Interwell interference analysis and well spacing optimization of tight oil wells based on geological engineering integration
-
摘要:
随着新井加密以及老井重复压裂的实施, 井间距缩小、单井改造规模扩大, 井间干扰程度高, 严重影响压裂效果及产量。为解决井间干扰程度评价及预防控制等问题, 应用地质工程一体化模拟技术, 综合利用三维位移不连续裂缝扩展方法及嵌入式离散裂缝技术, 建立水平井组地质工程一体化模拟模型, 评价单井及井组压裂改造后动用范围, 开展井间干扰程度影响因素分析。结果表明: (1)基质渗透率高于0.3×10-3 μm2、裂缝半长大于100 m、裂缝间距小于40 m, 压裂改造范围明显变大, 井间干扰程度越明显; (2)随着井间距增加, 井间干扰程度不断变弱, 当井间距增加到400 m时, 井间干扰对单井最终可采储量(EUR)的影响可以忽略; (3)当井间距大于400m时, 井组累计产油量降低幅度变大, 需要优化合理井间距来平衡区块采收率和单井累计产油量的关系。研究结果可为井距优化及重复压裂技术应用提供有效指导。
Abstract:With the implementation of infilling new wells and refracturing existing ones, the spacing between wells has decreased, the scale of stimulation for individual wells has expanded, and the level of interference among wells has heightened, significantly impacting fracturing effectiveness and production.
Objective Addresses issues related to evaluating and preventing interference between wells,
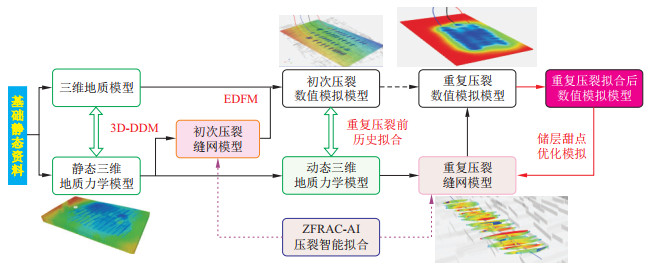
Methods based on an integrated geological engineering workflow, 3D DDM and EDFM technologies have been comprehensively used to establish an integrated geological engineering simulation model for horizontal well groups. Then, the operating range of single wells and well groups following fracturing stimulation was evaluated, and factors affecting the degree of interference between wells were analysed.
Results The findings indicate that (1) when the matrix permeability exceeds 0.3×10-3 μm2, the half-length of fractures is greater than 100 m, and the spacing between fractures is less than 40 m, a largerrange of fracturing transformation correlates with an increased degree of interwell interference. (2) As the well spacing increases, the degree of interwell interference diminishes. At a spacing of 400 m, the impact of interwell interference on a single well's EUR can be ignored. (3) It is essential to balance the relationship between the block recovery rate and cumulative production of a single well by optimizing and determining appropriate well spacing.
Conclusion The above research results can provide valuable insights for optimizing well spacing and enhancing the effectiveness of repeated fracturing technology.
-
表 1 地质模型基本参数
Table 1. Geological model parameters
属性 数值 属性 数值 有效厚度/m 18 含油饱和度/% 54.2 油藏埋深/m 1 520 原油黏度/(mPa·s) 7.3 平均孔隙度 0.09 原始地层压力/MPa 15.8 平均渗透率/(10-3μm2) 0.82 原油饱和压力/MPa 5.6 -
[1] 辛红刚, 田杨, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地典型夹层型页岩油地质特征及潜力评价: 以宁228井长7段为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 114-124. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220224XIN H G, TIAN Y, FENG S B, et al. Geological characteristics and potential evaluation of typical interlayer shale oil in the Ordos Basin: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Well Ning 228[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 114-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220224 [2] 杜现飞, 殷桂琴, 齐银, 等. 长庆油田华庆超低渗油藏水平井压裂裂缝优化[J]. 断块油气田, 2014, 21(5): 668-670.DU X F, YIN G Q, QI Y, et al. Optimization on fracturing fracture of horizontal well in Huaqing ultra-low permeability reservoir of Changqing Oilfield[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2014, 21(5): 668-670. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 任佳伟, 张先敏, 王贤君, 等. 致密砂岩油藏水平井密切割压裂改造参数优化[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(6): 859-864.REN J W, ZHANG X M, WANG X J, et al. Optimization of parameters of close cutting fracturing for horizontal well in tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(6): 859-864. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 樊庆军. 密切割体积压裂技术在致密油水平井的应用[J]. 中外能源, 2020, 25(3): 47-51.FAN Q J. Application of intensive volume fracturing technology to horizontal wells in tight oil reservoirs[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2020, 25(3): 47-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 杨春城. 页岩油水平井密切割体积压裂产能研究[J]. 中外能源, 2020, 25(5): 57-62.YANG C C. Study on productivity of horizontal wells with stimulated reservoir volume at tight fracturing spacing for shale oil[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2020, 25(5): 57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 于学亮, 胥云, 翁定为, 等. 页岩油藏"密切割" 体积改造产能影响因素分析[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(3): 132-143.YU X L, XU Y, WENG D W, et al. Factors influencing the productivity of the multi-fractured shale oil reservoir with tighter clusters[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(3): 132-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 胡勇, 梅青燕, 王继平, 等. 致密砂岩气藏井网加密优化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(9): 1326-1333.HU Y, MEI Q Y, WANG J P, et al. Optimization of well pattern infilling in tight sandstone gas reservoir[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(9): 1326-1333. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 陈民锋, 屈丹, 秦立峰, 等. 基于储量有效动用规律确定水平井加密调整策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(4): 70-77.CHEN M F, QU D, QIN L F, et al. Determination of infill adjustment strategy for horizontal wells based on the law of effective producing reserves[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(4): 70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 张家由, 滕小兰, 邱玲, 等. 加密井压裂井间干扰实例分析及技术对策[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2011, 25(1): 95-97.ZHANG J Y, TENG X L, QIU L, et al. Case study on wells interference and technical measures in infill well fracturing[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2011, 25(1): 95-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 何东博, 王丽娟, 冀光, 等. 苏里格致密砂岩气田开发井距优化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 458-464.HE D B, WANG L J, JI G, et al. Well spacing optimization for Sulige tight sand gas field, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 458-464. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 位云生, 王军磊, 齐亚东, 等. 页岩气井网井距优化[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(4): 129-137.WEI Y S, WANG J L, QI Y D, et al. Optimization of shale gas well pattern and spacing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(4): 129-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] WANG B, ZHOU F J, YANG C, et al. Experimental study on injection pressure response and fracture geometry during temporary plugging and diverting fracturing[J]. SPE Journal, 2020, 25(2): 573-586. [13] 雍锐, 常程, 张德良, 等. 地质-工程-经济一体化页岩气水平井井距优化: 以国家级页岩气开发示范区宁209井区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(7): 42-48.YONG R, CHANG C, ZHANG D L, et al. Optimization of shale-gas horizontal well spacing based on geology-engineering-economy integration: A case study of Well Block Ning 209 in the National Shale Gas Development Demonstration Area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(7): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 陈京元, 位云生, 王军磊, 等. 页岩气井间干扰分析及井距优化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(7): 931-940.CHEN J Y, WEI Y S, WANG J L, et al. Interwell-production interference and well spacing optimization in shale gas reservoir[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(7): 931-940. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 樊怀才, 张鉴, 岳圣杰, 等. 页岩气平台式井组井间干扰影响因素分析及井距优化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(4): 512-519.FAN H C, ZHANG J, YUE S J, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of interwell interference in shale gas well groups and well spacing optimization[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(4): 512-519. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 荆少东, 许国辉, 吴尚彬, 等. 基于三维精细化数值模型的地下油库水封安全评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 1-11. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220097JING S D, XU G H, WU S B, et al. Assessment of the water-sealed safety of underground crude oil storage based on a three-dimensional refined numerical model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220097 [17] 谢军, 鲜成钢, 吴建发, 等. 长宁国家级页岩气示范区地质工程一体化最优化关键要素实践与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2): 174-185.XIE J, XIAN C G, WU J F, et al. Optimal key elements of geoengineering integration in Changning National Shale Gas Demonstration Zone[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(2): 174-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 刘震, 张军华, 于正军, 等. 非常规储层脆性研究进展及展望[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2023, 58(6): 1499-1507.LIU Z, ZHANG J H, YU Z J, et al. Progress and prospects of brittleness research in unconventional reservoirs[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2023, 58(6): 1499-1507. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 李萧, 吴礼明, 王丙贤, 等. 渝东南地区龙马溪组构造应力场数值模拟及裂缝有利区预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 24-31. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603LI X, WU L M, WANG B X, et al. Numerical simulation of tectonic stress field and prediction of fracture target in the Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Chongqing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603 [20] 胡烨, 陈迎宾, 王彦青, 等. 川西大邑构造须家河组应力场数值模拟[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 92-97.HU Y, CHEN Y B, WANG Y Q, et al. Numerical simulation of stress field in Xujiahe Formation of Dayi structure region in western Sichuan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 92-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] LEE S H, LOUGH M F, JENSEN C L. Hierarchical modeling of flow in naturally fractured formations with multiple length scales[J]. Water Resources Research, 2001, 37(3): 443-455. [22] 白晓虎, 苏良银, 赵伯平, 等. 注采井网条件下水平井体积压裂重复改造优化设计[J]. 断块油气田, 2017, 24(2): 194-198.BAI X H, SU L Y, ZHAO B P, et al. Re-fracturing optimization for horizontal wells on condition of flooding pattern[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2017, 24(2): 194-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 隋阳, 刘德基, 刘建伟, 等. 低成本致密油层水平井重复压裂新方法: 以吐哈油田马56区块为例[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2018, 40(3): 369-374.SUI Y, LIU D J, LIU J W, et al. A new low-cost refracturing method of horizontal well suitable for tight oil reservoirs: A case study on Ma 56 Block in Tuha Oilfield[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2018, 40(3): 369-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 何海波. 致密油水平井缝网增能重复压裂技术实践[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(4): 170-174.HE H B. Practice of re-fracturing with network energization for horizontal well in tight oil reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(4): 170-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 黄婷, 苏良银, 达引朋, 等. 超低渗透油藏水平井储能压裂机理研究与现场试验[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2020, 48(1): 80-84.HUANG T, SU L Y, DA Y P, et al. Research and field test on energy storage fracturing mechanism of horizontal wells in ultra-low permeability reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(1): 80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] FARAH N, DING D Y, WU Y S. Simulation of the impact of fracturing fluid induced formation damage in shale gas reservoirs[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 2017, 20(3): 532-546. [27] WANG M Y, LEUNG J Y. Numerical investigation of fluid-loss mechanisms during hydraulic fracturing flow-back operations in tight reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 133: 85-102. -





 下载:
下载: