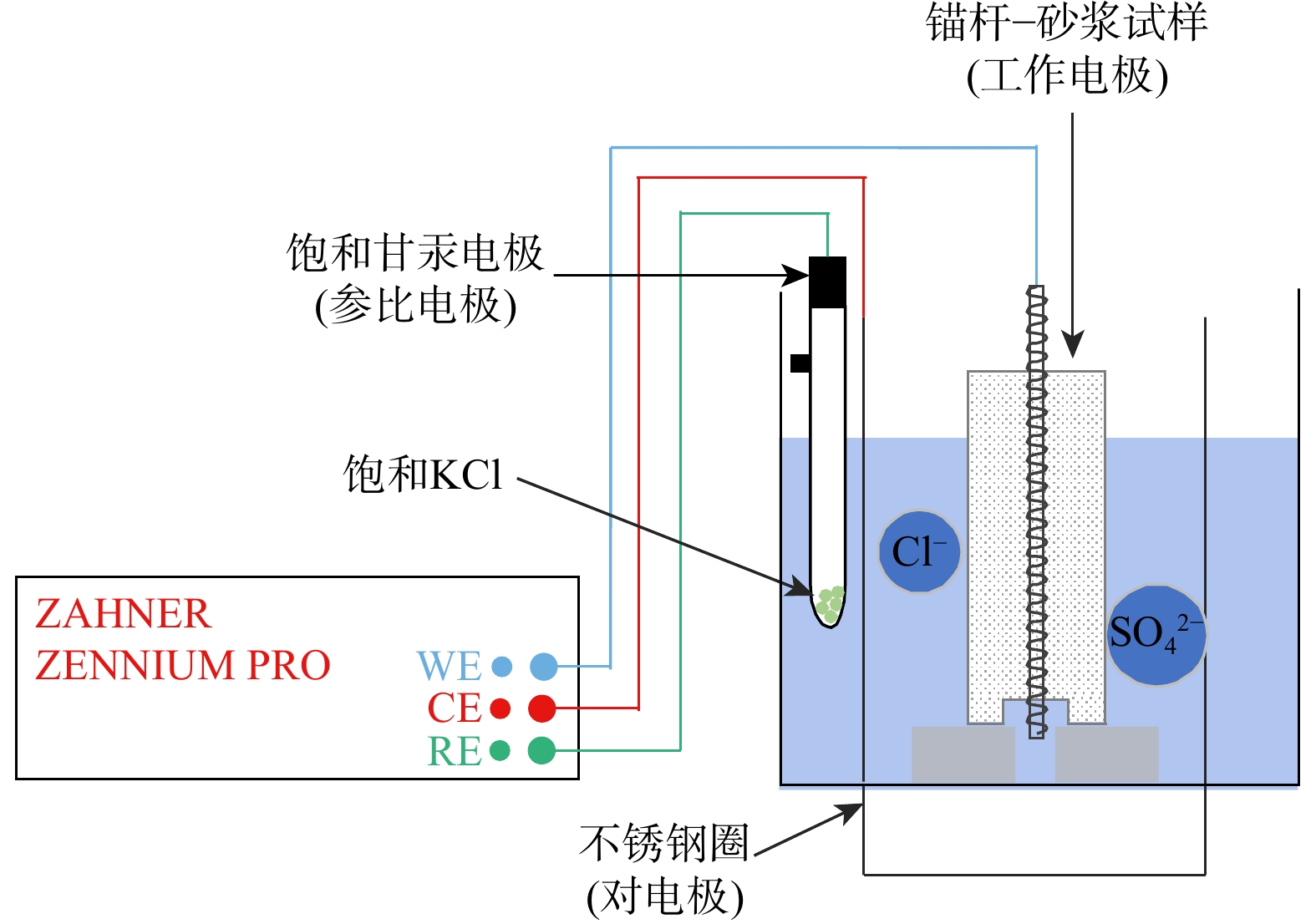
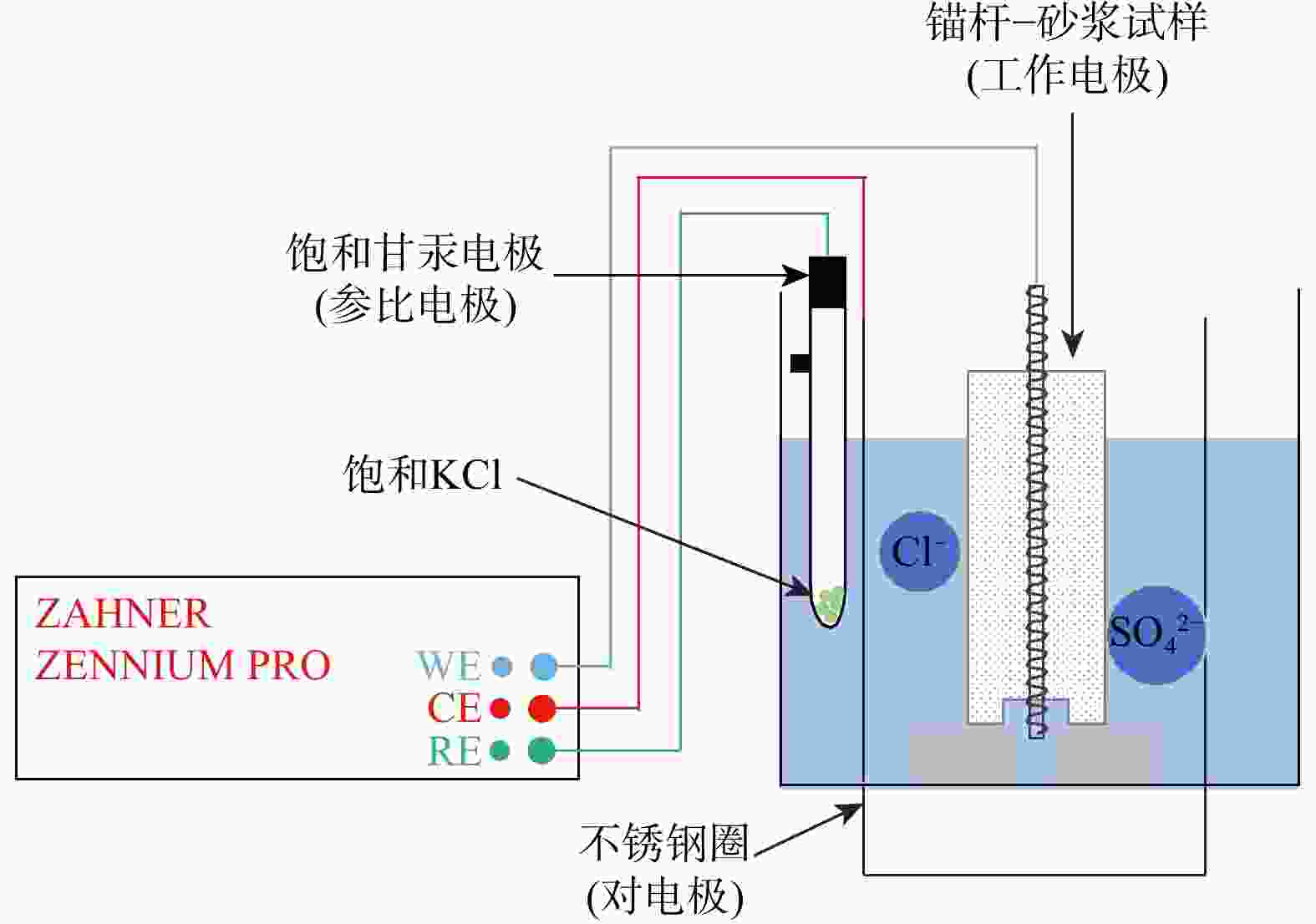
Bonding performance of anchor-mortar interface under multifactor action based on electrochemical impedance analysis
-
摘要:
影响锚杆−砂浆界面粘结性能的因素众多,而目前对该界面粘结性能的研究聚焦于单因素的影响,多因素作用下界面粘结性能的研究仍留有空白。以锚杆−砂浆为研究对象,采用电化学阻抗谱测试技术获取不同影响因素下的锚杆−砂浆界面状态以及电化学参数,通过拉拔试验获取锚杆−砂浆界面粘结强度,并结合电化学参数,探究试样养护完成时,电化学参数与拉拔荷载之间的关系,分析细砂粒径、锚杆直径和水灰比3个因素对锚杆−砂浆界面粘结性能的影响。由正交试验敏感性分析可知,试样的拉拔荷载主要受锚杆直径控制,孔隙溶液电阻(
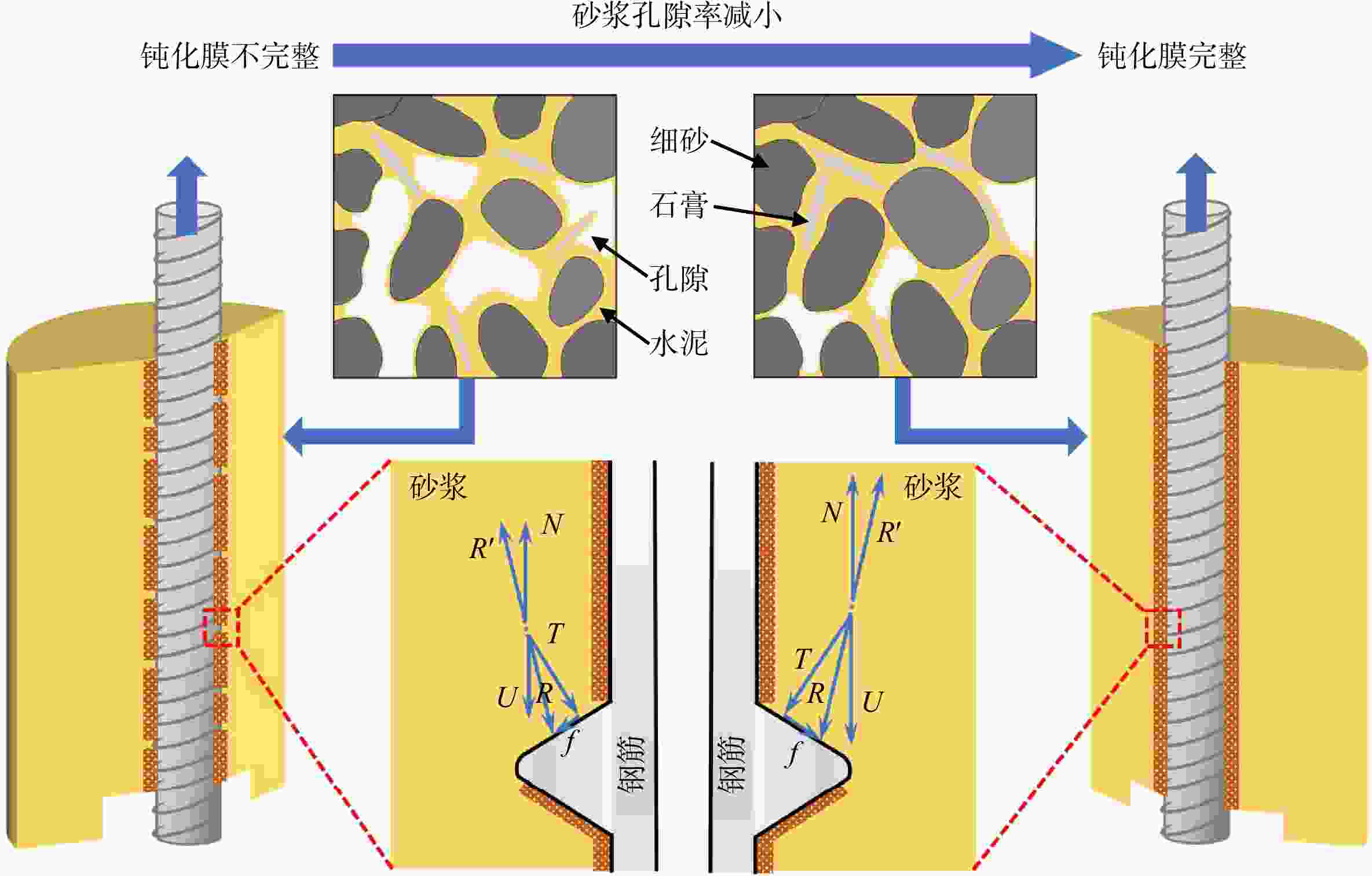
R s)主要受水灰比控制,电荷转移电阻(R ct)则没有明显的控制性因素;在试样养护完成时,受3个因素的影响,锚杆−砂浆界面会出现钝化膜完整与钝化膜不完整2种状态。研究结果表明,在试验所选择的范围内,拉拔荷载会随着细砂粒径的增大和水灰比的减小而增大,并且试样的拉拔荷载与孔隙溶液电阻(R s)和电荷转移电阻(R ct)呈正相关。研究成果对锚固结构砂浆配比及应用中的有效性验证具有重要意义。Abstract:Objective There are many factors affecting the bonding performance of the anchor-mortar interface, and the current research on the bonding performance of the interface focuses on the influence of a single factor, while the research on the bonding performance of the interface under the action of multiple factors still leaves a gap.
Methods In this paper, we take the anchor-mortar as the research object, using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to obtain the state of the anchor-mortar interface and electrochemical parameters under different influencing factors, obtain the bond strength of the anchor-mortar interface through the pullout test, and combines the electrochemical parameters to investigate the relationship between the electrochemical parameters and the pullout load when the specimen maintenance is completed and analyses the influence of the three factors on the bonding performance of the interface between the anchor-mortar.
Results The sensitivity analysis of orthogonal test shows that the pull-out load of the specimen is mainly controlled by the diameter of the anchor rod, the pore solution resistance (
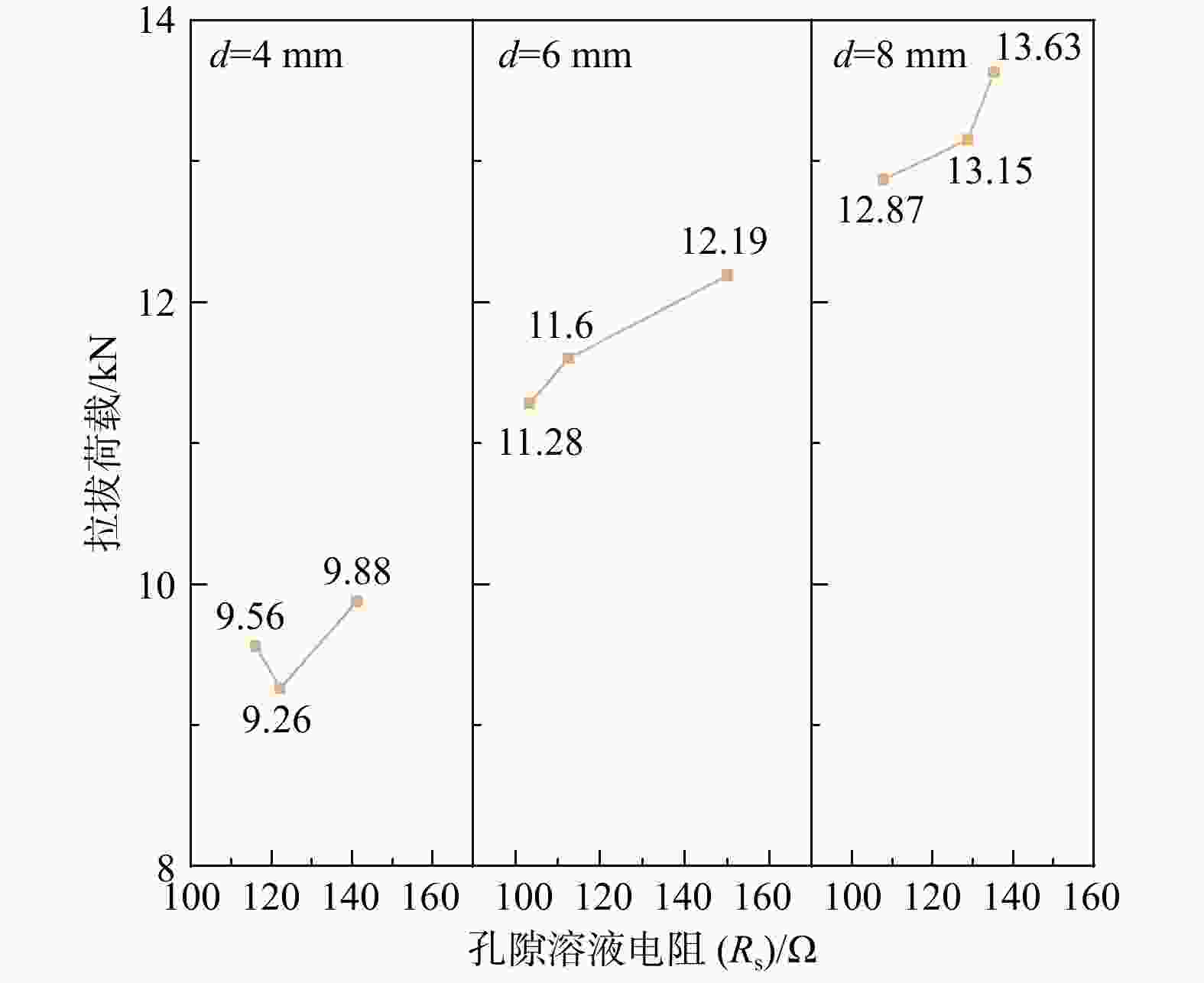
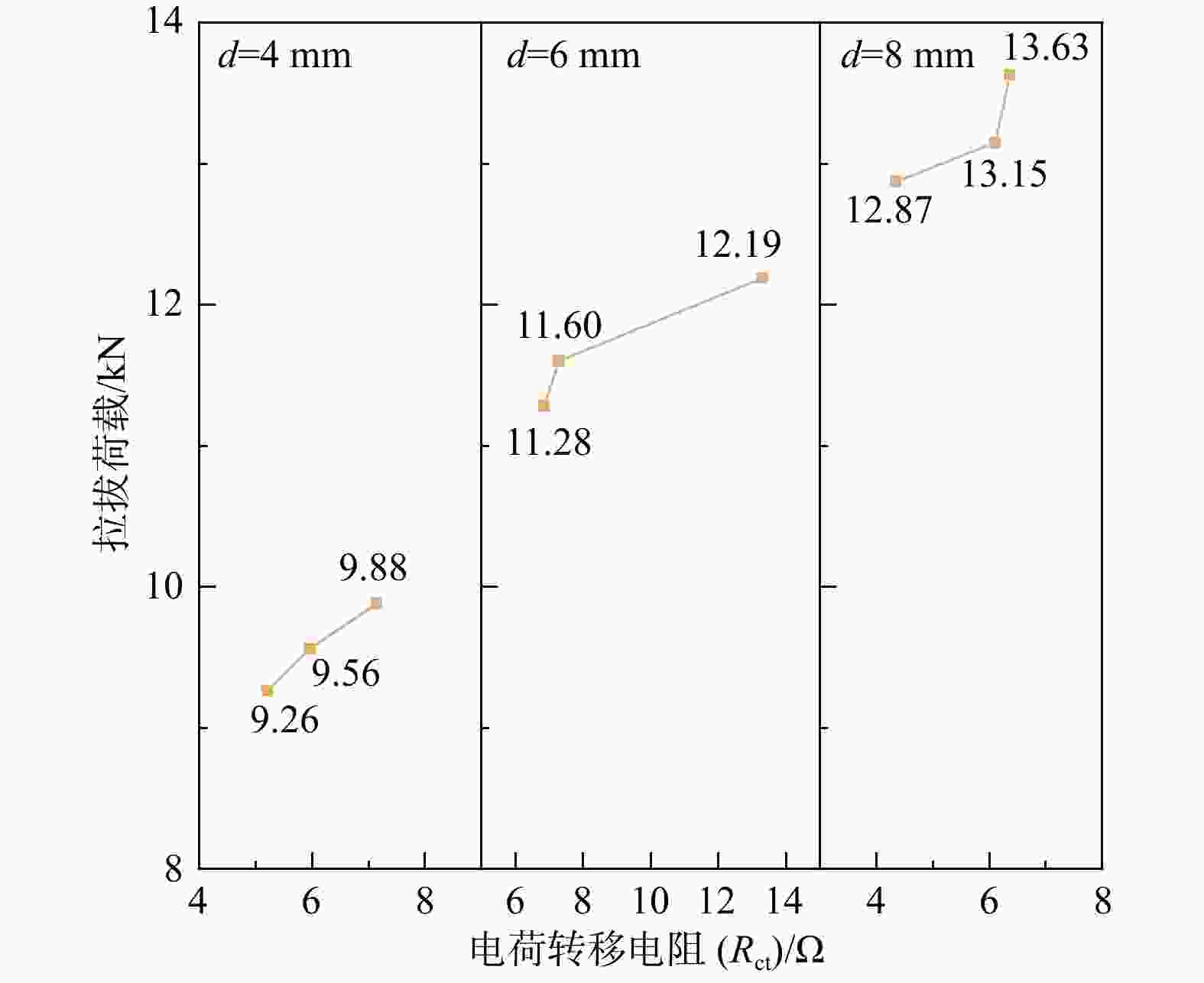
R s) is mainly controlled by the water-cement ratio, and there is no obvious controlling factor for the charge transfer resistance (R ct); at the early stage of specimen maintenance, under the influence of the three factors, there will be two kinds of states of the anchor-mortar interface, namely, complete passivation film and incomplete passivation film. The results of the study show that, within the range chosen for the test, the pullout load increases with the increase of fine sand particle size and the decrease of water-cement ratio, and the pullout load of the specimen is positively correlated with the pore solution resistance (R s) and charge transfer resistance (R ct).Conclusion The research results are of great significance for the validation of the effectiveness of anchored structural mortar proportioning and application.
-
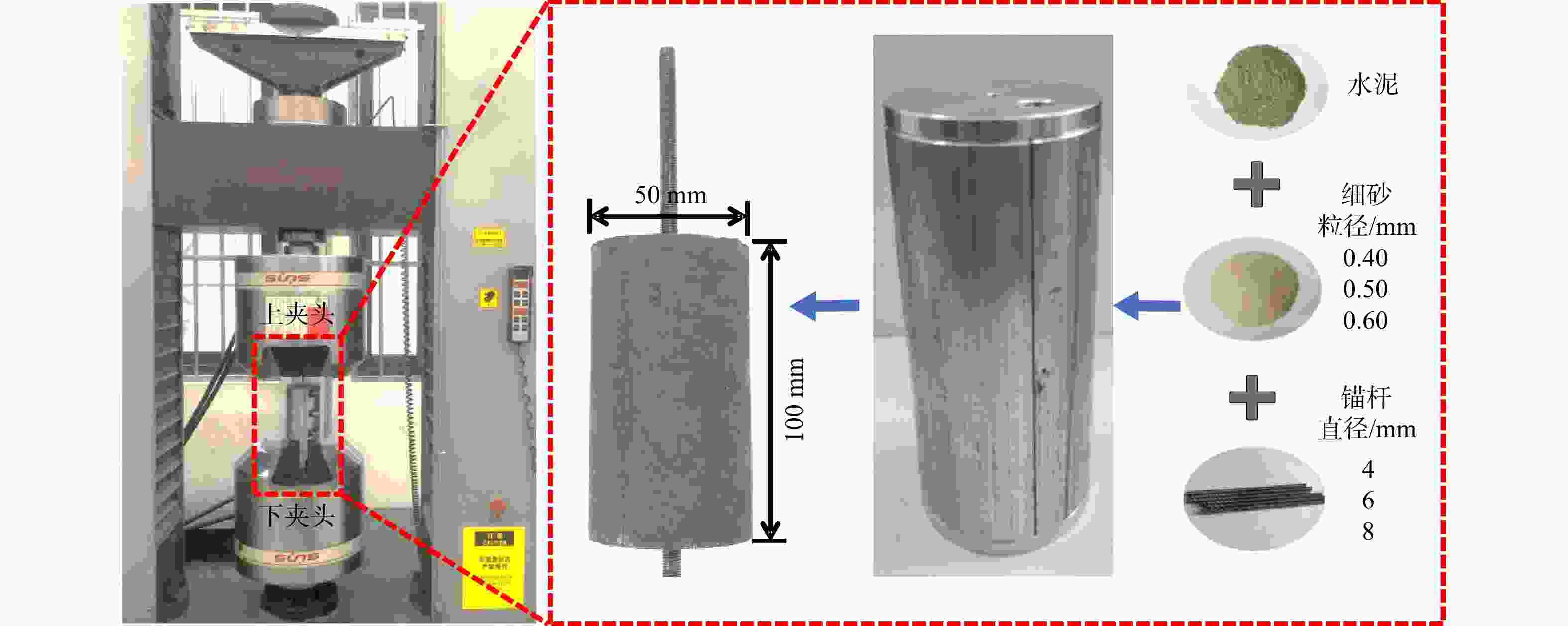
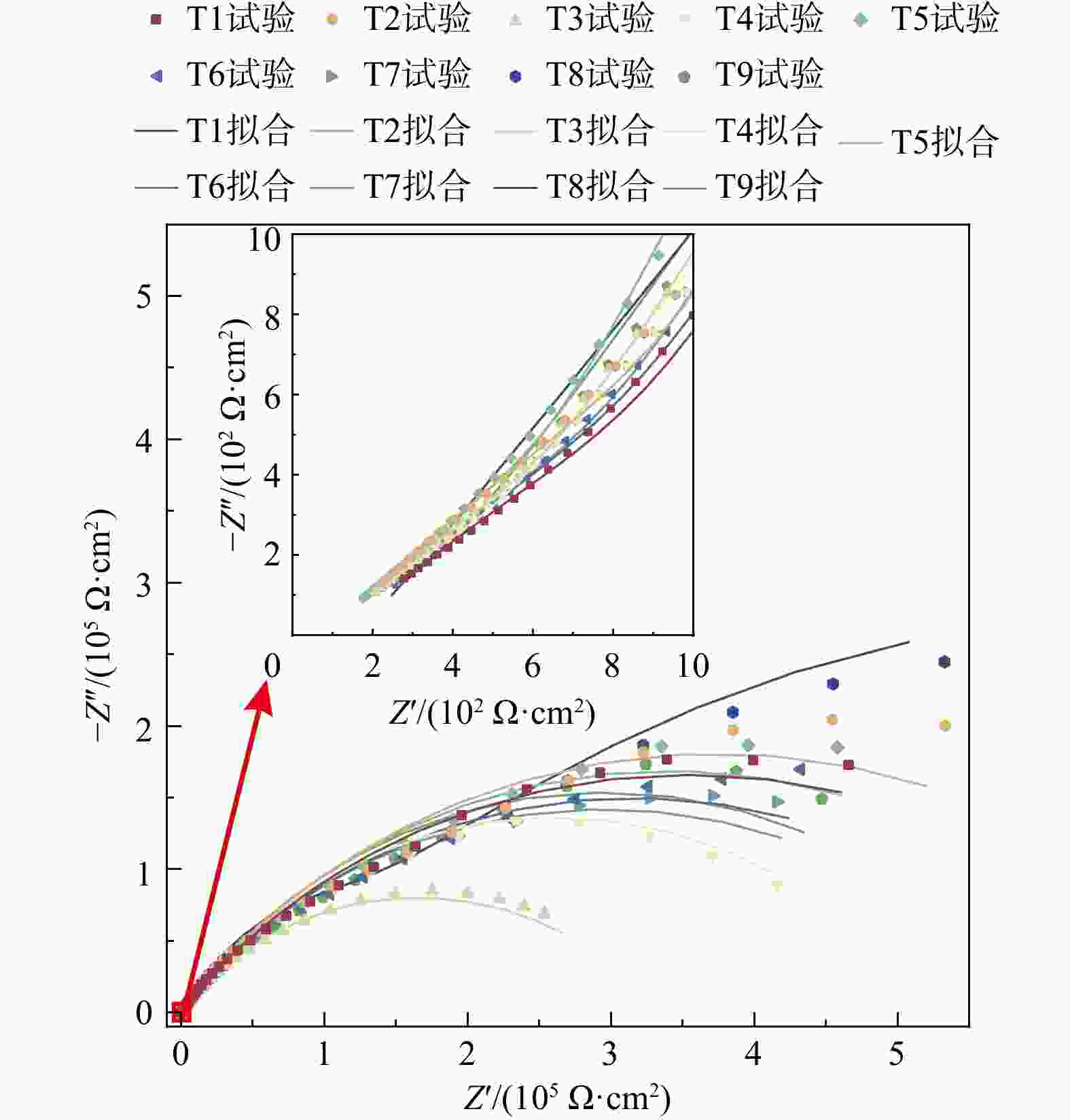
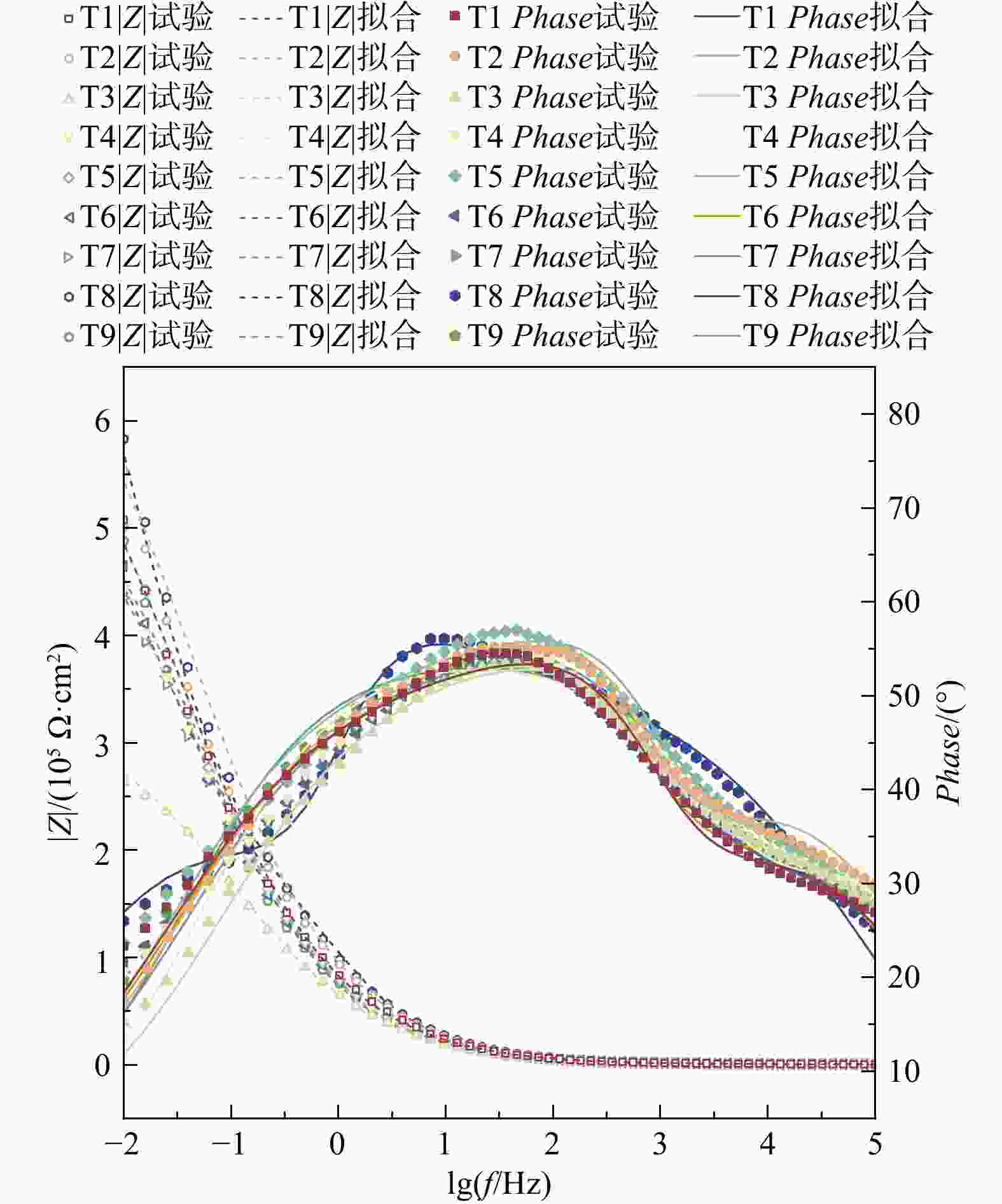
图 3 锚杆−砂浆试样Nyquist图(T1~T8设计方案见表1)
Z. 阻抗;Z'. 阻抗实部,即电阻分量;−Z''. 阻抗虚部,即电容或电阻分量
Figure 3. Nyquist diagram of anchor-mortar specimen
表 1 锚杆−砂浆试样设计方案
Table 1. Anchor-mortar specimen design programme
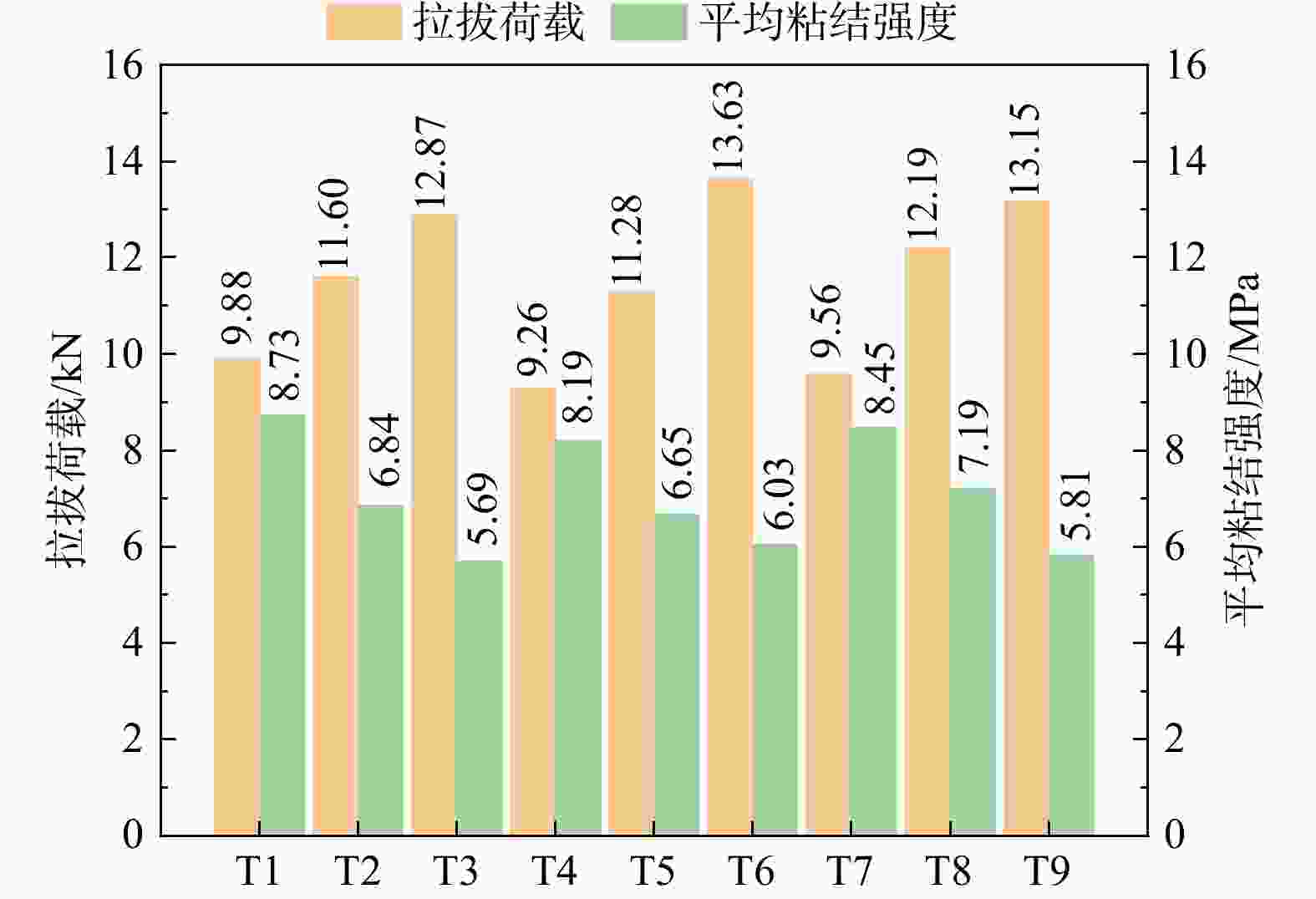
编号 细砂粒径/mm 锚杆直径/mm 水灰比 T1 0.40 4 0.40 T2 0.40 6 0.45 T3 0.40 8 0.50 T4 0.50 4 0.45 T5 0.50 6 0.50 T6 0.50 8 0.40 T7 0.60 4 0.50 T8 0.60 6 0.40 T9 0.60 8 0.45 表 2 硅酸盐水泥化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of silicate cement
wB/% SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 CaO MgO SO3 烧失量 23.5 4.1 7.4 56.4 3.2 2.2 3.2 表 3 钢筋的物理参数
Table 3. Physical parameters of reinforcing steel
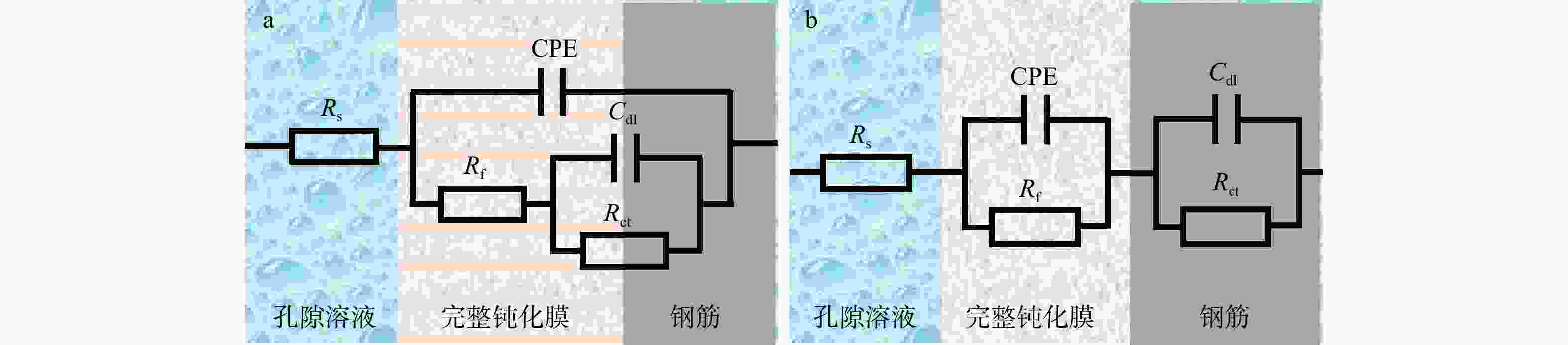
直径/mm 密度/(g·cm−3) 抗拉强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 4,6,8 7.85 540 400 196 表 4 拟合后锚杆−砂浆试样的EIS参数
Table 4. EIS parameters of fitted anchor-mortar specimens
试验组 $ {R}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $/$ \mathrm{\Omega } $ $ {C}_{{\mathrm{f}}} $/
($ {\mathrm{S}}·{{\mathrm{sec}}}^{{\mathrm{n}}} $)n1 $ R_{\mathrm{f}}$/$ \mathrm{\Omega } $ $ {C}_{{\mathrm{dl}}} $/
$ {\mathrm{S}}·{{\mathrm{sec}}}^{{\mathrm{n}}} $n2 $ {R}_{{\mathrm{ct}}} $/
$ {10}^{5}\mathrm{\Omega } $T1 141.2 3.709×10−6 0.5408 2322 2.796×10−8 0.8295 7.140 T2 112.5 3.215×10−6 0.5624 31310 1.349×10−7 0.8977 7.296 T3 107.8 4.286×10−6 0.5504 186.9 3.974×10−7 0.7969 4.336 T4 122.1 7.015×10−7 0.7039 258 3.632×10−6 0.6141 5.207 T5 103.3 3.901×10−6 0.5726 1946 2.003×10−7 0.8761 6.851 T6 135.2 3.947×10−6 0.5468 2542 2.763×10−6 0.8313 6.365 T7 116.1 3.9659×10−6 0.5949 2080 3.292×10−6 0.8147 5.960 T8 150.1 2.94×10−5 0.9071 67750 5.857×10−6 0.5370 13.330 T9 128.7 4.189×10−6 0.5527 1949 2.608×10−7 0.8431 6.107 注:Cf. 钢筋钝化膜电容;n1,n2. 均为弥散系数 表 5 拉拔荷载极差分析
Table 5. Extreme variance analysis of pullout loads
水平编号 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 1 11.450 9.567 10.674 2 11.390 11.690 11.337 3 11.633 13.217 11.237 极差 0.243 3.650 0.663 表 6 拉拔荷载方差分析
Table 6. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for pull-out loads
因素 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 误差 方差 0.096 20.162 0.767 0.050 自由度 2 2 2 2 F 1.922 401.984 15.300 p 0.342 0.002** 0.061 R2 0.998 **. 差异极其显著;*. 存在显著差异;注:F. 评估影响因素作用的显著程度;p衡量控制组与实验组差异大小;R2. 决定系数,用于衡量组间差异对总变异的解释程度;下同 表 7 孔隙溶液电阻(Rs)极差分析
Table 7. Extreme variance analysis of pore solution resistance(Rs)
水平编号 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 1 120.500 126.467 142.167 2 120.203 121.970 121.100 3 131.633 123.900 109.07 极差 11.43 4.497 33.097 表 8 孔隙溶液电阻(Rs)方差分析
Table 8. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for pore solution resistance(Rs)
因素 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 误差 方差 254.684 30.533 1683.915 44.121 自由度 2 2 2 2 F 5.772 0.692 38.166 p 0.148 0.591 0.026 *R2 0.978 表 9 电荷转移电阻(Rct)极差分析
Table 9. Charge Transfer Resistance (Rct) Polar Analysis Table
水平编号 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 1 6.257 6.102 8.945 2 6.141 9.159 6.203 3 8.466 5.603 5.715 极差 2.325 3.556 3.230 表 10 电荷转移电阻(Rct)方差分析
Table 10. ANOVA for charge transfer resistance(Rct)
因素 细砂粒径 锚杆直径 水灰比 误差 方差 10.296 22.236 18.186 2.056 自由度 2 2 2 2 F 5.007 10.813 8.843 p 0.166 0.085 0.102 R2 0.961 -
[1] 王上上,陈富,李东贤,等. 锚杆不确定性对加固边坡失稳概率的影响[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):282-289.WANG S S,CHEN F,LI D X,et al. Influence of anchor uncertainty on the failure probability of reinforced slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):282-289. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] WANG C L,ZHENG L B,WANG L Q,et al. Effects of the tensile and shear properties of bolts on the shear properties of bolted rock joints[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2024,35(5):1626-1639. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1749-3 [3] 周阳,来弘鹏,王兴广,等. 长锚杆/锚索改善深埋大跨度隧道初支结构受力试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2024,46(4):853-863. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20221533ZHOU Y,LAI H P,WANG X G,et al. Experimental study on improving mechanical characteristics of initial support structure of deep buried large-span tunnels with long bolts or cables[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2024,46(4):853-863. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE20221533 [4] 刘宇鹏,夏才初,吴福宝,等. 高地应力软岩隧道长、短锚杆联合支护技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(1):105-114.LIU Y P,XIA C C,WU F B,et al. A combined support technology of long and short bolts of soft rock tunnels under high ground stresses[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(1):105-114. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 张文翔,崔强,邱昊茨,等. 输电线路单群锚基础抗拔特征差异的现场足尺试验[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(6):114-124.ZHANG W X,CUI Q,QIU H C,et al. On-site full-scale test research for difference of anti-pull bearing characteristics between single anchor and group anchors foundation of transmission lines[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(6):114-124. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 孙益振,郑卫锋,范志强. 输电线路节理化岩体注浆锚杆基础抗拔力模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(1):78-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.013SUN Y Z,ZHENG W F,FAN Z Q. Tension model test research on grouted bolts foundation in jointed rock masses for transmission lines[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(1):78-82. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.01.013 [7] 吴善百,王亮清,吴琼,等. 地震作用下锚固岩质边坡动力响应研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(12):4456-4468.WU S B,WANG L Q,WU Q,et al. Advance and prospect for seismic dynamic response of anchored rock slope[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(12):4456-4468. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 李师毓,吴琼,王亮清,等. 地震作用下软硬互层顺层岩质边坡动力响应研究[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(8):3127-3136.LI S Y,WU Q,WANG L Q,et al. Study of dynamic response of soft and hard interbedded rock slopes under earthquakes[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(8):3127-3136. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面:从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):1-19.ZHU H H. Engineering geological interface:From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] YU S S,ZHU W C,NIU L L,et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of fully grouted long rockbolt load-transfer behavior[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,85:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.12.001 [11] HAIDAR H H,MUSSA F I,DAWOOD A O,et al. Experimental study of post installed rebar anchor systems for concrete structure[J]. Civil and Environmental Engineering,2020,16(2):308-319. doi: 10.2478/cee-2020-0031 [12] YANG S Y,CHEN X L,HAN M,et al. Effect of sulfate attack,drying-wetting cycles and freezing-thawing cycles on reinforced concrete columns under eccentric loads[J]. Structures,2022,45:1864-1877. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.10.011 [13] XU S H,LI A B,JI Z Y,et al. Seismic performance of reinforced concrete columns after freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,102:861-871. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.168 [14] MOOSAVI M,JAFARI A,KHOSRAVI A. Bond of cement grouted reinforcing bars under constant radial pressure[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2005,27(1):103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2003.12.002 [15] ZHANG N,GU Q,WU Y Z,et al. Refined peridynamic modeling of bond-slip behaviors between ribbed steel rebar and concrete in pull-out tests[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering,2022,148(12):04022197. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0003396 [16] HU Z J,SHAH Y I,YAO P F. Experimental and numerical study on interface bond strength and anchorage performance of steel bars within prefabricated concrete[J]. Materials,2021,14(13):3713. doi: 10.3390/ma14133713 [17] XU H. Research on anchor characteristics of anchorage body consideration of bolt corrosion[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,374/377:2497-2504. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.374-377.2497 [18] MENG F J,CHEN W X,MA J J,et al. Bond behaviors of BFRP bars in concrete using carbon fiber rib anchorage[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,345:128305. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128305 [19] KALTHOFF M,RAUPACH M. Pull-out behaviour of threaded anchors in fibre reinforced ordinary concrete and UHPC for machine tool constructions[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,33:101842. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101842 [20] EL ALAMI E,FEKAK F E,GARIBALDI L,et al. Numerical study of the bond strength evolution of corroded reinforcement in concrete in pull-out tests[J]. Applied Sciences,2022,12(2):654. doi: 10.3390/app12020654 [21] 姜凤娇. 混凝土水泥水化、氯离子扩散及钢筋锈蚀的电化学分析[D]. 辽宁大连:大连理工大学,2020.JIANG F J. Electrochemical analysis of cement hydration,chloride ion diffusion and steel corrosion of concrete[D]. DalianLiaoning:Dalian University of Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 黄俊. 电催化界面和反应的电化学阻抗谱研究:经典永不褪色[J]. 电化学,2020,26(1):1-18.HUANG J. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for electrocatalytic interfaces and reactions:Classics never die[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry,2020,26(1):1-18. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 李国翠. 水泥基材料水化过程基本特性的电化学阻抗谱研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2010.LI G C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study on basic characteristics of hydration process of cement-based materials[D]. Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] YANG L X,WU Y T,CHEN S,et al. A promising hybrid additive for enhancing the performance of alkaline aluminum-air batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2021,257:123787. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123787 [25] OLIVEIRA R L N,BRAGANÇA M O G P,MEDEIROS-JUNIOR R A. Effect of coarse aggregate size on corrosion of reinforced concrete exposed to carbonation and chloride ingress by electrochemical measurements[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,361:129665. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129665 [26] DONG B Q,QIU Q W,XIANG J Q,et al. Electrochemical impedance interpretation of the carbonation behavior for fly ash-slag-cement materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2015,93:933-942. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.05.066 [27] KE R,WANG L Q,ZOU Z X,et al. An analytical model for anchor-mortar interface bonding based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2023,142:105196. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.105196 [28] KE R,WANG L Q,ZHENG L B,et al. Deterioration of mechanical properties at the anchor-mortar interface considering the effect of two-phase corrosion[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,370:130664. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130664 [29] JIANG L H,NIU Y L,JIN W Z,et al. Influence of chloride salt type on chloride ion diffusion performance of alkali-activated slag mortar[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,351:128930. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128930 [30] DU F Y,JIN Z Q,SHE W,et al. Chloride ions migration and induced reinforcement corrosion in concrete with cracks:A comparative study of current acceleration and natural marine exposure[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,263:120099. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120099 [31] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部,中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 岩土锚杆与喷射混凝土支护工程技术规范: GB 50086-2015[S]. 北京:中国计划出版社,2015.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China,General Administration of Quality Supervision,Insplieation and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China.Technical code for engineering of ground anchorages and shotcrete support: GB 50086-2015[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [32] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构后锚固技术规程:JGJ145-2013[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2013.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Technical specification for post-installed fastenings in concrete structures: JGJ 145-2013[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press,2013. (in Chinese) [33] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部,中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 混凝土结构试验方法标准: GB/T 50152-2012 [S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2012.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China,General Administration of Quality Supervision,Insplieation and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test method of concrete structures: GB/T 50152-2012 [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [34] 伍远辉,罗宿星,付盈盈,等. 氯离子环境下混凝土钢筋的电化学阻抗谱特征[J]. 表面技术,2011,40(3):65-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3660.2011.03.018WU Y H,LUO S X,FU Y Y,et al. EIS characteristics of the steel in concrete in environment containing chloride ion[J]. Surface Technology,2011,40(3):65-67. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3660.2011.03.018 [35] 施锦杰,孙伟. 等效电路拟合钢筋锈蚀行为的电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术,2011,23(5):387-392.SHI J J,SUN W. Equivalent circuits fitting of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for corrosion of reinforcing steel in concrete[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology,2011,23(5):387-392. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] RIBEIRO D V,ABRANTES J C C. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to monitor the corrosion of reinforced concrete:A new approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,111:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.047 [37] CARÉ S,NGUYEN Q T,L’HOSTIS V,et al. Mechanical properties of the rust layer induced by impressed current method in reinforced mortar[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2008,38(8/9):1079-1091. [38] LIU G J,ZHANG Y S,WU M,et al. Study of depassivation of carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution using different equivalent circuits[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,157:357-362. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.09.104 [39] LI Y,YIN S P,LV H L. Performance of interface between TRC and existing concrete under a chloride dry-wet cycle environment[J]. Journal of Central South University,2020,27(3):876-890. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4338-6 [40] SHI T,ZHENG L W,XU X C. Evaluation of alkali reactivity of concrete aggregates via AC impedance spectroscopy[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,145:548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.053 [41] JIANG Z,CAI G J,TIAN G L,et al. Effect of aggregate particle size on mortar pore structure[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,352:128988. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128988 [42] ZHENG S J,LIU T L,JIANG G S,et al. Effects of water-to-cement ratio on pore structure evolution and strength development of cement slurry based on HYMOSTRUC3D and micro-CT[J]. Applied Sciences,2021,11(7):3063. doi: 10.3390/app11073063 [43] XIAOYU,ZHANG Y J,QU N,et al. Electrochemical analysis of passivation film formation on steel rebar in concrete[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2016,11(7):5870-5876. doi: 10.20964/2016.07.44 [44] GUTBERLET T,HILBIG H,BEDDOE R E. Acid attack on hydrated cement:Effect of mineral acids on the degradation process[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2015,74:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2015.03.011 -




 下载:
下载: