Geothermal chemical characteristics and genetic model of the Qingshankou Formation in the Daqingzijing area, southern Songliao Basin
-
摘要:
位于长岭凹陷鞍部的大情字井地区水热型地热资源丰富, 其中储层温度较高、岩性好、含水量高的青山口组是最佳热储层, 因此, 阐明地热水的成因模式对于该区地热资源的可持续开发利用具有重要意义。通过青山口组7口井地热水样的水化学测试, 结合收集的8组氢氧同位素数据, 研究了目标区地热水的来源及混合过程, 并分析了成因模式。结果表明, 青山口组地热水主要为部分平衡的Cl-Na型流体, 补给来源为长白山地区的大气降水和原生沉积水, 补给高程为2 347~2 370 m; 通过2 210~3 470 m的循环吸热过程形成现今温度为81.25~112.80 ℃的地热流体存储于半开放体系的青山口组碎屑岩储层中。另外, 研究区NE、NW向2组断裂系统是地热流体循环的主要导水通道, 地热流体在深循环过程中与围岩矿物发生水岩反应, 碳酸盐岩及硅酸盐矿物的溶解, 形成了以Na+、Cl-和HCO3-离子为主的地热水资源。
Abstract:Objective With high reservoir temperature, good lithology and high water content, the Qingshankou Formation is the best geothermal reservoir of Daqingzijing area, the saddle of the Changling Depression. Therefore, elucidating the genetic model of geothermal water is of great significance for the sustainable development and utilization of geothermal resources in this area.
Methods In this study, the source and mixing process of geothermal water in a target area were studied by hydrochemical testing of geothermal water samples collected from 7 wells in the Qingshankou Formation, combined with 8 groups of hydrogen and oxygen isotope data, and a genetic model was established.
Results The results show that the geothermal water of the Qingshankou Formation is mainly Cl-Na-type fluid, which is partially balanced. And the geothermal water is originated from the precipitation and primary sedimentary water in the Changbai Mountain area, with recharge elevation of 2 347-2 370 m. A geothermal fluid with a reservoir temperature of 81.25-112.80 ℃ was formed after the cyclic heat absorption process and was stored in the clastic rock reservoir of the Qingshankou Formation in a semi-open system.
Conclusion In addition, the northeast-oriented and northwest-oriented fault systems in the study area are the main water conducting channels for geothermal fluid circulation. During the deep circulation, geothermal fluid reactions with surrounding rock minerals, resulting in the dissolution of carbonate and silicate minerals, forming geothermal water resources dominated by Na+, Cl- and HCO3- ions.
-
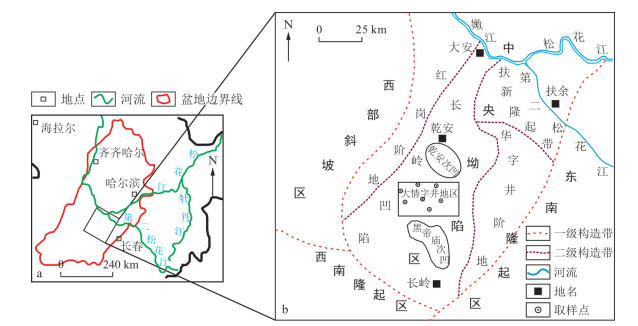
图 1 松辽盆地位置图(a)和大情字井地区构造图(b) (据文献[36]修改)
Figure 1. Location of the Songliao Basin (a) and tectonic map of the Daqingzijing area (b)
图 2 松辽盆地构造演化图(据文献[37]修改)
Q.第四系; E+N.古近系+新近系; K2.上白垩统; K1.下白垩统; J3.侏罗系; T.三叠系
Figure 2. Tectonic evolution map of the Songliao Basin
图 3 大情字井地区断裂构造纲要图(据文献[41]修改)
a.T1反射层(相当于嫩江组底界);b.T2反射层(相当于青山口组底界)
Figure 3. Outline of the fault structure in the Daqingzijing area
图 11 长岭凹陷地热水资源成因模式图(据文献[60]修改)
Figure 11. Genetic model of geothermal water resources in the Changling Sag
表 1 研究区水样测试数据
Table 1. Analysis results of geothermal water sampling in the study area
水样编号 深度/ m TDS K+ Na+ Ca+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- I- Br- B3+ SiO2 ρB/(mg·L-1) S1 1 484.1 14 178.9 42.4 5 303.5 41.7 19.0 7 801.1 43.7 927.5 3.2 9 3.7 30.0 S2 1 847.6 14 129.2 46.8 5 344.8 20.0 12.2 6 579.2 132.1 1 994.1 4.7 9 6.4 57.6 S3 2 030.5 9 763.4 98.9 3 348.0 31.3 43.0 3 658.4 144.1 1 439.7 2.9 1 2 53.5 S4 2 302.4 16 395.1 58.8 6 027.6 91.8 17.0 8 644.1 312.2 1 243.6 3.8 9 5.8 58.9 S5 2 240.4 19 697.8 59.6 7 081.6 110.2 13.4 8 804.7 118.1 1 510.2 4.2 7 10.7 59.5 S6 2 409.5 9 426.5 49.2 3 363.9 36.3 6.9 4 200.8 754.6 1 014.8 6.5 3 12.2 63.0 S7 2 489.8 13 846.0 82.1 4 970.0 52.7 16.3 6 490.5 905.4 1 329.0 3.2 7 13.4 63.2 水样编号 深度/m T/℃ pH值 变质系数(γNa+/γCl-) 盐化系数Cl-/(HCO3-+CO32-) 氯镁系数(γCl-/γMg2+) 脱硫系数(100×γSO42-/γCl-) S1 1 484.1 64.0 7.5 1.04 8.41 140.77 0.41 S2 1 847.6 81.4 9.0 1.25 3.29 184.89 1.46 S3 2 030.5 87.4 9.0 1.43 2.54 29.17 22.81 S4 2 302.4 93.0 7.0 1.07 6.95 174.33 2.63 S5 2 240.4 94.0 7.0 1.23 5.83 225.28 17.54 S6 2 409.5 97.8 7.0 1.24 4.14 208.74 13.09 S7 2 489.8 100.0 7.0 1.28 4.88 236.52 10.17 注:储层岩性为粉砂岩 表 2 水样的同位素测试结果
Table 2. Isotopic results of water samples
表 3 研究区地热水补给高程
Table 3. Geothermal water supply elevation in the study area
水样编号 采样高程/m 样品δD/‰ 大气降水δD/‰ K/(‰ (100 m)-1) 补给高程/m D7 1 667 -98.10 -63.30 -4.95 2 370 D8 1 657 -97.40 -63.30 -4.95 2 347 表 4 地热水热储温度
Table 4. Thermal storage temperature of geothermal water
水样编号 ρ(SiO2)/ (mg·L-1) 热储温度/℃ 石英(无蒸汽损失)地温计 石英(有蒸汽损失)地温计 SiO2计算/℃ K-Mg温标/℃ S1 30.00 79.40 83.10 81.25 94.80 S2 57.57 108.60 108.40 108.50 103.56 S3 53.50 105.00 105.40 105.20 106.90 S4 58.93 109.70 109.40 109.55 105.31 S5 59.53 110.20 109.80 110.00 109.09 S6 63.00 112.90 112.20 112.55 113.18 S7 63.23 113.20 112.40 112.80 115.61 表 5 地热水循环深度调查
Table 5. Investigated geothermal water circulation depth
水样编号 地热增温级/ (m·℃-1) SiO2热储温度/℃ 年平均气温/℃ 恒温带深度[38]/m 循环深度/m S1 29.41 81.25 4.5 25 2 282 S2 21.14 108.50 4.5 25 2 222 S3 25.71 105.20 4.5 25 2 612 S4 23.81 111.50 4.5 25 2 572 S5 24.10 110.00 4.5 25 2 572 S6 31.95 112.55 4.5 25 3 482 S7 27.47 112.80 4.5 25 3 002 -
[1] 马伟斌, 龚宇烈, 赵黛青, 等. 我国地热能开发利用现状与发展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(2): 199-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201602008.htmMA W B, GONG Y L, ZHAO D Q, et al. Geothermal energy exploitation, utilization, and its development trend in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(2): 199-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201602008.htm [2] 杨峰田, 石宇佳, 李文庆. 基于水文地球化学特征的辽宁丹东地区地热水成因模式研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 474-483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202202008.htmYANG F T, SHI Y J, LI W Q. Genesis model of geothermal water in Dandong area of Liaoning Province based on hydrogeochemical characteristics[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(2): 474-483. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202202008.htm [3] GRAIG L A. Health of nations: An international perspective on U.S. health care reform[M]. Array Washington, D.C. : Congressional Quarterly, 1999. [4] SCHIMMELMANN A, MASTALERZ M, GAO L, et al. Dike intrusions into bituminous coal, Illinois Basin: H, C, N, O isotopic responses to rapid and brief heating[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(20): 6264-6281. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.07.027 [5] MAGRO G, GHERARDI F, BAYON F E B. Noble and reactive gases of Palinpinon geothermal field (Philippines): Origin, reservoir processes and geodynamic implications[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 339: 4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.09.036 [6] CAPACCIONI B, VASELLI O, TASSI F, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of the thermal waters from the Sciacca Geothermal Field (Sicily, southern Italy)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 396(3/4): 292-301. [7] KARINGITHI C W, ARNÓRSSON S, GRÖNVOLD K. Processes controlling aquifer fluid compositions in the Olkaria geothermal system, Kenya[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2010, 196(1): 57-76. [8] 沈照理. 水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.SHEN Z L. Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985. (in Chinese) [9] 王恒纯. 同位素水文地质概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991.WANG H C. Introduction to isotope hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991. (in Chinese) [10] 陈墨香. 中国地热资源的分布及其开发利用[J]. 自然资源, 1991, 13(5): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY199105006.htmCHEN M X. Distribution and development of geothermal resources in China[J]. Natural Resources, 1991, 13(5): 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY199105006.htm [11] 汪集旸. 中低温对流型地热系统[J]. 地学前缘, 1996, 3(3): 96-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202101022.htmWANG J Y. Medium-low temperature convective geothermal system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996, 3(3): 96-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202101022.htm [12] 王贵玲, 刘彦广, 朱喜, 等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001002.htmWANG G L, LIU Y G, ZHU X, et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001002.htm [13] 王贵玲, 李郡, 吴爱民, 等. 河北容城凸起区热储层新层系-高于庄组热储特征研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5): 533-541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805003.htmWANG G L, LI J, WU A M, et al. A study of the thermal storage characteristics of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, a new layer system of thermal reservoir in Rongcheng uplift area, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(5): 533-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201805003.htm [14] 王贵玲, 张薇, 蔺文静, 等. 京津冀地区地热资源成藏模式与潜力研究[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1074-1085. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706004.htmWANG G L, ZHANG W, LIN W J, et al. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(6): 1074-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706004.htm [15] 王贵玲, 高俊, 张保建, 等. 雄安新区高阳低凸起区雾迷山组热储特征与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 1970-1980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.006WANG G L, GAO J, ZHANG B J, et al. Study on the thermal storage characteristics of the Wumishan Formation and huge capacity geothermal well parameters in the Gaoyang low uplift area of Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 1970-1980. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.006 [16] 王贵玲, 蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 1923-1937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002WANG G L, LIN W J. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 1923-1937. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002 [17] 王贵玲, 蔺文静, 刘峰, 等. 地热系统深部热能聚敛理论及勘查实践[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(3): 639-660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.03.001WANG G L, LIN W J, LIU F, et al. Theory and survey practice of deep heat accumulation in geothermal system and exploration practice[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(3): 639-660. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.03.001 [18] WANG G L, WANG W L, LUO J, et al. Assessment of three types of shallow geothermal resources and ground-source heat-pump applications in provincial capitals in the Yangtze River basin, China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 111: 392-421. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.029 [19] WANG G L, LIN W J, ZHANG W, et al. Research on formation mechanisms of hot dry rock resources in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2016, 90(4): 1418-1433. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12776 [20] WANG G L, LIU G H, ZHAOZ H, et al. A robust numerical method for modeling multiple wells in city-scale geothermal field based on simplified one-dimensional well model[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 139: 873-894. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.02.131 [21] LIN W J, WANG G L, GAN H N, et al. Heat source model for Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) under different geological conditions in China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 122: 243-259. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.08.007 [22] 董艳辉, 符韵梅, 王礼恒, 等. 甘肃北山-河西走廊-祁连山区域地下水循环模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 79-89. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0012DONG Y H, FU Y M, WANG L H, et al. Regional groundwater flow pattern in Beishan, Hexi Corridor and Qilian Mountain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 79-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0012 [23] 孙明行, 张起钻, 刘德民, 等. 广西干热型地热资源成因机制与赋存模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 330-340. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0037SUN M H, ZHANG Q Z, LIU D M, et al. Genesis and occurrence models of hot-dry geothermal resources in Guangxi[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 330-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0037 [24] 宋晓光, 芦岩, 梁仕凯, 等. 张家口坝下地区高氟地下水成因分析与健康风险评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 240-250. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0070SONG X G, LU Y, LIANG S K, et al. Analysis of high-fluoride groundwater formation mechanisms and assessment of health risk in Baxia region, Zhangjiakou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 240-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0070 [25] 黄靖宇, 许模, 许汉华, 等. 滇中高原岩溶关键带典型含水系统水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 347-356. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0217HUANG J Y, XU M, XU H H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of typical aquifer system in karst critical zone of Central Yunnan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 347-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0217 [26] 杨峰田, 庞忠和, 王彩会, 等. 苏北盆地老子山地热田成因模式[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(2): 468-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201202024.htmYANG F T, PANG Z H, WANG C H, et al. Genesis model of Laozishan geothermal field, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(2): 468-475. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201202024.htm [27] 汪名鹏, 韩光海, 顾萍. 洪泽县老子山地热矿区地热资源赋存特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2009, 37(2): 47-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200902014.htmWANG M P, HAN G H, GU P. Geololgical features of geothermal resource in Laozi Mountain area of Hongze County[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2009, 37(2): 47-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200902014.htm [28] 尚敏, 易武, 张兰新. 济南北部地区地热资源形成条件研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 30(4): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHYC200804006.htmSHANG M, YI W, ZHANG L X. Research on forming condition of geothermal resources in North region of Jinan[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences), 2008, 30(4): 22-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHYC200804006.htm [29] 赵玉祥, 李常锁, 邢立亭. 济南北部地热田的成生条件[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 23(4): 406-409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3559.2009.04.019ZHAO Y X, LI C S, XING L T. Forming conditions of geothermal field in northern Jinan[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2009, 23(4): 406-409. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3559.2009.04.019 [30] 朱焕来. 松辽盆地北部沉积盆地型地热资源研究[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2011.ZHU H L. Research on the sedimentary geothermal resources in North Songliao Basin[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 单玄龙, 蔡壮, 郝国丽, 等. 地球化学温标估算长白山地热系统热储温度[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(3): 662-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201903004.htmSHAN X L, CAI Z, HAO G L, et al. Estimation of thermal storage temperature of geothermal system in Changbai Mountain by geothermometers[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(3): 662-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201903004.htm [32] 王洪涛, 赵向辉, 陈家林, 等. 长岭凹陷潜在地热初步探讨[J]. 吉林地质, 2009, 28(1): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ200901013.htmWANG H T, ZHAO X H, CHEN J L, et al. Primary discussion on potential geotherm within Changling Sag[J]. Jilin Geology, 2009, 28(1): 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ200901013.htm [33] 宫明旭. 吉林省中西部地热资源探测与分布规律研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.GONG M X. Study on geothermal resources prospecting and distribution in Midwest of Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 赵盼. 前郭县地热资源潜力研究[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2013.ZHAO P. Study on geothermal resource potential of Qianguo[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 刘志宏, 宋健, 刘希雯, 等. 松辽盆地南部白垩纪-古近纪挤压构造的发现与盆地性质探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(8): 2383-2393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202008008.htmLIU Z H, SONG J, LIU X W, et al. Discovery of the Cretaceous-Paleogene compressional structure and basin properties of the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(8): 2383-2393. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202008008.htm [36] 李建忠, 杨涛, 王立武, 等. 松辽南部大情字井地区断裂构造特征及其控油作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(1): 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200401005.htmLI J Z, YANG T, WANG L W, et al. The fault structure and its controlling role to hydrocarbon accumulation in Daqingzijing area southern Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(1): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200401005.htm [37] 伍小雄. 松辽盆地北部干热岩地热资源研究[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2014.WU X X. Research of geothermal resources on hot dry rock in North Songliao Basin[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 张翘然, 肖红平, 饶松, 等. 松辽盆地现今地温场特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 191-204. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230058ZHANG Q R, XIAO H P, RAO S, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of the present geothermal field in the Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 191-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230058 [39] 郭昂青. 松辽盆地北部热储体系特征及开发利用[J]. 地质与资源, 2016, 25(4): 380-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD201604013.htmGUO A Q. Characteristics and development of the thermal storage system in the North of Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2016, 25(4): 380-385. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD201604013.htm [40] 葛荣峰, 张庆龙, 徐士银, 等. 松辽盆地长岭断陷构造演化及其动力学背景[J]. 地质学刊, 2009, 33(4): 346-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200904006.htmGE R F, ZHANG Q L, XU S Y, et al. Structure evolution and its kinetic setting of Changling Fault Depression in Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Geology, 2009, 33(4): 346-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200904006.htm [41] 胡望水. 松辽盆地"T2 "断层系及青山口早期伸展裂陷[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(2): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK502.001.htmHU W S. "T2" fault system and early Qingshankou stretched rifiting in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1995, 22(2): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK502.001.htm [42] 李晓波, 赵新村, 李明毅, 等. 泰安市城区岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 2022, 38(9): 23-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202209004.htmLI X B, ZHAO X C, LI M Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation analysis of karst groundwater in district area of Tai'an City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2022, 38(9): 23-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202209004.htm [43] 王祥, 韩剑发, 于红枫, 等. 塔中北斜坡奥陶系鹰山组地层水特征与油气保存条件[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2012, 34(5): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201205006.htmWANG X, HAN J F, YU H F, et al. Characteristics of formation water of Ordovician Yingshan Formation in the northern slope of Tazhong palaeouplift and condition of hydrocarbon preservation[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2012, 34(5): 25-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201205006.htm [44] 叶智强, 牟雨亮, 成鹏, 等. 贵州省石阡县花桥镇地热水水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 中国水运(下半月), 2022, 22(9): 128-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSUX202209048.htmYE Z Q, MU Y L, CHENG P, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal water in Huaqiao Town, Shiqian County, Guizhou Province[J]. China Water Transport, 2022, 22(9): 128-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSUX202209048.htm [45] 胡绪龙, 李瑾, 张敏, 等. 地层水化学特征参数判断气藏保存条件: 以呼图壁、霍尔果斯油气田为例[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2008, 31(4): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200804005.htmHU X L, LI J, ZHANG M, et al. Judge gas reservoir preservation by chemical characteristic parameters of formation water: Examples from Hutubi and Huo'erguosi oil-gas fields[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2008, 31(4): 23-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200804005.htm [46] 刘桂凤, 王莉, 李春涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部地层水化学特征与油气成藏关系[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2007, 28(1): 54-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200701014.htmLIU G F, WANG L, LI C T, et al. Relationship between chemical characteristic of formation water and hydrocarbon accumulation in hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2007, 28(1): 54-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200701014.htm [47] GIBBSR J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. [48] VERMA S, MUKHERJEE A, MAHANTA C, et al. Influence of geology on groundwater-sediment interactions in arsenic enriched tectono-morphic aquifers of the Himalayan Brahmaputra River basin[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 540: 176-195. [49] FAYE S, MALOSZEWSKI P, STICHLER W, et al. Groundwater salinization in the Saloum (Senegal) delta aquifer: Minor elements and isotopic indicators[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 343(1/3): 243-259. [50] 陈凯, 孙林华. 任楼煤矿地下水化学组成及其控制因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(10): 240-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201910032.htmCHEN K, SUN L H. Analysis of chemical composition and control factors of groundwater in Renlou Coal Mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(10): 240-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201910032.htm [51] 庞忠和, 樊志成, 汪集旸. 漳州盆地水热系统的氢氧稳定同位素研究[J]. 岩石学报, 1990, 6(4): 75-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199004008.htmPANG Z H, FAN Z C, WANG J Y. The study on stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the Zhangzhou Basin hydrothermal system[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1990, 6(4): 75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199004008.htm [52] 王兆荣. 中国东部温泉水和井水的氢氧同位素初步研究[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 1993, 23(2): 213-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJD199302014.htmWANG Z R. Study on isotope hydrogen and oxygen of hot spring water and well water in the East of China[J]. Journal of China University of Science and Technology, 1993, 23(2): 213-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJD199302014.htm [53] 张洪平, 刘恩凯, 王东升, 等. 中国大气降水稳定同位素组成及影响因素[C]//佚名. 中国地质科学院水文地质工程地质研究所文集(7). 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 10.ZHANG H P, LIU E K, WANG D S, et al. Composition of stable isotopes of precipitation and controlling factors in China[C]//Anon. Bull. Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology Cags (7). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991: 10. (in Chinese) [54] 张兵, 宋献方, 张应华, 等. 第二松花江流域地表水与地下水相互关系[J]. 水科学进展, 2014, 25(3): 336-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201403004.htmZHANG B, SONG X F, ZHANG Y H, et al. Relationship between surface water and groundwater in the Second Songhua River basin[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2014, 25(3): 336-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201403004.htm [55] 刘轶男, 孙凤霞, 崔月菊, 等. 吉林省松原地区地震监测台站水化学特征[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(8): 810-817. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201708004.htmLIU Y N, SUN F X, CUI Y J, et al. Hydrachemical characteristics at the seismic stations in Songyuan district, Jilin Province[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(8): 810-817. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201708004.htm [56] 史婷婷, 成建梅, 解习农, 等. 松辽盆地北部地层水同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(2): 399-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201202023.htmSHI T T, CHENG J M, XIE X N, et al. Isotopic characteristics of formation waters in the North of Songliao Basin and its geological significances[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(2): 399-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201202023.htm [57] CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science, 1961, 133(3465): 1702-1703. [58] 李小飞, 张明军, 马潜, 等. 我国东北地区大气降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(9): 2924-2931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201209005.htmLI X F, ZHANG M J, MA Q, et al. Characteristics of stable isotopes in precipitation over Northeast China and its water vapor sources[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(9): 2924-2931. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201209005.htm [59] 闫佰忠. 长白山玄武岩区地热水资源成因机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.YAN B Z. Study on the formation mechanism of geothermal water resources in Changbai Mountain basalt area[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [60] 王俊峰. 松辽盆地南部长岭凹陷青山口组地热水资源成因分析[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2022.WANG J F. Genesis analysis of geothermal water resources in Qingshankou Formation Changling Sag southern Songliao Basin[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: