Automatic classification of pore structures of low-permeability sandstones based on self-organizing-map neural network algorithm
-
摘要:
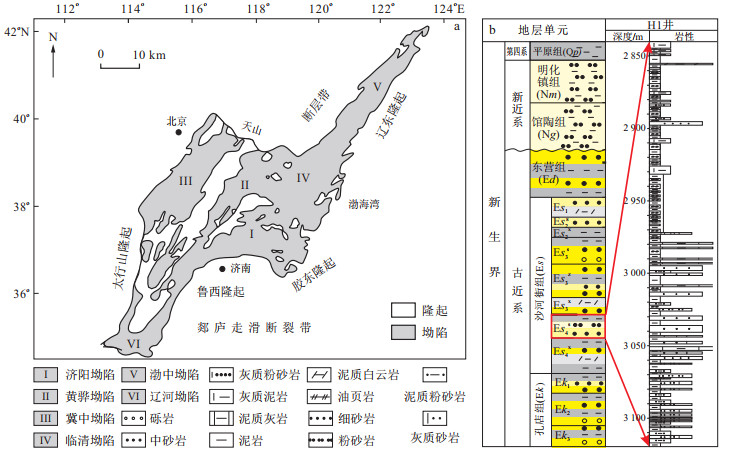
低渗透砂岩储层的孔隙系统复杂, 孔隙-喉道大小分布多变, 是决定储层宏观岩石物理性质和控制流体在砂岩中渗流行为的关键因素。以往的低渗透砂岩孔隙结构分级评价工作多基于孔隙-喉道大小分布的几何形态或参数回归分析, 受人为因素干扰大, 缺乏精确的分级评价标准。以渤海湾盆地G油田沙四上亚段低渗透砂岩储层为研究对象, 综合运用岩相学分析、高压压汞、核磁共振及X射线CT扫描等技术手段, 详细探讨了低渗透砂岩微观孔隙结构特征。在此基础上, 选取了15个能够反映低渗透砂岩微观孔隙结构特征的储层评价参数, 并采用无监督模式下的自组织映射神经网络算法将取心层段的70组岩心样本自动划分为4类孔隙结构。研究结果表明, Ⅰ类孔隙结构以大孔喉为主, 中值喉道半径
r 50主要分布在0.38~2.35 μm的范围内; 孔喉连通性好, 对渗透率贡献作用显著。Ⅱ类孔隙结构的渗流性能和连通性能仅次于Ⅰ类孔隙结构, 可动流体孔隙度在2.76%~5.61%之间, 中值喉道半径r 50主要分布在0.01~0.23 μm的范围内。Ⅲ类孔隙结构具有较好的孔喉连通性和较强的微观非均质性, 储集和渗流性能与Ⅰ类和Ⅱ孔隙结构相比明显较差。Ⅳ型孔隙结构内小孔喉占主导, 孔喉连通性差, 不利于流体在砂岩中的渗流。基于自组织映射神经网络算法可以实现多参数情况下的孔隙结构类型自动分类。分类结果不受不准确的用户自定义信息的影响, 并且对参与训练过程的参数数量没有限制, 在基于多参数的孔隙结构分类方面应用效果显著。建立的基于自组织特征映射(self-organizing feature map, 简称SOM)神经网络算法的孔隙结构分类评价标准, 对于研究低渗透砂岩储层的微观渗流行为和储层质量评价意义重大。Abstract:Objective The pore system of low-permeability sandstone reservoirs is intricate, and the distribution of pore-throat sizes is highly variable. The microscopic pore structure significantly influences the reservoir′s petrophysical properties and plays a critical role in controlling fluid flow within sandstone reservoirs. Traditional approaches for evaluating pore structures primarily rely on morphological analyses of pore throat size distributions or regression analyses of pore structure parameters. These methods are significantly affected by human bias and often lack precise evaluation frameworks.
Methods Poroperm analysis, mercury injection capillary pressure, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements, and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) scanning experiments were performed to characterize the pore structures of the E
s 4s low-permeability sandstones in the G oilfield, Bohai Bay Basin. On this basis, 15 parameters that reflect the microscopic features of low-permeability sandstones were selected, and four types of pore structures were classified by applying an unsupervised self-organizing-map neural network algorithm.Results The findings reveal that the Type Ⅰ pore structure predominantly features large pore throats, with a median throat radius (
r 50) ranging from 0.38 to 2.35 μm. This type exhibits excellent pore connectivity, contributing significantly to permeability. The petrophysical properties and pore connectivity of Type Ⅱ pore structures are second only to those of Type Ⅰ pore structures. The movable fluid porosity ranges from 2.76% to 5.61%, and the median throat radius (r 50) is primarily distributed in the range of 0.01 to 0.23 μm. Type Ⅲ pore structures display good pore connectivity along with considerable microscopic heterogeneity. The petrophysical properties and seepage properties of Type Ⅲ pore structures are comparable to those of Type Ⅰ and Type Ⅱ pore structures. The Type Ⅳ pore structures are characterized by small pore throats and poor microscopic connectivity, which hinders fluid movement within the sandstones.Conclusion The self-organizing map neural network algorithm effectively classifies pore structure types in cases involving multiple parameters. The classification results are not affected by inaccurate user-defined information, and there is no limitation on the number of parameters involved in the training process, making the application effect in pore structure classification remarkable. The established pore structure evaluation scheme, which is based on a self-organizing feature map neural network algorithm, is vital for investigating the microscopic seepage behavior and reservoir quality of low-permeability sandstones.
-
图 4 沙四上亚段砂岩储集空间及成岩作用特征
a.残余粒间孔隙、次生溶孔及中期碳酸盐胶结物,G89井, 2 599.2 m;b.残余粒间孔隙、次生溶孔及中期碳酸盐胶结物,G89井, 2 599.7 m;c.长石颗粒溶蚀孔与粒间孔组成的扩大孔,C37井, 2 686.9 m;d.基底式早期碳酸盐胶结作用和“浮粒结构”,F15井,2 728.5 m;e.中期孔隙充填式方解石胶结物,F15-1井,2 687.0 m;f.沿着长石解理溶蚀形成的微孔隙,Quanta200 FEG-SEM,F14-1井, 3 113.3 m
Figure 4. Pore systems and diagenesis in the Es4s sandstone reservoirs
图 11 SOM神经网络的网络结构(a)和竞争层(b) (据文献[27]修改)
Figure 11. Typical network structure(a) and competitive layer(b) of SOM neural network
图 12 基于SOM神经网络算法的自组织映射拓扑图(a)、三维Sammon投影(b)和三维聚类树状图(c)
DT.MICP分形维数; We.退汞效率; σ.分选系数; Pd.排驱压力; k.渗透率; φ.孔隙度; rapex.峰点孔喉半径; rmax.最大孔喉半径; r50.中值孔喉半径; RQI为储层品质指数(reservoir quality index)
Figure 12. Topological mapping(a), 3D Sammon mapping(b) and 3D clustering tree(c) based on SOM neural network algorithm
-
[1] 操应长, 杨田, 王健, 等. 东营凹陷南坡沙四上亚段滩坝砂岩有效储层成因[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(6): 1-9.CAO Y C, YANG T, WANG J, et al. Genesis of effective reservoirs of beach-bar sandstone in upper part of the Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation in the southern slope of Dongying Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2013, 37(6): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 操应长, 杨田, 宋明水, 等. 陆相断陷湖盆低渗透碎屑岩储层特征及相对优质储层成因: 以济阳坳陷东营凹陷古近系为例[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(7): 727-743.CAO Y C, YANG T, SONG M S, et al. Characteristics of low-permeability clastic reservoirs and genesis of relatively high-quality reservoirs in the continental rift lake basin: A case study of Paleogene in the Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(7): 727-743. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] WU Y Q, TAHMASEBI P, LIN C Y, et al. A comprehensive study on geometric, topological and fractal characterizations of pore systems in low-permeability reservoirs based on SEM, MICP, NMR, and X-ray CT experiments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103: 12-28. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.02.003 [4] YAN J P, FAN J, WANG M, et al. Rock fabric and pore structure of the Shahejie sandy conglomerates from the Dongying Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 624-638. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.07.009 [5] 贾艳聪, 操应长, 林畅松, 等. 东营凹陷博兴洼陷沙四上亚段滩坝优质储层形成机理与分布特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(3): 652-664.JIA Y C, CAO Y C, LIN C S, et al. Formation mechanism and distribution of high-quality reservoirs for beach-bar sandstones in upper part of Es4 in Boxing Sag, Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2018, 48(3): 652-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 陈儒贤, 侯加根. 高尚堡油田高3102断块沙三2+3亚段中低渗透储层可动流体赋存特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 174-186. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220184CHEN R X, HOU J G. Occurrence characteristics and influencing factors of movable fluid in the medium- and low-permeability reservoirs of the Es32+3 submember of the Gao 3102 fault block in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 174-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220184 [7] 龚建涛, 魏繁荣, 闫旭光, 等. 基于X-CT扫描的石油地质岩心储层渗透率估算[J]. 天然气与石油, 2023, 41(4): 67-73.GONG J T, WEI F R, YAN X G, et al. Permeability estimation of petroleum geological core reservoir based on X-CT scanning[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2023, 41(4): 67-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 赖锦, 王贵文, 孟辰卿, 等. 致密砂岩气储层孔隙结构特征及其成因机理分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(1): 217-227.LAI J, WANG G W, MENG C Q, et al. Pore structure characteristics and formation mechanisms analysis of tight gas sandstones[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(1): 217-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 吴松涛, 朱如凯, 李勋, 等. 致密储层孔隙结构表征技术有效性评价与应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(2): 191-203.WU S T, ZHU R K, LI X, et al. Evaluation and application of porous structure characterization technologies in unconventional tight reservoirs[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(2): 191-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 汪贺, 师永民, 徐大卫, 等. 非常规储层孔隙结构表征技术及进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(5): 21-30.WANG H, SHI Y M, XU D W, et al. Unconventional reservoir pore structure characterization techniques and progress[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(5): 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 张芥瑜, 张凤奇, 刘阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地WL地区延长组储层成岩作用与孔隙结构差异成因[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 162-173. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220607ZHANG J Y, ZHANG F Q, LIU Y, et al. Causes of reservoir diagenesis and pore structure differences of the Yanchang Formation in the WL area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 162-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220607 [12] WANG Y, YANG S C, ZHANG Y F, et al. Investigation of pore structure and reservoir quality of Eocene beach-bar sandstones in Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 189: 106854. [13] LAI J, WANG G W, CAO J T, et al. Investigation of pore structure and petrophysical property in tight sandstones[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 91: 179-189. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2772482856 [14] KOHONEN T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1982, 43(1): 59-69. [15] KOHONEN T. Self-organizing maps[M]. Third Edition. Berlin: Springer, 2001. [16] 李阳, 代宗仰, 张洁伟, 等. 基于无监督学习的多参数储层评价: 以蒲包山地区下三叠统飞仙关组礁滩储层为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 285-292. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0154LI Y, DAI Z Y, ZHANG J W, et al. Multiparameter reservoir evaluation method based on unsupervised learning: A case study of the reef beach reservoir of the Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation in the Pubaoshan area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 285-292. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0154 [17] 斯扬, 蔡明俊, 张家良, 等. 基于自组织神经网络及K最近邻算法的储层渗流屏障定量识别方法[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4): 35-47.SI Y, CAI M J, ZHANG J L, et al. Quantitative identification method of reservoir flow barriers based on self-organizing neural network and K-nearest neighbor algorithm[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(4): 35-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 王亚, 杨少春, 路研, 等. 基于测井岩石物理相识别的低渗透储层评价方法: 以东营凹陷高青地区蒙阴组上段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(6): 1264-1275.WANG Y, YANG S C, LU Y, et al. Evaluation method of low permeability reservoirs based on logging petrophysical facies identification: A case study of the upper member of Mengyin Formation in Gaoqingarea, Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(6): 1264-1275. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] WANG Y, LU Y. Diagenetic facies prediction using a LDA-assisted SSOM method for the Eocene beach-bar sandstones of Dongying Depression, East China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 108040. [20] BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369. [21] LAI J, WANG G W, WANG Z Y, et al. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 436-457. [22] SWANSON B F. A simple correlation between permeabilities and mercury capillary pressures[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1981, 33(12): 2498-2504. [23] LAI J, WANG G W. Fractal analysis of tight gas sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion techniques[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 24: 185-196. [24] 郭思祺, 肖佃师, 卢双舫, 等. 徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密储层孔径分布定量表征[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(11): 3742-3751.GUO S Q, XIAO D S, LU S F, et al. Quantificational characterization of tight reservoir pore size distribution of Shahezi Formation in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(11): 3742-3751. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] CHEN X J, ZHOU K, JIANG P, et al. Identification, characterization, and up-scaling of pore structure facies in the low permeability reservoirs: Insight into reservoir quality evaluation and sweet-spots analysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2024, 162: 106646. [26] HUANG Y Y, WANG G W, ZHANG Y, et al. Logging evaluation of pore structure and reservoir quality in shale oil reservoir: The Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023, 156: 106454. [27] BAUER K, KULENKAMPFF J, HENNINGES J, et al. Lithological control on gas hydrate saturation as revealed by signal classification of NMR logging data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2015, 120(9): 6001-6017. -





 下载:
下载: