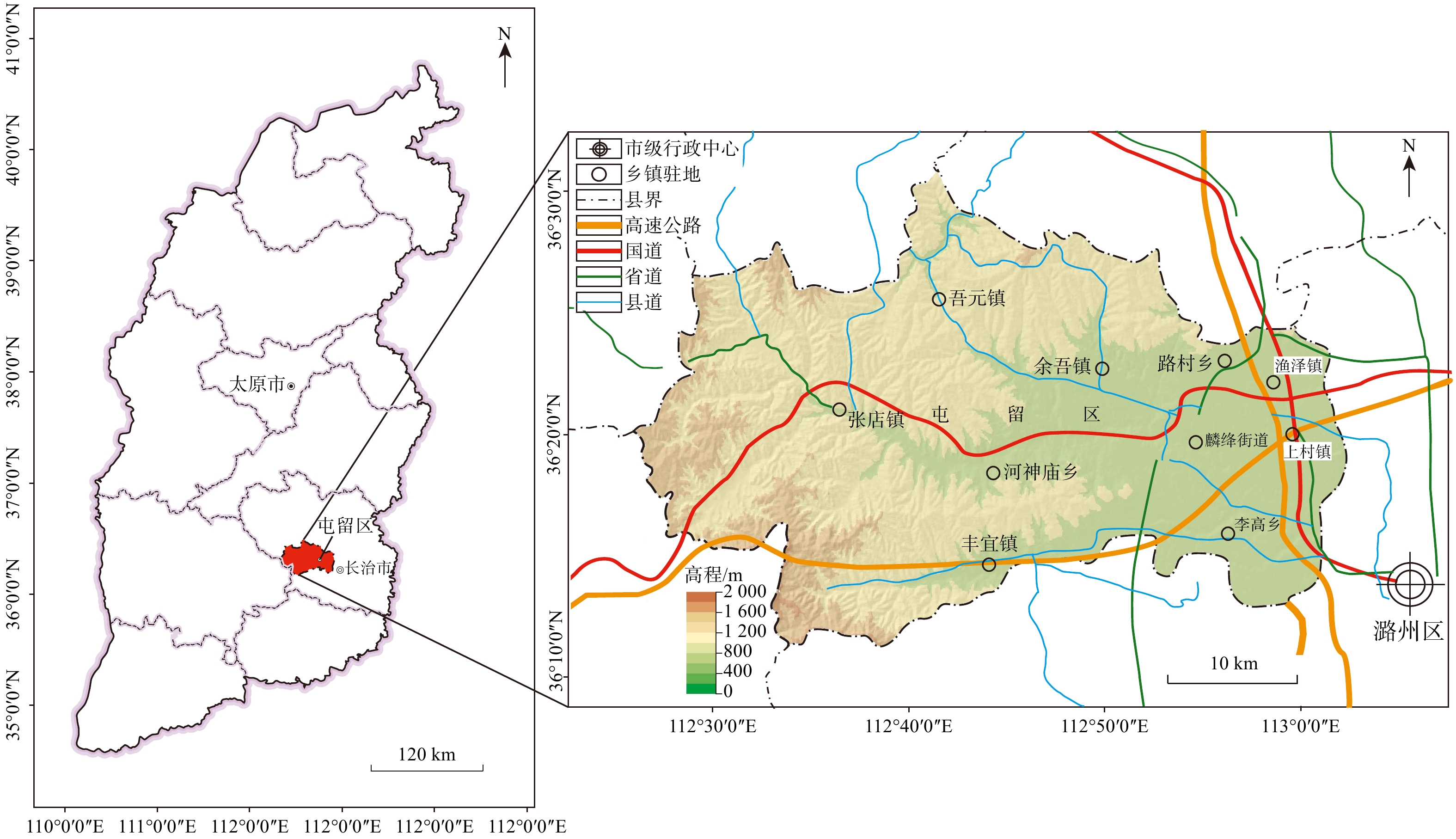
Research on comprehensive evaluation and utilization of selenium-rich land quality in Tunliu District, Shanxi Province, China
-
摘要:
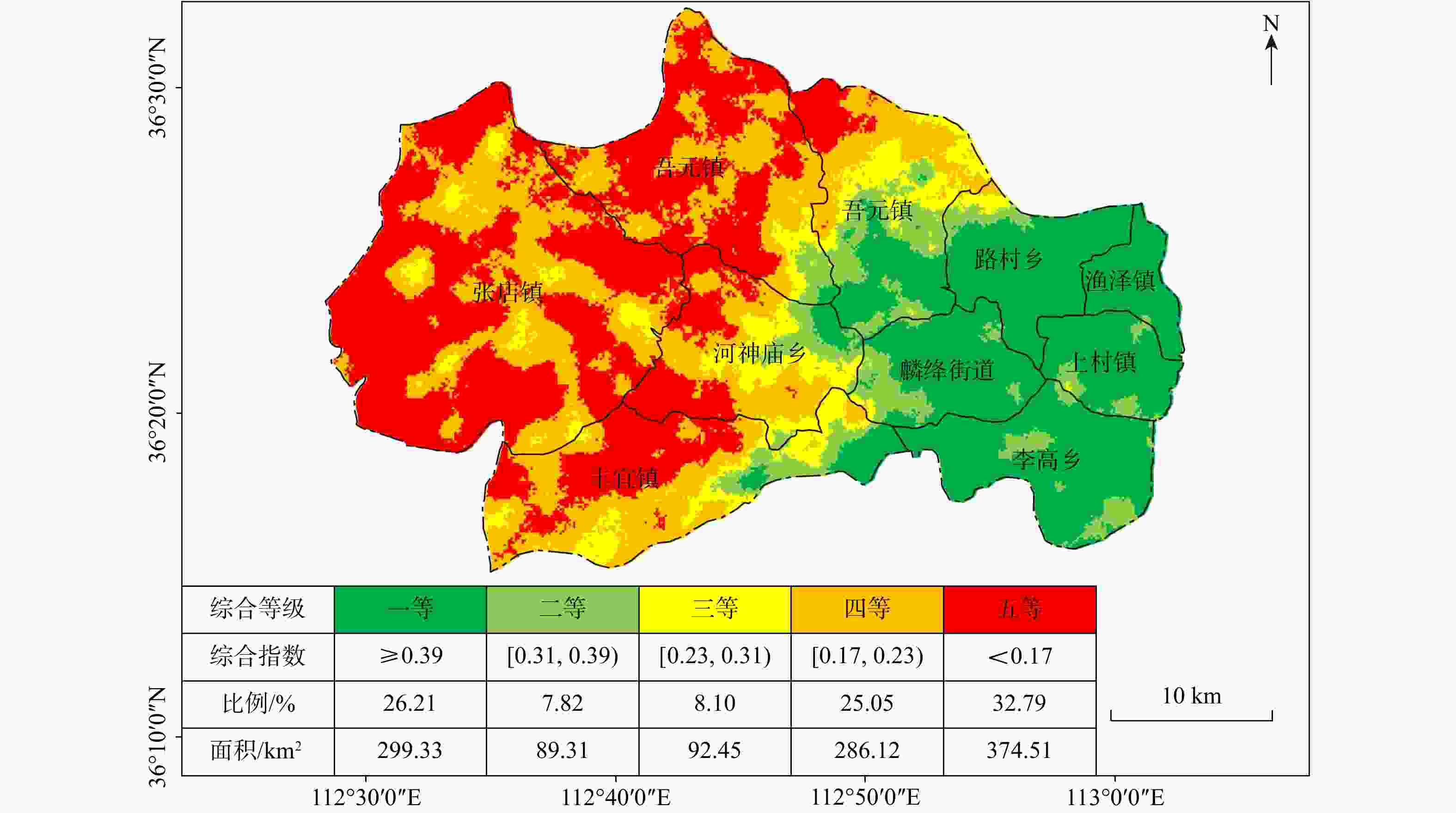
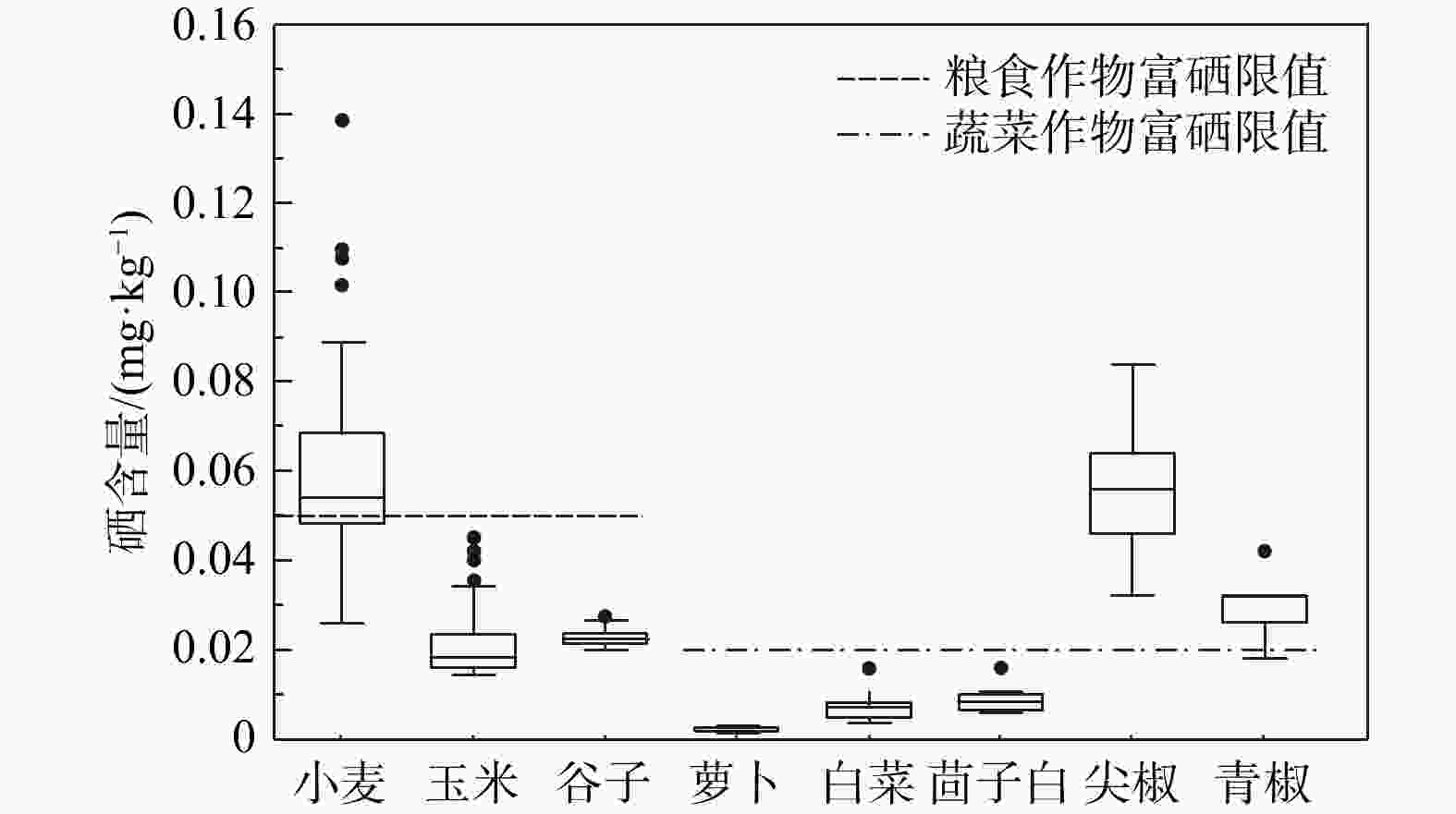
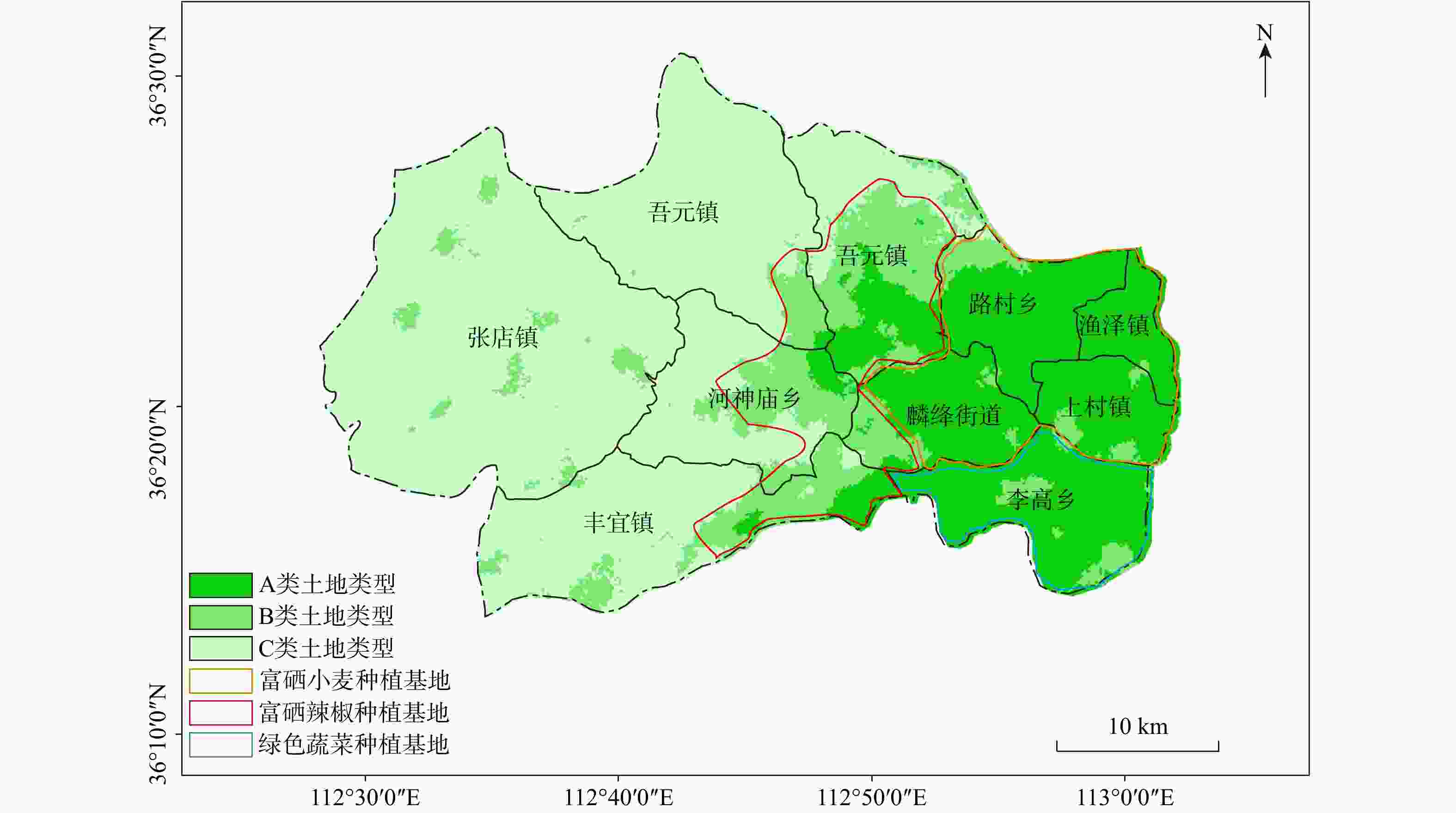
开展土地调查与评价并发展特色产业是实现乡村振兴,巩固脱贫成果的重要工作。为了更加精准有效地指导区域农业生产布局和特色产业开发,在山西省长治市屯留区开展了富硒土地调查与评价工作。选取了富硒产业质量、生态环境和耕地地力三方面的指标来构建富硒土地综合质量评价体系,运用模糊数学法、熵权法、综合指数法等方法评价与划分土地等级。结果表明:①屯留区硒含量等级为高和适量的土壤占比54.47%,集中分布于全区东部;耕地地力等级分布不均,整体为西低东高;全域生态环境状况清洁。②全区一等富硒土地面积299.33 km2,占比26.61%,集中分布于东部平原地区。③屯留区小麦、尖椒和青椒达到富硒标准,尖椒富硒率为100%,农作物清洁状况良好。依据评价结果,结合屯留区国土空间规划,划分出三类土地:A类地(富硒富肥且清洁)规划种植富硒小麦和绿色蔬菜,同时发展观光农业;B类地(硒适量且清洁)规划种植富硒辣椒,同时发展农产品深加工;C类地(非富硒富肥)打造农产品深加工体系,同时发展农贸和旅游。为屯留区富硒农业产业规划以及区域协同发展提供了理论支持及科学建议。
Abstract:Objective Carrying out land surveys and evaluations and developing special industries is a very important task for China to realize rural revitalization and consolidate the results of poverty alleviation. In order to more accurately and effectively guide regional agricultural production layout and specialty industry development, a selenium-rich land survey and evaluation was conducted in Tunliu District, Changzhi City, Shanxi Province, China.
Methods Therefore, the indicators of selenium-rich industry quality, ecological environment and arable land strength were selected to construct a comprehensive quality evaluation system for selenium-rich land, and then fuzzy mathematical method, entropy weighting method, and composite index method were applied to evaluate and grade the land in the study area, and ArcGIS was used to implement the results.
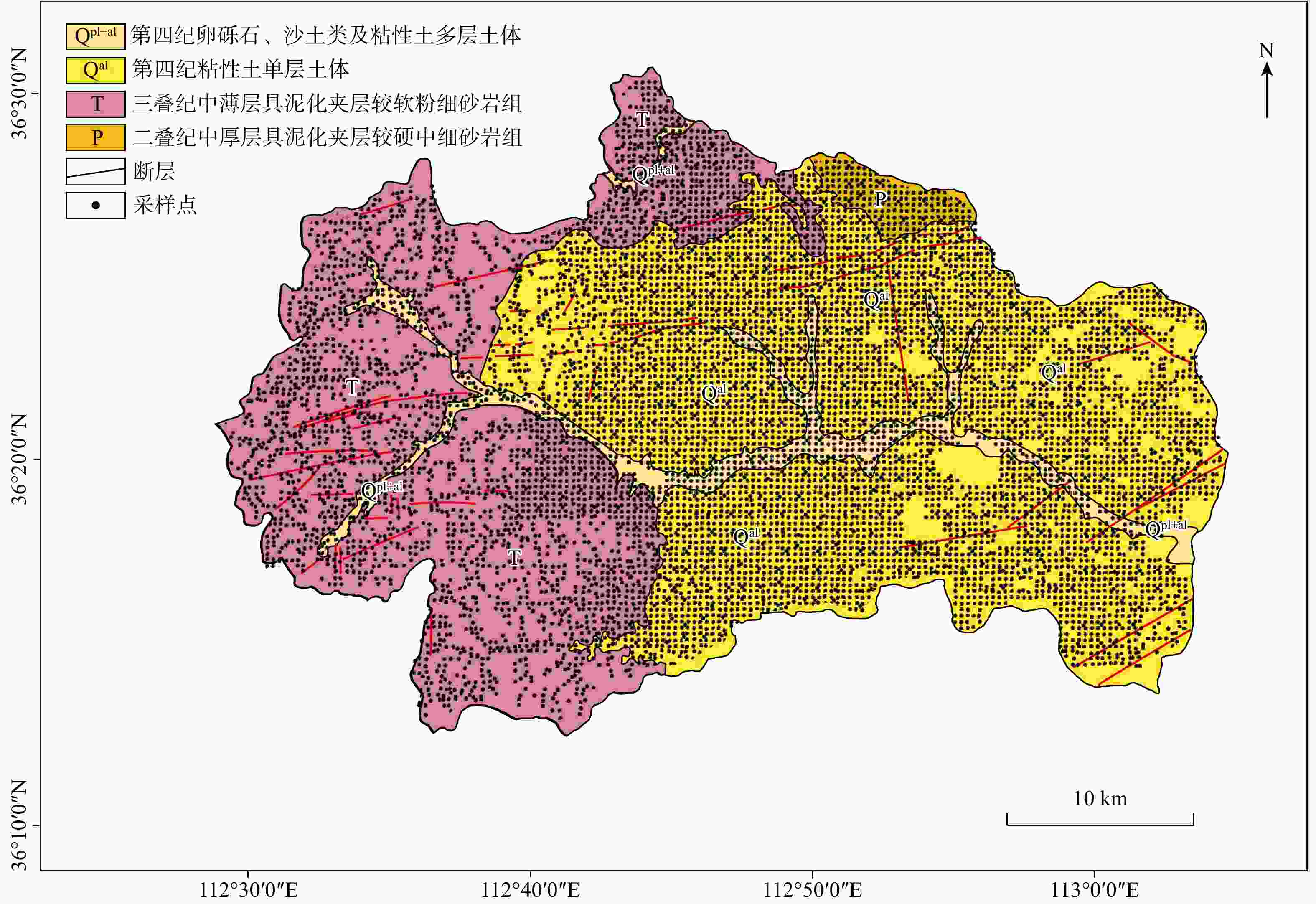
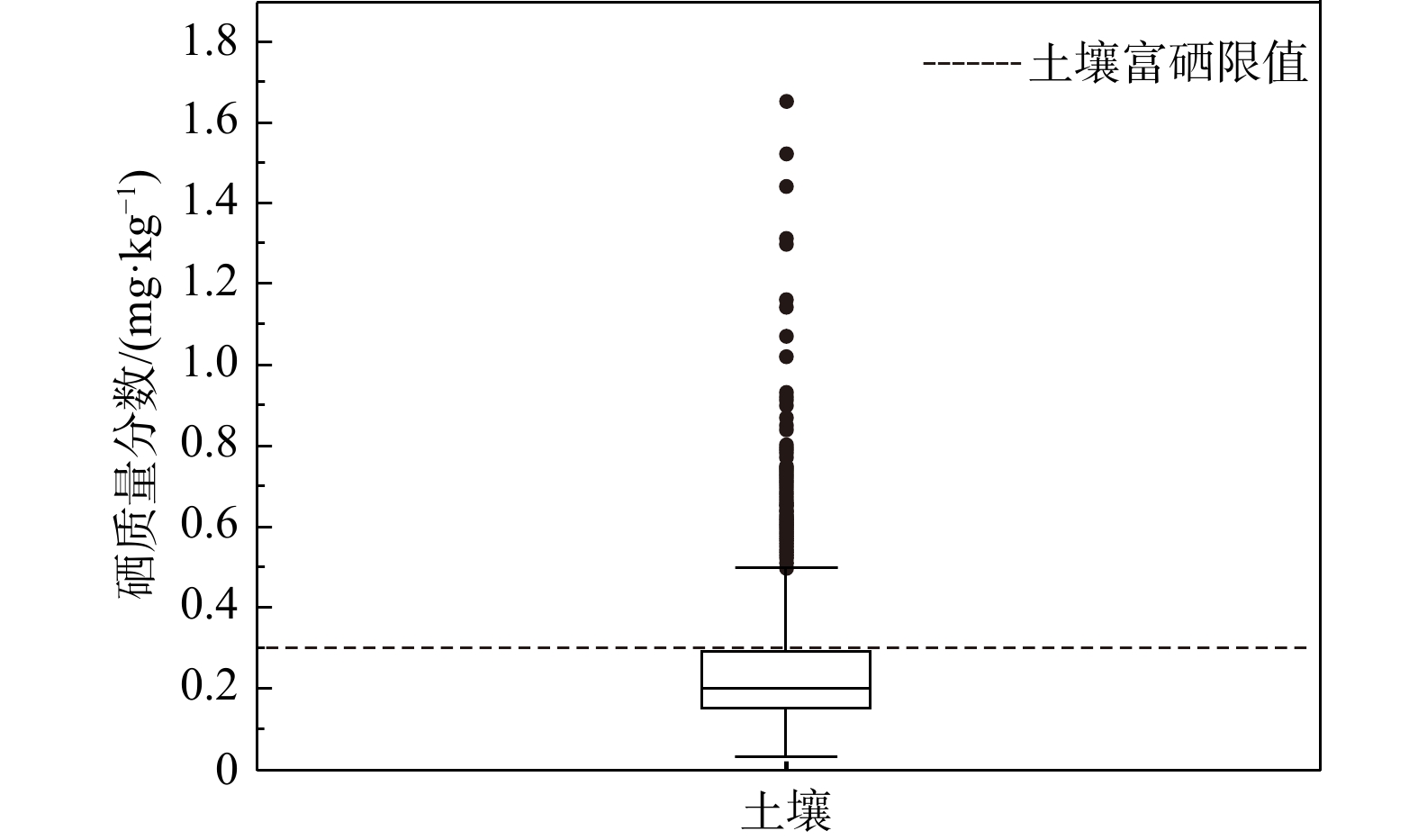
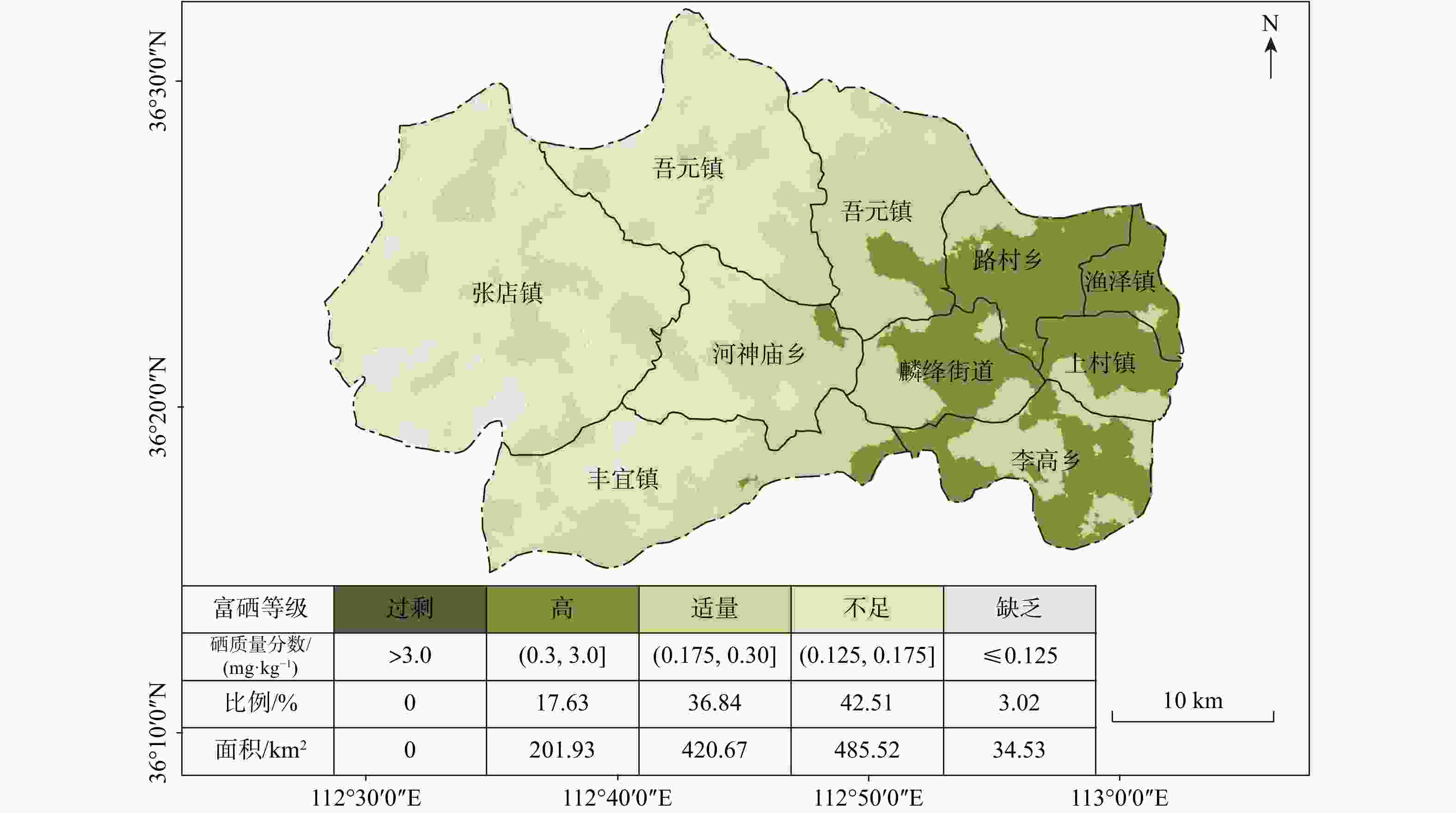
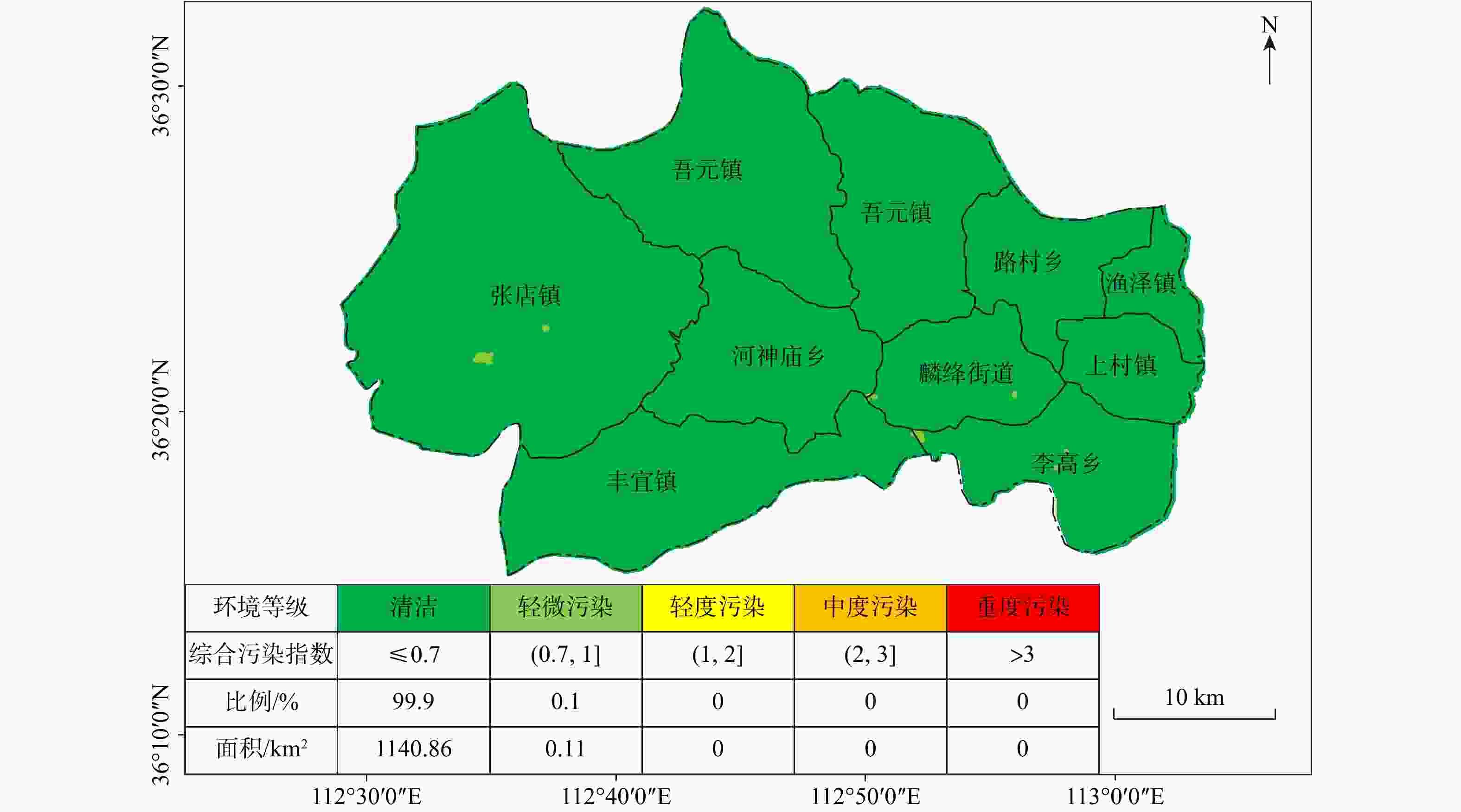
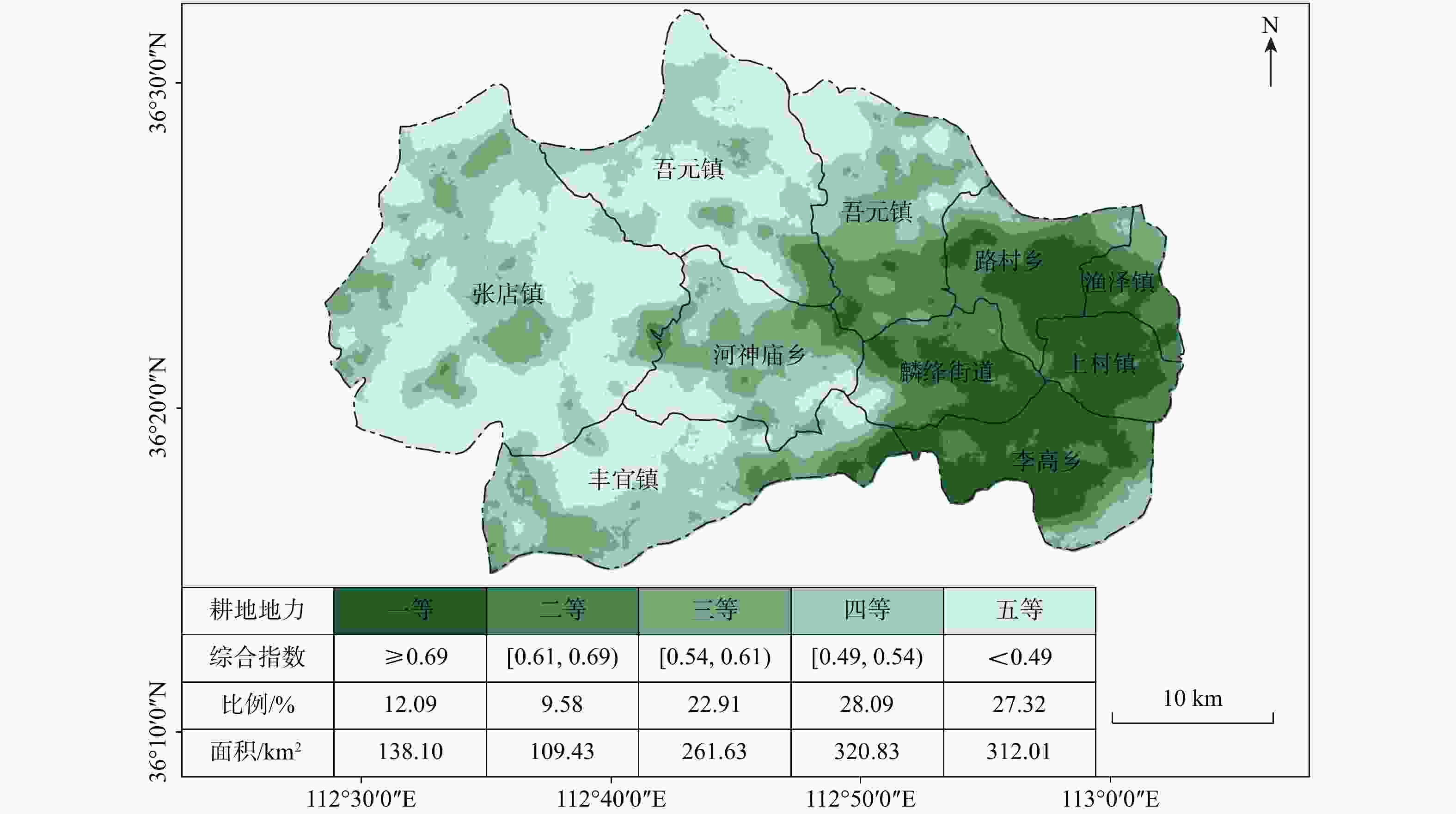
Results The results show that: ① the land with soil selenium content grades of high selenium and moderate selenium in Tunliu District accounted for 54.47% of the statistical area, and these soils were concentrated in the eastern part of the district; the distribution of cultivated land strength grades in Tunliu District was uneven, and the overall characteristics showed that it was low in the western part and high in the eastern part; the results of the evaluation of ecological environment grades were clean in the whole district. ② There are 299.33 square kilometers of selenium-enriched land in Tunliu District with comprehensive quality grade of first class, accounting for 26.61% of the statistical area, and concentrating in the plain area in the east. ③ Wheat, sharp peppers and green peppers in Tunliu have reached the standard of selenium enrichment of crops. Among them, the selenium enrichment rate of sharp peppers is 100%. In addition, the results of heavy metal element testing show that the crops in the district are in good clean condition.
Conclusion Based on the evaluation results of land and crops, and in conjunction with the spatial planning of land in Tunliu District, the land is divided into three types: A, B and C. Among them, type A land is characterized by high soil selenium content, rich nutrients and clean environment, so it is recommended to build selenium-enriched wheat and green vegetable planting bases in the area where this type of land is concentrated and develop tourism agriculture at the same time. Class C land is characterized by low soil selenium and nutrient content, which is unsuitable for planting crops, so it is recommended to build deep-processing factories for agricultural products in the areas where this type of land is concentrated, and to develop agricultural trade and tourism at the same time. It provides theoretical support and scientific suggestions for the planning of selenium-rich agriculture industry in Tunliu District and the synergistic development of the region.
-
表 1 耕地地力指标相关系数矩阵
Table 1. Matrix of correlation coefficients of indicators of land productivity of arable land
指标 氮 有效磷 速效钾 有机质 pH 地形部位 土壤质地 利用现状 氮 1 有效磷 0.301** 1 速效钾 0.366** 0.445** 1 有机质 0.591** 0.190** 0.253** 1 pH 0.004 0.019 0.011 0.099** 1 地形部位 0.127** 0.174** 0.119** 0.206** 0.298** 1 土壤质地 0.140** 0.080** 0.001 0.158** 0.125** 0.312** 1 利用现状 0.184** 0.134** 0.072** 0.298** 0.320** 0.568** 0.350** 1 注:**在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著 表 2 屯留区富硒土地综合质量评价体系及指标权重
Table 2. Evaluation system of comprehensive quality of selenium-rich land in Tunliu District and weights of indicators
目标层 准则层 指标层 富硒土地
综合质量富硒产业质量
(0.394)土壤硒 生态环境
(0.001)土壤环境
(砷、镉、汞、铅、铬、镍、铜、锌)耕地地力
(0.604)氮(0.10) 有效磷(0.11) 速效钾(0.01) 有机质(0.22) pH(0.08) 地形部位(0.07) 土壤质地(0.02) 利用现状(0.39) 注:括号中数据代表权重 表 3 土壤生态环境等级评价划分标准
Table 3. Criteria for classifying soil environmental grades
等级 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 清洁 轻微污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 单因子污染指数P单 ≤1 (1,2] (2,3] (3,5] >5 综合污染指数P综 ≤0.7 (0.7,1] (1,2] (2,3] >3 表 4 概念型指标隶属度
Table 4. Conceptual indicator affiliation
指标 隶属度 地形部位 平原 盆地 低山丘陵 山地 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 土壤质地 中壤土 轻壤土 重壤土 砂壤土、粘壤土、粘土 砂土 1 0.85 0.8 0.6 0.4 利用现状 水浇地 旱地 1 0.7 表 5 数值型指标隶属度计算方法及函数转折点
Table 5. Numerical indicator affiliation calculation method and function turning points
耕地地力
指标计算公式 函数转折点 x1 x2 x3 x4 氮 $ f\left(x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{c}\quad\qquad\ 1.0,x\ge {x}_{2}\\\dfrac{0.9\left(x-{x}_{1}\right)}{{x}_{2}-{x}_{1}}+0.1,{x}_{1}\le x < {x}_{2}\\ \quad\qquad\ \ 0.1,x < {x}_{1}\end{array}\right. $ 0.75 2 有效磷 5 40 速效钾 50 200 有机质 10 40 pH $ f\left(x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{c}\dfrac{0.9\left({x}_{4}-x\right)}{{x}_{4}-{x}_{3}}+0.1,{x}_{3}\le x < {x}_{4}\\\qquad\qquad\ \ \ \ \ 1.0,{x}_{2} < x < {x}_{3}\\\dfrac{0.9\left(x-{x}_{1}\right)}{{x}_{2}-{x}_{1}}+0.1,{x}_{1}\le x < {x}_{2}\\\quad\qquad\ \ 0.1,x < {x}_{1}\end{array}\right. $ 5.5 6.5 7.5 8.5 注:氮、有机质单位为g/kg,有效磷、速效钾单位为mg/kg,pH为无量纲;x为指标实测值;x1、x2、x3、x4分别为评价因子在函数曲线中转折点取值。 表 6 富硒土地综合质量评价指标隶属度
Table 6. Affiliation of indicators for comprehensive evaluating selenium-rich land quality
准则层指标 隶属度 隶属度函数转折点 x1 x2 富硒产业质量 $f\left(x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{c}\quad\qquad\ 1.0,x\ge {x}_{2}\\\dfrac{0.9\left(x-{x}_{1}\right)}{{x}_{2}-{x}_{1}}+0.1,{x}_{1}\le x < {x}_{2}\\ \quad\qquad\ \ 0.1,x < {x}_{1}\end{array}\right. $ 0.125 0.3 生态环境 0.7 1 耕地地力 0.48 0.69 表 7 屯留区富硒土地综合质量评价结果
Table 7. Results of the comprehensive quality assessment of selenium-rich land in Tunliu District
区域 总面积/
km2等级 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 张店镇 319.69 比例/% 0 0.02 15.28 37.03 53.30 面积/km2 0 0.02 14.14 105.98 199.65 吾元镇 160.39 比例/% 0.40 6.28 6.93 21.49 22.84 面积/km2 1.21 5.61 6.41 61.49 85.57 余吾镇 119.84 比例/% 9.27 29.59 25.45 10.06 3.52 面积/km2 27.74 26.44 23.55 28.80 13.17 路村乡 69.90 比例/% 20.16 6.32 3.31 0.32 0 面积/km2 60.34 5.65 3.06 0.91 0 渔泽镇 30.02 比例/% 9.88 0.32 0 0 0 面积/km2 29.57 0.28 0 0 0 河神庙乡 101.26 比例/% 1.51 12.88 23.94 11.57 8.02 面积/km2 4.52 11.51 22.15 33.13 30.05 上村镇 43.57 比例/% 12.75 5.88 0.14 0 0 面积/km2 38.17 5.25 0.13 0 0 麟绛街道 64.29 比例/% 16.73 14.30 1.27 0.07 0 面积/km2 50.08 12.77 1.17 0.19 0 丰宜镇 146.38 比例/% 3.57 13.35 23.62 19.44 12.30 面积/km2 10.70 11.92 21.85 55.63 46.07 李高乡 86.64 比例/% 25.72 11.02 0 0 0 面积/km2 77.01 9.85 0 0 0 表 8 屯留区农作物及根系土硒元素特征统计
Table 8. Statistical of selenium characteristics of crops and root soil in Tunliu District
样品 种类 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变异系数 富集系数 富硒标准 富硒件数 富硒率/% 根系土 小麦 30 0.242 0.529 0.390 0.070 0.18 / >0.3 27 90.00 玉米 105 0.119 0.912 0.336 0.145 0.43 / 55 52.38 谷子 30 0.194 0.411 0.254 0.061 0.24 / 3 16.67 萝卜 15 0.290 0.407 0.357 0.031 0.09 / 14 93.33 白菜 15 0.315 0.359 0.343 0.012 0.04 / 15 100.00 茴子白 15 0.301 0.376 0.345 0.017 0.05 / 15 100.00 尖椒 15 0.099 0.461 0.269 0.093 0.35 / 7 46.67 青椒 15 0.301 0.423 0.377 0.031 0.08 / 15 100.00 农作物 小麦 30 0.026 0.138 0.062 0.025 0.40 0.16 ≥0.05 20 66.67 玉米 105 0.015 0.042 0.020 0.006 0.30 0.06 0 0 谷子 30 0.020 0.028 0.023 0.002 0.08 0.09 0 0 萝卜 15 0.001 0.003 0.002 0.000 0.18 0.01 ≥0.02 0 0 白菜 15 0.004 0.016 0.007 0.003 0.43 0.02 0 0 茴子白 15 0.006 0.016 0.009 0.003 0.30 0.03 0 0 尖椒 15 0.032 0.084 0.057 0.015 0.26 0.21 15 100.00 青椒 15 0.018 0.042 0.031 0.007 0.22 0.08 14 93.33 注:农作物富集系数为农作物元素含量平均值/根系土元素含量平均值,单位为mg/kg 表 9 屯留区作物重金属超标情况
Table 9. Exceedance of heavy metals in crops in Tunliu District
指标 样品 样本数 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准离差 变异系数 富集系数 安全限值 超标数 超标率/% 镉 尖椒 15 0.042 0.086 0.059 0.012 0.209 0.412 0.05 12 80.00 青椒 15 0.026 0.074 0.045 0.015 0.322 0.254 4 26.67 铬 尖椒 15 0.516 1.050 0.670 0.143 0.213 0.010 0.5 15 100.00 青椒 15 0.322 0.588 0.445 0.077 0.174 0.007 2 13.33 铅 萝卜 15 0.040 0.111 0.078 0.023 0.299 0.003 0.1 2 13.33 尖椒 15 0.182 0.472 0.252 0.078 0.308 0.010 15 100.00 青椒 15 0.146 0.272 0.203 0.037 0.183 0.008 15 100.00 注:农作物富集系数为农作物元素含量平均值/根系土元素含量平均值;单位:mg/kg -
[1] XU Z N,LIN Z Q,ZHAO G S,et al. Biogeochemical behavior of selenium in soil-air-water environment and its effects on human health[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2024,21(1):1159-1180. doi: 10.1007/s13762-023-05169-0 [2] EKUMAH J N,MA Y K,AKPABLI-TSIGBE N D K,et al. Global soil distribution,dietary access routes,bioconversion mechanisms and the human health significance of selenium:A review[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,41:100960. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.100960 [3] CHEN N,ZHAO C H,ZHANG T H. Selenium transformation and selenium-rich foods[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,40:100875. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100875 [4] BOUMA J. Soil security in sustainable development[J]. Soil Systems,2019,3(1):5. doi: 10.3390/soilsystems3010005 [5] 王新峰,龚磊,刘元晴,等. 水土质量调查评价与人群健康关系的融合路径研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):305-314.WANG X F,GONG L,LIU Y Q,et al. Integration path research of water and soil quality investigation and evaluation and human health relationship[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):305-314. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] YU T,HOU W L,HOU Q Y,et al. Safe utilization and zoning on natural selenium-rich land resources:A case study of the typical area in Enshi County,China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2020,42(9):2803-2818. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00519-0 [7] 汤奇峰,徐春丽,刘斯文,等. 江西赣州市瑞金盆地天然富硒土地资源特征与保护利用[J]. 地质通报,2020,39(12):1932-1943.TANG Q F,XU C L,LIU S W,et al. Characteristics and protection and utilization of natural selenium-rich land resources in Ruijin Basin,Ganzhou,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2020,39(12):1932-1943. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 土地质量地球化学评价规范:DZ/T 0295-2016[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2016.Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. Specification for geochemical evaluation of land quality:DZ/T 0295-2016[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] LIU Y L,LIU S L,ZHAO W,et al. Assessment of heavy metals should be performed before the development of the selenium-rich soil:A case study in China[J]. Environmental Research,2022,210:112990. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112990 [10] 徐雪生,骆检兰,黄逢秋,等. 富硒耕地质量评价体系构建及其在湖南省新田县新圩镇的应用[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(3):789-801.XU X S,LUO J L,HUANG F Q,et al. Construction of the evaluation system for Se-rich arable land and its application in Xinxu Town,Xintian County,Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(3):789-801. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 杨晓帆,蔡海生,张学玲,等. 富硒耕地质量综合评价及利用分区研究:以宜春市袁州区为例[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2023,45(2):482-493.YANG X F,CAI H S,ZHANG X L,et al. Study on comprehensive evaluation and zoning of selenium-enriched arable land quality:A case study of Yuanzhou District,Yichun[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2023,45(2):482-493. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 农业灌溉水质标准:GB 5084-2021[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2021.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Agricultural irrigation water quality standards:GB 5084-2021[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 天然富硒土地划定与标识(试行):DD 2019-10[S]. 北京:中国地质调查局,2019.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China, China Geological Survey. Delimitation and the logo for natural selenium-enriched land:DD 2019-10[S]. Beijing:China Geological Survey,2019. [14] 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 中华人民共和国市场监督管理局. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行):GB 15618-2018[S]. 北京:中国环境出版社 ,2018.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, Administration for Market Regulation of the People's Republic of China. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land:GB 15618-2018[S]. Beijing:China Environment Press,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 邹山进洪. 闽侯县表层土壤及农产品硒含量特征[J]. 物探与化探,2023,47(1):247-256.ZOU S. Selenium contents in surface soil and agricultural products in Minhou County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2023,47(1):247-256. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] FU Z B,HE N J,MA M,et al. Source apportionment and probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metals in selenium-rich soils in Hainan Province,China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2023,251:107241. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2023.107241 [17] ZHAO R,WU K N,LI X L,et al. Discussion on the unified survey and evaluation of cultivated land quality at county scale for China’s 3rd national land survey:A case study of Wen County,Henan Province[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(5):2513. doi: 10.3390/su13052513 [18] 赵洪宝,蒋冬梅,李岳,等. 河曲露天矿排土场不同复垦区土壤质量评价[J]. 矿业科学学报,2023,8(3):419-427.ZHAO H B,JIANG D M,LI Y,et al. Evaluation of soil quality in different reclamation areas of Hequ open-pit mine dump[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2023,8(3):419-427. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 庞馨月. 巴彦淖尔市耕地地力评价[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2021.PANG X Y. Evaluation of cultivated land fertility in Bayannur City[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 陕西省市场监督管理局,陕西省质量技术监督局. 富硒含硒食品与相关产品硒含量标准:DB61/T 556-2018[S]. 陕西,陕西省地方标准出版社,2018Shaanxi Provincial Administration for Market Regulation,Shaanxi Provincial Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Selenium-rich selenium-containing foods and related products selenium content standards:DB61/T 556-2018[S]. Shanxi,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 中华人民共和国市场监督管理总局,中华人民共和国卫生健康委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量:GB 2762-2017[S]. 北京,中国标准出版社,2017.State Administration for Market Regulation of the People's Republic of China, Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. National Food Safety Standard Limits for Contaminants in Food:GB 2762-2017[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] TAN J A,ZHU W Y,WANG W Y,et al. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2002,284(1/3):227-235. [23] 时章亮,金立新,廖超,等. 四川雷波县重点耕地区土壤硒含量特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探,2020,44(5):1253-1260.SHI Z L,JIN L X,LIAO C,et al. Content characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in important cultivated areas of Leibo County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2020,44(5):1253-1260. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 武芝亮,李致坤,侯青叶,等. 四川省邻水县土壤及作物硒地球化学特征及其研究意义[J]. 现代地质,2021,35(6):1752-1761.WU Z L,LI Z K,HOU Q Y,et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils and crops and its research significance in Linshui County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(6):1752-1761. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 侯拓. 安康西部县域土壤−作物体系中硒镉影响因素及土地安全区划研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2020.HOU T. Study on selenium and cadmium influencing factors and soil safety in the soil-crop system in the western county of Ankang[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] LI M L,YANG B Y,XU K Y,et al. Distribution of Se in the rocks,soil,water and crops in Enshi County,China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2020,122:104707. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104707 [27] 陈继平,钞中东,任蕊,等. 陕西关中富硒土壤区农作物重金属含量相关性及安全性评价[J]. 西北地质,2021,54(2):273-281.CHEN J P,CHAO Z D,REN R,et al. Correlation and safety evaluation of crop heavy metal content in Shaanxi Guanzhong selenium-enriched areas[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021,54(2):273-281. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] MA L,ABUDUWAILI J,LIU W. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in surface soils of Bosten Lake Basin,central Asia[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2019,16(19):3741. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193741 [29] KHORSHIDI N,PARSA M,LENTZ D R,et al. Identification of heavy metal pollution sources and its associated risk assessment in an industrial town using the K-means clustering technique[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2021,135:105113. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105113 [30] 覃星铭,马国斌,蒋忠诚,等. 典型石漠化峰丛洼地土壤重金属的空间分异特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(5):283-292.QIN X M,MA G B,JIANG Z C,et al. Spatial variations and influencing factors analysis of heavy metals in the soil of typical rocky desertification peak cluster depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(5):283-292. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] XIANG M T,LI Y,YANG J Y,et al. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,278:116911. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116911 [32] WANG X J,LI W B,WANG D Y,et al. Trinity assessment method applied to heavy-metal contamination in peri-urban soil-crop systems:A case study in NorthEast China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2021,132:108329. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108329 [33] 邓远文,江林香. 基于熵权−层次分析法的土壤质量综合评价:以甘洛县松树坪村为例[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2023,41(4):33-35.DENG Y W,JIANG L X. Comprehensive evaluation of soil quality based on entropy weight-analytic hierarchy process:Taking songshuping village in Ganluo County as an example[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2023,41(4):33-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] KUSHWAHA A,GOSWAMI L,LEE J,et al. Selenium in soil-microbe-plant systems:Sources,distribution,toxicity,tolerance,and detoxification[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology,2022,52(13):2383-2420. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2021.1883187 [35] ULLAH H,LIU G J,YOUSAF B,et al. A comprehensive review on environmental transformation of selenium:Recent advances and research perspectives[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2019,41(2):1003-1035. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0195-8 [36] 张亚丽,张志敏,张继军,等. 安康西部农田土壤硒形态及农作物富硒特征[J]. 西北地质,2021,54(3):229-235.ZHANG Y L,ZHANG Z M,ZHANG J J,et al. Soil selenium speciation in cropland of western Ankang and the characteristics of crop selenium enrichment[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021,54(3):229-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] LI D X,LIU G N,LI X S,et al. Heavy metal(loid)s pollution of agricultural soils and health risk assessment of consuming soybean and wheat in a typical non-ferrous metal mine area in NorthEast China[J]. Sustainability,2022,14(5):2953. doi: 10.3390/su14052953 [38] TITOV A F,KAZNINA N M,KARAPETYAN T A,et al. Role of selenium in plants,animals,and humans[J]. Biology Bulletin Reviews,2022,12(2):189-200. doi: 10.1134/S2079086422020104 [39] KAZI TANI L S,DENNOUNI-MEDJATI N,TOUBHANS B,et al. Selenium deficiency:From soil to thyroid cancer[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(15):5368. doi: 10.3390/app10155368 [40] KUMAR A,PRASAD K S. Role of nano-selenium in health and environment[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2021,325:152-163. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.11.004 [41] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试,2020,39(3):319-336.ZHOU G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2020,39(3):319-336. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 张俊,戴亮亮,巩浩,等. 基于预测农作物Se含量构建富硒土地质量评价体系:以湖南龙山县为例[J/OL]. 中国地质,1-16[2025-02-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20221008.1839.006.html.ZHANG J,DAI L L,GONG H,et al. Construction of Se-enriched land quality evaluation system based on predicted Se content in crops:A case study of Longshan County,Hunan Province[J/OL]. Geology in China,1-16[2025-02-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20221008.1839.006.html. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 曾庆良. 湖北省恩施市沙地乡富硒土地安全利用区划研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018.ZENG Q L. Study on the safe utilization of selenium-rich land resources in Shadi County,Enshi City,Hubei Province[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] XIE S Y,WAN X,DONG J B,et al. Quantitative prediction of potential areas likely to yield Se-rich and Cd-low rice using fuzzy weights-of-evidence method[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2023,889:164015. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164015 [45] LIANG R Y,SONG S,SHI Y J,et al. Comprehensive assessment of regional selenium resources in soils based on the analytic hierarchy process:Assessment system construction and case demonstration[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,605:618-625. [46] TOOR G S,YANG Y Y,DAS S,et al. Chapter Four:Soil health in agricultural ecosystems:Current status and future perspectives[J]. Advances in Agronomy,2021,168:157-201. [47] 屯留区人民政府. 屯留县国土空间总体规划(2021-2035年) [R]. 长治:屯留区人民政府,2023.The People's Government of Tunliu District. Tunliu County Land and Space Master Plan (2021-2035) [R]. Changzhi The People's Government of Tunliu District,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [48] 黎莉莉,胡晓群,陈松柏. 新世纪中国粮食生产特征及粮食安全政策取向[J]. 宏观经济研究,2023(1):70-83.LI L L,HU X Q,CHEN S B. Characteristics of China’s grain production and grain security policy orientation in the new century[J]. Macroeconomics,2023(1):70-83. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 万继磊,李密,徐立甫. 辣椒地土壤重金属含量与植株重金属富集的相关性研究[J]. 耕作与栽培,2022,42(6):91-93.WAN J L,LI M,XU L F. Study on the correlation between heavy metal content in pepper field soil and plant metal enrichment[J]. Tillage and Cultivation,2022,42(6):91-93. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: