Characteristics of hydrochemical distribution of mineral water in Huangshui River Catchment and source analysis of threshold value elements
-
摘要:
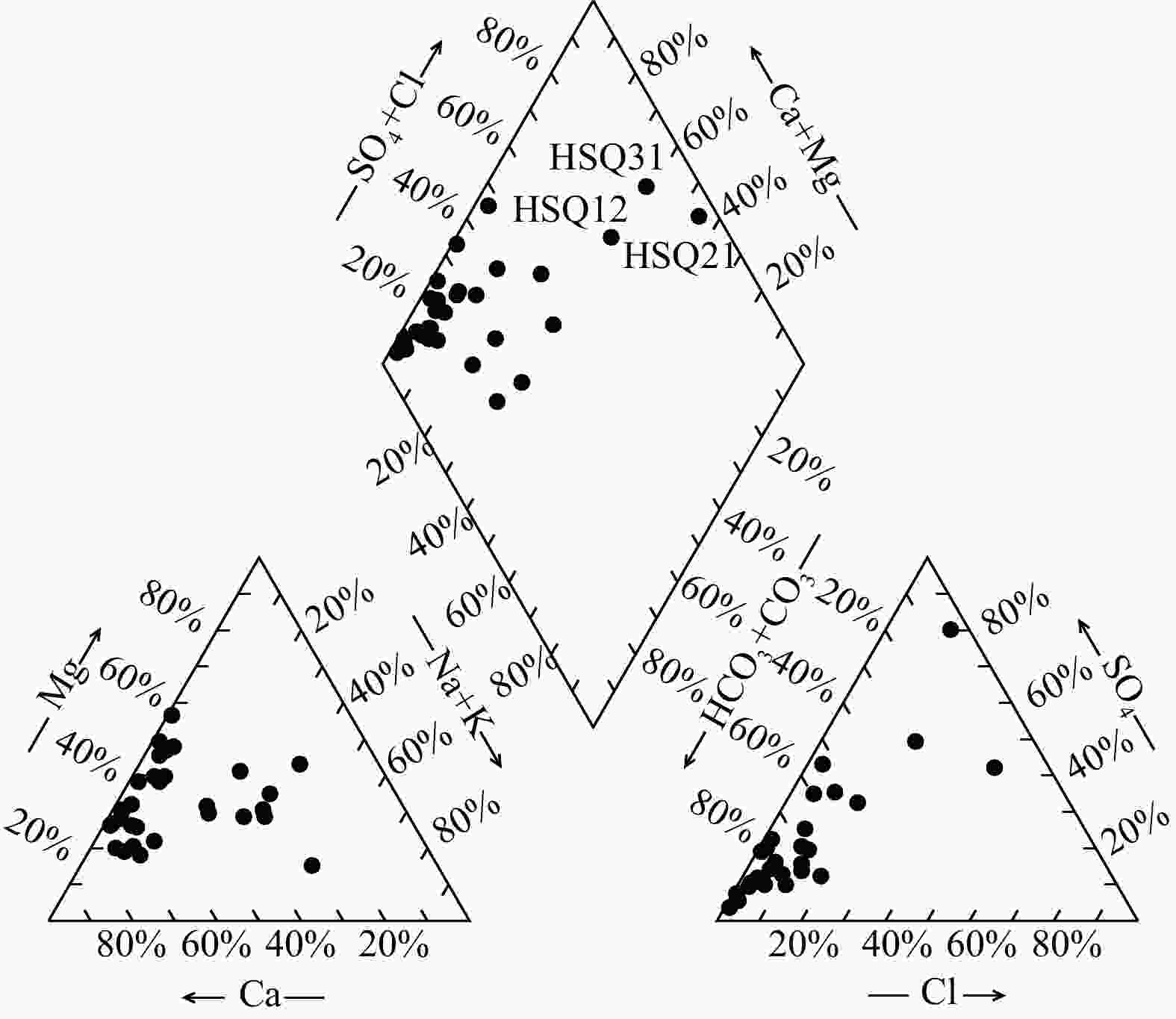
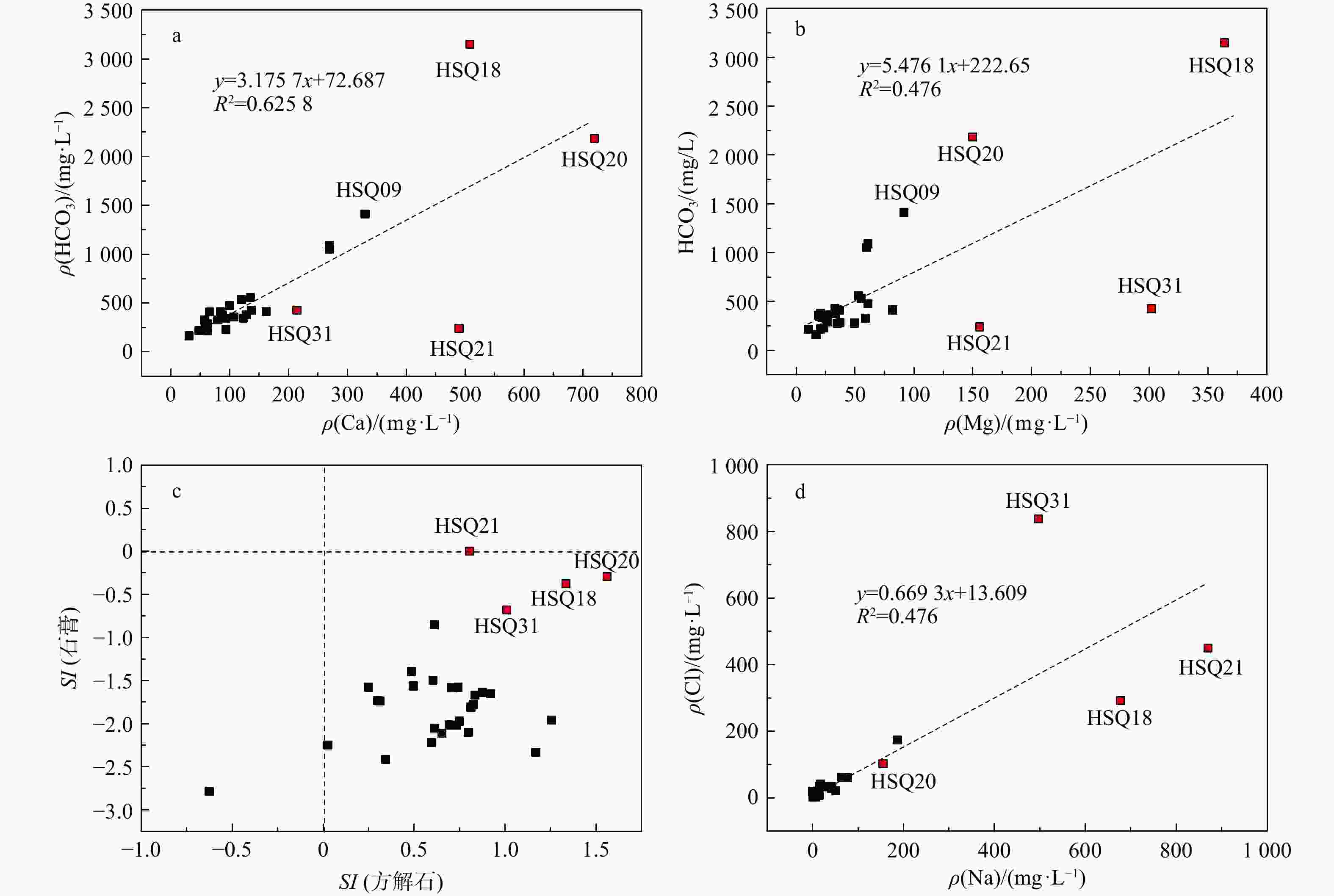
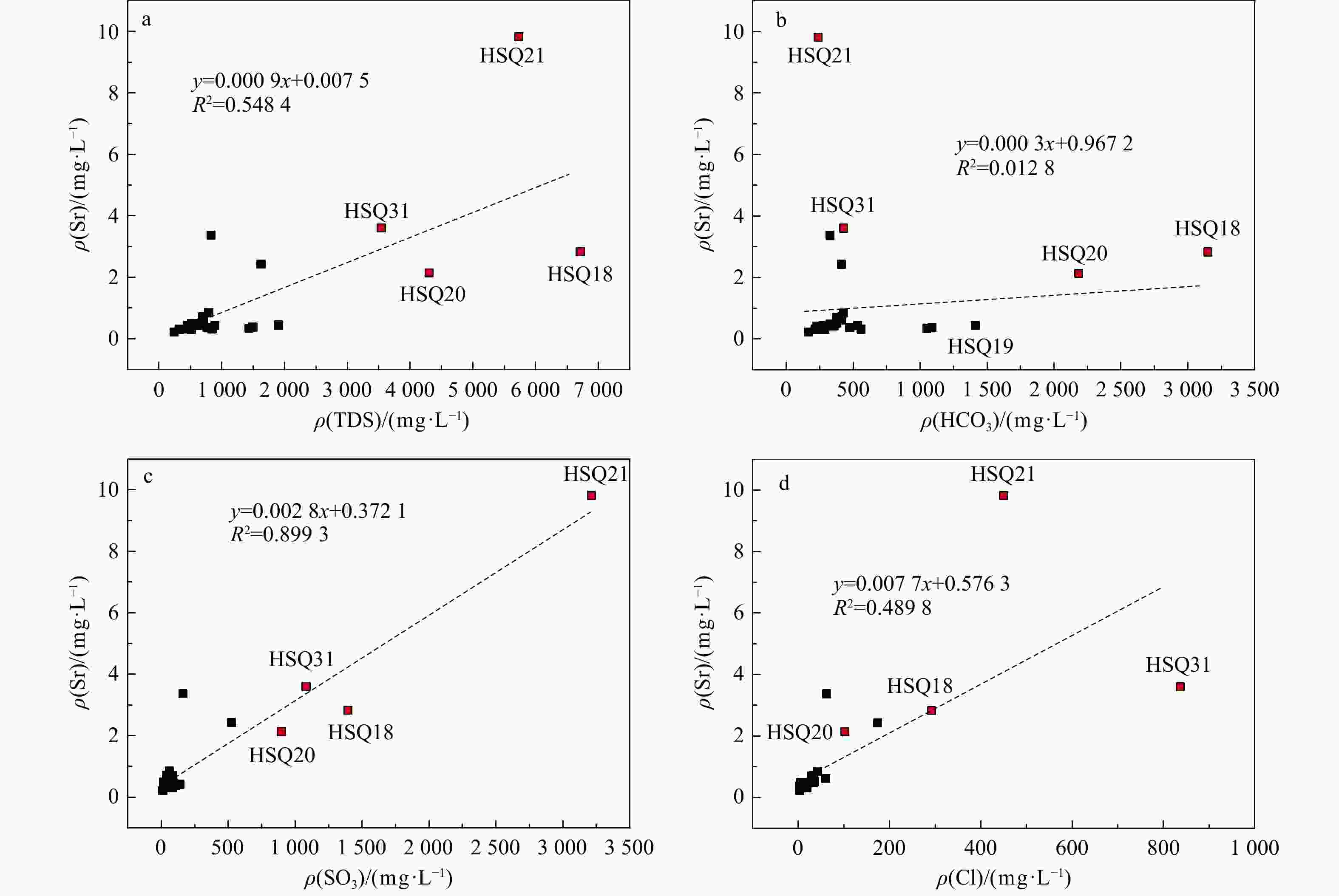
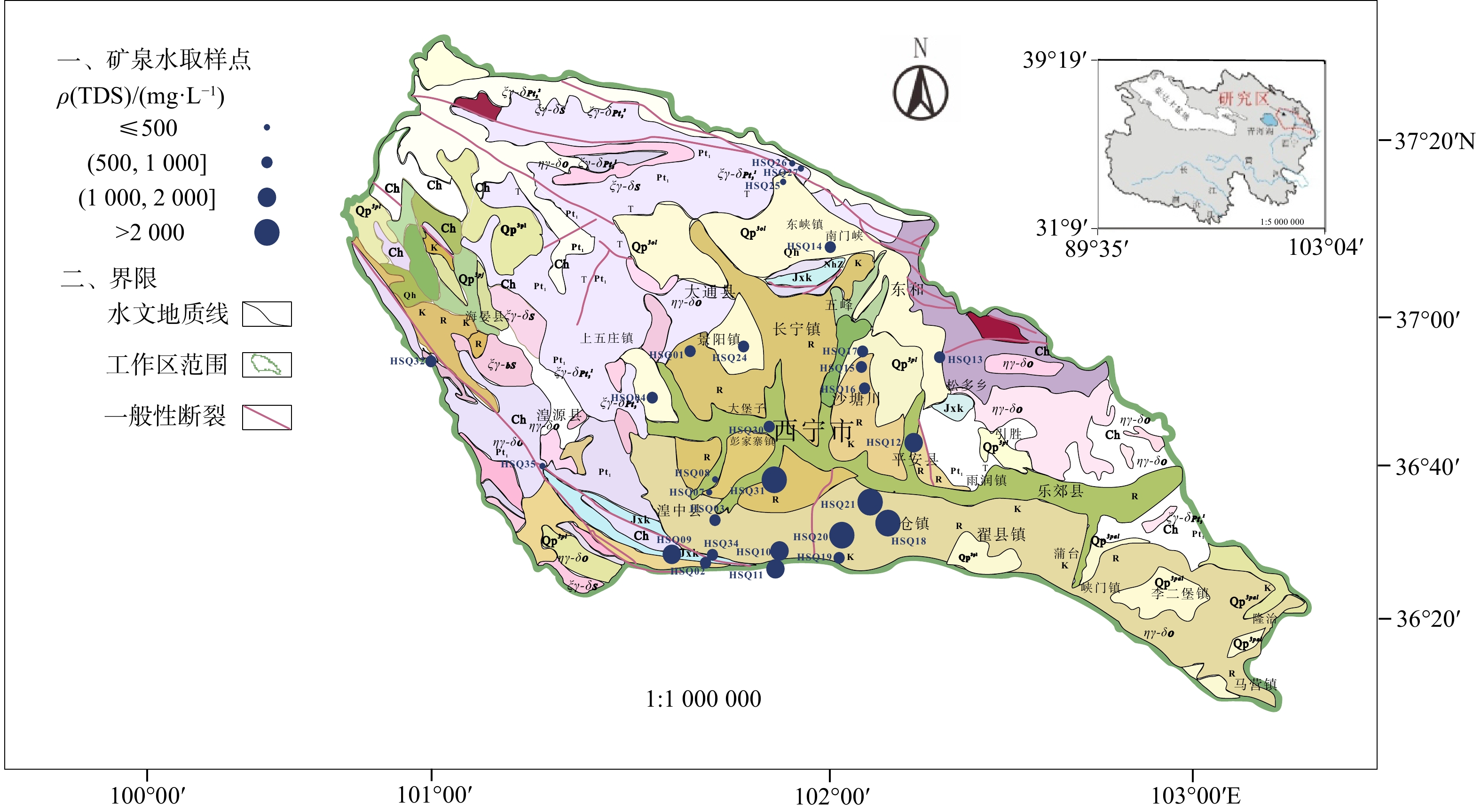
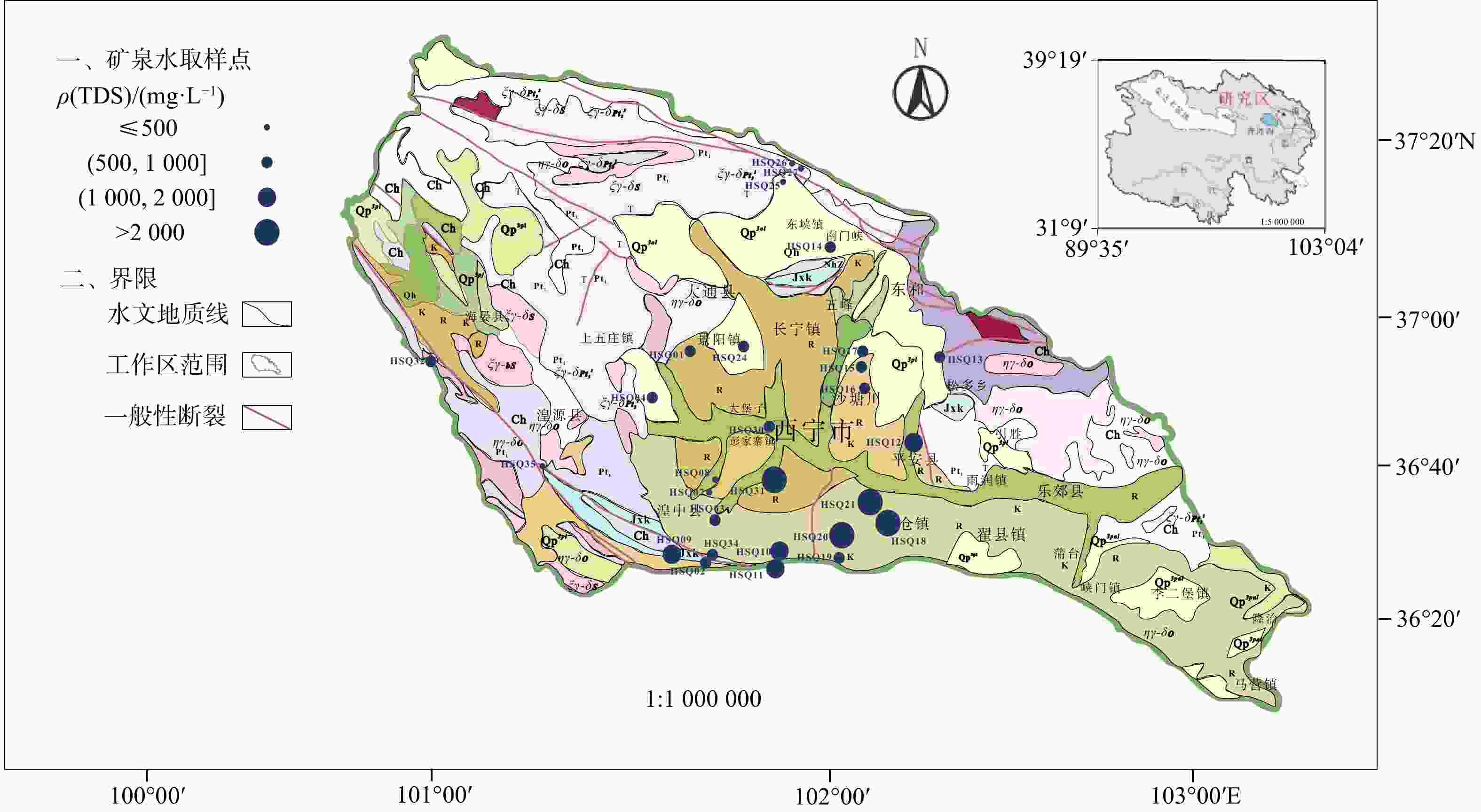
天然矿泉水不仅是宝贵的矿产资源,还能够为地表水环境系统(例如湿地与河岸带)提供补给水源,在保持生态系统多样化方面扮演重要角色。发源于青海省海晏、湟源的湟水河流域内发现了大量富锶矿泉水,少量泉水同时富含锂和偏硅酸。然而,目前对矿泉水中这些界限指标的来源及其相关水化学演化过程尚缺乏研究,同时个别采样点存在限量指标超标的情况,直接影响了矿泉水的开发利用,是目前亟待解决的问题。以青海湟水河流域为研究区,通过采集流域内天然泉水样品,采用水文地球化学分析及物质迁移模拟方法揭示矿泉水水化学特征与成因机制,这对理解湟水河流域地下水水化学演化过程具有重要意义。研究区地下水样品中大部分达到了国家饮用天然矿泉水的标准,且锶含量全部大于0.2 mg/L,少数样品富含锂和偏硅酸。水化学分析结果表明,地下水从补给区到排泄区,其水化学类型逐渐从HCO3-Ca·Mg型过渡到SO4-Na型,这是地下水在运移过程中不断溶解石膏层的结果。从Sr与HCO3−、SO42-和Cl−的相关性分析中可以看出,碳酸盐岩对地下水Sr含量的贡献程度有限;相反,由于Ca与Sr化学性质相似,在矿物中易发生原子交换,从而石膏层或蒸发岩类矿物中可能富集含Sr矿物,此类岩层在水岩作用下会释放一定量的Sr。地下水中锂的来源主要与古咸水湖沉积环境有关,过量的偏硅酸则来源于地热水在深循环过程中溶滤的铝硅酸盐矿物。通过物质迁移模拟分析发现,在北部流径上,地下水主要溶解石膏、石盐和伊利石,而天青石和锂辉石的溶解贡献了锶和锂;在南部流径上,石膏和石盐的溶解导致高TDS值,且去白云石化过程显著。研究成果能够为矿泉水资源的合理开发利用和保护提供科学依据。
Abstract:Natural mineral water is not only a kind of valuable mineral resource, but also a water supply source for surface water system (e.g., wet land and riparian zone), which is critical for keeping the biological diversity. A large amount of strontium-rich mineral water has been discovered in the Huangshui River catchment, which originates in Haiyan and Huangyuan, Qinghai Province, with a few springs also containing lithium and metasilicic acid.
Objective However, the study on the genesis of threshold-value elements and the related hydrochemical evolution processes are rare. In addition, some sampling points have exceeded the threshold value, which directly affects the development and utilization of mineral water and is an urgent problem that needs to be solved.
Methods In this study, the Huangshui River Catchment was considered as a target area. Hydrogeochemical and modeling methods were employed to uncover the hydrochemical features and genesis of mineral water by collecting spring samples from the catchment, which can play an important role in understanding the hydrogeochemical processes within the groundwater system in the Huangshui River Catchment.
Results Most of the groundwater samples in this study area reach the standards of the National Drinking Natural Mineral Water, and all the strontium concentration is higher than 0.2 mg/L with a few samples being rich in lithium and metasilicic acid. The Hydrogeological result shows that the groundwater moving from recharge area to discharge area has a transition of hydrochemical type from HCO3-Ca·Mg to SO4-Na, which is the result of gypsum dissolving in groundwater. The relationships between Sr and the major anions such as HCO3−、SO42− and Cl− show that carbonates have a limited contribution on Sr concentration in groundwater. Instead, the gypsum layers may contain a certain number of Sr-bearing minerals because of the atom exchange between Ca and Sr. Those Sr-bearing minerals are responsible for the high concentration of Sr in groundwater. In terms of the genesis of Li and Si in groundwater, the ancient salt lake sedimental environment may explain the former one and the dissolving of aluminumsilicate minerals may explain the latter. The inverse modeling shows that the groundwater mainly dissolves gypsum, rock salt and illite, while the dissolution of azurite and lithium pyroxene contributes strontium and lithium in the northern catchment. The dissolution of gypsum and halite leads to the high TDS of groundwater in the southern catchment, combined with the dedolomitization process.
Conclusion The whole research findings can serve as scientific basis for exploration and preservation of mineral waters.
-
表 1 青海省湟水河流域地下水现场物理指标
Table 1. On-site physical indicators of groundwater in Huangshui River Catchment, Qinghai Province
泉点
编号地理位置 水温/℃ 感官要求 色度/(°) 浑浊度/(°) 滋味 气味 状态 ≤10 NTU≤1 无 透明 HSQ01 湟中区李家山镇饮用天然矿泉水 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ02 湟中区 4 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ03 湟中区 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ04 湟中区 7 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ06 湟中区田家寨镇阴坡村黑沟峡 11 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ07 湟中西堡葛一村 9 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ08 湟中西堡葛一村 9 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ09 湟中区 38 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ10 湟中区田家寨子沟峡 18.5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ11 湟中区田家寨子沟峡 15.5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ12 互助县红崖子沟米子弯 9.5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ13 互助县佑宁寺矿泉水 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ14 互助县南门峡镇西山根村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ15 互助县东山乡大庄村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ16 互助县东山乡大泉村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ17 互助县东山乡哈家沟村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ18 平安县冰岭山村 20~25 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ19 平安区佛岭饮用天然矿泉水 7 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ20 平安区上尧村 7 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ21 平安县洪水泉乡下马圈村 9.5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ24 大通县景阳乡天然饮用矿泉水 7 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ25 大通县向化乡下滩村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ26 大通县向化乡上滩村 5.5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ27 大通县药水庄天然饮用矿泉水 5 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ30 西宁市共字桥 9 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ31 城中区泉尔湾村 10 <5 <0.5 无臭微咸 无 HSQ32 海晏县文迦牧场 3 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ33 海晏县甘子河达玉村 51 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ34 湟中区门旦峡 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 HSQ35 湟源县加牙麻村 6 <5 <0.5 无 无 注:NTU. nephelometric turbidity unit,是一种国际公认的浊度测量单位。 表 2 青海省湟水河流域地下水界限指标
Table 2. Groundwater threshold value elements of Huangshui River Basin, Qinghai Province
泉点
编号界限指标ρB/(mg·L)−1 锂 Li 锶 Sr 锌 Zn 硒 Se 偏硅酸 游离CO2 溶解性总固体 ≥0.2 ≥0.2 ≥0.2 ≥0.01 ≥25 ≥250 ≥ 1000 HSQ01 0.009 0.846 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 12.7 4.07 790 HSQ02 0.005 0.304 0.001 < 0.00025 9.17 1.02 518 HSQ03 0.011 0.491 0.002 < 0.00025 16 1.02 520 HSQ04 0.011 0.510 0.004 < 0.00025 15.3 2.03 670 HSQ06 0.005 0.311 0.017 < 0.00025 7.4 145 846 HSQ07 0.01 0.442 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 9.07 4.47 455 HSQ08 0.011 0.387 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 9.21 2.23 458 HSQ09 0.028 0.448 0.004 < 0.00025 31.3 113 1904 HSQ10 0.011 0.341 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 15.8 132 1435 HSQ11 0.013 0.380 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 17.6 232 1496 HSQ12 0.038 2.432 0.016 < 0.00025 13.2 4.47 1624 HSQ13 0.004 0.417 0.028 < 0.00025 6.06 3.35 516 HSQ14 0.01 0.428 0.004 < 0.00025 13 5.08 533 HSQ15 0.01 0.490 0.003 < 0.00025 9.89 1.02 541 HSQ16 0.016 0.610 0.008 < 0.00025 13.2 2.03 705 HSQ17 0.014 0.711 0.002 < 0.00025 11.2 4.07 696 HSQ18 0.447 2.827 0.025 < 0.00025 14.8 79.2 6713 HSQ19 0.016 0.702 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 12.8 6.03 693 HSQ20 0.118 2.135 0.02 < 0.00025 22.1 141 4302 HSQ21 0.349 9.818 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 16.4 3.35 5734 HSQ24 0.007 0.479 0.002 < 0.00025 11.3 5.08 662 HSQ25 0.007 0.313 0.002 < 0.00025 9.35 7.81 442 HSQ26 0.003 0.307 0.0008 < 0.00025 8.93 1.12 322 HSQ27 0.004 0.220 0.007 < 0.00025 6.32 1.01 240 HSQ30 0.054 3.370 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 13.6 3.35 828 HSQ31 0.057 3.603 0.001 < 0.00025 12.1 3.05 3542 HSQ32 0.005 0.428 0.007 < 0.00025 12.9 1.01 607 HSQ33 0.051 0.437 0.003 < 0.00025 45.6 20.1 890 HSQ34 0.006 0.372 0.004 < 0.00025 12.5 3.05 764 HSQ35 0.003 0.312 < 0.0008 < 0.00025 8.58 2.01 346 表 3 青海省湟水河流域地下水限量指标
Table 3. Groundwater limit indicators for Huangshui River catchment, Qinghai Province
泉点
编号限量指标ρB/(mg·L)−1 硒 Se 锑 Sb 铜 Cu 钡Ba 铬Cr 锰 Mn 镍 Ni 银 Ag 溴酸盐 硼酸盐 氟化物 耗氧量 挥发酚 氰 矿物油 阴离子
合成
洗涤剂总β放
射性<0.05 <0.005 <1.0 <0.7 <0.05 <0.4 <0.02 <0.05 <0.01 <5 <1.5 <2.0 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.3 <1.50Bq/L HSQ01 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.287 0.007 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.223 0.87 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.22 HSQ02 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.075 0.006 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.153 1.11 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.06 HSQ03 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.199 0.008 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.359 0.87 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.08 HSQ04 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.137 0.006 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.243 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.17 HSQ06 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 0.001 0.099 0.006 0.023 0.003 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.17 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.15 HSQ07 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.169 0.002 0.001 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.055 0.79 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.07 HSQ08 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.174 0.002 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.1 0.79 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.07 HSQ09 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.399 0.005 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / 0.53 0.327 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 2.55 HSQ10 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.229 0.005 0.005 0.001 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.281 0.71 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.29 HSQ11 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.266 0.007 0.032 0.001 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.328 1.19 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.35 HSQ12 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.025 0.006 0.004 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 0.46 0.466 1.19 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.09 HSQ13 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.071 < 0.00009 0.002 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.142 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.07 HSQ14 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.193 < 0.00009 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.229 1.03 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.05 HSQ15 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.034 0.002 0.003 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.519 1.03 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ16 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.036 0.002 0.002 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.395 1.11 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ17 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.086 < 0.00009 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.661 1.03 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.05 HSQ18 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.099 0.005 0.431 0.077 < 0.00003 <0.005 2.82 1.11 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 6.8 HSQ19 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.204 0.007 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.428 1.11 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.03 HSQ20 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.044 0.005 0.305 0.012 < 0.00003 <0.005 1.96 1.97 1.43 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ21 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 0.001 0.229 0.009 0.031 0.002 < 0.00003 <0.005 2.51 1.86 2.3 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ24 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.154 0.006 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.13 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.06 HSQ25 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.156 < 0.00009 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.114 0.63 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ26 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.193 < 0.00009 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.075 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 HSQ27 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.197 < 0.00009 0.001 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.092 0.87 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.16 HSQ30 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.63 0.014 0.05 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 0.29 0.789 1.03 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.04 HSQ31 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.009 0.018 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / 1.41 0.826 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.28 HSQ32 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.048 < 0.00009 0.002 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.175 3.01 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.17 HSQ33 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.131 < 0.00009 0.058 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 0.44 2.94 1.35 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.24 HSQ34 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.156 0.007 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 / <0.20 0.146 0.95 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 0.17 HSQ35 < 0.00025 < 0.00008 < 0.00009 0.152 < 0.00009 < 0.00006 < 0.00007 < 0.00003 <0.005 <0.20 0.145 1.19 <0.002 <0.002 <0.01 <0.05 <0.01 表 4 青海省湟水河流域地下水主要常量组分及水化学类型
Table 4. Main constant components and hydrochemical types of groundwater in huangshui River Catchment, Qinghai Province
泉点
编号主要常量组分ρB/(mg·L)−1 Sr 钙 镁 钠 钾 重碳
酸根硫酸根 氯化物 硝酸根 pH 铁 碳酸根 亚硝酸根 磷酸根 氟化物 总硬度 水化学类型 HSQ01 0.846 137 32.9 17.7 1.45 427 61.9 42 65.6 7.63 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.223 477.89 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ02 0.304 61.6 49.7 0.53 1.53 279 84.2 19.4 5.9 8.03 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.153 358.63 HCO3·SO4-Mg·Ca HSQ03 0.491 84.9 25.7 4.76 0.46 365 17.1 4.91 12.6 8.12 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.359 317.89 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ04 0.510 128 20.8 15.7 0.85 377 63.3 35.4 41.5 7.65 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.243 405.52 HCO3-Ca HSQ06 0.311 135 53 3.84 2.47 559 82.4 2.53 2.71 6.86 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.17 556.31 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ07 0.442 59.6 34.9 4.68 2.05 278 44.4 11.4 14.4 7.81 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.055 292.47 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ08 0.387 58.8 37.1 6.41 2.19 284 39.6 10.8 13.2 7.85 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.1 299.57 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ09 0.448 330 91.6 9.49 2.35 1412 34.8 7.07 0.748 6.77 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.327 1202.35 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ10 0.341 270 59.9 5.16 2.21 1051 39.1 2.44 1.86 6.41 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.281 921.09 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ11 0.380 269 61.1 6.34 2.47 1090 39 2.46 0.772 6.41 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.328 924.20 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ12 2.432 162 81.9 187 18.7 412 524 174 47.9 7.4 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.466 740.78 SO4-Na HSQ13 0.417 93.8 23.5 2.84 3.08 228 139 7.45 0.557 7.6 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.142 331.15 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ14 0.428 92.6 22 8.61 1.95 338 32.3 12.3 17 7.62 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.229 321.99 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ15 0.490 57.1 25.5 51.6 3.06 326 41.9 21.3 14.4 7.96 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.519 247.58 HCO3-Mg·Na·Ca HSQ16 0.610 65.7 36.9 77.7 3.87 411 56.5 60.5 18.4 7.78 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.395 315.89 HCO3-Mg·Na·Ca HSQ17 0.711 84.1 34.9 42.4 3.38 415 39.2 33.6 49.1 7.64 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.661 353.57 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ18 2.827 508 364 677 18.1 3148 1394 292 <0.016 7.02 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 1.11 2766.38 HCO3·SO4-Na·Mg·Ca HSQ19 0.702 87.7 33.4 41.7 12 378 85.7 28.9 12.9 7.78 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.428 356.63 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ20 2.135 720 150 155 43.8 2185 898 102 <0.016 7.17 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 1.97 2414.86 HCO3·SO4-Ca·Mg HSQ21 9.818 490 156 870 276 239 3212 450 56.1 7.65 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 1.86 1864.66 SO4-Na HSQ24 0.479 123 20 23.7 3.55 344 74.3 33.1 43.7 7.57 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.13 389.21 HCO3-Ca HSQ25 0.313 61.6 26.5 7.91 2.24 289 25.9 5.43 6.86 7.17 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.114 262.89 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ26 0.307 47.7 20.8 3.94 1.82 217 20.2 3.58 4.43 7.7 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.075 204.79 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ27 0.220 31 16.8 1.25 1.7 164 11.5 2.6 4.72 7 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.092 146.68 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ30 3.370 79.6 58.9 63.9 6.33 328 161 62.1 49.7 7.68 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.789 441.20 HCO3-Mg·Ca HSQ31 3.603 214 302 497 10.5 427 1081 837 92.7 7.81 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.826 1781.08 Cl-Na·Mg HSQ32 0.428 107 19.1 15 3.89 358 33.6 15.7 28.2 8.13 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.175 345.42 HCO3-Ca HSQ33 0.437 120 55.2 14.4 9.4 533 95 6.23 <0.016 7.18 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 2.94 525.73 HCO3-Ca·Mg HSQ34 0.372 99.1 61.1 2.84 0.65 475 106 5.32 11.9 7.52 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.146 499.26 HCO3·SO4-Ca·Mg HSQ35 0.312 62.8 10.4 3.18 4.04 216 23.8 5.21 11.4 7.84 <0.05 0 <0.016 <0.051 0.145 199.68 HCO3-Ca 表 5 研究区HSQ27→HSQ15→HSQ12流径上水化学演化模拟结果
Table 5. Simulation results of hydrochemical evolution on the flow path HSQ27→HSQ15→HSQ12 in the study area
矿物名称 化学式 摩尔转移量/(mol·L−1) HSQ27→HSQ15 HSQ15→HSQ12 钠长石 NaAlSi3O8 1.81×10−3 −1.92×10−3 方解石 CaCO3 4.07×101 4.29×101 天青石 SrSO4 0 1.01×10−5 玉髓 SiO2 0 0 白云石 CaMg(CO3)2 −4.07×101 −4.29×101 萤石 CaF2 6.46×10−6 −3.09×10−5 石膏 CaSO4·2H2O 7.10×10−5 3.80×10−3 石盐 NaCl 3.77×10−4 3.01×10−3 伊利石 K0.6Mg0.25Al1.8Al0.5Si3.5 1.63×102 1.72×102 高岭石 Al2Si2O5(OH)4 −1.38×102 −1.46×102 白云母 KAl3Si3O10(OH)2 1.84×10−3 −1.54×10−3 菱锶矿 SrCO3 −2.07×10−6 0 CO2 CO2 4.07×101 4.29×101 钾长石 KAlSi3O8 −9.77×101 −1.03×102 锂辉石 LiAlSi2O6 1.44×10−6 1.21×10−6 表 6 研究区HSQ02→HSQ10→HSQ20→HSQ18流径上水化学演化模拟结果
Table 6. Simulation results of hydrochemical evolution on the flow paths HSQ02→HSQ10→HSQ20→HSQ18 in the study area
矿物名称 化学式 摩尔转移量/(mol·L−1) HSQ02→HSQ10 HSQ10→HSQ20 HSQ20→HSQ18 钠长石 NaAlSi3O8 3.21×10−4 3.88×10−3 1.75×10−2 方解石 CaCO3 2.62×10−3 1.50×10−3 0 天青石 SrSO4 2.81×10−6 2.45×10−5 7.94×10−6 玉髓 SiO2 −7.60×101 −1.10×102 0 白云石 CaMg(CO3)2 1.49×10−3 6.18×10−3 −9.58×10−3 萤石 CaF2 6.13×10−6 5.20×10−5 −2.27×10−5 石膏 CaSO4·2H2O 1.28×10−4 9.36×10−3 5.20×10−3 石盐 NaCl −1.04×10−4 2.89×10−3 5.40×10−3 伊利石 K0.6Mg0.25Al1.8Al0.5Si3.5 0 0 7.24×10−2 高岭石 Al2Si2O5(OH)4 3.80×101 5.49×101 −8.69×10−2 白云母 KAl3Si3O10(OH)2 −3.80×101 −5.49×101 1.69×10−2 菱锶矿 SrCO3 0 0 0 CO2 CO2 1.02×10−2 2.19×10−2 3.51×10−2 钾长石 KAlSi3O8 3.80×101 5.49×101 −6.10×10−2 锂辉石 LiAlSi2O6 9.88×10−7 1.73×10−5 4.79×10−5 -
[1] BODOR K,TOKOS B,BODOR Z,et al. Hydro-geochemical characterization of the main European mineral water brands[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,122:105438. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105438 [2] LI Y H,BIAN J M,LI J L,et al. Hydrochemistry and stable isotope indication of natural mineral water in Changbai Mountain,China[J]. Journal of Hydrology:Regional Studies,2022,40:101047. [3] 陈皓龙,谢杰,宋武元,等. 安徽泾县榔桥镇马渡村饮用天然矿泉水成因及水化学特征研究[J]. 地下水,2023,45(5):50-52.CHEN H L,XIE J,SONG W Y,et al. Study on the origin and the water chemical characteristics of drinking natural mineral water in Madu Village,Langqiao Town,Jing County,Anhui Province[J]. Ground Water,2023,45(5):50-52. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 李云峰,张庆,周小平,等. 安庆大别山区矿泉水化学特征及成因模式[J]. 华东地质,2021,42(2):193-201.LI Y F,ZHANG Q,ZHOU X P,et al. Chemical characteristics and genetic model of mineral water in Dabie Mountain area of Anqing City[J]. East China Geology,2021,42(2):193-201. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 祁泽学,汪生斌,李祥坤,等. 柴达木盆地东缘天峻县阳陇沟天然饮用矿泉水成因分析[J/OL]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版):1-6[2025-03-05]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/64.1006.N.20230504.1505.016.html.QI Z X,WANG S B,LI X K,et al. Genetic analysis of natural drinking mineral water in Yanglonggou eastern of Qaidam Basin[J/OL]. Journal of Ningxia University(Natural Science Edition):1-6[2025-03-05]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/64.1006.N.20230504.1505.016.html. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] TOMASCAK P B,WIDOM E,BENTON L D,et al. The control of lithium budgets in island arcs[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,196(3/4):227-238. [7] 党学亚,顾小凡,曾庆铭. 柴达木盆地矿泉水资源前景和开发利用条件[J]. 西北地质,2021,54(3):213-221.DANG X Y,GU X F,ZENG Q M. Prospect,development and utilization of the mineral water resources in Qaidam Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021,54(3):213-221. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 刘延兵,张彦林,刘海生,等. 甘肃省河西地区锶矿泉水富集分布规律和水质特征分析[J]. 城市地质,2023,18(3):112-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2023.03.015LIU Y B,ZHANG Y L,LIU H S,et al. Strontium mineral water enrichment,distribution and water quality characteristics in Hexi region of Gansu Province[J]. Urban Geology,2023,18(3):112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2023.03.015 [9] 侯利朋,赵振,王万平,等. 青海海东地区矿泉水的形成条件及特征分析[J]. 地下水,2016,38(5):44-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.05.017HOU L P,ZHAO Z,WANG W P,et al. Formation conditions and characteristics of mineral water in Haidong area of Qinghai Province[J]. Ground Water,2016,38(5):44-46. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2016.05.017 [10] 韦华鹏,许伟林,罗银飞,等. 基于层次分析法的青海省矿泉水开发利用潜力评价[J]. 地下水,2022,44(4):1-4.WEI H P,XU W L,LUO Y F,et al. Evaluation of the development and utilization potential of mineral water in Qinghai Province based on the analytic hierarchy process[J]. Ground Water,2022,44(4):1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 廖先远,胡雨柔. 青海曲海天然饮用富锶型矿泉水形成机制分析[J]. 四川地质学报,2017,37(4):592-595. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2017.04.014LIAO X Y,HU Y R. Genetic mechanism for the Sr-rich mineral water in Quhai,Qinghai[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2017,37(4):592-595. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2017.04.014 [12] 杨小波,张晓冬,陈海斌,等. 青海省大柴旦镇马海地区矿泉水水源地的水文地质特征分析[J]. 中国锰业,2018,36(6):75-77.YANG X B,ZHANG X D,CHEN H B,et al. An analysis on hydrogeologic characteristics of mineral water source in Mahai area of Qinghai Province[J]. China's Manganese Industry,2018,36(6):75-77. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 赵振,陈惠娟,罗银飞,等. 青海玉树热水沟天然矿泉水形成条件及水质分析[J]. 地下水,2013,35(6):4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2013.06.002ZHAO Z,CHEN H J,LUO Y F,et al. A Study on the formation condition and quality analysis of natural mineral water in Reshuigou in Qinghai[J]. Ground Water,2013,35(6):4-6. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2013.06.002 [14] XUE F,TAN H B,ZHANG X Y,et al. Contrasting sources and enrichment mechanisms in lithium-rich salt lakes:A Li-H-O isotopic and geochemical study from northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2024,15(2):101768. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101768 [15] 巴瑞寿,袁有靖,李文斌,等. 黄河流域化隆段天然矿泉水成因机理研究[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(增刊1):57-59.BA R S,YUAN Y J,LI W B,et al. Study on genetic mechanism of natural mineral water in Hualong Section of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(S1):57-59. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] APPELO C A J,POSTMA D. Geochemistry,groundwater and pollution[M]. Boca Raton:CRC Press,2004. [17] 陈万利,刘虹,王惠东,等. 安化县玉溪村地段矿泉水成因水文地球化学模拟分析[J]. 陕西水利,2023(10):89-91.CHEN W L,LIU H,WANG H D,et al. Hydrogeochemical simulation analysis of mineral water genesis in Yuxi Village,Anhua County[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources,2023(10):89-91. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 李义连,王焰新,周来茹,等. 地下水矿物饱和度的水文地球化学模拟分析:以娘子关泉域岩溶水为例[J]. 地质科技情报,2002,21(1):32-36.LI Y L,WANG Y X,ZHOU L R,et al. Hydrogeochemical modeling on saturation of minerals in groundwater:A case study at Niangziguan,northern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2002,21(1):32-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 何家宝,杨章贤. 砀山县浅层地下水盐分反向水文地球化学模拟研究[J]. 地下水,2021,43(4):56-58.HE J B,YANG Z X. Reverse hydrogeological simulation study of shallow groundwater salinity in Dangshan County[J]. Ground Water,2021,43(4):56-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 苏宏建,杨瑞,多晓松,等. 承德市矿泉水资源分布规律及其形成的地球化学条件[J]. 化工矿产地质,2019,41(1):27-34.SU H J,YANG R,DUO X S,et al. Distribution rules and geochemical conditions of mineral water resources in Chengde City[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,2019,41(1):27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 文美霞,郑晓明,周爱国. 湖北省饮用天然矿泉水分布特征与赋存规律研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2020,27(6):13-22.WEN M X,ZHENG X M,ZHOU A G. Study on the distribution characteristics and occurrence of drinking natural mineral water of Hubei Province[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2020,27(6):13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 杨致萍,宋晨,金翔霖,等. 贵州六盘水太阳沟天然矿泉水特征与成因分析[J]. 地下水,2020,42(4):22-23.YANG Z P,SONG C,JIN X L,et al. Characteristics and cause analysis of natural mineral water in Liupanshui Yanggou,Guizhou Province[J]. Ground Water,2020,42(4):22-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 李翠明,彭红明,毛绪美,等. 地下水H、O、C同位素揭示的末次冰盛期以来青海东部岩溶发育响应[J]. 地球与环境,2023,51(6):583-592.LI C M,PENG H M,MAO X M,et al. Response of karstification in eastern Qinghai since the Last Glacial Maximum revealed by groundwater H,O and C isotopes[J]. Earth and Environment,2023,51(6):583-592. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 胥彪. 晚中新世西宁盆地沉积演化及环境变化[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2017.XU B. Sedimentary evolution and environmental changes in Xining Basin in Late Miocene[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 张海云,马海州,程怀德,等. 青海上庄含碳酸岩杂岩体的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 盐湖研究,2024,32(2):62-71. doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.202402009ZHANG H Y,MA H Z,CHENG H D,et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the Shangzhuang carbonate complex,Qinghai[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research,2024,32(2):62-71. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.202402009 [26] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局.食品安全国家标准饮用天然矿泉水检验方法:GB 8538-2022[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2022.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Food safety national standard test methods for drinking natural mineral water:GB 8538-2022[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press,2022. (in Chinese) [27] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,国家市场监督管理总局.食品安全国家标准饮用天然矿泉水:GB 8537-2008[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2008.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Food safety national standard for drinking natural mineral water:GB 8537-2008[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press,2008. (in Chinese) [28] 江峰,吉勤克补子,高峰,等. 贵州省饮用天然矿泉水化学特征及锶型矿泉水分布规律[J]. 地下水,2021,43(2):17-20.JIANG F,JI Q,GAO F,et al. Chemical characteristics and distribution law of strontium type natural mineral water for drinking in Guizhou Province[J]. Ground Water,2021,43(2):17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 苏春田,罗飞,杨杨,等. 湖南新田富锶矿泉水形成机理浅析[J]. 中国矿业,2019,28(增刊1):347-348.SU C T,LUO F,YANG Y,et al. Analysis on the formation mechanism of strontium-rich mineral water in Xintian,Hunan Province[J]. China Mining Magazine,2019,28(S1):347-348. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 杨文亮,蒲秀超,曹振东. 贵州纳雍县沙包镇下木村富锶矿泉水成因分析及开采量计算[J]. 矿产与地质,2023,37(4):823-830.YANG W L,PU X C,CAO Z D. Origin analysis and mining quantity calculation of strontium-rich mineral water of Xiamu Village,Shabao Town,Nayong County,Guizhou[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2023,37(4):823-830. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 李辉,翟星,刘硕,等. 冀东都山地区富锶矿泉水锶的运移与赋存特征分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(2):458-464.LI H,ZHAI X,LIU S,et al. Analysis on the migration of strontium and occurrence characteristics of the strontium mineral water in Dushan area,eastern Hebei Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(2):458-464. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 刘硕,马百衡,翟星,等. 华北克拉通北缘典型高锶花岗岩区域锶型矿泉水分布特征及成因[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(5):1721-1729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.05.007LIU S,MA B H,ZHAI X,et al. Distribution characteristics of strontium mineral water in the typical high-Sr granite area in the northern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(5):1721-1729. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.05.007 [33] DUGAMIN E J M,RICHARD A,CATHELINEAU M,et al. Groundwater in sedimentary basins as potential lithium resource:A global prospective study[J]. Scientific Reports,2021,11(1):21091. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99912-7 [34] LI Y L,MIAO W L,HE M Y,et al. Origin of lithium-rich salt lakes on the western Kunlun Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from hydrogeochemistry and lithium isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,155:105356. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105356 [35] KESLER S E,GRUBER P W,MEDINA P A,et al. Global lithium resources:Relative importance of pegmatite,brine and other deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2012,48:55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.05.006 [36] 陈晨,闫庆贺,章荣清,等. 锂的圈层循环与资源富集过程:从高原盐湖到造山带伟晶岩[J]. 岩石学报,2024,40(2):591-604. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2024.02.13CHEN C,YAN Q H,ZHANG R Q,et al. Lithium mineralization in plateau brines and orogen pegmatites:A lithium cycling perspective[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2024,40(2):591-604. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2024.02.13 [37] 张亚峰,姬丙艳,沈骁,等. 西宁盆地咸水湖相沉积型富硒土壤的形成机理及意义[J]. 物探与化探,2023,47(2):470-476.ZHANG Y F,JI B Y,SHEN X,et al. Formation mechanisms and significance of saline-lacustrine Se-rich soils in the Xining Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2023,47(2):470-476. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] BLOUNT C W,DICKSON F W. Water-rock interactions and the chemical evolution of a paleozoic groundwater system[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1971,35(4):401-419. [39] 何锦,马雪梅,邓启军,等. 河北省张北县新生代玄武岩偏硅酸矿泉水化学特征及成因[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(6):1887-1902. doi: 10.12029/gc20201027001HE J,MA X M,DENG Q J,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of metasilicate mineral water in a Cenozoic basaltic aquifer in Zhangbei County,Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(6):1887-1902. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20201027001 [40] 梁坤萍,程国繁,覃庆炎,等. 贵州织金新华磷矿区风化磷块岩形成条件及风化淋滤富集机制初步研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(4):172-183.LIANG K P,CHENG G F,QIN Q Y,et al. A preliminary study on the formation conditions and weathering leaching enrichment mechanism of secondary phosphorite in the Xinhua phosphate mining area,Zhijin,Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(4):172-183. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 李虹霖,郭涛,张如才,等. 辽西凸起斜坡区风化壳油气运移特征及控藏作用[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(4):109-116.LI H L,GUO T,ZHANG R C,et al. Hydrocarbon migration characteristics and its controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation of weathering crust in slope area of Liaoxi Uplift[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(4):109-116. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: