Research on the main control factors of carbon dioxide flooding and storage based on random forest algorithm
-
摘要:
在碳达峰、碳中和目标背景下, 二氧化碳驱油与封存是经济可行的碳减排的主要技术手段。明确影响二氧化碳驱油与封存效果的主控因素, 是实现二氧化碳高效驱油与封存的基础。在行业标准算例PUNQ-S3模型的基础上, 综合考虑二氧化碳与原油混相作用和二氧化碳构造、残余、溶解、矿化封存机理, 构建了二氧化碳提高原油采收率与地质封存一体化数值模拟模型, 结合随机森林智能算法, 开展了影响二氧化碳驱产油量和封存量的储层和生产参数特征重要性分析, 考虑驱油与封存时间尺度的差异, 建立了参数时序特征重要性分析方法, 实现了在不同二氧化碳驱油与封存阶段的主控因素分析。结果表明, 二氧化碳驱油与封存时序随机森林模型准确性高, 在二氧化碳驱油与封存前期, 二氧化碳构造封存量受储层含水饱和度控制, 溶解封存量受地层水矿化度控制; 在二氧化碳驱油与封存中、后期, 二氧化碳构造封存量则受储层渗透率控制, 溶解封存量则受储层渗透率与地层水矿化度控制; 残余封存量在二氧化碳驱油与封存前期较小, 导致其主控因素不明显, 在二氧化碳驱油与封存中后期受储层渗透率与含水饱和度控制; 二氧化碳矿化封存量在整个二氧化碳驱油与封存阶段受地层水pH值与矿化度控制; 二氧化碳驱油量在整个二氧化碳驱油与封存阶段受储层渗透率及含水饱和度控制。时序随机森林算法可以明确不同二氧化碳驱油与封存阶段的主控因素, 为二氧化碳提高原油采收率和地质封存的高效实施提供了技术支撑。
Abstract:Objective To achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals, carbon dioxide flooding and storage are the main technical means for carbon emission reduction. It is crucial to clarify the main controlling factors of carbon dioxide flooding and storage under reservoir conditions, which provides the basis for realizing the efficient development of carbon dioxide flooding and storage.
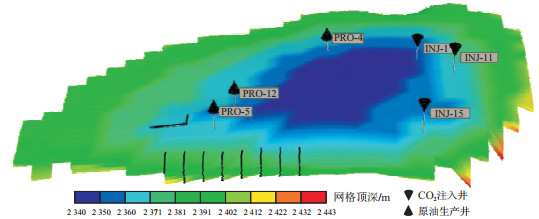
Methods In this study, with the widely used PUNQ-S3 case study as the basis, an integrated numerical simulation model of carbon dioxide flooding and geological storage is constructed. It considers the miscible interaction between carbon dioxide and crude oil as well as storage mechanisms, including structural, residual, dissolved, and mineral trapping. By employing the random forest intelligent algorithm, a feature importance analysis of reservoir and production parameters during the carbon dioxide flooding and storage process is carried out. The differences between carbon dioxide flooding and storage at different time scales are considered. A time series-based feature importance analysis method is established, and the main controlling factors in the different carbon dioxide flooding and storage stages are analysed. Through the fluctuation of the evaluation index, the influence of reservoir and production parameters on different stages of carbon dioxide flooding and storage is inferred.
Results The results show that the time series-based random forest model for carbon dioxide flooding and storage has high accuracy. In the early stage of carbon dioxide flooding and storage, the amount of carbon dioxide structural storage is controlled by the reservoir water saturation, and the amount of dissolved storage is controlled by the salinity of the formation brine; In the middle and later stages of carbon dioxide flooding and storage, the amount of carbon dioxide structural storage is controlled by reservoir permeability, while the amount of dissolved storage is controlled by reservoir permeability and formation water salinity; The residual storage capacity is small in the early stage of carbon dioxide flooding and storage, resulting in unclear main controlling factors.In the later stage of carbon dioxide flooding and storage, it is controlled by reservoir permeability and water saturation; The amount of mineralization storage is controlled by the pH value and the salinity of the formation brine throughout the entire CO2 flooding and storage stage; The amount of carbon dioxide production is controlled by reservoir permeability and water saturation throughout the entire carbon dioxide flooding and storage stage.
Conclusion The time-series-based random forest algorithm can identify the main controlling factors of different carbon dioxide flooding and storage stages and can provide support for cimproving crude oil recovery and implementing efficient geological storage with carbon dioxide.
-
表 1 拟组分划分结果
Table 1. Pseudo-components partition
序号 原油组分 拟组分 拟组分摩尔分数/% 1 CO2 CO2 1.01 2 H2S, N2, C1 C1_ 13.02 3 C2, C3 C2_3 13.63 4 IC4, NC4, IC5, NC5, FC6, C6H6, CC6 C4_6 22.71 5 FC7, FC8, FC9, NC7, NC8, NC9 C7_9 26.26 6 FC13-20 C13_20 12.65 7 FC21+ C21+ 10.72 注:IC.异烷烃; NC.正烷烃; FC.广义碳组分; C6H6.苯; CC6.环己烷 表 2 储层参数及生产参数
Table 2. Reservoir and production parameters
类型 名称 范围 储层参数 地层水pH值 6~8 地层水矿化度/(g·L-1) 20~200 初始含水饱和度 0.4~0.6 储层渗透率/10-3 μm2 50~100 生产参数 二氧化碳注入速率/(104 m3·d-1) 10~90 生产井关井时二氧化碳见气百分比阈值/% 20~90 -
[1] 秦积舜, 李永亮, 吴德斌, 等. CCUS全球进展与中国对策建议[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(1): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHDJ202401007.htmQIN J S, LI Y L, WU D B, et al. CCUS global progress and China's policy suggestions[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(1): 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHDJ202401007.htm [2] 张宏伟, 朱海波, 吴欣茹, 等. "双碳"目标下绿色清洁能源技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(5): 555-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.05.054ZHANG H W, ZHU H B, WU X R, et al. Status quo and future trends of green and clean energy technology toward "dual carbon" goal[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(5): 555-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.05.054 [3] 李阳. 低渗透油藏CO2驱提高采收率技术进展及展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202001002.htmLI Y. Technical advancement and prospect for CO2 flooding enhanced oil recovery in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202001002.htm [4] 胡文瑞, 魏漪, 鲍敬伟. 中国低渗透油气藏开发理论与技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4): 646-656. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804011.htmHU W R, WEI Y, BAO J W. Development of the theory and technology for low permeability reservoirs in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4): 646-656. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804011.htm [5] 叶航, 刘琦, 彭勃. 基于二氧化碳驱油技术的碳封存潜力评估研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(2): 107-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJMS202102010.htmYE H, LIU Q, PENG B. Research progress in evaluation of carbon storage potential based on CO2 flooding technology[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(2): 107-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJMS202102010.htm [6] 王栋. 碳达峰背景下我国石油化工企业参与碳排放权交易市场建设路径分析[J]. 现代管理科学, 2021(5): 3-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-368X.2021.05.002WANG D. Analysis on the participation of China's petrochemical enterprises into the constrction of carbon emission right trading market under the background of carbon peak[J]. Modern Management Science, 2021(5): 3-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-368X.2021.05.002 [7] 唐旭, 李依霖. 迈向零碳未来: 碳排放核算与管理研究综述[J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(4): 522-534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.04.040TANG X, LI Y L. Towards a zero-carbon future: A literature review of carbon emission accounting and management[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(4): 522-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2023.04.040 [8] CHEN Z, SU Y L, LI L, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of supercritical CO2 flooding under different factors in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Science, 2022, 19(3): 1174-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2022.01.016 [9] AL-ABRI A, AMIN R. Phase behaviour, fluid properties and recovery efficiency of immiscible and miscible condensate displacements by SCCO2 injection: Experimental investigation[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2010, 85(3): 743-756. doi: 10.1007/s11242-010-9589-5 [10] 李士伦, 汤勇, 侯承希. 注CO2提高采收率技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(3): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1426.2019.03.001LI S L, TANG Y, HOU C X. Present situation and development trend of CO2 injection enhanced oil recovery technology[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(3): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1426.2019.03.001 [11] YANG F, BAI B J, TANG D Z, et al. Characteristics of CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers[J]. Petroleum Science, 2010, 7(1): 83-92. doi: 10.1007/s12182-010-0010-3 [12] ALFREDO VISKOVIC V F, VLADIMIR V. Carbon capture and storage[J]. Energy, 2014, 70: 325-337. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.007 [13] 叶斌, 叶为民. 地下咸水层封存CO2的研究现状及展望[J]. 科技资讯, 2012, 10(36): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2012.36.049YE B, YE W M. Research status and prospect of CO2 sequestration in deep saline aquifer[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2012, 10(36): 66-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2012.36.049 [14] 高志豪, 赵锐锐, 成建梅. 砂岩含水层CO2封存中考虑盐沉淀反馈作用的数值模拟: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073GAO Z H, ZHAO R R, CHENG J M. Numerical simulation of CO2 sequestration in sandstone aquifers with feedback effect of salt precipitation: A case study of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0073 [15] BARKER J W, CUYPERS M, HOLDEN L. Quantifying uncertainty in production forecasts: Another look at the PUNQ-S3 problem[J]. SPE Journal, 2001, 6(4): 433-441. doi: 10.2118/74707-PA [16] 付晓泰, 王振平, 卢双舫, 等. 天然气在盐溶液中的溶解机理及溶解度方程[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(3): 89-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.03.018FU X T, WANG Z P, LU S F, et al. Mechanism of natural gas dissolving in brines and the dissolving equation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(3): 89-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.03.018 [17] LAND C S. Calculation of imbibition relative permeability for two-and three-phase flow from rock properties[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1968, 8(2): 149-156. doi: 10.2118/1942-PA [18] 王建秀, 吴远斌, 于海鹏. 二氧化碳封存技术研究进展[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2013, 9(1): 81-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201301015.htmWANG J X, WU Y B, YU H P. Review of the technology for sequestration of carbon dioxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2013, 9(1): 81-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201301015.htm [19] 王奕森, 夏树涛. 集成学习之随机森林算法综述[J]. 信息通信技术, 2018, 12(1): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OXXT201801009.htmWANG Y S, XIA S T. A survey of random forests algorithms[J]. Information and Communications Technologies, 2018, 12(1): 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OXXT201801009.htm [20] 吕红燕, 冯倩. 随机森林算法研究综述[J]. 河北省科学院学报, 2019, 36(3): 37-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBKX201903005.htmLV H Y, FENG Q. A review of random forests algorithm[J]. Journal of the Hebei Academy of Sciences, 2019, 36(3): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBKX201903005.htm [21] 姚登举, 杨静, 詹晓娟. 基于随机森林的特征选择算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(1): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201401024.htmYAO D J, YANG J, ZHAN X J. Feature selection algorithm based on random forest[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(1): 137-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201401024.htm [22] 汪正, 胡顺, 马瑞, 等. 基于随机森林的电容式土壤水分传感器校准研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 249-256. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0133WANG Z, HU S, MA R, et al. Calibration of capacitive soil moisture sensor based on random forest[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 249-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0133 [23] 曹正凤. 随机森林算法优化研究[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学, 2014.CAO Z F. Study on optimization of random forests algorithm[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Business, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] BREIMAN L. Randomizing outputs to increase prediction accuracy[J]. Machine Learning, 2000, 40(3): 229-242. [25] 彭漂. 基于随机森林的变量重要性度量和核密度估计算法研究[D]. 福建厦门: 厦门大学, 2017.PENG P. Variable importance measure and kernel density estimation based on random forest[D]. Xiamen Fujian: Xiamen University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: