Rockfall damage evaluation and treatment suggestions for mountain highways based on three-dimensional kinematic simulations
-
摘要:
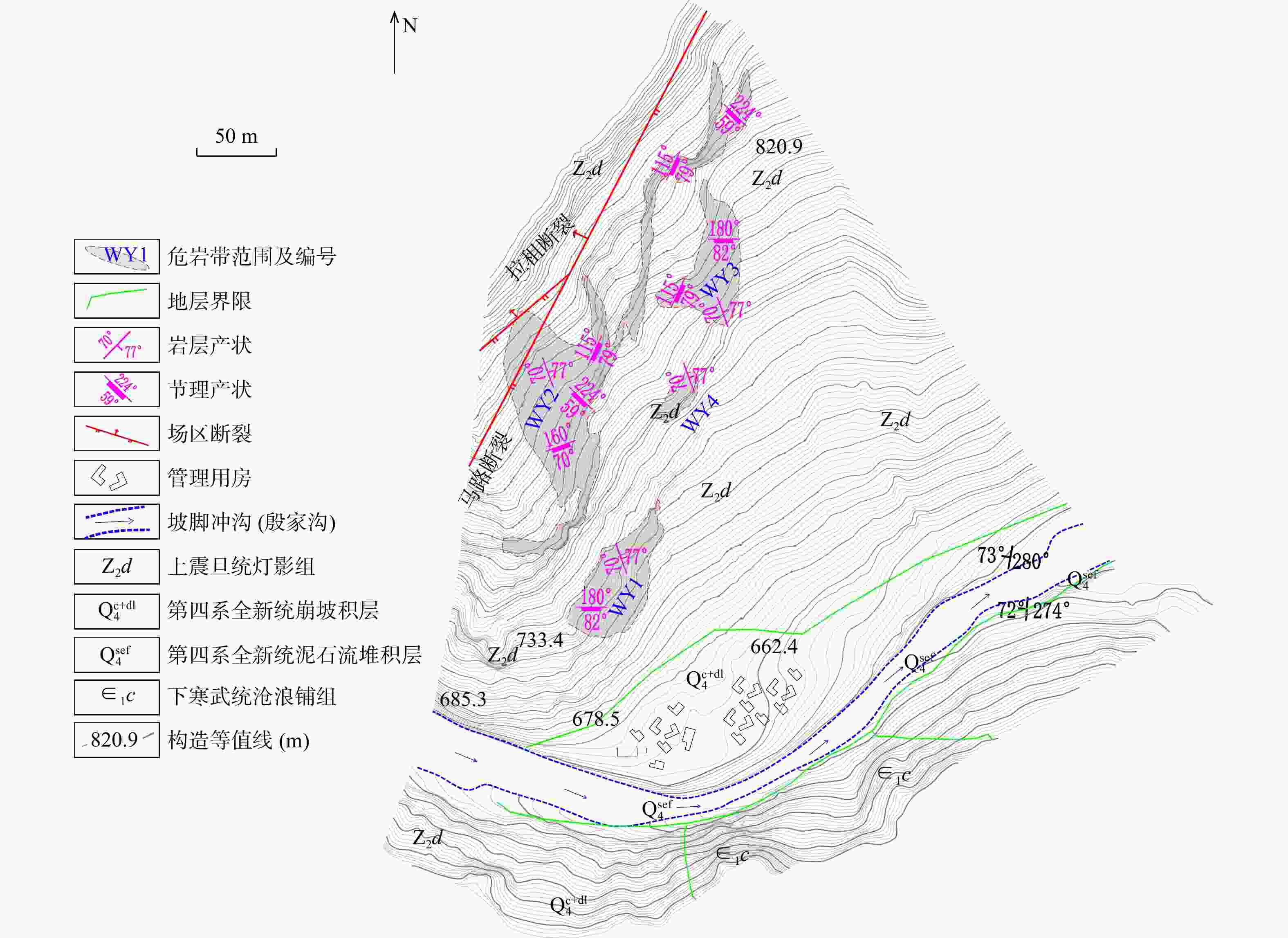
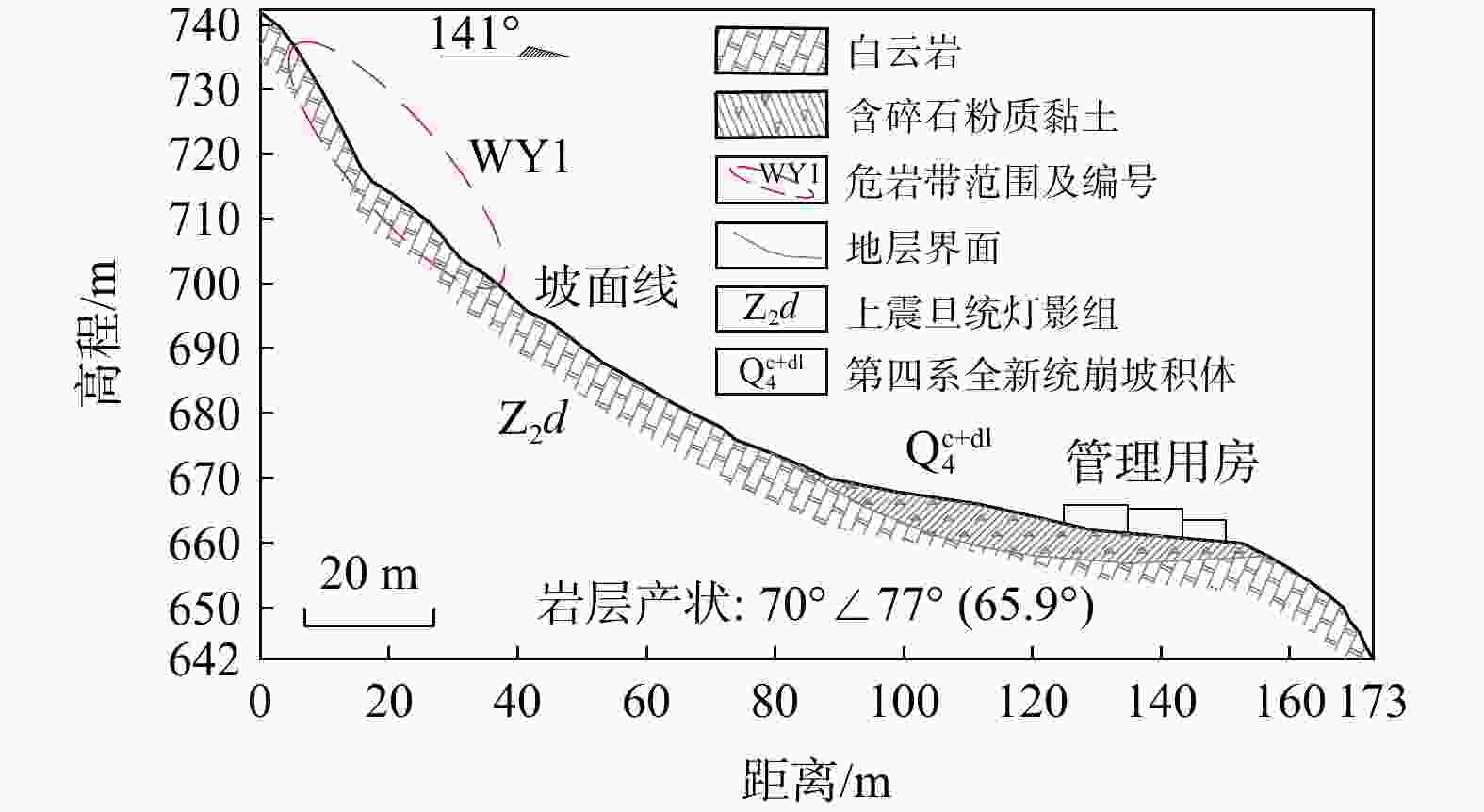
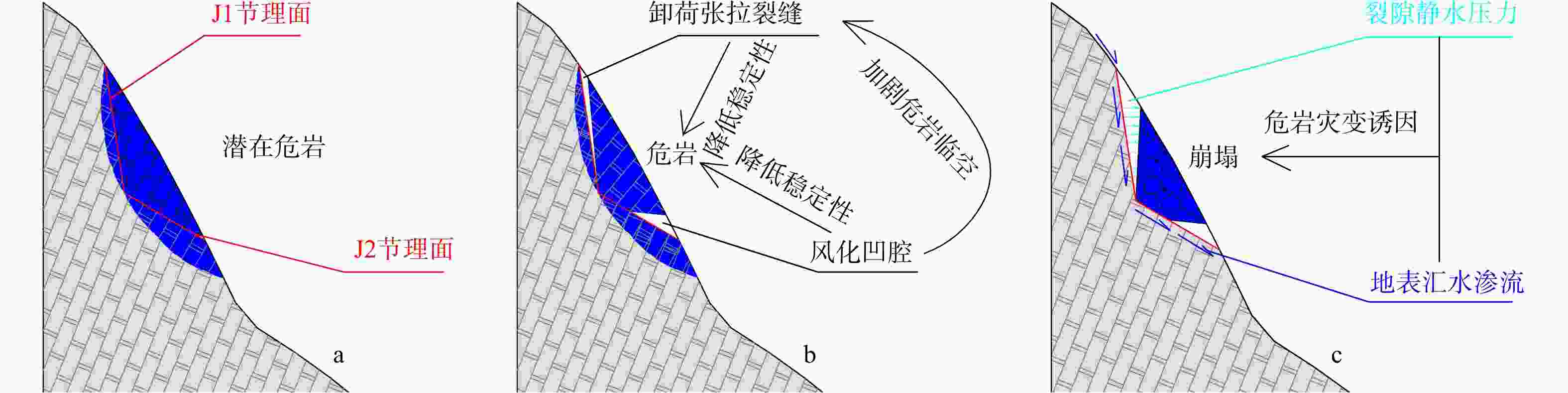
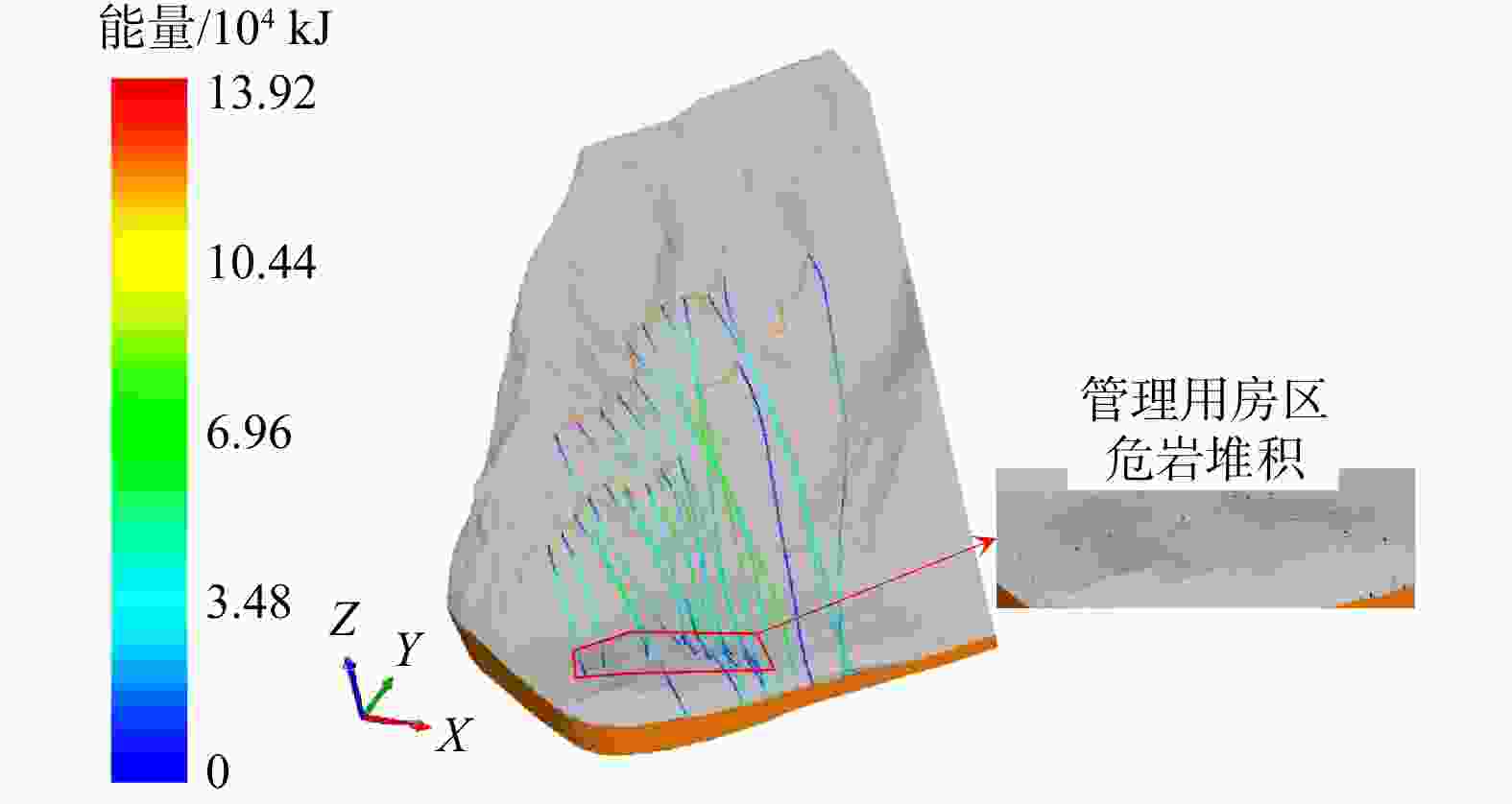
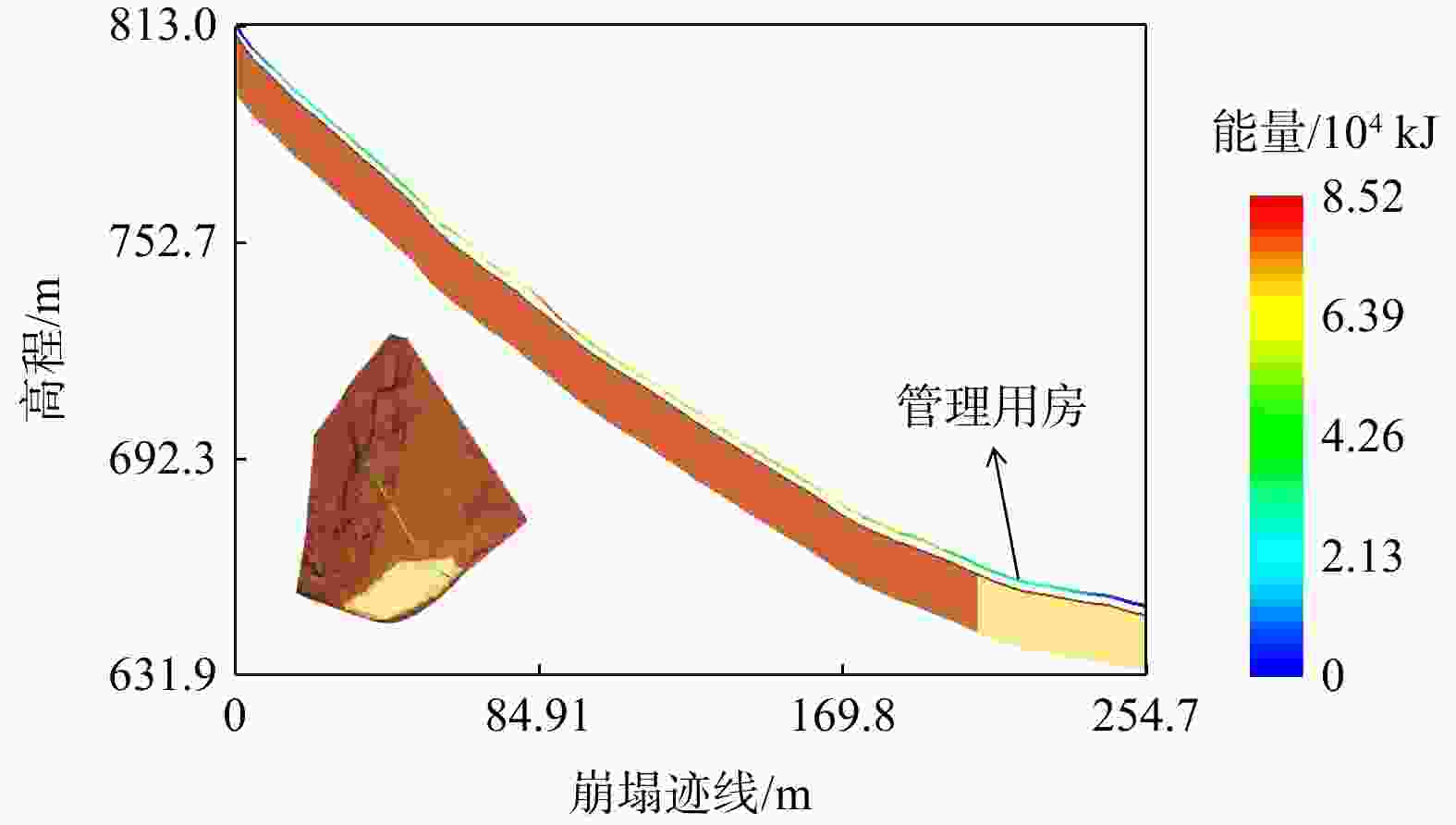
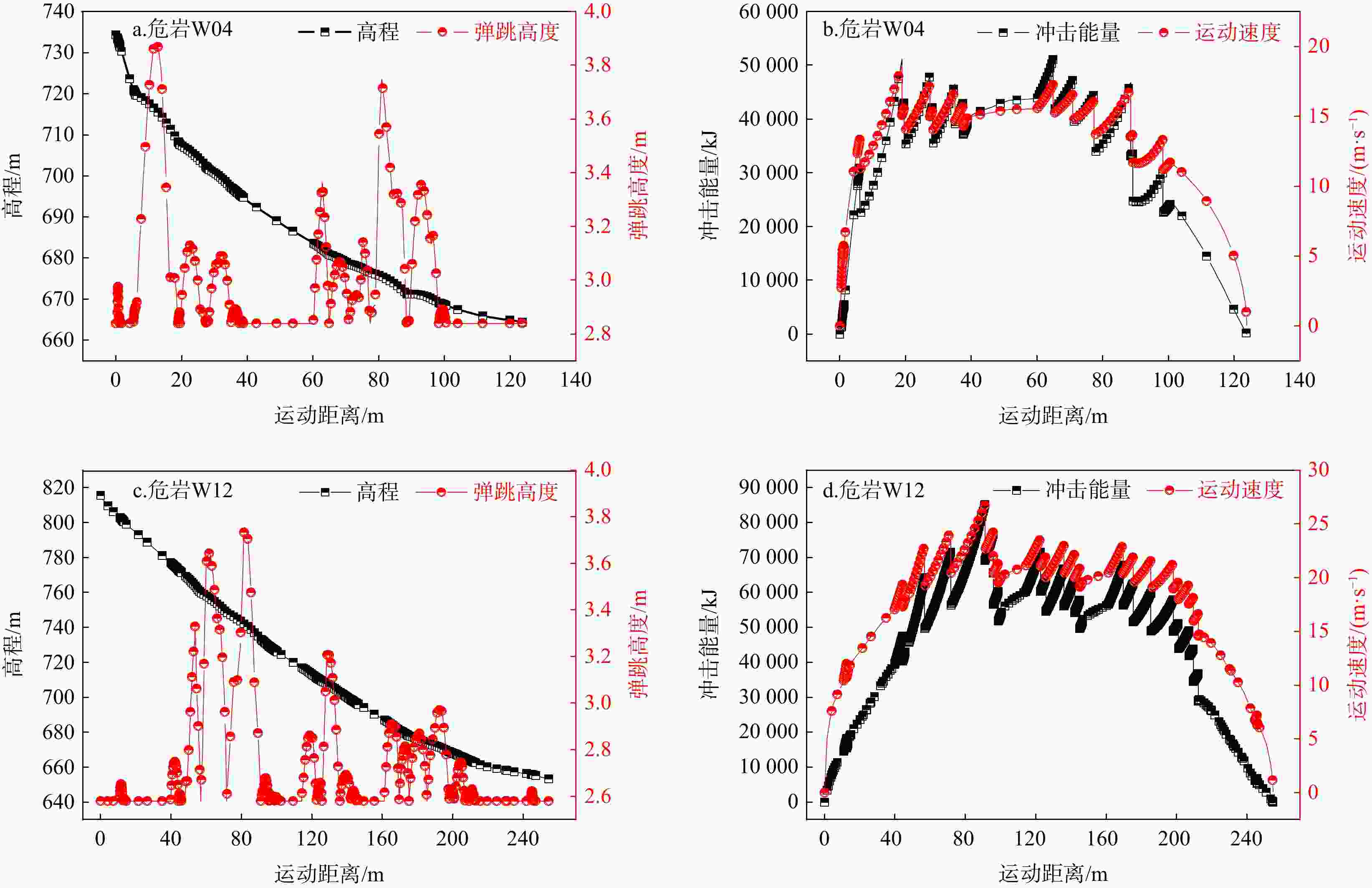
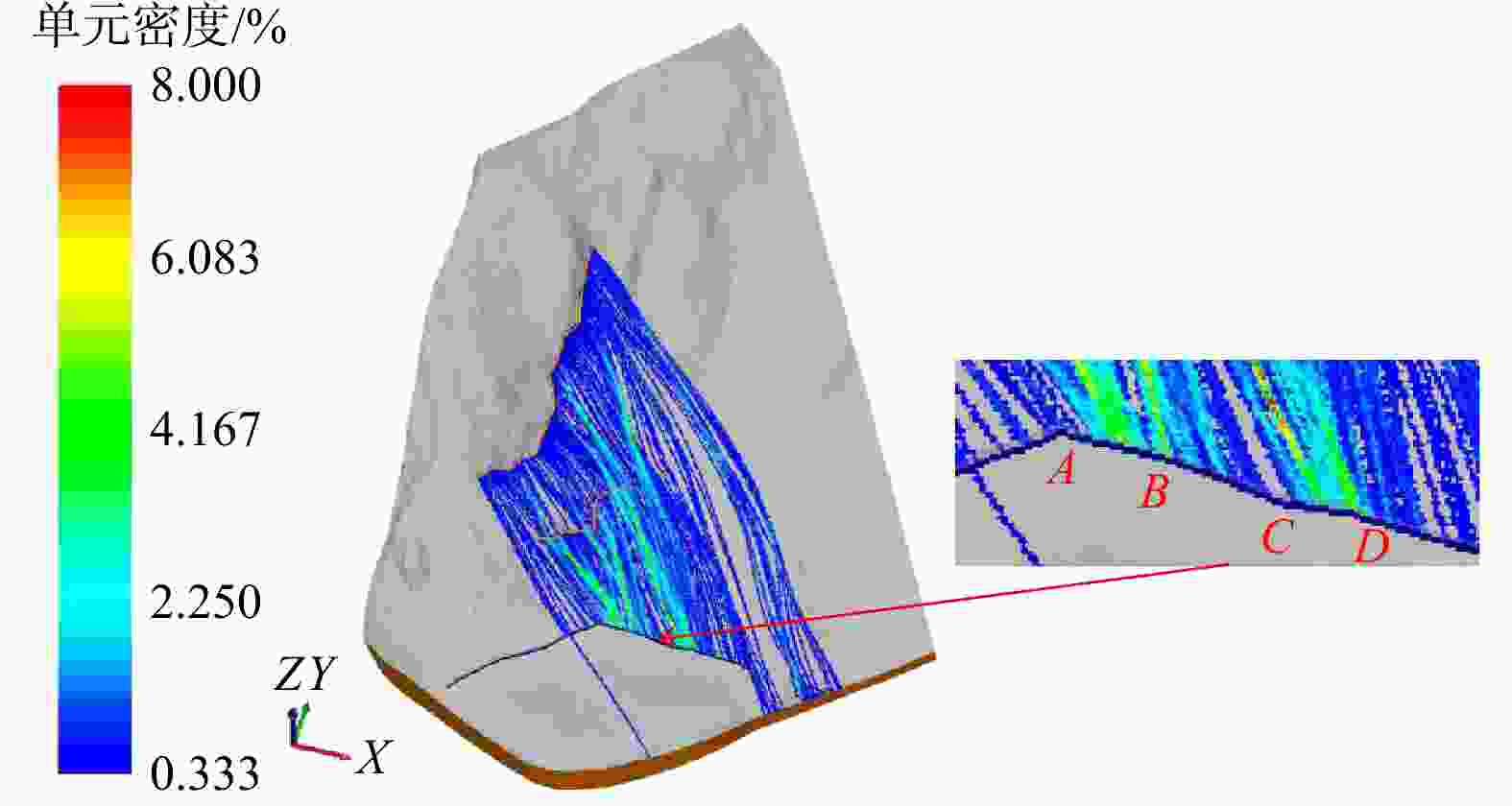
考虑斜坡地貌特征的运动学三维模拟是山区公路危岩崩塌灾害损伤评价的重要依据,其计算结果亦可支撑崩塌灾害治理。基于实地调查和无人机航测,分析了研究区危岩分布、物质组成和灾变特征,并采用RocPro3D软件进行危岩崩塌运动学三维模拟,对灾害损伤情况进行评价,并计算不同粒径落石和防护设施下的工程治理效果。结果表明,构造挤压和临空卸荷产生的组合节理切割形成了危岩,底部风化凹腔降低了危岩稳定性,后缘裂隙静水推力和裂隙渗水是危岩崩塌的典型诱因;危岩崩塌后运动速度和冲击能量先增大后减小,弹跳高度起伏波动且整体趋于降低;研究区危岩带对坡脚管理用房具有重大威胁,清方至危岩直径低于0.8 m,并采用高6.0 m、防护能级
1000 kJ的被动防护网是有效的处置措施;危岩崩塌运动迹线空间分布局部集中位置应适当增强防护。运动学三维模拟能够获取危岩崩塌运动迹线、速度、能量、弹跳高度和单元密度等信息,突破了二维剖面计算在空间上的局限性,对灾害损伤评价和地质灾害防治具有重要意义。Abstract:Objective Three-dimensional kinematic simulation, which takes into account the characteristics of slope topography, serves as a crucial foundation for assessing rockfall risks in mountainous highways. Additionally, its computational outcomes can significantly enhance management strategies for rockfall mitigation.
Methods Leveraging field investigations and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) aerial surveys, we conducted a detailed analysis of the distribution, material composition, and disaster characteristics of hazardous rocks within the study area. Using RocPro3D software, we simulated the three-dimensional kinematics of rockfall to evaluate the disaster's impact and assess the effectiveness of engineering interventions for rockfalls of various particle sizes, complemented by protective measures.
Results Our findings indicate that joints formed due to tectonic compression and stress relief from unloading segment the precarious rock masses, while weathering cavities at their bases diminish stability. Hydrostatic thrust exerted by trailing edge cracks, along with water seepage through these fractures, are identified as typical triggers of rockfall events. Post-collapse, the velocity and impact energy of falling rocks initially increase and then decline, while bounce height exhibits variability before showing a decreasing trend. Hazardous rock zones within the study area pose a significant threat to management facilities situated at the foot of the slope. An effective remedial measure involves clearing areas adjacent to dangerous rocks with diameters less than 0.8 meters and implementing a passive protection net measuring 5.0 meters in height, designed to withstand an energy level of
1000 kJ. Localized concentration areas within the spatial distribution of rockfall movement traces should be appropriately reinforced.Conclusion Three-dimensional kinematic simulation provides detailed information on rockfall movement traces, velocity, energy, bounce height, and unit density. This approach transcends the spatial limitations inherent in two-dimensional cross-sectional analyses, proving immensely valuable for evaluating disaster damage and enhancing geological disaster prevention efforts.
-
Key words:
- mountain highway /
- rockfall /
- kinematics /
- three-dimensional simulation /
- RocPro3D /
- damage evaluation /
- engineering treatment
-
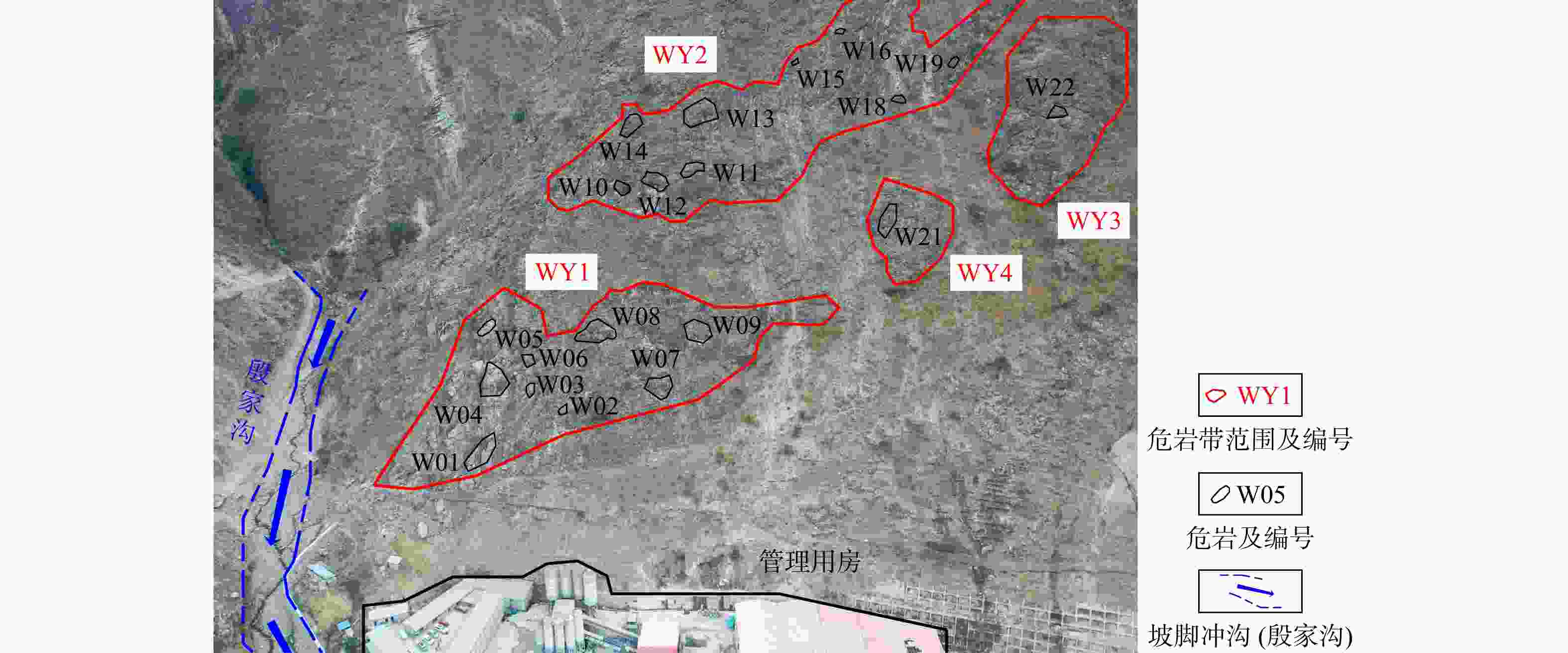
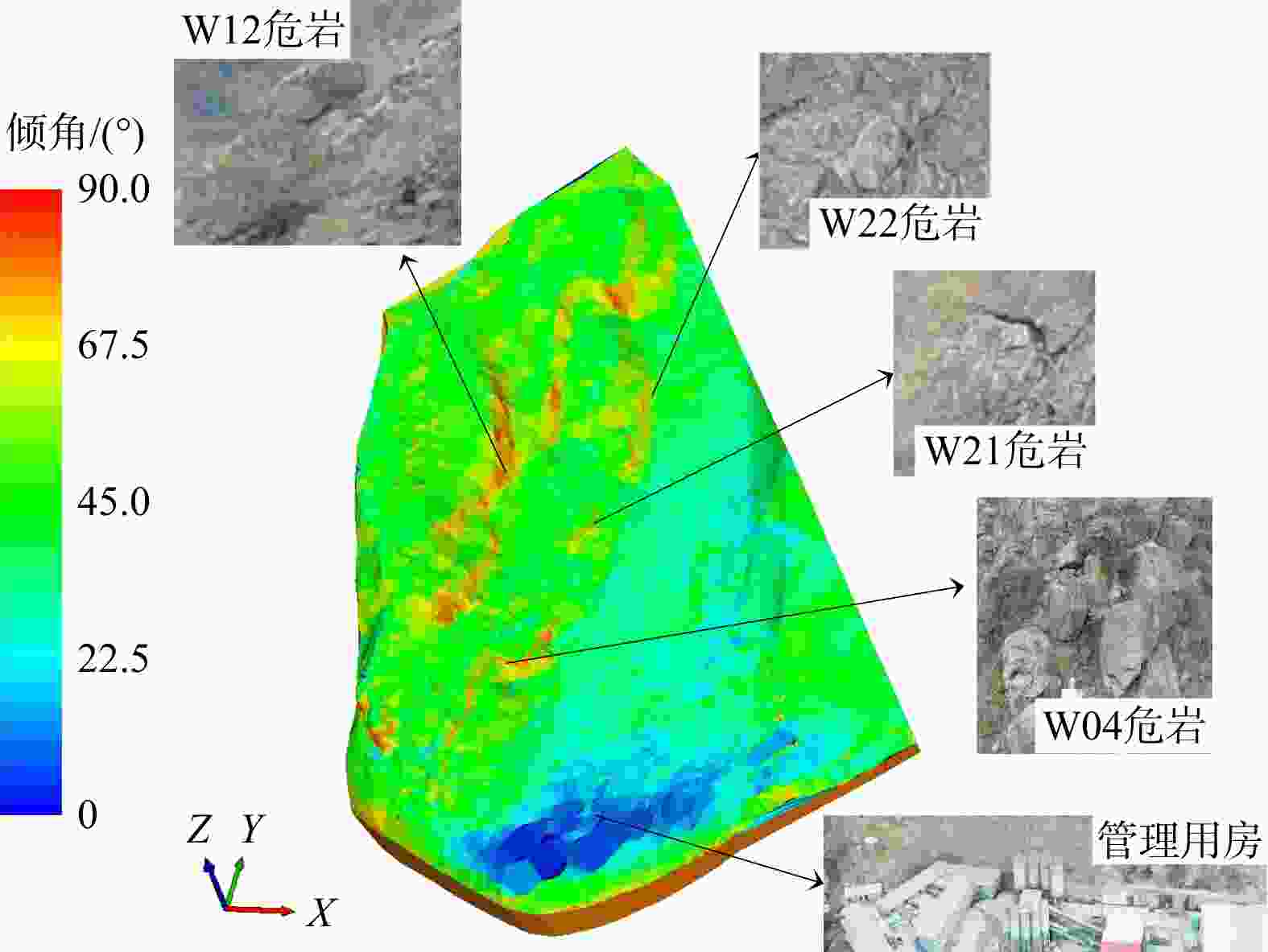
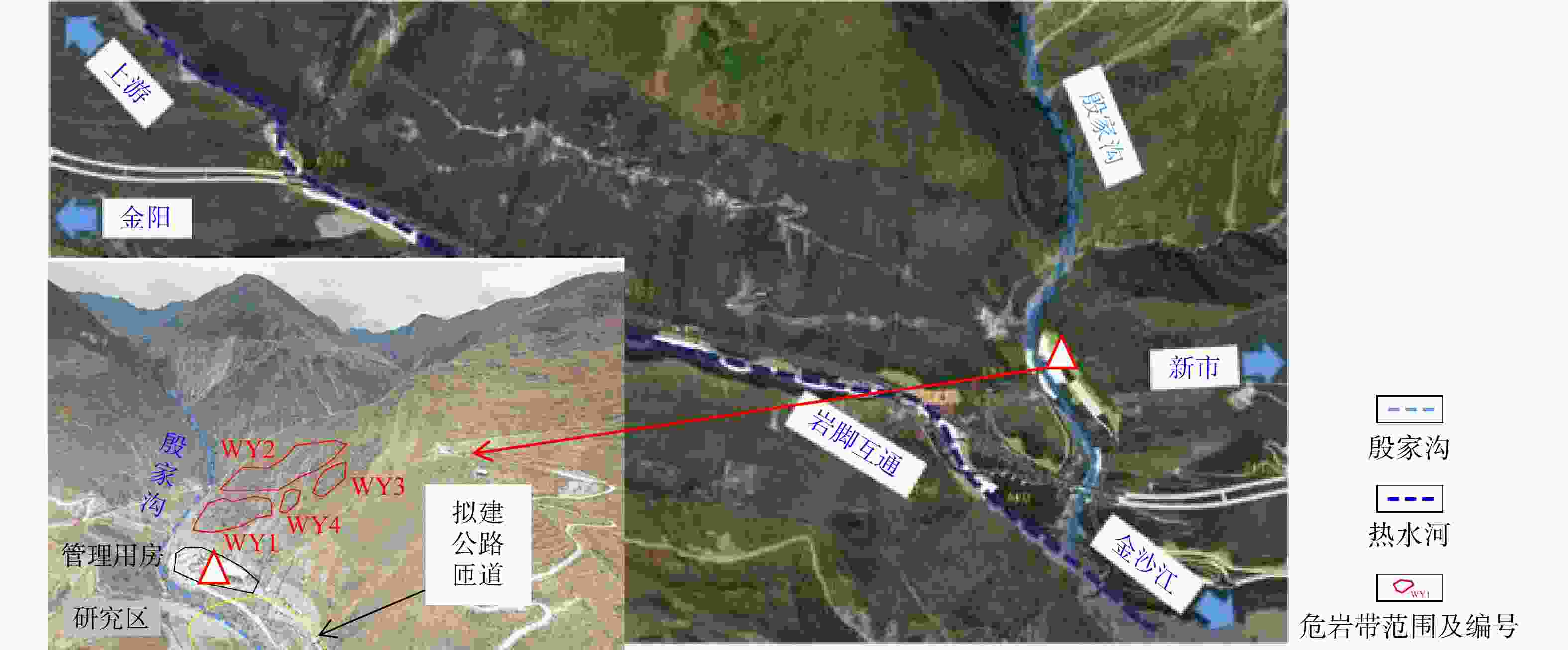
表 1 研究区22处危岩基本特征统计
Table 1. Statistics of the basic characteristics of 22 dangerous rocks in the study area
危岩带 危岩
编号分布高
程/m危岩尺寸
(长×宽×厚)/ m3体积/
m3变形破坏
模式WY1 W01 697~703 6×6×2 72 拉裂−滑移 W02 705~707 2×2×1 4 拉裂−滑移 W03 718~720 2×1.5×1.5 4.5 拉裂−滑移 W04 718~722 6×4×4 96 拉裂−滑移 W05 738~740 4×4×4 64 拉裂−滑移 W06 723~731 8×8×4 256 拉裂−滑移 W07 718~722 2×3×1.5 9 拉裂−滑移 W08 725~729 5×4×1 20 拉裂−滑移 W09 720~725 6×5×1.5 45 拉裂−滑移 WY2 W10 775~780 4×5×2 40 拉裂−滑移 W11 777~780 8×3×1 24 拉裂−滑移 W12 802~814 3×12×2 72 拉裂−滑移 W13 840~843 3×3×2 18 拉裂−滑移 W14 843~845 1×2×1 2 拉裂−滑移 W15 843~846 4×3×1 12 拉裂−滑移 W16 840~843 6×3×2 36 拉裂−滑移 W17 885~910 5×25×2 250 拉裂−滑移 W18 885~910 2×3×2 12 滑移 W19 820~832 5×12×2 120 拉裂−滑移 W20 820~825 5×5×2 50 拉裂−滑移 WY4 W21 760~765 4×5×2 40 滑移 WY3 W22 760~763 3×3×2 18 拉裂−滑移 表 2 危岩体特征参数
Table 2. Characteristics parameters of the dangerous rock mass
危岩带 代表性危岩 块石密度/
(kg·m−3)形状 直径/m 危岩数量/个 WY1 W04 2700 球体 5.68 9 WY2 W12 2700 球体 5.16 11 WY3 W22 2700 球体 3.25 1 WY4 W21 2700 球体 4.24 1 表 3 斜坡地表岩土体计算参数
Table 3. Calculation parameters of the rock and soil on the slope surface
参数分类 参数 岩土体 白云岩 崩坡积体 恢复系数 法向值Rn 0.44 0.32 切向值Rt 0.88 0.82 变化范围△_R/% 4 3 极限速度V_R(lim)/(m·s−1) 10 10 极限变化范围△_R(lim)/% 2 1 恢复系数的
横向偏差变化范围△_$\theta_{\mathrm{h}} $ /(°) 20 12.5 极限速度V_$\theta_{\mathrm{h}} $(lim)/(m·s−1) 10 10 极限变化范围△_$\theta_{\mathrm{h}} $(lim)/% 10 6.25 恢复系数的
竖向偏差变化范围△_$\theta_{\mathrm{v}} $/(°) 2 2 极限速度V_$\theta_{\mathrm{v}} $(lim)/(m·s−1) 10 10 极限变化范围△_$\theta_{\mathrm{v}} $(lim)/% 4 4 摩擦系数 k值 0.45 0.6 变化范围△_k/% 12 12 极限速度V_k(lim)/(m·s−1) 10 10 极限变化范围△_k (lim)/% 10 10 转换参数 角度β_lim/(°)[锐角] 2 5 角度β_lim/(°)[钝角] 25 40 表 4 场区崩塌防治模拟计算
Table 4. Simulation calculations of rockfalls in the study area
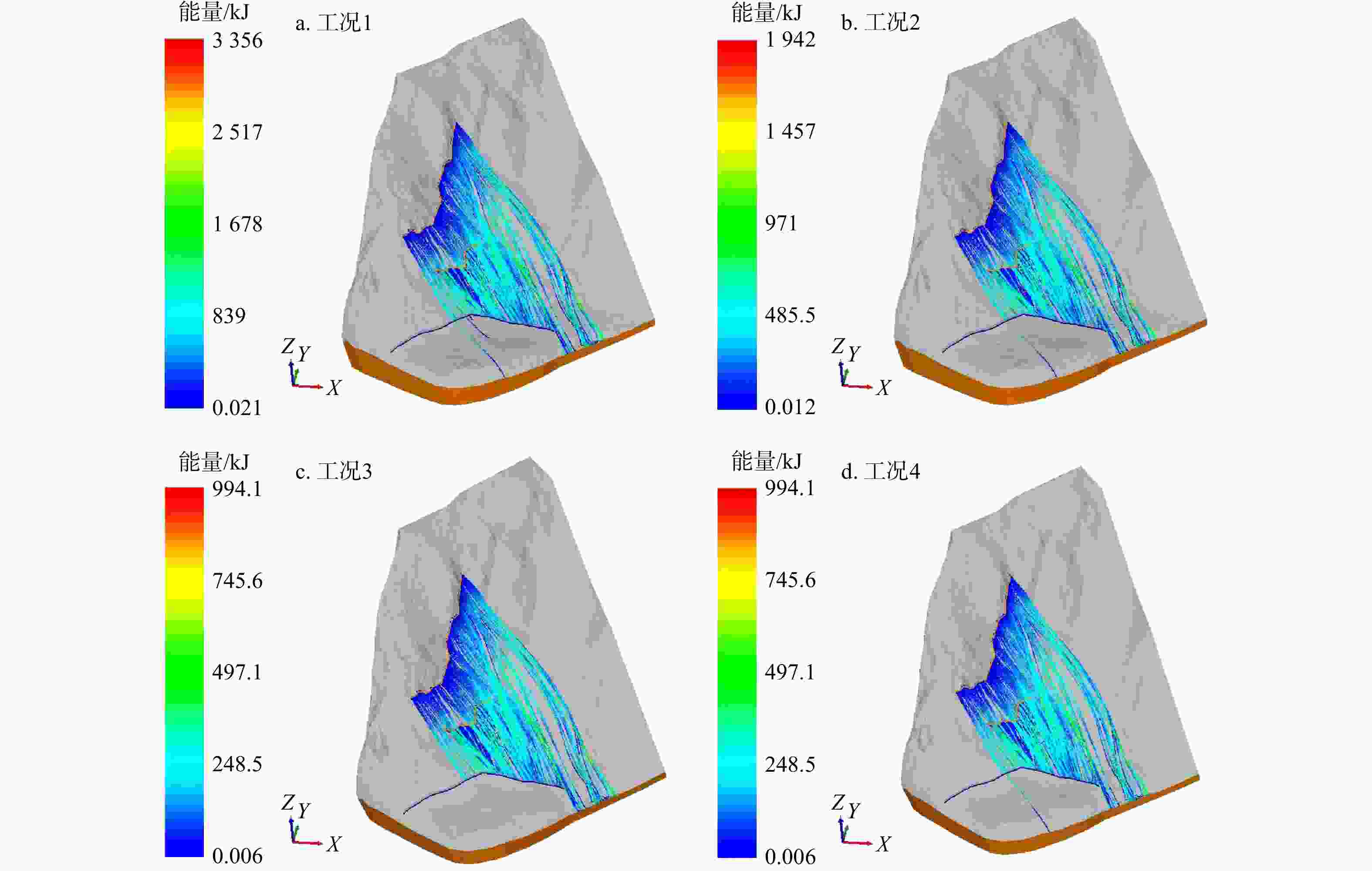
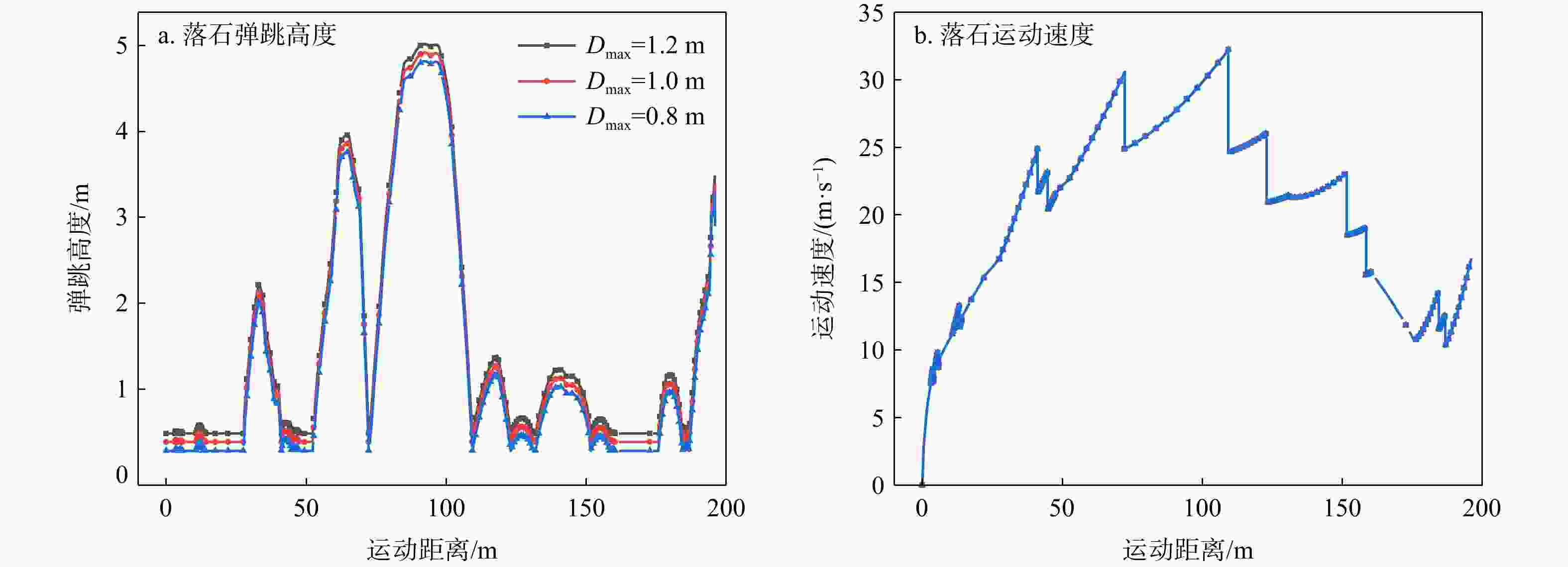
工况编号 危岩规模 被动防护网 防护位置计算结果 防护效果 清方下限直径Dmax/m 数量 高度/ m 能级/ kJ 最大弹跳高度/ m 最大冲击能量/ kJ 1 1.2 危岩带WY1设置100处 5.0 1000 5.13 952 无效 2 1.0 5.0 5.03 551 无效 3 0.8 危岩带WY2设置200处 5.0 4.93 254 有效 4 0.8 4.5 4.93 282 无效 -
[1] 黎尤,何坤,胡卸文,等. 震裂山体崩塌形成特征及运动学三维模拟:以汶川县三官庙村崩塌为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(2):542-552.LI Y,HE K,HU X W,et al. Formation characteristics and kinematics 3D simulation of rockfall evolved from shattered mountain:Case study of Sanguanmiao Village rockfall in Wenchuan Country[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(2):542-552 (in Chinese with English abstract [2] FANOS A M,PRADHAN B. A novel rockfall hazard assessment using laser scanning data and 3D modeling in GIS[J]. Catena,2019,172:435-450. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.012 [3] 向波,罗晗玲,邬凯,等. 山区公路顺层边坡首次失稳长度影响因素及确定方法[J]. 自然灾害学报,2024,33(5):48-60.XIANG B,LUO H L,WU K,et al. Influencing factors and determination method of the initial instability length of bedding slope along mountainous highways[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2024,33(5):48-60. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 王炎. 基于ROCPRO3D的大华桥水库坝肩危岩体风险性评价[D]. 郑州:华北水利水电大学,2023.WANG Y. Risk evaluation of dangerous rock mass at dam abutment of Dahuaqiao reservoir based on RocPro3D[D]. Zhengzhou:North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 王忠福,罗干,杨晓洁. 基于RocPro3D的大华桥水电站危岩体数值模拟研究[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2025,46(1):152-160.WANG Z F,LUO G,YANG X J,et al. Rockfall simulation study at Dahua Qiao hydropower station using RocPro3D[J/OL]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (natural science edition),2025,46(1):152-160.(in Chinese with English abstract [6] 张蕴灵,傅宇浩,李为乐,等. 2020年9月20日雅西高速姚河坝崩塌调查[J]. 山地学报,2021,39(3):450-460.ZHANG Y L,FU Y H,LI W L,et al. Preliminary investigation on the Yaoheba rockfall along the Ya'an-Xichang Highway on september 20,2020,Sichuan,China[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(3):450-460 (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 邬凯,易雪斌,付晓东,等. 泸定地震震中海螺沟景区道路地质灾害发育规律及灾后重建对策[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2024,43(8):1909-1922.WU K,YI X B,FU X D,et al. Geohazard development rules and post disaster reconstruction strategies of Hailuogou scenic road in the epicenter of Luding earthquake[J],Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2024,43(8):1909-1922. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] WANG X,FU X D,WU K,et al. Analysis of historical evolution characteristics and collapse process on July 18,2023,of a dangerous rock mass at Guanyinyan in Baoxing Country,Sichuan Province,China[J]. 2024,21(6):1367-1383. [9] 刘洪博,佟磊,张龙,等. S303公路边坡崩塌灾害体发育特征及其危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):34-38.LIU H B,TONG L,ZHANG L,et al. Slope collapse hazard development characteristics and risk assessment of S303 Highway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):34-38. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 何宇航,裴向军,梁靖,等. 基于Rockfall的危岩体危险范围预测及风险评价:以九寨沟景区悬沟危岩体为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):24-33.HE Y H,PEI X J,LIANG J,et al. Risk assessment and range prediction of dangerous rockmass based on Rockfall:A case study of the Xuangou Collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):24-33. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 王翔,牌立芳,吴红刚. 拉林铁路变坡面倾角崩塌落石对桥梁结构破坏作用的模拟分析与试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1622-1633.WANG X,PAI L F,WU H G. Simulation analysis and experimental study on the damage of bridge structure caused by tilt collapse and rockfall on the slope of Lalin Railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1622-1633. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 张涛,杨志华,张永双,等. 四川茂县新磨村高位滑坡铲刮作用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):138-145.ZHANG T,YANG Z H,ZHANG Y S,et al. An analysis of the entrainment of the Xinmo high-position landslide in Maoxian County,Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):138-145. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] SENGANI F,MULENGA F. An improved hazard assessment chart for rock falls in near vertical blocky rock environments[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(18):647. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09950-7 [14] LIU L W,DONG J X,XU H H,et al. Trajectory analysis and risk evaluation of dangerous rock mass instability of an overhang slope,southwest of China[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2021,2021(1):7153535. [15] 吕权儒,曾斌,孟小军,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影技术的崩塌隐患早期识别及影响区划分方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(6):313-325.LÜ Q R,ZENG B,MENG X J,et al. Early identification and influence range division method of collapse hazards based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(6):313-325. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 卢彦丞,李军,梁风,等. 岩溶典型区崩塌落石被动防护网失效概率模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):240-250.LU Y C,LI J,LIANG F,et al. Failure probability simulation of passive protection net for collapses and rockfalls in typical karst area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):240-250. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 张先林,张继,刘桃,等. 基于三维数值模拟的单体崩塌风险评价:以西藏樟木口岸扎美拉山为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(4):61-69.ZHANG X L,ZHANG J,LIU T,et al. Risk assessment of monomer rockfall based on 3D numerical simulation:A case study of Zhameila Mountain at Zhangmu port,Tibet[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(4):61-69. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 王颂,张路青,周剑,等. 青藏铁路设兴村段崩塌特征分析与运动学模拟[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4):784-792.WANG S,ZHANG L Q,ZHOU J,et al. Characteristic analysis and kinematic simulation of rockfall along Shexing Village section of Qinghai-Tibet Railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(4):784-792. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] DUPIRE S,BOURRIER F,MONNET J M,et al. The protection effect of forests against rockfalls across the French Alps:Influences of forest diversity[J]. Forest Ecology and Management,2016,382:269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.10.020 [20] SAROGLOU C,ASTERIOU P,ZEKKOS D,et al. UAV-based mapping,back analysis and trajectory modeling of a coseismic rockfall in Lefkada Island,Greece[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2018,18(1):321-333. doi: 10.5194/nhess-18-321-2018 [21] SARRO R,RIQUELME A,CARLOS J,et al. Rockfall simulation based on UAV photogrammetry data obtained during an emergency declaration:Application at a cultural heritage site[J]. Remote sending,2018,10(12):1923. doi: 10.3390/rs10121923 [22] GUERRIERO L,CORONA M A,MARTIRE D D,et al. Rockfall susceptibility analysis of the "San Michele Arcangelo" historic trail (Central Italy) based on virtual outcrops and multiple propagation models[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2024,83:263. doi: 10.1007/s10064-024-03764-0 [23] 黄军朋,邓睿,凌斯祥,等. 映秀2号隧道出口高陡斜坡落石运动学模拟和危险性评估[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(3):216-229.HUANG J P,DENG R,LING S X,et al. Kinematic simulation and hazard assessment of rockfalls at the Yingxiu No. 2 Tunnel exit high-steep hillslope[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(3):216-229. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] SARRO R,MATEOS R M,GARCíA-MORENO I,et al. The Son Poc rockfall (Mallorca,Spain) on the 6th of March 2013:3D simulation[J]. Landslides,2014,11(3):493-503. doi: 10.1007/s10346-014-0487-8 [25] 王军义,梁风,彭雄武,等. 基于GIS技术的单体崩塌危险范围评价方法研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(1):188-198.WANG J Y,LIANG F,PENG X W,et al. Study on assessment method of single collapse risk range based on GIS technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(1):188-198. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 凌斯祥,李乐,石奥博,等. 上木江坪高陡斜坡危岩特征与定量风险评估[J]. 工程地质学报,2024,32(3):1083-1097.LING S X,LI L,SHI A B,et al. Development characteristics and quantitative risk assessment of dangerous exit high-steep Shangmujiangping hillslope at mountain transportation corridor[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2024,32(3):1083-1097. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] GUZZETTI F,REICHENBACH P,GHIGI S,et al. Rockfall hazard and risk assessment along a transportation corridor in the Nera valley,central Italy[J]. Environment Management,34(2):191-208. [28] OTHMAN A,SHAABAN F,ABOTALIB A Z,et al. Hazard assessment of rockfalls in mountainous urban areas,western Saudi Arabia[J]. Arabian Journal for Sciences and Engineering,2021,46:5717-5731. doi: 10.1007/s13369-020-05098-x [29] 庞鑫,袁明,卢渊,等. 基于无人机LiDAR仿地飞行技术的高陡边坡危岩体快速识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):21-30.PANG X,YUAN M,LU Y,et al. Rapid identification method for the dangerous rock mass of a high-steep slope based on UAV LiDAR and ground imitation flight[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] JI Z M,CHEN T L,WU F Q,et al. Assessment and prevention on the potential rockfall hazard of high-steep rock slope:A case study of Zhongyuntai Mountain in Lianyungang,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2023,115(3):2117-2139. doi: 10.1007/s11069-022-05630-2 [31] DUAN S Z,JIN W,SUN J L,et al. Trajectory analysis of the rockfall based on the effect of rotating angular velocity[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2022,40(1):121-131. doi: 10.1007/s10706-021-01863-3 [32] 柳万里,晏鄂川,戴航,等. 南漳保康两县碳酸盐岩崩塌发育特征及影响程度分区[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2):104-112.LIU W L,YAN E C,DAI H,et al. Development characteristics and influence degree zoning of carbonate rock collapse in Nanzhang and Baokang Counties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(2):104-112. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 黄生根,何铭健. 浙江嵊州−新昌地区红层软岩崩解能量耗散研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):235-243.HUANG S G,HE M J. Energy dissipation during disintegration of red-bed soft rock in the Shengzhou-Xinchang area of Zhejiang Province,China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):235-243. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 邓日朗,张庆华,刘伟,等. 基于改进两步法采样策略和卷积神经网络的崩塌易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):186-200.DENG R L,ZHANG Q H,LIU W,et al. Collapse susceptibility evaluation based on an improved two-step sampling strategy and a convolutional neural network[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):186-200. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] GARDEZI H,LI X Y,HUANG Y. Effect of geometric obstructions,particle size distribution,and release angle on the mobility and deposit distribution along the runout zone of rock avalanches[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2025,84:24. doi: 10.1007/s10064-024-04040-x [36] ZHANG Y F,HE J Y,YUAN K,et al. Investigation on deformation behavior of unstable rock belt based on multi-source data analysis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2025,84:5. doi: 10.1007/s10064-024-03991-5 [37] 龚学强,蹇代君,胡卸文,等. 九寨沟强震区熊猫海-五花海段震裂山体发育特征及崩塌动力学分析[J]. 灾害学,2024,39(4):192-199.GONG X Q,JIAN D J,HU X W,et al. Development characteristics and kinematic analysis of rockfall from shattered mountain in the Panda Lake to Five-Flower Lake,Jiuzhaigou strong earthquake area[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2024,39(4):192-199. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] JIANG N,LI H B,ZHOU J W. Quantitative hazard analysis and mitigation measures of rockfall in a high-frequency rockfall region[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(4):3439-3456. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02137-1 [39] 吴建利. 高位崩塌落石冲击桩板墙-缓冲层材料消能机理研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2022.WU J L. Research on the energy dissipation mechanism of high-level falling rock impacting on pile-slab wall with cushion layer[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] CLEMENTE,J A,SPIZZICHINO,D,LEONI,G. et al. Rockfall susceptibility analysis through 3D simulations in marine protected areas of the Portofino coastline:Case studies of San Fruttuoso and Paraggi bays[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82:122. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03133-3 -




 下载:
下载: