Evolution of structural characteristics with multistage stress fields in the Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
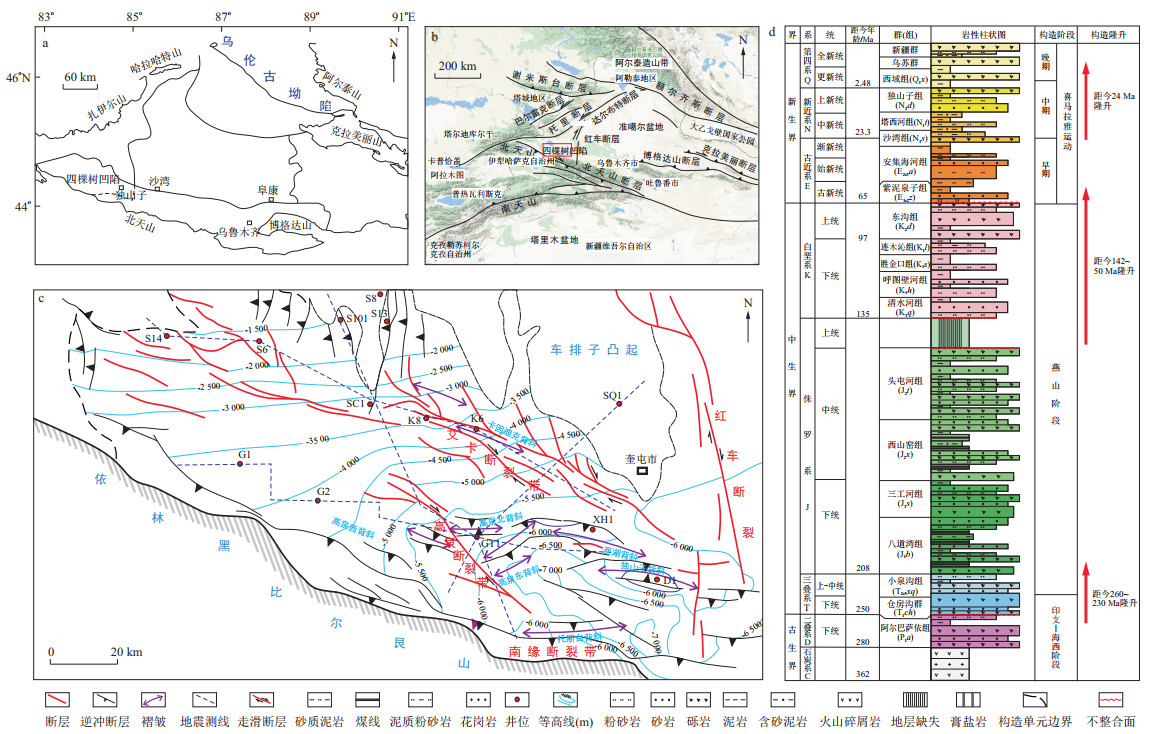
准噶尔盆地南缘四棵树凹陷位于北天山山前冲断带西段, 盆地自古生代以来经历了多期、多向的构造运动; 明确研究区构造系统特征及其演化过程, 对此类含油气盆地的油气勘探开发具有重要意义。在前人地质研究的基础上, 结合详细的地震资料解释、地质调查与地层发育特征, 根据研究区构造发育背景, 以四棵树凹陷构造格局的变动和多期应力场为线索, 对四棵树凹陷构造演化过程进行了系统性分析。研究表明, 四棵树凹陷深部发育挤压反转-走滑构造层、浅部发育推覆-滑脱构造层; 平面上根据构造样式发育特征可划分为南部挤压断褶带、中部走滑压扭带、北部隆起带; 凹陷经历了2期强烈的构造隆升期, 对应2期断裂活动高峰期; 构造环境及应力场条件发生了多次转变, 晚石炭世至早中二叠世为弧后裂陷背景下的NNW-SSE向伸展裂陷期、晚二叠世至三叠纪为扎伊尔山造山运动下NNW-SSE向挤压的断坳转换期、晚侏罗世至古近纪为周缘造山带与车排子凸起的共同作用下NNW-SSE向挤压陆内坳陷期、新近纪为北天山强烈的造山活动背景下NS向挤压作用的复活前陆盆地期。通过探讨多期应力场作用下四棵树凹陷的构造演化特征, 进一步深入认识了此类含油气盆地整体构造格局的变动过程, 也为研究区油气资源下一步勘探提供了新思路。
Abstract:Objective The Sikeshu Sag of the southern Junggar Basin is tectonically located in the western thrust belt of the North Tianshan Mountains. The basin has undergone multiple stages and multidirectional tectonic movements since the Palaeozoic. Clarifying the structural characteristics and evolutionary process of the structural system in the study area is critical for petroleum exploration and development in such petroliferous basins.
Methods Utilizing the seismic data interpretation and the outcrop geological investigation of the Sikeshu Sag, spatial-temporal variations in the structural patterns and stress fields were revealed, and a tectonic evolution model was established.
Results This study indicates that the compressional inversion and strike-slip structures were widely developed in the deep-buried layers of the Sikeshu Sag, but the thrust and decollement structures were more prevail in the shallow layers of the Sikeshu Sag. According to the structural style, the Sikeshu Sag can be divided into the southern compressional fault-fold belt, central strike-slip compressive-torsional belt, and northern uplift belt. The Sikeshu Sag experienced two periods of strong tectonic uplift, corresponding to the peak period of two stages of fault activity. The tectonic environment and stress field conditions underwent multiple changes: the NNW-SSE extension driven by the back-arc rifting during the late Carboniferous to early-middle Permian, the rift-depression transition triggered by the NNW-SSE extrusion of the Zaire orogenic movement during the late Permian to Triassic, the regional depression induced by the NNW-SSE extrusion of the peripheral orogenic belt and Chepaizi uplift during the late Jurassic to Palaeogene, and the reactivation of foreland caused by NS extrusion of North Tianshan Mountains during the Neogene.
Conclusion This study explores the tectonic evolution of the Sikeshu Sag under multiphase stress fields, which favors the better understanding of the overall tectonic pattern changes in similar petroliferous basins and provides new insights for the next steps of petroleum exploration in the study area.
-
Key words:
- southern Junggar Basin /
- Sikeshu Sag /
- foreland thrust belt /
- structural pattern /
- structural evolution /
- stress field
-
图 8 四棵树凹陷构造演化剖面(剖面位置见图 1c, 下同)
a.GT1-SC1井构造演化剖面;b.G1-GT1井构造演化剖面
Figure 8. Structural evolution profiles of the Sikeshu Sag
表 1 二叠系岩墙走向与共轭缝指示应力方向
Table 1. Strike of the Permian dyke and the stress direction indicated by conjugate joints
二叠系岩墙走向/(°) 数量/条 C-P共轭缝应力方向/(°) 数量/组 J-K共轭缝应力方向/(°) 数量/组 E-N共轭缝应力方向/(°) 数量/组 [0, 15) 0 [0, 15) 0 [0, 15) 21 [0, 15) 11 [15, 30) 0 [15, 30) 0 [15, 30) 13 [15, 30) 15 [30, 45) 0 [30, 45) 0 [30, 45) 0 [30, 45) 0 [45, 60) 0 [45, 60) 0 [45, 60) 0 [45, 60) 8 [60, 75) 0 [60, 75) 0 [60, 75) 4 [60, 75) 0 [75, 90) 0 [75, 90) 0 [75, 90) 0 [75, 90) 0 [90, 105) 0 [90, 105) 10 [90, 105) 2 [90, 105) 0 [105, 120) 12 [105, 120) 20 [105, 120) 0 [105, 120) 0 [120, 135) 5 [120, 135) 0 [120, 135) 0 [120, 135) 0 [135, 150) 3 [135, 150) 16 [135, 150) 0 [135, 150) 5 [150, 165) 0 [150, 165) 0 [150, 165) 6 [150, 165) 0 [165, 180] 0 [165, 180] 4 [165, 180] 12 [165, 180] 24 表 2 四棵树凹陷南缘断层产状数据
Table 2. Fault occurrence data for the south margin of the Sikeshu Sag
断层倾向/(°) 数量/条 断层倾角/(°) 数量/条 [0, 30) 15 [0, 15) 49 [30, 60) 21 [15, 30) 28 [60, 90) 6 [30, 45) 19 [90, 120) 4 [45, 60) 14 [120, 150) 7 [60, 75) 7 [150, 180) 12 [75, 90] 6 [180, 210) 16 [210, 240) 26 [240, 270) 5 [270, 300) 2 [300, 330) 5 [330, 360] 4 -
[1] 靳军, 王飞宇, 任江玲, 等. 四棵树凹陷高探1井高产油气成因与烃源岩特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(2): 145-151.JIN J, WANG F Y, REN J L, et al. Genesis of high-yield oil and gas in Well Gaotan-1 and characteristics of source rocks in Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(2): 145-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 庄新明. 准噶尔盆地四棵树凹陷石油地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 新疆地质, 2006, 24(4): 429-433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2006.04.020ZHUANG X M. Petroleum geology features and prospecting targets of Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2006, 24(4): 429-433. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2006.04.020 [3] 赵进雍, 冀冬生, 吴见, 等. 准噶尔盆地四棵树凹陷侏罗系-白垩系储层岩石力学参数研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(4): 573-582.ZHAO J Y, JI D S, WU J, et al. Research on rock mechanics parameters of the Jurassic-Cretaceous reservoir in the Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(4): 573-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 孟元库, 施发剑, 汪新文. 准噶尔盆地南缘四棵树凹陷构造变形特征分析[J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 2012, 25(2): 116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5132.2012.02.025MENG Y K, SHI F J, WANG X W. Analysis of the structure and deformation of Sikeshu Sag in the southern part of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Ningbo University(Natural Science & Engineering Edition), 2012, 25(2): 116-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5132.2012.02.025 [5] 杨迪生, 肖立新, 阎桂华, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘四棵树凹陷构造特征与油气勘探[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(2): 138-144.YANG D S, XIAO L X, YAN G H, et al. Structural characteristics and petroleum exploration in Sikeshu Sag, southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(2): 138-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 漆家福, 陈书平, 杨桥, 等. 准噶尔-北天山盆山过渡带构造基本特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(2): 252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.02.015QI J F, CHEN S P, YANG Q, et al. Characteristics of tectonic deformation within transitional belt between the Junggar Basin and the northern Tianshan Mountain[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(2): 252-260. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.02.015 [7] 朱明, 袁波, 梁则亮, 等. 准噶尔盆地周缘断裂属性与演化[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(9): 1163-1173.ZHU M, YUAN B, LIANG Z L, et al. Fault properties and evolution in the periphery of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 1163-1173. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 朱文, 吴朝东, 王家林, 等. 准噶尔盆地四棵树凹陷三叠系物源及其构造意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(5): 512-518.ZHU W, WU C D, WANG J L, et al. Triassic provenance and its tectonic significance in Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(5): 512-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] VELOSO E E, GOMILA R, CEMBRANO J, et al. Stress fields recorded on large-scale strike-slip fault systems: Effects on the tectonic evolution of crustal slivers during oblique subduction[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 664: 244-255. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.09.022 [10] 蔡忠贤, 陈发景, 贾振远. 准噶尔盆地的类型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010CAI Z X, CHEN F J, JIA Z Y. Types and tectonic evolution of Junger Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010 [11] 梁则亮, 庞志超, 冀冬生, 等. 四棵树凹陷超深层裂谷盆地的厘定及油气勘探意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(1): 18-24.LIANG Z L, PANG Z C, JI D S, et al. Discovery of ultra-deep rift basin and its petroleum exploration significance in Sikeshu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(1): 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861.HE D F, ZHANG L, WU S T, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 康积伦, 王家豪, 马强, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组细粒湖底扇沉积及其页岩油储层意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 82-93. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0074KANG J L, WANG J H, MA Q, et al. Fine-grained sublacustrine fan deposits and their significance in shale oil reservoirs in the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 82-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0074 [14] 胡小文, 杨晓勇, 任伊苏, 等. 准噶尔盆地沉积环境-构造演化对砂岩型铀矿成矿的控制作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(4): 725-741.HU X W, YANG X Y, REN Y S, et al. Sedimentary environment and tectonic evolution of Junggar Basin: Constrains on the mineralization of sandstone-type uranium deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(4): 725-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 王家林, 吴朝东, 朱文, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘二叠纪-三叠纪构造-沉积环境与原型盆地演化[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(4): 643-660.WANG J L, WU C D, ZHU W, et al. Tectonic-depositional environment and prototype basin evolution of the Permian-Triassic in southern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2016, 18(4): 643-660. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] ZHU Z J, LI Q, CHEN H H, et al. Tectonic-geomorphological evolution and provenance-sedimentary response: Insights from the Middle Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023, 158: 106514. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106514 [17] XIANG D F, ZHANG Z Y, XIAO W J, et al. Episodic meso-cenozoic denudation of Chinese Tianshan: Rvidence from detrital apatite fission track and zircon U-Pb data, southern Junggar Basin margin, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 175: 199-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.07.042 [18] JIA Y Y, SUN J M, LYU L X. Late Cenozoic tectono-geomorphologic evolution of the northern Tianshan Mountain range: Insight from U-Pb ages of detrital zircon grains from the Upper Oligocene-Quaternary sediments of the southern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 194: 104286. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104286 [19] 王向东, 王任, 石万忠, 等. 中国东部典型裂谷盆地构造活动特征及演化: 以松辽盆地孤店断陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 85-95. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0089WANG X D, WANG R, SHI W Z, et al. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of typical rift basins in eastern China: A case study in the Gudian area, Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 85-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0089 [20] ZHOU Y X, WU C D, YUAN B, et al. Cenozoic tectonic patterns and their controls on growth strata in the northern Tianshan fold and thrust belt, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 198: 104237. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104237 [21] HOU S Q, LI D, HE D F, et al. A Late Carboniferous transition from subduction to collision: Tectono-sedimentary evidence from southern Junggar, NW China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2024, 15(3): 101796. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2024.101796 [22] LI D, HE D F, LU Y, et al. Diverse origins of Late Paleozoic calc-alkaline magmatic rocks from the Bogda tectonic belt: Implications for the geodynamic evolution of the eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2021, 404: 106442. [23] TANG W B, ZHANG Y Y, PE-PIPER G, et al. Permian rifting processes in the NW Junggar Basin, China: Implications for the post-accretionary successor basins[J]. Gondwana Research, 2021, 98: 107-124. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.06.005 [24] 肖芳锋, 侯贵廷, 王延欣, 等. 准噶尔盆地及周缘二叠纪以来构造应力场解析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 46(2): 224-230.XIAO F F, HOU G T, WANG Y X, et al. Study on structural stress fields since Permian, Junggar Basin and adjacent areas[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2010, 46(2): 224-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 陈发景, 汪新文, 汪新伟. 准噶尔盆地的原型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.010CHEN F J, WANG X W, WANG X W. Prototype and tectonic evolution of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.010 [26] 吴林, 朱明, 冯兴强, 等. 准噶尔盆地四棵树凹陷构造应力场与构造变形解析[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 494-506.WU L, ZHU M, FENG X Q, et al. Interpretation on tectonic stress and deformation of Sikeshu Sag in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 494-506. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 徐盛林, 陈宣华, 马飞宙, 等. 西准噶尔拉巴岩体的成因: 来自岩石学、年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(6): 875-894.XU S L, CHEN X H, MA F Z, et al. Petrogenesis of Laba plutons in west Junggar, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from petrology, chronology, and geochemistry[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 875-894. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 李辛子, 韩宝福, 李宗怀, 等. 新疆克拉玛依中基性岩墙群形成力学机制及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2005, 51(5): 39-44.LI X Z, HAN B F, LI Z H, et al. Mechanism of the Karamay basic-intermediate dyke swarm from Xinjiang and tectonic implications[J]. Geological Review, 2005, 51(5): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 齐进英. 新疆准噶尔脉岩群地质及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(3): 288-299. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1993.03.007QI J Y. Geology and genesis of vein rock group in western Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(3): 288-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1993.03.007 [30] ZHU Z J, LI Q, CHEN H H, et al. Tectonic-geomorphological evolution and provenance-sedimentary response: Insights from the Middle Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023, 158: 106514. [31] GUI L L, ZHUO Q G, LU X S, et al. Restoration of reservoir diagenesis and hydrocarbon accumulation process by calcite in-situ U-Pb dating and fluid inclusion analysis: A case study on Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan Structure, southern Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50-6: 386-1397. [32] FANG Y N, WU C D, WANG Y Z, et al. Topographic evolution of the Tianshan Mountains and their relation to the Junggar and Turpan Basins, Central Asia, from the Permian to the Neogene[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 75: 47-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.03.020 [33] WU Z J, YANG X Y, SUN S J, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of Late Mesozoic strata in the Junggar Basin, NW China: Implications for the timing of collision between the Karakoram-Lhasa Block and the Eurasian Continent[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2023, 254: 105755. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105755 [34] ZHANG H H, ZHANG Z C, TANG W H, et al. Burial and exhumation history of Jurassic sedimentary rocks in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin: Implications for the growth of the northern Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 236: 105339. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105339 [35] 赵俊猛, 张培震, 张先康, 等. 中国西部壳幔结构与动力学过程及其对资源环境的制约: "羚羊计划" 研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(5): 230-259.ZHAO J M, ZHANG P Z, ZHANG X K, et al. Crust-mantle structure and geodynamic processes in western China and their constraints on resources and environment: Research progress of the ANTILOPE Project[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(5): 230-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] MARTIN C D, LANYON G W. Measurement of in situ stress in weak rocks at Mont Terri Rock Laboratory, Switzerland[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7/8): 1077-1088. [37] CHANG C D, LEE J B, KANG T S. Interaction between regional stress state and faults: Complementary analysis of borehole in situ stress and earthquake focal mechanism in southeastern Korea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 485(1/2/3/4): 164-177. [38] MAFAKHERI BASHMAGH N, LIN W R, MURATA S, et al. Magnitudes and orientations of present-day in situ stresses in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq: Insights into combined strike-slip and reverse faulting stress regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 239: 105398. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105398 [39] 计文化, 李荣社, 陈奋宁, 等. 中国西北地区南华纪-古生代构造重建及关键问题讨论[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(5): 634-655.JI W H, LI R S, CHEN F N, et al. Tectonic reconstruction of Northwest China in the Nanhua-Paleozoic and discussions on key issues[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(5): 634-655. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] NI X H, WANG B, CLUZEL D, et al. Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Tianshan Belt: New structural and geochronological constraints from meta-sedimentary rocks and migmatites in the Harlik Range(NW China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 210: 104711. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104711 [41] 杨光华, 张炜波, 郭永峰, 等. 北天山四棵树花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(2): 83-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.02.010YANG G H, ZHANG W B, GUO Y F, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb chronology and geological implications of Sikeshu stitching pluton in the North Tianshan suture zone, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2014, 47(2): 83-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.02.010 [42] JIN M, JIE Y. The Neogene Dingshanyanchi Formation in northern Junggar Basin of Xinjiang and its stratigraphic implications[J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2008, 46(2): 90-110. [43] HE Z Y, WANG B, NI X H, et al. Structural and kinematic evolution of strike-slip shear zones around and in the Central Tianshan: Insights for eastward tectonic wedging in the southwest Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2021, 144: 104279. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104279 -





 下载:
下载: