Spatial characteristics and genetic mechanism of geothermal resources in Zhangye Basin by multi-source fusion modeling and heat-flow coupling simulation
-
摘要:
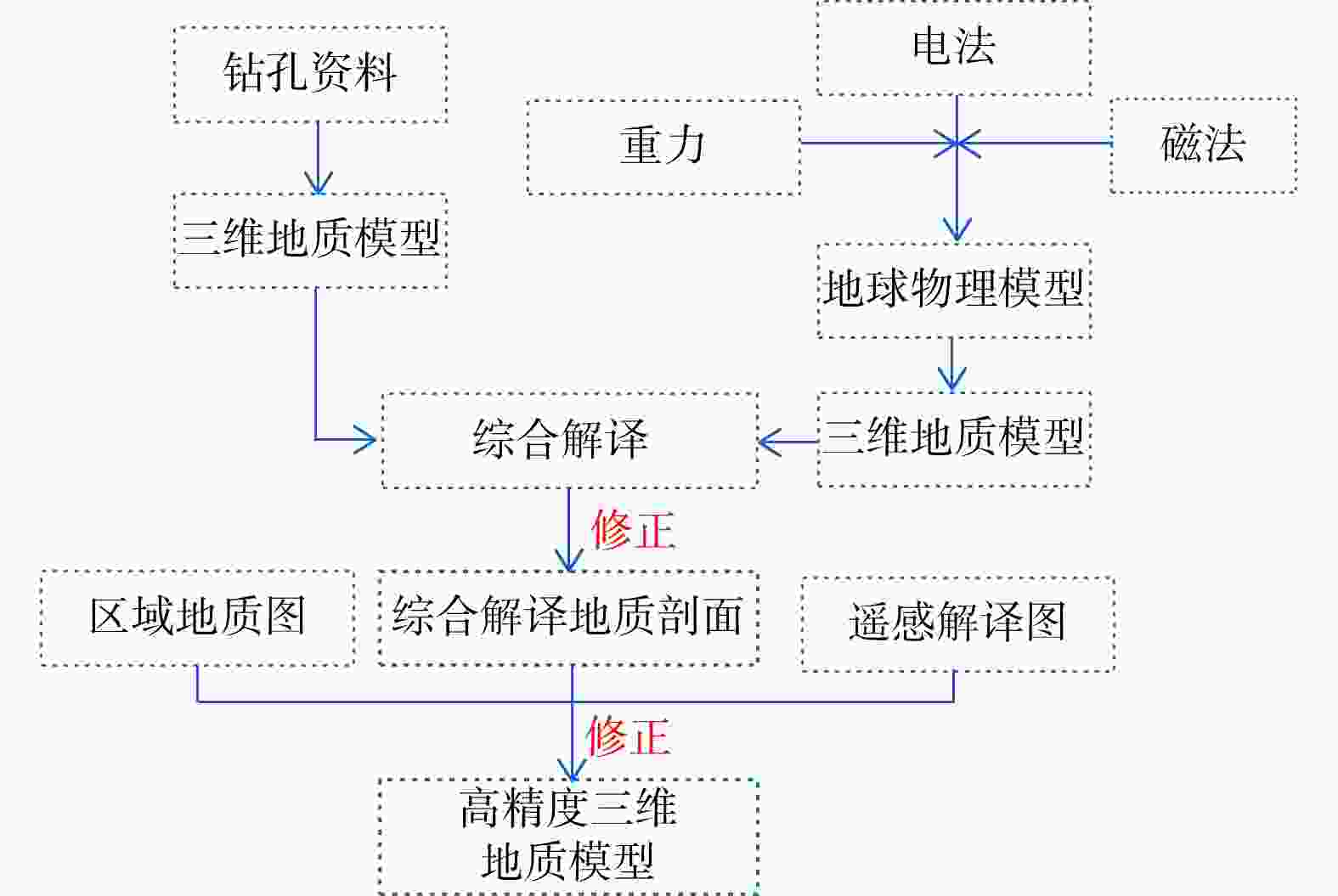
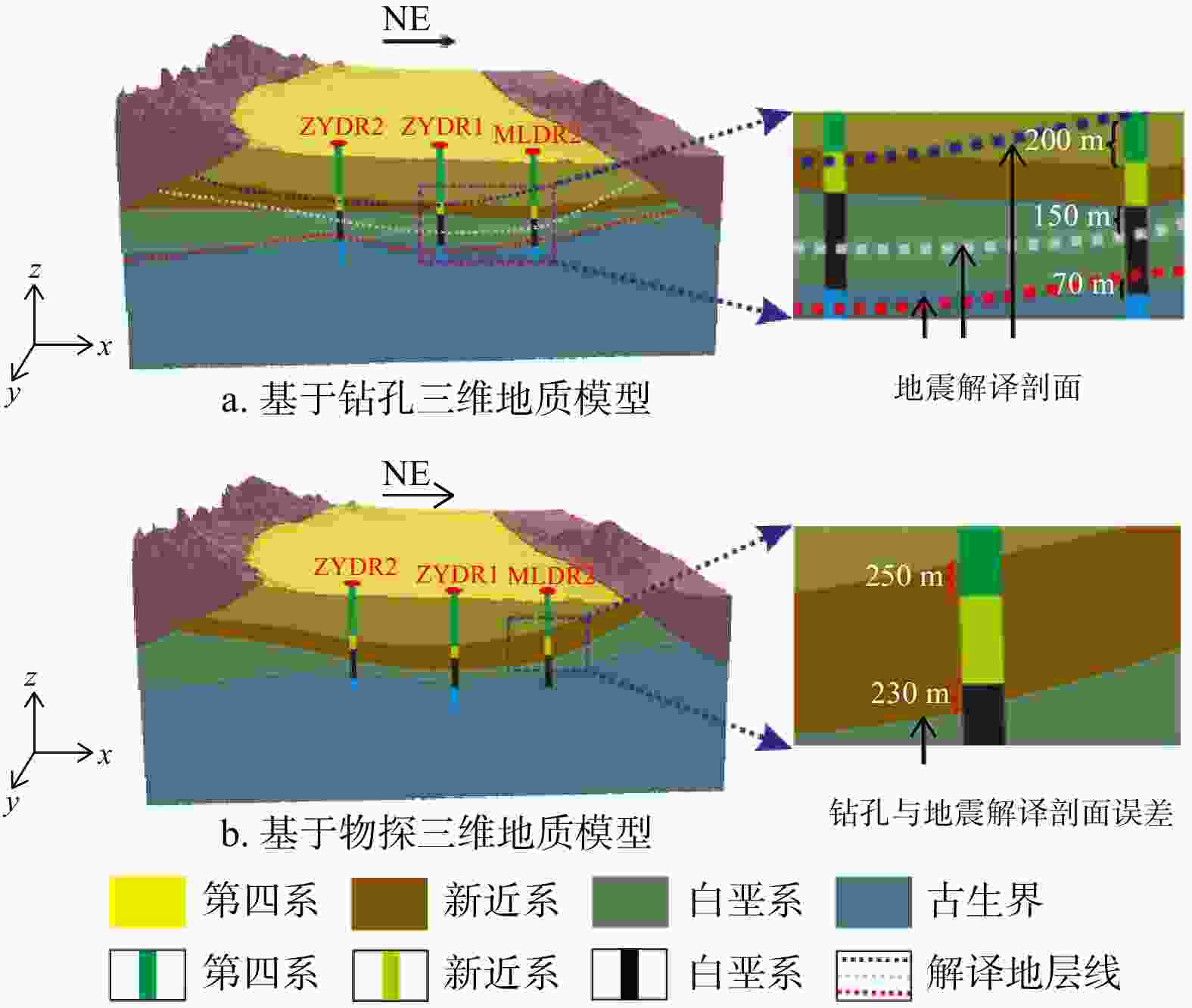
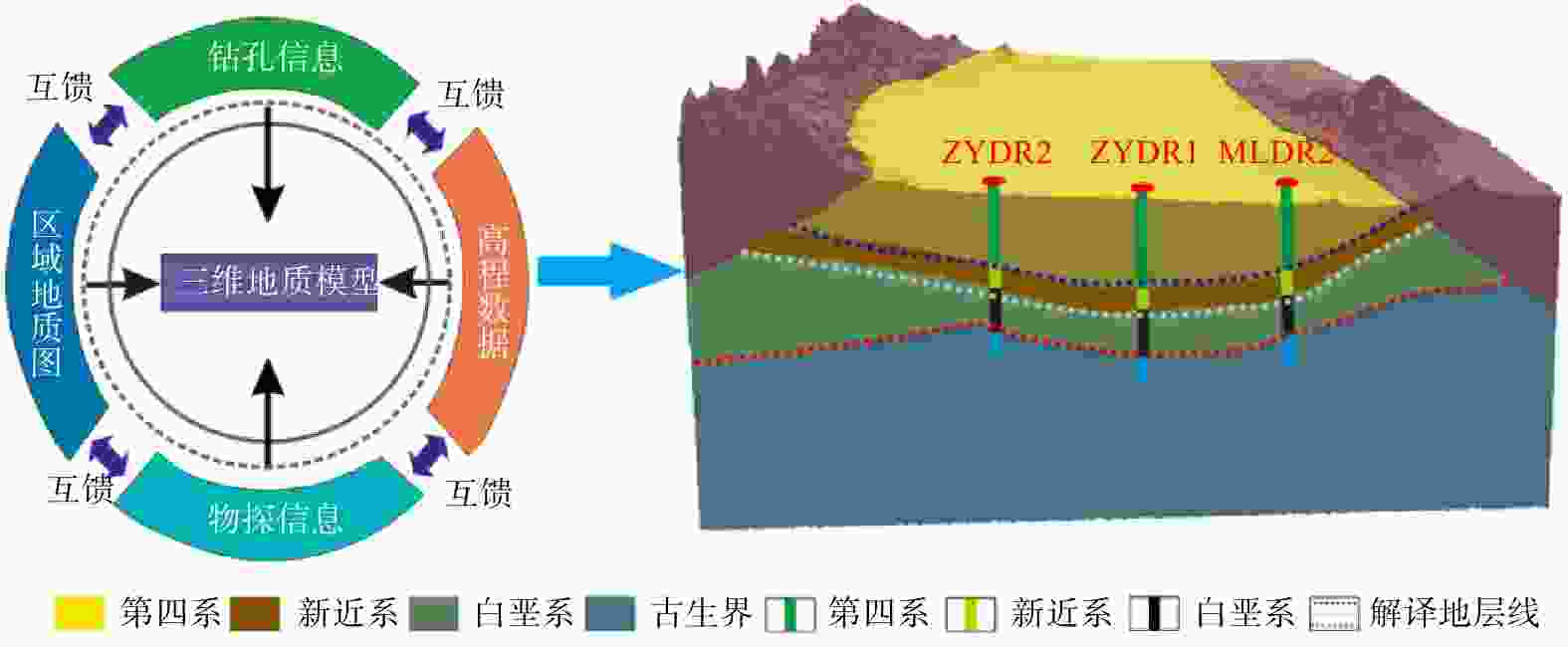
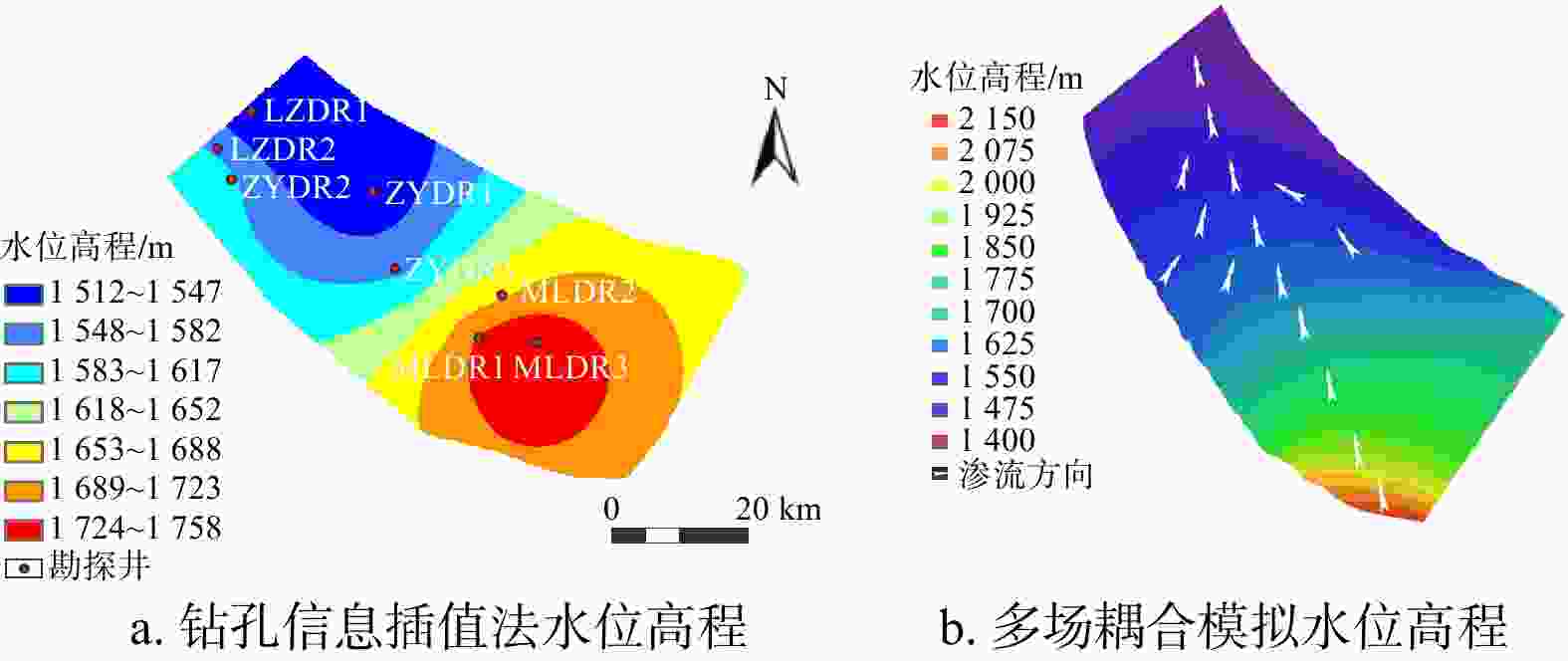
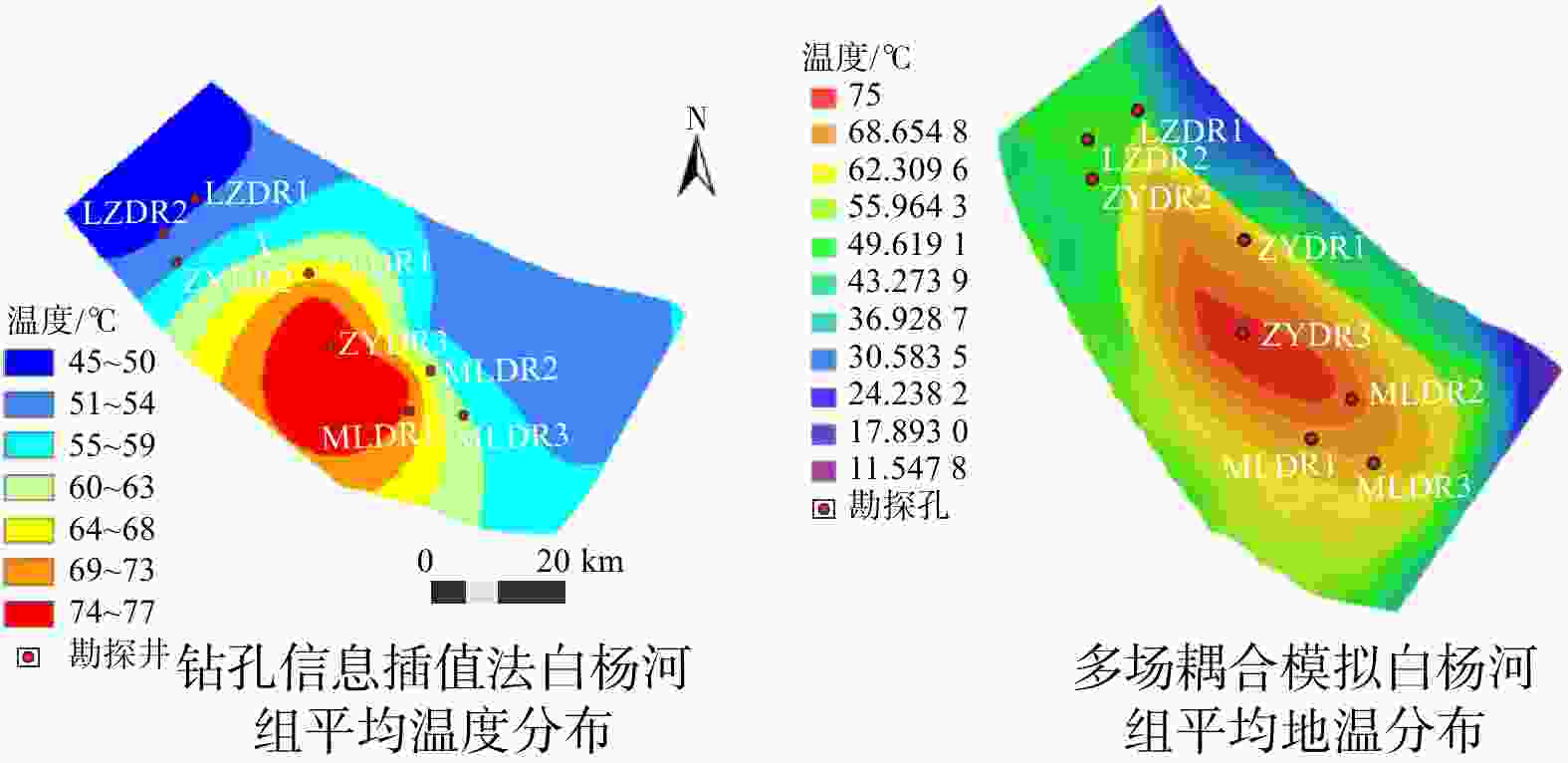
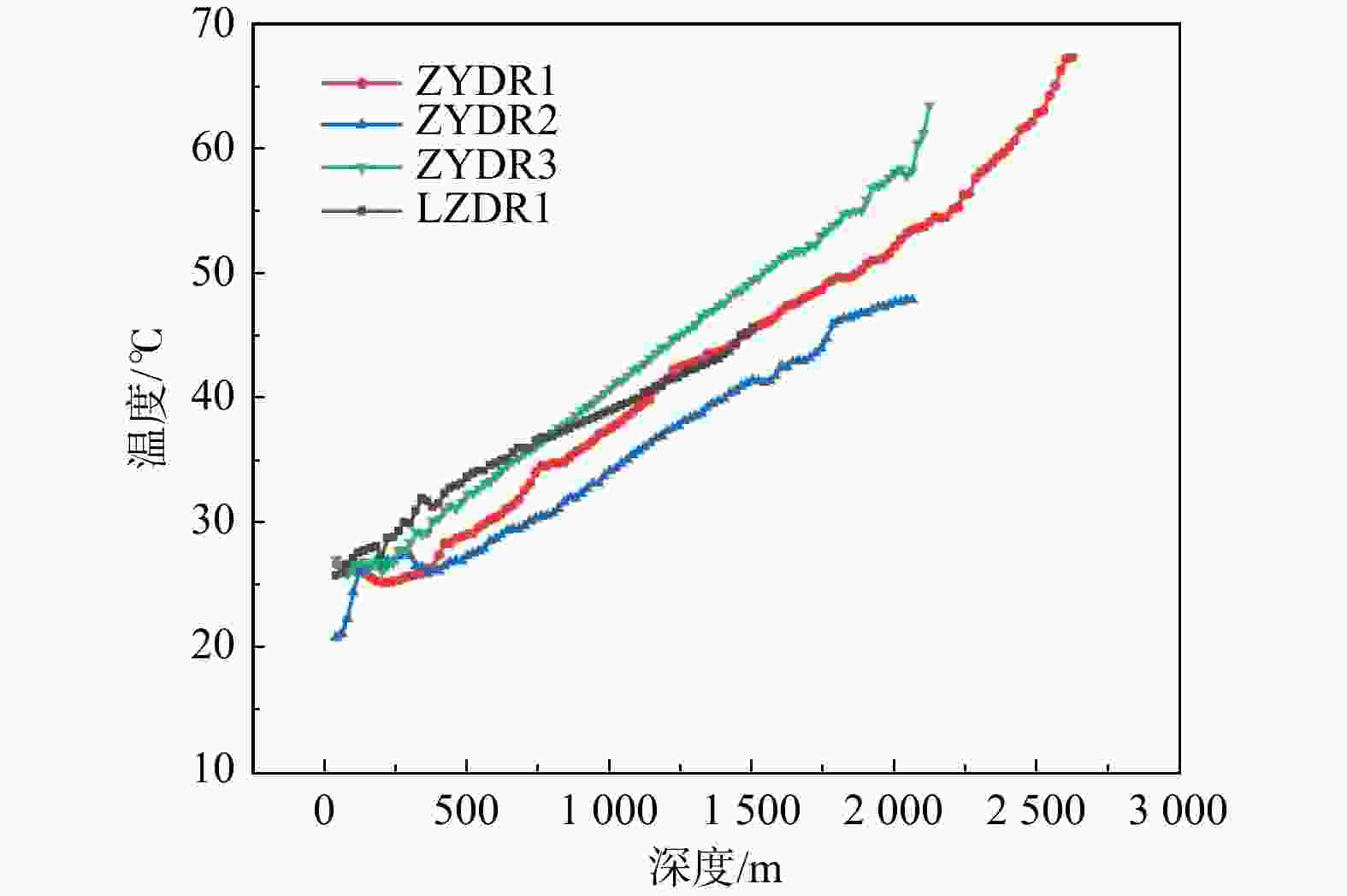
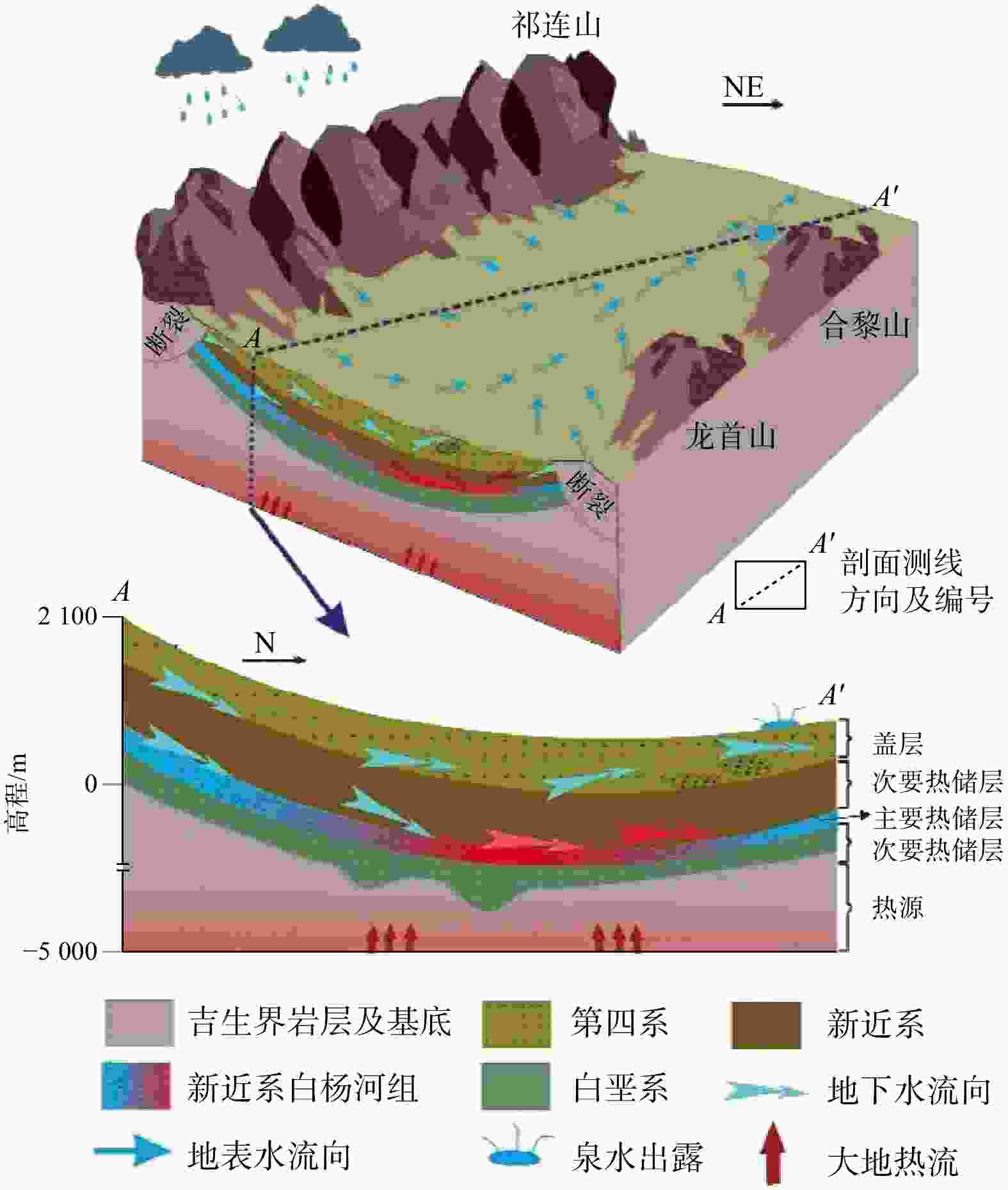
传统基于已有钻孔数据插值的温压场分析方法不能很好地反映地热资源渗流−传热耦合过程,造成对地热资源的成因机制认识不足。首先基于钻孔信息、物探信息、高程数据等多源数据进行相互融合,建立了张掖盆地高精确度三维地质模型。对比传统插值模型可知,多源数据融合建模能提升孔间地层精度50~300 m。基于三维地质模型开展了盆地渗流−传热场耦合数值模拟,对比关键点空间插值法,多场耦合分析更合理地揭示研究区储层温压特征。研究区地热水头在盆地中心靠东南处较高,逐渐向盆地北东方向降低,呈现整体由南东向北西渗流,经断层补给储层,渗流过程中被地温场充分地加热,随后由于储存埋深变浅和盖层变薄失去热量,温度场表现为中间高四周低,中心温度可达78℃。最后,建立了三维地热概念模型,结合构造、水文地质和地热地质条件等综合解释了盆地地热资源的成因机制。较之以往的二维模型,本研究三维概念模型和热−流耦合的方法更准确地描述了资源地空间分布特征和更合理地解释了资源成因机制。研究结果揭示了储层地下水由南东向北西渗流过程及盆地地热资源菱形叶状分布的成因机制,为精确圈定地热靶区和资源合理开发利用提供理论依据。
Abstract:The traditional temperature and pressure field analysis approach is based on the interpolation of existing borehole data, which cannot accurately represent the seepage-heat transfer coupling process of geothermal resources, resulting in insufficient understanding of the genetic mechanism of geothermal resources. To overcome the drawbacks of the conventional approach, this paper built a three-dimensional geological model of Zhangye Basin by combining multi-source data including borehole information, geophysical information and elevation data. Compared with the traditional model, multi-source data fusion modeling can improve the accuracy of inter-hole strata by 50-300 m. The numerical simulation of basin seepage-heat transfer field coupling process shows that the multi-field coupling analysis describing the temperature and pressure field more reasonable than that of key-point-spatial-interpolation approach. The analysis shows the higher water head in the southeast of the basin and relatively lower heat in the northeast. this leads to the geothermal water flows from southeast to northwest and was heated up during the seepage process, and the heat was lost later when the burying depth of the reservoir becomes shallower and the cap becomes thinner. As a result, the higher temperature was determined in the basin center which can reach up to 78℃ and the lower temperature was observed in the areas surrounding with the center. Finally, a 3D geothermal conceptual model is developed to better understand the genetic mechanism of geothermal resources in terms of structural, hydrogeological, and geothermal geological perspectives. This 3D conceptual mode coupling with heat-flow transfer modeling more specifically explains the spatial distribution and reveal more clearly the underlying mechanism of forming the geothermal resources compared with conventional 2D model.The study showed the groundwater in the reservoir flows from south-east toward north-west and revealed also the formation of the rhombic-lobe shaped distribution of geothermal resources in the basin, which provides theoretical basis for the precise localization of high potential geothermal zones and for the sustainable development of geothermal resources.
-
表 1 ZYDR1抽水实验成果
Table 1. ZYDR1 pumping test results
降 次 1 2 3 静水高度/m 5.77 5.77 5.77 动水位埋深/m 130.66 84.68 48.37 水位降深/m 136.43 90.45 54.14 出水量/(m3·d−1) 2640.00 1728.00 1032.00 单位出水量/(L·s−1·m−1) 0.22 0.22 0.22 井口出水温度/(℃) 56 55 55 抽水延续时间/h 56.5 18.25 8.75 稳定时间/h 48 16 8 表 2 水力学参数确定
Table 2. The determined hydraulic parameters of aquifers
储层
钻孔编号第四系 新近系 白垩系 HQ3 HQ4 LZDR1 ZYDR1 ZYDR3 ZYDR2 渗透系数K/(m·d−1) 28.80 26.13 0.35 0.48 0.35 0.097 导水系数C/(m2·d−1) 1696.90 1370.26 49.18 257.28 65.39 16.77 表 3 岩土物理参数及热物性参数测试结果
Table 3. Physical parameters and thermal parameters of the collected samples
储层 颗粒密度/
(g·cm−3)孔隙率/
%导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)比热容/
(kJ·kg−1·K−1)热扩散系数/
(mm2·s−1)第四系 2.60 40 1.610 0.878 0.705 新近系(砂岩) 2.67 27.3 1.264 0.311 1.860 新近系(泥岩) 2.63 10.6 1.460 0.260 3.400 白垩系(砂岩) 2.02 25.4 1.593 0.962 0.91 白垩系(泥岩) 2.56 5.6 1.104 0.345 1.510 表 4 地质钻孔信息
Table 4. Geological drilling information
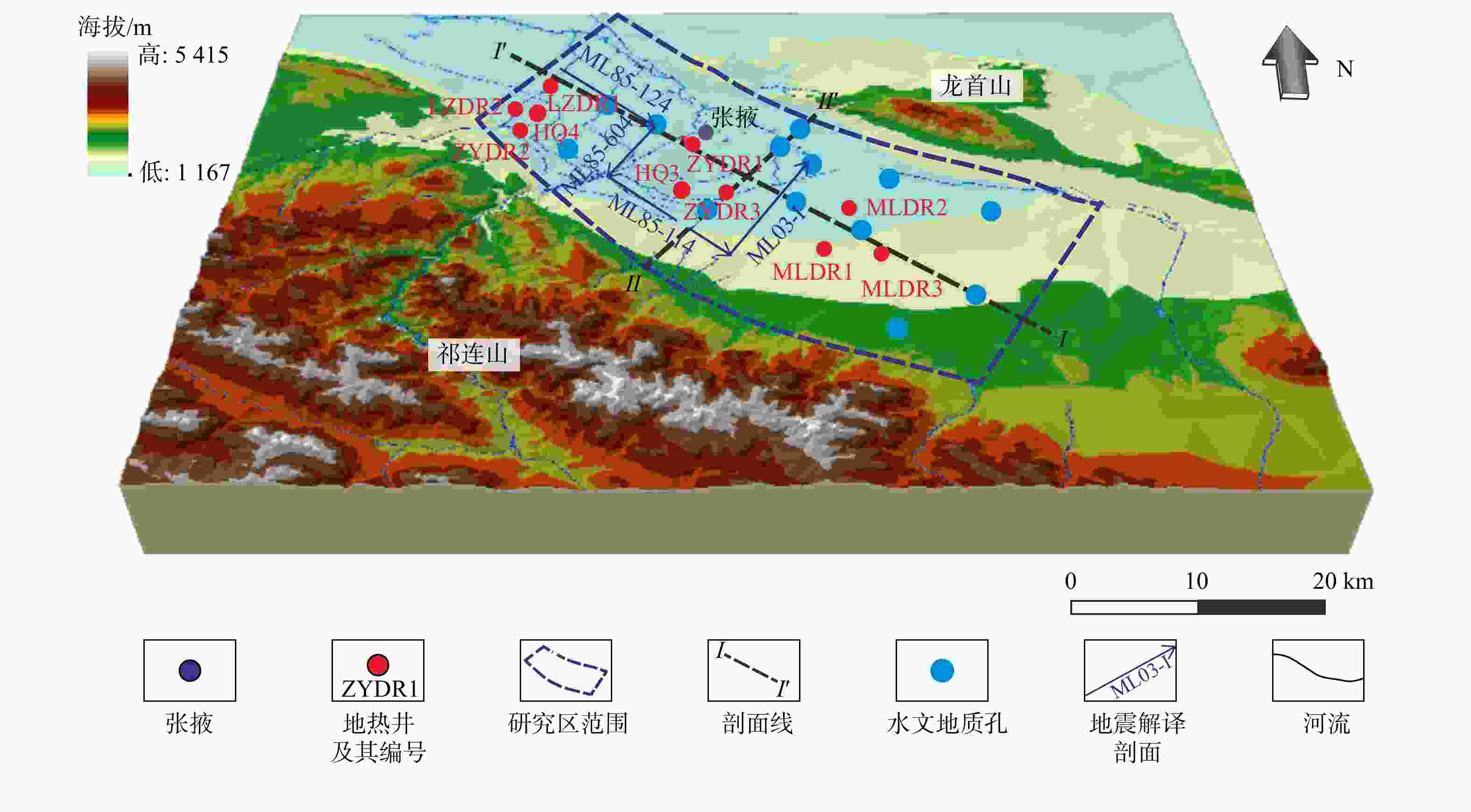
井号 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 井深/m 地面高程/m 祁连山山前断裂/m 龙首山山前断裂/m 第四系底/m 新近系底/m 白垩系底/m ZYDR1 100.4211 38.94694 2601.22 1487 21.7 17.6 834 −318 − 2093 ZYDR2 100.1253 38.98694 2053.08 1644 1.7 29.8 1045 13 − 1112 ZYDR3 100.4842 38.79778 2714.03 1536 23.3 28.4 949 −484 − 4279 MLDR1 100.6383 38.66139 2269.18 1778 23.2 34.1 1127 −417 − 1384 MLDR2 100.682 38.75419 1567.02 1646 34.3 23.7 1030 −674 − 1283 MLDR3 100.7289 38.64698 2350.79 1827 26.1 32.5 1064 −667 − 1148 LZDR1 100.1697 39.12476 1500.59 1463 14.9 16.6 1023 432 − 1760 LZDR2 100.1119 39.04029 1701.75 1587 4.2 25.9 767 261 − 1280 -
[1] 李曼,张薇,廖煜钟,等. 鲁中南典型地热区地热水氟分布特征及其驱动机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):36-47.LI M,ZHANG W,LIAO Y Z,et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of fluorine enrichment in the geothermal water of south central Shandong Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):36-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 尚建波,卫兴,曹园园,等. 不同类型地热水硼的地球化学特征及对地热系统成因机制的指示[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):288-297.SHANG J B,WEI X,CAO Y Y,et al. Boron geochemical characteristics in different types of geothermal water and its indications for the genesis mechanism of geothermal systems[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):288-297. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 王贵玲,陆川. 碳中和目标驱动下地热资源开采利用技术进展[J]. 地质与资源,2022,31(3):412-425.WANG G L,LU C. Progress of geothermal resources exploitation and utilization technology driven by carbon neutralization target[J]. Geology and Resources,2022,31(3):412-425. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 解经宇,王丹,李宁,等. 干热岩压裂建造人工热储发展现状及建议[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(3):321-329.XIE J Y,WANG D,LI N,et al. Development status and suggestions of hot dry rock hydraulic fracturing for building geothermal reservoirs[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(3):321-329. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 许天福,姜振蛟,袁益龙. 中深部地热资源开发利用研究现状与展望[J]. 中国基础科学,2023,25(3):11-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2023.03.002XU T F,JIANG Z J,YUAN Y L. Research status and prospects of middle and deep geothermal resources exploitation and utilization[J]. China Basic Science,2023,25(3):11-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2023.03.002 [6] LEPTOKAROPOULOS K,STASZEK M,LASOCKI S,et al. Evolution of seismicity in relation to fluid injection in the north-western part of The Geysers geothermal field[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2018,212(2):1157-1166. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx481 [7] 闫坪卉. 我国地热产业持续高质量发展[N]. 中国石化报,2023-09-18(2).YAN P H. China 's geothermal industry continues to develop with high quality[N]. China Petrochemical New,2023-09-18(2). (in Chinese) [8] 刘德民,张昌生,孙明行,等. 干热岩勘查评价指标与形成条件[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):1-11.LIU D M,ZHANG C S,SUN M H,et al. Evaluation indexes and formation conditions of hot dry rock exploration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 汪集暘,庞忠和,程远志,等. 全球地热能的开发利用现状与展望[J]. 科技导报,2023,41(12):5-11.WANG J Y,PANG Z H,CHENG Y Z,et al. Current state,utilization and prospective of global geothermal energy[J]. Science & Technology Review,2023,41(12):5-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 朱喜,王贵玲,马峰,等. 雄安新区地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):1093-1106.ZHU X,WANG G L,MA F,et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources of the Xiongan New Area[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):1093-1106. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 杜垚森,封优生,伍晓龙,等. 深部地热能开发保温管技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 钻探工程,2022,49(6):138-145. doi: 10.12143/j.ztgc.2022.06.019DU Y S,FENG Y S,WU X L,et al. Research status and consideration of thermal insulation pipe technology for deep geothermal energy development[J]. Drilling Engineering,2022,49(6):138-145. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12143/j.ztgc.2022.06.019 [12] 王贵玲,杨轩,马凌,等. 地热能供热技术的应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 华电技术,2021,43(11):15-24.WANG G L,YANG X,MA L,et al. Status quo and prospects of geothermal energy in heat supply[J]. Huadian Technology,2021,43(11):15-24. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 尹政,田辽西,张旭儒,等. 张掖城区及外围地热资源普查报告[R]. 兰州:甘肃省地矿局水文地质工程地质勘察院,2018.YIN Z,TIAN L X,ZHANG X R,et al. Geothermal resources survey in Zhangye City and its periphery[R]. Lanzhou:Institute of Hydrogeoloical and Engineering Geology,Gansu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development,2018. (in Chinese) [14] 张振杰,李兴海,胡潇. 综合物探方法在张掖城区及外围深部地热资源勘查中的应用研究[J]. 地下水,2018,40(4):52-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2018.04.016ZHANG Z J,LI X H,HU X. The application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method in the exploration of deep geothermal resources in Zhangye City and its periphery[J]. Ground Water,2018,40(4):52-54. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2018.04.016 [15] 俞兆虎,滕汉仁,李百祥. 张掖−民乐盆地地质−地球物理信息揭示的地热资源前景与勘查方法优化组合[J]. 甘肃地质,2018,27(增刊1):79-84.YU Z H,TENG H R,LI B X. On geothermal resource potential and optimization prospecting methods in terms of geology-geophysical information in Zhangye-Minle Basin[J]. Gansu Geology,2018,27(S1):79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 梁雨东,任康辉,姜鑫,等. 活性炭测氡法在地热勘探中的应用:以张掖−民乐盆地为例[J]. 物探与化探,2022,46(6):1419-1424.LIANG Y D,REN K H,JIANG X,et al. Application of the activated charcoal radon measurement in the geothermal exploration:A study of the Zhangye-Minle Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2022,46(6):1419-1424. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 魏红军,李百祥. 张掖−民乐盆地地质构造特征与张掖市地热资源开发可行性分析[J]. 甘肃地质,2007,16(4):73-76.WEI H J,LI B X. Characteristics of geological structures in Zhangye-Minle Basin and feasibility study of geothermal resources in Zhangye City[J]. Gansu Geology,2007,16(4):73-76. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 尹政,柳永刚,张旭儒,等. 张掖−民乐盆地中新生界地层结构及对地热的控制作用[J]. 甘肃地质,2021,30(3):49-56.YIN Z,LIU Y G,ZHANG X R,et al. Mesozoic Cenozoic stratigraphic structure and its control on geothermal energy in Zhangye-Minle Basin[J]. Gansu Geology,2021,30(3):49-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 王具文,张旭儒,宁天祥,等. 张掖盆地地热资源流体化学特征研究[J]. 地下水,2019,41(4):17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.04.006WANG J W,ZHANG X R,NING T X,et al. Study on fluid chemical characteristics of geothermal resources in Zhangye Basin[J]. Ground Water,2019,41(4):17-19. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.04.006 [20] 王具文,张旭儒,宁天祥,等. 张掖盆地地热资源地质特征分析与研究[J]. 地下水,2019,41(3):5-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.03.002WANG J W,ZHANG X R,NING T X,et al. Analysis and research on geological characteristics of geothermal resources in Zhangye Basin[J]. Ground Water,2019,41(3):5-6. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2019.03.002 [21] 张旭儒,冯建宏,李小燕. 甘肃省张掖盆地地热资源量评价分析[J]. 地下水,2020,42(4):73-75.ZHANG X R,FENG J H,LI X Y. Evaluation and analysis of geothermal resources in Zhangye Basin,Gansu Province[J]. Ground Water,2020,42(4):73-75. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] MOHAMMADI Z,BAGHERI R,JAHANSHAHI R. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of Changal thermal springs,Zagros region,Iran[J]. Geothermics,2010,39(3):242-249. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.06.007 [23] WANG M M,ZHOU X,LIU Y,et al. Major,trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of geothermal waters from the Rehai high-temperature geothermal field in Tengchong of China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2020,119:104639. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104639 [24] LI X,QI J H,YI L,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of geothermal waters in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis geothermal field,southern Tibet[J]. Geothermics,2021,97:102233. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102233 [25] 孙红丽,马峰,蔺文静,等. 西藏高温地热田地球化学特征及地热温标应用[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(3):171-177.SUN H L,MA F,LIN W J,et al. Geochemical characteristics and geothermometer application in high temperature geothermal field in Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2015,34(3):171-177. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] ELENGA H I,TAN H B,SU J B,et al. Origin of the enrichment of B and alkali metal elements in the geothermal water in the Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from B and Sr isotopes[J]. Geochemistry,2021,81(3):125797. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2021.125797 [27] 张薇,王贵玲,刘峰,等. 中国沉积盆地型地热资源特征[J]. 中国地质,2019,46(2):255-268. doi: 10.12029/gc20190204ZHANG W,WANG G L,LIU F,et al. Characteristics of geothermal resources in sedimentary basins[J]. Geology in China,2019,46(2):255-268. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20190204 [28] 翟光明. 中国石油地质志−卷十三−玉门油田[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1989:236-261.ZHAI G M. Yumen Oilfield,petroleum geology of China(Vol. 13)[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1989:236-261. (in Chinese) [29] KUMAR R,YAZDAN M M S. Evaluating preventive measures for flooding from groundwater:A case study[J]. J,2023,6(1):1-16. [30] PAYNE K,CHAMI P,ODLE I,et al. Machine learning for surrogate groundwater modelling of a small carbonate island[J]. Hydrology,2023,10(1):2. [31] WEI T,TAO Y Z,REN H L,et al. The analytical solution of an unsteady state heat transfer model for the confined aquifer under the influence of water temperature variation in the river channel[J]. Water,2022,14(22):3698. doi: 10.3390/w14223698 [32] KARMAKAR S,TATOMIR A,OEHLMANN S,et al. Numerical benchmark studies on flow and solute transport in geological reservoirs[J]. Water,2022,14(8):1310. doi: 10.3390/w14081310 [33] 李俊亭,王愈吉. 地下水动力学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1987.LI J T,WANG Y J. Groundwater water dynamics[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1987. (in Chinese) [34] 汪集暘,庞忠和,程远志,等. 全球地热能的开发利用现状与展望[J]. 科技导报,2023,41(12):5-11.WANG J Y,PANG Z H,CHENG Y Z,et al. Current state,utilization and prospective of global geothermal energy[J]. Science & Technology Review,2023,41(12):5-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] RASTORGUEV I A,LUKANOV D D. Application of codes for dynamic adaptation of a grid model in solving problems of drawdown in the DHI FEFLOW software[J]. Power Technology and Engineering,2023,56(5):698-702. doi: 10.1007/s10749-023-01576-y [36] DIERSCH H,BAUER D,HEIDEMANN W,et al. Finite element formulation for borehole heat exchangers in modeling geothermal heating systems by FEFLOW[J]. WASY Software FEFLOW White Paper,2010,5:5-96. [37] DIERSCH H G. Discrete feature modeling of flow,mass and heat transport processes[M]. Berlin,Heidelberg:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2013:711-756. [38] 孙明行,张起钻,刘德民,等. 广西干热型地热资源成因机制与赋存模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(3):330-340.SUN M H,ZHANG Q Z,LIU D M,et al. Genesis and occurrence models of hot-dry geothermal resources in Guangxi[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(3):330-340. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 毛绪美,叶建桥,董亚群,等. 地热驱动力:广东阳江新洲地热田驱动地热水运移的一种额外非重力作用的分析方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):137-145.MAO X M,YE J Q,DONG Y Q,et al. Geothermal driving force:A new additional non-gravity action driving the migration of geothermal water in the Xinzhou geothermal field of Yangjiang,Guangdong[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):137-145. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 姜光政,高堋,饶松,等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2892-2910. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815JIANG G Z,GAO P,RAO S,et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2892-2910. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815 -




 下载:
下载: