Application of machine learning models to geothermal groundwater temperature prediction
-
摘要:
地热作为一种清洁能源具有广阔的应用前景,可持续地开发和利用地热资源中地热水的温度评估是重要的研究课题。人工智能技术已成为矿产和油气资源勘探开发研究的热点和前沿方向,然而在地热资源开发方面相关研究和应用较少。剖析了油气资源开发中大数据与人工智能应用的重要价值,对当前地热资源开发中人工智能技术的应用与探索进行了介绍。以陕西咸阳地热田为例,采用长短期记忆(long short-term memory,简称LSTM)神经网络构建了以灌定采模式下单井水温的时间序列模型;采用随机森林和XGBoost算法,建立了多个井地热水温度的预测模型。研究结果表明,建立的机器学习模型在地热水温度预测方面表现优秀,模型准确度均在95%以上,且速度快。该地区地热水温的首要影响因素是取水段顶深,模型验证了渭北断裂带对热储的重要作用。实例应用验证了机器学习模型在解决地热资源开发复杂难题中的优越性,人工智能技术的合理应用能够为地热资源的高效开发和科学降本提质增效提供更多有效的决策依据。
Abstract:Geothermal energy as a kind of clean energy has broad application prospects. The temperature assessment of geothermal water in sustainable development and utilization of geothermal resources is an important research topic.
Objective Artificial intelligence technology has become a hot spot and frontier direction in the exploration and development of mineral and oil and gas fields, but in the field of geothermal field development, there are few relevant studies. This paper first analyzes the important value of large data and artificial intelligence application in oil and gas field development, and then introduces the application of artificial intelligence in geothermal field development at present.
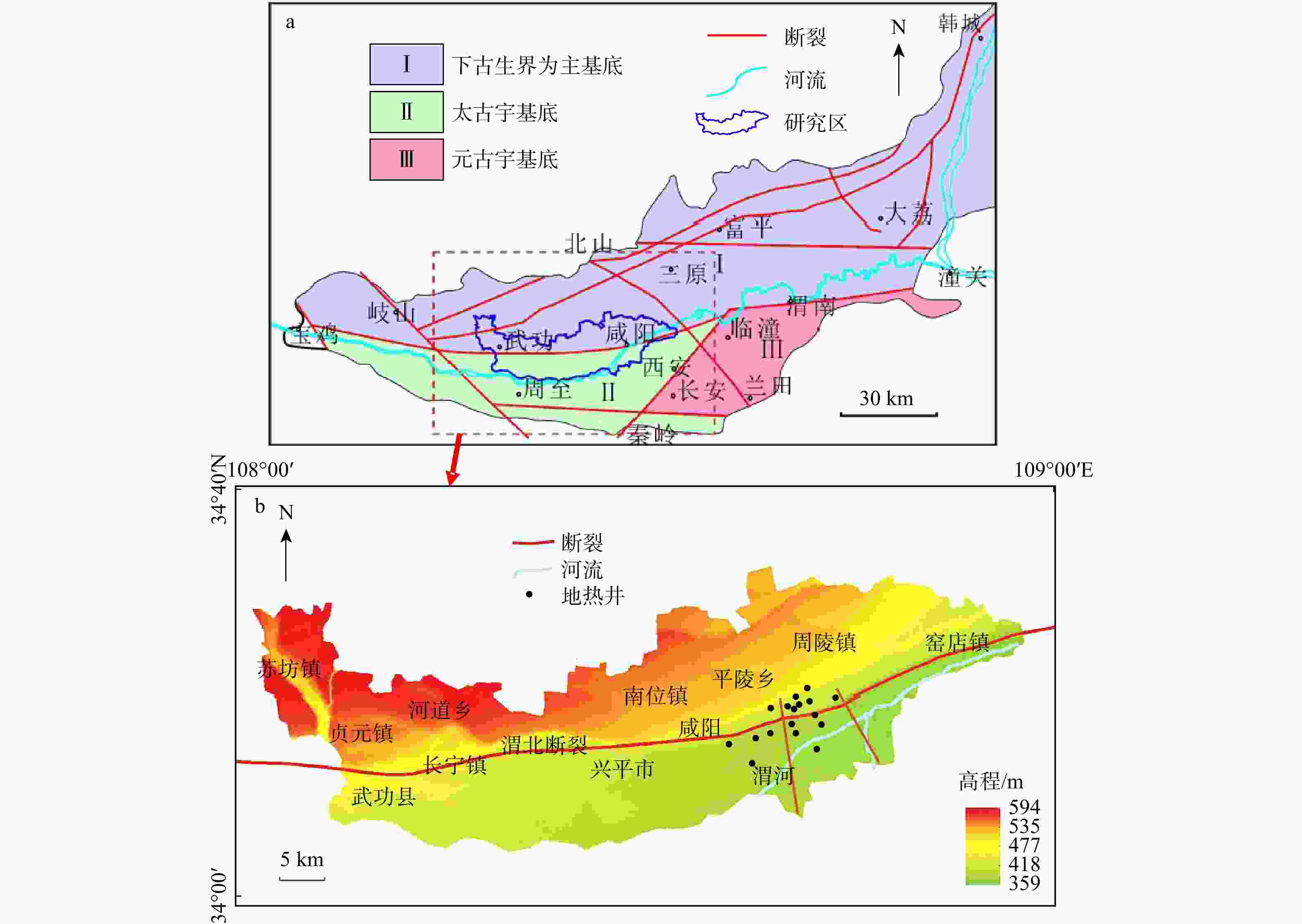
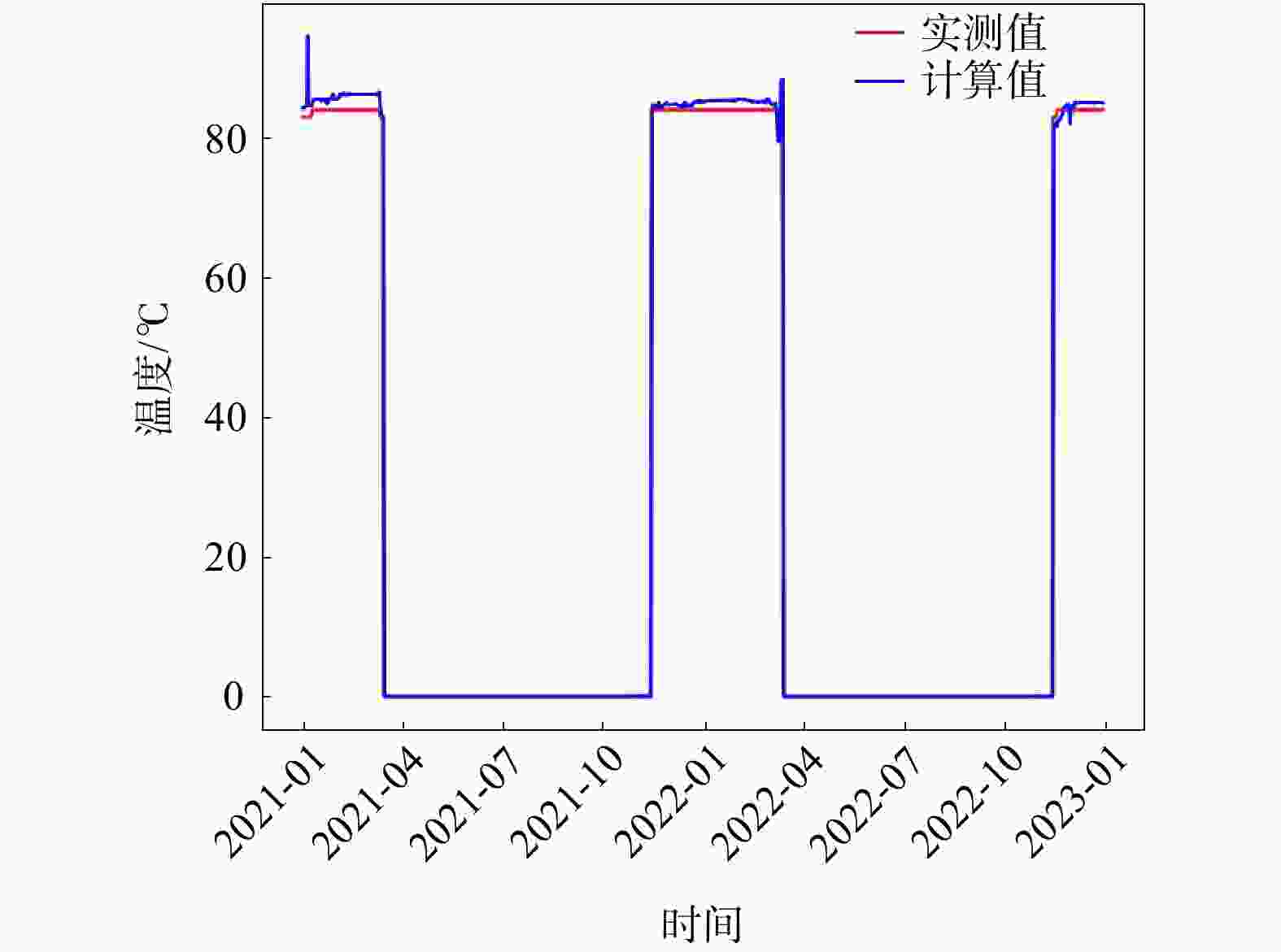
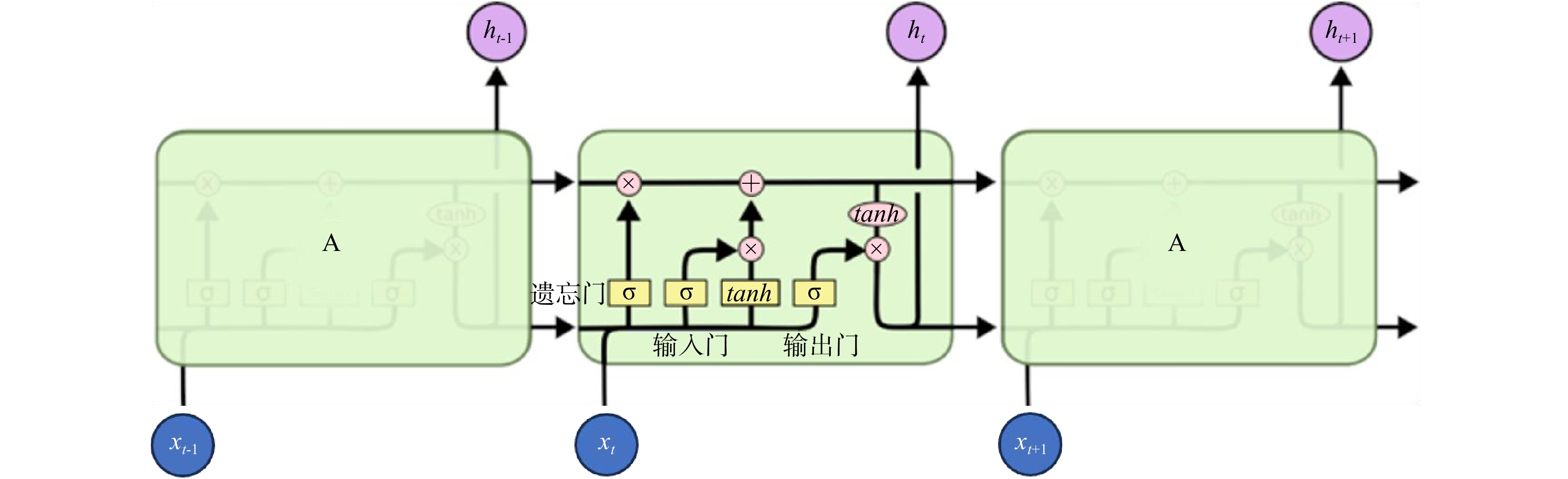
Methods Taking Xianyang geothermal field in Shaanxi province as an example, the single well geothermal water temperature time series model was constructed by using long and short term memory neural network (LSTM) under the predestined production mode. Random forest and XGBoost algorithm were used to predict the groundwater temperature of multiple geothermal wells.
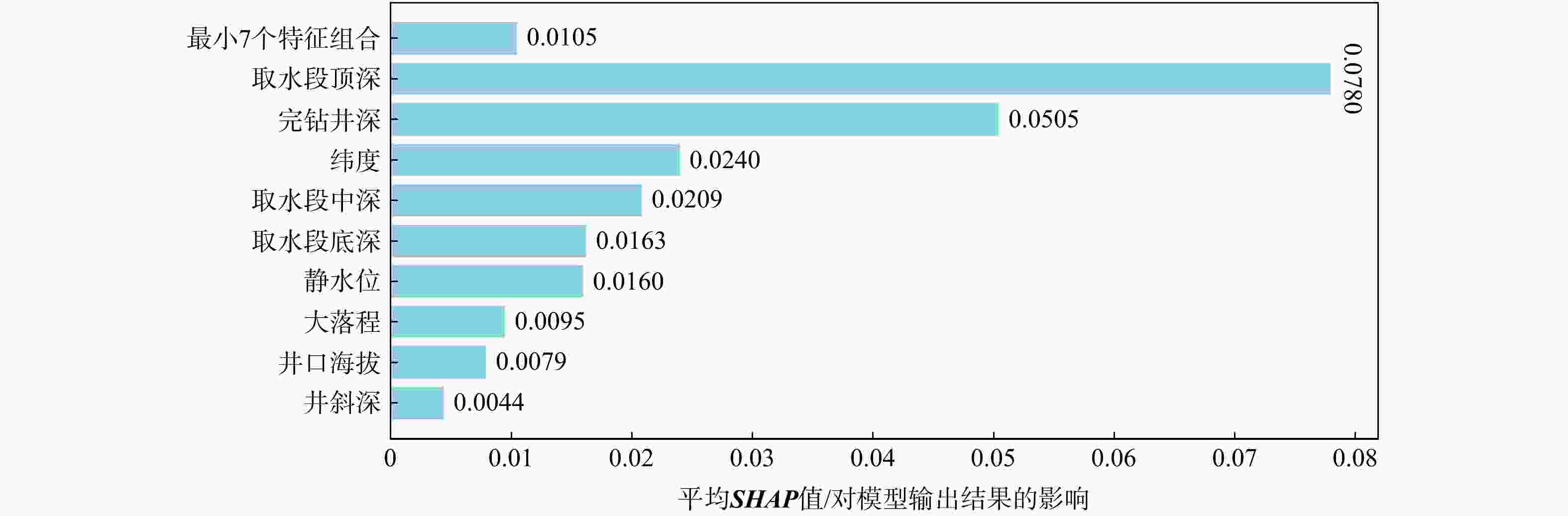
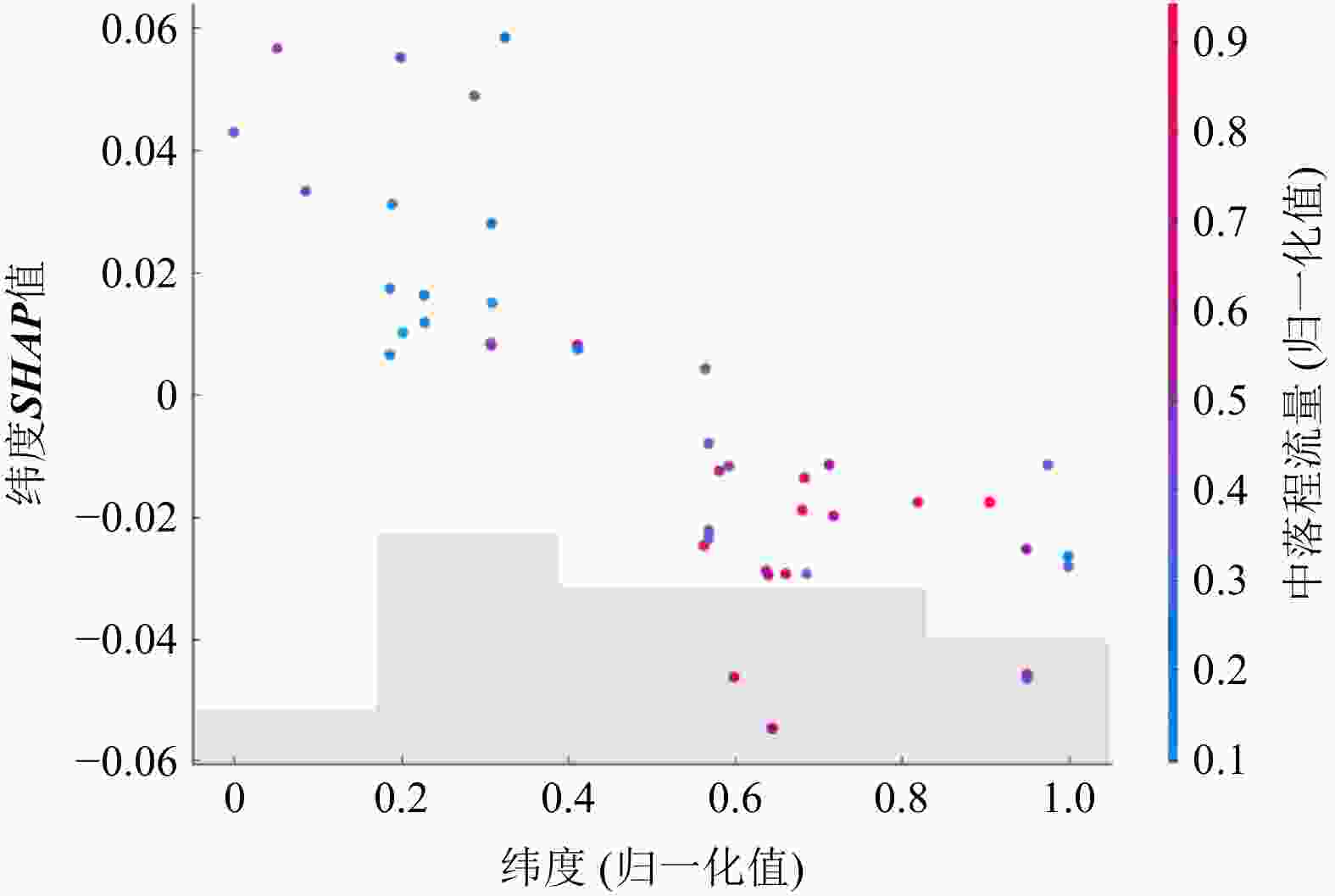
Results The accuracy of the three models was above 95%, and the running speed is fast. The depth at the top of the water intake section is the primary influencing factor of geothermal water temperature in this area. The model verifies that the fault zone plays an important role in heat storage.
Conclusion The application of the example verifies the superiority of machine learning in solving complex problems in geothermal field development, and the reasonable application of artificial intelligence technology can provide more effective decision-making basis for the efficient development of geothermal field and scientific cost reduction, quality improvement and efficiency improvement.
-
Key words:
- geothermal development /
- machine learning /
- modeling /
- groundwater /
- hydrothermal prediction
-
表 1 咸阳54口地热井试验资料数据内容
Table 1. Content of test data of 54 geothermal wells in Xianyang
序号 特征名称 单位 1 井类型 / 2 经度 ° 3 纬度 ° 4 井口海拔 m 5 完钻井深 m 6 井斜深 m 7 取水段顶深 m 8 取水段底深 m 9 取水段中深 m 10 静水位 m 11 中落程降深 m 12 中落程流量 m3/h 13 大落程降深 m 14 大落程流量 m3/h 15 小落程降深 m 16 小落程流量 m3/h 17 中落程温度 ℃ 表 2 咸阳部分地热井的抽水试验实测数据
Table 2. Pumping test data of some geothermal wells in Xianyang
井名 取水段顶深/m 取水段底深/m 取水段中深/m 静水位/m 中落程降深/m 中落程流量/(m3·h−1) 中落程温度/℃ WR3 2060.9 2724.9 2392.90 12 19 120 82 WR5 1581.5 2961.6 2271.55 −52.5 28 121.03 75 WR6 2003.31 3033.78 2518.55 6 18 130.66 83 WR9 1055.2 1599.13 1327.17 −8 14 102 61 WT2 909.7 1699.93 1304.82 −9 31 120 50 表 3 LSTM模型参数优选结果
Table 3. LSTM model parameter optimization results
参数 参数取值 优选值 时间步长 5,10,20,40 5 网络层数 1,2 1 隐藏层神经元 128,256 128 学习率 0.01,0.005,0.001 0.001 迭代的次数 50,100,200 200 表 4 随机森林和XGBoost模型参数优选结果
Table 4. Optimization results of random forest and XGBoost model parameters
模型 参数 参数取值 优选值 随机森林 决策树的个数 40,80,100,200, 1000 200 决策树最大特征数 ‘auto’,‘sqrt’,‘log2’ ‘auto’ 决策树最大深度 None,10,20,30 10 叶子节点含有的最少样本 2,3,5 3 节点可分的最小样本数 9,10,11 9 XGBoost 学习率 0.01,0.05,0.1 0.1 树的最大深度 2,3,4,5 3 训练中树的个数 50,100,200 100 最小叶子节点样本权重和 1,3,5,7 1 gamma 0,0.1,0.3,0.5 0 表 5 模型评价指标对比
Table 5. Comparison of model evaluation indexes
评价指标 LSTM 随机森林 XGBoost 决定系数R2 0.9741 0.9558 0.9943 解释方差EV 1.0000 0.9652 0.9960 平均绝对误差MAE 0.0198 0.0216 0.0130 均方根误差MSE 0.0058 0.0017 0.0002 计算时间/s 16.5625 0.1318 0.0928 -
[1] 汪集旸,胡圣标,庞忠和,等. 中国大陆干热岩地热资源潜力评估[J]. 科技导报,2012,30(32):25-31. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.32.002WANG J Y,HU S B,PANG Z H,et al. Estimate of geothermal resources potential for hot dry rock in the continental area of China[J]. Science & Technology Review,2012,30(32):25-31. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.32.002 [2] 武选民,柏琴,苑惠明,等. 冰岛地热资源开发利用现状[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(5):129-130.WU X M,BAI Q,YUAN H M,et al. Development and utilization of geothermal resources in Iceland[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(5):129-130. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 姜光政,高堋,饶松,等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2892-2910. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815JIANG G Z,GAO P,RAO S,et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2892-2910. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815 [4] 陈墨香,汪集旸. 中国地热研究的回顾和展望[J]. 地球物理学报,1994,37(增刊1):320-338.CHEN M X,WANG J Y. Review and prospect on geothermal studies in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,1994,37(S1):320-338. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 文冬光,张二勇,王贵玲,等. 干热岩勘查开发进展及展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(4):1-13.WEN D G,ZHANG E Y,WANG G L,et al. Progress and prospect of hot dry rock exploration and development[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(4):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] GUO Q H,WANG Y X,LIU W. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental impact of geothermal waters from Yangyi of Tibet,China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2009,180(1):9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.11.034 [7] GONG B,LIANG H B,XIN S L,et al. Numerical studies on power generation from co-produced geothermal resources in oil fields and change in reservoir temperature[J]. Renewable Energy,2013,50:722-731. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2012.07.026 [8] 邹才能,杨智,朱如凯,等. 中国非常规油气勘探开发与理论技术进展[J]. 地质学报,2015,89(6):979-1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.001ZOU C N,YANG Z,ZHU R K,et al. Progress in China’s unconventional oil & gas exploration and development and theoretical technologies[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2015,89(6):979-1007. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.001 [9] 张凯,赵兴刚,张黎明,等. 智能油田开发中的大数据及智能优化理论和方法研究现状及展望[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(4):28-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2020.04.004ZHANG K,ZHAO X G,ZHANG L M,et al. Current status and prospect for the research and application of big data and intelligent optimization methods in oilfield development[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2020,44(4):28-38. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2020.04.004 [10] 钟仪华,王淑宁,罗兰,等. 用深度学习挖掘油田开发指标预测模型的知识[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(6):63-74.ZHONG Y H,WANG S N,LUO L,et al. Knowledge mining for oilfield development index prediction model using deep learning[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition),2020,42(6):63-74. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 王洪亮,穆龙新,时付更,等. 基于循环神经网络的油田特高含水期产量预测方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(5):1009-1015. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.05.15WANG H L,MU L X,SHI F G,et al. Production prediction at ultra-high water cut stage via recurrent neural network[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2020,47(5):1009-1015. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.05.15 [12] 谷建伟,周梅,李志涛,等. 基于数据挖掘的长短期记忆网络模型油井产量预测方法[J]. 特种油气藏,2019,26(2):77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.02.013GU J W,ZHOU M,LI Z T,et al. Oil well production forecast with long-short term memory network model based on data mining[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2019,26(2):77-81. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.02.013 [13] 刘想平,汪崎生,汤军. 用神经网络建立自喷井井底流压预测模型[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1997,24(5):92-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1997.05.023LIU X P,WANG Q S,TANG J. An application of neural network in developing a model for predicting flowing bottomhole pressure of flowing wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,1997,24(5):92-94. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1997.05.023 [14] 张进平,王煜曦,刘桂宏,等. 通州区地热资源优化开采模式动态研究[J]. 工程力学,2022,39(6):247-256. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.01.0086ZHANG J P,WANG Y X,LIU G H,et al. Dynamic study on optimal exploitation mode of geothermal resources in Beijing Tongzhou District[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2022,39(6):247-256. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.01.0086 [15] 段晓飞,康凤新,吴晓华,等. 基于采灌均衡模拟的砂岩热储合理采灌井距计算方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(5):170-180.DUAN X F,KANG F X,WU X H,et al. A methodology for determining the optimal well spacing in sandstone geo-thermal reservoirs through production-reinjection equilibrium simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(5):170-180. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 马峰,高俊,王贵玲,等. 雄安新区容城地热田碳酸盐岩热储采灌数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(5):1534-1548.MA F,GAO J WANG G L,et al. Numerical simulation of exploitation and reinjection of carbonate geothermal reservoir in Rongcheng geothermal field,Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(5):1534-1548. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 赵敬波,刘健,周志超,等. 基于离散裂隙网络模型的地下水流并行模拟方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):55-64.ZHAO J B,LIU J,ZHOU Z C,et al. Parallel groundwater flow simulation method based on a discrete fracture network model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):55-64. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] XU T F,YUAN Y L,JIA X F,et al. Prospects of power generation from an enhanced geothermal system by water circulation through two horizontal wells:A case study in the Gonghe Basin,Qinghai Province,China[J]. Energy,2018,148:196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.135 [19] 张娟娟,林建旺,林黎,等. 基于AHP和BP神经网络的深部地热水可持续开发能力评价[J]. 地下水,2008,30(6):46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2008.06.014ZHANG J J,LIN J W,LIN L,et al. Evaluation of deep geothermal water sustainable development ability based on AHP and BP neural network[J]. Ground Water,2008,30(6):46-48. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2008.06.014 [20] 董华松,黄文辉. 利用遗传算法优化的小波神经网络实现地热资源预测[J]. 资源与产业,2014,16(3):101-106.DONG H S,HUANG W H. Prediction of geothermal resources by means of wavelet neural network optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Resources & Industries,2014,16(3):101-106. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 赵磊,张海雄,贺婷婷. 基于LSTM神经网络的地热井回灌压力预测方法研究[J]. 当代化工研究,2023(4):119-123.ZHAO L,ZHANG H X,HE T T. Reinjection pressure prediction of geothermal well with LSTM neural network model[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2023(4):119-123. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] REN Y Q,KONG Y L,PANG Z H,et al. A comprehensive review of tracer tests in enhanced geothermal systems[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2023,182:113393. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113393 [23] WU H,FU P C,MORRIS J P,et al. Characterization of flow and transport in a fracture network at the EGS Collab field experiment through stochastic modeling of tracer recovery[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,593:125888. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125888 [24] HAWKINS A J,FOX D B,KOCH D L,et al. Predictive inverse model for advective heat transfer in a short-circuited fracture:Dimensional analysis,machine learning,and field demonstration[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(11):e2020WR027065. doi: 10.1029/2020WR027065 [25] JIANG G Z,HU S B,SHI Y Z,et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China:Updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics,2019,753:36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.01.006 [26] 罗璐,朱霞,何春艳,等. 陕西咸阳地热田地热流体成因研究[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1422-1430.LUO L,ZHU X,HE C Y,et al. Study on the genesis of geothermal fluid in Xianyang geothermal field[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(6):1422-1430. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 杨剑锋,乔佩蕊,李永梅,等. 机器学习分类问题及算法研究综述[J]. 统计与决策,2019,35(6):36-40.YANG J F,QIAO P R,LI Y M,et al. A review of machine-learning classification and algorithms[J]. Statistics & Decision,2019,35(6):36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] BI Y X,GUAN J W,BELL D. The combination of multiple classifiers using an evidential reasoning approach[J]. Artificial Intelligence,2008,172(15):1731-1751. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2008.06.002 [29] CHEN T Q,LI H,YANG Q,et al. General functional matrix factorization using gradient boosting[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta,Georgia,USA:[s. n. ],2013:436-444. [30] 尹宝才,王文通,王立春. 深度学习研究综述[J]. 北京工业大学学报,2015,41(1):48-59. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2014100026YIN B C,WANG W T,WANG L C. Review of deep learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2015,41(1):48-59. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2014100026 [31] GRAVES A. Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks[M]. Berlin:Springer,2012. [32] LUNDBERG S M,LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems,2017:21889700. [33] GUIDOTTI R,MONREALE A,RUGGIERI S,et al. A survey of methods for explaining black box models[J]. ACM Computing Surveys,2019,51(5):1-42. [34] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中华人民共和国建设部. 供水水文地质勘察规范:GB50027-2001[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2001.General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China,Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic China. Standard for hydrogeological investigation of water-supply:GB50027-2001[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press,2001. (in Chinese) [35] 赵志宏,刘桂宏,王佳铖,等. 城市深层地热能可持续开采多场耦合效应数值模拟研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(3):1126-1138.ZHAO Z H,LIU G H,WANG J C,et al. Coupled multi-field effect on sustainable development of deep geothermal energy in cities[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2023,48(3):1126-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] HUO A D,WANG X F,LYU Y,et al. Simulation research on the reinjection temperature fields of deep geothermal wells based on real-scale experiment[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation,2019,37(2):646-662. [37] 陶晔,杜景林. 基于随机森林的长短期记忆网络气温预测[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2019,40(3):737-743.TAO Y,DU J L. Temperature prediction using long short term memory network based on random forest[J]. Computer Engineering and Design,2019,40(3):737-743. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 柯婷婷,黄少鹏,许威,等. 关中盆地沣西地区地热对井采灌开发模式的数值模拟[J]. 第四纪研究,2019,39(5):1252-1263. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2019.05.17KE T T,HUANG S P,XU W,et al. Numerical modeling of doublet well system for extracting heat from sandstone geothermal reservoir:A case study of Fengxi area,the Guanzhong Basin,NW China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2019,39(5):1252-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2019.05.17 [39] 高俊义. 地热温度和生产井深度对岩体水流−传热温度影响机理研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2020,35(5):1659-1664. doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0370GAO J Y. Study on mechanism of the influence of geothermal temperature and production well depth on water flow and heat transfer temperature in rock mass[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2020,35(5):1659-1664. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0370 [40] 杨国华,李婉露,孟博. 基于机器学习方法的地下水氨氮时空分布规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(6):1982-1995.YANG G H,LI W L,MENG B. Spatiotemporal distribution of groundwater ammonia nitrogen based on machine learning methods[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(6):1982-1995. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 肖立志. 机器学习数据驱动与机理模型融合及可解释性问题[J]. 石油物探,2022,61(2):205-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.02.002XIAO L Z. The fusion of data-driven machine learning with mechanism models and interpretability issues[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,2022,61(2):205-212. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.02.002 -




 下载:
下载: