An artificial neural network for standard penetration blow counts of karst strata in Shenzhen
-
摘要:
潜在岩溶地质灾害威胁粤港澳大湾区广州、深圳等核心城市安全及其地下空间开发与利用。标准贯入试验是岩溶地层勘察的必备手段之一,为土层划分、承载力评估、基础选型等提供重要依据。针对传统的标准贯入试验提高工程成本并受操作人员技能水平影响较大的问题,本研究提出了一种快速且准确获取岩溶区土层标贯击数的新方法。以深圳市岩溶区为例,收集了
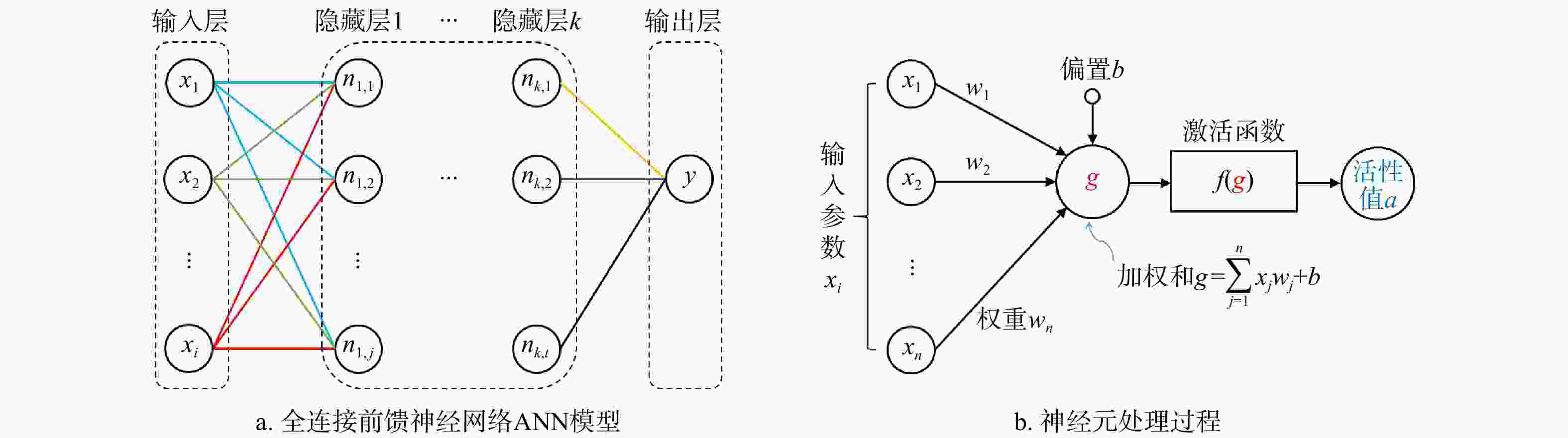
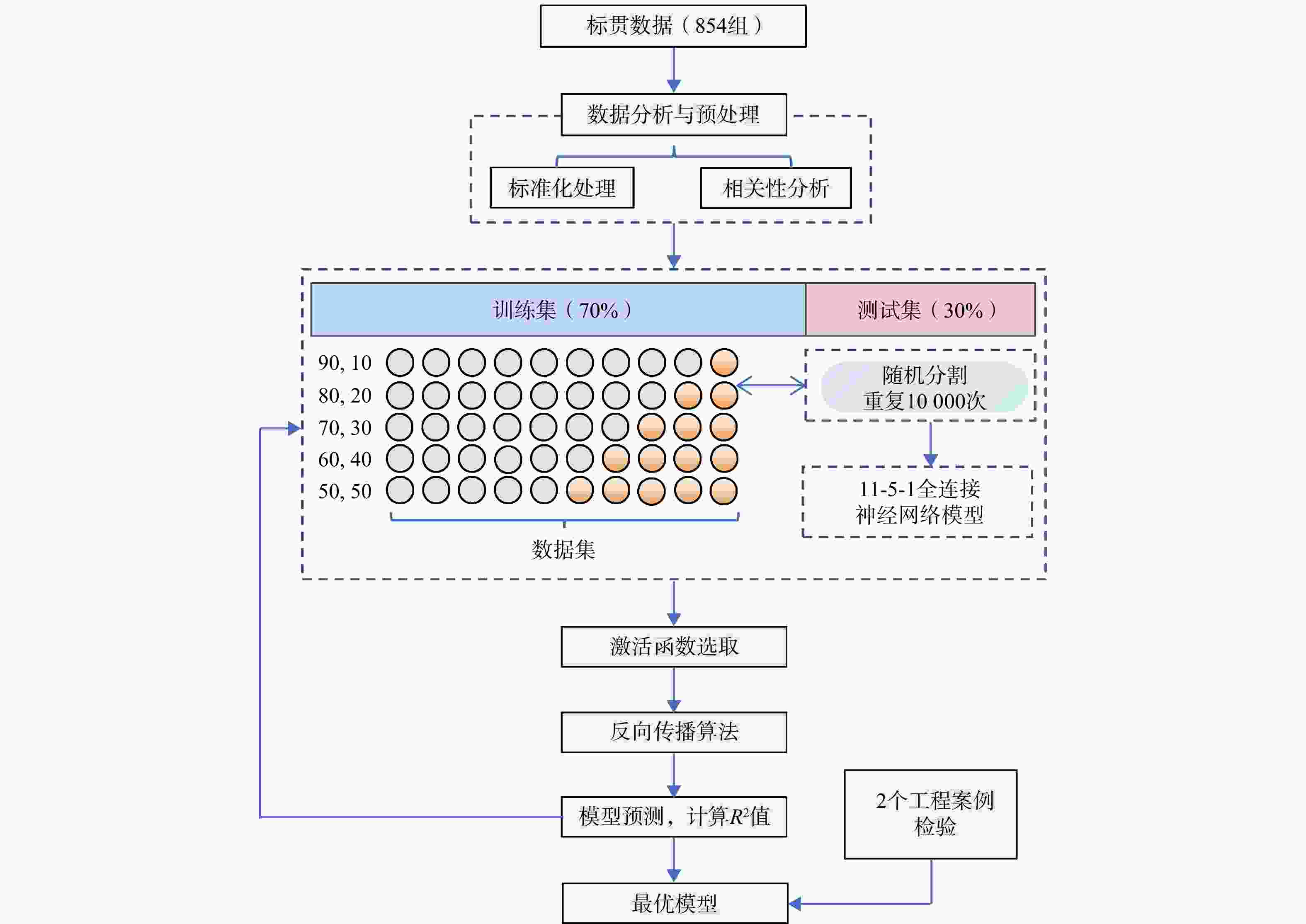
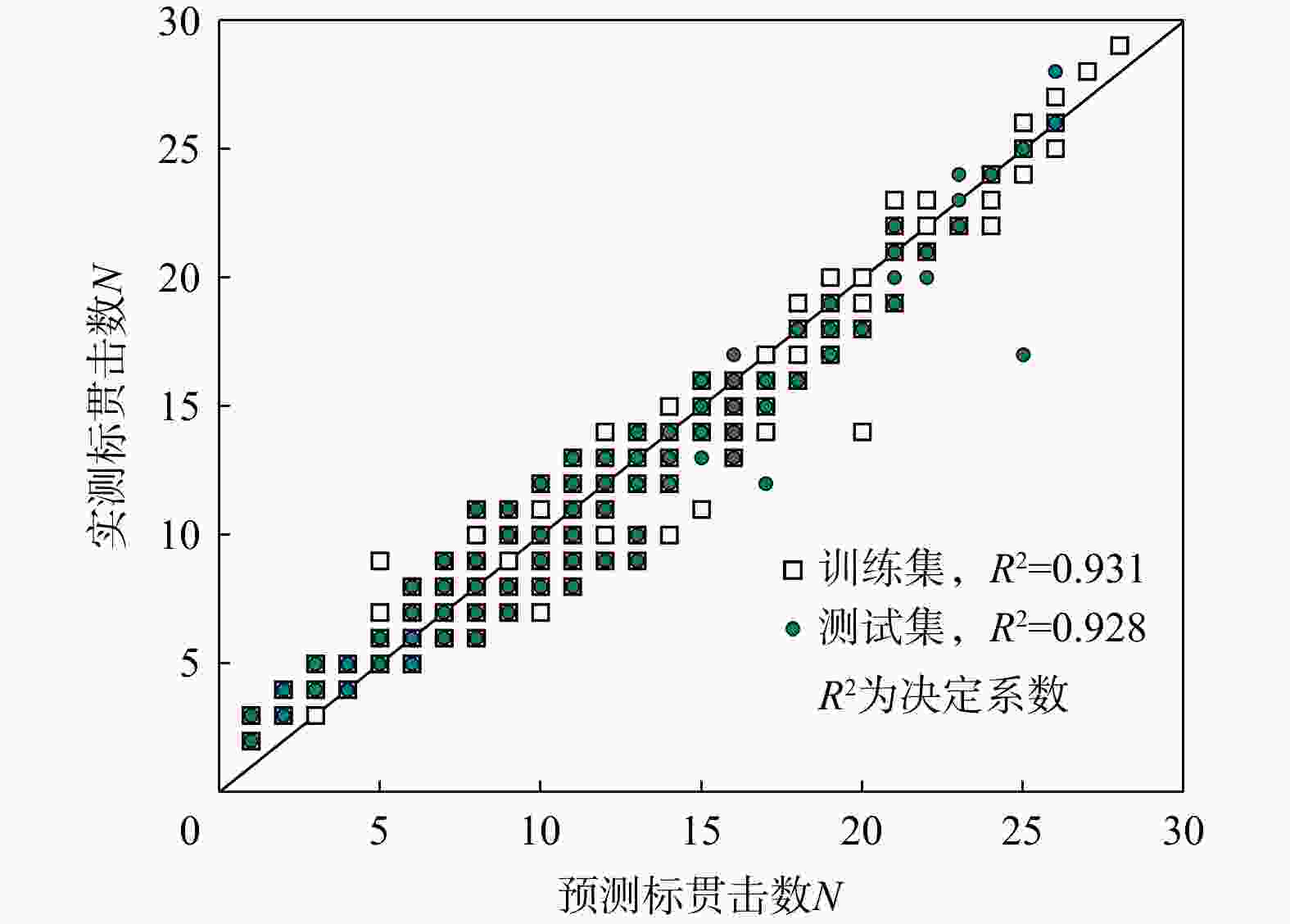
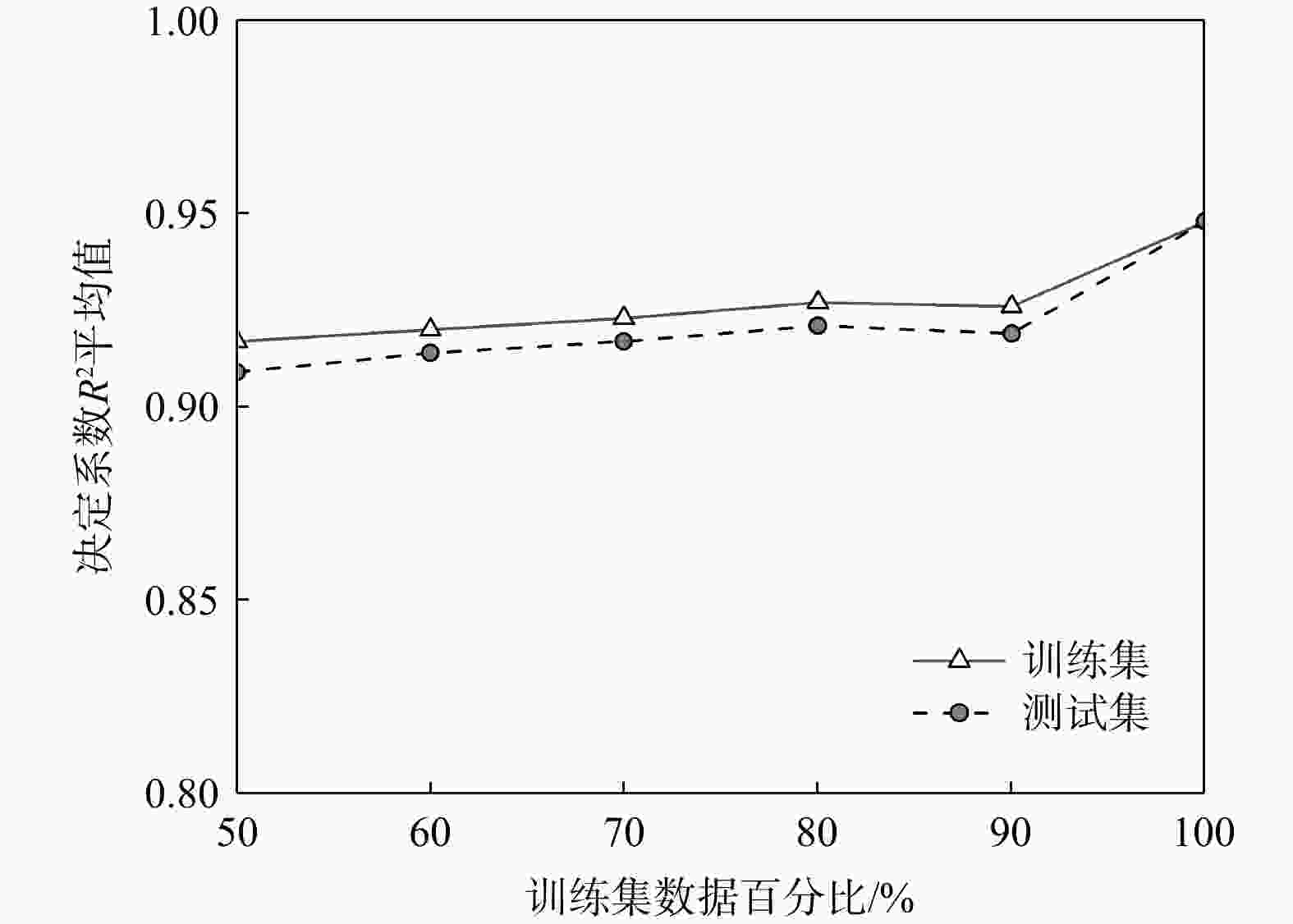
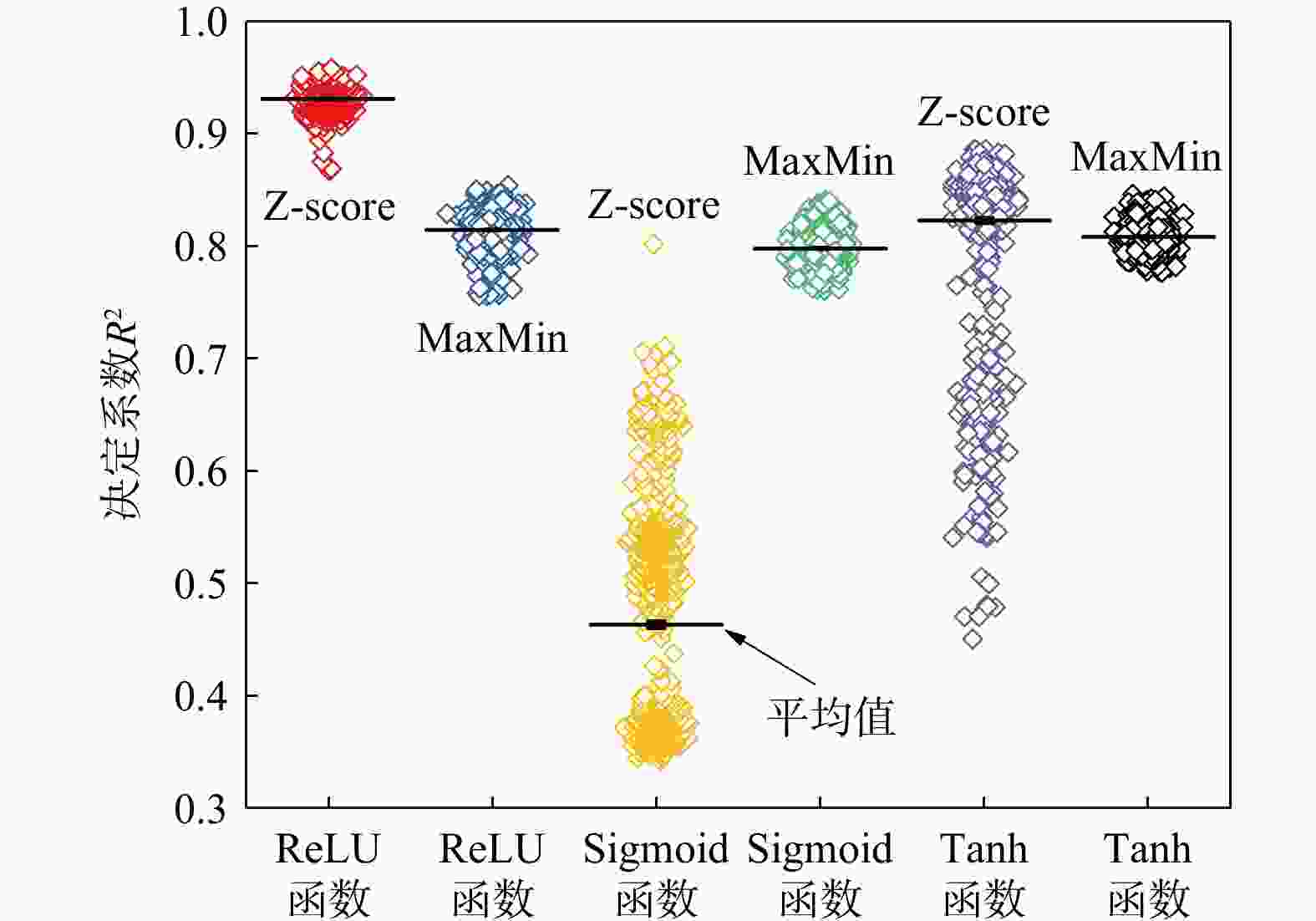
1006 组土层标贯数据,建立了一个11-5-1结构的单隐藏层神经网络模型,该模型仅拥有5个神经元,具有解析解,易于计算。研究结果显示,该神经网络模型的决定系数达到了0.93,表明模型拥有高度的准确性;模型因子平均值为1.04,变异系数介于9%~23%。总体上,模型精度高,预测偏差离散性低。讨论了影响模型稳定性和预测性能的多种因素,如隐藏层神经元数量、数据标准化方法、激活函数选择、数据分割比例和随机抽样效应等。通过在深圳市龙岗区2个独立工程案例的应用,验证了该神经网络模型在工程实践中的实用价值。本研究为未来岩溶区工程勘察方法的发展提供了重要参考。Abstract:Objective This study addresses the threat of potential karst geological disasters to the core cities of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, such as Guangzhou and Shenzhen, impacting the safety and development of their underground spaces. Standard penetration testing, a crucial method for investigating karst strata, plays a vital role in soil layer classification, load-bearing capacity evaluation, and foundation selection. However, traditional standard penetration tests can escalate project costs and are significantly influenced by the skill level of the operators.
Methods To deal with these challenges, this paper introduces a new method for rapidly and accurately obtaining standard penetration test data in karst areas. Focusing on the karst regions of Shenzhen, we collected
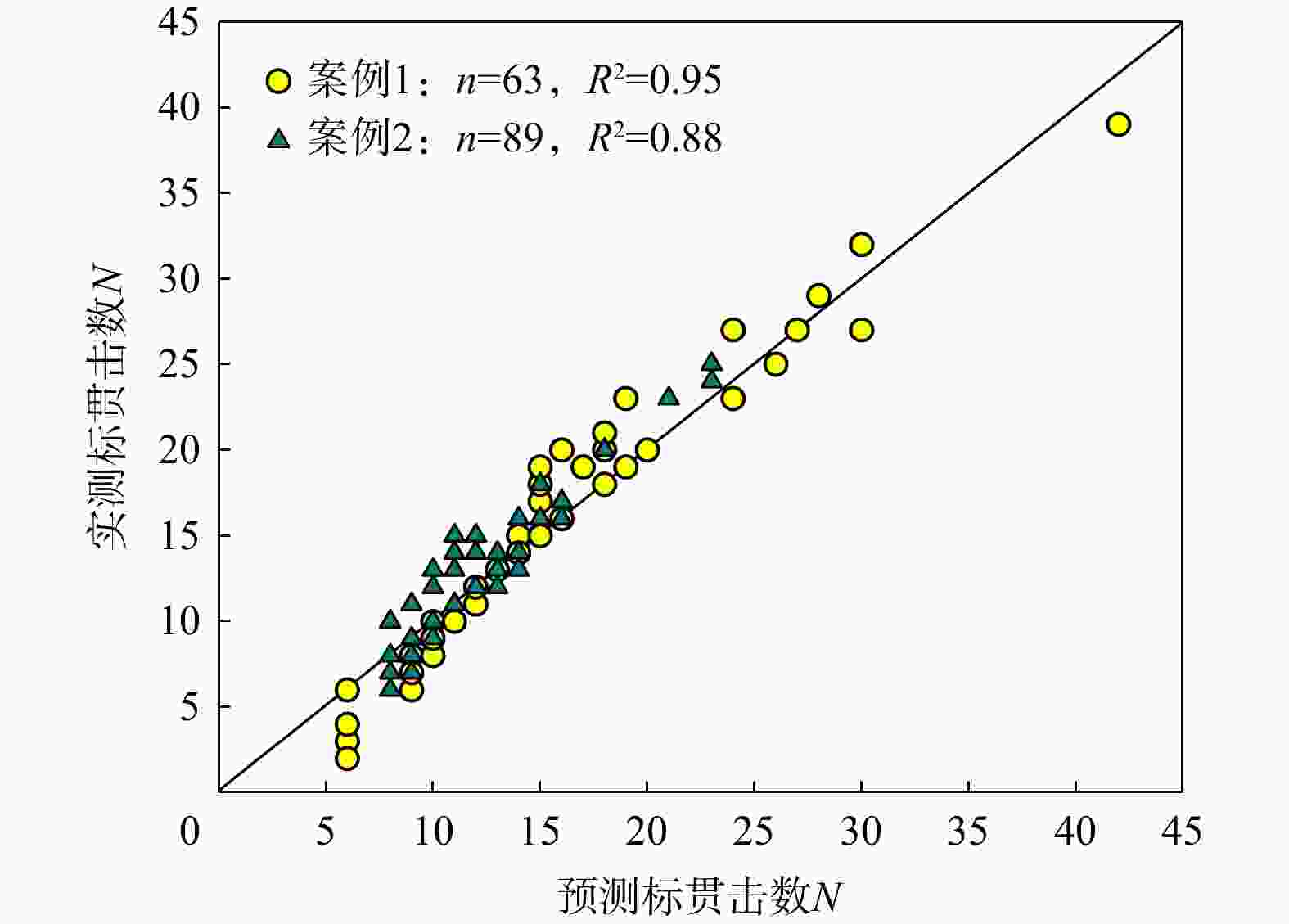
1006 sets of soil penetration data and developed a single hidden layer neural network model with an 11-5-1 structure; this model is featured by only five neurons and has an analytical form that enables easy computation.Results The research findings reveal that this neural network model has a high determination coefficient of 0.93, indicating its high accuracy in prediction. The model factor has a mean value of 1.04, with a coefficient of variation (COV) ranging between 9% and 23%. Overall, the model demonstrates high precision and low predictive dispersion. The paper thoroughly examines various factors affecting the model's stability and predictive performance, including the number of neurons in the hidden layer, data normalization methods, choice of activation functions, data splitting ratios, and the impact of random sampling. The practical applicability of this neural network model has been validated through its implementation in two independent engineering projects in the Longgang District of Shenzhen.
Conclusion This study offers significant insights for the advancement of engineering survey methods in karst regions.
-
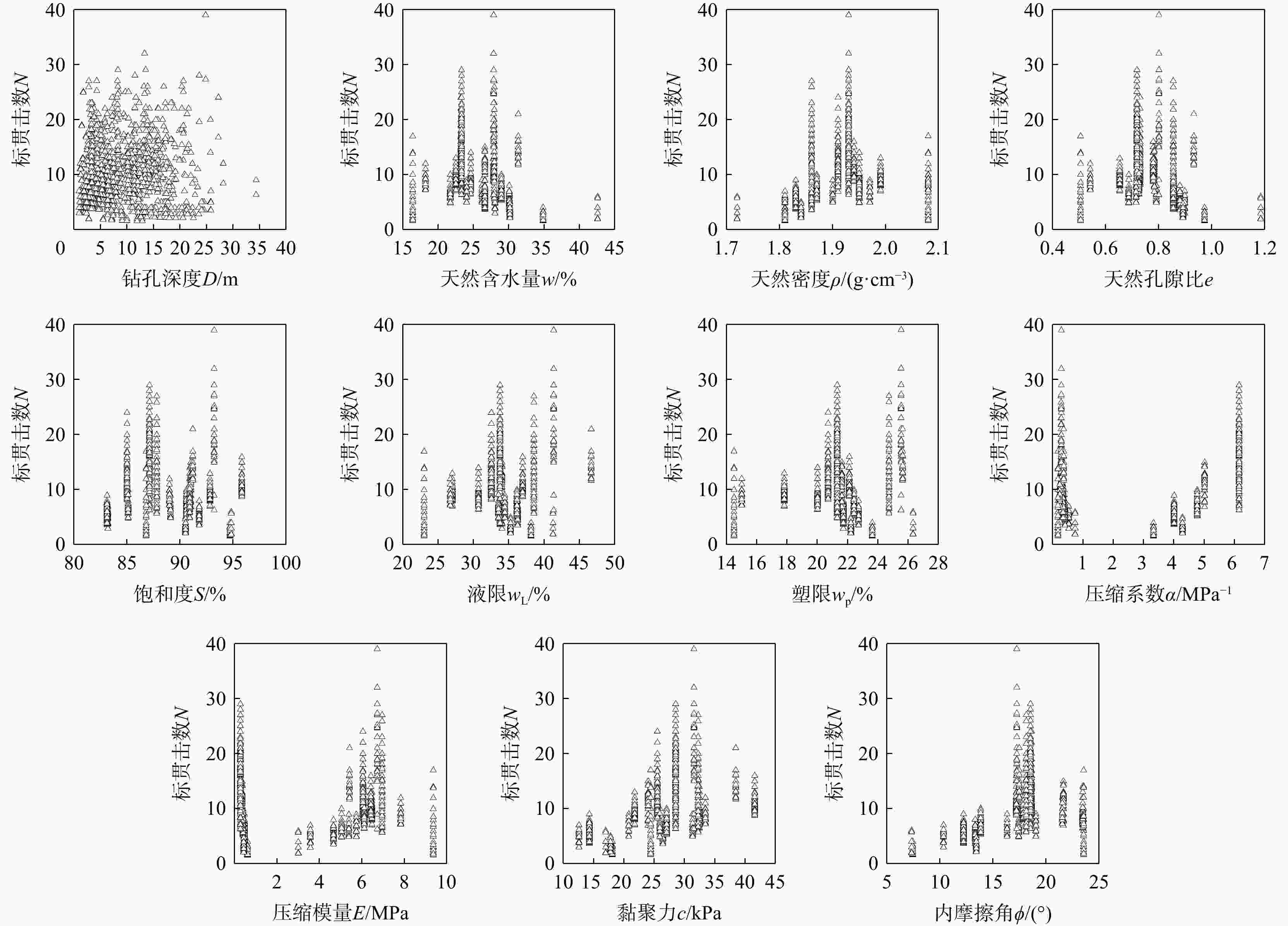
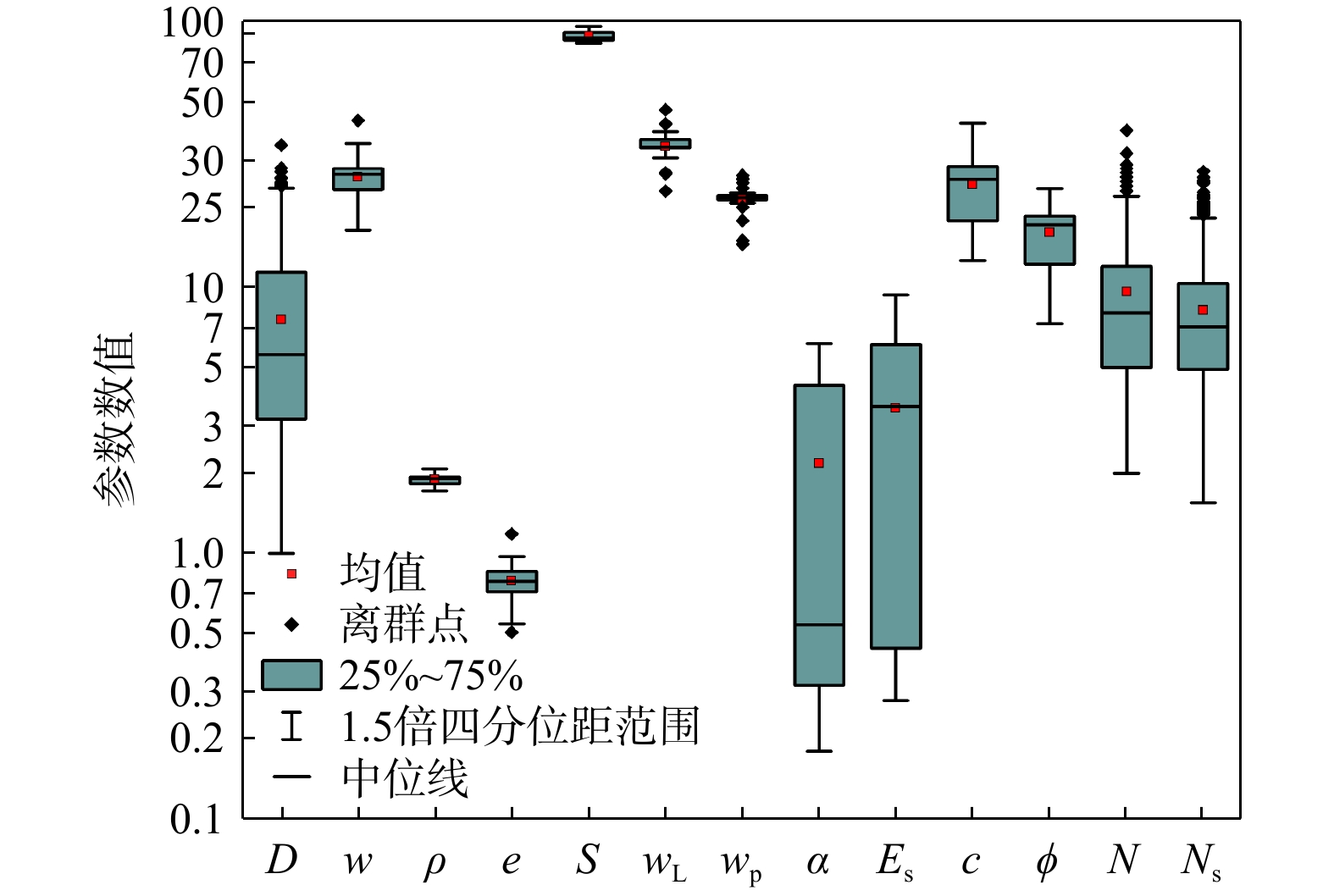
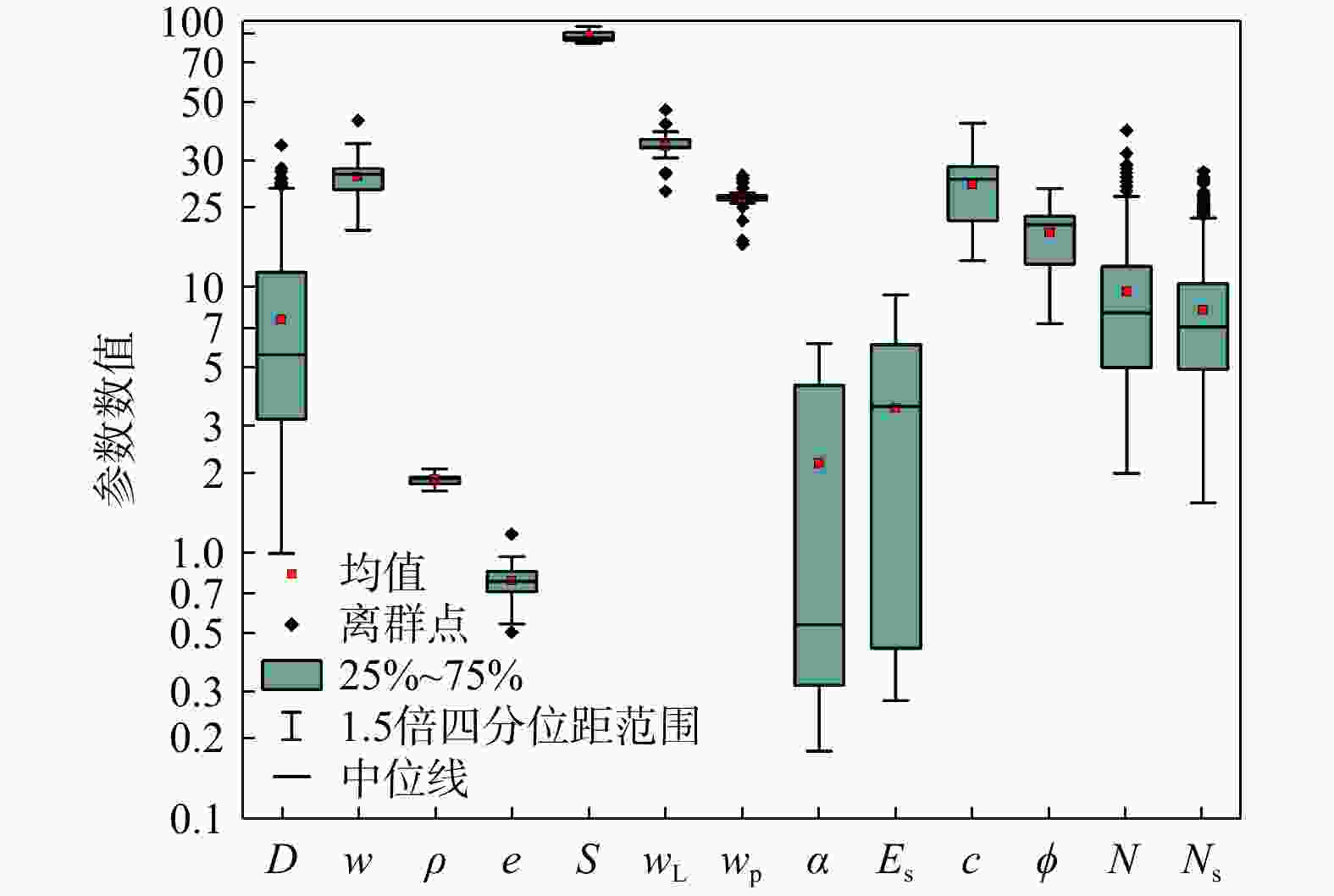
图 1 标贯数据库土体物理力学参数统计分布情况
$ D $. 钻孔深度,m;$ w $. 天然含水量,%;$ \rho $. 天然密度,g/cm3;$ e $. 天然孔隙比;$ S $. 饱和度,%;$ {w}_{{\mathrm{L}}} $. 液限,%;$ {w}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $. 塑限,%;$ \alpha $. 压缩系数,MPa−1;$ {E}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $. 压缩模量,MPa;$ c $. 黏聚力,kPa;$ \phi $. 内摩擦角,%;$ N $. 标贯击数;$ {N}_{s} $. 标贯修正击数;下同
Figure 1. Distributions of soil physical properties and mechanical indices from the SPT database
表 1 岩土工程项目土层具体情况
Table 1. Geotechnical project soil specifics
分层特征描述 项目1 项目2 项目3 项目4 项目5 项目6 项目7 第四系
填土层
(Qml )填土 褐黄色、土黄色,稍湿−湿,结构松散,主要由黏性土堆填而成,局部含少量砂砾、碎石以及砖块、砼块等建筑垃圾和塑料、布条等生活垃圾 褐色、褐灰色,稍湿−湿,较松散−稍密状,主要由粉质黏土堆填而成,含少量碎石,局部含碎砖、砼块等 灰黄色、土黄色,不均匀,主要由黏性土堆填而成,大部分地段顶部不均匀,含少量砼块和碎石,碎石直径多为5~10 cm 灰色,湿,以稍密状为主,局部较松散,不均匀,基本完成自重固结,主要由黏性土堆填而成,含少量砂砾和碎石,部分钻孔夹少量塑料垃圾,局部含碎砖、砼块等 褐红色、褐灰色、褐黄色,以粉质黏土为主,湿,稍松−中密状态,局部地段含碎块石及碎砖块等 灰色,稍湿,稍密,主要由由碎石、砾砂及中粗砂堆填而成,岩心采取率90%~93% 褐黄色,松散,稍湿,主要成分为粉质黏土,顶层含有砖块,均匀性差,多为欠压密土,结构松散,强度较低、压缩性高 第四系
冲洪积层
(Qal+pl)粉质
黏土土黄色、灰黄色,湿,可塑状,黏性较好,不均匀,含少量粉细砂,干强度较高,韧性中等 褐红色、褐黄色,湿,可塑状态,土质较均匀,局部含有少量砂砾,切面光滑,干强度高,韧性高 土黄色、褐红色、褐黄色等,稍湿−湿,以可塑为主,少量为硬塑状,黏性较好,干强度、韧性中等,局部含少量砂,局部为粉土 灰色、褐灰色,稍湿−湿,密实,黏性差,手抓易散,含少量有机质;褐红色、褐黄色,湿,可塑,黏性较好,干强度、韧性中等 深灰色、灰黑色,饱和,流塑状态;灰黄色、褐黄色,湿,软塑−硬塑状态 灰黄色,可塑,含少量砾石,土质不均,具虫孔,局部为粉土;灰白色,很湿,稍密;黄色、黄褐色,稍湿,可塑−硬塑状 灰褐色、褐灰色、褐黄色,软塑−可塑,土质不均匀,由砂岩风化岩残积而成,以黏性土为主,含10%~20%的砂粒和砾石,局部夹碎石,含大量风化碎屑,遇水易软化、崩解 细/中/
粗砂土黄色、灰白色,饱和,松散−稍密,成分主要为石英,分选性一般,不均匀含少量黏土,岩心呈散粒状、团块状 深灰色、灰黄色、灰白色,饱和,以松散为主,含少量泥质,岩心呈筒状 土黄色、灰白色、灰黄色,饱和,以稍密状为主,局部为中密状,岩心呈散粒状、团块状,分选性差,砂粒为石英,颗粒级配不良 — — 灰色、灰黄色、灰白色,岩心呈团块状,分选性一般,主要成分为石英,粒径大于0.5 mm的颗粒含量超过50%,饱和,以中密为主,局部稍密 — 砾砂 土黄色、灰白色,饱和,稍密−中密,成分主要为石英,分选性一般,不均匀,含少量黏土和卵石 灰黄色,局部灰白色,饱和,稍密−中密,岩心呈松散状、团块状 — 灰黄色,局部灰白色,饱和,稍密−中密,岩心呈松散状、团块状,含少量黏性土,局部钻孔含较多卵石 灰色、灰黄色、褐黄色,饱和,稍松状态 灰黄色夹灰白色,硬塑,为砂岩风化残积土。由黏粒、粉粒及风化碎石及砾砂组成 — 粉质
黏土土黄色,湿,可塑状,黏性较好,不均匀,含少量石英砾 — — 褐黄色、褐色、褐灰色,湿,可塑状,局部软塑状,黏性较差,局部为粉土,含少量砂 褐黄色、褐灰色,湿,以可塑为主,近岩面附近含水量增大,多变为软可塑−软塑状态 褐黄色、深褐色,稍少量风化碎屑,局部含少量碎石,软塑 — 第四系
残积层
(Qel )粉质
黏土褐黄色、褐红色,局部呈灰白色或灰黑色,可塑−硬塑状,黏性一般,主要由粉砂岩风化残积而成,原岩结构可辨 褐黄色、土黄色,湿,硬塑状,局部可塑状,由砂岩风化残积而成 褐黄色、褐红色、土黄色,湿,可塑−硬塑状,由砂岩风化残积而成,原岩结构可辨 — — — 褐黄色,灰褐色,中密,土质不均,含水量较高,由砂岩风化残积而成,以碎石土为主,含12%~25%的粉质黏土 下石炭统测水组
(C1c1)全风化
粉砂岩红色、褐黄色,不均匀,局部夹灰黑色碳质泥岩,岩石完全风化解体,原岩结构已破坏,但尚可辨认 土黄色、青褐色,岩石完全风化,原岩结构已破坏,但尚可辨认,岩心呈坚硬土状,手捏易散,遇水易软化 土黄色,褐黄色,岩石完全风化,原岩结构尚可辨认,岩心呈坚硬土状,手掰易碎,泡水易软化、崩解 — 下石炭统(C1):场区内下伏基岩为大理岩或大理岩化灰岩,主要矿物成分为方解石及少量白云石等,微晶−隐晶结构,块状构造 — 褐黄色、灰褐色,原岩结构,构造基本已破坏,仅外观可辨认,岩心呈土柱状,夹强风化碎块,一般块径 2~8 cm,岩体基本质量等级为5级 强风化
粉砂岩褐黄色、褐红色,局部夹灰黑色炭质泥岩,岩石因强烈风化而解体,岩芯呈碎块混土状、碎块状,合金可钻进,裂隙很发育,岩体极破碎,岩石为极软岩 土黄色、青褐色、青灰色,裂隙很发育,岩芯呈土状及土混碎块状,碎块大多手折可断,合金可钻进 砖红色,褐黄色,岩芯呈碎块状,块状,局部呈碎块混土状,不均匀夹含少量中风化碎块,岩芯泡水易崩解软化 — — 褐黄色、灰褐色,原岩结构可辨,岩石风化强烈,岩心呈碎块状,一般块径 2~15 cm,岩体基本质量等级为5级 中风化
粉砂岩灰色,砂状结构,层状构造,岩心以碎块状为主,少量柱状,裂隙发育,锤击声哑,岩石为较软岩,岩体破碎,岩体基本质量等级为Ⅳ级 — 青灰色,主要矿物为石英,细砂状结构,中厚层状构造,岩心呈块状、少量呈短柱状,风化裂隙较发育,敲击声哑,岩石坚硬程度为较软岩,岩体完整程度为较破碎,岩体基本质量等级为Ⅳ级 — — — 微风化
石灰岩灰白色,隐晶质结构,薄层−中厚层构造,裂隙少量发育,岩心呈短柱状,岩质硬脆,锤击声脆,岩石为较硬岩 — — 微风化大理岩:灰白色,主要矿物成分为方解石,变晶结构,块状构造,岩心呈短柱状、柱状,局部为碎块状,为较硬岩−坚硬岩,岩体较完整 — 青灰色、灰白色,隐晶质结构,中厚层状构造,节理裂隙发育,该层受附近断裂带影响,岩体较破碎,岩心呈碎块状 表 2 标贯数据库土体物理力学指标统计特征值汇总
Table 2. Summary of statistics for soil physical properties and mechanical indices in the SPT database
数据统计
特征标贯深度
$ D $/m天然含
水量$ w $/%天然密度
$ \rho $/(g·cm−3)天然孔
隙比$ e $饱和度
$ S $/%液限
$ {w}_{{\mathrm{L}}} $/%塑限
$ {w}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $/%压缩系数
$ \alpha $/MPa−1压缩模量
$ {E}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $/MPa黏聚力
$ c $/kPa内摩擦角
$ \phi $/(°)标贯击
数$ N $标贯修
正击数$ {N}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $平均值 7.62 26.25 1.89 0.80 88.08 34.03 21.58 2.32 3.23 24.06 15.75 9.69 8.25 最大值 34.30 42.50 1.99 1.18 95.80 41.30 26.30 6.15 6.94 41.50 23.42 39.00 27.30 75%分位数 11.50 28.00 1.94 0.86 91.00 36.10 22.20 4.29 6.04 28.50 18.50 12.00 10.38 50%分位数 5.70 26.60 1.91 0.80 87.10 33.70 21.70 0.54 3.56 25.90 17.17 8.00 7.02 25%分位数 3.20 23.30 1.83 0.72 85.00 33.50 21.30 0.32 0.44 17.00 12.20 5.00 4.91 最小值 1.00 21.70 1.72 0.65 83.10 27.00 17.80 0.27 0.28 12.60 7.30 2.00 1.55 变异系数 − 0.126 0.032 0.113 0.046 0.082 0.069 0.978 0.824 0.323 0.237 0.584 0.545 表 3 标贯数据库土体物理力学指标之间相关性汇总
Table 3. Summary of Pearson correlations among soil physical properties and mechanical indices in the SPT database
数据统计
特征钻孔深度
$ D $/m含水量
$ w $/%密度
$ \rho $/(g·cm−3)孔隙比
$ e $饱和度
$ S $/%液限
$ {w}_{{\mathrm{L}}} $/%塑限
$ {w}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $/%压缩系数
$ \alpha $/MPa−1压缩模量
$ {E}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $/MPa黏聚力
$ c $/kPa内摩擦角
$ \phi $/(°)标贯
击数$ N $标贯修
正击数$ {N}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $标贯深度$ D $/m 1 –0.10 0.26 –0.21 0.25 –0.05 –0.11 0.03 0.11 0.35 0.36 0.39 0.23 含水量$ w $ /% –0.10 1 –0.74 0.93 0.31 0.68 0.70 0.04 –0.23 –0.18 –0.63 –0.41 –0.41 密度$ \rho $ 0.26 –0.74 1 –0.93 0.41 –0.49 –0.59 –0.20 0.48 0.66 0.84 0.54 0.53 孔隙比$ e $ –0.21 0.93 –0.93 1 –0.06 0.65 0.71 0.11 –0.36 –0.45 –0.79 –0.52 –0.51 饱和度$ S $ /% 0.25 0.31 0.41 –0.06 1 0.16 0.04 –0.18 0.33 0.65 0.30 0.19 0.18 液限$ {w}_{{\mathrm{L}}} $/% –0.05 0.68 –0.49 0.65 0.16 1 0.97 0.11 –0.17 0.20 –0.37 –0.02 0.00 塑限$ {w}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $/% –0.11 0.70 –0.59 0.71 0.04 0.97 1 0.11 –0.20 0.06 –0.41 –0.08 –0.05 压缩系数$ \alpha $/MPa−1 0.03 0.04 –0.20 0.11 –0.18 0.11 0.11 1 –0.93 –0.19 –0.11 0.12 0.13 压缩模量$ {E}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $/MPa 0.11 –0.23 0.48 –0.36 0.33 –0.17 –0.20 –0.93 1 0.47 0.40 0.17 0.15 黏聚力$ c $/kPa 0.35 –0.18 0.66 –0.45 0.65 0.20 0.06 –0.19 0.47 1 0.69 0.56 0.54 内摩擦角$ \phi $/(°) 0.36 –0.63 0.84 –0.79 0.30 –0.37 –0.41 –0.11 0.40 0.69 1 0.61 0.59 标贯击数$ N $ 0.39 –0.41 0.54 –0.52 0.19 –0.02 –0.08 0.12 0.17 0.56 0.61 1 0.98 标贯修正击数$ {N}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $ 0.23 –0.41 0.53 –0.51 0.18 0 –0.05 0.13 0.15 0.54 0.59 0.98 1 表 4 不同隐藏层神经元数量时训练集和测试集决定系数$ {R}^{2} $的平均值与变异系数汇总
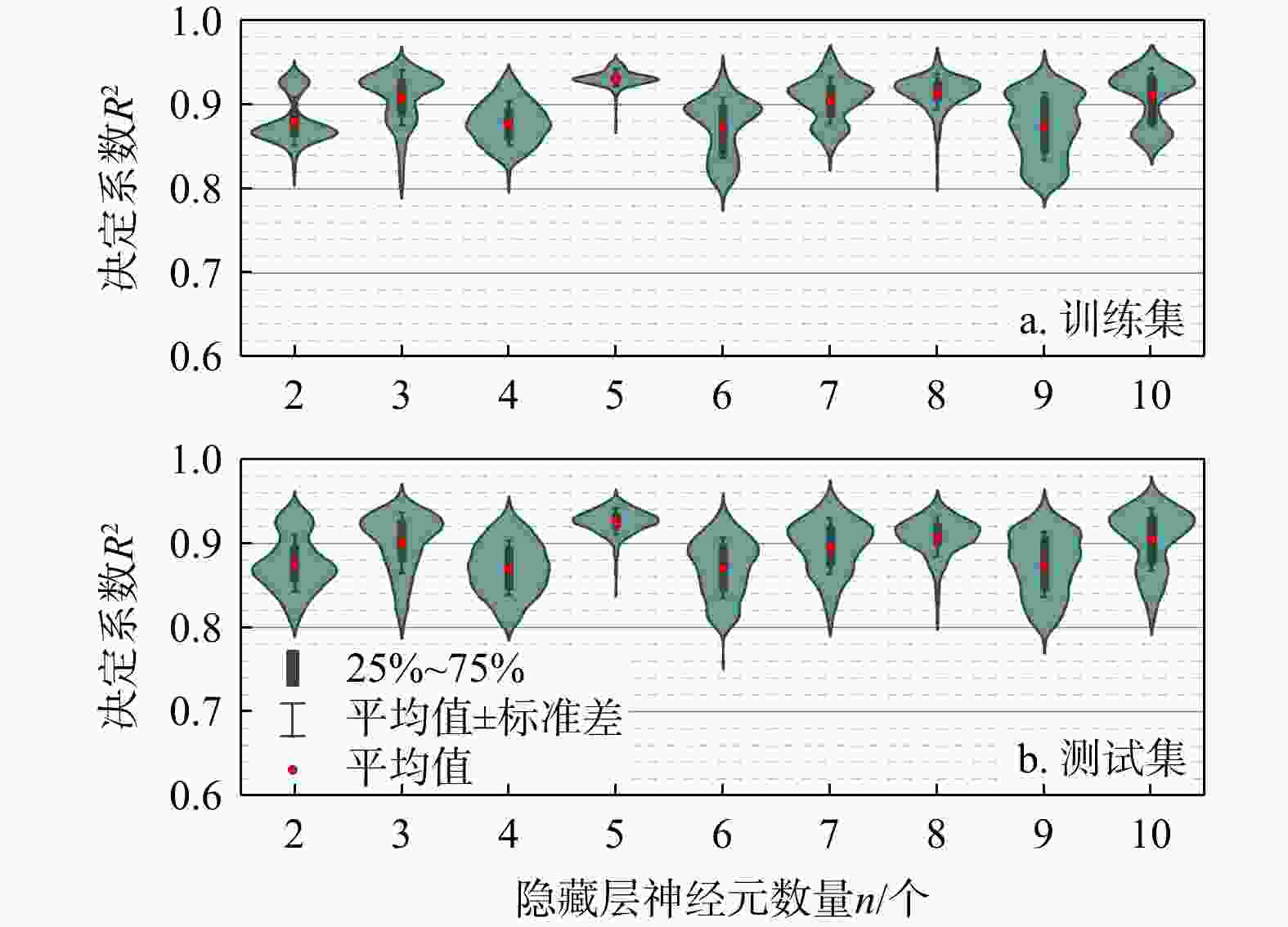
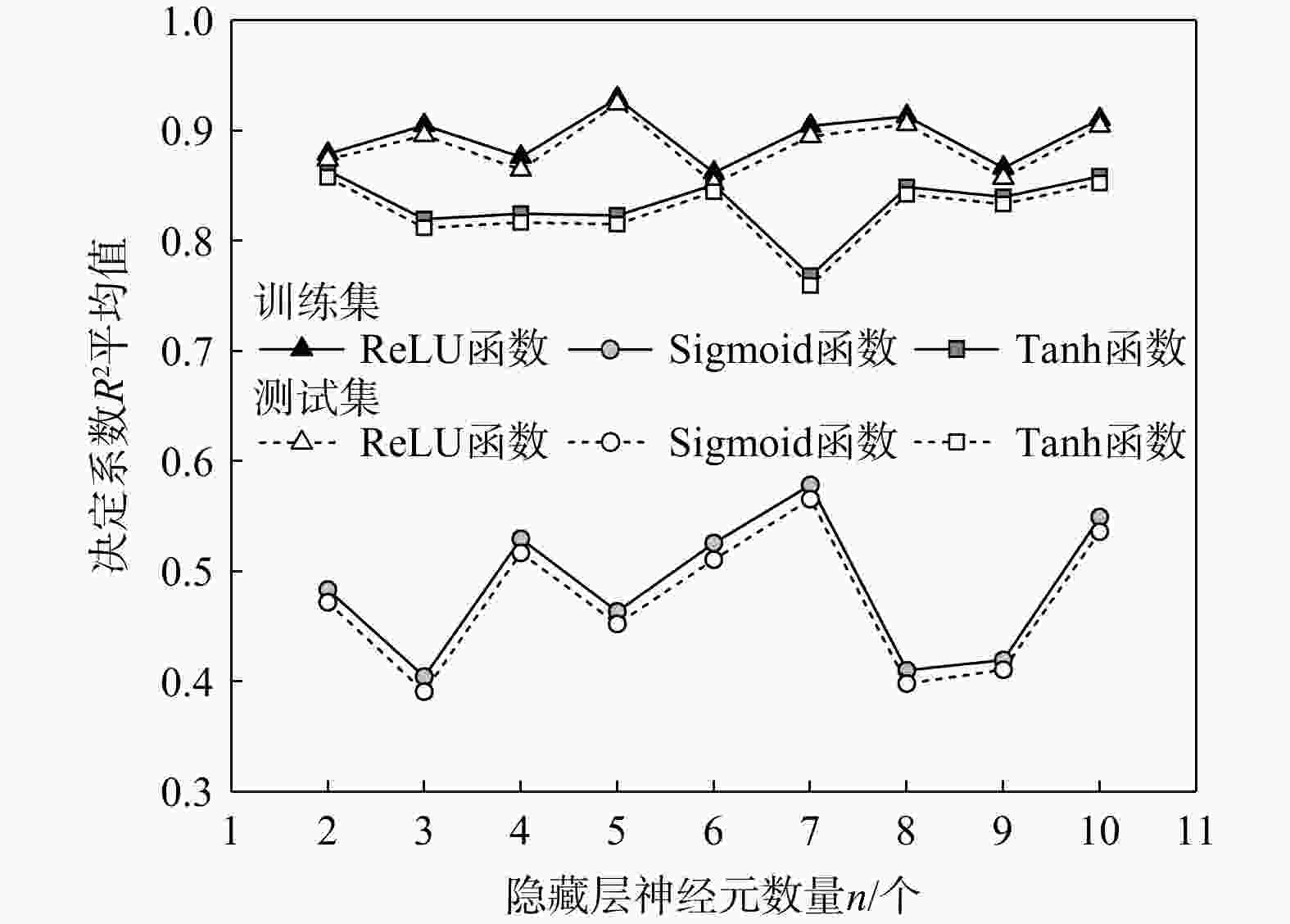
Table 4. Summary of means and COVs of $ {R}^{2} $ for both training and validation datasets corresponding to different numbers of neurons in the hidden layer
隐藏层神经
元数量n/个训练集$ {R}^{2} $ 测试集$ {R}^{2} $ 均值 变异系数 均值 变异系数 2 0.88 0.031 0.88 0.038 3 0.91 0.034 0.90 0.038 4 0.88 0.028 0.87 0.037 5 0.93 0.010 0.93 0.015 6 0.87 0.040 0.87 0.040 7 0.90 0.029 0.90 0.036 8 0.91 0.022 0.91 0.025 9 0.87 0.043 0.87 0.042 10 0.91 0.035 0.90 0.040 表 5 2个工程案例土层的物理属性、力学指标与实测标贯击数范围
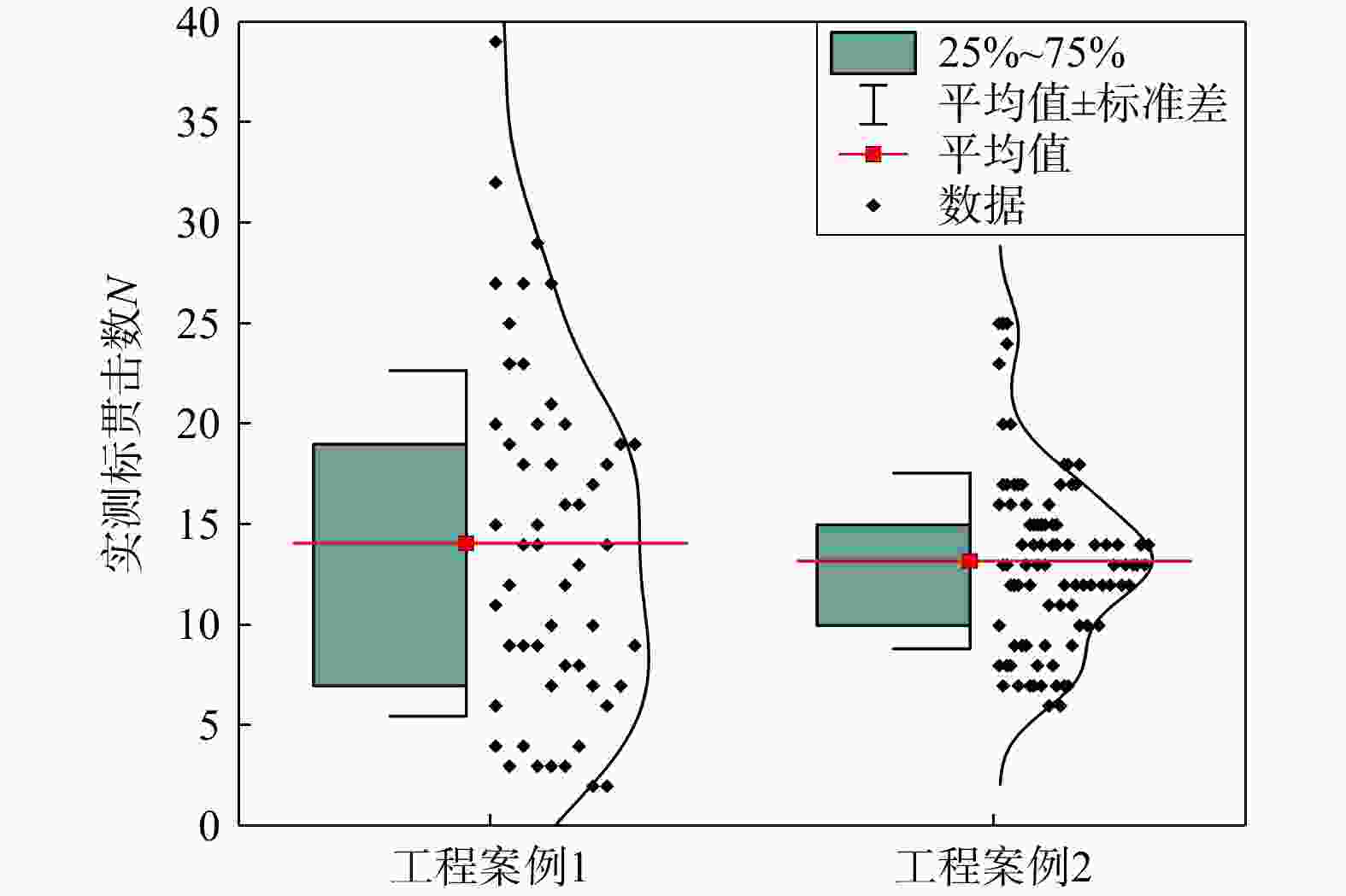
Table 5. Ranges for soil physical properties, mechanical indices and measured SPT blow counts for the two real cases
数据统计特征 案例1 案例2 标贯深度D/m 1.0~24.8 1.0~38.2 含水量w/% 27.8~42.5 22.0~36.4 密度ρ/(g·cm−3) 1.72~1.93 1.83~1.95 孔隙比$ e $ 0.80~1.18 0.68~0.99 饱和度S/% 87.8~94.8 81.9~98.3 液限wL/% 38.5~41.3 31.5~42.5 塑限wp/% 24.7~26.3 20.2~24.8 压缩系数$ \alpha $/MPa−1 0.28~0.74 0.27~0.53 压缩模量$ {E}_{{\mathrm{s}}} $/MPa 2.99~6.94 3.51~6.17 黏聚力$ c $/kPa 17.0~32.2 10.1~28.3 内摩擦角$ \phi $/(°) 7.3~18.1 9.6~22.5 标贯击数$ N $ 2~39 6~25 -
[1] 化建新,郑建国. 工程地质手册(5版)[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2018.HUA J X,ZHENG J G. Geological engineering handbook 5th, ed[M]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2018. (in Chinese) [2] PAPADOPOULOU-VRYNIOTI K,BATHRELLOS G D,SKILODIMOU H D,et al. Karst collapse susceptibility mapping considering peak ground acceleration in a rapidly growing urban area[J]. Engineering Geology,2013,158:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.02.009 [3] 罗小杰,沈建. 我国岩溶地面塌陷研究进展与展望[J]. 中国岩溶,2018,37(1):101-111.LUO X J,SHEN J. Research progress and prospect of karst ground collapse in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2018,37(1):101-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 何万平. 岩溶隧道底部结构力学特性分析及安全性评价[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2020.HE W P. Ayalysis of mechanical characteristics and safety evaluation of bottom structure of tunnels in karst stratum[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 徐晨,方勇,康海波,等. 大断面富水岩溶隧道二次衬砌受力特征研究[J]. 公路交通科技,2016,33(9):84-91.XU C,FANG Y,KANG H B,et al. Study on mechanical characteristics of secondary lining for large cross-section tunnel in water-rich karst strata[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2016,33(9):84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 樊浩博,周定坤,刘勇,等. 富水管道型岩溶隧道衬砌结构力学响应特征研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(7):1884-1898.FAN H B,ZHOU D K,LIU Y,et al. Mechanical response characteristics of lining structure of pipeline karst tunnels in water-rich areas[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(7):1884-1898. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 王庆. 隐伏溶洞对隧道衬砌结构受力特性的影响研究[D]. 重庆:重庆交通大学,2020.WANG Q. Study on the influence of hidden karst cave on the mechanical characteristics of tunnel lining structure[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing Jiaotong University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 谭信荣,樊浩博,宋玉香,等. 管道型岩溶隧道衬砌结构受力特征试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2021,17(6):1847-1856.TAN X R,FAN H B,SONG Y X,et al. Experimental study on the mechanical characteristics of the lining structure of pipe-type karst tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2021,17(6):1847-1856. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 谭忠盛,李健,薛斌,等. 岩溶隧道衬砌水压力分布规律研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2009,11(12):87-92.TAN Z S,LI J,XUE B,et al. Research of water distribution of tunnel lining in karst region[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2009,11(12):87-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张中善. 岩溶地区灌注桩溶(土)洞及漏浆处理技术[J]. 施工技术,2017,46(增刊2):238-241.ZHANG Z S. Treatment technology for karst cave and soil cave of filling pile in karst region[J]. Construction Technology,2017,46(S2):238-241. (in Chinese) [11] 赵明华,朱志仁,黄明华,等. 考虑基桩嵌岩段侧阻的岩溶区顶板安全厚度计算[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(11):4201-4209.ZHAO M H,ZHU Z R,HUANG M H,et al. Study on thickness of safety for cave roofs suffered bending failure in karst areas[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(11):4201-4209. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 雷勇,陈秋南,马缤辉. 基于极限分析的桩端岩层冲切分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(3):631-638.LEI Y,CHEN Q N,MA B H. Punching analysis of rock at pile tip base on limit analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(3):631-638. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 赵明华,张锐,胡柏学,等. 岩溶区桩端下伏溶洞顶板稳定性分析研究[J]. 公路交通科技,2009,26(9):13-16.ZHAO M H,ZHANG R,HU B X,et al. Analysis of stability of cave roof under pile tip in karst area[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2009,26(9):13-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 赵明华,程晔,曹文贵. 桥梁基桩桩端溶洞顶板稳定性的模糊分析研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(8):1376-1383.ZHAO M H,CHENG Y,CAO W G. Fuzzy method for the stability analysis of cave roof under pile tip in karst region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(8):1376-1383. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 赵明华,肖尧,徐卓君,等. 岩溶区嵌岩桩桩端承载性能研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(6):1123-1129.ZHAO M H,XIAO Y,XU Z J,et al. Bearing capacity at tip of rock-socketed pile in karst areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(6):1123-1129. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 赵明华,蒋冲,曹文贵. 岩溶区嵌岩桩承载力及其下伏溶洞顶板安全厚度的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2007,29(11):1618-1622.ZHAO M H,JIANG C,CAO W G. Study on bearing capacity of rock-socked piles and safe thickness of cave roofs in karst region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2007,29(11):1618-1622. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 赵明华,雷勇,张锐. 岩溶区桩基冲切破坏模式及安全厚度研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(2):524-530.ZHAO M H,LEI Y,ZHANG R. Study of punching failure mode and safe thickness of pile foundation in karst region[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(2):524-530. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 刘勇健,刘雅恒,刘湘秋,等. 广花盆地岩溶地面塌陷特征及形成机理研究[J]. 广东工业大学学报,2013,30(1):25-30.LIU Y J,LIU Y H,LIU X Q,et al. Study of collapse characteristics of karst ground in the Guanghua Basin and its formation mechanism[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology,2013,30(1):25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 卢丹美. 广州市金沙洲地区地面塌陷特征及危险性评价[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2013.LU D M. Characteristic and risk assessment of karst collapse in Jinshazhou area,Guangzhou City[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 李卓骏,蒙彦,董志明,等. 土洞型岩溶塌陷发育过程气体示踪试验研究:以广州金沙洲为例[J]. 中国岩溶,2021,40(2):238-245.LI Z J,MENG Y,DONG Z M,et al. Experimental study of gas tracer simulation of karst collapse development process:An example of Jinshazhou,Guangzhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2021,40(2):238-245. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 桂林. 广州地铁五号线岩溶地区盾构隧道工程技术研究[J]. 桂林工学院学报,2008,28(3):324-329.GUI L. Engineering technique for shield tunnel in karst region of Guangzhou metro Line 5[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2008,28(3):324-329. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 胡让全,黄健民. 综合物探方法在广州市金沙洲岩溶地面塌陷、地面沉降地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探,2014,38(3):610-615.HU R Q,HUANG J M. The application of integrated geophysical techniques to the investigation of karst ground collapse and ground subsidence in Jingshazhou area,Guangzhou City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2014,38(3):610-615. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 蒙彦,黄健民,贾龙. 基于地下水动力特征监测的岩溶塌陷预警阈值探索:以广州金沙洲岩溶塌陷为例[J]. 中国岩溶,2018,37(3):408-414.MENG Y,HUANG J M,JIA L. Early warning threshold of sinkhole collapse based on dynamic characteristics from groundwater monitoring:A case study of Jinshazhou of Guangzhou,China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2018,37(3):408-414. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 郑小战,郭宇,戴建玲,等. 广州市典型岩溶塌陷区岩溶发育及影响因素[J]. 热带地理,2014,34(6):794-803.ZHENG X Z,GUO Y,DAI J L,et al. Karst development and influencing factors in typical karst collapse districts of Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2014,34(6):794-803. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 郑小战,黄健民,李德洲. 广花盆地南部金沙洲岩溶演变及环境特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(1):138-143.ZHENG X Z,HUANG J M,LI D Z. Karst evolution and environmental features in Jinshazhou in the southern Guangzhou-Huadu Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(1):138-143. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 雷金山,阳军生,肖武权,等. 广州岩溶塌陷形成条件及主要影响因素[J]. 地质与勘探,2009,45(4):488-492.LEI J S,YANG J S,XIAO W Q,et al. Analysis of forming conditions and main influential factors of karst collapse in Guanzhou[J]. Geology and Exploration,2009,45(4):488-492. (in Chinese) [27] 黄健民,吕镁娜,郭宇,等. 广州金沙洲岩溶地面塌陷地质灾害成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶,2013,32(2):167-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.02.007HUANG J M,LÜ M N,GUO Y,et al. Research on the reason for geologic disaster by karst surface collapse at Jinshazhou in Guangzhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2013,32(2):167-174. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.02.007 [28] 黄健民,邓雄文,胡让全. 广州金沙洲岩溶区地下水位变化与地面塌陷及地面沉降关系探讨[J]. 中国地质,2015,42(1):300-307.HUANG J M,DENG X W,HU R Q. The relationship between groundwater and ground collapse and land subsidence in Jinshazhou,Guangzhou City[J]. Geology in China,2015,42(1):300-307. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 黄健民,郑小战,胡让全,等. 广州金沙洲岩溶地面塌陷灾害预警预报研究[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(2):421-432.HUANG J M,ZHENG X Z,HU R Q,et al. A study of warning and forecasting of karst collapse geological disaster in Jinshazhou of Guangzhou[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(2):421-432. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 黎秉林. 广州岩溶地区盾构地铁线路勘察研究:以广州地铁九号线工程为例[D]. 广州:华南理工大学,2017.LI B L. The research on reconnaissance of shield metro tunnel in karst area of Guangzhou:Take Guangzhou metro Line 9 engineering as an example[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 刘恒. 深圳地铁14号线隧道岩溶处理技术方案对比及优化[J]. 黑龙江交通科技,2020,43(12):142-144.LIU H. Experimental research on the influencing factors of the shear characteristics of the contact surface between coarse sand and concrete[J]. Communications Science and Technology Heilongjiang,2020,43(12):142-144. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 徐正宣. 深圳地铁3号线工程岩溶洞穴勘察及病害处理技术研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2008.XU Z X. Research on karst cave investigation and disaster treatment technology of the Shenzhen No. 3 subway engineering[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2008. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 李勇峰. 深圳大运中心场地岩溶地面塌陷危险性评价研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2013.LI Y F. Study on the hazard assessment of karst ground collapse in Shenzhen Universiade Center[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 李清明,徐腾飞,李勇国,等. 深圳地铁8号线岩溶发育特征及施工处理措施[J]. 桂林理工大学学报,2017,37(3):405-411.LI Q M,XU T F,LI Y G,et al. Karst characteristics and construction measures in Shenzhen metro Line 8[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2017,37(3):405-411. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 李雪平,徐光黎,吴强,等. 基于GIS的Logistic模型在深圳大运中心岩溶空间发育规律评价中的应用[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(增刊2):276-280.LI X P,XU G L,WU Q,et al. Application of GIS-based Logistic model to karst spatial prognosis studying in Shenzhen Universiade Center[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(S2):276-280. (in Chinese) [36] 梁永国,程小勇. 深圳龙岗区葵涌岩溶地质勘查[J]. 矿产勘查,2009,12(7):23-26.LIANG Y G,CHENG X Y. Geological exploration of Kuiyong karst in Longgang district,Shenzhen[J]. Mineral Exploration,2009,12(7):23-26. (in Chinese) [37] 龚选波,张继伟,周玉凤,等. 综合物探技术在深圳地铁16号线岩溶勘察中的应用[J]. 工程勘察,2018,46(7):62-67.GONG X B,ZHANG J W,ZHOU Y F,et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical technology in karst investigation in Line No. 16 of Shenzhen Metro[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2018,46(7):62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 刘动,林沛元,陈贤颖,等. 深圳岩溶空间发育规律统计分析[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(7):1899-1912.LIU D,LIN P Y,CHEN X Y,et al. Statistical analysis of karst spatial distribution in Shenzhen[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(7):1899-1912. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 刘动. 岩溶地区桩基检测与缺陷处理研究[J]. 钻探工程,2021,48(2):110-116.LIU D. Pile testing and defect treatment in the karst area[J]. Drilling Engineering,2021,48(2):110-116. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 沈珠江. 原状取土还是原位测试:土质参数测试技术发展方向刍议[J]. 岩土工程学报,1996,18(5):94-95.SHEN Z J. Undisturbed soil borrowing or in situ testing: Discussion on the development direction of soil parameter testing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1996,18(5):94-95. (in Chinese) [41] 中华人民共和国建设部. 建筑地基基础设计规范:GB 50007-2002[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2004.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of building foundation:GB 50007-2002[S]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2004. (in Chinese) [42] 中华人民共和国建设部. 岩土工程勘察规范:GB50021-2001[S]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2004.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering:GB50021-2001[S]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,2004. (in Chinese) [43] 广西华蓝岩土工程有限公司. 广西岩溶地区建筑地基基础技术规范:DBJ45/024-2016[S]. 南宁:广西壮族自治区住房和城乡建设厅,2016.Guangxi Hualan Geotechnical Engineering Co. ,LTD. Technical code for building foundation in karst area in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region:DBJ45/024-2016[S]. Nanning:Housing and Urban Rural Development Area of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region,2016. (in Chinese) [44] 广州市设计院. 岩溶地区建筑地基基础技术规范:DBJ/T 15-136-2018[S]. 广州:广东省住房和城乡建设厅,2018.Guangzhou Designing Institute. Technical code for building foundation in karst area:DBJ/T15-136-2018[S]. Guangzhou:Housing and Urban Rural Development Area of Guangdong,2018. (in Chinese) [45] 吴莉,张国海,李开文. 岩溶地区基础设计与处理[J]. 地球与环境,2005,33(增刊1):445-448.WU L,ZHANG G H,LI K W. The rock dissolves the region foundation design with handles[J]. Earth and Environment,2005,33(S1):445-448. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] 蒋进. 宜阳地区地基土标贯击数与主要力学参数的相关性分析[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学,2018.JIANG J. Correlation analysis of SPT number and the main mechanical parameters of foundation soil in Yiyang area[D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] LUNNE T,BERRE T,ANDERSEN K H,et al. Effects of sample disturbance and consolidation procedures on measured shear strength of soft marine Norwegian clays[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2006,43(7):726-750. doi: 10.1139/t06-040 [48] 杨福见,胡大伟,周辉,等. 动载扰动后花岗岩物理力学特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(6):1459-1467.YANG F J,HU D W,ZHOU H,et al. Physical and mechanical properties of granite after dynamic disturbance[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(6):1459-1467. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 朱耀庭,胡文华,吴福泉,等. 溶洞上覆土层注浆加固应用分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版),2017,41(6):954-957.ZHU Y T,HU W H,WU F Q,et al. Application analyse on grouting reinforcement in overburden layer of karst cave[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering),2017,41(6):954-957. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] 杨光华,李思平,杜秀忠,等. 岩溶地区高层建筑筏板基础的实践[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(增刊2):3363-3371.YANG G H,LI S P,DU X Z,et al. Practice of highrise building with raft foundation in karst region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(S2):3363-3371. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] 肖泽忠. 桂林岩溶区红粘土地基承载特性研究[D]. 广西桂林:桂林理工大学,2018.XIAO Z Z. Study on the characteristics of bearing capacity of red clay foundation in karst area of Guilin[D]. Guilin Guangxi:Guilin University of Technology,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] 孙钧,温海洋. 人工智能科学在软土地下工程施工变形预测与控制中的应用实践:理论基础、方法实施、精细化智能管理(示例)[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2020,40(1):1-8.SUN J,WEN H Y. Application of artificial intelligence science to construction deformation prediction and control of underground engineering in soft soil:Cases study on theoretical foundation,method application and fine intelligent technical management[J]. Tunnel Construction,2020,40(1):1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] 兰鹏,李海潮,叶新宇,等. PINNs算法及其在岩土工程中的应用研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(3):586-592. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202103023LAN P,LI H C,YE X Y,et al. PINNs algorithm and its application in geotechnical engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(3):586-592. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE202103023 [54] 仉文岗,顾鑫,刘汉龙,等. 基于贝叶斯更新的非饱和土坡参数概率反演及变形预测[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(4):1112-1122.ZHANG W G,GU X,LIU H L,et al. Probabilistic back analysis of soil parameters and displacement prediction of unsaturated slopes using Bayesian updating[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(4):1112-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] 江巍,欧阳晔,闫金洲,等. 边坡岩土体抗剪强度的逆向迭代修正反演方法[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(8):2287-2295.JIANG W,OUYANG Y,YAN J Z,et al. Inversion iterative correction method for estimating shear strength of rock and soil mass in slope engineering[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(8):2287-2295. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] 刘喜凤,朱鸿鹄,王家琛,等. 基于神经网络的改进型土壤水分光纤感测技术研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2022,44(9):1721-1729. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202209017LIU X F,ZHU H H,WANG J C,et al. Improved fiber optic sensing technology of soil moisture based on neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2022,44(9):1721-1729. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE202209017 [57] 王才进,蔡国军,武猛,等. 基于人工智能算法预测土体导热系数[J]. 岩土工程学报,2022,44(10):1899-1907.WANG C J,CAI G J,WU M,et al. Prediction of thermal conductivity of soils based on artificial intelligence algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2022,44(10):1899-1907. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] 赵泽宁,段伟,蔡国军,等. 基于机器学习CPTU智能算法的黏性土应力历史评价[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(增刊2):104-107. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2021S2025ZHAO Z N,DUAN W,CAI G J,et al. Evaluation of stress history of clays based on intelligent CPTU machine learning algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(S2):104-107. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE2021S2025 [59] LIN P Y,CHEN X Y,JIANG M J,et al. Mapping shear strength and compressibility of soft soils with artificial neural networks[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,300:106585. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106585 [60] ZHANG J,HU J Z,LI X,et al. Bayesian network based machine learning for design of pile foundations[J]. Automation in Construction,2020,118:103295. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103295 [61] LIN P Y,NI P P,GUO C C,et al. Mapping soil nail loads using Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) simplified models and artificial neural network technique[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2020,57(10):1453-1471. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2019-0440 [62] LIU D,LIN P Y,ZHAO C Y,et al. Mapping horizontal displacement of soil nail walls using machine learning approaches[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2021,16(12):4027-4044. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01345-z [63] 黄发明,曹昱,范宣梅,等. 不同滑坡边界及其空间形状对滑坡易发性预测不确定性的影响规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(增刊2):3227-3240.HUANG F M,CAO Y,FAN X M,et al. Effects of different landslide boundaries and their spatial shapes on the uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(S2):3227-3240. (in Chinese with English abstract [64] 姜宇航,王伟,邹丽芳,等. 基于粒子群−变分模态分解、非线性自回归神经网络与门控循环单元的滑坡位移动态预测模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(增刊1):601-612.JIANG Y H,WANG W,ZOU L F,et al. Research on dynamic prediction model of landslide displacement based on particle swarm optimization-variational mode decomposition,nonlinear autoregressive neural network with exogenous inputs and gated recurrent unit[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(S1):601-612. (in Chinese with English abstract [65] 邬礼扬, 殷坤龙, 曾韬睿, 等. 不同栅格尺寸下输电线路地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):241-252.WU L Y, YIN K L, ZENG T R, et al. Evaluation of geological disaster susceptibility of transmission lines under different grid resolutions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):241-252.(in Chinese with English abstract [66] 郭衍昊, 窦杰, 向子林, 等. 基于优化负样本采样策略的梯度提升决策树与随机森林的汶川同震滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):251-265.GUO Y H, DOU J, XIANG Z L, et al. Susceptibility evaluation of Wenchuan coseismic landslides by gradient boosting decision tree and random forest based on optimal negative sample sampling strategies[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):251-265.(in Chinese with English abstract [67] 钟国强,王浩,李莉,等. 基于SFLA-GRNN模型的基坑地表最大沉降预测[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(2):792-798.ZHONG G Q,WANG H,LI L,et al. Prediction of maximum settlement of foundation pit based on SFLA-GRNN model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(2):792-798. (in Chinese with English abstract [68] ZHANG W G,LI H R,WU C Z,et al. Soft computing approach for prediction of surface settlement induced by earth pressure balance shield tunneling[J]. Underground Space,2021,6(4):353-363. doi: 10.1016/j.undsp.2019.12.003 [69] 吴志军,方立群,翁磊,等. 基于TBM掘进性能的岩体分级及可掘性等级感知识别方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(增刊1):2684-2699.WU Z J,FANG L Q,WENG L,et al. A classification and boreability perception and recognition method for rock mass based on TBM tunneling performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(S1):2684-2699. (in Chinese with English abstract [70] 李明亮,李克钢,秦庆词,等. 岩爆烈度等级预测的机器学习算法模型探讨及选择[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(增刊1):2806-2816.LI M L,LI K G,QIN Q C,et al. Discussion and selection of machine learning algorithm model for rockburst intensity grade prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(S1):2806-2816. (in Chinese with English abstract [71] 汤志立,徐千军. 基于9种机器学习算法的岩爆预测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(4):773-781.TANG Z L,XU Q J. Rockburst prediction based on nine machine learning algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(4):773-781. (in Chinese with English abstract [72] 刘德军,戴庆庆,左建平,等. 基于Stacking集成算法的岩爆等级预测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(增刊1):2915-2926.LIU D J,DAI Q Q,ZUO J P,et al. Research on rockburst grade prediction based on Stacking integrated algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2022,41(S1):2915-2926. (in Chinese with English abstract [73] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面: 从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):1-19.Zhu H H. Engineering geological interface: From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):1-19.(in Chinese with English abstract [74] SHAHIN M A. A review of artificial intelligence applications in shallow foundations[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,9(1):49-60. doi: 10.1179/1939787914Y.0000000058 [75] SHAHIN M A. State-of-the-art review of some artificial intelligence applications in pile foundations[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2016,7(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2014.10.002 [76] SHAHIN M A,JAKSA M B,MAIER H R. State of the art of artificial neural networks in xengineering[J]. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2008,13(I):1-25. [77] ZHANG W G,CHING J,GOH A T C,et al. Big data and machine learning in geoscience and geoengineering:Introduction[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(1):327-329. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.05.006 [78] ZHANG W G,ZHANG R H,WU C Z,et al. State-of-the-art review of soft computing applications in underground excavations[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2020,11(4):1095-1106. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.12.003 [79] ZHANG W G,PRADHAN B,STUYTS B,et al. Application of artificial intelligence in geotechnical and geohazard investigations[J]. Geological Journal,2023,58(6):2187-2194. doi: 10.1002/gj.4779 [80] WU S C,ZHANG J M,WANG R. Machine learning method for CPTu based 3D stratification of New Zealand geotechnical database sites[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics,2021,50:101397. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2021.101397 [81] KHATTI J,GROVER K S. Prediction of geotechnical properties of soil using artificial intelligence framework[J]. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering,2021,10(4):218-227. [82] 刘勇健,李彰明. 软土物理力学性质指标与微结构参数的灰色关联-神经网络模型[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(4):1018-1024.LIU Y J,LI Z M. Grey-relation analysis and neural networks model for relationship between physico-mechanical indices and microstructure parameters of soft soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(4):1018-1024. (in Chinese with English abstract [83] SAMUI P,HOANG N D,NHU V H,et al. A new approach of hybrid bee colony optimized neural computing to estimate the soil compression coefficient for a housing construction project[J]. Applied Sciences,2019,9(22):4912. doi: 10.3390/app9224912 [84] BHARDWAJ A,KUMAR V. Prediction of coefficient of compression of soil using artificial neural network[M]//LATHA GALI M,RAGHUVEER RAO P,eds. Lecture notes in civil engineering. Singapore:Springer Singapore,2020:917-926. [85] 赵挚南,年帅,郝龙,等. 基于BP神经网络邻近地铁基坑土体参数反演分析[J]. 施工技术,2020,49(增刊1):661-663.ZHAO Z N,NIAN S,HAO L,et al. Inversion analysis of soil parameters of adjacent subway foundation excavation based on BP neural network[J]. Construction Technology,2020,49(S1):661-663. (in Chinese with English abstract [86] 程凯华. 深圳地区岩溶分布特征分析[J]. 城市住宅,2020,27(5):234-235.CHENG K H. Analysis of karst distribution characteristics in Shenzhen area[J]. City & House,2020,27(5):234-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [87] 曲志鹏,王芳芳,张云银,等. 基于关联规则与随机森林的地震多属性砂体厚度预测[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):211-218.QU Z P,WANG F F,ZHANG Y Y,et al. Thickness prediction of seismic multi-attributes sand based on association rules and random forests[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):211-218. (in Chinese with English abstract [88] 窦强. 基于GIS和层次分析法的深圳市废弃矿山地质环境评价[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2020.DOU Q. Geological environment evaluation of abandoned mines in Shenzhen City based on GID and AHP[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [89] 蔡建斯,龚鹏,任宏剑. 深圳市某片区岩溶塌陷致塌成因分析及预防措施[J]. 中国矿业,2022,31(2):173-179.CAI J S,GONG P,REN H J. Cause analysis and preventive measures of karst collapse in a certain area of Shenzhen City[J]. China Mining Magazine,2022,31(2):173-179. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: