Characterization of the present-day lithospheric thermal structure and main controlling factors in Songliao Basin
-
摘要:
松辽盆地的热结构分析多局限在南北分区的沉积层尺度,缺乏岩石圈尺度的全盆地热结构刻画,制约了以地球动力学为背景的成因分析。综合利用已发表的地表热流、地温梯度以及热物性参数,补充了姚家组、青山口组和泉头组的热物性测试分析,并增加了多个地温场数据,全面刻画了整个松辽盆地的地温场特征,剖析了现今岩石圈尺度的热结构特征。结果表明,松辽盆地地温梯度范围是21.10~63.45℃/km,平均值是41.41 ±7.97℃/km,高于全球平均的地温梯度值30℃/km;地表热流值的分布范围是30.38~106.58 mW/m2,平均值是71.85 ± 12.87 mW/m2,也高于全球平均的地表热流值60 mW/m2,是一个典型的“热”盆。受太平洋板块俯冲作用、拆沉作用和热侵蚀作用的影响,热岩石圈明显减薄至现今的58.59 km。由减薄地壳中放射性元素生热产生的热流仅为16.40 mW/m2,占地表热流的22.83%;而受滞留板片脱水作用的影响,部分熔融的地幔热物质上涌,地幔热流贡献高达55.45 mW/m2,占地表热流的77.17%。因此,受控于岩石圈减薄作用和地幔上涌作用,松辽盆地具有“热”盆属性和“热幔冷壳”的岩石圈热结构特征。
Abstract:Objective Thermal structure analyses in the Songliao Basin are mostly confined to the sedimentary scale in the north-south zoning, and the lack of basin-wide thermal structure portrayal at the lithospheric scale constrains the genesis analysis in a geodynamic background.
Methods Based on the published parameters of surface heat flow, geothermal gradient and thermophysical properties, this paper supplements the thermophysical properties of Yaojia Formation, Qingshankou Formation and Quantou Formation, and adds several geothermal field data to comprehensively characterize the geothermal field of the whole Songliao Basin, and analyze the characteristics of the present-day lithospheric thermal structure.
Results The results show that the geothermal gradient in Songliao Basin ranges from 21.10 to 63.45℃/km, with an average value of 41.41℃/km, which is higher than the global average value of 30℃/km; the distribution of surface heat flow values ranges from 30.38 to 106.58 mW/m2, with an average value of 71.85 mW/m2, which is higher than the global average value of 60 mW/m2 and belongs to a typical "hot" basin. Under the influence of the Pacific plate subduction, the delamination and thermal erosion made the thinned thickness of the thermal lithosphere of 58.59 km. The heat flow contribution by radioactive elements in the thinned crust is only 16.40 mW/m2, accounting for 22.83% of the surface heat flow; and under the influence of the dehydration of the stagnant plate, part of the molten mantle heat material is upwelled, the mantle heat flow contributes as high as 55.45 mW/m2, accounting for 77.17% of the surface heat flow.
Conclusion Therefore, controlled by lithospheric thinning and mantle upwelling, the Songliao Basin has "hot" basin properties and "hot mantle and cold crust" lithospheric thermal structure characteristics.
-
沉积盆地现今岩石圈热结构特征是不同阶段岩石圈构造−热演化的结果,指示着地球内部热状态,反映着地球内部各种动力学之间的能量平衡,是了解大陆岩石圈演化的主要指标[1-2]。岩石圈热结构的研究内容主要聚焦在地表热流、地温梯度、壳幔热流分配、热物性参数(放射性生热率、热导率等)、岩石圈各层温度分布以及热岩石圈厚度等内容[3]。刻画岩石圈热结构的方法有很多,例如利用剪切波速特征、地震分布特征、流变学特征、基于地质学和地球物理方法的数值模拟以及利用岩石热物性和测井温度数据进行热结构特征反演[4-8]。由于地球物理手段反演具有多解性,因此利用地下温度数据结合热参数来制约岩石圈热结构是最直接、最常用、最可靠的方法,并且在许多地区已经得到了应用[7,9-12]。松辽盆地是一个大型陆内含油气盆地,近年来,许多学者对松辽盆地南部或者北部含油气的沉积层热结构特征展开了分析。其中,最聚焦的研究是沉积层内温度变化对烃类的生成、降解、相态变化等过程的影响[13-14]。关于全盆地岩石圈尺度的热结构特征的研究较为缺乏,这在一定程度上制约了以地球动力学过程为基础的控制因素分析,特别是在太平洋板块西向俯冲的背景下,对于岩石圈和软流圈如何协同影响松辽盆地现今热结构的过程方面认识不清。因此,本研究结合已发表的松辽盆地南部和北部的热结构数据,补充了相应层位的热物性参数测试,并依据油田测井温度资料,剖析了整个松辽盆地在岩石圈尺度的热结构特征以及主控因素。
1. 区域地质背景
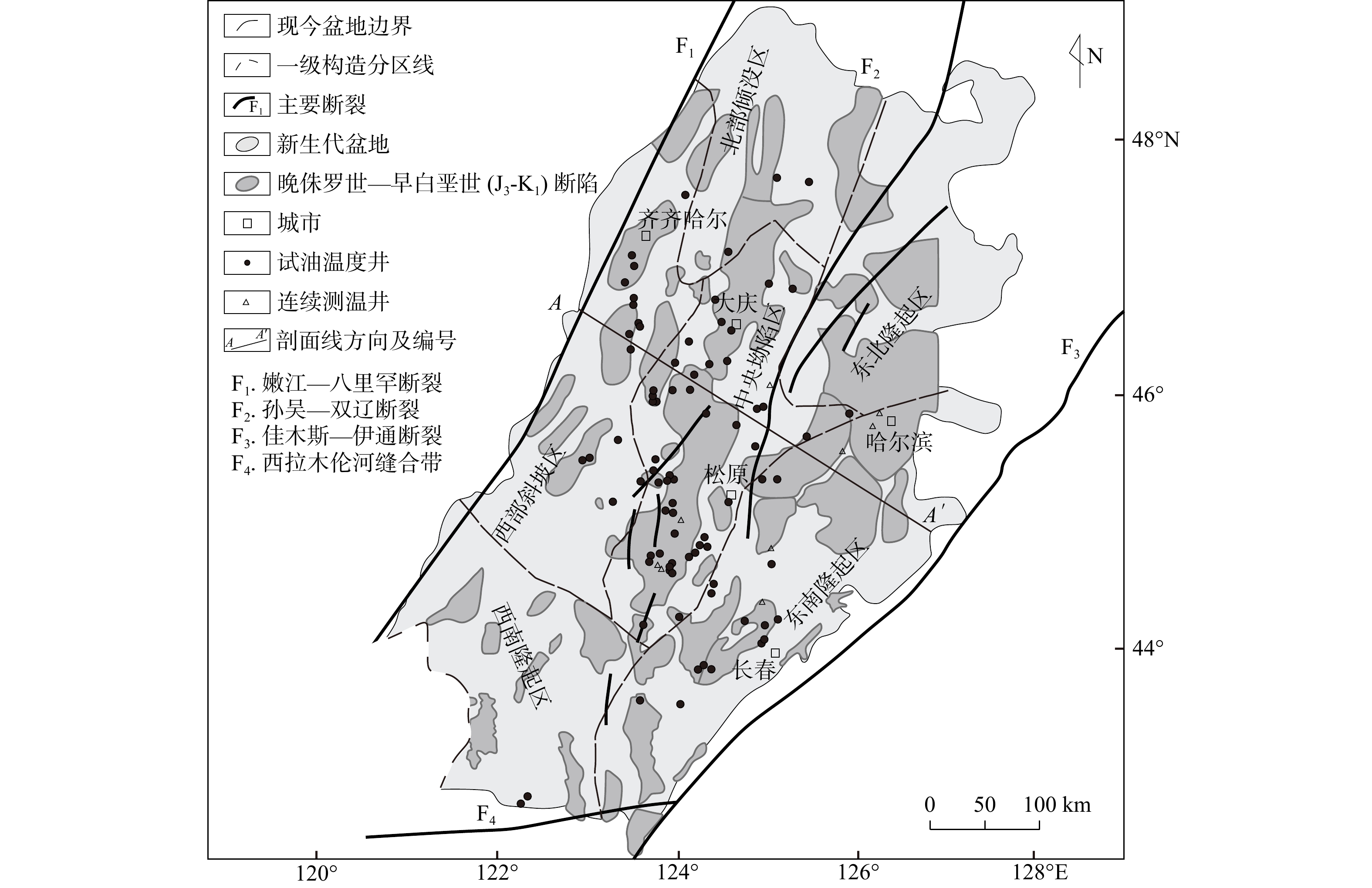
松辽盆地位于欧亚板块东北部,被西部的大兴安岭、北部的小兴安岭和东南部的长白山脉所环绕,面积约为26×104 km2(图1)。依据构造特征,松辽盆地被划分成6个主要构造区,分别是北部倾没区、中央坳陷区、东北隆起区、东南隆起区、西南隆起区和西部斜坡区。地震层析成像揭示了现今太平板块俯冲到了松辽盆地下方[16]。利用重力资料反演的松辽盆地莫霍面埋深介于29~33 km之间,是陆上较薄的盆地之一[17]。伴随古亚洲洋的闭合,松辽地块和众多微陆块发生拼合,形成了东北地区的雏形。自侏罗纪以来,古太平洋板块开始形成并向欧亚板块俯冲,盆地开始经历3个主要阶段[18-22]:①地幔上涌和裂陷阶段,形成了早侏罗世至早白垩世的火山喷发序列,并伴随着岩石圈的伸展和减薄;②后裂陷热沉降阶段,形成了一套巨厚的碎屑岩储层(图2),伴随着古俯冲板片的回返和滞留板片的形成;③持续至今的构造反转阶段,形成了一套固结性较差的碎屑岩层,伴随着太平洋板块的东撤以及欧亚板块的东移,使得现今太平洋板块的较老部分停滞在地幔转换带中,整体构成了东北亚大地幔楔结构。
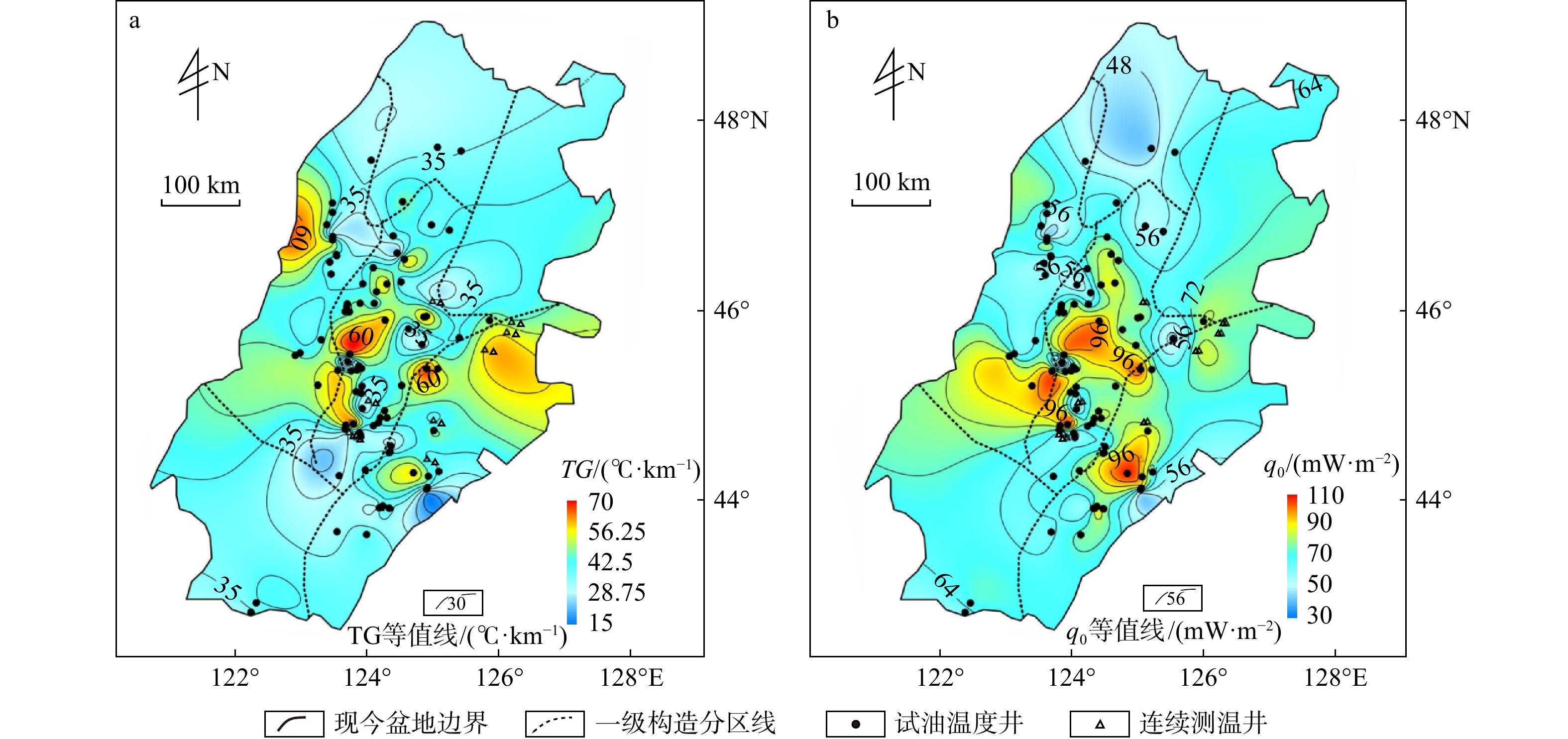
 图 1 松辽盆地构造单元及测温井分布图[15]Figure 1. Tectonic units and temperature measuring wells in the Songliao Basin
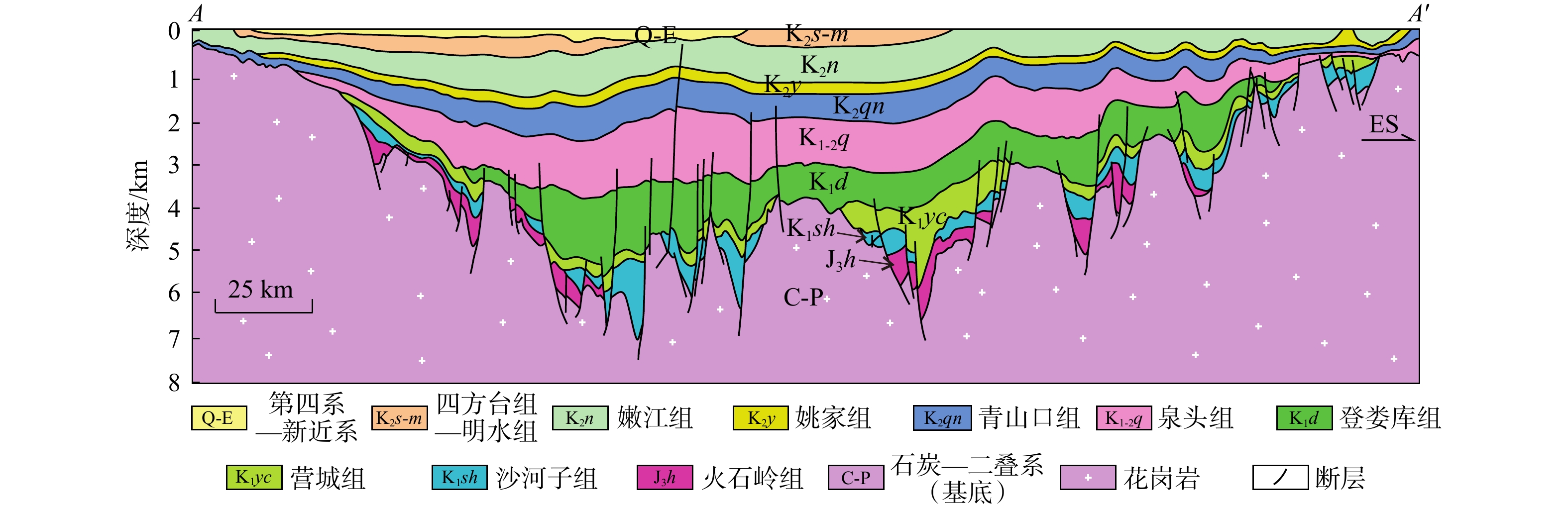
图 1 松辽盆地构造单元及测温井分布图[15]Figure 1. Tectonic units and temperature measuring wells in the Songliao Basin 图 2 松辽盆地中部构造剖面图[18](部分调整)Figure 2. Tectonic profile in the central part of Songliao Basin
图 2 松辽盆地中部构造剖面图[18](部分调整)Figure 2. Tectonic profile in the central part of Songliao Basin2. 研究方法
2.1 钻井温度数据
地下温度数据最为可靠的是连续性稳态温度测井和钻孔试油温度数据,可以反映地下最接近真实的温度分布情况。近年来,随着油田企业在地热资源勘探方面的大力推进,特别是连续性系统测温数据的采集,以及在油气勘探过程中积累的大量试油温度数据,为地下温度场刻画提供了得天独厚的条件(图1)。
2.2 热物性参数数据
岩石热物性参数主要包括岩石热导率(K)和放射性生热率(A),分别表征热量传递能力和自身产热能力的大小,是岩石圈热结构研究的重要基础。由于已有的姚家组(K2y)、青山口组(K2qn)和泉头组(K1-2q)热物性参数较少,本次研究针对性地补充了144个热导率和144个放射性生热率测试分析,所有测试均在东北石油大学完成。其中,热导率测试设备的测试范围为0.2~25.0 W/(m·K),分辨率为0.001 W/(m·K),测试准确度为 ± 3%。对于上、中、下地壳以及岩石圈地幔的热导率值,主要采用已经发表的经验值,分别是2.85,2.60,2.00以及3.20 W/(m·K)[23];放射性生热率的测试设备为电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)以及体积密度分析仪GeoPyc
1365 ,基底、中地壳、下地壳和岩石圈地幔的放射性生热率均为常数,分别取0.82,0.46,0.20和0.03 μW/m3[23-24],上地壳的放射性生热率值采用指数衰减模型:A=A(−Z/D)0, (1) 式中:A0为近地表岩石的放射性生热率,取值为1.50 μW/m3[25];Z为埋藏深度,km;D为放射性层厚度,km。
2.3 地温梯度(TG)和地表热流(q0)
利用线性最小二乘回归法,可以计算出具有连续稳态温度数据的整个井段的地温梯度,在计算时,应剔除受地下水混入影响的连续测温数据段[26]。对于试油温度,可通过公式(2)计算地温梯度:
TG=(TS−T0)/(ZS−Z0), (2) 式中:TG为地温梯度,℃/km;TS为深度S处的试油温度,℃;T0为恒温带温度,℃;ZS为试油深度,km;Z0为恒温带深度,km。松辽盆地中的T0和Z0分别取5℃和0.03 km[7]。
q0表示单位面积内从地球内部转移到地球表面并散发出的热量,直接地反映了地球表面各种动态过程的能量平衡。在数值上,地表热流值等于TG与K的乘积:
q0=KdTdZ, (3) 式中:q0为地表热流,mW/m2;K为热导率,W/(m·K); dT/dZ为地温梯度,℃/km。
2.4 岩石圈热结构
根据地壳分层结构模型以及地表热流等参数,采用一维稳态热传导方程,即可得到岩石圈各圈层温度分布 [27]:
Ti=Ti−1+(qi×Zi)/Ki−(Ai×Z2i)/(2Ki), (4) 式中:i为层序数;Ti为第i层底部的温度,℃;qi为第i层顶部的热流,mW/m2;Zi为第i层的厚度,km;Ki为第i层的热导率,W/(m·K);Ai为第i层的放射性生热率, μW/m3。
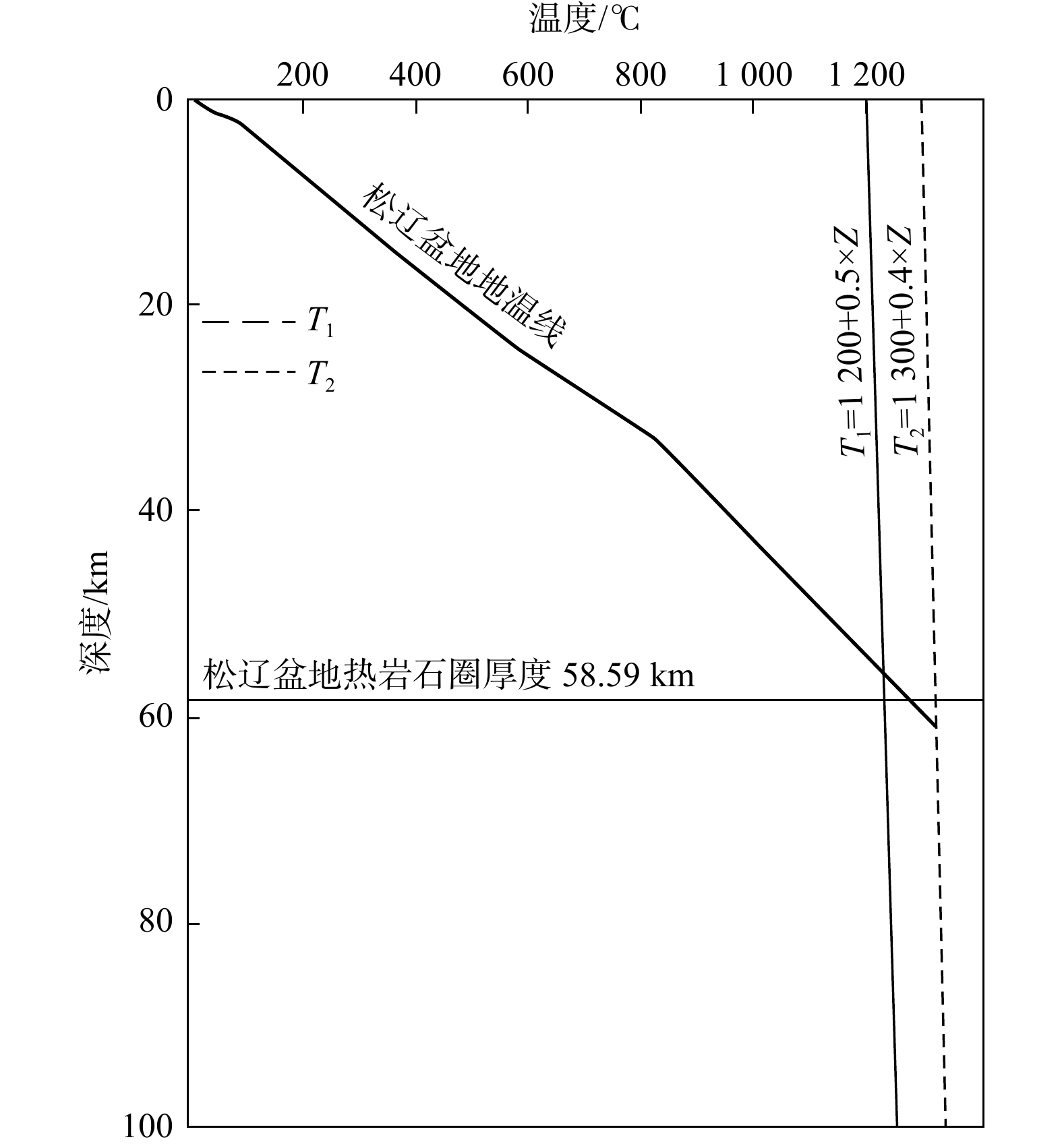
根据钻井分层数据、地震解译数据,可以获得沉积盖层的分层结构模型;而对于上、中、下地壳的结构,本研究采用了最新的地壳分层结构模型数据库Crust1.0进行刻画。在评估热岩石圈厚度时,将2个干玄武岩固相温度线作为热岩石圈底部温度的上限T1和下限T2,其中间值即为热岩石圈厚度:
T1=1 200+0.5×Z, (5) T2=1 300+0.4×Z, (6) 式中:Z为埋藏深度。
当放射性生热率A采用分层函数模型时,地表热流的二元结构关系表示如下:
q0=qm+qc=qm+∫Zmoho0A(Z)dZ=qm+n∑i=1AiZi, (7) 式中:qc为地壳中放射性产生热流的总和;qm为地幔热流,qm=q0-qc;Zmoho为莫霍面的深度,km。
因此,可以计算壳幔热流比。根据热流配分大小,岩石圈热结构可分为2类热状态:一类是“热幔冷壳”型,qm/q0>0.5;另一类是“冷幔热壳”型,qc/q0≥0.5[28]。
3. 结 果
3.1 热物性参数特征
测试结果表明,144块样品的热导率值范围是1.1~2.64 W/(m·K),平均值为1.96 W/(m·K)。其中,中砂岩的热导率平均值最大,约为2.44 W/(m·K);砾岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩和粉砂岩的热导率平均值相差不大,分别为1.97,1.95,1.92和1.99 W/(m·K),泥岩的热导率平均值最低,为1.89 W/(m·K)。不同层位的热导率平均值统计结果显示,姚家组(K2y)为1.80 ± 0.23 W/(m·K)(样品数n=35),青山口组(K2qn)为2.06 ± 0.23 W/(m·K)(样品数n=64),泉头组(K1-2q)为1.93 ± 0.40 W/(m·K) (样品数n=45)。整体来看,3个层位的热导率值相差不大。针对同一层位的测试数据和前人已有数据,本次研究采用平均数和标准差合成的方法进行合并(公式8和9,表1)。
表 1 松辽盆地热导率(K)和放射性生热率(A)Table 1. Thermal conductivity (K) and radiative heating rate (A) in Songliao Basin岩石圈
分层K A 平均值W·(m−1·K−1) 范围W·(m−1·K−1) 样品数n 数据来源 平均值/(μW·m−3) 范围/(μW·m−3) 样品数n 数据来源 沉积
盖层K2n 1.44 ± 0.20 0.89~2.32 47 文献[7] 1.67 ± 0.27 1.36~1.96 4 文献[7] K2y 1.79 ± 0.24 — 38 文献[29],本次研究 1.09 ± 0.17 0.43~1.30 35 本次研究 K2qn 2.10 ± 0.28 1.30~2.78 69 1.15 ± 0.20 0.63~2.19 64 K1-2q 1.96 ± 0.38 1.17~2.84 63 文献[7],本次研究 1.09 ± 0.13 0.50~1.26 45 K1d 2.54 ± 0.25 1.85~3.12 22 文献[7] 1.66 ± 1.34 0.86~5.30 11 文献[7] K1yc 2.59 ± 0.26 1.92~3.15 34 0.94 ± 0.28 0.30~1.40 34 K1sh 2.61 ± 0.35 1.91~4.48 164 0.77 ± 0.36 0.32~1.91 52 J3h 2.93 ± 0.32 2.03~3.78 109 0.81 ± 0.34 0.23~1.69 31 C-P 3.01 ± 0.43 2.22~4.39 107 0.82 ± 0.24 0.33~1.31 38 上地壳 2.85 — — 文献[23] 1.50(-Z/D) — — 文献[25] 中地壳 2.60 — — 0.46 — — 文献[23] 下地壳 2.00 — — 0.20 — — 岩石圈地幔 3.20 — — 0.03 — — 总样品数 653 314 注:表中数据K综合了测试数据和前人已有研究数据,3.1节正文仅为本次实验测试数据两者不一致;K2n. 嫩江组;K2y. 姚家组;K2qn. 青山口组;K1-2q. 泉头组;K1d. 登娄库组;K1yc. 营城组;K1sh. 沙河子组;J3h. 火石岭组;C-P. 石炭−二叠系(基层);下同 Mean=N1M1+N2M2N1+N2, (8) SD=√(N1−1)SD21+(N2−1)SD22+N1N2N1+N2(M21+M22−2M1M2)N1+N2−1, (9) 式中:Mean为平均值;N1和N2分别为第1组数据和第2组数据的数量;M1和M2为2组数据的均值;SD1和SD2分别为2组数据的标准偏差;SD为2组数据合在一起的标准偏差。
合并之后建立了松辽盆地的热导率(表1)。数据显示,沉积盖层中基底的热导率最高,嫩江组的最低,这可能与压实作用有关。越老地层经历的压实作用可能越强烈,颗粒之间排列越紧密,越有助于热量的传导,热导率值越高,而年轻地层则相反。
放射性生热率测试结果显示,泥岩具有最大的放射性生热率,为1.3 μW/m3(样品数n=47),粉砂质泥岩具有最低的放射性生热率,为1.06 μW/m3(样品数n=13)。不同层位的放射性生热率平均值统计结果显示,姚家组(K2y)为1.09 ± 0.17 μW/m3(样品数n=35),青山口组(K2qn)为1.15 ± 0.20 μW/m3(样品数n=64),泉头组(K1-2q)为1.09 ± 0.13 μW/m3(样品数n=45)。同样,本研究建立了松辽盆地放射性生热率表(表1)。数据显示,沉积盖层中,嫩江组(K2n)的放射性生热率最高,沙河子组(K1sh)的放射性生热率最低,这可能与泥质含量的多少有关,泥质含量越高,吸收的放射性元素就越多。
3.2 地温梯度和地表热流特征
依据试油温度和连续稳态测温资料,计算得到的松辽盆地整体地温梯度范围是21.10~63.45℃/km,平均值是41.41 ± 7.97℃/km,高于全球平均的地温梯度值30℃/km;地表热流值的分布范围是30.38~106.58 mW/m2,平均值是71.85 ± 12.87 mW/m2,也高于全球平均的地表热流值60 m W/m2,是一个典型的“热”盆,并运用克里金插值法绘制了全盆地的地温梯度图和地表热流图(图3)[30]。从平面分布特征看,地温梯度和地表热流的变化规律基本相同,主要受控于盆地基底的起伏形态。东南隆起区和中央坳陷区呈现较高的地温梯度和地表热流,西部斜坡的东北部和东南部也呈现高值特征,而盆地的北部与南部基本都为低值区,这可能与测温数据点的分布多少有关。
3.3 岩石圈热结构
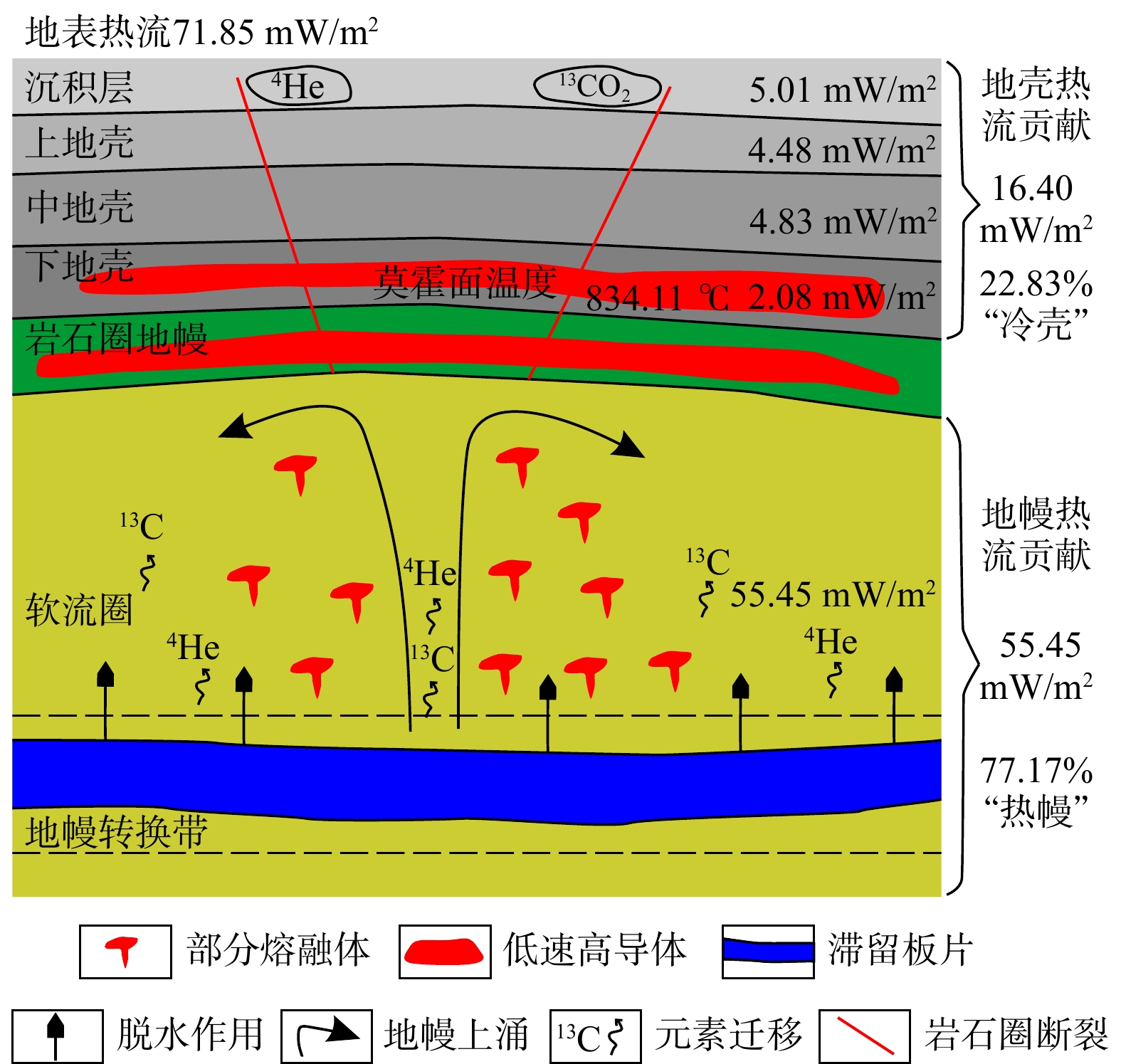
依据地壳分层结构模型、热物性参数以及公式(4)~(6),计算得到的地壳热流贡献为16.40 mW/m2,地幔热流贡献为55.45 mW/m2(图4)。地幔热流占地表热流的77.17%,指示着“热幔冷壳”的热结构,这种研究结果同前人研究是一致的[31-32];计算得到的松辽盆地热岩石圈厚度为58.59 km(图5),同前人的计算结果55 km相近[33],同盆地西侧的大兴安岭岩石圈厚度160 km相比,减薄了近100 km;同东侧张广才岭的115 km的岩石圈厚度相比,减薄了近55 km;同南部华北克拉通100 km的岩石圈厚度相比,减薄了近40 km[34-35]。
4. 讨 论
现今岩石圈的减薄状态与其经历的构造过程密不可分。前人研究表明,松辽盆地及其邻区的岩石圈主要经历了4个深部动力学过程:伸展期(三叠纪T−晚侏罗世J3)、裂解期(晚侏罗世J3−早白垩世K1)、拆沉期(早白垩世K1−晚白垩世K2)和弱增长期(晚白垩世K2−古近纪E)[35]。在伸展期,中国东部大陆岩石圈总体处于拉张的应力场背景中,岩石圈发生大规模的减薄;在裂解期,受古亚洲构造域和西太平洋构造域叠加过程的影响,岩石圈进一步裂解、弱化和减薄[36];在拆沉期,上涌的地幔热物质在壳−幔过渡带处发生复杂的物理−化学作用,致使老的岩石圈地幔底部逐渐撕裂,进而发生了拆沉作用。拆沉下来的古老岩石圈块体进入到两侧的大兴安岭和张广才岭下部的岩石圈下部,促使其快速隆升;在弱增长期,松辽盆地的岩石圈经历了小幅增厚,但整体上仍处于减薄的状态。现今状态下,停滞在地幔转换带中的滞留板片仍发生着脱水作用,触发的部分熔融体密度降低,从深部上升至岩石圈地幔底部,发生着热侵蚀作用,继续维持岩石圈的减薄状态[37]。
在整个岩石圈减薄的动力学过程中,地壳部分也发生减薄的过程。作为主要的放射性生热层,减薄地壳的热流贡献仅为16.40 mW/m2,占比22.83%。此外,由于固体岩石圈地幔具有极其低的放射性生热率(0.03 μW/m3),本次研究忽略了其热流贡献。与地壳不同的是,地幔热流占据了地表热流的50%以上。一方面,停滞在地幔转换带中的太平洋板片持续性脱水,软流圈地幔发生部分熔融,温度升高,密度降低,熔融的热物质不断上涌,形成了较强的地幔热流,构成了地表热流的主要热量来源;另一方面,深部上涌的幔源热在上地幔和下地壳中也有体现。通过现代地球物理技术,识别出现今盆地下方存在2个高导体[38],分别位于下地壳和上地幔,且与地震手段探测出来的低速度体的位置相吻合,它们被称作“低速高导体”,并被解释为与上涌地幔热物质相关的部分熔融层[39]。此外,在浅部沉积层内发现了地幔成因的4He气体以及13CO2气藏[40-41],其很可能是被深部地幔热物质通过岩石圈断裂携带至浅部聚集成藏。通过计算可得,盆地莫霍面的温度为834.11℃,但是在一般情况下,简单的剪切作用很难形成这种较高的温度,而上涌的地幔热物质作为热源,可以加热莫霍面[42](图6)。因此,在太平洋板块西向俯冲的大背景下,松辽盆地形成了“热幔冷壳”的岩石圈热结构特征。
5. 结 论
(1)松辽盆地地温梯度范围是21.10~63.45℃/km,平均值是41.41 ± 7.97℃/km,高于全球平均地温梯度值30℃/km;地表热流值的分布范围是30.38~106.58 mW/m2,平均值是71.85 ± 12.87 mW/m2,高于全球平均的地表热流值60 mW/m2,是一个典型的“热”盆。
(2)沉积盖层中基底的热导率最高(3.01 ± 0.43 W/(m·K)),嫩江组的最低(1.44 ± 0.20 W/(m·K)),这可能与压实作用有关。越老地层经历的压实作用越强烈,颗粒之间排列越紧密,越有助于热量的传导,热导率值越高,而年轻地层则相反;沉积盖层中嫩江组的放射性生热率最高(1.67 ± 0.27 μW/m3),沙河子组的放射性生热率最低(0.77 ± 0.36 μW/m3)。
(3)受太平洋板块西向俯冲作用、岩石圈拆沉作用以及滞留板片脱水作用的影响,松辽盆地现今热岩石圈厚度仅为58.59 km,具有明显减薄的特征。受减薄作用的控制,岩石圈地壳热流贡献仅为16.40 mW/m2,占地表热流的22.83%;处在地幔转换带中的滞留板片,发生的脱水作用引起软流圈地幔的部分熔融并不断上涌,形成了较高的地幔热流值55.45 mW/m2,占到地表热流的77.17%,具有了“热幔冷壳”的岩石圈热结构特征。
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
-
图 1 松辽盆地构造单元及测温井分布图[15]
Figure 1. Tectonic units and temperature measuring wells in the Songliao Basin
图 2 松辽盆地中部构造剖面图[18](部分调整)
Figure 2. Tectonic profile in the central part of Songliao Basin
表 1 松辽盆地热导率(K)和放射性生热率(A)
Table 1. Thermal conductivity (K) and radiative heating rate (A) in Songliao Basin
岩石圈
分层K A 平均值W·(m−1·K−1) 范围W·(m−1·K−1) 样品数n 数据来源 平均值/(μW·m−3) 范围/(μW·m−3) 样品数n 数据来源 沉积
盖层K2n 1.44 ± 0.20 0.89~2.32 47 文献[7] 1.67 ± 0.27 1.36~1.96 4 文献[7] K2y 1.79 ± 0.24 — 38 文献[29],本次研究 1.09 ± 0.17 0.43~1.30 35 本次研究 K2qn 2.10 ± 0.28 1.30~2.78 69 1.15 ± 0.20 0.63~2.19 64 K1-2q 1.96 ± 0.38 1.17~2.84 63 文献[7],本次研究 1.09 ± 0.13 0.50~1.26 45 K1d 2.54 ± 0.25 1.85~3.12 22 文献[7] 1.66 ± 1.34 0.86~5.30 11 文献[7] K1yc 2.59 ± 0.26 1.92~3.15 34 0.94 ± 0.28 0.30~1.40 34 K1sh 2.61 ± 0.35 1.91~4.48 164 0.77 ± 0.36 0.32~1.91 52 J3h 2.93 ± 0.32 2.03~3.78 109 0.81 ± 0.34 0.23~1.69 31 C-P 3.01 ± 0.43 2.22~4.39 107 0.82 ± 0.24 0.33~1.31 38 上地壳 2.85 — — 文献[23] 1.50(-Z/D) — — 文献[25] 中地壳 2.60 — — 0.46 — — 文献[23] 下地壳 2.00 — — 0.20 — — 岩石圈地幔 3.20 — — 0.03 — — 总样品数 653 314 注:表中数据K综合了测试数据和前人已有研究数据,3.1节正文仅为本次实验测试数据两者不一致;K2n. 嫩江组;K2y. 姚家组;K2qn. 青山口组;K1-2q. 泉头组;K1d. 登娄库组;K1yc. 营城组;K1sh. 沙河子组;J3h. 火石岭组;C-P. 石炭−二叠系(基层);下同 -
[1] 王超,渠淼,喻慧阳. 地球物质科学的基本原理:固体地球科学中的热力学研究历史与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):191-204.WANG C,QU M,YU H Y. Principle of Earth materials:A historical perspective of thermodynamics of the Earth[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):191-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 段和肖,刘彦广,王贵玲,等. 沧县隆起中部大地热流及岩石圈热结构特征:以献县地热田为例[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(3):988-1001.DUAN H X,LIU Y G,WANG G L,et al. Characteristics of the terrestrial heat flow and lithospheric thermal structure in central Cangxian uplift:A case study of Xianxian geothermal field[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(3):988-1001. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 黄方,何丽娟,吴庆举. 鄂尔多斯盆地深部热结构特征及其对华北克拉通破坏的启示[J]. 地球物理学报,2015,58(10):3671-3686. doi: 10.6038/cjg20151020HUANG F,HE L J,WU Q J. Lithospheric thermal structure of the Ordos Basin and its implications to destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2015,58(10):3671-3686. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg20151020 [4] MCKENZIE D,JACKSON J,PRIESTLEY K. Thermal structure of oceanic and continental lithosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,233(3/4):337-349. [5] EMMERSON B,MCKENZIE D. Thermal structure and seismicity of subducting lithosphere[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2007,163(1/4):191-208. [6] LIMBERGER J,VAN WEES J D,TESAURO M,et al. Refining the thermal structure of the European lithosphere by inversion of subsurface temperature data[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2018,171:18-47. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.07.009 [7] 单斌,周万里. 岩石圈结构成像方法的进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(5):112-121.SHAN B,ZHOU W L. Methods and prospects for lithospheric structure imaging[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(5):112-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 袁晶,陈艳,唐春花,等. 遥感地热GIS预测方法研究:以江西宁都地区为例[J]. 华东地质,2023,44(4):424-438.YUAN J,CHEN Y,TANG C H,et al. Remote sensing geothermal GIS prediction method:A case study in Ningdu City,Jiangxi Province[J]. East China Geology,2023,44(4):424-438. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 徐明,赵平,朱传庆,等. 江汉盆地钻井地温测量和大地热流分布[J]. 地质科学,2010,45(1):317-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.01.026XU M,ZHAO P,ZHU C Q,et al. Borehole temperature logging and terrestrial heat flow distribution in Jianghan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology(Scientia Geologica Sinica),2010,45(1):317-323. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.01.026 [10] ZUO Y H,JIANG S,WU S H,et al. Terrestrial heat flow and lithospheric thermal structure in the Chagan Depression of the Yingen-Ejinaqi Basin,north central China[J]. Basin Research,2020,32(6):1328-1346. doi: 10.1111/bre.12430 [11] LIAO Y Z,LIU Y G,LIU F,et al. Lithospheric thermal structure in Jinggangshan City:Implications for high geothermal background[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022,10:854232. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.854232 [12] 卫兴,师红杰,陈松,等. 水文地球化学方法在地热资源勘查中的应用:以湖北省应城市为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):68-80.WEI X,SHI H J,CHEN S,et al. Application of hydrogeochemical methods in geothermal resource exploration:A case study of Yingcheng City,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):68-80. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 邹才能,贾承造,赵文智,等. 松辽盆地南部岩性−地层油气藏成藏动力和分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2005,32(4):125-130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.021ZOU C N,JIA C Z,ZHAO W Z,et al. Accumulation dynamics and distribution of lithostratigraphic reservoirs in South Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2005,32(4):125-130. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.021 [14] 何文渊,柳波,张金友,等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油地质特征及关键科学问题探索[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(1):49-62.HE W Y,LIU B,ZHANG J Y,et al. Geological characteristics and key scientific and technological problems of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(1):49-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 高航,王璞珺,高有峰,等. 松辽盆地南部上、下白垩统界线研究:以松辽盆地国际大陆科学钻探松科3井为例[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(3):425-440.GAO H,WANG P J,GAO Y F,et al. The Upper-Lower Cretaceous boundary in the southern Songliao Basin:A case study of ICDP borehole SK-3[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2023,30(3):425-440. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] MA J C,TIAN Y,LIU C,et al. P-wave tomography of Northeast Asia:Constraints on the western Pacific plate subduction and mantle dynamics[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2018,274:105-126. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2017.11.003 [17] 刘晨璞,钟鑫,朱焕来. 松辽盆地北部中低地温场形成机制探讨[J]. 地质调查与研究,2016,39(4):316-320.LIU C P,ZHONG X,ZHU H L. Research on the formation mechanism for the medium-low geothermal field in the north of Songliao Basin[J]. Geological Survey and Research,2016,39(4):316-320. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] FENG Z Q,JIA C Z,XIE X N,et al. Tectonostratigraphic units and stratigraphic sequences of the nonmarine Songliao Basin,Northeast China[J]. Basin Research,2010,22(1):79-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2009.00445.x [19] LIU X,ZHAO D P,LI S Z,et al. Age of the subducting Pacific slab beneath East Asia and its geodynamic implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2017,464:166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.02.024 [20] 唐杰,许文良,王枫,等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史:东北亚陆缘中生代−古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2018,48(5):549-583.TANG J,XU W L,WANG F,et al. Subduction history of the Paleo-Pacific slab beneath Eurasian continent:Mesozoic-Paleogene magmatic records in Northeast Asia[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae),2018,48(5):549-583. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] LI Z Q,CHEN J L,ZOU H,et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and dynamics of the Songliao Basin,NE Asia:Implications for the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Ocean[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2021,218:103471. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103471 [22] 许文良,王旖旎,王枫,等. 西太平洋俯冲带的演变:来自东北亚陆缘增生杂岩的制约[J]. 地质论评,2022,68(1):1-17.XU W L,WANG Y N,WANG F,et al. Evolution of western Pacific subduction zones:Constraints from accretionary complexes in NE Asian continental margin[J]. Geological Review,2022,68(1):1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] FURLONG K P,CHAPMAN D S. Heat flow,heat generation,and the thermal state of the lithosphere[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2013,41:385-410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100051 [24] VILÀ M,FERNÁNDEZ M,JIMÉNEZ-MUNT I. Radiogenic heat production variability of some common lithological groups and its significance to lithospheric thermal modeling[J]. Tectonophysics,2010,490(3/4):152-164. [25] LACHENBRUCH A H. Crustal temperature and heat production:Implications of the linear heat-flow relation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1970,75(17):3291-3300. doi: 10.1029/JB075i017p03291 [26] HAENEL R,RYBACH L,STEGENA L,et al. Handbook of terrestrial heat-flow density determination:With guidelines and recommendations of the International Heat Flow Commission[M]. Dordrecht,Boston:Kluwer Academic Publishers,1988. [27] 饶松,胡圣标,朱传庆,等. 准噶尔盆地大地热流特征与岩石圈热结构[J]. 地球物理学报,2013,56(8):2760-2770. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130824RAO S,HU S B,ZHU C Q,et al. The characteristics of heat flow and lithospheric thermal structure in Junggar Basin,Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2013,56(8):2760-2770. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg20130824 [28] QIU N S,XU W,ZUO Y H,et al. Meso-Cenozoic thermal regime in the Bohai Bay Basin,eastern North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review,2015,57(3):271-289. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.1002818 [29] 吴乾蕃,谢毅真. 松辽盆地大地热流[J]. 地震地质,1985,7(2):59-64.WU Q F,XIE Y Z. Geothermal heat flow in the Songhuajiang-Liaoning Basin[J]. Seismology and Geology,1985,7(2):59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] SAEMUNDSSON K,AXELSSON G,STEINGRÍMSSON B. Geothermal systems in global perspective[J]. Environmental Science,Geology,Engineering,2013:55169275. [31] JIANG G Z,HU S B,SHI Y Z,et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China:Updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics,2019,753:36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.01.006 [32] 刘雨晨,柳波,朱焕来,等. 松辽盆地现今地温场分布特征及主控因素[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(8):2715-2727.LIU Y C,LIU B,ZHU H L,et al. The distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of present-day geothermal regime of the Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(8):2715-2727. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 付健,李思其,贾小江,等. 松辽盆地中央坳陷区中−新生代岩石圈厚度演化[J]. 地质科学,2023,58(3):798-809. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2023.045FU J,LI S Q,JIA X J,et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic lithospheric thickness evolution in the central depression of Songliao Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2023,58(3):798-809. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2023.045 [34] 许文良,孙德有,尹秀英. 大兴安岭海西期造山带的演化:来自花岗质岩石的证据[J]. 长春科技大学学报,1999,29(4):319-323.XU W L,SUN D Y,YIN X Y. Evolution of Hercynian orogenic belt in Daxing’anling Mt:Evidence from granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology,1999,29(4):319-323. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 韩江涛,郭振宇,刘文玉,等. 松辽盆地岩石圈减薄的深部动力学过程[J]. 地球物理学报,2018,61(6):2265-2279. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0155HAN J T,GUO Z Y,LIU W Y,et al. Deep dynamic process of lithosphere thinning in Songliao Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2018,61(6):2265-2279. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0155 [36] 杨宝俊,张梅生,王璞珺,等. 论中国东部大型盆地区及邻区地质—地球物理复合尺度解析[J]. 地球物理学进展,2002,17(2):317-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.02.019YANG B J,ZHANG M S,WANG P J,et al. Composite scale analysis of geology-geophysics in the major basins and surrounding areas in the eastern China[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2002,17(2):317-324. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.02.019 [37] SUN P,GUO P Y,NIU Y L. Eastern China continental lithosphere thinning is a consequence of paleo-Pacific plate subduction:A review and new perspectives[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2021,218:103680. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103680 [38] GUO Z,WANG K,YANG Y J,et al. The origin and mantle dynamics of quaternary intraplate volcanism in Northeast China from joint inversion of surface wave and body wave[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2018,123(3):2410-2425. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014948 [39] 牛璞,韩江涛,曾昭发,等. 松辽盆地北部地热场深部控制因素研究:基于大地电磁探测的结果[J]. 地球物理学报,2021,64(11):4060-4074. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0453NIU P,HAN J T,ZENG Z F,et al. Deep controlling factors of the geothermal field in the northern Songliao Basin derived from magnetotelluric survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2021,64(11):4060-4074. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0453 [40] 戴金星. 天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J]. 天然气地球科学,1993,4(增刊1):1-40.DAI J X. Characteristics of hydrocarbon isotopes in natural gas and identification of various types of natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,1993,4(S1):1-40. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] WANG X F,LIU Q Y,LIU W H,et al. Accumulation mechanism of mantle-derived helium resources in petroliferous basins,eastern China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2022,65(12):2322-2334. doi: 10.1007/s11430-022-9977-8 [42] DAI D L,ZHAO R S,HU J,et al. The lithospheric thermal structure in the Songliao Basin inferred from thermal parameter analyses:Implications for the background of geothermal resources[J]. Natural Resources Research,2024,33(3):1103-1129. doi: 10.1007/s11053-023-10303-3 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载: