Effects of concentrated recharge conditions on hydrological processes and pollution responses of karst underground rivers
-
摘要:
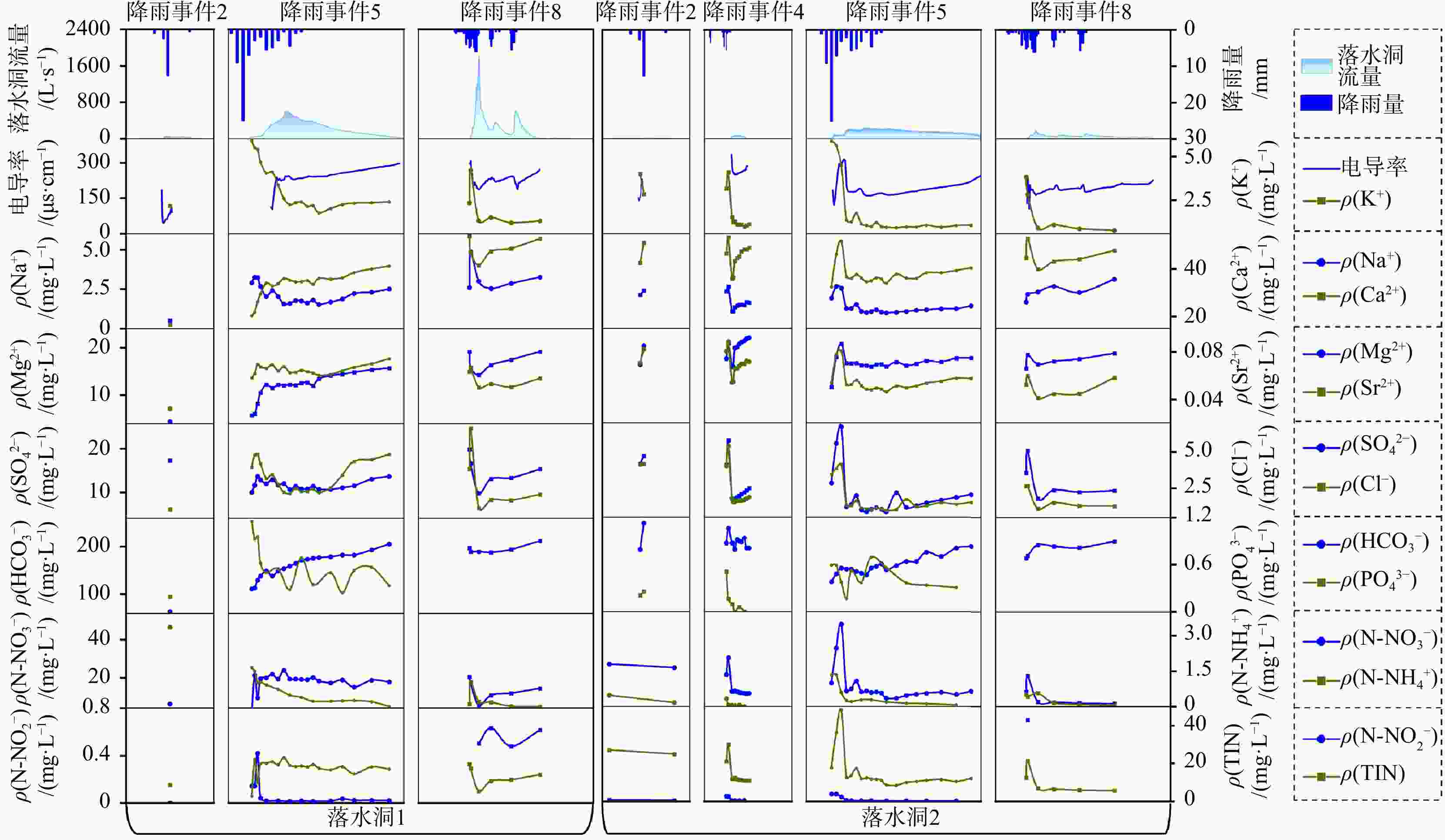
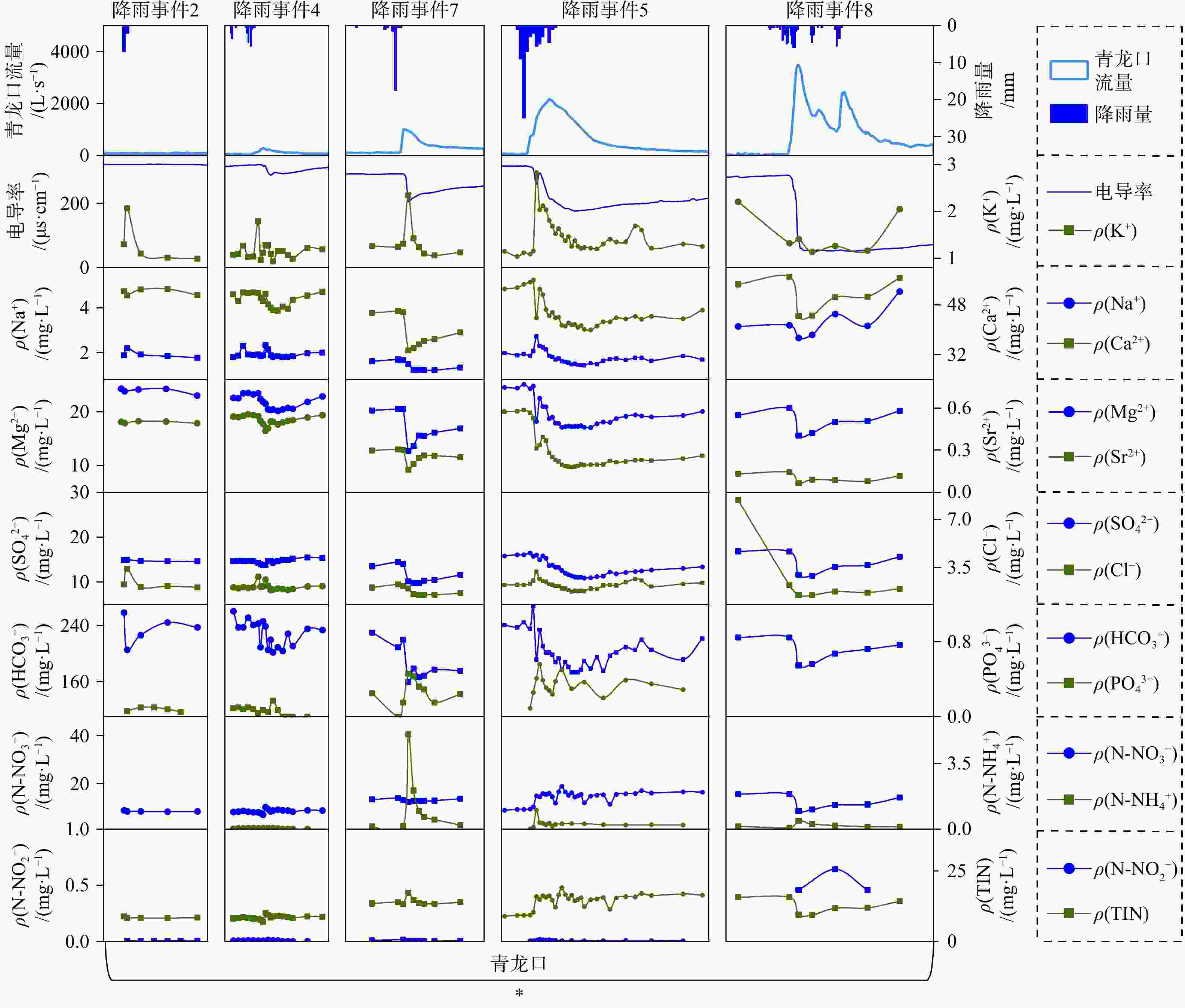
集中补给条件往往对岩溶地下河的水量和水质有显著影响,因此明晰不同集中补给条件对其的影响具有重要意义。本研究基于水文地球化学调查,对鄂西青龙口地下河系统的落水洞入口和地下河出口同步进行水文和水化学动态监测,探讨了不同补给条件对地下河水量和水质的影响。结果表明:补给强度和土壤含水率直接控制着落水洞的产汇流过程及岩溶地下河的流量响应,未达到阈值的降雨事件不会引起地下河流量响应;降雨集中汇流至落水洞入口的过程中,各水化学离子浓度均有明显的提高,而青龙口地下河出口水化学响应受补给强度影响,强降雨下地下河受落水洞入口水化学离子浓度富集影响强烈;降雨后的水质波动主要源于降雨形成地表径流携带的面源污染,暴雨后的总无机氮和磷酸盐在落水洞口出现聚集,集中补给输入的污染物对地下河产生直接污染,浓度可达天然背景值的2~3倍;水化学响应中氨氮先于硝态氮进入岩溶水循环,地下河系统出口的硝态氮和总无机氮通量相较入口有所增加,氨氮通量随补给时间逐渐减少,推测管道内发生了硝化反应。本研究结果可为岩溶地下河的污染防控和水环境治理提供科学依据。
Abstract:Objective Concentrated recharge conditions often significantly impact the water quantity and quality of karst underground rivers. Therefore, it is of great importance to clarify the effects of different concentrated recharge conditions on these aspects.
Methods Based on hydrogeochemical surveys, this study simultaneously monitored the hydrological and hydrochemical dynamics at the sinkhole entrance and underground river outlet of the QLK underground river system in western Hubei, to explore the impacts of different recharge conditions on the water quantity and quality of the underground river.
Results The results show that recharge intensity and soil moisture content directly control the generation and convergence processes of flow within the sinkhole, as well as the flow response of the karst underground river system. Rainfall events that do not reach a threshold will not trigger a flow response in the underground river.As concentrated runoff converges towards the sinkhole entrance, the concentrations of various hydrochemical ions increase significantly.The hydrochemical response observed at the outlet of the QLK underground river system is influenced by the intensity of recharge. Under heavy rainfall conditions, this response is further intensified due to the enrichment of hydrochemical ion concentrations at the sinkhole entrance.Following heavy rainfall, TIN (Total Inorganic Nitrogen) and phosphates accumulate at the sinkhole entrance, leading to concentrations that are 2 to 3 times higher than the natural background levels. Pollutants introduced through concentrated recharge directly contaminate the underground river. In the hydrochemical response, N-${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $ enters the karst water cycle prior to N-${\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $, and the fluxes of nitrate and TIN increase at the outlet of the underground river system relative to the inlet. Meanwhile, the flux of ammonium N-${\mathrm{NH}}_4^+ $ gradually decreases over time as recharge occurs, suggesting nitrification reactions within the conduits.
Conclusion The results of this study can provide a scientific basis for pollution prevention and control, as well as water environmental management of karst underground rivers.
-
Key words:
- Karst spring /
- Hydrochemistry /
- Pollutant /
- Concentrated recharge
-
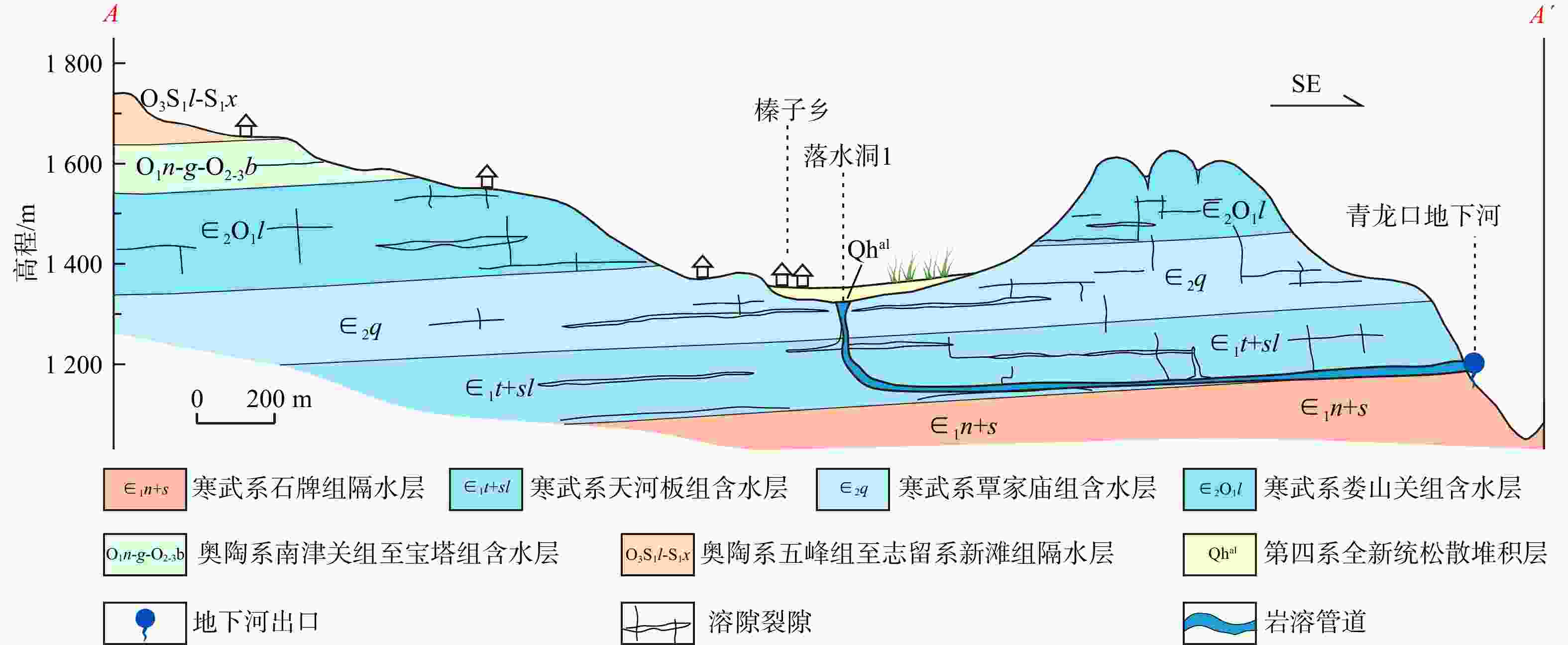
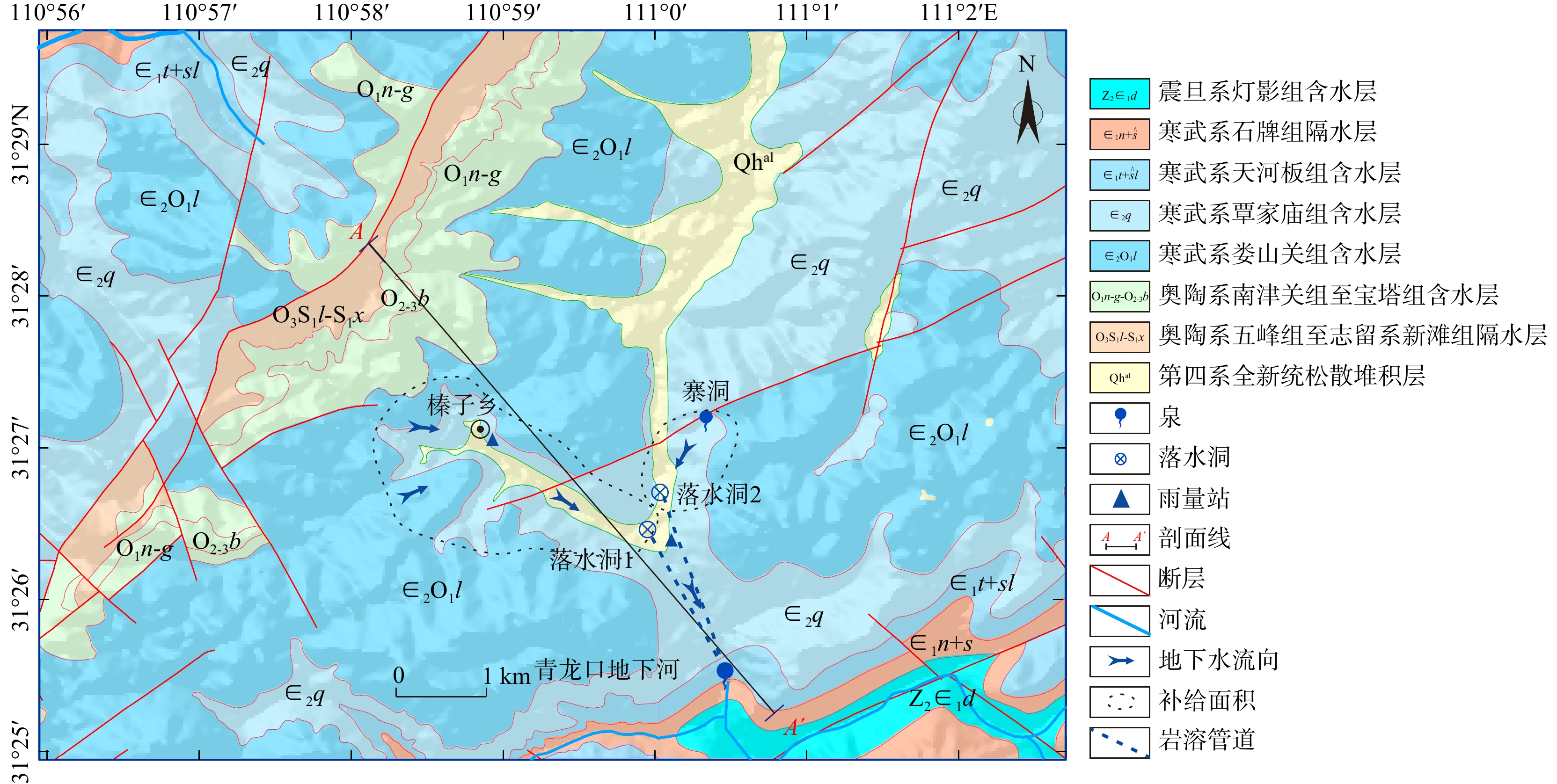
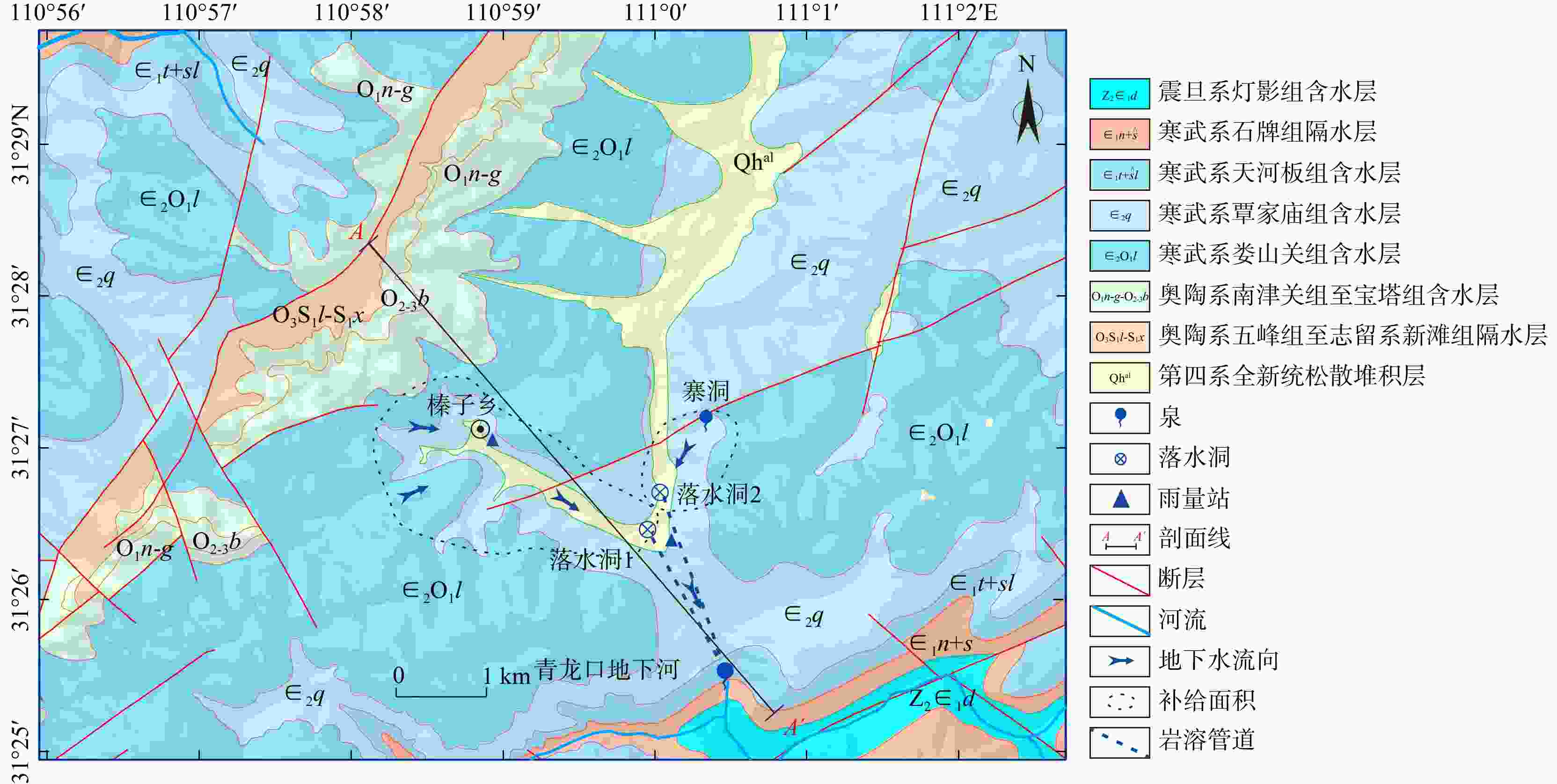
图 2 青龙口地下河系统A−A'水文地质剖面图(剖面A−A'位置见图1)
Figure 2. A−A' hydrogeologic profile of the study area
表 1 青龙口地下河系统降雨流量响应情况
Table 1. Changes in the hydrologic dynamic response of the underground river system at Qinglongkou
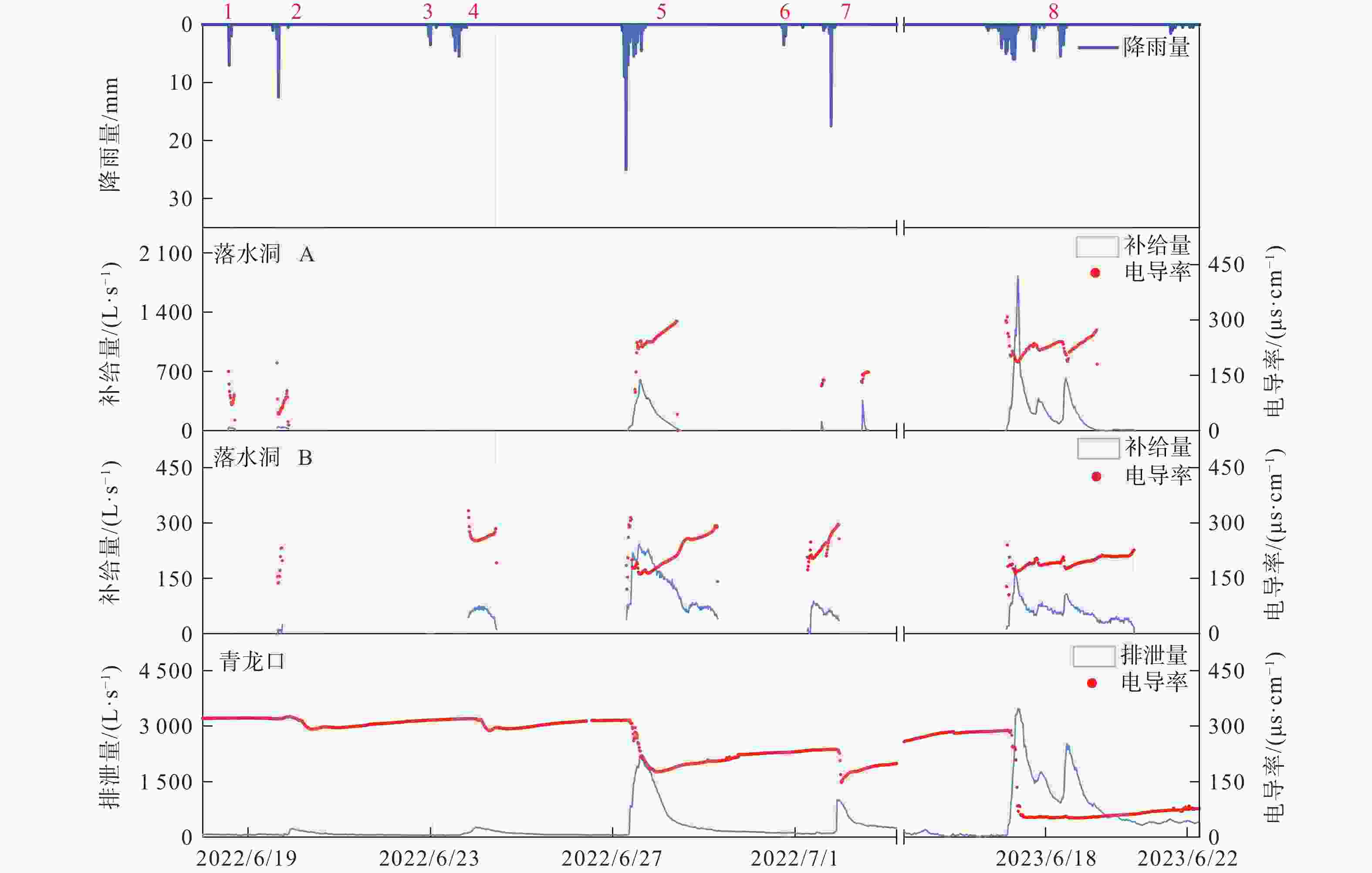
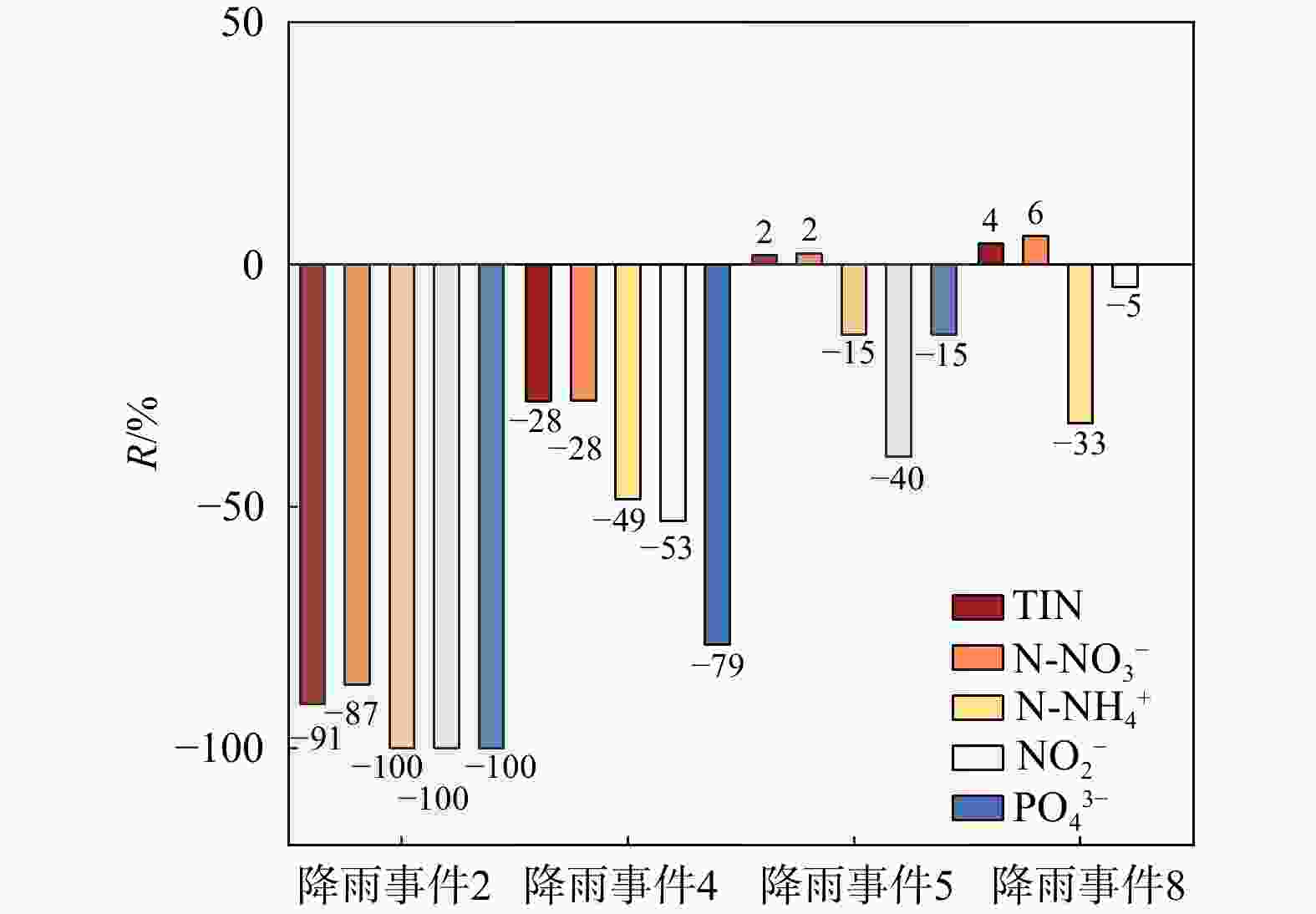
降雨编号 降雨时间 次降雨量/mm 最大降雨强度/(mm‧h−1) 落水洞1产流情况 落水洞2产流情况 青龙口流量响应情况 降雨事件1 2022/6/18 14:00 9 7 产流 未产流 未响应 降雨事件2 2022/6/19 13:00 16 12.5 产流 产流 响应 降雨事件3 2022/6/22 23:00 6 3.5 未产流 未产流 未响应 降雨事件4 2022/6/23 11:00 15.5 5.5 未产流 产流 响应 降雨事件5 2022/6/27 05:00 67 25 产流 产流 响应 降雨事件6 2022/6/30 17:00 6 3.5 未产流 未产流 未响应 降雨事件7 2022/7/1 15:00 21.5 17.5 产流 产流 响应 降雨事件8 2023/6/16 08:00 68.5 5.5 产流 产流 响应 表 2 青龙口地下河主要离子质量浓度特征统计
Table 2. Characteristic statistics of mass concentration of major ions in the underground river of Qinglongkou
项目 pH ρB/(mg‧L−1) TDS K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ ${\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ Cl- ${\mathrm{HCO}}_3^- $ ${\mathrm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ TIN 弱降雨(降雨事件4) 最小值 7.85 195.30 0.93 1.80 46.14 20.19 13.67 1.84 201.67 0.00 7.00 最大值 8.05 231.56 1.79 2.34 52.18 23.51 15.44 2.81 260.04 0.17 10.20 平均值 7.96 213.80 1.15 1.94 49.66 21.81 14.59 2.08 228.20 0.06 8.50 标准差 0.07 11.39 0.19 0.16 2.12 1.20 0.46 0.24 17.56 0.05 0.67 变异系数/% 0.83 5.33 16.19 8.11 4.27 5.51 3.18 11.70 7.70 78.86 7.89 强降雨(降雨事件5) 最小值 7.56 175.08 1.07 1.44 39.98 17.07 10.81 1.72 173.36 0.09 8.88 最大值 7.96 246.03 3.16 2.72 55.91 25.15 16.40 3.17 267.12 0.56 19.08 平均值 7.80 198.93 1.57 1.78 45.34 19.48 13.13 2.20 202.16 0.34 14.60 标准差 0.10 19.18 0.43 0.28 4.80 2.56 1.83 0.32 23.78 0.10 2.66 变异系数/% 1.32 9.64 27.64 15.67 10.58 13.14 13.97 14.44 11.76 30.05 18.23 -
[1] 袁道先,朱德浩,翁金桃,等. 中国岩溶学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1994.YUAN D X,ZHU D H,WENG J T,et al. Chinese karstology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1994. (in Chinese) [2] 杨立铮. 中国南方地下河分布特征[J]. 中国岩溶,1985,4(增刊1):98-106.YANG L Z. Distribution characteristics of underground rivers in southern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,1985,4(S1):98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 刘伟江,袁祥美,张雅,等. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学特征及演化过程分析[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(6):245-251.LIU W J,YUAN X M,ZHANG Y,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of karst groundwater in Guiyang City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(6):245-251. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] LI S L,XU S,WANG T J,et al. Effects of agricultural activities coupled with karst structures on riverine biogeochemical cycles and environmental quality in the karst region[J]. Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,2020,303:107120. [5] 吴华英,李腾芳,程瑞瑞,等. 我国岩溶地下水受污染的原因与污染特征[J]. 中国矿业,2021,30(增刊1):101-104.WU H Y,LI T F,CHENG R R,et al. Causes and characteristics of the pollution of karst groundwater in China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2021,30(S1):101-104. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 王志恒,梁永平,史浙明,等. 古堆−南梁泉域岩溶水环境问题现状与泉源区保护[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(5):228-240.WANG Z H,LIANG Y P,SHI Z M,et al. Current situation of karst groundwater environmental problems and spring source protection in the Gudui-Nanliang spring basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(5):228-240. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 廖春来,罗明明,周宏. 鄂西岩溶槽谷区洼地的水位响应特征及产流阈值估算[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(6):802-809. doi: 10.11932/karst20200602LIAO C L,LUO M M,ZHOU H. Water level response characteristics and runoff threshold estimation of karst depressions in a valley region,western Hubei Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(6):802-809. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11932/karst20200602 [8] 甘凤玲. 喀斯特槽谷区水土流/漏失过程与水动力学机制研究[D]. 重庆:西南大学,2019.GAN F L. The process and characteristics of surface loss and underground leakage and hydrodynamic parameters in typical Karst Trough Valley[D]. Chongqing:Dissertation of Southwest University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] KUCZERA G,KAVETSKI D,FRANKS S,et al. Towards a Bayesian total error analysis of conceptual rainfall-runoff models:Characterising model error using storm-dependent parameters[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2006,331(1/2):161-177. [10] YUE F J,WALDRON S,LI S L,et al. Land use interacts with changes in catchment hydrology to generate chronic nitrate pollution in karst waters and strong seasonality in excess nitrate export[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,696:134062. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134062 [11] ZENG J,YUE F J,LI S L,et al. Agriculture driven nitrogen wet deposition in a karst catchment in Southwest China[J]. Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,2020,294:106883. [12] YANG P H,WANG Y Y,WU X Y,et al. Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:114835. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114835 [13] 贺秋芳,邱述兰,张兴波. 降雨过程中岩溶地下河微生物污染及其指示意义[J]. 三峡环境与生态,2012,34(6):9-13.HE Q F,QIU S L,ZHANG X B. The microbial contamination and its source tracing during a storm event in a karst underground stream[J]. Environment and Ecology in the Three Gorges,2012,34(6):9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LU M,YUE F J,WANG X D,et al. Identify nitrogen transport paths and sources contribution in karst valley depression area using isotopic approach[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2023,337:117751. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117751 [15] 王凤康,梁作兵,于正良,等. 岩溶地下河水文地球化学对降雨的响应:以重庆雪玉洞地下河系统为例[J]. 环境科学,2014,35(10):3716-3721.WANG F K,LIANG Z B,YU Z L,et al. Formation of geochemistry in underground river under rainfall conditions:An example for underground river at Xueyu cave,Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science,2014,35(10):3716-3721. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] WANG Z J,YUE F J,LU J,et al. New insight into the response and transport of nitrate in karst groundwater to rainfall events[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,818:151727. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151727 [17] WANG Y,WANG F F,FANG Y,et al. Storm-induced nitrogen transport via surface runoff,interflow and groundwater in a pomelo agricultural watershed,Southeast China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2024,346:123629. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123629 [18] 邹艳娥,蒋萍萍,张强,等. 碧水岩地下河中微量金属元素对降雨的响应特征及来源分析[J]. 环境科学,2015,36(12):4464-4470.ZOU Y E,JIANG P P,ZHANG Q,et al. Response mechanism of trace metals in the Bishuiyan subterranean river to the rainfall and their source analysis[J]. Environmental Science,2015,36(12):4464-4470. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 文浩龙,杨平恒,华茂松,等. 岩溶地下河硝酸盐转化与来源对比研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2023,45(5):172-184.WEN H L,YANG P H,HUA M S,et al. Comparative study of nitrate transformation and sources in karst underground rivers[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2023,45(5):172-184. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] PENG T,WANG S J. Effects of land use,land cover and rainfall regimes on the surface runoff and soil loss on karst slopes in Southwest China[J]. Catena,2012,90:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.001 [21] 常威. 复杂岩溶水系统识别及其在隧道涌水量预测的应用研究:以张吉怀高铁大青山隧道为例[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2022.CHANG W. Study on the identification of complex karst water system and its application in tunnel water disaster prediction:A case study of Zhangjiajie-Jishou-Huaihua high-speed railway Daqing mountain tunnel[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences(Wuhan),2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 陈文俊,黄显强,宋怀则,等. 中国南方岩溶地下水[J]. 地质学报,1981,55(2):149-160.CHEN W J,HUANG X Q,SONG H Z,et al. Karst ground water in South China[J]. Acta Geological Sinica,1981,55(2):149-160. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LUO M M,CHEN Z H,ZHOU H,et al. Identifying structure and function of karst aquifer system using multiple field methods in karst trough valley area,South China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(9):824. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5630-5 [24] CHEN J,LUO M M,WAN L,et al. Accumulation,conversion and storage of solute from sinkholes to karst spring under concentrated recharge conditions[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023,620:129396. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129396 [25] GIL-MÁRQUEZ J M,ANDREO B,MUDARRA M. Combining hydrodynamics,hydrochemistry,and environmental isotopes to understand the hydrogeological functioning of evaporite-karst springs. An example from southern Spain[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,576:299-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.055 [26] WANG S,YAN Y,FU Z Y,et al. Rainfall-runoff characteristics and their threshold behaviors on a karst hillslope in a peak-cluster depression region[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,605:127370. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127370 [27] 芮孝芳. 产流模式的发现与发展[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2013,33(1):1-6.RUI X F. The discovery and development of runoff formation models[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2013,33(1):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] CAETANO BICALHO C,BATIOT-GUILHE C,SEIDEL J L,et al. Geochemical evidence of water source characterization and hydrodynamic responses in a karst aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2012,450:206-218. [29] 黄荣,王发,陈洪松,等. 不同类型表层岩溶泉水源划分及对降雨的响应[J]. 水文,2022,42(3):20-26.HUANG R,WANG F,CHEN H S,et al. The water source division of different types of epikarst springs and their response to rainfall[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2022,42(3):20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 滕跃,张文强,王金晓. 淄河流域岩溶地下水化学特征及控制因素分析[J]. 环境化学,2023,42(6):1945-1956. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012104TENG Y,ZHANG W Q,WANG J X. Analysis on hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of karst groundwater in Zihe River basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2023,42(6):1945-1956. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022012104 [31] 李峰峰,叶禹,余义常,等. 碳酸盐岩成岩作用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):170-190.LI F F,YE Y,YU Y C,et al. Research progress of carbonate rock diagenesis[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):170-190. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] GRANT S B,AZIZIAN M,COOK P,et al. Factoring stream turbulence into global assessments of nitrogen pollution[J]. Science,2018,359(6381):1266-1269. doi: 10.1126/science.aap8074 [33] ZHANG Z C,CHEN X,CHENG Q B,et al. Coupled hydrological and biogeochemical modelling of nitrogen transport in the karst critical zone[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,732:138902. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138902 [34] BAO J,WU X S,ZHANG Q,et al. Unveiling the nitrogen transport and transformation in different karst aquifers media[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023,620:129335. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129335 [35] 蒋萍萍,邹艳娥,张强,等. 广西贺州松木寨地下水中氨氮的自然降解过程分析[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(7):62-66.JIANG P P,ZOU Y E,ZHANG Q,et al. Natural degradation of ammonia nitrogen in groundwater in Songmu Village of Hezhou,Guangxi[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(7):62-66. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 徐璐,蒋勇军,段世辉,等. 基于双同位素(δ15N - $ {\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $- δ18O - $ {\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $)和IsoSource模型的岩溶槽谷区地下水硝酸盐来源的定量示踪[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(8):3637-3645.XU L,JIANG Y J,DUAN S H,et al. Quantification of nitrate sources to groundwater in karst trough-vally areas based on dual stable isotopes of δ15N - $ {\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $ and δ18O - $ {\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $ and the IsoSource model[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(8):3637-3645. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] RICHA A,TOUIL S,FIZIR M. Recent advances in the source identification and remediation techniques of nitrate contaminated groundwater:A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,316:115265. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115265 [38] 赵然,韩志伟,申春华,等. 典型岩溶地下河流域水体中硝酸盐源解析[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(6):2664-2670.ZHAO R,HAN Z W,SHEN C H,et al. Identifying nitrate sources in a typical karst underground river basin[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(6):2664-2670. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZHANG Z C,CHEN X,LI S L,et al. Linking nitrate dynamics to water age in underground conduit flows in a karst catchment[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,596:125699. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125699 [40] 王佳琪,马瑞,孙自永. 地表水与地下水相互作用带中氮素污染物的反应迁移机理及模型研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(4):270-280.WANG J Q,MA R,SUN Z Y. Reactive transport and model of nitrogen pollutants in the surface water-ground water interaction zones:A review[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(4):270-280. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: