Identification of karst micropaleogeomorphology and reservoir characteristics of Maokou Formation in Yunjin area, South Sichuan
-
摘要:
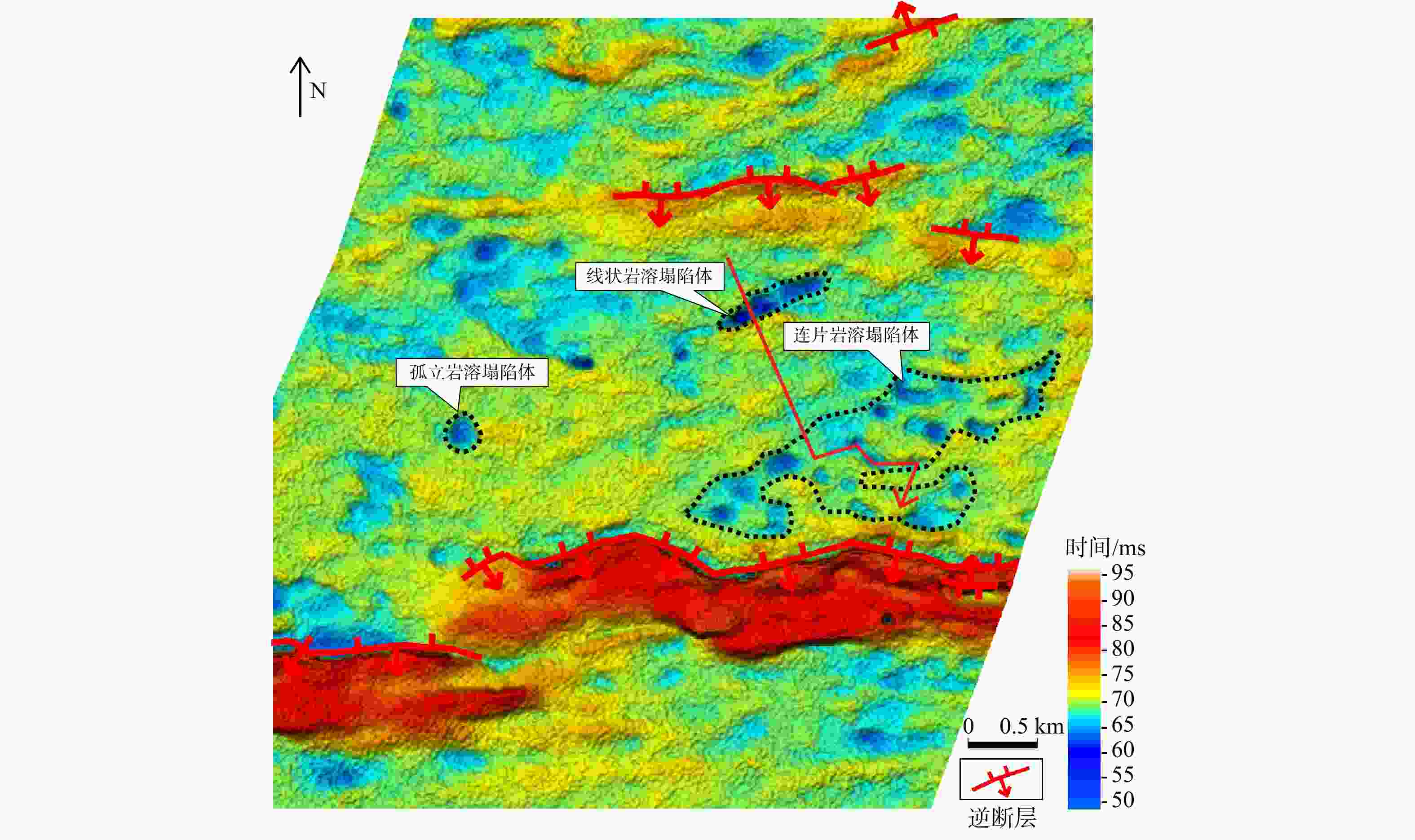
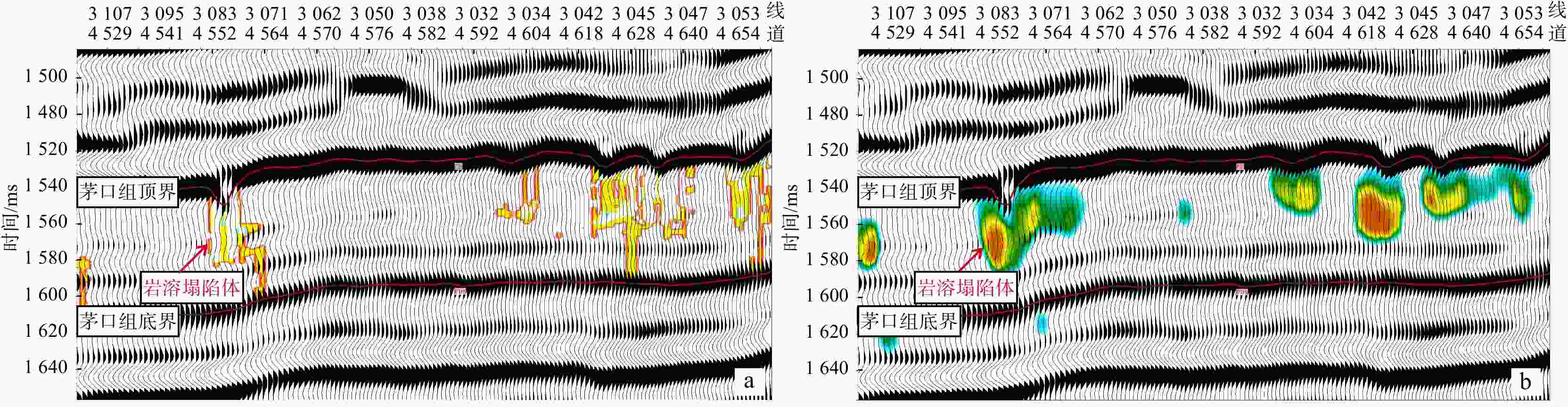
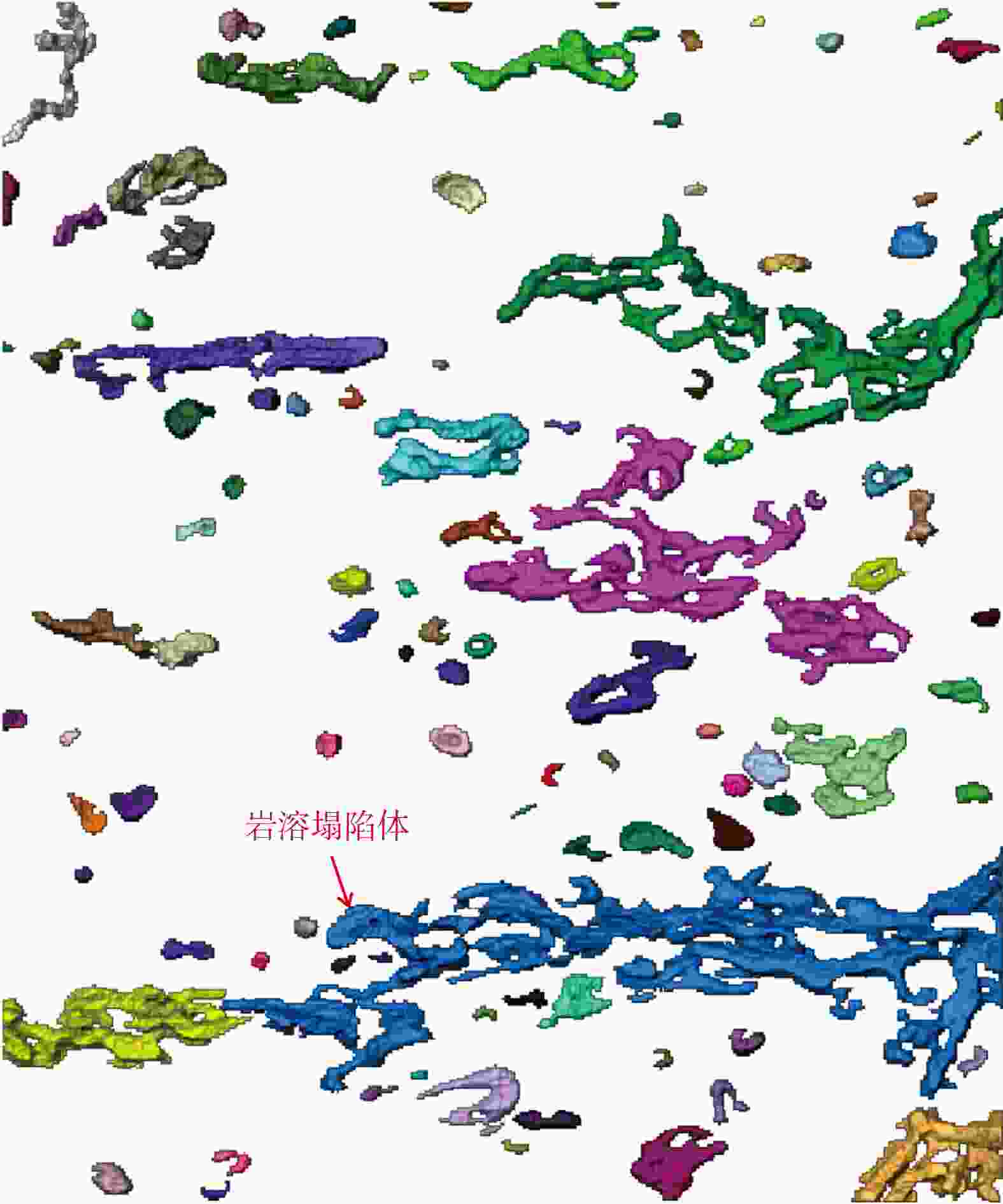
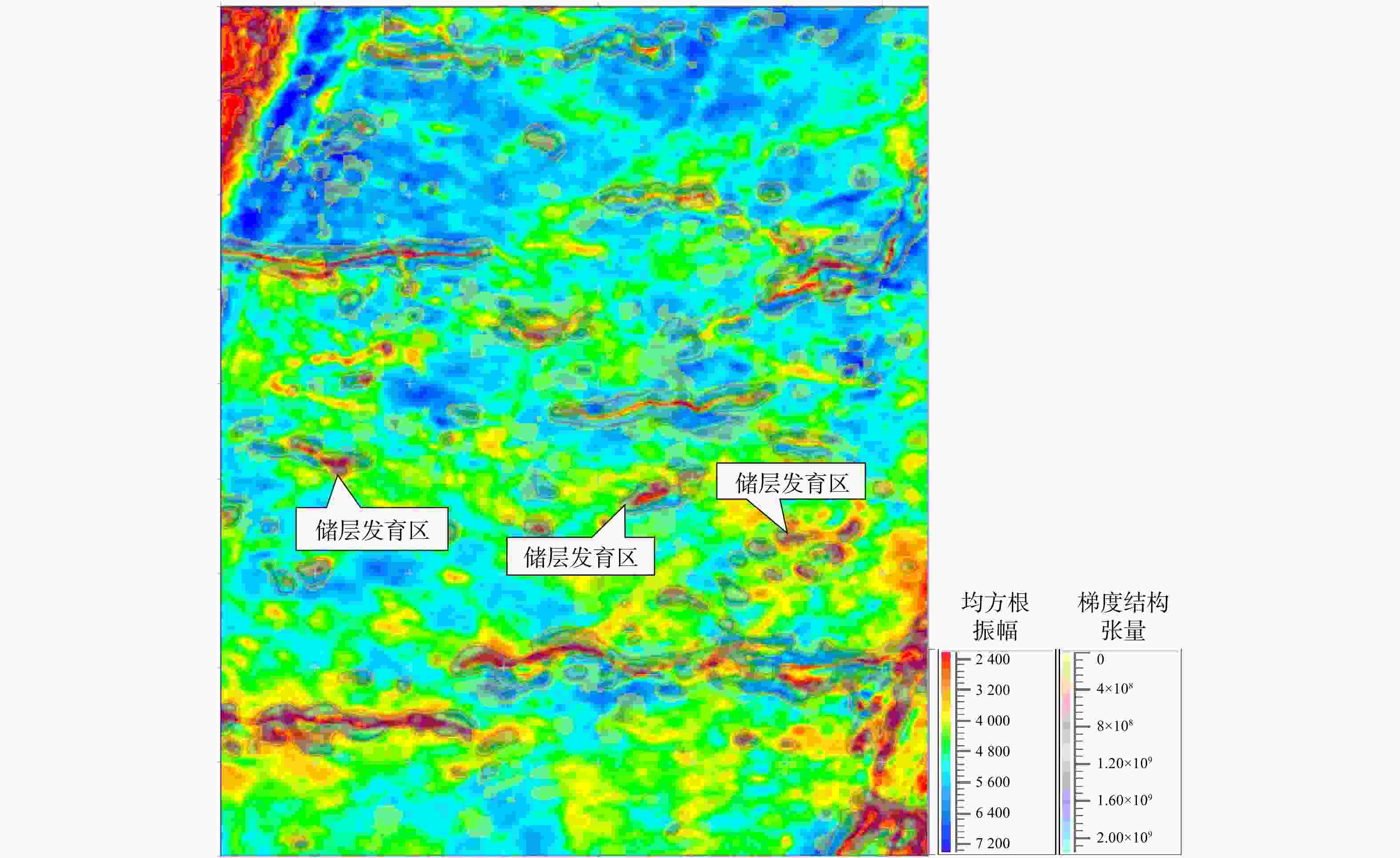
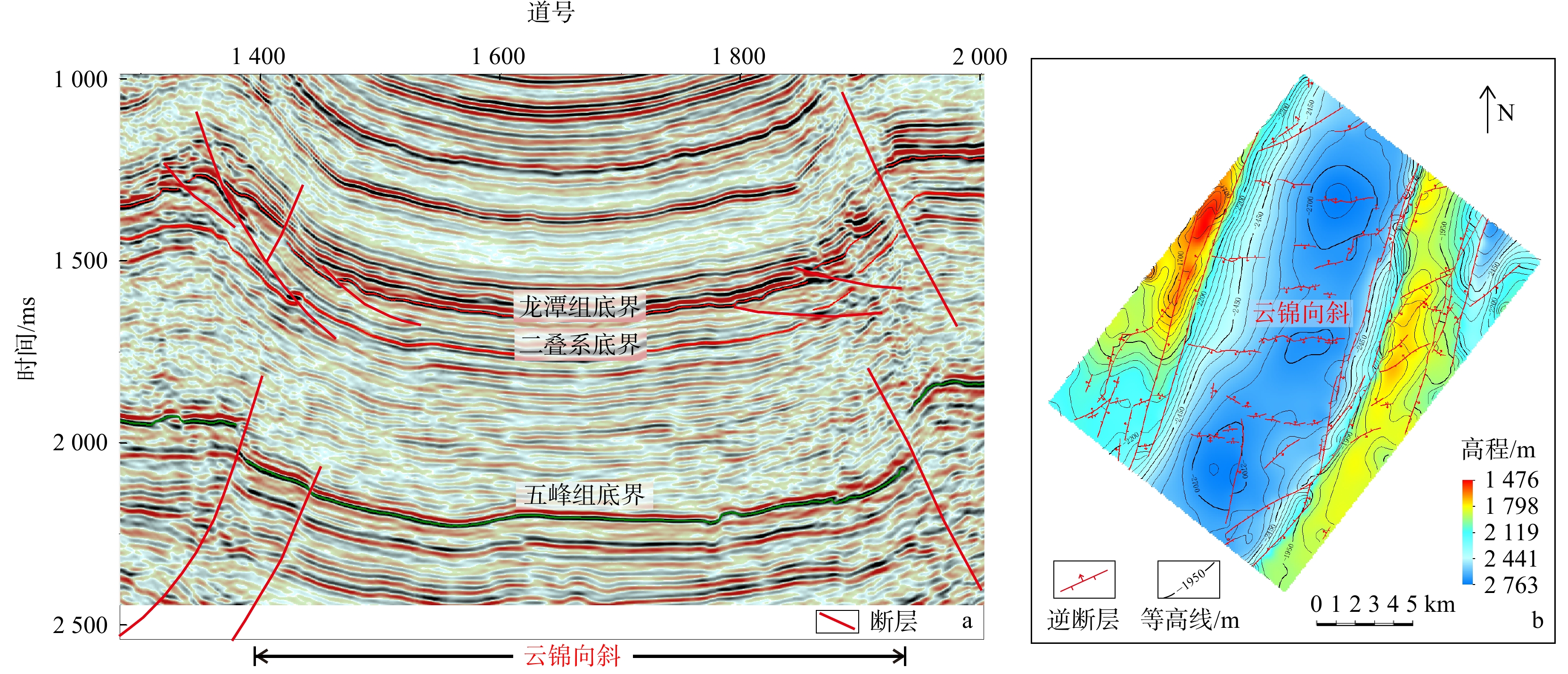
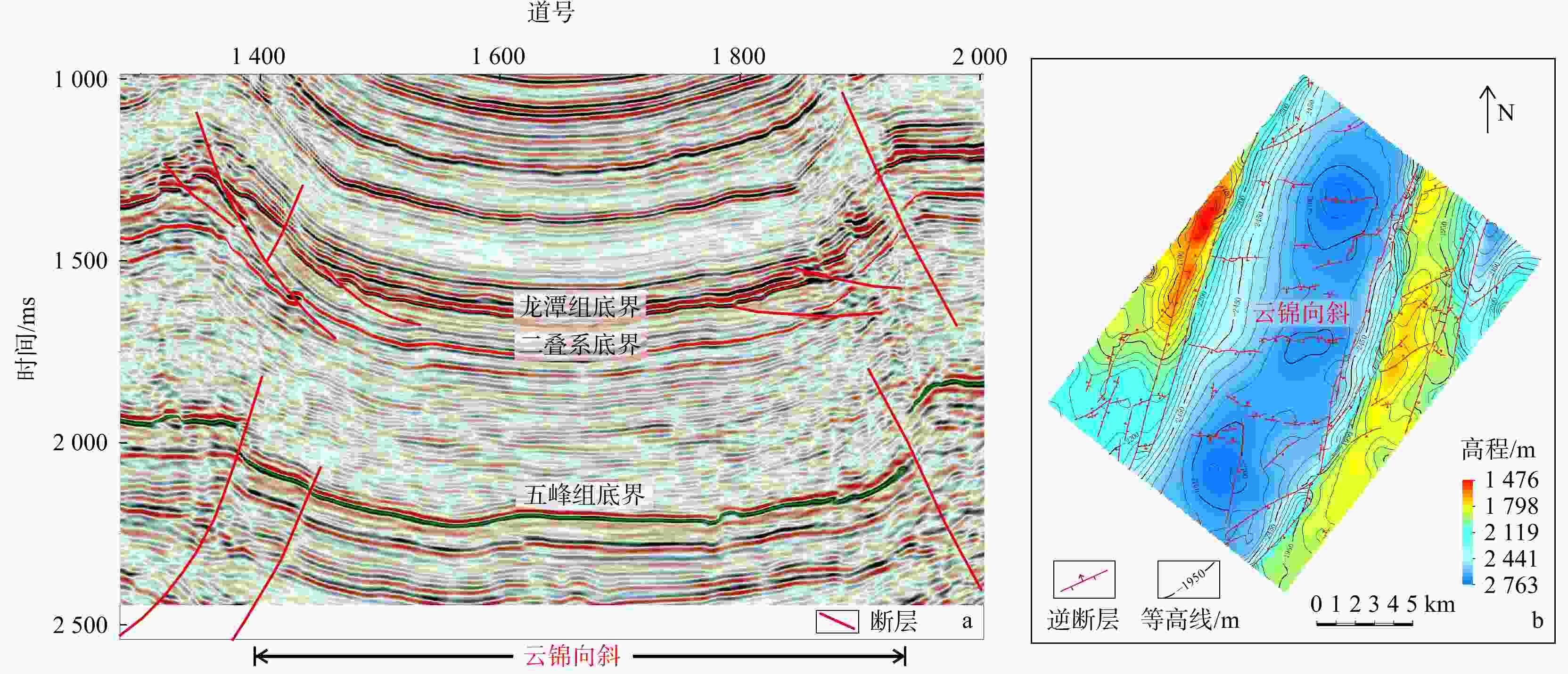
川南地区下二叠统茅口组岩溶储层发育,是川南常规油气勘探关键层系。表生岩溶型储层发育程度直接受控于丰富多变的岩溶微地貌,所形成的岩溶储层横向非均质性强。利用三维地震资料,结合地层厚度、梯度结构张量属性和地质体雕刻技术刻画了云锦地区东吴期岩溶微地貌特征,并通过模型正演和振幅属性,预测了表生岩溶储层有利区带。研究结果表明:①云锦地区在东吴期岩溶微地貌差异大,发育一系列岩溶塌陷体,在地震上表现为茅口组顶界地震同相轴“下拉”的特征;②利用梯度结构张量属性结合地质体雕刻技术有效刻画了云锦向斜区岩溶塌陷体,分析了其展布规律,平面上呈孤立、线状或连片3种展布方式;③岩溶塌陷体边缘两侧地震振幅减弱区,岩溶作用强烈,溶蚀孔洞发育,为储层发育有利区带。研究成果对后续川南云锦地区茅口组储层预测工作具有指导意义。
Abstract:Objective The development of karst reservoirs in the Maokou Formation of the Lower Permian in southern Sichuan is a key formation for conventional oil and gas exploration in southern Sichuan. The development level of supergene karst reservoirs is directly controlled by the rich and varied karst microgeomorphology, resulting in strong lateral heterogeneity of karst reservoirs.
Methods This paper uses 3-D seismic data, combined with strata thickness, gradient structure tensor attributes, and geological body carving techniques, to characterize the microgeomorphic characteristics of Dongwu karst in the Yunjin area. Predicting favorable zones for surface karst reservoirs through model forward modeling and amplitude attributes.
Results Research suggests that:①The Yunjin area had significant differences in karst micro- geomorphology during the Dongwu period, with a series of karst caves developed, which exhibited a seismic feature of "pull-down" of the seismic event event axis at the top boundary of the Maokou Formation;②Effectively characterizing the distribution pattern of karst collapse bodies in Yunjin syncline area using gradient structure tensor attributes combined with geological body carving technology. There are three distribution patterns of karst collapse bodies on the plane: isolated, linear, or contiguous;③The seismic amplitude on both sides of the edge of the karst collapse body is weakened, and the karst process is strong, with the development of karst caves, which is a favorable zone for reservoir development.
Conclusion This research result has guiding significance for the subsequent prediction of Maokou Formation reservoirs.
-
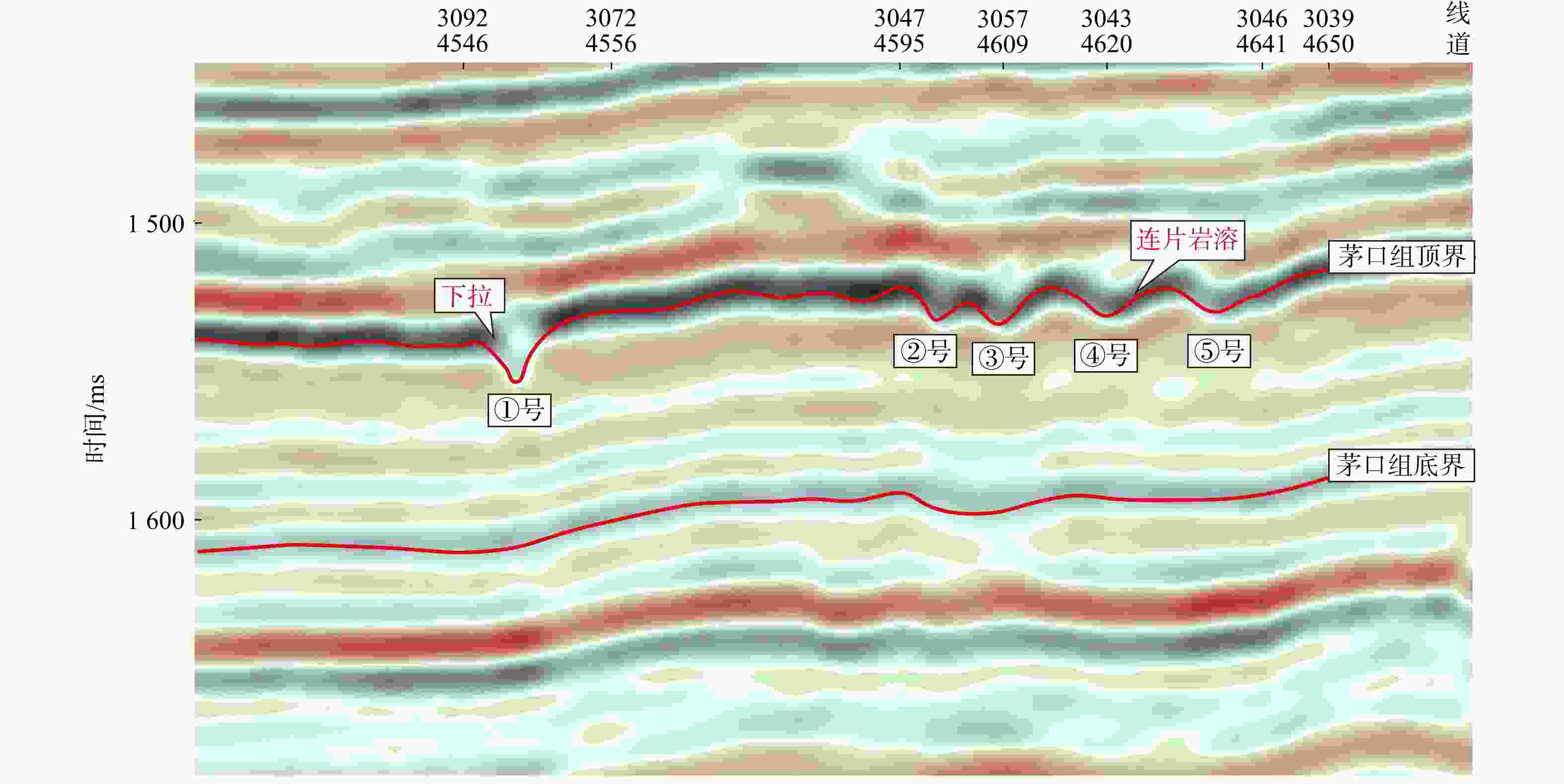
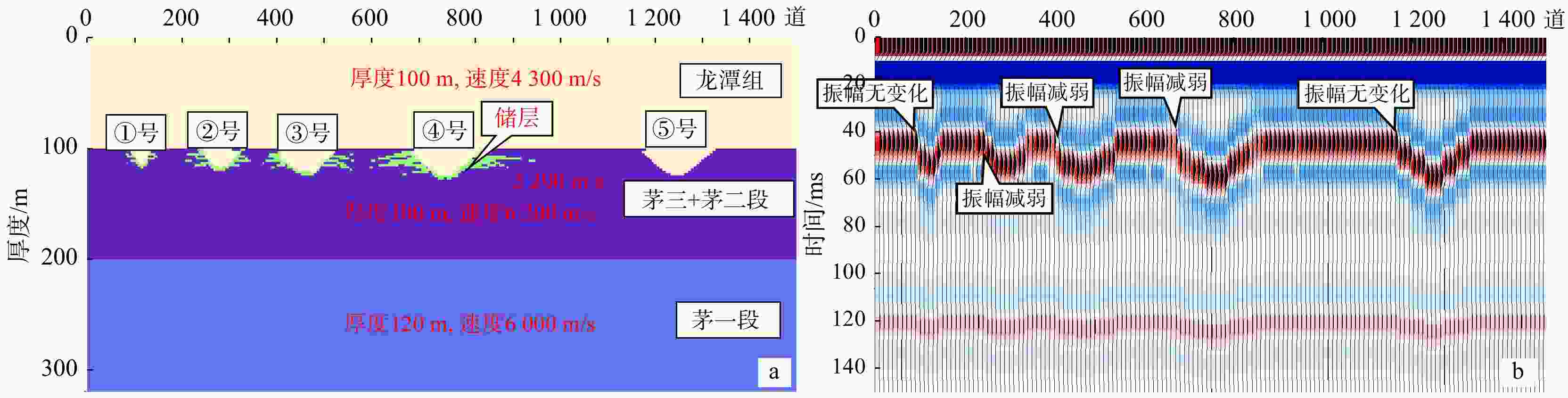
表 1 正演岩溶塌陷体发育尺度
Table 1. Scale for the development of karst collapse bodies in forward modeling
尺度 ①号岩溶
塌陷体②号岩溶
塌陷体③号岩溶
塌陷体④号岩溶
塌陷体⑤号岩溶
塌陷体直径/m 40 80 120 160 160 深度/m 15 18 21 24 24 -
[1] 桑琴,未勇,程超,等. 蜀南地区茅口组气藏气水分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 中国地质,2012,39(3):634-644.SANG Q,WEI Y,CHENG C,et al. Gas-water distribution characteristics and control factors of Maokou Formation in Shunan (south Sichuan) area[J]. Geology in China,2012,39(3):634-644. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 王雷,纪学武,屈卫华,等. 蜀南自贡地区茅口组岩溶储层成因及地震预测方法[J]. 石油物探,2024,63(2):437-448.WANG L,JI X W,QU W H,et al. Genesis and seismic prediction of Maokou karst reservoirs in Zigong,southern Sichuan[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,2024,63(2):437-448. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 江青春. 川中−蜀南地区茅口组岩溶储层油气成藏条件与有利区带预测[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2024,43(4):48-58.JIANG Q C. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions of karst reservoirs of Maokou Formation in central-southern Sichuan Basin and favorable plays prediction[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2024,43(4):48-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 韩冰,朱斗星,刘冬民,等. 蜀南地区茅口组断溶模式及储层地震预测[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2022,57(增刊1):110-116.HAN B,ZHU D X,LIU D M,et al. Fault-karst model and prediction based on seismic data of Maokou Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting,2022,57(S1):110-116. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 桑琴,黄静,程超,等. 蜀南地区茅口组古岩溶地貌与缝洞系统发育关系研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2012,31(2):212-219.SANG Q,HUANG J,CHENG C,et al. Research on the relation between the ancient karst landform and the development features of fissure-cavity system in the Maokou Formation in Shunan region[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2012,31(2):212-219. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 黄士鹏,江青春,冯庆付,等. 川南地区中二叠统茅口组岩溶储集层类型与分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(2):281-289.HUANG S P,JIANG Q C,FENG Q F,et al. Type and distribution of Mid-Permian Maokou Formation karst reservoirs in southern Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2019,46(2):281-289. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 聂国权,淡永,徐亮,等. 蜀南Z工区茅口组顶岩溶古地貌、古水系特征与刻画[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(6):911-917.NIE G Q,DAN Y,XU L,et al. Characteristics and characterization of karst paleo-geomorphology and paleo-water system on the top of the Maokou Formation in the Z area in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(6):911-917. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 淡永,邹灏,梁彬,等. 塔北哈拉哈塘加里东期多期岩溶古地貌恢复与洞穴储层分布预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2016,37(3):304-312.DAN Y,ZOU H,LIANG B,et al. Restoration of multistage paleogeomorphology during Caledonian Period and paleokarst cavernous reservoir prediction in Halahatang area,northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2016,37(3):304-312. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 江青春,胡素云,汪泽成,等. 四川盆地茅口组风化壳岩溶古地貌及勘探选区[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(6):949-960.JIANG Q C,HU S Y,WANG Z C,et al. Paleokarst landform of the weathering crust of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in Sichuan Basin and selection of exploration regions[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(6):949-960. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张坦,贾梦瑶,孙雅雄,等. 四川盆地南部中二叠统茅口组岩溶古地貌恢复及特征[J]. 岩性油气藏,2024,36(1):111-120.ZHANG T,JIA M Y,SUN Y X,et al. Restoration and characteristics of karst paleogeomorphology of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2024,36(1):111-120. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 张亚,陈双玲,张晓丽,等. 四川盆地茅口组岩溶古地貌刻画及油气勘探意义[J]. 岩性油气藏,2020,32(3):44-55.ZHANG Y,CHEN S L,ZHANG X L,et al. Restoration of paleokarst geomorphology of Lower Permian Maokou Formation and its petroleum exploration implication in Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2020,32(3):44-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 徐祖新. 川东地区中二叠统茅口组天然气成因及气源[J]. 特种油气藏,2019,26(2):16-22.XU Z X. Genesis and source of gas in Middle Permian Maokou Formation of eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2019,26(2):16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 胡明毅,胡忠贵,魏国齐,等. 四川盆地茅口组层序岩相古地理特征及储集层预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2012,39(1):45-55.HU M Y,HU Z G,WEI G Q,et al. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography and reservoir prediction of the Maokou Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2012,39(1):45-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 周进高,姚根顺,杨光,等. 四川盆地栖霞组−茅口组岩相古地理与天然气有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(4):8-15. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.04.002ZHOU J G,YAO G S,YANG G,et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography and favorable gas exploration zones of Qixia and Maokou Fms in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2016,36(4):8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.04.002 [15] 何钊,高兆龙,李国蓉,等. 川南云锦地区茅口组储集层溶蚀期次及模式[J]. 新疆石油地质,2022,43(5):537-545.HE Z,GAO Z L,LI G R,et al. Dissolution stage and pattern of reservoirs in Maokou Formation in Yunjin area,southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2022,43(5):537-545. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 刘冉,罗冰,李亚,等. 川西地区二叠系火山岩展布与茅口组岩溶古地貌关系及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(3):575-585.LIU R,LUO B,LI Y,et al. Relationship between Permian volcanic rocks distribution and karst paleogeomorphology of Maokou Formation and its significance for petroleum exploration in western Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(3):575-585. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 桑琴,未勇,程超,等. 蜀南地区二叠系茅口组古岩溶地区水系分布及岩溶地貌单元特征[J]. 古地理学报,2012,14(3):393-402. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2012.03.013SANG Q,WEI Y,CHENG C,et al. Distribution of palaeokarst water system and palaeogeomorphic unit characteristics of the Permian Maokou Formation in southern Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),2012,14(3):393-402. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2012.03.013 [18] 熊晓军,陈容,袁野,等. 四川盆地卧龙河构造茅口组岩溶储层地震预测[J]. 石油学报,2021,42(6):724-735.XIONG X J,CHEN R,YUAN Y,et al. Seismic prediction of karst reservoirs of the Maokou Formation in Wolonghe structure of Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2021,42(6):724-735. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 杨帆,刘立峰,冉启全,等. 四川盆地磨溪地区灯四段风化壳岩溶储层特征[J]. 岩性油气藏,2020,32(2):43-53.YANG F,LIU L F,RAN Q Q,et al. Characteristics of weathering crust karst reservoir of Deng 4 Member in Moxi area,Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2020,32(2):43-53. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 拜文华,吕锡敏,李小军,等. 古岩溶盆地岩溶作用模式及古地貌精细刻画:以鄂尔多斯盆地东部奥陶系风化壳为例[J]. 现代地质,2002,16(3):292-298.BAI W H,LÜ X M,LI X J,et al. The mode of palaeokarstification and the fine recon struction of the palaeogeomorphology in the karst basin:Taking Ordovician karst in eastern Ordos Basin for example[J]. Geoscience,2002,16(3):292-298. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 胡修权,施泽进,田亚铭,等. 川东南地区茅口组岩溶古地貌恢复及特征[J]. 地质通报,2014,33(6):874-882.HU X Q,SHI Z J,TIAN Y M,et al. The restoration of karst ancient landform of the Maokou Formation in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2014,33(6):874-882. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 樊婷婷,周梦影,郭远智,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地胡尖山地区前侏罗纪古地貌特征与油气成藏模式[J]. 能源与环保,2024,46(7):1-7.FAN T T,ZHOU M Y,GUO Y Z,et al. Pre-Jurassic palaeogeomorphology characteristics and oil and gas reservoir-forming mode in Hujianshan area of Ordos Basin[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection,2024,46(7):1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 毛飞跃,侯长冰,苟幸福,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇原油田侏罗系古地貌与油成藏关系分析[J]. 岩性油气藏,2013,25(5):44-48.MAO F Y,HOU C B,GOU X F,et al. Relation between Jurassic paleogeomorphology and hydrocarbon accumulation in Zhenyuan Oilfield,Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2013,25(5):44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 朱正平,罗文军,潘仁芳,等. 川中高石梯−磨溪地区灯四段古地貌恢复及其对储层的控制作用[J]. 中国石油勘探,2019,24(6):730-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.005ZHU Z P,LUO W J,PAN R F,et al. The paleogeomorphology restoration of Sinian Deng 4 Member and its control on reservoir formation in the Gaoshiti-Moxi area in central Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2019,24(6):730-738. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.005 [25] 冯磊,刘宏,谭磊,等. 岩溶古地貌恢复及油气地质意义:以四川盆地泸州地区中二叠统茅口组为例[J]. 断块油气田,2023,30(1):60-69.FENG L,LIU H,TAN L,et al. Karst paleogeomorphology restoration and hydrocarbon geological significance:A case study of Middle Permian Maokou Formation in Luzhou area of Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,2023,30(1):60-69. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 贾浪波,刘海锋,薛云龙,等. 靖边气田东侧陕X区块古地貌和气水分布规律[J]. 科学技术与工程,2023,23(12):5022-5032. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.12.05022JIA L B,LIU H F,XUE Y L,et al. Paleo-geomorphology and gas-water distribution law in Shaan X Block on the east side of Jingbian gas field[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2023,23(12):5022-5032. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.12.05022 [27] 胡明毅,魏国齐,胡忠贵,等. 四川盆地中二叠统栖霞组层序:岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报,2010,12(5):515-526. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.05.002HU M Y,WEI G Q,HU Z G,et al. Sequence-lithofacies palaeogeography of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),2010,12(5):515-526. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.05.002 [28] 戴晓峰,冯周,王锦芳. 川中茅口组岩溶储层地球物理特征及勘探潜力[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2017,52(5):1049-1058.DAI X F,FENG Z,WANG J F. Geologic and geophysical characteristics and exploration potential of karst reservoirs at Maokou Formation in the central Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting,2017,52(5):1049-1058. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] RANDEN T,MONSEN E,SIGNER C,et al. Three-dimensional texture attributes for seismic data analysis[C]//Anon. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2000. [S. l. ]:Society of Exploration Geophysicists,2000:668-671. [30] BAKKER P. Image structure analysis for seismic interpretation[M]. Nethelands:Technische Universiteit Delft,2003. [31] 张军华,董猛,周振晓,等. 基于GST的相干体方法研究及应用[J]. 天然气工业,2007,27(增刊1):381-383.ZHANG J H,DONG M,ZHOU Z X,et al. Research and application of coherent volume method based on GST[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2007,27(S1):381-383. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 张晟,李亚林,肖又军,等. 利用梯度结构张量刻画碳酸盐岩缝洞体边界[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2022,57(4):907-915.ZHANG S,LI Y L,XIAO Y J,et al. Research and application of carbonate fracture-cavity boundary characterization method based on gradient structure-tensor[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting,2022,57(4):907-915. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 崔正伟,程冰洁,徐天吉,等. 基于构造导向滤波与梯度结构张量相干属性的储层裂缝预测方法及应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2021,56(3):555-563.CUI Z W,CHENG B J,XU T J,et al. Reservoir fracture prediction method and application based on structure-oriented filtering and coherent attributes of gradient structure tensor[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting,2021,56(3):555-563. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 李笑天,潘仁芳,鄢杰,等. 四川盆地灯四段岩溶古地貌精细刻画及油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(3):191-195.LI X T,PAN R F,YAN J,et al. Karst paleogeomorphology features of the Fourth Member of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin and the significance of oil and gas exploration[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(3):191-195. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] WIDESS M B. How thin is a thin bed?[J]. Geophysics,1973,38(6):1176-1180. doi: 10.1190/1.1440403 [36] KALLWEIT R S,WOOD L C. The limits of resolution of zero-phase wavelets[J]. Geophysics,1982,47(7):1035-1046. doi: 10.1190/1.1441367 [37] 李敏. 薄层地震响应特征及预测方法研究[D]. 湖北荆州:长江大学,2023.LI M. Study on seismic response characteristics and prediction method of thin layer[D]. Jingzhou Hubei:Yangtze University,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 潘蓓,顾汉明. 碎屑岩储层模型的转换波正演模拟波场特征及其分辨率分析[J]. 地质科技情报,2014,33(2):186-191.PAN B,GU H M. Analysis of wave field characteristics and resolution of converted wave forward modeling based on clastic reservoir model[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2014,33(2):186-191. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 杨柳,朱亚东,刁永波,等. 川南荷包场地区茅口组油气地质条件新认识[J/OL]. 天然气地球科学:1-16[2025-01-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20230901.1559.011.html.YANG L,ZHU Y D,DIAO Y B,et al. New understanding of the oil and gas geological conditions of the Maokou Formation in the Hebaochang area of southern Sichuan Basin[J/OL]. Natural Gas Geoscience:1-16[2025-01-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20230901.1559.011.html. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 肖笛,谭秀成,郗爱华,等. 四川盆地南部中二叠统茅口组碳酸盐岩岩溶特征:古大陆环境下层控型早成岩期岩溶实例[J]. 古地理学报,2015,17(4):457-476.XIAO D,TAN X C,XI A H,et al. Palaeokarst characteristics of carbonate rocks of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in southern Sichuan Basin:Example of strata-bound eogenetic karst in palaeo-continental settings[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),2015,17(4):457-476. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 张宏光. 川南地区茅口组岩溶缝洞群气藏成藏主控因素[J]. 天然气技术与经济,2020,14(1):21-26. doi: 10.12155/j.issn.2095-1132.2020.01.004ZHANG H G. Main factors controlling hydrocarbon accumulation in fractured-vuggy karst gas reservoirs of Maokou Formation,southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy,2020,14(1):21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12155/j.issn.2095-1132.2020.01.004 [42] 黎荣,胡明毅,杨威,等. 四川盆地中二叠统沉积相模式及有利储集体分布[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(2):369-379.LI R,HU M Y,YANG W,et al. Sedimentary facies model and favorable reservoir distribution of the Middle Permian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2019,40(2):369-379. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: