Grain-size characteristics and sedimentary environmental significance of terrestrial red sandstone in the Dongying Depression with a gentle slope zone
-
摘要:
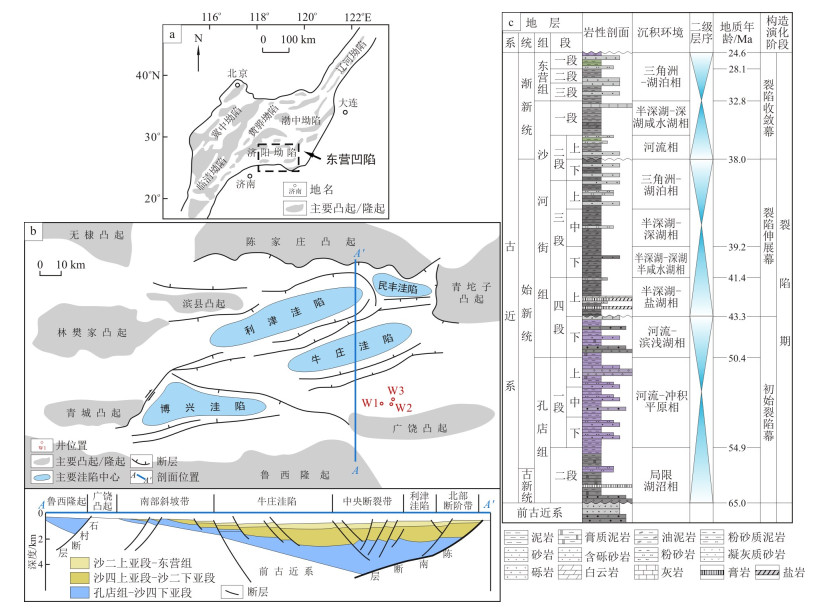
东营凹陷古近系红层已被证实拥有巨大的勘探潜力。断陷盆地缓坡带广泛分布以砂、泥岩频繁互层为特征的红层沉积, 而这种沉积物究竟形成于何种环境尚未形成统一认识。为明确这种干旱气候背景下发育的大规模陆相红层的沉积类型, 以东营凹陷南部缓坡带王家岗地区W1、W2和W3井为例, 系统解剖了孔一段-沙四下亚段红层储层的粒度分布特征、粒度参数特征及粒度概率累计曲线特征。结果显示: 研究区红层储层砂岩具有单砂体厚度较薄(1~7.7 m)、粒度较细(平均粒径为2.24
ϕ ~4.73ϕ )的特点; 粒度频率曲线主要为单峰正偏态型, 表明沉积物以粗组分为主; 粒度参数判别函数和判别图解均指示河流沉积环境; 大多数样品的累计概率曲线具有显著的过渡组分(>50%),C -M 图形与C =M 线平行, 表现出密度流特征。测井曲线主要为中-高幅箱型和钟型, 指示加积和侧积作用占主导地位; 岩心上常见反映快速堆积的块状层理、代表单向水流的平行层理和反映弱水流的小型交错层理等构造。基于研究区盆山相间的古地貌格局和炎热干旱的古气候背景的综合分析表明, 红层砂岩形成于分支河流体系, 其沉积特征表现为: 从上游至下游, 随着水动力条件的衰减, 河道分汊加强, 洪水侵蚀能力减弱, 单砂体厚度和沉积物粒度逐渐减小, 流体性质由密度流逐渐演变为牵引流。该研究的新认识为研究区红层油气勘探提供了新的思路, 在开展此类型储层预测工作时, 应重视古物源、古流向的分析, 并加强对单期水道的识别和刻画。Abstract:Objective In the gentle slope zone of the Dongying Depression, the first member of the Kongdian Formation and the lower part of the fourth member of the Shahejie Formation can be split by a distinctive assemblage of reddish sediments, which originated from both fluvial and lacustrine processes. Extensive research has substantiated the significant exploration potential of the Palaeogene red bed in the Dongying Depression. Nevertheless, the sedimentary facies type of the red bed remains a subject of debate among researchers.
Methods To address this issue, we present a comprehensive analysis of wells W1, W2, and W3, which are located in the Wangjiagang area within the southern gentle slope zone of the Dongying Depression. This analysis mainly focused on evaluating the grain size distribution, grain size parameters, and grain size probability accumulation curves of the red bed.
Results This study revealed the distinctive characteristics of the red sandstone reservoirs in the study area. These include thin single sand body thicknesses ranging from 1 to 7.7 m and fine particle sizes, changing from 2.24
ϕ to 4.73ϕ . The grain size distribution is mainly characterized by unimodal positive skewness curves, suggesting the dominance of the relatively coarse fraction. The grain-size parameter discriminant function and bivariate grain-size parameter plots suggest a fluvial environment. The grain size accumulation probability curves of most samples exhibit a significant transition component (over 50%), and the graphs in theC -M bivariate plot are parallel to theC =M baseline, reflecting the characteristics of density flow. Moreover, the logging curves mainly exhibit box and bell shapes with medium to high amplitudes, indicating that the sedimentary processes primarily involved vertical accretion and lateral accretion. The core analysis revealed the presence of blocky bedding indicative of rapid sediment accumulation, parallel bedding characteristic of unidirectional flow, and small cross-bedding suggestive of weak flow.Conclusion In conclusion, it is believed that the red sandstone resulted from distributive fluvial systems deposited with both palaeo-geomorphic features and hot-arid palaeo-climate factors in the study area. From upstream to downstream, the hydrodynamic conditions gradually weakened, the bifurcation of river channels strengthened, the flood erosion ability decreased, the single sand body thickness and sediment grain size decreased progressively, and the fluid properties transitioned from density flow to traction flow. The novel insights of this study offer a fresh perspective for the exploration of petroleum in the red sandstone of the study area. In forecasting such reservoirs, particular emphasis should be placed on analyzing palaeo-provenance and paleo-current while enhancing the identification and characterization of individual-stage flood channels.
-
图 2 东营凹陷王家岗地区W1-W2-W3井连井剖面图(井位置见图 1c)
Figure 2. Cross section along wells W1, W2 and W3 in the Wangjiagang area of the Dongying Depression
图 3 东营凹陷王家岗地区W1、W2、W3井各目的层岩性柱及岩心照片(岩性图例同图 1)
a~j依次为目的层A~J的岩性柱及岩心照片,岩心长度均为1 m
Figure 3. Lithologic column and core photograph of the target intervals in Wells W1, W2 and W3 in the Wangjiagang area of the Dongying Depression
表 1 东营凹陷王家岗地区古近系红层砂岩粒度参数范围和平均值
Table 1. Range and average of grain-size parameter of the Paleogene red sandstone in the Wangjiagang area of the Dongying Depression
目的层 平均粒径Mz /ϕ 标准偏差σ1 偏度SK1 峰度KG C值/ϕ M值/ϕ 范围值 平均值 范围值 平均值 范围值 平均值 范围值 平均值 范围值 平均值 范围值 平均值 A 3.20~4.10 3.59 0.79~1.58 1.10 0.54~0.73 0.63 1.67~3.11 2.26 1.49~2.67 2.14 2.99~3.54 3.30 B 2.63~3.27 2.94 0.55~0.87 0.71 0.37~0.68 0.49 1.23~2.01 1.57 1.26~2.50 1.83 2.50~3.12 2.79 C 3.76~4.73 4.23 1.08~1.71 1.43 0.37~0.58 0.48 1.30~1.97 1.73 1.14~2.66 2.37 3.64~4.16 3.88 D 3.03~4.13 3.54 1.10~1.70 1.38 0.35~0.54 0.45 1.56~1.98 1.82 1.57~2.27 1.87 2.92~3.70 3.29 E 2.95~3.28 3.10 1.03~1.29 1.10 0.32~0.41 0.35 1.66~1.74 1.70 1.49~1.77 1.64 2.87~3.10 3.00 F 2.24~3.24 2.65 0.88~1.25 1.01 0.19~0.39 0.30 1.24~1.90 1.63 0.71~1.92 1.23 2.18~3.20 2.59 G 3.59~4.38 3.93 1.10~1.49 1.26 0.35~0.47 0.41 1.42~1.87 1.71 1.95~2.47 2.31 3.34~4.01 3.73 H 2.99~3.19 3.06 0.85~1.07 0.96 0.28~0.35 0.31 1.73~1.80 1.77 1.71~1.82 1.78 2.94~3.11 3.01 I 2.30~3.19 2.74 0.85~1.27 1.05 0.24~0.38 0.32 1.42~1.74 1.63 0.78~1.74 1.31 2.27~3.08 2.65 J 2.47~4.19 3.20 1.02~1.63 1.41 0.32~0.52 0.42 1.41~1.55 1.50 0.99~2.14 1.37 2.37~3.80 2.91 -
[1] ABBASSI N, KUNDRAT M, ATAABADI M M. Avian ichnia from the Miocene red beds of NW Iran[C]//Anon. 15th Czech Polish Slovak Paleontological Conference. Banská Bystrica: Geological Institute of Slovak Academy of Sciences, 2014: 7-9. [2] 蒋昊原, 夏燕青, 刘善品, 等. 陆相沉积物风化强度与颜色成因探讨: 以四川盆地中侏罗统上沙溪庙组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(4): 1025-1039.JIANG H Y, XIA Y Q, LIU S P, et al. Weathering intensity and color genesis of continental sediments: A case study from the Shangshaximiao Formation of the Middle Jurassic in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(4): 1025-1039. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 杨兵. 陆相红层型铜铅锌矿床与红层盆地热卤水成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(3): 441-455.YANG B. Red bed Cu-Pb-Zn deposits and mineralization of hot brine in continental red bed basin[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(3): 441-455. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 徐伟祥. 胶莱盆地万家至蓝村一带白垩纪陆相"红层" 火山岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊1): 29-36.XU W X. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age of Cretaceous continental "red bed" volcanic rocks in the area from Wanjia to Lancun, Jiaolai Basin and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(S1): 29-36. (in Chinese) [5] 谭聪, 于炳松, 袁选俊, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地下三叠统刘家沟组与和尚沟组红层成色机制[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(4): 769-783.TAN C, YU B S, YUAN X J, et al. Color origin of the Lower Triassic Liujiagou and Heshanggou Formations red beds in the Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(4): 769-783. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] ZHANG J L, ZHANG X. Composition and provenance of sandstones and siltstones in Paleogene, Huimin Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 19(3): 252-270. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60044-8 [7] XU H, LIU Y Q, KUANG H W, et al. Jurassic-Cretaceous terrestrial transition red beds in northern North China and their implication on regional paleogeography, paleoecology, and tectonic evolution[J]. Palaeoworld, 2017, 26(2): 403-422. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2016.05.007 [8] 陈金牛, 毛学刚, 师永辉, 等. 闽西晚白垩世红层的古环境探究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(4): 1553-1568.CHEN J N, MAO X G, SHI Y H, et al. Study on the Late Cretaceous paleoenvironment documented by red beds in the western Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(4): 1553-1568. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 王晓宁, 岳大鹏, 赵景波. 榆林西南部下白垩统砂岩粒度组成与成因分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(10): 1088-1100. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.068WANG X N, YUE D P, ZHAO J B. Grain size composition and genesis of Lower Cretaceous sandstone in southwestern Yulin[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(10): 1088-1100. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.068 [10] 吴文斌, 陈留勤, 丁婷, 等. 广丰盆地晚白垩世周田组红层沉积特征及古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(3): 485-496.WU W B, CHEN L Q, DING T, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and paleoclimatic significance of the Late Cretaceous Zhoutian Formation red beds in the Guangfeng Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(3): 485-496. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 刘见宝, 闫云明, 宋志敏, 等. 济阳坳陷孔店组沉积体系及其构造成因[J]. 地质与资源, 2017, 26(5): 467-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2017.05.006LIU J B, YAN Y M, SONG Z M, et al. Sedimentary system and structural genesis of Kongdian Formation in Jiyang Depression[J]. Geology and Resources, 2017, 26(5): 467-472. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2017.05.006 [12] 刘海宁, 李红梅, 魏文, 等. 东营凹陷北带西段沙四上纯下-沙四下砂体沉积特征研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2014, 4(3): 8-13.LIU H N, LI H M, WEI W, et al. Study on the sand body sedimentary characteristics of Es4scx-Es4x Formation in the western part of the northern region in Dongying Depression[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2014, 4(3): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 年涛, 杨金川, 姜在兴, 等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷始新统红层沉积再认识[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(1): 150-169.NIAN T, YANG J C, JIANG Z X, et al. Rethinking the Eocene red-bed sedimentation in the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(1): 150-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 王健, 操应长, 刘惠民, 等. 东营凹陷沙四下亚段沉积环境特征及沉积充填模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(2): 274-282.WANG J, CAO Y C, LIU H M, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary environment and filling model of the lower submember of the Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(2): 274-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 袁静. 济阳坳陷南部古近系洪水-漫湖沉积[J]. 中国地质, 2005, 32(4): 131-138.YUAN J. Paleogene flooded lake sediments in the southern part of the Jiyang Depression[J]. Geology in China, 2005, 32(4): 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 年涛, 姜在兴, 刘惠民, 等. 东营凹陷孔一段"红-灰" 岩层旋回沉积记录: 以王家岗地区王46井为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 32-43. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0072NIAN T, JIANG Z X, LIU H M, et al. Cyclic sedimentary record of "red-greyish green" beds in the First Member of Eocene Kongdian Formation(Ek1), Dongying Sag: An example from the Well Wang 46 in Wangjiagang area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 32-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0072 [17] 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 第4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 1-478.ZHU X M. Sedimentary petrology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 1-478. (in Chinese) [18] 于兴河. 碎屑岩系油气储层沉积学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 1-513.YU X H. Sedimentology of oil and gas reservoirs in clastic rock series[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 1-513. (in Chinese) [19] 王铸坤, 李宇志, 操应长, 等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷永北地区沙河街组三段砂砾岩粒度概率累积曲线特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(2): 230-240.WANG Z K, LI Y Z, CAO Y C, et al. Probability cumulative grain-size distribution curves and their implications for sedimentary environment identification of coarse clastic rocks of the Es3 in Yongbei area, the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(2): 230-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 袁红旗, 王蕾, 于英华, 等. 沉积学粒度分析方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(2): 380-393.YUAN H Q, WANG L, YU Y H, et al. Review of sedimentary grain size analysis methods[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(2): 380-393. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] ZHANG X N, ZHANG H C, CHANG F Q, et al. Long-range transport of aeolian deposits during the last 32 kyr inferred from rare earth elements and grain-size analysis of sediments from Lake Lugu, southwestern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 567: 110248. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110248 [22] OGBE O B. Reservoir sandstone grain-size distributions: Implications for sequence stratigraphic and reservoir depositional modelling in Otovwe field, onshore Niger Delta Basin, Nigeria[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 203: 108639. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108639 [23] 吴靖, 姜在兴, 梁超. 东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段细粒沉积岩岩相特征及与沉积环境的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(10): 1110-1122.WU J, JIANG Z X, LIANG C. Lithofacies characteristics of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the upper submember of Member 4 of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag and their relationship with sedimentary environment[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 1110-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 宋国奇, 王永诗, 程付启, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系二级层序界面厘定及其石油地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(5): 1-7.SONG G Q, WANG Y S, CHENG F Q, et al. Ascertaining secondary-order sequence of Palaeogene in Jiyang Depression and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2014, 21(5): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] SHI J Y, JIN Z J, LIU Q Y, et al. Terrestrial sedimentary responses to astronomically forced climate changes during the Early Paleogene in the Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 502: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.01.006 [26] 孟凡超, 邱隆伟, 刘魁元, 等. 济阳坳陷埕东凸起基底岩石组合、原岩恢复及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3): 707-720.MENG F C, QIU L W, LIU K Y, et al. Rock association, protolith restoration of basement rocks in Chengdong Salient, Jiyang Depression and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(3): 707-720. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 山东省地质矿产局. 山东省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 1-526.Shandong Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional geology of Shandong Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991: 1-526. [28] FOLK R L, WARD W C. Brazos River bar(Texas): A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27: 3-26. [29] FRIEDMAN G M. Dynamic processes and statistical parameters compared for size frequency distribution of beach and river sands[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1967, 37(2): 327-354. [30] 郑浚茂. 陆源碎屑沉积环境的粒度标志[M]. 武汉: 武汉地质学院, 1982: 1-105.ZHENG J M. The granularity of the depositional environment of the terrigenous clast[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Geosciences, 1982: 1-105. [31] SAHU B K. Depositional mechanisms from the size analysis of clastic sediments[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(1): 73-83. [32] KANHAIYA S, SINGH B P, TRIPATHI M, et al. Lithofacies and particle-size characteristics of Late Quaternary floodplain deposits along the middle reaches of the Ganga River, central Ganga Plain, India[J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 284: 220-228. [33] PASSEGA R. Texture as characteristic of clastic deposition[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1957, 27: 3-26. [34] 蒲秀刚, 周立宏, 韩文中, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段斜坡区重力流沉积与致密油勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2): 138-149.PU X G, ZHOU L H, HAN W Z, et al. Gravity flow sedimentation and tight oil exploration in lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in slope area of Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 138-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] VISHER G S. Grain size distributions and depositional processes[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1969, 39(3): 1074-1106. [36] 贾海波, 季汉成, 吴智平, 等. 东营凹陷西部红层沉积期沉积体系及物源方向研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1058-1069.JIA H B, JI H C, WU Z P, et al. Sedimentary system and provenance orientation of the red-bed sedimentary period in Dongying Sag[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(5): 1058-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 舒婷, 刘桂珍, 郭健. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长63重力流沉积特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 140-150. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220452SHU T, LIU G Z, GUO J. Characteristics of gravity flow sedimentation of Chang 63 in the Huaqing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 140-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220452 [38] DOUST H, OMATSOLA E. Niger delta[C]//Edwards J D, Santogrossi P A. Divergent/passive margin basins. [S. l.]: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1990, 48: 201-238. [39] 叶传永, 王志明, 赵世勤, 等. 柴达木盆地西部尕斯库勒盐湖280 ka以来沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1): 85-92.YE C Y, WANG Z M, ZHAO S Q, et al. Sedimentary characteristics since 280 ka B.P. in Gasikule Salt Lake in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 85-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] 张祥辉, 张昌民, 冯文杰, 等. 苏干湖盆地周缘分支河流体系的几何形态及影响因素分析[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11): 2947-2959.ZHANG X H, ZHANG C M, FENG W J, et al. Geometry and control factors of distributive fluvial system around the Sugan Lake Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(11): 2947-2959. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] 张昌民, 宋新民, 支东明, 等. 陆相含油气盆地沉积体系再思考: 来自分支河流体系的启示[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(2): 127-153.ZHANG C M, SONG X M, ZHI D M, et al. Rethinking on the sedimentary system of terrestrial petroliferous basins: Insights from distributive fluvial system[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(2): 127-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] 张昌民, 胡威, 朱锐, 等. 分支河流体系的概念及其对油气勘探开发的意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(3): 1-9.ZHANG C M, HU W, ZHU R, et al. Concept of distributive fluvial system and its significance to oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(3): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) [43] DAVIDSON S K, HARTLEY A J, WEISSMANN G S, et al. Geomorphic elements on modern distributive fluvial systems[J]. Geomorphology, 2013, 180/181: 82-95. [44] OWEN A, NICHOLS G J, HARTLEY A J, et al. Vertical trends within the prograding Salt Wash distributive fluvial system, SW United States[J]. Basin Research, 2017, 29(1): 64-80. [45] SOARES M V T, BASILICI G, DAL'BÓ P F, et al. Climatic and geomorphologic cycles in a semiarid distributive fluvial system, Upper Cretaceous, Bauru Group, SE Brazil[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 372: 75-95. [46] SOARES M V T, BASILICI G, LORENZONI P, et al. Landscape and depositional controls on palaeosols of a distributive fluvial system(Upper Cretaceous, Brazil)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 410: 105774. [47] 李相博, 刘化清, 邓秀芹, 等. 干旱环境河流扇概念与鄂尔多斯盆地延长组"满盆砂" 成因新解[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(5): 1208-1221.LI X B, LIU H Q, DENG X Q, et al. The concept of fluvial fans in an arid environment: A new explanation of the origin of "sand-filled basins" in the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(5): 1208-1221. (in Chinese with English abstract) [48] 张金亮. 曲流河扇相模式及应用[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(2): 408-430.ZHANG J L. The facies model of a meandering fluvial fan and its application[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(2): 408-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) [49] 何苗, 秦兰芝, 尹太举, 等. 分支河流体系在东海西湖凹陷南部的运用及其对油气潜力的指示[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(3): 820-831.HE M, QIN L Z, YIN T J, et al. The application of the distributive fluvial system in the south Xihu Depression, East China Sea and its indication of oil and gas potential[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(3): 820-831. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] 蔡进功. 东营箕状断陷沉积物源的演变[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2001, 8(6): 5-8.CAI J G. The evaluation of sedimental source in Dongying dustpan-like rift[J]. Oil & Gas Recovery Techinology, 2001, 8(6): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) [51] 纪友亮, 任红燕, 张世奇, 等. 渤海湾盆地古近纪古地理特征与油气[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(4): 611-633.JI Y L, REN H Y, ZHANG S Q, et al. Paleogene palaeogeography and oil and gas distribution in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2022, 24(4): 611-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) [52] 王冠民, 林国松. 济阳坳陷古近纪的古气候区分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(5): 505-509.WANG G M, LIN G S. Eogene paleoclimate zone study in the Jiyang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(5): 505-509. (in Chinese with English abstract) [53] WANG Q, SPICER R A, YANG J, et al. The Eocene climate of China, the early elevation of the Tibetan Plateau and the onset of the Asian Monsoon[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(12): 3709-3728. [54] 贺振建, 刘书会, 王长轩, 等. 基于气候变化特征的红层划分对比: 以东营凹陷南坡为例[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(5): 839-845.HE Z J, LIU S H, WANG C X, et al. Study on division and correlation of red beds based on climate change feature: A case study on the southern slope of Dongying Depression[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(5): 839-845. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: