Safety analysis of geothermal water recharge coupled with CO2 geological storage system
-
摘要:
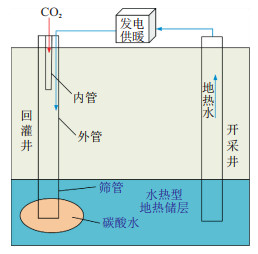
在圈闭良好的水热型地热储层, 开展CO2随回灌水同时注入储层的研究, 既具有经济效益又具有碳封存的环境效益。建立了3D储层模型, 对不同井距、地层倾角、筛管位置和采灌速率下CO2突破时间以及富含CO2的盐水在储层中的运移情况进行了研究。结果表明: (1)在采灌速率为20 kg/s, 20 a运行时间内井距为1 200 m时CO2未突破; (2)在倾斜地层中, 当回灌井位于开采井下游时, 随地层倾角增加, CO2突破时间延长, 沿地层下倾方向碳酸水运移距离增大; (3)综合考虑筛管位置对突破时间和突破后开采井中CO2质量分数的影响, 回灌井筛管位于储层上部30 m、开采井筛管位于储层下部30 m时, 有利于CO2地质封存的安全性和有效性; (4)采灌速率对CO2突破时间影响较大, 当采灌速率为12 kg/s时, CO2未突破; 当采灌速率增加到28 kg/s时, 突破时间缩短到11.8 a。因此, 在实际工程应用中可以通过对操作参数和地层固有特性的研究延缓CO2突破, 提高CO2地质封存安全性。
Abstract:Objective In well-trapped hydrothermal geothermal reservoirs, the research on injecting CO2 into reservoirs simultaneously with recharge water is carried out, which has both economic and environmental benefits for carbon sequestration.
Methods A 3D reservoir model was established to study the CO2 breakthrough time and the migration of CO2-rich brine in a reservoir under different well spacings, formation inclination angles, sieve tube positions and exploitation and reinjection rates.
Results The results show that (1) when the exploitation and reinjection rate is 20 kg/s and the well spacing is 1 200 m within 20 years of operation, there is no CO2 breakthrough. (2) In inclined formations, when the recharge well is located downstream of the production well, as the formation inclination angle increases, the CO2 breakthrough time increases, and the migration distance of carbonated water increases along the downdip direction of the formation. (3) Considering the impact of the screen position on the breakthrough time and CO2 mass fraction in the production well after breakthrough, it is beneficial to ensure the safety and effectiveness of CO2 geological storage when the recharge well sieve tube is located 30 m above the reservoir and the production well sieve is located 30 m below the reservoir. (4) The exploitation and reinjection rates have greater impacts on the CO2 breakthrough time. When the exploitation and reinjection rate is 12 kg/s, there is no CO2 breakthrough. When the exploitation and reinjection rate increases to 28 kg/s, the breakthrough time decreases to 11.8 years.
Conclusion Therefore, in practical engineering applications, the CO2 breakthrough time can be delayed, and the safety of CO2 geological storage can be improved through the study of operating parameters and the inherent characteristics of the formation.
-
Key words:
- geothermal water recharge /
- CO2 geological storage /
- delayed breakthrough /
- safety
-
图 8 筛管位置对CO2突破时间的影响(方案参数见表 2, 下同)
Figure 8. Effect of sieve tube position on CO2 breakthrough time
表 1 储层及注入参数[23]
Table 1. Reservoir and injection parameters
主要参数 参数取值 孔隙度/% 20 水平渗透率/10-3 μm2 600 垂直渗透率/10-3 μm2 30 岩石密度/(kg·m-3) 2 650 岩石热传导率/(W·m-1·℃-1) 2.5 岩石比热容/(J·kg-1·℃-1) 920 回灌温度/℃ 35 CO2注入速率/(kg·s-1) 0.8 地热水回灌速率/(kg·s-1) 12~28 表 2 不同方案的参数设置
Table 2. Parameter settings for different solutions
方案 回灌井位置/m 开采井位置/m 井距/m 地层倾角/(°) 筛管位置/m 采灌速率/(kg·s-1) 备注 1 500 -500 1 000 0 60 20 基础方案 2 300 -300 600 0 60 20 井距 3 400 -400 800 0 60 20 4 600 -600 1 200 0 60 20 5 700 -700 1 400 0 60 20 6 500 -500 1 000 2 60 20 地层倾角 7 500 -500 1 000 4 60 20 8 500 -500 1 000 6 60 20 9 500 -500 1 000 8 60 20 10 500 -500 1 000 10 60 20 11 500 -500 1 000 0 回灌井:储层上部30 m
开采井:储层上部30 m20 筛管位置 12 500 -500 1 000 0 回灌井:储层上部30 m
开采井:储层下部30 m20 13 500 -500 1 000 0 回灌井:储层下部30 m
开采井:储层上部30 m20 14 500 -500 1 000 0 回灌井:储层下部30 m
开采井:储层下部30 m20 15 500 -500 1 000 0 60 12 采灌速率 16 500 -500 1 000 0 60 16 17 500 -500 1 000 0 60 24 18 500 -500 1 000 0 60 28 -
[1] YANG B L, SHAO C, HU X L, et al. Advances in carbon dioxide storage projects: Assessment and perspectives[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(3): 1757-1776. [2] LI M W, QIN J R, HAN Z Y, et al. Low-carbon economic optimization method for integrated energy systems based on life cycle assessment and carbon capture utilization technologies[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2023, 11(11): 4238-4255. [3] 章程, 肖琼, 孙平安, 等. 岩溶碳循环及碳汇效应研究与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 190-198. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0193ZHANG C, XIAO Q, SUN P A, et al. Progress on karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effect study and perspective[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 190-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0193 [4] PARK J, PARK S S, CHO J, et al. Analysis on caprock and aquifer properties related with leakage during CO2 storage[J]. Geosystem Engineering, 2016, 19(4): 188-196. doi: 10.1080/12269328.2016.1165632 [5] 王贵玲, 蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 1923-1937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202007002.htmWANG G L, LIN W J. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 1923-1937. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202007002.htm [6] 王贵玲, 刘彦广, 朱喜, 等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001002.htmWANG G L, LIU Y G, ZHU X, et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001002.htm [7] BROWN D. A hot dry rock geothermal energy concept utilizing supercritical CO2 instead of water[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering. Stanford, California, United States: Stanford University, 2000: 233-238. [8] PRUESS K. On production behavior of enhanced geothermal systems with CO2 as working fluid[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49(6): 1446-1454. [9] RANDOLPH J B, SAAR M O. Coupling carbon dioxide sequestration with geothermal energy capture in naturally permeable, porous geologic formations: Implications for CO2 sequestration[J]. Energy Procedia, 2011, 4: 2206-2213. [10] PAN C J, CHÁVEZ O, ROMERO C E, et al. Heat mining assessment for geothermal reservoirs in Mexico using supercritical CO2 injection[J]. Energy, 2016, 102: 148-160. [11] SALIMI H, WOLF K H. Integration of heat-energy recovery and carbon sequestration[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 6: 56-68. [12] GANJDANESH R, BRYANT S L, ORBACH R L, et al. Coupled carbon dioxide sequestration and energy production from geopressured/geothermal aquifers[J]. SPE Journal, 2014, 19(2): 239-248. [13] BUSCHECK T A, CHEN M, SUN Y, et al. Two-stage, integrated, geothermal-CO2 storage reservoirs: An approach for sustainable energy production, CO2-sequestration security, and reduced environmental risk[R]. Livermore, California, United States: Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), 2012. [14] JING J, YANG Y L, TANG Z H. Assessing the influence of injection temperature on CO2 storage efficiency and capacity in the sloping formation with fault[J]. Energy, 2021, 215: 119097. [15] WANG F G, JING J, XU T F, et al. Impacts of stratum dip angle on CO2 geological storage amount and security[J]. Greenhouse Gases (Science and Technology), 2016, 6(5): 682-694. [16] WANG F, JING J, YANG Y, et al. Impacts of injection pressure of a dip-angle sloping strata reservoir with low porosity and permeability on CO2 injection amount[J]. Greenhouse Gases Science & Technology, 2017, 7(1): 92-105. [17] 林鹏威, 曾平, 林署炯, 等. 增强型地热系统热储层研究进展[J]. 中外能源, 2015, 20(10): 21-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201510007.htmLIN P W, ZENG P, LIN S J, et al. Advances in research on reservoirs of enhanced geothermal system[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2015, 20(10): 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201510007.htm [18] PRUESS K. ECO2N: A TOUGH2 fluid property module for mixtures of water, NaCl, and CO2[M]. Berkeley, CA, United States: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2005. [19] ZHANG K, WU Y S, PRUESS K. User's guide for TOUGH2-MP: A massively parallelversion of the TOUGH2 code[R]. Berkeley, CA, United States: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2008. [20] 杨艳林, 许天福, 靖晶. OpenMP在CO2地质储存数值模拟并行计算中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2018, 45(5): 129-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201805019.htmYANG Y L, XU T F, JING J. Application of parallel computing with OpenMP in numerical simulation of CO2 geological storage[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(5): 129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201805019.htm [21] PRUESS K, OLDENBURG C, MORIDIS G. TOUGH2 user's guide version 2[R]. Berkeley, CA, United States: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 1999. [22] 李红斌, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组页岩工程品质测井评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692LI H B, WANG G W, PANG X J, et al. Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of the Paleogene Funing Formation oil shales in the Subei Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692 [23] 莫绍星, 龙星皎, 李瀛, 等. 基于TOUGHREACT-MP的苏北盆地盐城组咸水层CO2矿物封存数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(5): 1647-1658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201405025.htmMO S X, LONG X J, LI Y, et al. Numerical modeling of CO2 sequestration in the saline aquifer of Yancheng Formation in Subei Basin using TOUGHREACT-MP[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(5): 1647-1658. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201405025.htm [24] BU F, XU T, WANG F, et al. Influence of highly permeable faults within a low-porosity and low-permeability reservoir on migration and storage of injected CO2[J]. Geofluids, 2016, 16(4): 769-781. [25] MUKHOPADHYAY S, DOUGHTY C A, BACON D H, et al. Preliminary model comparison results from the Sim-SEQ project using TOUGH2, STOMP, Eclipse, and VESA approach[R]. Richland, WA, United States: Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 2013. [26] SPYCHER N, PRUESS K. CO2-H2O mixtures in the geological sequestration of CO2: Ⅱ. Partitioning in chloride brines at 12-100 ℃ and up to 600 bar[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(13): 3309-3320. [27] 王福刚, 郭兵, 杨永智, 等. 中高渗倾斜地层与水平地层中CO2地质封存的差异性对比[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(2): 246-255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202002009.htmWANG F G, GUO B, YANG Y Z, et al. Comparison on the difference of CO2 geological storage between sloping and horizontal strata with mid-high permeability[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(2): 246-255. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202002009.htm [28] JING J, YANG Y L, TANG Z H, et al. Impacts of salinity on CO2 spatial distribution and storage amount in the formation with different dip angles[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(22): 22173-22188. [29] JING J, TANG Z H, YANG Y L, et al. Impact of formation slope and fault on CO2 storage efficiency and containment at the Shenhua CO2 geological storage site in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2019, 88: 209-225. -





 下载:
下载: