Influence of aggregation angle of aggregated landslide debris flows based on discrete element model
-
摘要:
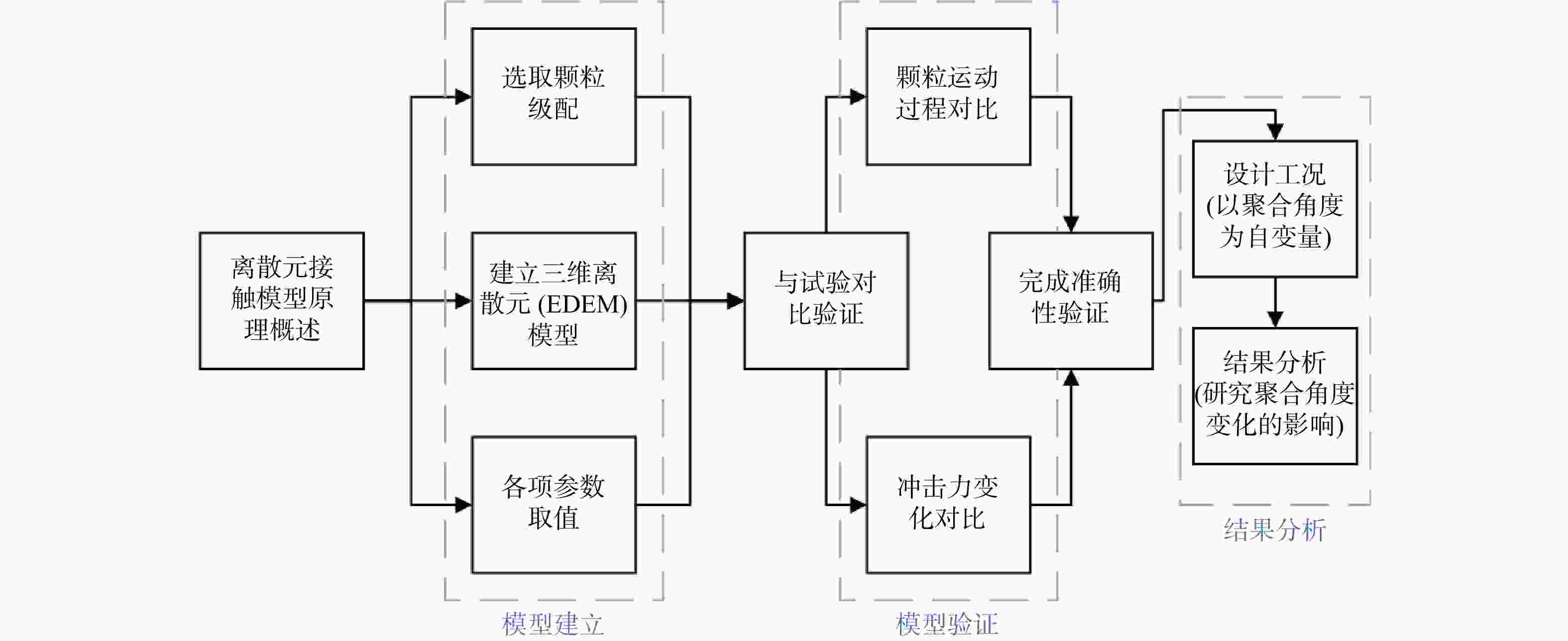
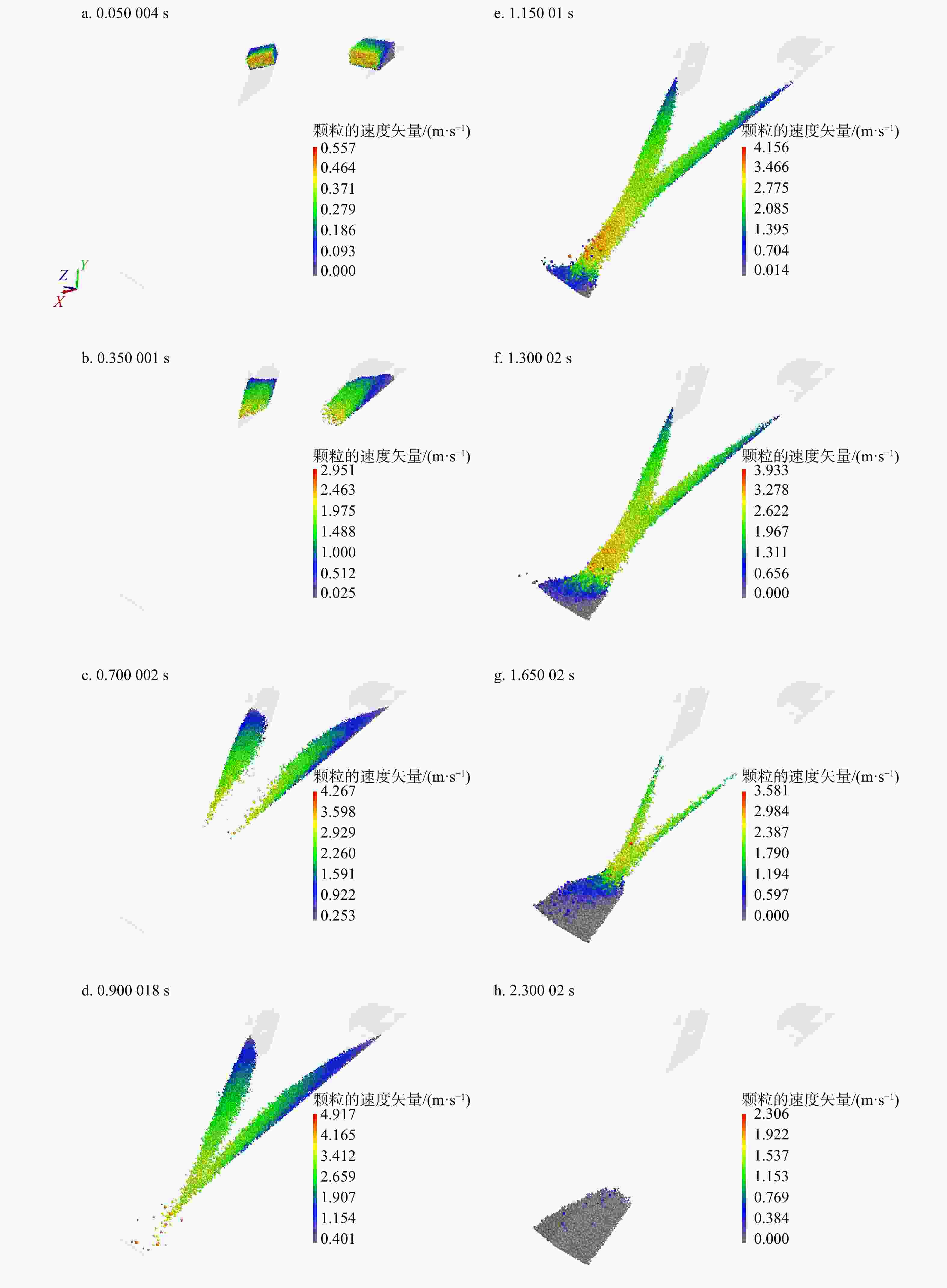
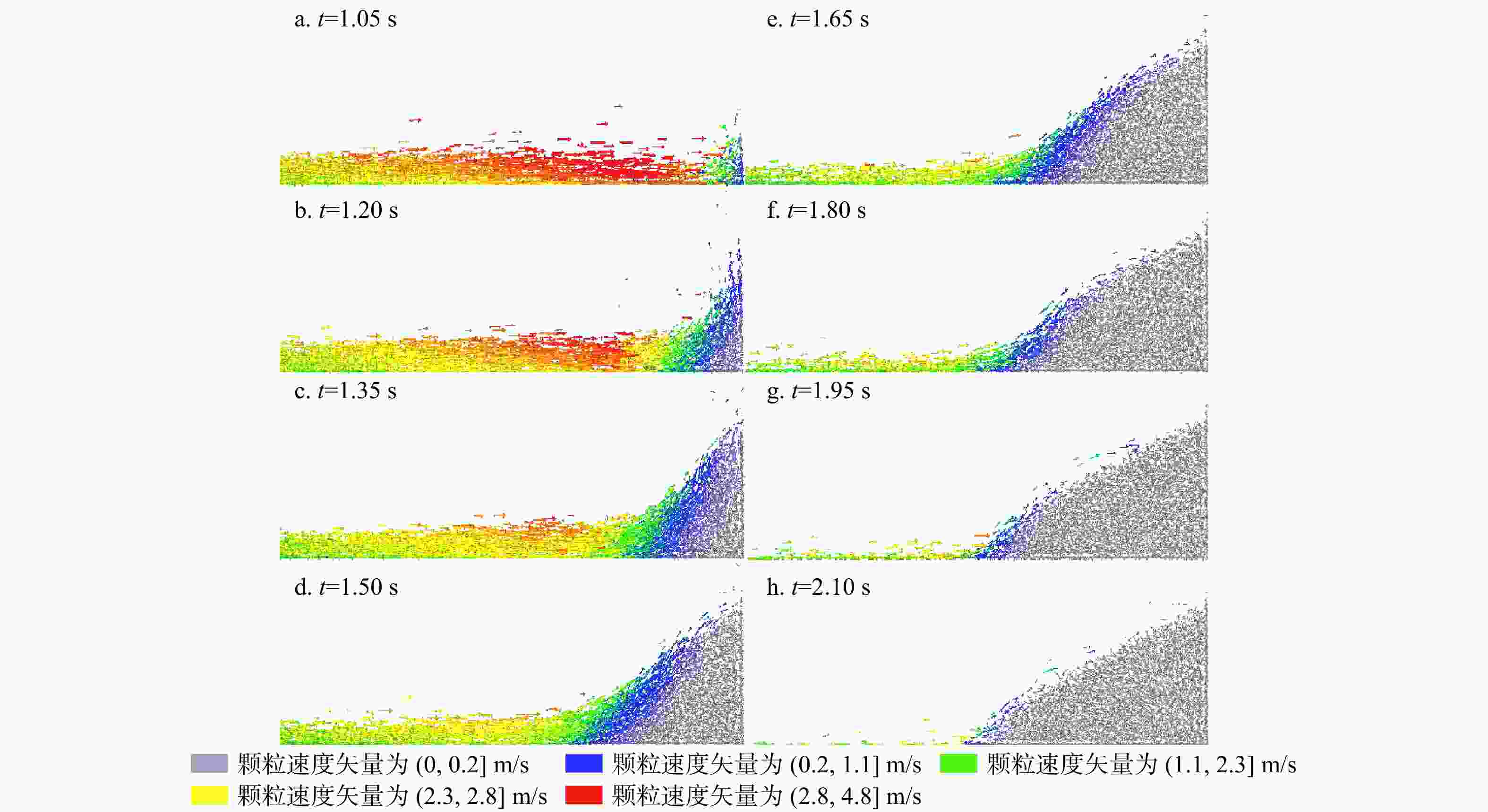
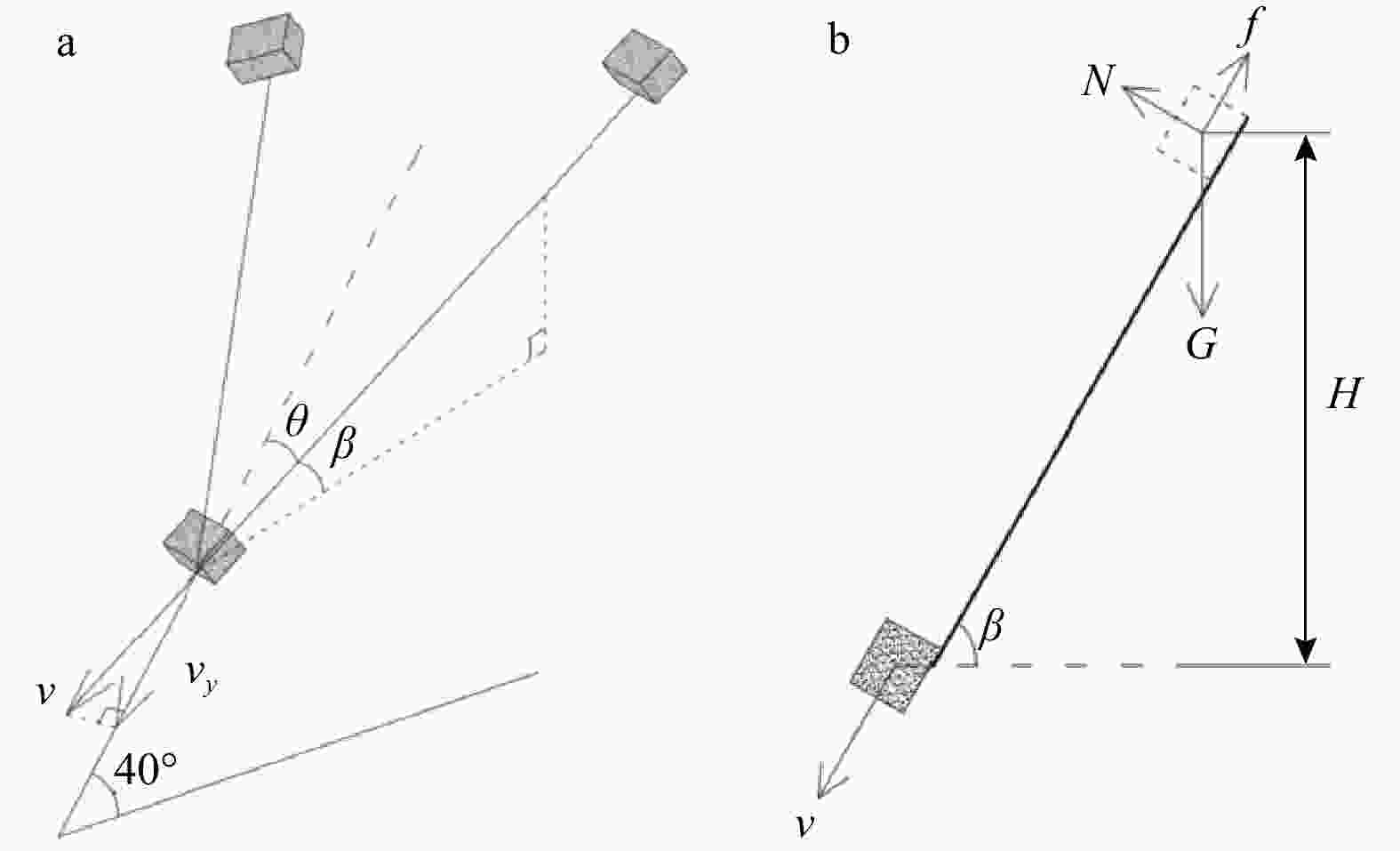
滑坡碎屑流是一种常见的地质灾害,它有着规模宏大、滑动距离远、速度快的特征,而山坡沟谷等地形会影响滑坡碎屑流的运动轨迹,进而对其产生阻拦、转向、堆积等一系列影响,所以滑坡碎屑流不仅仅只有简单的直线路径,受到地形因素的影响,其运动路径复杂多样。本研究主要基于滑坡碎屑流不同运动轨迹中的聚合行为,采用EDEM软件,分析对称聚合型滑坡碎屑流在不同聚合角度中的运动冲击和堆积特性。研究结果表明:①聚合角度对于运动速度的影响:聚合角度越大,颗粒到达聚合点时沿主坡道的速度分量
v y 越小,滑坡碎屑流分离程度越高,滑坡滑动时间越长;②聚合角度对于堆积形态的影响:聚合角度越大,滑坡稳定在坡脚处,其堆积区的形态,在滑道一侧的长度越长,而在拦挡结构处的高度越小;③聚合角度对于冲击性能的影响:聚合角度越大,对拦挡结构的冲击力峰值越低且越晚出现峰值;在停止运动形成静态堆积区后的残余冲击力也越低,残余冲击力的值也与冲击力峰值越接近。研究成果为滑坡碎屑流复杂路径运动深入研究提供了基础作用,为滑坡碎屑流防治结构优化提供了理论参考。Abstract:Objective Landslide debris flows are common geological disasters characterized by large scale, long sliding distances, and high speeds. The terrain of hillside ravines and valleys significantly influences the trajectory of these flows, causing them to block, turn, pile up, and exhibit a series of complex behaviors. Therefore, the movement path of landslide debris flows is not a simple straight line but is influenced by various terrain factors, resulting in complex and varied trajectories.
Methods This study focuses on the aggregation behavior of landslide debris flows along different motion trajectories. Using EDEM software, we analyzed the impact and accumulation characteristics of symmetrically aggregated landslide debris flows at various aggregation angles.
Results This study has reached results in three aspects. 1) Effect of the aggregation angle on movement velocity: Larger aggregation angles result in lower
v y values, higher degrees of separation of the landslide debris flow, and longer sliding times. 2) Effect of the aggregation angle on accumulation morphology: Larger aggregation angles cause the landslide to stabilize at the foot of the slope, with the accumulation zone lengthening on the slide side and decreasing in height at the blocking structure. 3) Effect on impact performance: Larger aggregation angles lead to lower and later peak impact forces on the barrier structure. Additionally, the residual impact force after the formation of a static accumulation area is lower and closer to the peak impact force.Conclusion These findings provide a fundamental basis for the in-depth study of the complex movement paths of landslide debris flows and offer theoretical references for optimizing landslide debris flow control structures.
-
Key words:
- landslide debris flow /
- aggregation angle /
- kinematic properties /
- force of impact /
- discrete element /
- EDEM
-
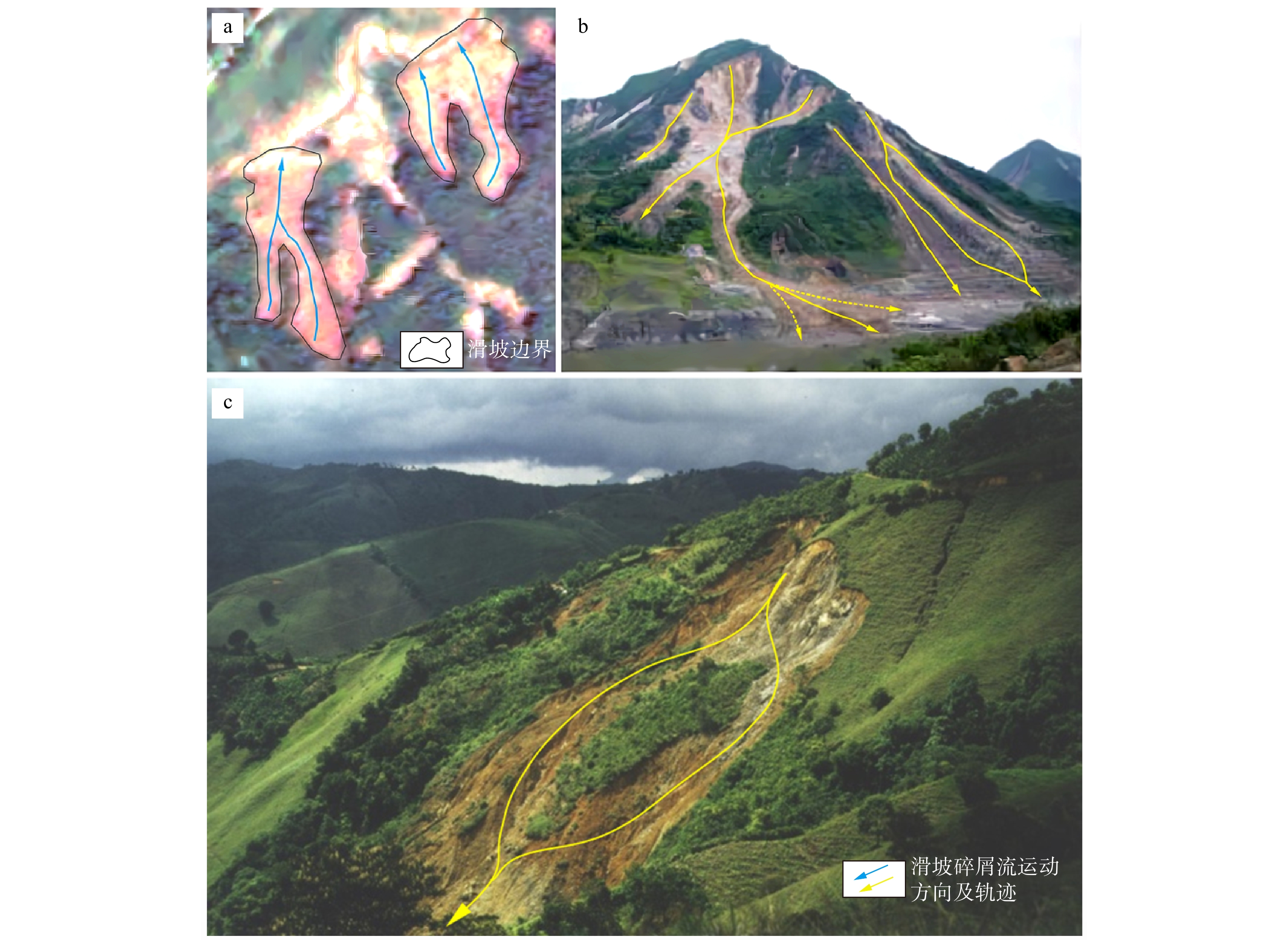
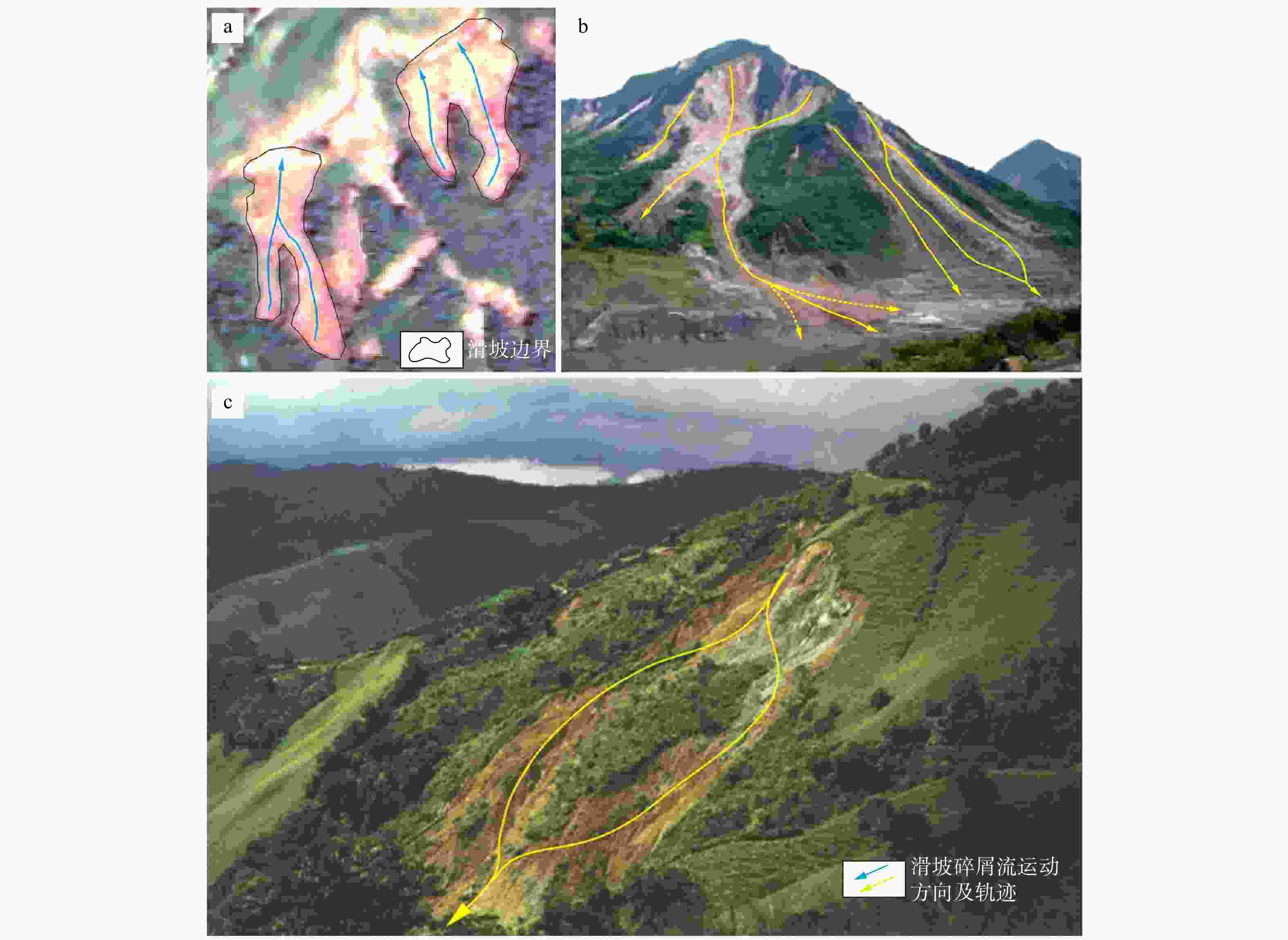
图 1 滑坡6种复杂行为的部分案例
a. 福建南平滑坡;b. 汶川地震引发的滑坡;c. 交织滑坡(据文献[35]修改)
Figure 1. Selected cases of six complex behaviors of landslides
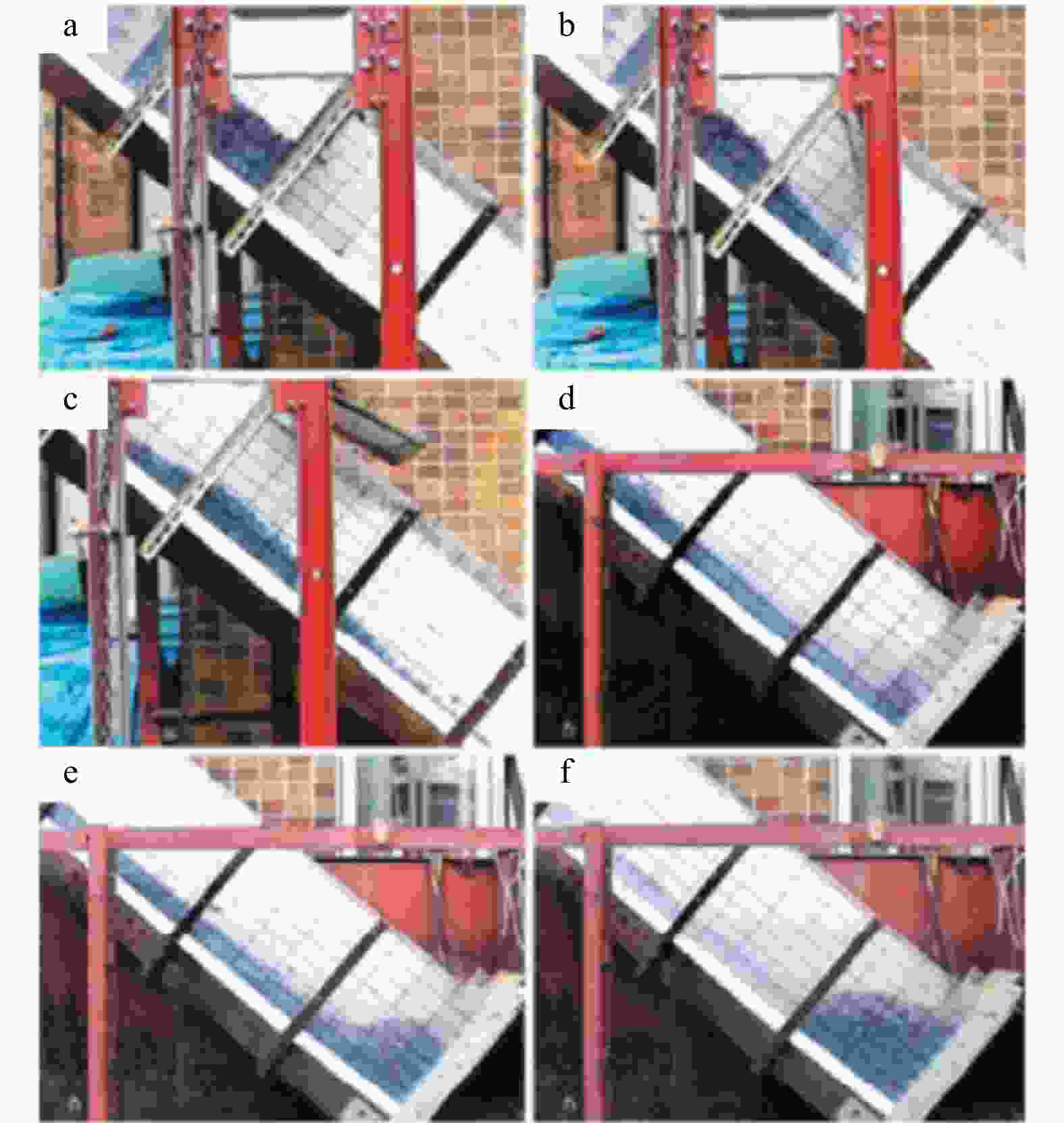
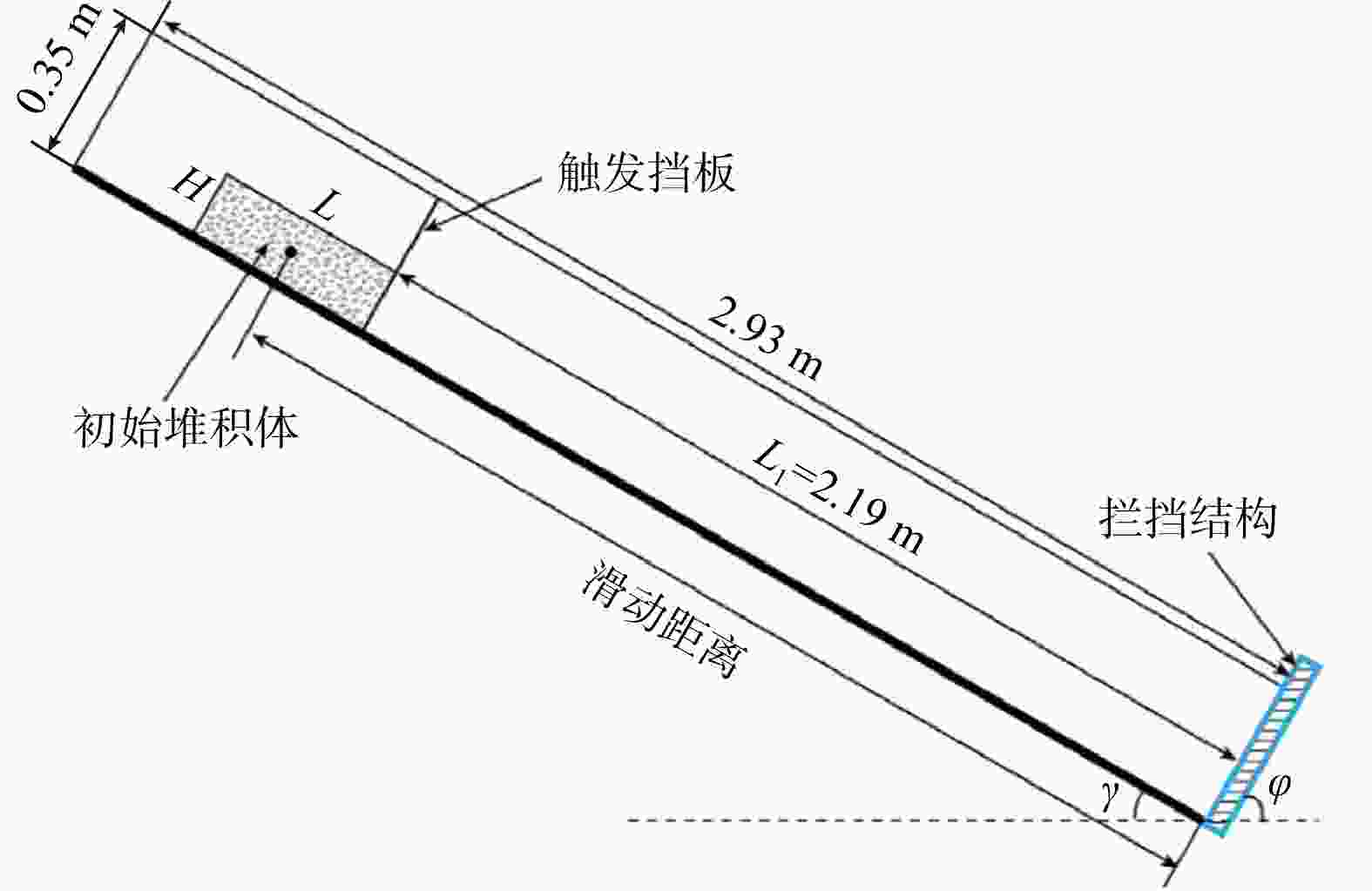
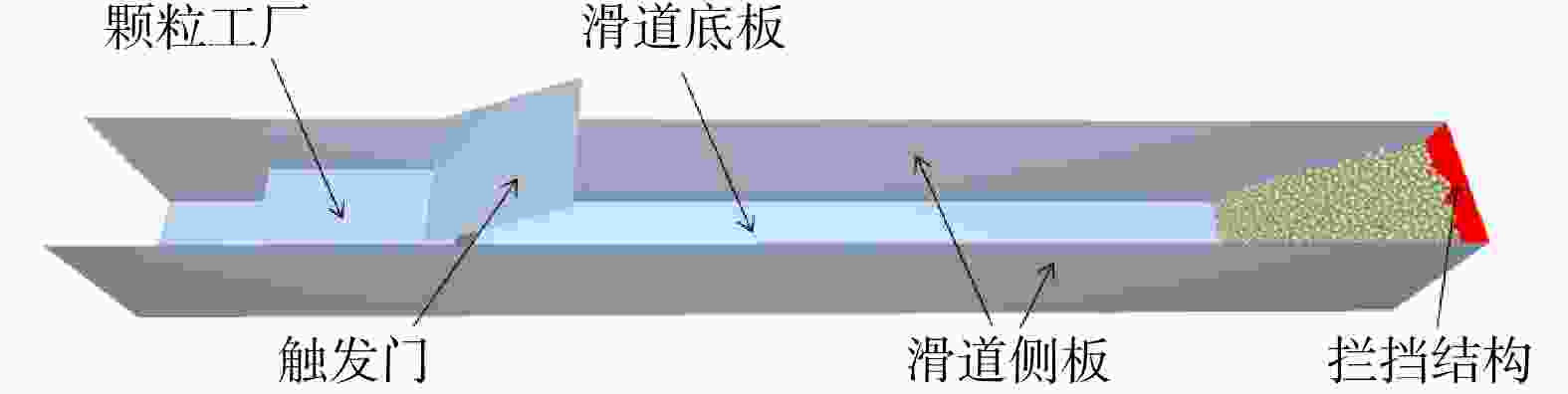
图 6 滑道试验装置示意图(据文献[34]修改)
L1. 触发挡板到拦挡结构的距离;L. 滑坡体长度; H.滑坡体高度;γ. 滑道底板与水平面夹角;$\varphi $. 拦挡结构与水平面夹角
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the slide test setup
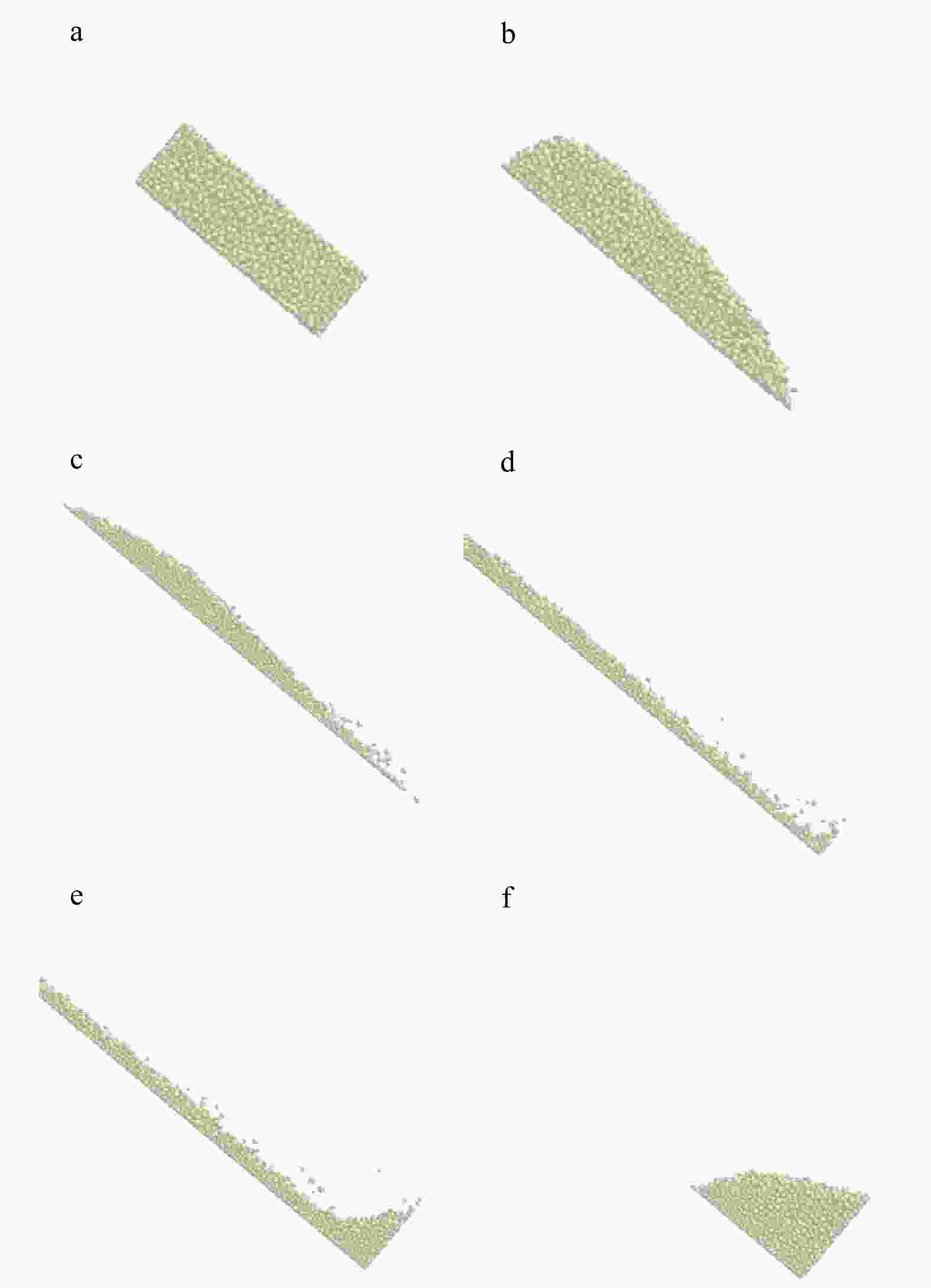
图 8 滑坡试验中颗粒运动过程图(据文献[33]修改)
a,b. 失稳阶段;c,d. 滑动阶段;e,f. 堆积阶段
Figure 8. Diagram of particle motion process in landslide test
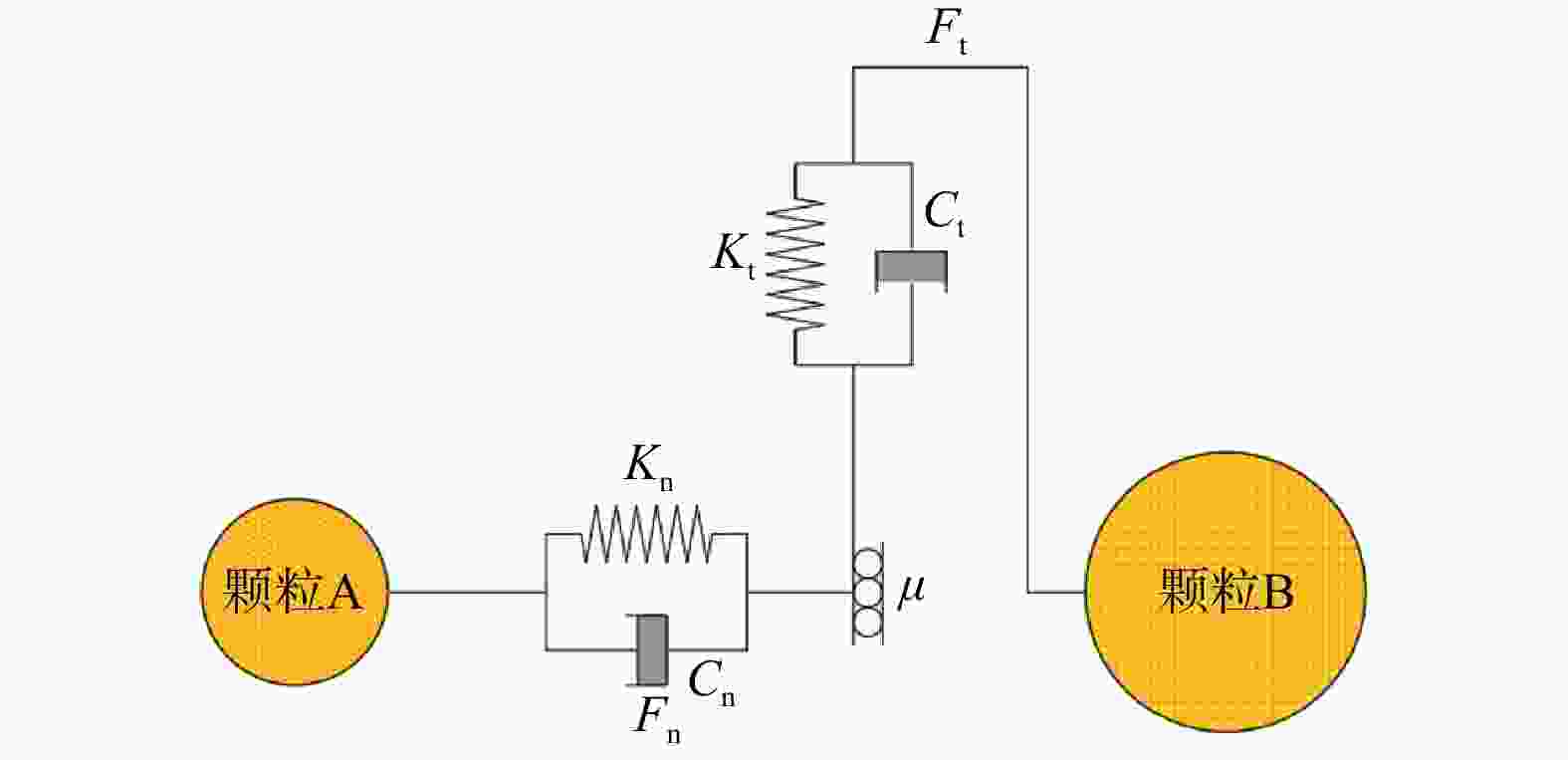
表 1 EDEM中接触系数选取
Table 1. Value of contact coefficients in EDEM
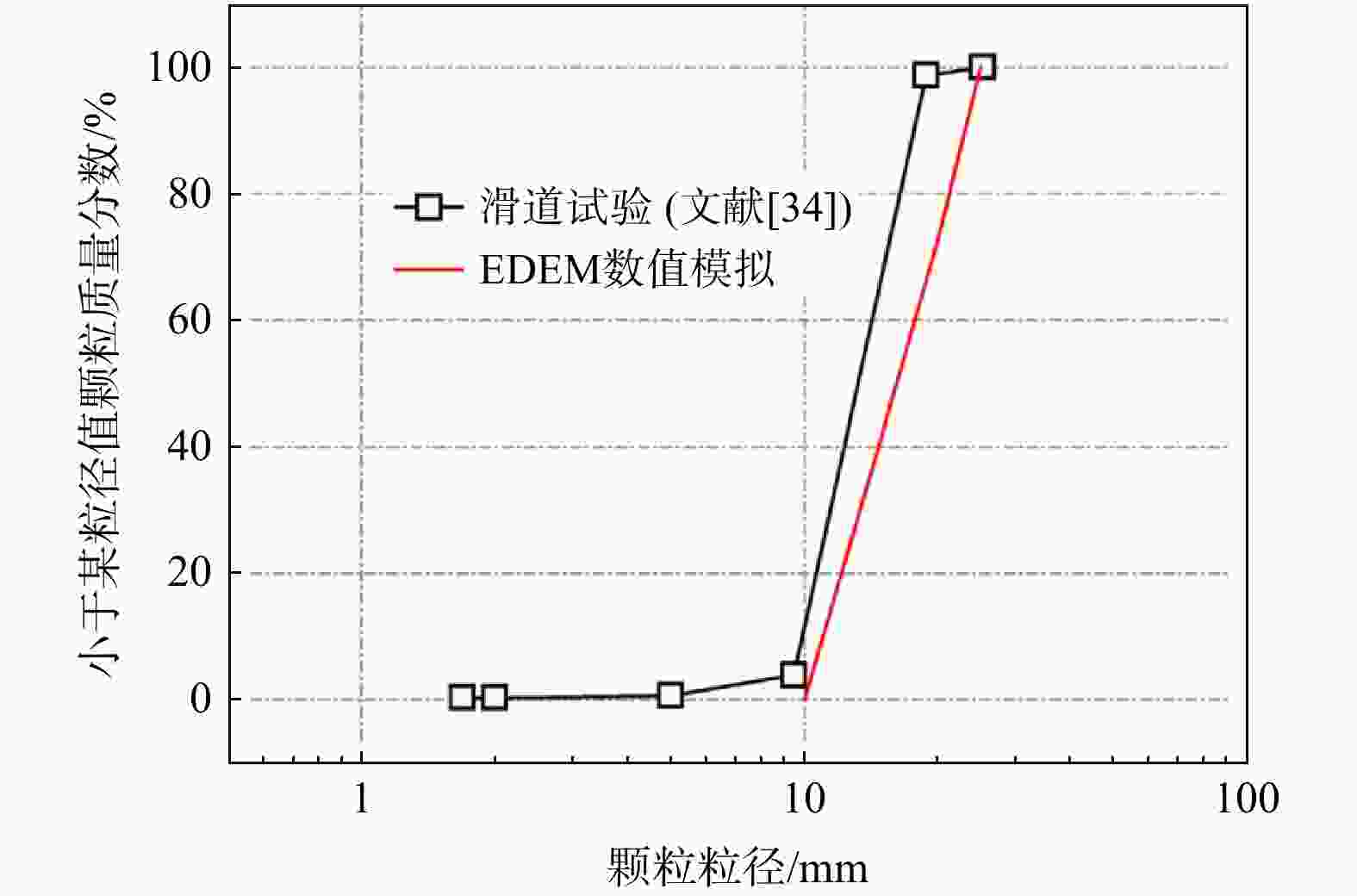
接触参数 取值 恢复系数 0.5 颗粒静摩擦系数 1.330 颗粒滚动摩擦系数 0.080 滑道静摩擦系数 0.466 滑道滚动摩擦系数 0.010 拦挡结构静摩擦系数 0.384 拦挡结构滚动摩擦系数 0.010 表 2 EDEM中模型与颗粒的属性取值
Table 2. Value of equipment material and bulk material in EDEM
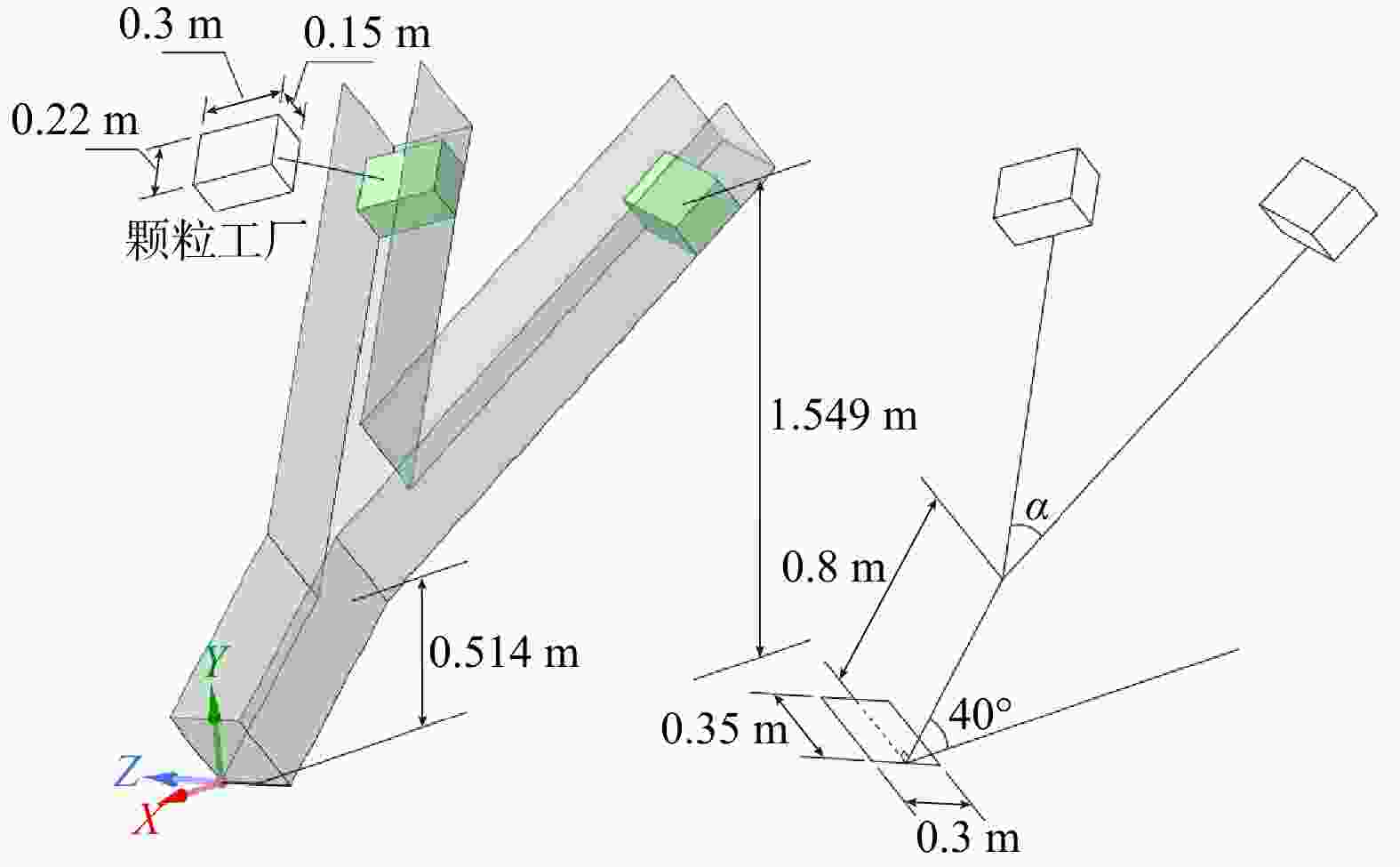
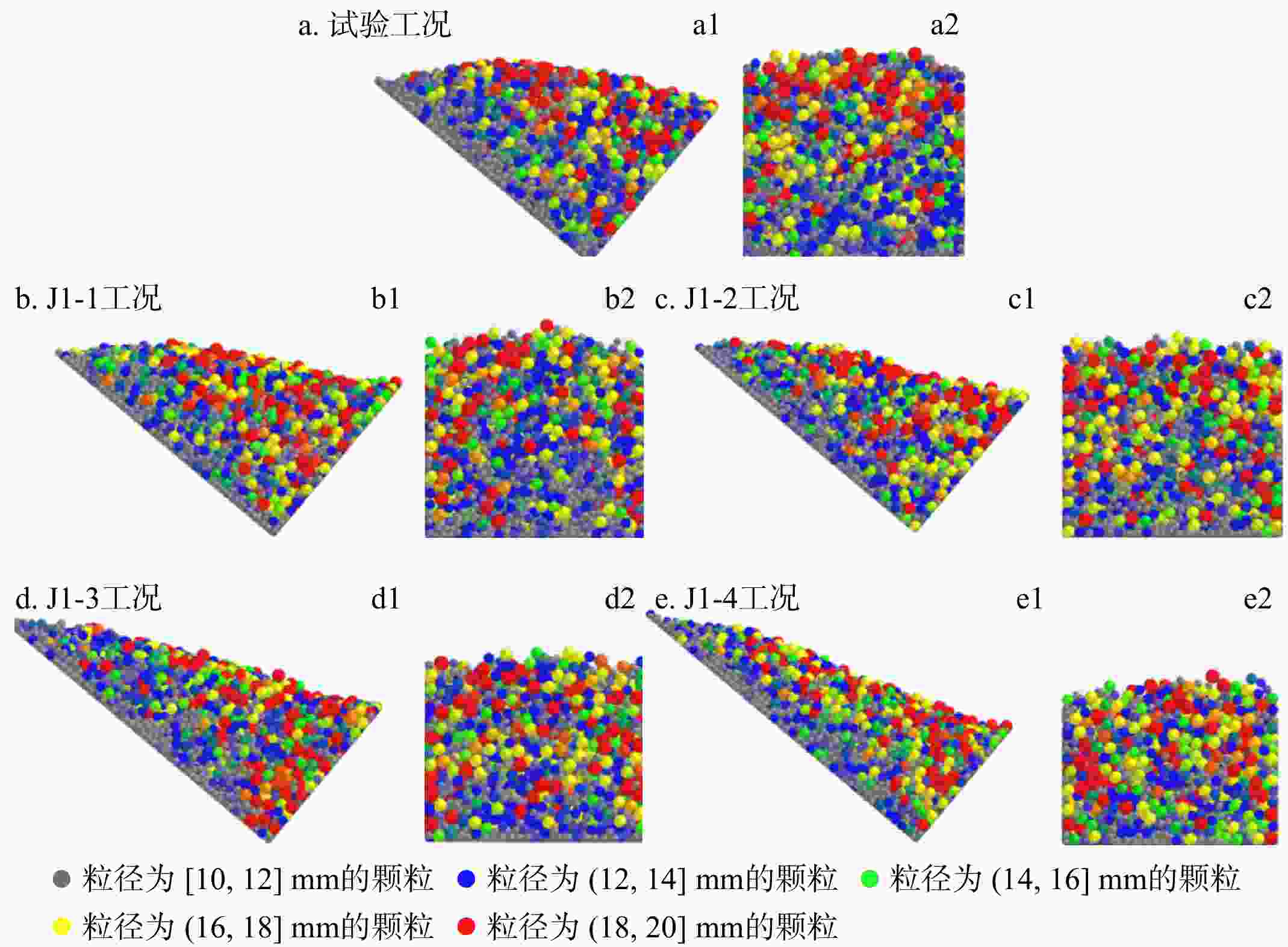
模型与颗粒的属性 取值 滑道/拦挡结构泊松比 0.3 滑道/拦挡结构密度/(kg·m−3) 7900 滑道/拦挡结构杨氏模量/MPa 2×105 颗粒泊松比 0.25 颗粒密度/(kg·m−3) 2550 颗粒杨氏模量/MPa 100 颗粒粒径/mm 10~20 表 3 4组EDEM工况设计
Table 3. Four groups condition design in EDEM
工况 聚合角度α/(°) 颗粒级配分布 J1-1 30 总质量27 kg
10~20 mm
颗粒线性分布J1-2 40 J1-3 50 J1-4 60 表 4 各工况下堆积区对照表
Table 4. Comparison table of stacking area under each working condition
试验
工况J1-1
工况J1-2
工况J1-3
工况J1-4
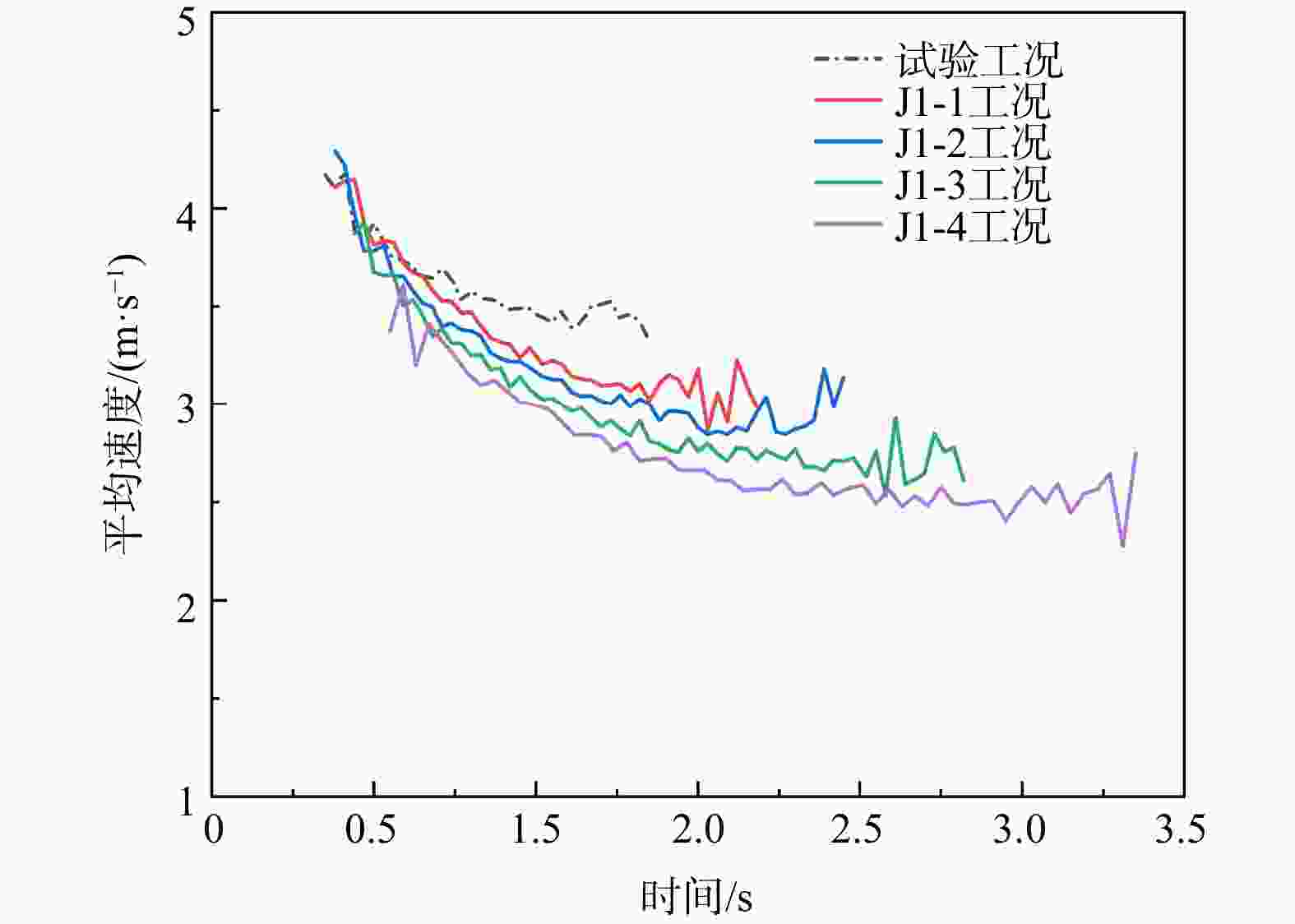
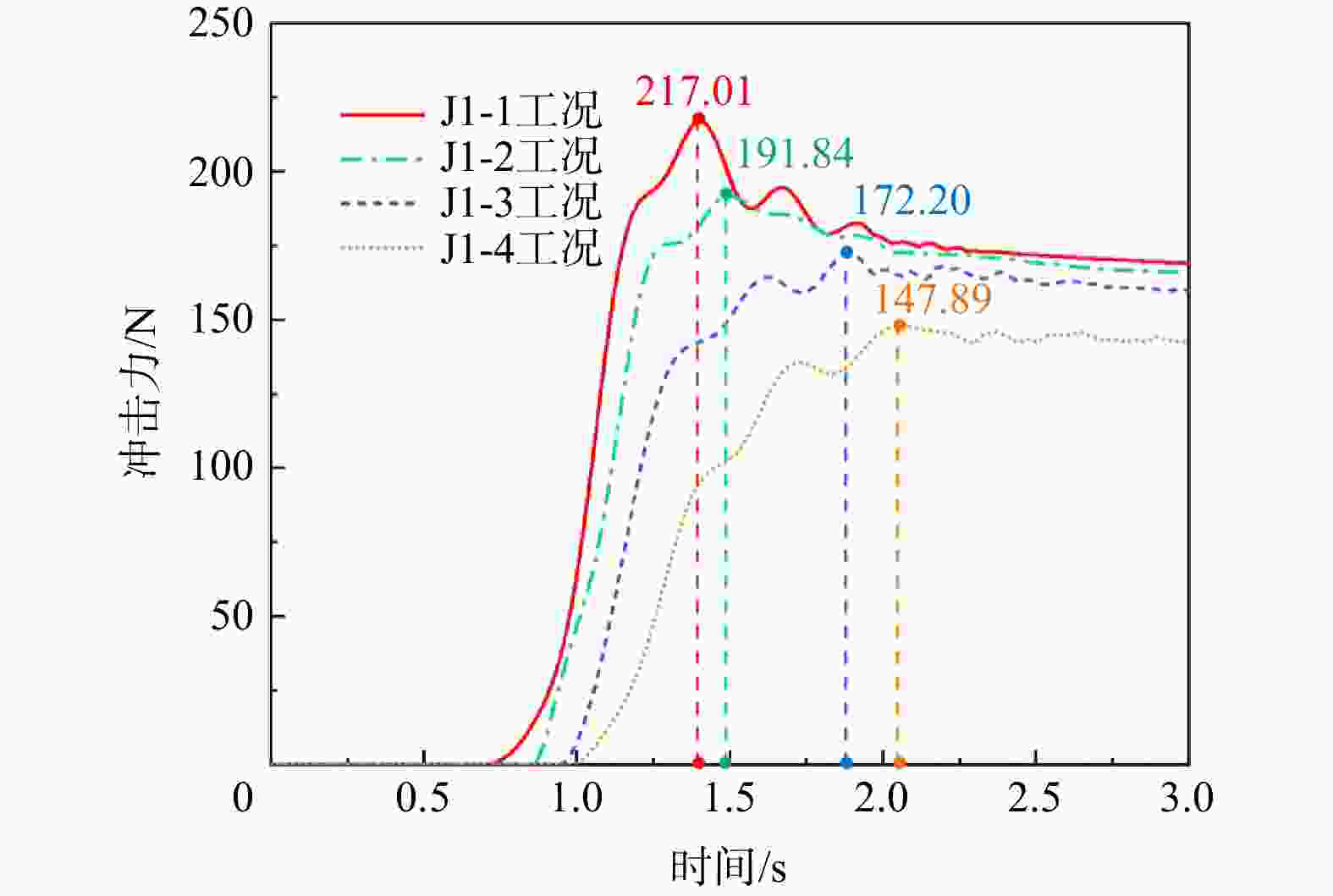
工况沿拦挡结构面堆积的高度/mm 287.19 284.56 278.05 254.55 234.95 沿滑道面堆积的长度/mm 388.9 416.94 443.38 497.78 560.04 表 5 各工况下冲击力对照表
Table 5. Comparison table of impact force under each working condition
试验工况 J1-1工况 J1-2工况 J1-3工况 J1-4工况 冲击力峰值/N 223.61 217.01 191.84 172.20 147.89 残余冲击力/N 177.16 169.08 165.94 160.12 141.13 (峰值/残余) /% 126 128 115 107 104 -
[1] 程谦恭,张倬元,黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报,2007,25(1):72-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007CHENG Q G,ZHANG Z Y,HUANG R Q. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches:State of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2007,25(1):72-84. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007 [2] CUI Y F,CHOI C E,LIU L H D,et al. Effects of particle size of mono-disperse granular flows impacting a rigid barrier[J]. Natural Hazards,2018,91(3):1179-1201. doi: 10.1007/s11069-018-3185-3 [3] MANZELLA I,LABIOUSE V. Empirical and analytical analyses of laboratory granular flows to investigate rock avalanche propagation[J]. Landslides,2013,10(1):23-36. doi: 10.1007/s10346-011-0313-5 [4] 马东涛,张金山,冯自立,等. 2004.7. 20云南盈江滑坡泥石流山洪灾害成因及减灾对策[J]. 灾害学,2005,20(1):67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2005.01.015MA D T,ZHANG J S,FENG Z L,et al. Main causes of the landslide,debris flow and torrential flood disasters on July 20,2004 in Yingjiang of Yunnan and the disaster reduction measures[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2005,20(1):67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2005.01.015 [5] 余峙丹,张辉,郭荣芬. 云南楚雄特大滑坡泥石流气象成因[J]. 气象科技,2010,38(1):136-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2010.01.026YU Z D,ZHANG H,GUO R F. Analysis of meteorological causes of an exceptional landslide and debris flow event in Chuxiong[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology,2010,38(1):136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2010.01.026 [6] 解超,赵叶江,高福兴. 贵州镇远小云盘滑坡特征及成因分析[J]. 四川地质学报,2024,44(4):671-676.XIE C,ZHAO Y J,GAO F X. Analysis on characteristics and genesis of Xiaoyunpan landslide in Zhenyuan,Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2024,44(4):671-676. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 王兴菊,杨忠明,陈贞红. 安顺市一次特大暴雨过程分析评估[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(4):2015-2019.WANG X J,YANG Z M,CHEN Z H. Analysis evaluation of a severe storm process in Anshun City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(4):2015-2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 梁京涛,成余粮,王军,等. 2013年7月10日四川省都江堰三溪村五里坡特大滑坡灾害遥感调查及成因机制浅析[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(6):1194-1203.LIANG J T,CHENG Y L,WANG J,et al. Remote sensing investigation and formation mechanism on Wulipo landslide of July 10,2013 in Sanxi Village,Dujiangyan,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(6):1194-1203. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 温铭生,方志伟,王阳谷. 都江堰市五里坡特大滑坡灾害特征与致灾成因[J]. 现代地质,2015,29(2):448-453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.032WEN M S,FANG Z W,WANG Y G. Characteristics and disaster causes of Wulipo landslide in Dujiangyan City[J]. Geoscience,2015,29(2):448-453. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.02.032 [10] YIN Y P,LI B,WANG W P,et al. Mechanism of the December 2015 catastrophic landslide at the Shenzhen landfill and controlling geotechnical risks of urbanization[J]. Engineering,2016,2(2):230-249. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2016.02.005 [11] 甘建军,樊俊辉,唐春,等. 浙江遂昌苏村滑坡基本特征与成因机理分析[J]. 灾害学,2017,32(4):73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.04.012GAN J J,FAN J H,TANG C,et al. Sucun landslide in Suichang County of Zhejiang Province:Characteristices and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017,32(4):73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.04.012 [12] 邵崇建,李芃宇,李勇,等. 茂县滑坡的滑动机制与震后滑坡形成的地质条件[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,44(4):385-402.SHAO C J,LI P Y,LI Y,et al. Sliding mechanism of Maoxian landslide and geological condition analysis of formation of post-earthquake landslide[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2017,44(4):385-402. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 薛智文,许冲,付登文,等. 2024年1月22日云南镇雄滑坡灾害成因分析[J]. 地震研究,2025,48(1):80-88.XUE Z W,XU C,FU D W,et al. Analysis of the causes of the landslide disaster in Zhenxiong,Yunnan on January 22,2024[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2025,48(1):80-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 朱晨光,刘春,许强,等. 滑坡滑带摩擦热离散元数值模拟研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(3):651-658.ZHU C G,LIU C,XU Q,et al. Discrete element numerical simulation research on friction heat in sliding zone of the landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(3):651-658. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LUO H,XING A G,JIN K P,et al. Discrete element modeling of the Nayong rock avalanche,Guizhou,China constrained by dynamic parameters from seismic signal inversion[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2021,54(4):1629-1645. doi: 10.1007/s00603-021-02363-9 [16] SCARINGI G,FAN X M,XU Q,et al. Some considerations on the use of numerical methods to simulate past landslides and possible new failures:The case of the recent Xinmo landslide (Sichuan,China)[J]. Landslides,2018,15(7):1359-1375. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0953-9 [17] 汪志林,叶海旺,李子旋,等. 含双裂隙组灰岩边坡渐进失稳过程分析[J]. 矿冶工程,2021,41(2):20-23.WANG Z L,YE H W,LI Z X,et al. Analysis of progressive instability process of limestone slope with two groups of fissures[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2021,41(2):20-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] XUE Y D,ZHOU J,HUANG H W,et al. Analysis of large soil rock mixture slope based on DEM[J]. International Society for Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2019,27(3):651-658. [19] FANG K,TANG H M,LI C D,et al. Centrifuge modelling of landslides and landslide hazard mitigation:A review[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2023,14(1):101493. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101493 [20] GONG Y F,YAO A J,LI Y L,et al. Model test study on sliding-toppling composite deformation evolution of anti-dip layered rock slope[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(5):194. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03213-4 [21] 肖捷夫,李云安,蔡浚明. 水位涨落作用下藕塘滑坡响应特征模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(5):1049-1056.XIAO J F,LI Y A,CAI J M. Model test research on response characteristics of outang landslide under water level fluctuation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(5):1049-1056. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 詹志发,贺建先,郑博文,等. 边坡模型相似材料配比试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(3):1236-1243. doi: 10.6038/pg2019DD0176ZHAN Z F,HE J X,ZHENG B W,et al. Experimental study on similar material proportion of slope model[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2019,34(3):1236-1243. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/pg2019DD0176 [23] 许强,刘汉香,邹威,等. 斜坡加速度动力响应特性的大型振动台试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(12):2420-2428.XU Q,LIU H X,ZOU W,et al. Large-scale shaking table test study of acceleration dynamic responses characteristics of slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(12):2420-2428. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 张睿骁,樊晓一,杨海龙,等. 不同拦挡距离对滑坡碎屑流冲击效应影响的离散元模拟[J]. 西南科技大学学报,2018,33(3):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2018.03.008ZHANG R X,FAN X Y,YANG H L,et al. Discrete element simulation of the effects of different baffle distances on the impact of landslide-debris flow[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology,2018,33(3):37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2018.03.008 [25] 张睿骁,苏栋,樊晓一,等. 场地条件对滑坡−碎屑流运动冲击特征的影响研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2022,41(2):229-239.ZHANG R X,SU D,FAN X Y,et al. Influence of site conditions on the motion and impact effect of rock avalanches[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2022,41(2):229-239. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 孙立娟,沈方铭,张互助. 基于滑带土强度劣化的库水复活型滑坡渐进失稳机理研究[J]. 吉林建筑大学学报,2022,39(4):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0185.2022.04.004SUN L J,SHEN F M,ZHANG H Z. Study on progressive instability mechanism of reservoir water resurrection laudslide based on strength deterioration of sliding zone soil[J]. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University,2022,39(4):18-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0185.2022.04.004 [27] 王飞,徐楚,黎伟. 基于MatDEM的黄泥扁滑坡支护效果分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(5):52-60.WANG F,XU C,LI W. Supporting effect analysis of the Huangnibian landslide based on MatDEM[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(5):52-60. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 张玉洁,许国庆,汪洋,等. 约束条件对滑坡涌浪特征影响的室内试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):309-314.ZHANG Y J,XU G Q,WANG Y,et al. Laboratory experiment on the influence of constraint conditions on landslide-generated waves[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):309-314. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 任雨欣,喻志鹏. 基于物理模型实验的高速远程滑坡碎屑流堆积特征分析[J]. 四川建筑,2023,43(2):144-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2023.02.044REN Y X,YU Z P. Analysis of debris flow accumulation characteristics of high-speed remote landslide based on physical model experiment[J]. Sichuan Architecture,2023,43(2):144-146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2023.02.044 [30] YANG Q Q,CAI F,UGAI K,et al. Some factors affecting mass-front velocity of rapid dry granular flows in a large flume[J]. Engineering Geology,2011,122(3/4):249-260. [31] 赵运会,樊晓一. 基于正交设计的滑坡运动参数模型试验[J]. 山地学报,2016,34(1):92-99.ZHAO Y H,FAN X Y. Model test of movement parameters of landslide based on orthogonal design[J]. Mountain Research,2016,34(1):92-99. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 雷先顺,谢沃,卢坤林,等. 无黏性土滑动和堆积特性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(2):226-236. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201602005LEI X S,XIE W,LU K L,et al. Model tests of sliding and accumulation characteristics of cohesionless soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(2):226-236. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE201602005 [33] JIANG Y J,TOWHATA I. Experimental study of dry granular flow and impact behavior against a rigid retaining wall[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2013,46(4):713-729. [34] SHEN W G,ZHAO T,ZHAO J D,et al. Quantifying the impact of dry debris flow against a rigid barrier by DEM analyses[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,241:86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.05.011 [35] 李郎平,兰恒星. 滑坡运动路径复杂度研究:综述与展望[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(12):4663-4680.LI L P,LAN H X. Complexities of landslide moving path:A review and perspective[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(12):4663-4680. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 龙艳梅. 侧向约束对碎屑流运动与堆积特征的影响分析[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021.LONG Y M. Effects of lateral confinement on the propagation and depositional characteristics of granular flow[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 袁锦涛,韩培锋,田述军,等. 滑坡碎屑流颗粒级配及地形偏转对其冲击和堆积过程的影响研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2022,19(5):1319-1330.YUAN J T,HAN P F,TIAN S J,et al. Impact of landslide debris flow particle gradation and terrain deflection on its impact and accumulation process[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2022,19(5):1319-1330. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 胡晓波,樊晓一,田述军. 沟道偏转地形对滑坡碎屑流运动的影响研究[J]. 山地学报,2019,37(3):371-381.HU X B,FAN X Y,TIAN S J. Influence of channel deflection on the movement of a flowing landslide[J]. Mountain Research,2019,37(3):371-381. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 杨海龙,樊晓一,赵运会,等. 偏转角度对滑坡-碎屑流运动影响的模型试验[J]. 山地学报,2017,35(3):316-322.YANG H L,FAN X Y,ZHAO Y H,et al. Model tests on influence of deflection angle on the movement of landslide-debris avalanches[J]. Mountain Research,2017,35(3):316-322. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 成浩,韩培锋,苏有文. 基于离散元方法的松散体滑动堆积特性及影响因素分析[J]. 物理学报,2020,69(16):165-180.CHENG H,HAN P F,SU Y W. Sliding and accumulation characteristics of loose materials and its influencing factors based on discrete element method[J]. Acta Physica Sinica,2020,69(16):165-180. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] MINDLIN R D. Compliance of elastic bodies in contact[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1949,16(3):259-268. doi: 10.1115/1.4009973 [42] 潘青,张清照,李艺灵. 基于EDEM的碎屑流运动规律及冲击性能研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(5):1057-1065.PAN Q,ZHANG Q Z,LI Y L. Discrete element simulation study of debris flow movement law and impact performance[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(5):1057-1065. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] SALCIARINI D,TAMAGNINI C,CONVERSINI P. Discrete element modeling of debris-avalanche impact on earthfill barriers[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth(Parts A/B/C),2010,35(3/4/5):172-181. [44] 刘清,甘建军,陈浩,等. 赣东小型土质滑坡形成机理及降雨因子稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(6):235-243.LIU Q,GAN J J,CHEN H,et al. Failure mechanism of small-scale soil landslide and quantitative evaluation of rain-induced disaster factors in eastern Jiangxi[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(6):235-243. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] 漆芍见,范宣梅,夏明垚,等. 跨逆断层岩质边坡上下盘动力响应和破坏模式振动台试验[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(1):138-149.QI S J,FAN X M,XIA M Y,et al. Shaking table test of dynamic responses and failure mechanism of hanging wall and footwall on rock slope across reverse faults[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(1):138-149. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载: