Geological characteristics, controlling factors and prospecting directions of associated cobalt deposits in the Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia
-
摘要:
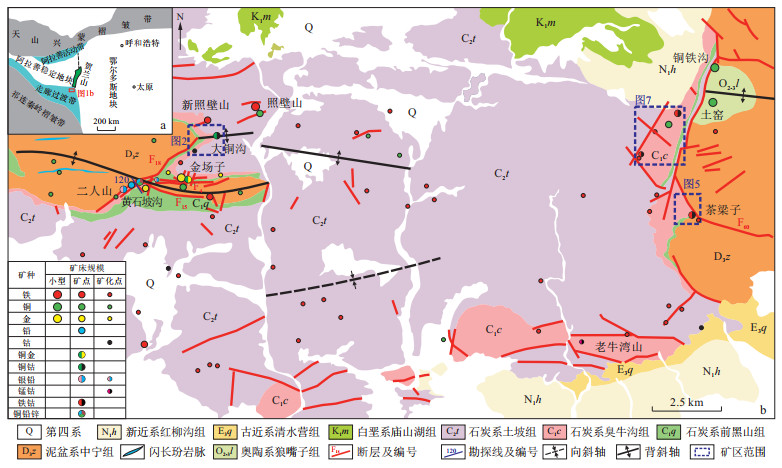
卫宁北山地区位于北祁连造山带东段, 是宁夏境内钴矿成矿条件最好的地区之一。为详细了解该地区钴矿形成条件及矿化规律, 在详细野外调查基础上, 综合前人勘查成果, 对卫宁北山地区典型伴生钴矿床地质特征、控矿因素及时空分布规律进行了总结, 提出了下一步找矿方向。研究表明: 大铜沟铜钴矿、茶梁子铁钴矿和土窑铁钴矿是该地区目前已发现的3个代表性伴生钴矿床, 其中大铜沟铜钴矿共发现铜钴矿体3个, Co品位最高达0.06%, 含钴矿物主要为辉砷钴矿、含钴黄铁矿和含钴褐铁矿; 茶梁子铁钴矿分布有4条矿带共8个铁钴矿体, Co品位最高达0.03%, 含钴矿物主要为含钴褐铁矿; 土窑铁钴矿只发现1条铁钴矿体, Co品位最高为0.20%, 含钴矿物与茶梁子相似。钴矿受断裂构造控制明显, 其中西部主要受EW向断裂及其与NE向断裂联合控制, 东部主要受SN向断裂控制。钴矿主要赋存于上石炭统土坡组中, 为主要矿源层; 岩性控矿主要表现在"硅钙面"和能干性不同的岩性组合界面, 控制了矿质沉淀。钴矿化形成时间主要为印支期, Co成矿主要与Cu、Au、Fe和Mn关系密切, 且与Cu、Au有关的钴矿主要分布于西部, 而与Fe、Mn有关的钴矿分布于东部。多期构造叠加及热液改造可能是造成该地区矿种多样的主要原因。卫宁北山西部EW向断裂及其与NE向断裂交汇部位、东部SN向石炭系和泥盆系界面断裂、土坡组内"硅钙面"和能干性不同的岩性组合界面是寻找钴矿最有利部位, 孔雀石化、褐铁矿化等围岩蚀变是铜钴矿、铁钴矿最重要的找矿标志。
Abstract:Weiningbeishan is located in the eastern section of the North Qilian orogenic belt, which is one of the regions with the most favorable conditions for cobalt mineralization in Ningxia.
Objective To understand the formation conditions and mineralization regularity of cobalt deposits in this area,
Methods this paper summarizes the geological characteristics, controlling factors, and spatiotemporal distribution patterns of typical associated cobalt deposits in Weiningbeishan based on detailed field investigations and previous exploration results and proposes future exploration directions.
Results Research has shown that the Datonggou copper cobalt deposit, Chaliangzi iron cobalt deposit, and Tuyao iron cobalt deposit are currently three representative associated cobalt deposits discovered in Weiningbeishan area. Among them, three copper cobalt ore bodies were discovered in Datonggou, with the highest Co grade of 0.06%. Cobalt-bearing minerals mainly include pyroxenite, cobalt-bearing pyrite and cobalt-bearing limonite. There are 4 ore belts and 8 iron cobalt ore bodies are distributed in Chaliangzi, with the highest Co grade of 0.03%. The cobalt-bearing minerals are mainly cobalt-bearing limonite. Only one iron cobalt ore body was found in Tuyao, with the highest Co grade of 0.20%. The cobalt-bearing minerals are similar to those of Chaliangzi. Cobalt mineralization is evidently controlled by faults, with the western cobalt deposit mainly controlled by east-west faults and their combined control with northeast faults, while the eastern cobalt deposits are mainly controlled by north-south faults. Cobalt ore are mainly found in the Upper Carboniferous Tupo Formation, which was the main source strata. Lithological control is mainly observed at the "silica-calcium interface" and the lithological combination interface with different competence, which controlled the mineral precipitation. The cobalt metallogenic era was the Indosinian. Cobalt was closely related to Cu, Au, Fe and Mn. Cobalt related to Cu and Au were mainly distributed in the west, while cobalt related to Fe and Mn were mainly distributed in the east. The diversity of mineral species in this region may be attributed to the multistage superimposition of structures and hydrothermal activity.
Conclusion The most favourable locations for identifying cobalt deposits are the east-west faults and their intersections with the northeast faults in the western part, the north-south Carboniferous and Devonian interface faults in the eastern part, the " silica-calcium interface " within the Tupo Formation, and the lithological combination interfaces with different competence. Malachite alteration and ferritization are the most important prospecting indicators for copper cobalt deposits and iron cobalt deposits.
-
图 2 大铜沟铜钴矿区地质简图(据文献[26]修改)
Figure 2. Simplified geological map of the Datonggou copper cobalt mining area
图 4 大铜沟铜钴矿典型矿石(体)特征及矿物组成(引自文献[35])
a.含钴铁质结核;b.含钴褐铁矿化透镜体;c.含钴黄铁矿石英脉;d.辉砷钴矿与辉铜矿共生;e.辉砷钴矿呈环带状交代含钴黄铁矿;f.含钴褐铁矿
Figure 4. Typical ore(body) characteristics and mineral composition of the Datonggou copper cobalt mine
图 5 茶梁子铁钴矿区地质简图(a)及203号勘探线剖面图(b) (据文献[36]修改)
Figure 5. Simplified geological map(a) and profile of exploration Line 203(b) of the Chaliangzi iron cobalt mine area
图 6 茶梁子铁钴矿石(体)特征(a~b引自文献[36])
a.F61断层破碎带;b.铁钴矿(化)体氧化露头;c~f.角砾岩型铁钴矿石,其中c、e和f由胶结物形成
Figure 6. Characteristics of ore(body) from the Chaliangzi iron cobalt mine
图 7 土窑铁钴矿区地质简图(a)及301号勘探线剖面图(b) (据文献[36]修改)
Figure 7. Simplified geological map(a) and profile of exploration Line 301(b) of the Tuyao iron cobalt mine area
图 10 二人山-大铜沟一带1∶25 000钴岩石测量地球化学图(据文献[35]修改)
Figure 10. Geochemical map of cobalt from 1∶25 000 rock measurements in Errenshan-Datonggou area
图 11 宁夏卫宁北山1∶50 000水系沉积物综合异常图(据文献[36]修改)
Figure 11. Comprehensive anomaly map of 1∶50 000 stream sediment in Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia
图 12 宁夏卫宁北山西部构造控矿模式图(据文献[41]修改)
Figure 12. Structure-controlling model in the western part of Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia
表 1 大铜沟铜钴矿主要铜钴矿体特征 [35]
Table 1. Characteristics of main copper cobalt ore body in the Datonggou copper cobalt mine
矿体编号 位置 赋矿地层及含矿岩性 规模/m 产状/(°) 真厚度/m 平均品位wB/% 长度 斜深 倾向 倾角 Cu Co Ⅰ号 大铜沟背斜南翼 石炭系土坡组(C2t),褐铁矿化石英岩状砂岩和褐铁矿化粉砂岩 200 40* 145 65 2.50 — 0.03 Ⅱ号 大铜沟背斜南翼 断层破碎带,断层角砾岩 100 40* 140 80 7.91 — 0.03 54号 大铜沟背斜倾伏端 石炭系土坡组(C2t),灰白色富含黄铁矿石英岩状砂岩、含黄铁矿石英脉 200* 154* 100 57 7.78 0.47 0.06 注:“*”代表推测值;“—”代表无数据 表 2 茶梁子铁钴矿主要铁钴矿体特征 [36]
Table 2. Characteristics of main iron cobalt ore body in the Chaliangzi iron cobalt mine
矿带编号 矿体编号 赋矿地层及含矿岩性 规模/m 埋深/m 产状/(°) 平均品位(品位)wB/% 长度 真厚度 倾向 倾角 TFe Co Ⅰ Ⅰ-1 泥盆系中宁组第六岩性段(D3z6),褐铁矿化构造角砾岩、断层泥及石英砂岩透镜体夹层 123* 2.88 42.32 260 80 32.98 0.03 Ⅰ-2 123* 3.45 52.42 270 83 26.30 0.02 Ⅰ-3 123* 2.01 61.93 270 83 — 0.02 Ⅰ-4 648 13.57 0 270 83 30.25 0.02 Ⅱ Ⅱ-1 505 6.95 0 270 80 28.41 0.01 Ⅱ-2 540 6.25 0 270 83 35.58 0.02 Ⅲ Ⅲ-1 石炭系前黑山组(C1q),褐铁矿化构造角砾岩、断层泥及石英砂岩透镜体夹层 100* 5.31 0 235 65 10.67~47.50 0.01~0.03 Ⅳ Ⅳ-1 石炭系臭牛沟组(C1c),褐铁矿化构造角砾岩、断层泥及石英砂岩透镜体夹层 20* 0.76 0 320 86 29.10 0.01 注:“*”代表推测值;“—”代表无数据 表 3 金场子矿区化探剖面测量钴含量(异常)统计结果
Table 3. Statistical results of Co content(anomaly) in geochemical profile measurement of Jinchangzi mining area
取样位置 达到异常样品数 主要岩性 w(Co)/10-6 区间值 平均值 最大值 金场子南部76勘探线探槽TC7601 4 粉砂岩 66.7~81.7 73.9 81.7 金场子南部75勘探线探槽TC7502 14 粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩 22.2~127.0 41.0 127.0 金场子南部74勘探线西侧 7 泥质粉砂岩 23.5~76.9 39.9 76.9 金场子南部71勘探线 2 钙质粉砂岩 22.0~56.8 39.4 56.8 金场子南部69勘探线 5 泥岩、灰岩 21.1~57.8 43.0 57.8 金场子南部65勘探线 4 粉砂质泥岩 20.0~28.2 23.8 28.2 金场子西部35勘探线 10 弱硅化泥岩、石英砂岩 25.5~205.0 70.5 205.0 金场子西部38勘探线 3 粉砂岩 22.4~34.2 27.9 34.2 金场子西部39勘探线 10 泥岩 20.8~111.0 51.4 111.0 金场子西部93勘探线 5 构造角砾岩 20.1~65.9 41.3 65.9 金场子西部92勘探线 8 构造角砾岩、泥质粉砂岩 21.0~79.8 44.5 79.8 金场子西部35勘探线斜井XJ12 20 粉砂岩 20.1~135.0 43.3 135.0 金场子西部35勘探线斜井XJ12内XJ12-1沿脉 15 矿化破碎带(断层泥) 21.6~177.0 78.3 177.0 注:钴异常品位边界为20×10-6 -
[1] 赵俊兴, 李光明, 秦克章, 等. 富含钴矿床研究进展与问题分析[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(24): 2484-2500.ZHAO J X, LI G M, QIN K Z, et al. A review of the types and ore mechanism of the cobalt deposits[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(24): 2484-2500. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 刘东盛, 王学求, 周建, 等. 中国钴地球化学基准值特征及影响因素[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6): 807-817.LIU D S, WANG X Q, ZHOU J, et al. Characteristics of China's cobalt geochemical baselines and their influence factors[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 807-817. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 阎磊, 范裕, 刘一男. 安徽庐枞盆地龙桥铁矿床中钴的赋存状态和空间分布规律[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(9): 2778-2796.YAN L, FAN Y, LIU Y N. The occurrence and spatial distribution of cobalt in Longqiao iron deposit in Luzong Basin, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(9): 2778-2796. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral commodity summaries 2023[R]. Reston, Virginia: U.S. Geological Survey, 2023. [5] 曹明坚, 单鹏飞, 秦克章. 富钴斑岩型金铜矿床地质特征及存在问题: 以黑龙江金厂矿床为例[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(31): 3708-3723.CAO M J, SHAN P F, QIN K Z. Cobalt-rich characteristics and existing problems of porphyry gold-copper deposit: A case study of Jinchang deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(31): 3708-3723. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] GULLEY A L, MCCULLOUGH E A, SHEDD K B. China's domestic and foreign influence in the global cobalt supply chain[J]. Resources Policy, 2019, 62: 317-323. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.03.015 [7] SOVACOOL B K, ALI S H, BAZILIAN M, et al. Sustainable minerals and metals for a low-carbon future[J]. Science, 2020, 367: 30-33. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz6003 [8] 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.LIU Y J, CAO L M, LI Z L, et al. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984. (in Chinese) [9] WÄNKE H, DREIBUS G, JAGOUTZ E. Mantle chemistry and accretion history of the earth[C]//Anon. Archaean geochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984: 1-24. [10] SALTERS V J M, STRACKE A. Composition of the depleted mantle[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2004, 5(5): Q05B07. [11] 翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 等. 战略性关键金属矿产资源: 现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 106-111.ZHAI M G, WU F Y, HU R Z, et al. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(2): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 汤中立, 钱壮志, 姜常义, 等. 中国镍铜铂岩浆硫化物矿床与成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006.TANG Z L, QIAN Z Z, JIANG C Y, et al. Magmatic Ni-Cu-Pge sulphide deposits and metallogenic prognosis in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006. (in Chinese) [13] SLACK J F, KIMBALL B E, SHEDD K B. Cobalt[R]. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 2017. [14] 苏本勋, 秦克章, 蒋少涌, 等. 我国钴镍矿床的成矿规律、科学问题、勘查技术瓶颈与研究展望[J]. 岩石学报, 2023, 39(4): 968-980.SU B X, QIN K Z, JIANG S Y, et al. Mineralization regularity, scientific issues, prospecting technology and research prospect of Co-Ni deposits in China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2023, 39(4): 968-980. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 许德如, 王智琳, 聂逢君, 等. 中国钴矿资源现状与关键科学问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 125-132.XU D R, WANG Z L, NIE F J, et al. Cobalt resources in China: Current research status and key scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(2): 125-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 丰成友, 张德全. 世界钴矿资源及其研究进展述评[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(6): 627-633. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.06.020FENG C Y, ZHANG D Q. Cobalt mineral resources in the world and advance of the research on cobalt deposits[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(6): 627-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.06.020 [17] 付浩, 王加昇, 李金龙, 等. 全球钴矿资源时空分布及成因类型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(1): 1-22. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220431FU H, WANG J S, LI J L, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and genesis types of global cobalt resources[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(1): 1-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220431 [18] 张洪瑞, 侯增谦, 杨志明, 等. 钴矿床类型划分初探及其对特提斯钴矿带的指示意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(3): 501-510.ZHANG H R, HOU Z Q, YANG Z M, et al. A new division of genetic types of cobalt deposits: Implications for Tethyan cobalt-rich belt[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(3): 501-510. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 周涛发, 范裕, 陈静, 等. 长江中下游成矿带关键金属矿产研究现状与进展[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 3665-3677.ZHOU T F, FAN Y, CHEN J, et al. Critical metal resources in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(33): 3665-3677. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 艾宁. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子金矿矿床地质与地球化学研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014.AI N. Studies on the geochemical and geological characteristics of Weiningbeishan Jingchangzi gold deposit[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 吴文忠, 孟方, 王红, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山钴异常的物质来源研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2013, 44(4): 485-489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2013.04.017WU W Z, MENG F, WANG H, et al. Research on material sources of cobalt abnormality in the Weining Beishan of Ningxia[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2013, 44(4): 485-489. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2013.04.017 [22] 刘志坚. 宁夏卫宁北山金、铅、银多金属矿成矿地质特征[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.LIU Z J. Metallogenic characteristics of Weiningbeishan Au-Pb-Ag polymetallic deposit in Ningxia Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 海连富, 刘金科, 李海峰, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山多金属矿床地质特征与找矿方向[J]. 湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 35(1): 30-39.HAI L F, LIU J K, LI H F, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting directing of Weiningbeishan polymetallic deposit, Ningxia[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 35(1): 30-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 海连富, 刘安璐, 陶瑞, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子金矿床流体来源及矿床成因: 来自流体包裹体和C-H-O同位素证据[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(12): 4274-4290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2021.12.dqkx202112005HAI L F, LIU A L, TAO R, et al. Source of fluid and genesis of jinchangzi gold deposit in Weiningbeishan, Ningxia: Evidence from fluid inclusions and C-H-O isotopes[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(12): 4274-4290. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2021.12.dqkx202112005 [25] 海连富, 陶瑞, 张晓军, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区金场子金矿区找矿模型及成矿预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 19-32. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0250HAI L F, TAO R, ZHANG X J, et al. Prospecting model and metallogenic prediction of the Jinchangzi gold deposit in the Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 19-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0250 [26] 宋新华, 李红宇. 宁夏中卫市大铜沟铜矿地质特征及控矿因素浅析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2009, 23(2): 118-123.SONG X H, LI H Y. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Datonggou copper deposit in Zhongwei City of Ningxia[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2009, 23(2): 118-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 王改平, 张玉霞, 王兴强. 卫宁北山地区钴矿地质特征及找矿前景[J]. 中国西部科技, 2014, 13(4): 24-26.WANG G P, ZHANG Y X, WANG X Q. Geological characteristics and prospecting prospect of cobalt deposits in the Beishan area of Weining[J]. Science and Technology of West China, 2014, 13(4): 24-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 张连昌, 张爱奎, 刘永乐, 等. 沉积岩-变沉积岩型钴矿研究进展与问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2023, 39(4): 981-997.ZHANG L C, ZHANG A K, LIU Y L, et al. Research progresses and problems of sedimentary-metasedimentary rock-hosted cobalt deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2023, 39(4): 981-997. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 霍福臣, 潘行适, 尤国林, 等. 宁夏地质概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.HUO F C, PAN X S, YOU G L, et al. Introduction to Ningxia geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. (in Chinese) [30] 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 1-23.PAN G T, LU S N, XIAO Q H, et al. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(6): 1-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 郭佩, 刘池洋, 韩鹏, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘下-中侏罗统碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(5): 892-907.GUO P, LIU C Y, HAN P, et al. Geochronology of detrital zircon from the Lower-Middle Jurassic strata in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China, and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(5): 892-907. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 刘勇, 李廷栋, 王彦斌, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山金场子闪长玢岩岩脉地质特征及SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(6): 1575-1583.LIU Y, LI T D, WANG Y B, et al. Geological characteristics and zircon SHRIMP U-Pb data of Jinchangzi dioritic porphyrite dykes in Zhongwei City, Ningxia[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(6): 1575-1583. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 艾宁, 任战利, 李文厚, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区矿床类型及成矿时代[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(5): 941-948.AI N, REN Z L, LI W H, et al. Metallogenic epoch and ore-forming types of ore deposits in Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(5): 941-948. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] LIU A L, HAI L F, LIU J K, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the diorite porphyrites from the Weining Beishan area, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region: Constraints on their source and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2024, 35(2): 462-475. [35] 马瑞赟, 潘进礼, 吴文忠, 等. 宁夏中卫市卫宁北山大铜沟铜钴矿普查报告[R]. 银川: 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2014.MA R B, PAN J L, WU W Z, et al. Survey report on Datonggou copper cobalt mine in Weiningbeishan, Zhongwei City, Ningxia[R]. Yinchuan: Geological Survey Institute of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, 2014. (in Chinese) [36] 王改平, 王泽晶, 王红, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区多金属矿调查报告[R]. 银川: 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2012.WANG G P, WANG Z J, WANG H, et al. Investigation report on polymetallic deposits in Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia[R]. Yinchuan: Geological Survey Institute of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, 2012. (in Chinese) [37] 赵鹏大, 池顺都, 李志德, 等. 矿床勘查理论与方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2001.ZHAO P D, CHI S D, LI Z D, et al. Theories and methods for mineral exploration[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2001. (in Chinese) [38] CAO H, SUN Z L, JIANG Z K, et al. Source origin and ore-controlling factors of hydrothermal sulfides from the Tianzuo hydrothermal field, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 134: 104168. [39] MUCHEZ P, CORBELLA M. Factors controlling the precipitation of copper and cobalt minerals in sediment-hosted ore deposits: Advances and restrictions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 118: 38-46. [40] 刘金科, 张晓军, 李海峰, 等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区金场子金矿床成因及成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2022.LIU J K, ZHANG X J, LI H F, et al. Genesis and metallogenic regularity of Jinchangzi gold deposit in Beishan area of Weining, Ningxia[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2022. (in Chinese) [41] 海连富. 宁夏卫宁北山地区金场子金矿床成因与找矿潜力评价[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2023.HAI L F. Genesis and prospecting potential evaluation of Jinchangzi gold deposit in Weiningbeishan area, Ningxia[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] DONG Y P, ZHANG G W, NEUBAUER F, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen, China: Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(3): 213-237. [43] 骆必继. 西秦岭造山带印支期岩浆作用及深部过程[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2013.LUO B J. Petrogenesis and geodynamic processes of the Indosinian magmatism in the West Qinling Orogenic Belt, central China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] 刘家军, 刘冲昊, 王建平, 等. 西秦岭地区金矿类型及其成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 1-16.LIU J J, LIU C H, WANG J P, et al. Classification and mineralization of the gold deposits in the western Qinling region, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(5): 1-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 张进. 陕甘宁地区古生代以来的构造及演化特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2002.ZHANG J. A study on the structures and evolution of the juncture area of Shaanxi, Gansu Province and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region since Paleozoic time[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2002. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] QIU Z J, FAN H R, GOLDFARB R, et al. Cobalt concentration in a sulfidic sea and mobilization during orogenesis: Implications for targeting epigenetic sediment-hosted Cu-Co deposits[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 305: 1-18. [47] 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院. 中国区域地质志: 宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.Geological Survey Institute of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Regional geology of China: Ningxia annals[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: