0.39 0.39 0.48 0.59 0.46 0.45 0.48 Na2O 0.01 bdl 0.02 0.01 bdl bdl 0.02 bdl bdl bdl bdl 0.08 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 bdl bdl bdl 0.00 0.03 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 K2O 0.02 bdl 0.01 bdl bdl 0.01 bdl 0.01 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.02 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl bdl bdl bdl bdl bdl 0.00 bdl 0.00 bdl bdl bdl 0.01 0.00 总计 98.92 101.29 100.00 100.73 100.48 100.95 100.20 99.65 98.82 100.50 99.62 98.70 99.58 99.58 99.53 99.64 99.54 99.84 99.72 100.03 98.93 99.38 99.42 98.99 99.23 99.17 98.98 99.49 99.29 Si 原
子
数2.86 2.93 2.93 2.94 2.94 2.94 2.96 2.95 2.99 2.89 2.97 2.94 2.96 2.95 2.96 2.95 2.97 2.95 2.96 2.95 2.95 2.94 2.93 2.95 2.95 2.94 2.95 2.94 2.94 Ti 0.00 0.00 0.00 bdl 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 bdl 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 Al 1.82 1.86 1.87 1.84 1.84 1.86 1.87 1.88 1.97 1.88 1.87 1.94 1.98 1.95 1.97 1.97 1.99 1.98 1.97 1.93 1.91 1.88 1.92 1.91 1.90 1.88 1.89 1.90 1.90 Fe 1.88 1.85 1.82 1.89 1.74 1.73 1.71 1.70 1.60 1.74 1.70 1.61 2.08 1.79 1.71 1.65 1.68 1.77 1.97 1.37 1.40 1.22 1.38 1.34 1.21 1.21 1.20 1.19 1.22 Mn 1.23 1.22 1.24 1.18 1.32 1.30 1.33 1.33 1.33 1.28 1.33 1.33 0.84 1.16 1.25 1.29 1.26 1.17 0.97 1.58 1.56 1.77 1.56 1.64 1.77 1.78 1.80 1.79 1.77 Mg 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.07 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.10 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.06 Ca 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.03 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 Na 0.00 bdl 0.00 0.00 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl bdl 0.00 bdl 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 bdl bdl bdl 0.00 0.01 bdl 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Sps wB/% 44.49 42.94 43.35 42.00 47.16 45.92 46.61 46.38 44.25 44.43 46.38 45.62 28.54 39.51 42.16 43.97 42.46 39.83 32.70 54.06 54.09 61.77 53.80 56.64 60.97 61.98 62.89 61.90 61.19 Prp 0.78 0.89 0.73 1.22 1.42 1.42 1.43 1.21 1.46 1.37 1.24 1.34 2.34 1.55 0.97 1.10 0.98 1.25 1.88 2.88 3.17 2.80 3.29 2.42 2.44 2.40 2.43 2.62 2.18 Alm 53.23 54.70 54.42 55.16 49.69 51.01 50.18 50.75 52.32 52.45 50.47 51.34 68.27 57.56 55.64 53.69 55.26 57.62 64.17 41.96 41.70 34.02 41.76 39.92 35.21 34.08 33.59 34.27 35.32 Grs 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.66 0.00 0.00 1.65 0.85 0.86 1.14 1.24 1.30 1.30 1.26 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Adr 1.50 1.46 1.50 1.62 1.72 1.65 1.78 1.65 1.30 1.75 1.91 0.05 0.00 0.52 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.10 1.04 1.41 1.16 1.01 1.38 1.54 1.09 1.21 1.31 注:FeO为全铁含量;Sps. 锰铝榴石;Prp. 镁铝榴石;Alm. 铁铝榴石;Grs. 钙铝榴石;Adr. 钙铁榴石;bdl. 低于检测限;晶体化学式基于12个氧原子计算 表 3 断峰山地区伟晶岩中石榴子石 LA-ICP-MS原位微区分析微量元素成分
Table 3. LA-ICP-MS trace element compositions of garnets from pegmatites in the Duanfengshan area
样品号 成矿伟晶岩 未成矿伟晶岩 124-1 124-2 165-1 165-2 Lj-1 Lj-2 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 wB/10−6 Li 147.61 156.83 183.94 150.58 116.74 154.17 129.47 134.93 147.38 63.00 147.09 121.48 125.35 106.89 116.55 151.46 121.12 98.78 106.02 111.07 119.17 113.64 119.74 132.20 125.73 84.14 105.03 84.82 67.85 118.60 Be 0.00 0.20 0.18 0.13 0.10 0.19 0.05 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.31 0.31 0.32 0.00 0.00 0.32 0.06 0.00 0.25 0.51 0.05 0.05 0.26 0.13 0.11 0.11 0.00 0.24 0.00 B 1.81 0.03 1.88 0.27 0.47 4.36 0.00 1.67 0.00 1.44 1.76 1.21 0.00 0.14 2.36 0.00 0.35 1.06 0.74 1.37 2.15 1.38 1.46 1.37 0.12 0.96 2.92 0.94 0.00 0.51 Sc 4.22 6.83 11.64 5.98 20.17 20.60 16.57 15.56 14.77 4.91 14.79 13.24 14.29 7.31 5.65 7.73 11.94 9.27 8.61 7.92 4.48 5.37 5.25 4.82 2.53 6.83 4.75 2.60 2.46 2.64 V 0.03 0.00 0.12 0.04 0.04 0.11 0.13 0.00 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.06 0.09 0.00 0.10 0.01 0.04 1.41 0.86 1.19 0.14 0.07 0.12 0.79 0.06 0.15 0.09 1.48 0.74 0.99 Cr 2.64 0.81 2.06 0.99 0.00 0.00 0.58 0.00 0.00 0.70 2.23 0.19 1.52 0.00 0.00 0.97 0.06 0.97 0.00 0.88 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.46 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.88 0.00 0.21 Co 1.40 1.21 1.13 1.34 0.79 0.79 0.95 0.82 0.61 0.72 0.75 0.92 0.68 1.80 1.22 1.20 1.18 2.56 2.89 2.87 4.33 2.95 3.04 5.43 3.77 2.63 2.70 2.33 2.56 2.88 Ni 0.54 0.16 0.00 0.43 0.56 0.37 1.09 0.00 0.26 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.27 0.40 0.14 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.41 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.49 1.39 0.00 0.46 0.00 Cu 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.28 0.15 0.00 0.01 0.11 0.00 0.01 0.13 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.07 0.00 0.43 0.06 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.10 0.00 Zn 437.56 401.21 384.54 406.53 263.86 255.93 261.13 274.92 264.24 309.67 244.60 248.47 244.55 360.71 344.45 352.01 295.83 307.59 325.67 314.77 357.05 240.91 232.26 388.94 305.97 247.05 229.43 271.39 270.72 277.60 Ga 23.13 22.94 25.43 23.65 28.24 27.45 26.52 25.80 27.53 21.65 25.14 24.28 23.68 21.45 24.29 31.90 25.97 19.51 20.08 21.04 26.22 27.21 27.52 23.69 25.05 27.75 26.93 29.03 28.51 26.39 Rb 0.06 0.24 0.23 0.12 0.00 0.55 0.09 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.09 0.10 0.19 0.00 0.15 0.01 0.11 0.03 0.13 0.01 0.17 0.03 0.23 0.02 0.04 0.13 0.03 0.12 0.08 0.09 Sr 0.03 0.01 0.09 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.01 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.00 0.04 0.01 0.19 0.04 0.03 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.02 0.00 0.13 0.08 0.04 0.03 0.02 Y 412.70 491.11 719.37 399.24 613.71 551.78 514.67 457.63 549.46 41.67 532.36 527.06 549.03 321.23 379.42 454.46 208.79 254.55 568.45 742.88 712.33 775.60 849.18 585.37 462.66 831.41 679.86 606.30 497.87 517.41 Zr 12.82 13.11 13.36 12.34 17.74 19.41 17.95 18.90 19.33 8.91 19.34 17.76 17.85 8.96 8.80 8.67 10.93 6.93 7.17 7.52 21.13 18.18 18.33 9.55 14.29 20.84 20.26 23.40 21.48 17.26 Nb 0.30 0.38 0.74 0.31 1.00 1.00 0.96 0.84 0.98 0.26 1.07 0.71 0.68 0.12 0.69 1.97 0.63 0.02 0.02 0.05 5.14 2.88 3.81 1.52 0.70 2.32 4.86 5.70 3.77 0.93 Ag 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.05 0.01 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.00 0.00 Cd 11.24 10.41 12.40 10.70 7.62 10.55 9.05 8.47 6.06 6.94 6.79 6.91 6.97 8.31 7.89 10.14 6.55 7.93 10.09 7.23 6.90 6.14 5.43 8.10 6.81 7.97 6.19 8.64 9.66 10.15 Sn 6.61 6.79 7.38 5.64 6.29 6.22 6.98 6.57 7.03 1.68 7.69 7.12 6.67 3.89 4.31 6.49 6.35 1.63 1.18 0.91 11.41 12.10 11.42 6.11 7.88 12.94 12.87 9.85 9.67 9.44 Cs 0.04 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.03 1.36 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.06 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 Ba 0.08 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.06 0.00 0.04 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 La 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Ce 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Pr 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.02 Nd 0.11 0.11 0.01 0.09 0.31 0.15 0.26 0.22 0.40 0.12 0.22 0.35 0.30 0.07 0.02 0.03 0.20 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.17 0.19 0.20 0.02 0.15 0.23 0.24 0.24 0.21 0.15 wB/10−6 Sm 0.89 1.07 1.69 0.81 2.17 2.32 2.35 2.15 2.29 1.26 2.39 1.91 2.08 1.35 0.94 0.77 0.99 0.71 1.08 1.35 1.76 1.39 1.57 0.63 1.41 1.24 1.71 1.85 1.37 1.27 Eu 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.07 0.06 0.12 0.13 0.04 0.05 0.04 Gd 6.23 8.69 9.68 6.43 11.79 11.03 12.04 10.69 11.51 4.47 12.01 11.84 10.99 10.21 8.68 5.71 6.05 5.42 9.33 15.51 11.05 9.82 10.47 6.28 7.45 7.52 9.94 10.50 8.03 8.56 Tb 3.96 5.05 5.98 3.86 6.60 6.29 6.30 5.82 6.19 1.22 6.08 6.19 5.88 5.45 4.90 4.21 3.13 3.57 5.85 9.02 6.92 6.65 7.23 4.50 4.92 5.44 6.27 6.42 5.14 5.15 Dy 46.64 55.92 73.70 44.38 72.36 66.12 65.10 57.73 63.80 5.57 62.86 60.25 63.57 47.17 49.21 49.00 27.50 34.05 68.48 96.68 81.93 84.28 93.57 59.15 54.19 79.66 75.11 70.20 57.45 55.21 Ho 9.90 12.19 19.92 9.42 17.02 15.36 13.32 11.80 14.55 0.74 13.88 13.54 14.05 8.09 9.90 11.68 4.73 5.79 15.74 20.96 19.10 20.61 22.96 16.44 11.17 23.68 17.84 14.38 11.92 12.72 Er 33.20 39.76 79.42 30.52 61.37 51.80 47.58 40.31 50.85 2.57 46.29 44.72 49.46 19.37 28.69 43.56 13.91 15.51 48.30 66.16 66.28 76.52 85.58 63.21 34.77 113.59 69.14 46.86 39.66 43.41 Tm 6.76 7.74 19.50 6.22 13.84 10.98 10.32 8.58 11.15 0.62 9.87 9.99 11.15 3.44 5.53 10.22 2.68 2.40 9.53 12.84 14.53 17.87 20.85 13.09 6.45 34.21 17.01 9.78 8.22 8.81 Yb 57.11 63.16 187.59 52.81 122.96 99.92 96.19 81.37 98.13 5.56 89.30 89.26 103.69 24.38 46.96 92.96 22.01 17.89 72.94 100.04 128.98 169.54 196.62 106.20 49.22 381.86 171.94 84.68 71.18 79.36 Lu 6.37 7.10 25.15 5.63 15.52 12.40 12.36 10.10 12.38 0.67 11.22 11.49 13.68 2.40 5.21 11.81 2.41 1.77 8.34 11.82 16.01 22.40 25.85 14.69 5.32 57.98 22.96 10.11 8.90 9.59 Hf 0.32 0.37 0.53 0.46 0.58 0.62 0.66 0.49 0.70 0.24 0.64 0.68 0.63 0.31 0.36 0.34 0.47 0.23 0.13 0.25 1.05 0.90 1.00 0.53 0.48 0.80 1.18 1.16 1.00 0.70 Ta 0.46 0.34 0.89 0.37 1.13 1.07 1.01 0.90 1.15 0.40 0.90 0.69 0.79 0.15 0.39 1.66 1.44 0.07 0.06 0.05 3.24 2.30 2.90 1.92 1.17 3.03 2.83 4.54 3.58 1.68 Bi 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.04 0.01 0.09 0.08 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.07 Pb 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.36 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.03 0.11 0.00 0.16 Th 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.01 U 0.12 0.12 0.19 0.14 0.36 0.33 0.37 0.35 0.35 0.12 0.33 0.28 0.28 0.08 0.63 0.18 2.49 0.03 0.03 0.03 1.79 0.62 1.10 0.28 0.27 0.88 1.61 1.44 0.71 0.38 ∑REE 171.18 200.81 422.67 160.19 323.99 276.40 265.86 228.80 271.28 22.82 254.14 249.60 274.89 121.97 160.07 229.99 83.70 87.15 239.67 334.44 346.86 409.38 465.04 284.30 175.12 705.55 392.32 255.07 212.18 224.32 ∑LREE 1.02 1.20 1.74 0.92 2.52 2.50 2.65 2.40 2.71 1.41 2.65 2.30 2.41 1.46 0.99 0.83 1.27 0.75 1.17 1.42 2.07 1.70 1.90 0.74 1.63 1.62 2.10 2.14 1.67 1.50 ∑HREE 170.16 199.60 420.93 159.27 321.46 273.90 263.21 226.40 268.57 21.41 251.50 247.29 272.48 120.50 159.08 229.16 82.43 86.40 238.50 333.02 344.80 407.68 463.14 283.56 173.49 703.93 390.22 252.93 210.51 222.82 (La/Yb)N 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 (La/Sm)N 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 (Gd/Yb)N 0.09 0.11 0.04 0.10 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.10 0.66 0.11 0.11 0.09 0.35 0.15 0.05 0.23 0.25 0.11 0.13 0.07 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.13 0.02 0.05 0.10 0.09 0.09 Eu/Eu* 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.09 0.08 0.02 0.04 0.03 Y/Gd 66.27 56.54 74.35 62.10 52.05 50.01 42.73 42.82 47.75 9.33 44.33 44.51 49.94 31.46 43.72 79.56 34.50 46.93 60.93 47.91 64.48 78.96 81.08 93.27 62.14 110.62 68.37 57.76 61.96 60.45 Y/Dy 8.85 8.78 9.76 9.00 8.48 8.35 7.91 7.93 8.61 7.48 8.47 8.75 8.64 6.81 7.71 9.27 7.59 7.48 8.30 7.68 8.69 9.20 9.08 9.90 8.54 10.44 9.05 8.64 8.67 9.37 -
[1] 吕正航,张辉,赵景宇. 新疆柯鲁木特伟晶岩脉中石榴子石组成对岩浆−热液过程及Li矿化的制约[J]. 矿物学报,2017,37(3):247-257.LÜ Z H,ZHANG H,ZHAO J Y. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution and Li mineralization in pegmatite:Constraints from composition of garnet from kelumute No. 112 pegmatite,Xinjiang Autonomous Region,China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2017,37(3):247-257. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] KLECK W D,FOORD E E. The chemistry,mineralogy,and petrology of the George Ashley Block pegmatite body[J]. American Mineralogist,1999,84(5/6):695-707. [3] 梁祥济. 钙铝−钙铁系列石榴子石的特征及其交代机理[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,1994,13(4):342-352.LIANG X J. Garnets of grossular-andradite series:Their characteristics and metasomatic mechanism[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,1994,13(4):342-352. (in Chinese) [4] 冉子龙,李艳军. 伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床成矿作用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(2):13-23.RAN Z L,LI Y J. Research advances on rare metal pegmatite deposits[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(2):13-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] ALLAN B D,CLATKE D B. Ocurrence and origin of garmets in the South Mountain Batholith,Nova Scotia[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist,1981,19(1):19-24. [6] MILLER C F,STODDARD E F. The role of manganese in the paragenesis of magmatic garnet:An example from the old woman-piute range,California[J]. The Journal of Geology,1981,89(2):233-246. doi: 10.1086/628582 [7] WHITWORTH M P. Petrogenetic implications of garnets associated with lithium pegmatites from SE Ireland[J]. Mineralogical Magazine,1992,56:75-83. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1992.056.382.10 [8] SAMADI R,MILLER N R,MIRNEJAD H,et al. Origin of garnet in aplite and pegmatite from Khajeh Morad in northeastern Iran:A major,trace element,and oxygen isotope approach[J]. Lithos,2014,208:378-392. [9] HERNÁNDEZ-FILIBERTO L,RODA-ROBLES E,SIMMONS W B,et al. Garnet as indicator of pegmatite evolution:The case study of pegmatites from the Oxford pegmatite field (Maine,USA)[J]. Minerals,2021,11(8):802. doi: 10.3390/min11080802 [10] RAHMANI JAVANMARD S,TAHMASBI Z,DING X,et al. Geochemistry of garnet in pegmatites from the Boroujerd intrusive complex,Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone,western Iran:Implications for the origin of pegmatite melts[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology,2018,112(6):837-856. doi: 10.1007/s00710-018-0591-x [11] 陈欢,冯梦,康志强,等. 桂东北茅安塘伟晶岩中石榴子石的特征及对岩浆演化的指示意义[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(6):2059-2076.CHEN H,FENG M,KANG Z Q,et al. Characteristics of garnets in pegmatites of Mao'antang,northeast Guangxi,and their implications for magmatic evolution[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(6):2059-2076. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 周振华,车合伟,马星华,等. 初论稀有金属矿床研究的一些重要进展[J]. 地质与勘探,2016,52(4):614-626.ZHOU Z H,CHE H W,MA X H,et al. A preliminary discussion on some important advances of the rare metal deposit[J]. Geology and Exploration,2016,52(4):614-626. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 季浩,李艳军,李一鸣,等. 碱性花岗岩型稀有稀土矿床类型及成矿作用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):23-38.JI H,LI Y J,LI Y M,et al. Research advances on mineralization and types of the alkaline granite-related rare metal and rare earth element deposits[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):23-38. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 刘翔,周芳春,黄志飚,等. 湖南平江县仁里超大型伟晶岩型铌钽多金属矿床的发现及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2018,42(2):235-243.LIU X,ZHOU F C,HUANG Z B,et al. Discovery of Renli superlarge pegmatite-type Nb-Ta polymetallic deposit in Pingjiang,Hunan Province and its significances[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2018,42(2):235-243. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 李鹏,张立平,李建康,等. 江南造山带中段幕阜山地区稀有金属成矿规律及其在找矿中的应用[J]. 矿床地质,2021,40(4):819-841.LI P,ZHANG L P,LI J K,et al. Metallogenic regularity of rare metal deposits in Mufushan area of Central China,and its application in ore prospecting[J]. Mineral Deposits,2021,40(4):819-841. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 李鹏,周芳春,李建康,等. 湘东北仁里−传梓源铌钽矿床隐伏花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2020,44(3):486-500.LI P,ZHOU F C,LI J K,et al. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic compositions of the concealed granite of Renli-Chuanziyuan deposit,NE Hunan and geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2020,44(3):486-500. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LI P,LI J K,LIU X,et al. Geochronology and source of the rare-metal pegmatite in the Mufushan area of the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt:A case study of the giant Renli Nb-Ta deposit in Hunan,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,116:103237. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103237 [18] 文春华,罗小亚,陈剑锋,等. 湘东北幕阜山地区燕山期岩浆演化与稀有金属成矿的关系[J]. 中国地质调查,2019,6(6):19-28.WEN C H,LUO X Y,CHEN J F,et al. Relationship between Yanshanian magmatic activity and rare metal mineralization in Mufushan area of northeast Hunan[J]. Geological Survey of China,2019,6(6):19-28. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 王臻,陈振宇,李建康,等. 云母矿物对仁里稀有金属伟晶岩矿床岩浆−热液演化过程的指示[J]. 矿床地质,2019,38(5):1039-1052.WANG Z,CHEN Z Y,LI J K,et al. Indication of mica minerals for magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of Renli rare metal pegmatite deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits,2019,38(5):1039-1052. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 杨晗,陈振宇,李建康,等. 湘东北仁里−传梓源5号伟晶岩脉云母和长石成分的演化与成矿作用的关系[J]. 矿床地质,2019,38(4):851-866.YANG H,CHEN Z Y,LI J K,et al. Relationship between the mineralization and the evolution of mica and feldspar components of Renli-Chuanziyuan No. 5 pegmatite,northeast Hunan[J]. Mineral Deposits,2019,38(4):851-866. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 李鹏,刘翔,李建康,等. 湘东北仁里−传梓源矿床5号伟晶岩岩相学、地球化学特征及成矿时代[J]. 地质学报,2019,93(6):1374-1391.LI P,LIU X,LI J K,et al. Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of Renli-Chuanziyuan No. 5 pegmatite,NE Hunan,and its metallogenic age[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2019,93(6):1374-1391. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 湖北省第四地质大队. 湖北通城断峰山含铌钽花岗伟晶岩矿区地质勘探报告[R]. 咸宁:湖北省第四地质大队,1974.The 4th Geological Team of Hubei Geological Bureau. Geological exploration report of Duanfengshan niobium-tantalum granite pegmatite mining area in Tongcheng,Hubei[R]. Xianning:The 4th Geological Team of Hubei Geological Bureau,1974. (in chinese [23] 张文胜,尹近,黄艳华,等. 湖北省通城县断峰山含铌钽伟晶岩空间分布规律[J]. 现代矿业,2019,35(11):44-48.ZHANG W S,YIN J,HUANG Y H,et al. Spatial distribution law of the niobium tantalum pegmatite in Duanfengshan,Tongcheng County,Hubei Province[J]. Modern Mining,2019,35(11):44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 李乐广,王连训,田洋,等. 华南幕阜山花岗伟晶岩的矿物化学特征及指示意义[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(7):2532-2560.LI L G,WANG L X,TIAN Y,et al. Petrogenesis and rare-metal mineralization of the Mufushan granitic pegmatite,South China:Insights from in situ mineral analysis[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(7):2532-2560. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 张丽雅,张成乘,赵帆,等. 湖北省断峰山铌钽矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代矿业,2019,35(6):45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.06.012ZHANG L Y,ZHANG C C,ZHAO F,et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Duanfengshan niobium-tantalum deposit in Hubei Province[J]. Modern Mining,2019,35(6):45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.06.012 [26] 李鹏,李建康,裴荣富,等. 幕阜山复式花岗岩体多期次演化与白垩纪稀有金属成矿高峰:年代学依据[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(10):1684-1696.LI P,LI J K,PEI R F,et al. Multistage magmatic evolution and Cretaceous peak metallogenic epochs of Mufushan composite granite mass:Constrains from geochronological evidence[J]. Earth Science,2017,42(10):1684-1696. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 祝明明,邹建林,王闯,等. 幕阜山地区断峰山铌钽矿的矿物学、年代学和赋存状态[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(6):55-69.ZHU M M,ZOU J L,WANG C,et al. Mineralogy,geochronology and occurrence state of the Duanfengshan Nb-Ta deposit in Mufushan area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(6):55-69. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 李艳军,魏俊浩,张文胜,等. 幕阜山复式岩体西北缘新发现微斜长石伟晶岩型铌钽矿化[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(2):208-210.LI Y J,WEI J H,ZHANG W S,et al. Newly discovered microplagioclase pegmatite-type Nb-Ta mineralization in the northwestern margin of the Mufushan granitic complex[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(2):208-210. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 刘翔,周芳春,李鹏,等. 湖南仁里稀有金属矿田地质特征、成矿时代及其找矿意义[J]. 矿床地质,2019,38(4):771-791.LIU X,ZHOU F C,LI P,et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic age of Renli rare metal orefield in Hunan and its prospecting significance[J]. Mineral Deposits,2019,38(4):771-791. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 周芳春,李建康,刘翔,等. 湖南仁里铌钽矿床矿体地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 地质学报,2019,93(6):1392-1404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.017ZHOU F C,LI J K,LIU X,et al. Geochemical characteristics and genetic significance of ore bodies in Renli Nb-Ta deposit,Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2019,93(6):1392-1404. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.017 [31] 陕亮,柯贤忠,庞迎春,等. 湘东北栗山地区新元古代岩浆活动及其地质意义:锆石U-Pb年代学、Lu-Hf同位素证据[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(6):32-42.SHAN L,KE X Z,PANG Y C,et al. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb chronology,Lu-Hf isotopic characteristics and its geological significance of the Neoproterozoic magma activity in Lishan area from the northeastern Hunan Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(6):32-42. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] WANG L X,MA C Q,ZHANG C,et al. Genesis of leucogranite by prolonged fractional crystallization:A case study of the Mufushan complex,South China[J]. Lithos,2014,206:147-163. [33] JI W B,LIN W,FAURE M,et al. Origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous peraluminous granitoids in the northeastern Hunan Province (middle Yangtze region),South China:Geodynamic implications for the Paleo-Pacific subduction[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,141:174-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.07.005 [34] WAN L,JIN W,TIAN Y,et al. Petrogenesis of Late Jurassic Mufushan high-Mg diorites and Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern South China Block[J]. Gondwana Research,2023,121:118-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2023.04.001 [35] 文春华,陈剑锋,罗小亚,等. 湘东北传梓源稀有金属花岗伟晶岩地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2016,35(1):171-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.01.020WEN C H,CHEN J F,LUO X Y,et al. Geochemical features of the Chuanziyuan rare metal pegmatite in northeastern Hunan,China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2016,35(1):171-177. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.01.020 [36] LOCOCK A J. An excel spreadsheet to recast analyses of garnet into end-member components,and a synopsis of the crystal chemistry of natural silicate garnets[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2008,34(12):1769-1780. [37] LIU Y S,HU Z C,GAO S,et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology,2008,257(1/2):34-43. [38] SUN S S,MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications,1989,42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 [39] 高利娥,曾令森,石卫刚,等. 喜马拉雅造山带新生代花岗岩中两类石榴石的地球化学特征及其在地壳深熔作用中的意义[J]. 岩石学报,2012,28(9):2963-2980.GAO L E,ZENG L S,SHI W G,et al. Two types of garnets in the Cenozoic granites from the Himayalan Orogenic Belt:Geochemical characteristics and implications for crustal anatexis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2012,28(9):2963-2980. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 曾令森,赵令浩,高利娥,等. 喜马拉雅造山带中新世岩浆型石榴子石的矿物化学特征:从高Sr/Y花岗岩到淡色花岗岩[J]. 岩石学报,2019,35(6):1599-1626. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.06.01ZENG L S,ZHAO L H,GAO L E,et al. Magmatic garnet from Mid-Miocene co-genetic high Sr/Y granite and leucogranite from the Himalayan Orogenic Belt,southern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2019,35(6):1599-1626. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.06.01 [41] BEKELE B,SEN A K. The mineral chemistry of gahnite,garnet and columbite-group minerals (CGM):Implications for genesis and evolution of the Kenticha rare-element granite-pegmatite,Adola,Ethiopia[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,2020,162:103691. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.103691 [42] 付建刚,李光明,董随亮,等. 西藏拉隆穹窿淡色花岗岩中石榴子石矿物学研究及对岩浆−热液过程的指示[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2022,42(2):288-299.FU J G,LI G M,DONG S L,et al. Mineral chemistry of garnet and its implication for the magmatic-hydrothermal transition in rare metal leucogranites in the Lalong dome,southern Tibet,China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2022,42(2):288-299. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] STEVENS G,VILLAROS A,MOYEN J F. Selective peritectic garnet entrainment as the origin of geochemical diversity in S-type granites[J]. Geology,2007,35(1):9-12. [44] ZENG L S,GAO L,DONG C Y,et al. High-pressure melting of metapelite and the formation of Ca-rich granitic melts in the Namche Barwa Massif,southern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research,2012,21(1):138-151. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.023 [45] 孟繁聪,田广阔,段雪鹏,等. 东昆仑东段金水口石榴堇青石花岗岩成因:石榴子石证据[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2018,37(2):192-204.MENG F C,TIAN G K,DUAN X P,et al. Evidence from garnet for genesis of garnet-cordierite-granite in the Jinshuikou area,eastern segment of the East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2018,37(2):192-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] 冯帆,徐仲元,董晓杰,等. 内蒙古乌拉山地区石榴子石花岗岩中石榴子石转熔成因的显微结构及矿物学证据[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(11):3819-3833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.11.011FENG F,XU Z Y,DONG X J,et al. Microstructure and mineralogical evidence for peritectic garnet in thegarnet granite in the Wulashan area,Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(11):3819-3833. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.11.011 [47] GREEN T H. Garnet in silicic liquids and its possible use as a P-T indicator[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1977,65(1):59-67. doi: 10.1007/BF00373571 [48] SAMADI R,MIRNEJAD H,KAWABATA H,et al. Magmatic garnet in the Triassic (215 Ma) Dehnow pluton of NE Iran and its petrogenetic significance[J]. International Geology Review,2014,56(5):596-621. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.880659 [49] MANNING D A C. Chemical variation in garnets from aplites and pegmatites,peninsular Thailand[J]. Mineralogical Magazine,1983,47:353-358. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1983.047.344.10 [50] WHITWORTH M P,FEELY M. The compositional range of magmatic Mn-garnets in the Galway Granite,Connemara,Ireland[J]. Mineralogical Magazine,1994,58:163-168. [51] CLEMENS J D,WALL V J. Origin and crystallization of some peraluminous (S-type) granitic magmas[J]. Canadian Mineralogist,1981,19(1):111-131. [52] KERRICK D M. Experimental determination of muscovite + quartz stability with P H2O total[J]. American Journal of Science,1972,272(10):946-958. doi: 10.2475/ajs.272.10.946 [53] HARANGI S,DOWNES H,KÓSA L,et al. Almandine garnet in calc-alkaline volcanic rocks of the northern Pannonian Basin (eastern–central Europe):Geochemistry,petrogenesis and geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Petrology,2001,42(10):1813-1843. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.10.1813 [54] QUELHAS P,MATA J,DIAS Á A. Magmatic evolution of garnet-bearing highly fractionated granitic rocks from Macao,Southeast China:Implications for granite-related mineralization processes[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2021,32(6):1454-1471. [55] DAHLQUIST J A,GALINDO C,PANKHURST R J,et al. Magmatic evolution of the Peñón Rosado granite:Petrogenesis of garnet-bearing granitoids[J]. Lithos,2007,95(3/4):177-207. [56] FITTON J G. The genetic significance of almandine-pyrope phenocrysts in the calc-alkaline Borrowdale Volcanic Group,Northern England[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1972,36(3):231-248. doi: 10.1007/BF00371434 [57] FENG Y G,LEI R X,JU M H,et al. Origin and petrogenetic implications of garnet from Rb-rich pegmatites in North Qinling Orogen,China[J]. Geological Journal,2017,52(S1):215-237. doi: 10.1002/gj.3118 [58] MULLER A,KEARSLEY A,SPRATT J,et al. Petrogenetic implications of magmatic garnet in granitic pegmatites from southern Norway[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist,2012,50(4):1095-1115. doi: 10.3749/canmin.50.4.1095 [59] MORETZ L,HEIMANN A,BITNER J,et al. The composition of garnet as indicator of rare metal (Li) mineralization in granitic pegmatites[C]//Anon. Proceeding of the 6th International Symposium on Granitic Pegmatites. [S. l. ]:[S. n. ],2013,94-95. [60] BOGOCH R,BOURNE J,SHIRAV M,et al. Petrochemistry of a Late Precambrian garnetiferous granite,pegmatite and aplite,southern Israel[J]. Mineralogical Magazine,1997,61:111-122. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1997.061.404.11 [61] SELWAY J B. A review of rare-element (Li-Cs-Ta) pegmatite exploration techniques for the superior province,Canada,and large worldwide tantalum deposits[J]. Exploration and Mining Geology,2005,14(1/2/3/4):1-30. [62] YU M,XIA Q X,ZHENG Y F,et al. The composition of garnet in granite and pegmatite from the Gangdese Orogen in southeastern Tibet:Constraints on pegmatite petrogenesis[J]. American Mineralogist,2021,106(2):265-281. doi: 10.2138/am-2020-7388 [63] 姜鹏飞,李鹏,李建康,等. 幕阜山东部麦埚铍矿床伟晶岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质,2021,40(4):723-739.JIANG P F,LI P,LI J K,et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of Be-pegmatites in Maiguo deposit,eastern Mufushan,and their geological implications[J]. Mineral Deposits,2021,40(4):723-739. (in Chinese with English abstract [64] 石威科,周芳春,刘翔,等. 湖南仁里矿田锂辉石白云母伟晶岩地质特征及其找矿意义[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(3):817-835.SHI W K,ZHOU F C,LIU X,et al. Geological characteristics and the prospecting significance of the spodumene-muscovite pegmatite in the Renli ore-field,Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(3):817-835. (in Chinese with English abstract [65] BADANINA E V,VEKSLER I V,THOMAS R,et al. Magmatic evolution of Li-F,rare-metal granites:A case study of melt inclusions in the Khangilay complex,eastern Transbaikalia (Russia)[J]. Chemical Geology,2004,210(1/2/3/4):113-133. [66] KAETER D,BARROS R,MENUGE J F,et al. The magmatic-hydrothermal transition in rare-element pegmatites from southeast Ireland:LA-ICP-MS chemical mapping of muscovite and columbite-tantalite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2018,240:98-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.024 [67] MARKS M A W,MARSCHALL H R,SCHÜHLE P,et al. Trace element systematics of tourmaline in pegmatitic and hydrothermal systems from the Variscan Schwarzwald (Germany):The importance of major element composition,sector zoning,and fluid or melt composition[J]. Chemical Geology,2013,344:73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.025 [68] THOMAS R,FÖRSTER H J,HEINRICH W,et al. The behaviour of boron in a peraluminous granite-pegmatite system and associated hydrothermal solutions:A melt and fluid-inclusion study[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2003,144:457-472. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0410-5 [69] VEKSLER I V. Liquid immiscibility and its role at the magmatic-hydrothermal transition:A summary of experimental studies[J]. Chemical Geology,2004,210(1/2/3/4):7-31. [70] ZHANG X Y,WANG H,YAN Q H. Garnet geochemical compositions of the Bailongshan lithium polymetallic deposit in Xinjiang Province:Implications for magmatic-hydrothermal evolution[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,150:105178. [71] 王联魁,王慧芬,黄智龙. Li-F花岗岩液态分离的微量元素地球化学标志[J]. 岩石学报,2000,16(2):145. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2000.02.001WANG L K,WANG H F,HUANG Z L. Geochemical indicators of trace element in Li-F granite liquid segregation[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2000,16(2):145. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2000.02.001 [72] 鄢明才,迟清华,顾铁新,等. 中国东部地壳元素丰度与岩石平均化学组成研究[J]. 物探与化探,1997,21(6):451-459.YAN M C,CHI Q H,GU T X,et al. Chemical compositions of continental crust and rocks in eastern China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,1997,21(6):451-459. (in Chinese with English abstract [73] 孟玉净,骆杨,赵彦超,等. 泾河油田走滑断裂带长8-长6段致密砂岩构造成岩作用及控储分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(1):74-89.MENG Y J,LUO Y,ZHAO Y C,et al. Structural diagenesis and reservoir control analysis of tight sandstone in the strike-slip fault zones of the Chang 8 to Chang 6 Members in the Jinghe Oilfield[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(1):74-89. (in Chinese with English abstract [74] 花旗,夏庆霖,刘奇锋. 基于数据驱动的南岭地区花岗岩岩体含矿性判别[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(1):332-345.HUA Q,XIA Q L,LIU Q F. Ore-bearing discrimination of granite rock masses in the Nanling area via data-driven models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(1):332-345. (in Chinese with English abstract [75] 热西提·亚力坤,黄雷,杨帆,等. 烧变岩矿物相特征及其转化[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(8):134-144.REXITI Y L K,HUANG L,YANG F,et al. Characteristics and transformations of mineral phases in burnt rocks[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(8):134-144. (in Chinese with English abstract [76] 刘俊民,张关龙,赵乐强,等. 胜利探区油气共/伴生资源综合利用前景[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2024,31(4):207-216.LIU J M,ZHANG G L,ZHAO L Q,et al. Prospects for comprehensive utilization of symbiotic/associated oil and gas resources in exploration area of Shengli Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2024,31(4):207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: